Abstract
Esters were synthesized via the alcoholysis of red pitaya seed oil with oleyl alcohol catalyzed by immobilized lipase, Lipozyme RM IM. The effects of synthesis parameters, including temperature, time, substrate molar ratio and enzyme loading, on the yield and productivity of esters were assessed using a central composite response surface design. The optimum yield and productivity were predicted to be about 80.00% and 0.58 mmol h−1, respectively, at a synthesis temperature of 50.5 °C, time of 4 h, substrate molar ratio of 3.4 : 1 and with 0.17 g of enzyme. Esters were synthesized under the optimum synthesis conditions; it was found that the average yield and productivity were 82.48 ± 4.57% and 0.62 ± 0.04 mmol h−1, respectively, revealing good correspondence with the predicted values. The main esters were oleyl linoleate, oleyl oleate, oleyl palmitate and oleyl stearate. The synthesized esters exhibited no irritancy effects and their physicochemical properties showed their suitability for use as cosmeceutical ingredients.
Optimization of the alcoholysis reaction between red pitaya seed oil and oleyl alcohol catalyzed by Lipozyme RM IM was carried out.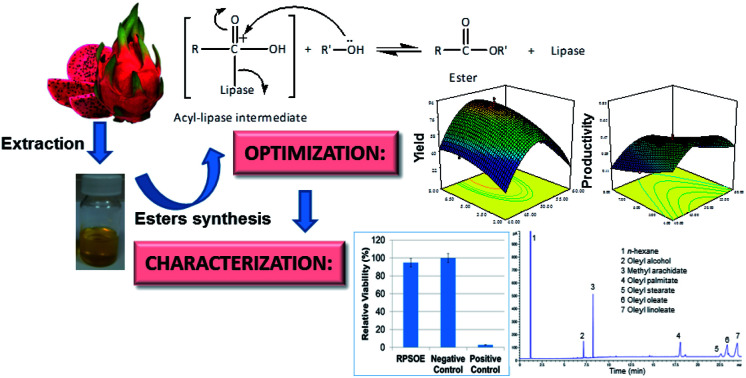
Introduction
Hylocereus polyrhizus is a beautiful oblong-shaped cactus fruit in the genus Hylocereus, derived from climbing epiphytes belonging to the Cactaceae family. It is also known as red pitaya due to its red pulpy skin and red flesh dotted with tiny black seeds. Originally from Mexico, Central and South America, red pitaya is currently grown commercially in Asian countries such as Vietnam, Malaysia, Taiwan and the Philippines. Locally, in southeast Asia, pitaya is more commonly known as dragon fruit.1
The tiny black seeds of red pitaya are often discarded as a by-product in juice manufacturing. The oil extracted from red pitaya seeds contains about 50% essential fatty acids (EFA), namely linoleic acid, oleic acid and linolenic acid. EFAs are necessary for proper skin function. Linoleic acid cannot be synthesized in the body; therefore, due to its health benefits, it must be obtained in the diet or from topical application.2 However, one weakness of the oil is often associated with its oily feel. Meanwhile, oil esters have attracted the attention of industry over the last decade due to their non-greasiness, non-toxicity, good solubility properties and excellent emollient behavior, but without the oily feeling.3 Oil esters are widely used as lubricants, polishes, plasticizers and antifoaming agents, and as raw materials in cosmetics and pharmaceutical products. Natural waxes or oil esters, such as esters derived from beeswax and jojoba oil, are often too expensive and limited in terms of supply.4 For this reason, a search has begun for alternatives and producing oil esters from red pitaya seed oil, which is a renewable resource, may help to produce substitutes of these natural oil esters to meet the growing demand.
Oil esters can be synthesized either via chemical5 or enzymatic reactions.6,7 However, the use of a conventional chemical-catalyzed method consumes more energy and often leads to many problems, including corrosion of equipment, risks in handling corrosive chemicals and degradation of the esters.8,9 On the other hand, the use of enzymatic methods offers mild reaction conditions and is a recognized “greener” method of ester synthesis compared to the conventional method. Furthermore, the use of immobilized enzymes can withstand high temperature and avoid thermal degradation of the esters. Lipases are among the most frequently used enzymes in biocatalysis.10–13 They are widely used because of their high specificity in action, so that only the preferred product is being catalysed.13,14
In this study, oil from red pitaya seeds was obtained using supercritical carbon dioxide (SC-CO2) extraction. This type of extraction method offers considerable advantages over traditional extraction processes due to its desirable properties, such as non-toxicity, non-flammability, cost efficiency (high purity of CO2 solvent available at low cost with the major advantage of lack of solvent residue in the product), non-explosiveness, higher extraction rate (shorter extraction time) and enhanced selectivity.15–18 Thus, the esters were synthesized via alcoholysis of red pitaya seed oil with oleyl alcohol catalyzed by immobilized lipase. For an enzymatic reaction, studies on the optimization of the reaction to increase the process efficiency are very crucial. To the best of our knowledge, no studies have ever been conducted on the optimization process of synthesizing esters from red pitaya seed oil. Response surface methodology (RSM) was utilized to optimize the alcoholysis reaction conditions so as to obtain the highest ester yields and productivity. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized esters were also assessed to facilitate potential uses.
Materials and methods
Materials
Red pitaya fruit was obtained locally from the vicinity of Sepang, Malaysia. Red pitaya seeds were then manually separated from the red flesh and pulp in the lab. The seeds were cleaned and washed under running water until all the flesh and pulp were removed. The seeds were then dried, crushed into small particles in a mill and kept in a desiccator until further analysis. Liquefied CO2 (99.9% purity) was supplied by Poly Gas Sdn. Bhd. in a pressurized deep tube cylinder. Immobilized lipase from Rhizomucor miehei (Lipozyme RM IM) was purchased from Novo Nordisk (Denmark). Oleyl alcohol (≥85% purity), n-hexane (≥99% purity) and isopropanol were supplied by Merck (Darmstadt, Germany). Reference standards of fatty acid oleyl esters, including oleyl palmitate, oleyl stearate, oleyl oleate, oleyl linoleate and methyl arachidate, were obtained from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, USA). MTT [(3-4,5 dimethyl triazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] was also purchased from Sigma Aldrich (St. Louis, USA), while reconstructed human epidermal model EpiDermTM (EPI-200) and 5% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) solution were obtained from Mattek Corporation (Ashland, USA). All other chemicals were of analytical grade.
Extraction of oil
Supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) using CO2 as a solvent was carried out in a 60 mL extraction vessel using an SFE system (OV-SCF) supplied by Taiwan Supercritical Technology Co., Ltd. Briefly, 20 g of dried, ground red pitaya seeds were placed into the extraction vessel (4.5 cm internal diameter and 14.5 cm in height). CO2 was fed from a gas cylinder equipped with a cooler circulator to keep the CO2 liquefied. The liquefied CO2 was pressurized at 4750 psi using an air-booster pump and fed into the vessel at a heating temperature of 47 °C. The precision of the temperature and pressure settings of the extraction system were ±0.5 °C and ±1 psi, respectively. The extracted oil was collected during extraction in a glass vial and stored in a sealed dark container until needed for further analysis.
