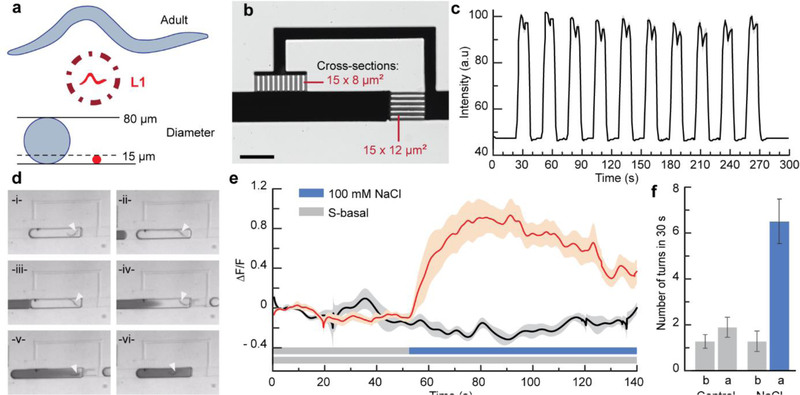
Figure 6.
Scalable technology: manipulation and chemical stimulation of first larval stage C. elegans. (a) L1 animals are very challenging to manipulate individually because of their small size, high motility, and flexibility. (b) Scaling-down of the Liquid Exchanger unit to suit the size of L1 animals (scale bar is 200 μm). (c) Square variation of the chemical profile of a droplet trapped in the miniaturized Liquid Exchanger shown in (b) and upon flowing a series of droplets with different dye concentrations. (d) Time-lapse sequence simulating the stimulation of an L1 animal using dye. (e) Functional neuronal imaging of ASH chemosensory neurons in L1s. The red curve is the average response upon stimulation with 100 mM NaCl solution, and the black curve is the average response for the control. Shaded areas indicate SEM (n = 20 for stimulus, n = 10 for control). (f) Behavioral response associated with (e): “b” is for a 30 s period before stimulation, and “a” is for a 30 s period after stimulation.