Figure 1.
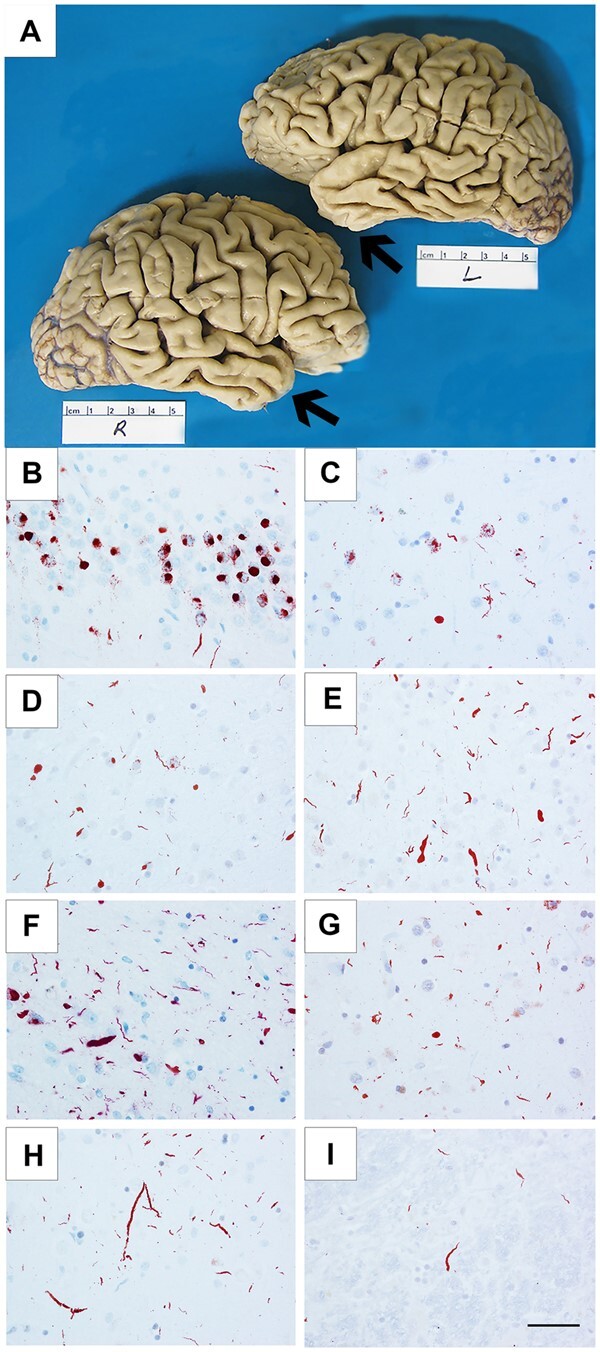
Cortical atrophy and TDP-43 immunoreactive pathology in FTLD-TDP-type C cases. Cortical atrophy of FTLD-TDP-type C is distinct in its selective and severe targeting of the temporal poles (arrows), seen in Case 3, a 71-year-old female with a 15-year duration of the semantic form of primary progressive aphasia (PPA-S), more severe on the left (A). Distribution of TDP-43-positive inclusions varied according to inclusion morphology and type (NCIs, short DNs, long DNs), suggesting that certain neuronal populations may be differentially vulnerable in TDP-type C. TDP-43-positive NCIs were severe in the dentate granular cells of hippocampus (B) and in the striatum (C), and mild in the middle frontal cortex (D). Short DNs were severe in the superior temporal cortex (E) and amygdala (F), and mild in the striatum (G). Long DNs were severe in the superior temporal cortex (H) and mild in the red nucleus (I). (B and H) Case 8; (C) Case 7; (D, E and I) Case 10; (F) Case 1; (G) Case 6. Scale bar = 50 μm in I, and also applies to B–H.