Alcoholysis reaction
Red pitaya seed oil and oleyl alcohol of different molar ratios were added to n-hexane to give a total volume of 10 mL, followed by different amounts of enzyme in a screw-capped glass reaction bottle. The mixture of red pitaya seed oil, oleyl alcohol and Lipozyme RM IM was shaken in a horizontal water bath shaker (200 rpm) at different reaction temperatures and reaction times, as shown in Table 1. The alcoholysis reaction was terminated by separating the enzyme from the mixture using Whatman no. 1 filter paper.9
Design of the experiments in term of coded variables.
| Variable | Unit | Coded levels | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| −2 | −1 | 0 | 1 | 2 | |||
| Corresponding operating value | |||||||
| Temperature | (A) | °C | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 |
| Time | (B) | h | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 |
| Substrate molar ratio | (C) | mmol | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| Enzyme loading | (D) | g | 0.10 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.18 | 0.20 |
Gas chromatography (GC) analysis
The reaction mixture was analyzed by means of gas chromatography using an Agilent Technologies 7890A gas chromatograph, equipped with an RTX65 capillary column (30 m × 250 μm i.d.; film thickness 0.25 μm; Restex Corporation, USA). A 1 μL aliquot of sample was injected into a split mode GC. The temperature of the oven was maintained at 150 °C for 2 min and then the temperature was increased to 250 °C with a ramping rate of 20°C min−1 and held for 14 min. The temperatures of the injector and detector were 250 °C and 260 °C, respectively. Helium with a total flow rate of 25 mL min−1 was utilized as a carrier gas. Methyl arachidate was used as an internal standard for product quantification. The sample (1 μL) was prepared by mixing 150 μL of the internal standard solution (5 mg mL−1), 200 μL of sample and 1150 μL of n-hexane in a vial, which was then injected into the gas chromatography instrument. The concentrations of esters were calculated using eqn (1):
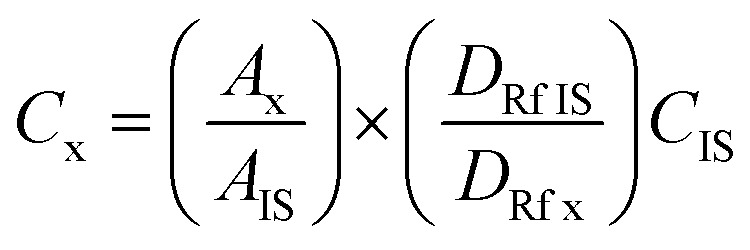 |
1 |
where: Cx = concentration of ester, CIS = concentration of the internal standard, Ax = peak area of the ester, AIS = peak area of the internal standard, DRf x = detector response factor of the ester (DRf x = Ax/Cx), DRf IS = detector response factor of the internal standard (DRf IS = AIS/CIS).
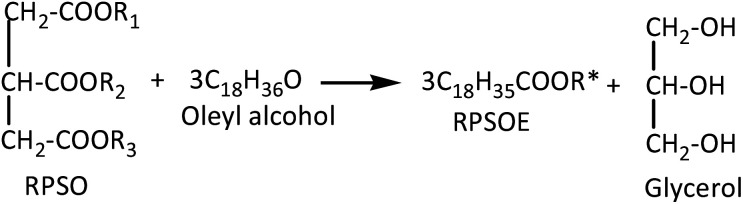
Based on the concentration of esters obtained, the number of moles of esters was determined. The percentage yield of esters was then further calculated by eqn (2). It is based on the assumption that 3 mol of red pitaya seed oil esters (RPSOE) will be produced from 1 mol of red pitaya seed oil (RPSO), as shown in eqn (3). The productivity of ester was calculated using eqn (4).
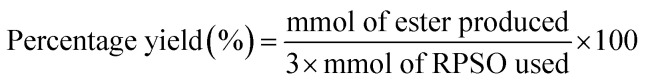 |
2 |
 |
3 |
where R* = R1, R2 or R3
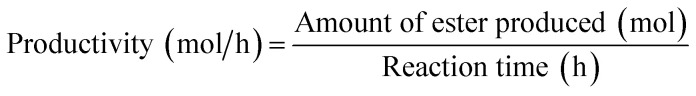 |
4 |
Experimental design and statistical analysis
RSM was applied in the optimization process and for an evaluation of the effect of four different operating variables, temperature (40–60 °C), time (2–10 h), substrate molar ratio (oleyl alcohol : red pitaya seed oil = 1.5 : 1) and enzyme loading (0.1–0.2 g), on the yield and productivity of ester. All other parameters were held constant, such as the total amount of solvent used in the synthesis reaction (10 mL of n-hexane); the reaction mixtures were shaken in a horizontal water bath shaker at 200 rpm. A four-factor, five-level rotatable central composite design (RCCD) was chosen for the synthesis of RPSOE, which resulted in 30 experimental runs consisting of 16 factorial points, 8 axial points and 6 central points. In order to minimize systematic errors, all experiments were carried out in random order and in triplicate. Table 1 represents the design of the experiments in terms of coded variables. The actual experiments carried out in developing the model are shown in Table 2.
Actual and predicted values of the models for CCD response surface analysis.
| Std. | Point type | A (°C) | B (h) | C (mmol) | D (g) | Response 1 yield (%) | Response 2 productivity (mmol h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Actual | Predicted | Actual | Predicted | ||||||
| 1 | Factorial | −1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 54.93 | 53.07 | 0.41 | 0.42 |
| 2 | Factorial | 1 | −1 | −1 | −1 | 43.8 | 47.10 | 0.33 | 0.38 |
| 3 | Factorial | −1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 56.24 | 55.59 | 0.21 | 0.20 |
| 4 | Factorial | 1 | 1 | −1 | −1 | 48.13 | 52.30 | 0.18 | 0.18 |
| 5 | Factorial | −1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 62.76 | 62.81 | 0.47 | 0.49 |
| 6 | Factorial | 1 | −1 | 1 | −1 | 62.37 | 62.04 | 0.47 | 0.48 |
| 7 | Factorial | −1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 66.42 | 70.00 | 0.25 | 0.25 |
| 8 | Factorial | 1 | 1 | 1 | −1 | 69.9 | 71.92 | 0.26 | 0.26 |
| 9 | Factorial | −1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 56.08 | 56.34 | 0.42 | 0.45 |
| 10 | Factorial | 1 | −1 | −1 | 1 | 59.09 | 56.91 | 0.44 | 0.45 |
| 11 | Factorial | −1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 58.57 | 60.30 | 0.22 | 0.21 |
| 12 | Factorial | 1 | 1 | −1 | 1 | 61.32 | 63.55 | 0.23 | 0.23 |
| 13 | Factorial | −1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 65.59 | 62.82 | 0.49 | 0.50 |
| 14 | Factorial | 1 | −1 | 1 | 1 | 65.66 | 68.59 | 0.49 | 0.53 |
| 15 | Factorial | −1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 72.48 | 71.45 | 0.27 | 0.24 |
| 16 | Factorial | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 76.64 | 79.90 | 0.29 | 0.29 |
| 17 | Axial | −2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 42.2 | 44.38 | 0.21 | 0.22 |
| 18 | Axial | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 52.73 | 46.87 | 0.26 | 0.23 |
| 19 | Axial | 0 | −2 | 0 | 0 | 62.2 | 64.34 | 0.83 | 0.76 |
| 20 | Axial | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 83.98 | 78.17 | 0.25 | 0.29 |
| 21 | Axial | 0 | 0 | −2 | 0 | 42.19 | 40.53 | 0.21 | 0.19 |
| 22 | Axial | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 68.65 | 66.63 | 0.34 | 0.33 |
| 23 | Axial | 0 | 0 | 0 | −2 | 75.89 | 72.59 | 0.38 | 0.35 |
| 24 | Axial | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 84.23 | 83.85 | 0.42 | 0.41 |
| 25 | Center | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 93.04 | 85.61 | 0.47 | 0.43 |
| 26 | Center | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 87.24 | 85.61 | 0.44 | 0.43 |
| 27 | Center | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 80.22 | 85.61 | 0.40 | 0.43 |
| 28 | Center | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 77.63 | 85.61 | 0.39 | 0.43 |
| 29 | Center | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 89.04 | 85.61 | 0.45 | 0.43 |
| 30 | Center | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 86.5 | 85.61 | 0.43 | 0.43 |
The experimental data was fitted into a multiple regression model (second order polynomial equation) and the general form of that equation is given by eqn (5):
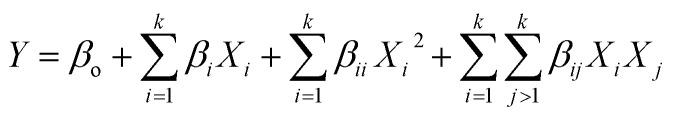 |
5 |
where Y is the response (percentage yield/productivity of esters); Xi and Xj are the independent variables (i and j range from 1 to k); βo is a constant (intercept coefficient), βi, βii and βij are coefficients of variables for linear, quadratic and interaction terms, respectively; k is the number of independent variables (k = 4 in this study).
In order to evaluate whether the constructed models were adequately fitted to the experimental data, the corresponding analysis of variance (ANOVA) was applied. The data obtained from experiments were analyzed using Design Expert Software version 7.0.0 (Stat-Ease Inc., Statistics Made Easy, Minneapolis, MN, USA) and interpreted. The numerical optimization function of the software was used to determine the optimum conditions for ester synthesis. Experiments were then carried out under the recommended conditions and the ester yields and productivity obtained were compared to those predicted by the software.
Isolation and purification of red pitaya seed oil esters
The isolation and purification of RPSOE were carried out according to the method of Gani et al. (2011).2 After removal of the enzyme from the mixture, n-hexane was then removed using a rotary vacuum evaporator at 68 °C. RPSOE were purified by adding ethanol in a separation funnel in a ratio of RPSOE to ethanol of 1 : 3. In the alcoholysis reaction between RPSO and oleyl alcohol, the products are not only RPSOE but also glycerol. The separatory funnel was shaken to remove the glycerol and remaining oleyl alcohol which are soluble in ethanol. The mixture was left to stand until two layers appeared. The RPSOE were in the bottom layer and the ethanol containing glycerol and oleyl alcohol was at the top. This step was repeated three times. RPSOE were then collected from the separation funnel. The RPSOE were further purified using a rotary evaporator to remove the remaining ethanol at ±78 °C and kept for further use.
Physicochemical properties of esters
A specific gravity bottle and refractometer at a room temperature of 25 °C were used to determine the specific gravity and refractive index, respectively. Iodine, saponification and acid values were determined according to standard Test Methods modified from the American Oil Chemists' Society (AOCS) as well as the Malaysian Palm Oil Board (MPOB) Test Methods.19 All measurements were performed in triplicate. Variations among the measurements were negligible and the mean values for each measurement were computed.
Irritation test
An irritation test was performed to determine whether the synthesized red pitaya seed oil esters can cause irritation to the in vitro skin model EpiDerm. The irritation test was carried out according to the standard operating procedure (SOP) developed at MatTek Corporation. This in vitro standard method was validated by the European Centre for the Validation of Alternative Methods (ECVAM) as an in vitro test method based on reconstructed human epidermis (RhE) technology. The test was conducted in line with the requirement of OECD Guidelines for Testing of Chemicals no. 439.20
The in vitro dermal irritation test comprises topical exposure of the synthesized esters to RhE model EpiDerm tissues, followed by a cell viability test. A sufficient amount of esters was applied on the surface of the three-dimensional RhE. The RhE model consists of non-transformed human-derived epidermal keratinocytes, which have been cultured to form a multilayered, highly differentiated model of the human epidermis. The components contain organized basal, spinous and granular layers, and a multilayer stratum corneum containing intercellular lamellar lipid layers which represent the main lipid classes similar to those found in vivo.
After 60 min of exposure, the tissues were thoroughly rinsed, blotted to remove the test extract and transferred to fresh medium. After a 24 h incubation period, the medium was changed and the tissues were incubated for another 18 h. An MTT [(3-4,5 dimethyl triazole-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide] assay was then performed by transferring the tissues to 6-well plates containing MTT medium (1 mg mL−1). After 3 h of incubation, the blue formazan salt formed by cellular mitochondria was extracted with 2.0 mL of isopropanol/tissue. The optical density of the extracted formazan was determined using a spectrophotometer at 570 nm. Relative cell viability was calculated for each tissue as the percentage (%) of the mean of the negative control tissues. The reduction in the viability of tissues exposed to the red pitaya seed oil esters was compared to the negative control (treated with deionized water) and positive control (treated with 5% sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) solution). The skin irritation potential was classified according to the remaining cell viability obtained after test item treatment. Irritant chemicals were identified by their ability to decrease cell viability below defined threshold levels (i.e. ≤50%, for UN GHS Category 2).
Results and discussion
Alcoholysis reaction
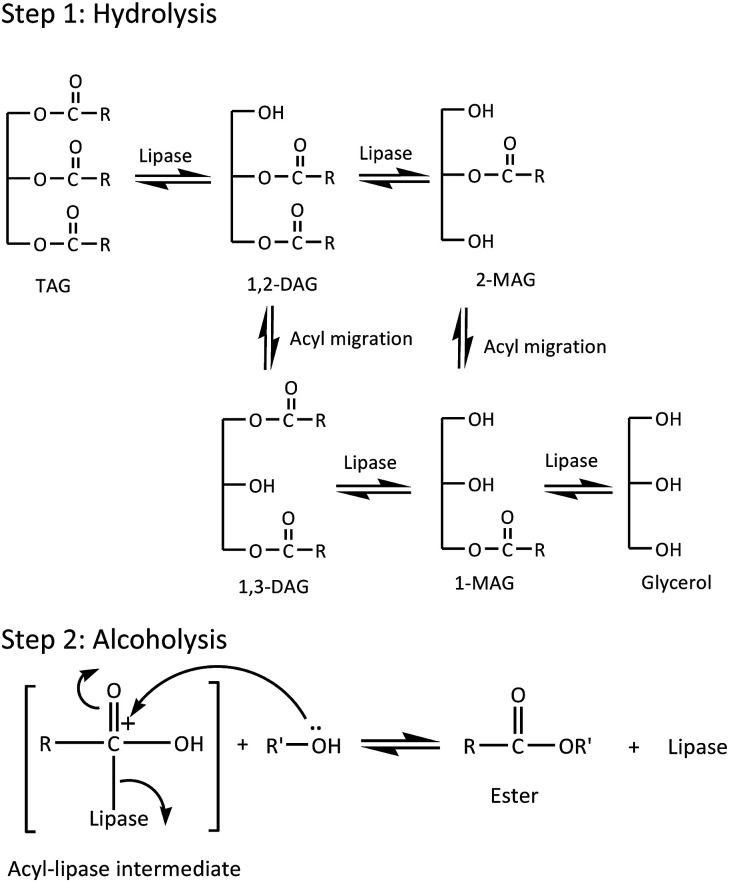
In the present work, Lipozyme RM IM was used to catalyze the alcoholysis reaction of triacylglyceride (TAG) from RPSO and oleyl alcohol to yield RPSOE. The proposed mechanism of the alcoholysis reaction catalyzed by Lipozyme RM IM is presented in Scheme 1. There are two steps in the mechanism, involving hydrolysis and alcoholysis reactions. In the hydrolysis reaction, TAG is first hydrolyzed to produce glycerol and three fatty acids in the presence of lipase. The fatty acid molecule from TAG then binds to the enzyme forming a lipase–acid complex, which then isomerizes to an acyl-enzyme intermediate (Step 2).21 In the alcoholysis reaction, the second reactant, which is the alcohol, is then reacted with the acyl-enzyme complex to form another binary complex. The −OR from the alcohol acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbonyl carbon in the acyl-lipase intermediate, so it creates a bond between the oxygen from −OR and the carbonyl carbon, which isomerizes unimolecularly to a lipase–ester complex that finally releases the ester and enzyme.21
Scheme 1. Proposed mechanism of the alcoholysis reaction by Lipozyme RM IM.
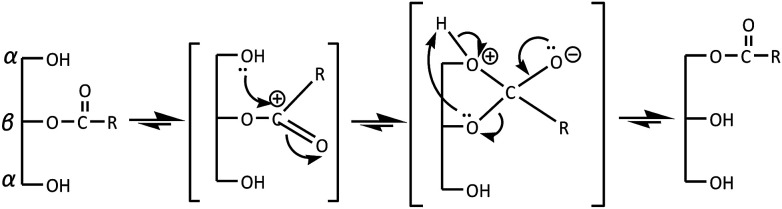
TAG from RPSO reacts with oleyl alcohol to produce DAG, MAG and free glycerol in three different steps. 1,2-DAG and 2-MAG, which formed initially (Step 1 in Scheme 1), are likely to undergo acyl migration processes for thermodynamic reasons, to produce 1,3-DAG and 1-MAG according to the mechanism in Scheme 2. Since 1,3-specific Lipozyme RM IM is unable to cleave at the β-position in 1,2-DAG and 2-MAG, it happens after the acyl migration takes place in the α-position before catalyzing the hydrolysis.22 As shown in Scheme 2, the acyl migration goes through a cyclic ester intermediate.23 The reaction is initiated by the nucleophilic attack of a lone pair of electrons of free hydroxyl oxygen at the α-carbon on the ester carbonyl carbon, which results in a five-member ring intermediate. Subsequently, the ring opens and results in acyl migration from the 2-position to the 1(3)-position.24
Scheme 2. Reaction mechanism of acyl migration.
Optimization of lipase-catalyzed synthesis of esters by CCD-RSM
Optimization was performed using an RCCD. From the model fitting technique, it was observed that the predicted values were sufficiently correlated with the observed values. After fitting the observed data to multiple models, such as linear, quadratic and cubic, ANOVA showed that the relation between both percentage yield (response 1) and productivity (response 2) with independent variables (temperature, time, substrate molar ratio and enzyme loading) were most suitably described with a quadratic polynomial model as in eqn (6) and (7):
| Yield (%) = 85.61 + 0.62A + 3.46B + 6.52C + 2.81D + 0.67AB + 1.30AC + 1.63AD + 1.17BC + 0.36BD − 0.81CD − 10.00A2 − 3.59B2 − 8.01C2 − 1.85D2 | 6 |
| Productivity (mmol h−1) = 0.43 + 2.106 × 10−3A − 0.12B + 0.034C + 0.015D + 4.491 × 10−3AB + 6.703 × 10−3AC + 9.548 × 10−3AD − 5.573 × 10−3BC − 3.937 × 10−3BD − 5.475 × 10−3CD − 0.052A2 + 0.024B2 − 0.042C2 − 0.011D2 | 7 |
where A is the temperature, B is time, C is the substrate molar ratio and D is the enzyme loading. The results of the model summary statistics are shown in Table 3. According to the results, linear and interactive (2FI) models showed lower R2, adjusted R2 and predicted R2 compared to the quadratic model, while the cubic model was reported to be aliased. The high R2, adjusted R2 and predicted R2 values and the good agreement between both predicted R2 and adjusted R2 values of the quadratic model clearly demonstrate that this model could be used to represent the real relationship among the studied parameters.25,26
Summary statistics of the RSM models.
| Source | Std. dev. | R-squared | Adjusted R-squared | Predicted R-squared | p-Value Prob > F | Press |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | ||||||
| Linear | 13.38 | 0.2521 | 0.1325 | 0.0186 | 0.1099 | 5869.78 |
| 2FI | 15.15 | 0.2708 | −0.1131 | −0.3374 | 0.9975 | 7999.15 |
| Quadratic | 4.82 | 0.9417 | 0.8874 | 0.7822 | <0.0001 | 1302.36 |
| Cubic | 5.41 | 0.9658 | 0.8583 | −0.0359 | 0.7447 | 6195.50 |
| Productivity | ||||||
| Linear | 0.082 | 0.6775 | 0.6259 | 0.5233 | <0.0001 | 0.25 |
| 2FI | 0.093 | 0.6847 | 0.5187 | 0.4182 | 0.9982 | 0.30 |
| Quadratic | 0.037 | 0.9596 | 0.9219 | 0.8012 | <0.0001 | 0.10 |
| Cubic | 0.033 | 0.9858 | 0.9411 | 0.0669 | 0.2725 | 0.49 |
From the ANOVA shown in Table 4, the high model F-values of 17.32 (yield) and 25.47 (productivity) with “Prob > F” value of <0.0001 for both models implied that the models were significant. There was only a 0.01% chance that an F-value this large could occur due to noise. The Prob > F values of the lack of fit were 0.7913 (yield) and 0.2168 (productivity), which indicated an insignificant lack of fit and the best fit of the developed model. Adequate precision (signal to noise ratio) values of 13.227 (yield) and 21.822 (productivity) for the responses indicated an adequate signal and the best fit of the developed models; these values should be greater than 4 to optimally navigate the design space. From the results, it was found that these RSM models can be used to predict the experimental data in the range of the studied domains.
ANOVA of the SC-CO2 extraction of pitaya seed oil.
| Source | Sum of squares | Degrees of freedom | Mean square | F-Value | Prob > F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Yield | |||||
| Model | 5632.46 | 14 | 402.32 | 17.32 | <0.0001a |
| Residual | 348.47 | 15 | 23.23 | ||
| Lack of fit | 185.32 | 10 | 18.53 | 0.57 | 0.7913b |
| Pure error | 163.15 | 5 | 32.63 | ||
| Cor total | 5980.93 | 29 | |||
| Productivity | |||||
| Model | 0.50 | 14 | 0.036 | 25.47 | <0.0001a |
| Residual | 0.021 | 15 | 1.403 × 10−3 | ||
| Lack of fit | 0.017 | 10 | 1.696 × 10−3 | 2.08 | 0.2168 b |
| Pure error | 4.079 × 10−3 | 5 | 8.15 × 10−4 | ||
| Cor total | 0.52 | 29 | |||
Significant at “Prob > F” less than 0.05.
Insignificant at “Prob > F” more than 0.05.
The coefficient of the empirical model is presented in Table 5. The high regression coefficient and smaller Prob > F value (Prob > F less than 0.05) for those variables and their interactions demonstrated that they had a significant impact on the response.27 Based on the results, the linear term of the substrate molar ratio (C), the quadratic term of temperature (A2) and the quadratic term of the substrate molar ratio (C2) had a more significant influence on the percentage yield with Prob > F values of <0.0001. Regarding the productivity of the alcoholysis reaction, the variables that had the most significant influence were the linear term of time (B), the quadratic term of temperature (A2) and the quadratic term of the substrate molar ratio (C2) with Prob > F values of <0.0001. Negative values of coefficient estimates denote a negative influence of the parameter on the reaction. It was observed that all the linear coefficients of the models had positive effects, except for the coefficient estimate for time (B) in the model for productivity. This may have occurred if the productivity of esters was negatively affected by a longer reaction time, as the rate of ester productivity decreases over time. Indeed, despite the negative value, time had the greatest effect on the response of productivity with an estimated effect of 0.12 and also strongly affected the response of yield with an estimated effect of 3.46.
Regression coefficient and p-value (Prob > F) of the model.
| Source | Yield (%) | Productivity (mmol h−1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Prob > F | Coefficient | Prob > F | |
| Intercept | 85.61 | 0.43 | ||
| A | 0.62 | 0.5375 | 2.106 × 10−3 | 0.7867 |
| B | 3.46 | 0.0031a | −0.12 | <0.0001a |
| C | 6.52 | <0.0001a | 0.034 | 0.0005a |
| D | 2.81 | 0.0119a | 0.015 | 0.0694 |
| AB | 0.67 | 0.5864 | 4.491 × 10−3 | 0.6384 |
| AC | 1.30 | 0.2977 | 6.703 × 10−3 | 0.4851 |
| AD | 1.63 | 0.1952 | 9.548 × 10−3 | 0.3240 |
| BC | 1.17 | 0.3475 | −5.573 × 10−3 | 0.5606 |
| BD | 0.36 | 0.7692 | −3.937 × 10−3 | 0.6801 |
| CD | −0.81 | 0.5091 | −5.475 × 10−3 | 0.5674 |
| A 2 | −10.00 | <0.0001a | −0.052 | <0.0001a |
| B 2 | −3.59 | 0.0014a | 0.024 | 0.0041a |
| C 2 | −8.01 | <0.0001a | −0.042 | <0.0001a |
| D 2 | −1.85 | 0.0630b | −0.011 | 0.1468 |
Significant at “Prob > F” less than 0.05.
Insignificant at “Prob > F” more than 0.05.
Effect of operating variables
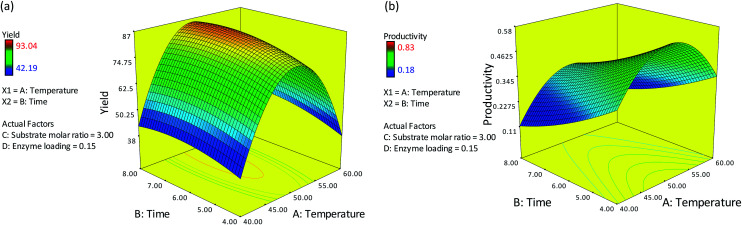
The final equations (eqn (6) and (7)) derived from regression analysis were then used to plot the response surfaces. Two parameters were plotted at any one time on the x1 and x2 axes, with the two remaining parameters set at their center point values (coded level: 0). Fig. 1(a) and (b) show the response surface plots as a function of temperature, time and their interaction on percentage yield and productivity of ester synthesis at a substrate molar ratio of 3 and 0.15 g of enzyme. The percentage yield increased with an increase in reaction time, but decreased when the temperature was above 50 °C. A further increase in temperature to 60 °C resulted in decreased percentage yield and productivity due to thermal degradation of the enzyme. Similar results were reported by Gunawan et al. (2005)8 and Rahman et al. (2011).9
Fig. 1. Response surface plot showing the effects of reaction temperature and time on ester synthesis in terms of (a) the yield response and (b) the productivity response (substrate molar ratio = 3.00; enzyme loading = 0.15 g).
The highest percentage yield was found within a reaction period of 5–7 h. After 7 h, the percentage yield was relatively constant. This may have occurred since the reactions had achieved equilibrium: i.e. the rate of the forward reaction was equal to the rate of the backward reaction. In the alcoholysis reaction between red pitaya seed oil and oleyl alcohol, the products are not only esters but also glycerol. Glycerol will accumulate, and this may inhibit the reaction by limiting the interaction between the substrate and the enzyme. Previous work reported by Rahman et al. (2011) showed that the alcoholysis of engkabang fat esters was more than 90% complete after 5 h.9 However, as for productivity, the productivity of esters was negatively affected by an increase in reaction time; the rate of ester productivity decreases over time. Productivity refers to the amount of product that was produced in a given reaction time. The rate of alcoholysis was faster at an early stage of the reaction and became slower as time progressed.
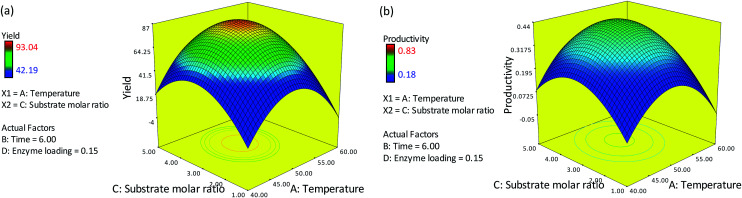
Fig. 2(a) and (b) depict the effect of varying the reaction temperature and substrate molar ratio on the percentage yield and productivity at a fixed time of 6 h and 0.15 g of enzyme. The optimum temperature of 50 °C and substrate molar ratio (oleyl alcohol : red pitaya seed oil) of 3.3 : 1 were used, which gave a maximum yield of 77.75% and productivity of 0.385 mmol h−1. However, a decrease in the percentage yield and productivity were observed when the temperature and substrate molar ratio were increased to 60 °C and 5 : 1, respectively. At low temperatures, the yield and productivity of esters were rather low due to mass transfer limitations. Meanwhile, at low substrate concentrations, less substrate is available for the reaction, resulting in a relatively low expected yield and productivity even at high temperatures. An increase in temperature to about 50 °C and substrate molar ratio to ∼3.3 led to an increase in the collision frequency between the substrate and the enzyme, thereby increasing the yield and productivity. A further increase in substrate molar ratio to 5 could inhibits the activity of the enzyme, as excess alcohol may affect the conformation of the lipase. The presence of alcohol in excess can distort the essential water layer that stabilizes the immobilized lipase, thus reducing the enzyme activity and resulting in a low percentage yield and productivity of esters.8,9
Fig. 2. Response surface plot showing the effects of reaction temperature and substrate molar ratio on ester synthesis in terms of (a) the yield response and (b) the productivity response (time = 6 h; enzyme loading = 0.15 g).
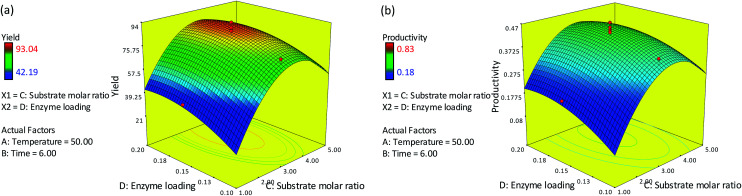
Fig. 3(a) and (b) show the response surface plots of the effect of varying the substrate molar ratio and enzyme loading on the alcoholysis of red pitaya seed oil at a reaction temperature of 50 °C and a reaction time of 6 h. An increase in the substrate molar ratio up to about 3.3 at any enzyme loading from 0.10 g to 0.20 g increased both the percentage yield and productivity. Reactions with a higher enzyme loading and a substrate molar ratio in the range of 3.3–3.5 provided the maximal percentage yield and productivity. Generally, with a high amount of substrate, there will be greater probability of substrate–enzyme interactions, resulting in a relatively high yield and productivity. This relationship is valid when there are no limiting factors such as the mass transfer problem, low substrate concentration or the presence of activators or inhibitors. However, it was found that further increases in the substrate molar ratio caused a reduction in both the percentage yield and productivity and there were no significant effects on either percentage yield or productivity by increasing the amount of enzyme to 0.20 g. As explained by Krishna et al. (2001),28 the presence of enzyme molecules in excess may reduce the exposure of active sites to the substrates. The active sites will remain inside the bulk of enzyme particles, and thus would not contribute significantly to the reaction. A high amount of substrate molar ratio caused high viscosity and thus led to mass transfer problems as well as saturation and inhibition of the enzyme due to excess substrate. Moreover, a reaction limiting factor caused by low concentrations of red pitaya seed oil also led to low ester yield and productivity with high amounts of oleyl alcohol and enzyme. Some workers have reported substrate concentration versus enzyme loading profiles where the saturation of enzyme with a large amount of substrate led to lower predicted yields. In the lipozyme-catalyzed synthesis of isoanyl butyrate, Krishna et al. (1999)29 found that moderate concentrations of the substrate (butyric acid and isobutyl alcohol) and high enzyme loading favored maximal esterification.
Fig. 3. Response surface plot showing the effects of the substrate molar ratio and enzyme loading on RPSOE in terms of (a) the yield response and (b) the productivity response (reaction temperature = 50 °C; time = 6 h).
Optimization of reaction and model validation
Within the experimental range studied, the optimal conditions for the lipozyme-catalyzed production of esters were predicted using the optimization function of Design Expert Software. Three solutions with different desirability values were used to predict the optimal conditions; the predicted and actual values are given in Table 6. The highest reaction yield (82.48%) and productivity (0.62 mmol h−1) were obtained in experiment 3. For this reason, experiment 3 was chosen as the optimal conditions. For all experiments, the actual values agreed well with the predicted values, implying that models derived from RSM can be used to adequately describe the relationship between factors and responses in the lipozyme-catalyzed synthesis of red pitaya seed oil esters. Thus, the optimum conditions for maximum ester production were successfully developed by the RSM model. Manufacturers have reported that lipozyme can work efficiently up to a temperature of 70 °C. However, as reported by Keng et al. (2005),30 a temperature of 50 °C was sufficient to produce a high yield (>90%) in the lipase-catalyzed alcoholysis of palm-based wax esters with a reaction period of 5 h. Higher temperatures will only increase energy consumption and the evaporation of n-hexane (the boiling point of n-hexane is 68 °C).
Optimum conditions for the synthesis of red pitaya seed oil esters.
| Exp | Optimum conditions | Yield (%) | Productivity (mmol h−1) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A (°C) | B (h) | C (mmol) | D (g) | Predicted | Actual | Relative deviation | Predicted | Actual | Relative deviation | |
| 1 | 50.3 | 4.0 | 3.3 | 0.16 | 80.14 | 80.36 | 3.18 | 0.58 | 0.60 | 0.03 |
| 2 | 49.0 | 4.0 | 3.7 | 0.14 | 76.66 | 78.20 | 3.12 | 0.56 | 0.59 | 0.03 |
| 3 | 50.5 | 4.0 | 3.4 | 0.17 | 80.00 | 82.48 | 4.57 | 0.58 | 0.62 | 0.04 |
Characterization of red pitaya seed oil esters
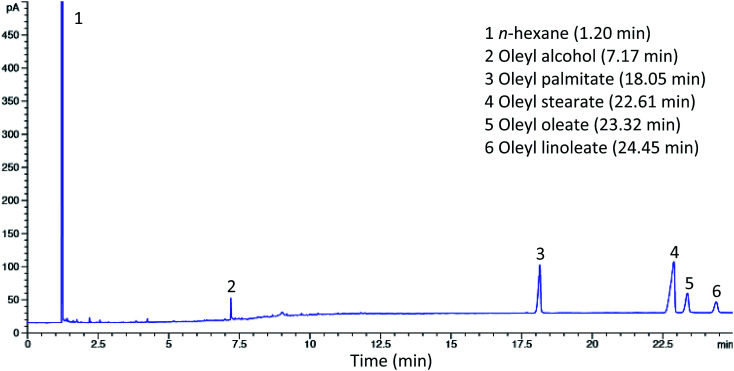
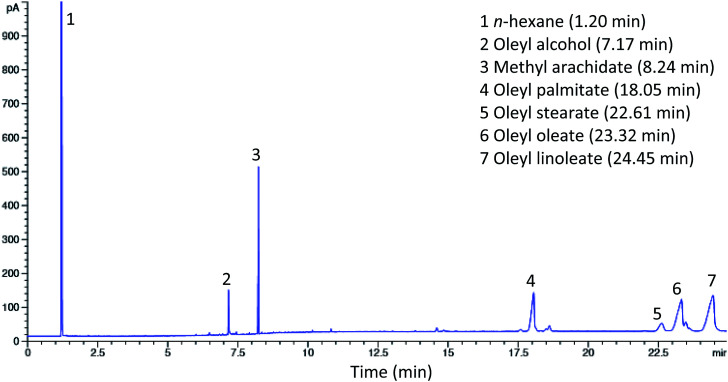
The synthesized esters from the alcoholysis reaction between red pitaya seed oil and oleyl alcohol using Lipozyme RM IM as a catalyst were examined by gas chromatography (GC). Fig. 4 shows the gas chromatogram of standard esters, while the results of the synthesized esters are shown in the chromatogram in Fig. 5. The esters were identified by matching the retention times of each peak to the fatty acid oleyl ester reference standard. Methyl arachidate with a retention time (Rt) of 8.24 min was added to the sample as an internal standard for quantitative analysis and determination of ester yield. The composition of the esters was oleyl palmitate (C34:1) (14.31%), oleyl stearate (C36:1) (3.17%), oleyl oleate (C36:2) (22.64%) and oleyl linoleate (C36:3) (42.36%), which were identified at Rt 18.05, 22.61, 23.32 and 24.45 min, respectively. The composition of the esters obtained under optimum conditions was observed to coincide with the composition of fatty acids in red pitaya seed oil. The unreacted oleyl alcohol was observed at Rt 7.17 min and another peak at Rt 1.2 min was from n-hexane (solvent).
Fig. 4. Gas chromatogram of standard esters.
Fig. 5. Gas chromatogram of red pitaya seed oil esters.
Physicochemical properties of red pitaya seed oil esters
Physicochemical characterizations of esters are important to evaluate their efficacy in industrial application. The physicochemical properties of the synthesized esters are depicted in Table 7. These properties were compared with the results on the corresponding physicochemical properties of red pitaya seed oil. Generally, both red pitaya seed oil and esters were yellow in color, but the yellow color of the esters was much lighter. In comparison to the oil, due to the lower molecular weight of the esters, a lower specific gravity and saponification value of the esters were obtained. The oil consists of a main component called triglycerides, which are esters that are formed from the combination of a glycerol and three different chain lengths of fatty acids. In order to saponify the three ester bonds in the triglyceride molecules of red pitaya seed oil, a larger amount of KOH was needed. On the other hand, a smaller amount of KOH was needed to saponify one ester bond in an ester molecule of red pitaya seed oil esters.31
Physicochemical properties of red pitaya seed oil (RPSO) and red pitaya seed oil esters (RPSOE).
| Properties | RPSO | RPSOE |
|---|---|---|
| Specific gravity (kg m−3) (25 °C) | 0.857 ± 0.001 | 0.832 ± 0.001 |
| Refractive index (25 °C) | 1.4675 ± 0.0005 | 1.457 ± 0.0002 |
| Iodine value (g of I2/100 g of oil) | 105.1 ± 2.5 | 118.5 ± 3.0 |
| Saponification value (mg of KOH/g of oil) | 133.4 ± 2.1 | 46.36 ± 0.3 |
| Acid value (mg of NaOH/g of oil) | 3.09 ± 0.10 | 0.53 ± 0.02 |
A lower refractive index value of the esters was observed when compared to that of red pitaya seed oil. The refractive index decreased as the temperature increased and decreased with a decrease in the alkyl carbon chain length, unsaturation and conjugation. Thus, red pitaya seed oil was predicted to show a higher refractive index compared to its esters, since the three acyl groups in the oil had a longer total carbon chain length. However, the iodine value of the esters was found to be higher than that of the oil. This was due to the introduction of one additional double bond from oleyl alcohol as it reacted with the acid moiety from the triglycerides of red pitaya seed oil to form long chain esters. Higher iodine values will foster the permeation rate of the compound into the stratum corneum when applied on the skin. Generally, a high iodine value indicates that the oil has greater liquidity. Red pitaya seed oil esters also exhibited low acidity values with a score of only 0.53 mg of NaOH/g sample. The acidity value indicates the amount of free fatty acids in the samples. A higher free fatty acid value is a drawback as it reduces the oxidative stability of the compounds and leads to rancidity.32
Irritation test
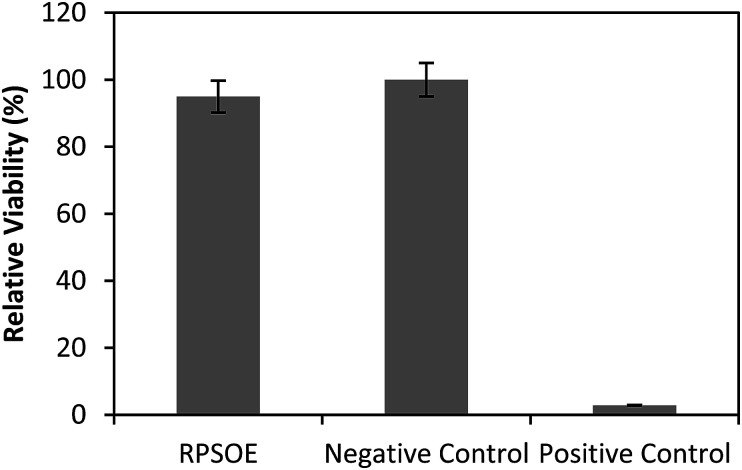
The dermal irritancy potential of the synthesized red pitaya seed oil esters is shown in Table 8 and the result was compared with the negative (non-irritant) and positive (irritant) samples, as shown in Fig. 6. Red pitaya seed oil esters were classified as non-irritant. No significant difference in the mean tissue viability of the esters was recorded when compared to the negative control, showing excellent properties. This result indicated the skin compatibility of the esters for use as a cosmeceutical ingredient.
Irritancy testing of red pitaya seed oil esters (RPSOE)a.
| Mean of OD | SD of OD | Mean of viability (%) | SD of viability | In vitro result | In vivo prediction | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RPSOE | 1.635 | 0.039 | 94.95 | 2.25 | Mean tissue viability > 50% | Non-irritant |
| Negative control | 1.722 | 0.070 | 100.00 | 4.19 | Mean tissue viability > 50% | Non-irritant |
| Positive control | 0.049 | 0.003 | 2.85 | 0.25 | Mean tissue viability ≤ 50% | Irritant |
OD: optical density; SD: standard deviation.
Fig. 6. Relative viability of red pitaya seed oil esters (RPSOE) and negative and positive controls.
Conclusions
Optimal reaction conditions for the lipozyme-catalyzed synthesis of red pitaya seed oil esters were obtained from responses (yield and productivity): temperature = 50.5 °C; time = 4 h; substrate molar ratio (oleyl alcohol : red pitaya seed oil = 3.4 : 1); and amount of enzyme = 0.17 g. These models can be used to predict the yield and productivity of esters under any given conditions within the experimental range and could be useful for scaled-up production to fulfill the high demand for oil esters in the current market. The physicochemical and non-irritancy properties indicated the skin compatibility of the esters for cosmeceutical applications.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) under the research university grant scheme Geran Putra-Inisiatif Putra Siswazah (GP-IPS) [grant number 9647000].
References
- Ariffin A. A. Bakar J. Ping Tan C. Abdul Rahman R. Karim R. Chun Loi C. Essential fatty acids of pitaya (dragon fruit) seed oil. Food Chem. 2009;114:561–564. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.09.108. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gani S. S. A. Kamairudin N. Razalli R. L. Basri M. Phase behaviour study of pitaya seed oil: jojoba oil with non-ionic surfactants in emulsion system. Asian J. Chem. 2015;27:3452–3456. doi: 10.14233/ajchem.2015.18891. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gani S. S. A. Basri M. Rahman M. B. A. Kassim A. Rahman R. N. Z. R. A. Salleh A. B. Ismail Z. Engkabang fat esters for cosmeceutical formulation. J. Surfactants Deterg. 2011;14:227–233. doi: 10.1007/s11743-010-1233-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Basri M. Noor R. Raja Z. Rahman A. Ebrahimpour A. Salleh A. B. Gunawan E. R. Basyaruddin M. Comparison of estimation capabilities of response surface methodology (RSM) with artificial neural network (ANN) in lipase-catalyzed synthesis of palm-based wax ester. BMC Biotech. 2007;7:53. doi: 10.1186/1472-6750-7-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aracil J. Martinez M. Sánchez N. Corma A. Formation of a jojoba oil analog by esterification of oleic acid using zeolites as catalyst. Zeolites. 1992;12:233–236. doi: 10.1016/S0144-2449(05)80288-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Trani M. Ergan F. André G. Lipase-catalyzed production of wax esters. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1991;68:20–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02660302. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Basri M. Kassim M. A. Mohamad R. Ariff A. B. Optimization and kinetic study on the synthesis of palm oil ester using Lipozyme TL im. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2013;85–86:214–219. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2012.09.013. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gunawan E. R. Basri M. Rahman M. B. A. Salleh A. B. Rahman R. N. Z. A. Study on response surface methodology (RSM) of lipase-catalyzed synthesis of palm-based wax ester. Enzyme Microb. Technol. 2005;37:739–744. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2005.04.010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rahman N. F. A. Basri M. Rahman M. B. A. Rahman R. N. Z. R. A. Salleh A. B. High yield lipase-catalyzed synthesis of Engkabang fat esters for the cosmetic industry. Bioresour. Technol. 2011;102:2168–2176. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.10.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ungcharoenwiwat P. Canyuk B. H-Kittikun A. Synthesis of jatropha oil based wax esters using an immobilized lipase from Burkholderia sp. EQ3 and Lipozyme RM IM. Process Biochem. 2016;51:392–398. doi: 10.1016/j.procbio.2015.12.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ungcharoenwiwat P. Kittikun A. H. Purification and characterization of lipase from Burkholderia sp. EQ3 isolated from wastewater from a canned fish factory and its application for the synthesis of wax esters. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2015;115:96–104. doi: 10.1016/j.molcatb.2015.02.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Calero J. Verdugo C. Luna D. Sancho E. D. Luna C. Posadillo A. Bautista F. M. Romero A. A. Selective ethanolysis of sunflower oil with Lipozyme RM IM, an immobilized Rhizomucor miehei lipase, to obtain a biodiesel-like biofuel, which avoids glycerol production through the monoglyceride formation. New Biotechnol. 2014;31:596–601. doi: 10.1016/j.nbt.2014.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manurung R. Hasibuan R. Taslim T. Rahayu N. S. Darusmy A. Enzymatic Transesterification of DPO to Produce Biodiesel by Using Lipozyme RM IM in Ionic Liquid System. Procedia Soc. Behav. Sci. 2015;195:2485–2491. doi: 10.1016/j.sbspro.2015.06.310. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma R. Chisti Y. Chand U. Banerjee U. C. Production, Purification, Characterization, and Applications of Lipases. Biotechnol. Adv. 2001;19:627–662. doi: 10.1016/S0734-9750(01)00086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai A. Mohanty B. Bhargava R. Supercritical extraction of sunflower oil: a central composite design for extraction variables. Food Chem. 2016;192:647–659. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.070. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa A. R. M. Freitas L. A. P. Mendiola J. Ibanez E. Copaifera langsdorffii supercritical fluid extraction: Chemical and functional characterization by LC/MS and in vitro assays. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2015;100:86–96. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2015.02.028. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shao Q. Deng Y. Liu H. Zhang A. Huang Y. Xu G. Li M. Essential oils extraction from Anoectochilus roxburghii using supercritical carbon dioxide and their antioxidant activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014;60:104–112. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.06.009. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay M., Natural Extracts Using Supercritical Carbon Dioxide, 2000 [Google Scholar]
- MPOB, Test methods, a compendium of test on palm oil products, palm kernel products, fatty acids, food related products and others, Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, 2005 [Google Scholar]
- OECD, in Vitro Skin Irritation: Reconstructed Human Epidermis Test Method. OECD Guidelines for the testing of Chemicals, Section 4, OECD Publishing, Paris, 2015 [Google Scholar]
- Keng P. S., Scale-up Production of Palm-based Wax Esters Using Lipozyme RM IM and Characterisation of the Esters, PhD Thesis, Universiti Putra Malaysia., 2008 [Google Scholar]
- Salis A. Solinas V. Monduzzi M. Wax ester synthesis from heavy fraction of sheep milk fat and cetyl alcohol by immobilized lipases. J. Mol. Catal. B: Enzym. 2003;21:167–174. doi: 10.1016/S1381-1177(02)00124-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Plücktun A. Dennis E. A. Acyl and phosphoryl migration in lysophospholipids: importance in phospholipid synthesis and phospholipase specificity. Biochemistry. 1982;21:1743–1750. doi: 10.1021/bi00537a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu X. Enzymatic production of structured lipids: Process reactions and acyl migration. Inform. 2000;11:1121–1131. [Google Scholar]
- Maran J. P. Manikandan S. Vigna Nivetha C. Dinesh R. Ultrasound assisted extraction of bioactive compounds from Nephelium lappaceum L. fruit peel using central composite face centered response surface design. Arabian J. Chem. 2013:2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Sodeifian G. Ghorbandoost S. Sajadian S. A. Saadati Ardestani N. Extraction of oil from Pistacia khinjuk using supercritical carbon dioxide: experimental and modeling. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2016;110:265–274. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2015.12.004. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- He W. H. Gao Y. X. Yuan F. Bao Y. N. Liu F. Z. Dong J. Q. Optimization of Supercritical Carbon Dioxide Extraction of Gardenia Fruit Oil and the Analysis of Functional Components. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2010;87:1071–1079. doi: 10.1007/s11746-010-1592-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna S. H. Divakar S. Prapulla S. G. Karanth N. G. Enzymatic synthesis of isoamyl acetate using immobilized lipase from Rhizomucor miehei. J. Biotechnol. 2001;87:193–201. doi: 10.1016/S0168-1656(00)00432-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishna S. H. Manohar B. Divakar S. Karanth N. G. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of isoamyl butyrate: optimization by response surface methodology. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999;76:1483–1488. doi: 10.1007/s11746-999-0189-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Keng P. S. Basri M. Rahman M. B. Abd. Salleh A. B. Rahman R. N. Z. Abd. Ariff A. Optimization of palm-based wax esters production using statistical experimental designs. J. Oleo Sci. 2005;54:519–528. doi: 10.5650/jos.54.519. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Keng P. S. Basri M. Zakaria M. R. S. Rahman M. B. A. Ariff A. B. Rahman R. N. Z. A. Salleh A. B. Newly synthesized palm esters for cosmetics industry. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009;29:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2008.04.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Frega N. Mozzon M. Lercker G. Effects of free fatty acids on oxidative stability of vegetable oil. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 1999;76:325–329. doi: 10.1007/s11746-999-0239-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]