C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds link molecules in the crystal into layers parallel to (011). The crystal packing is consolidated through C—Br⋯π and C—F⋯π interactions, as well as π–π stacking interactions.
Keywords: crystal structure, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds, C—Br⋯π interactions, C—F⋯π interactions, π–π stacking interactions, Hirshfeld surface analysis
Abstract
In the title compound, C14H8Br2FN3O2, the 4-fluorophenyl ring and the nitro-substituted phenyl ring form a dihedral angle of 64.37 (10)°. Molecules in the crystal are connected by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds into layers parallel to (011). The crystal packing is consolidated by C—Br⋯π and C—F⋯π interactions, as well as by π–π stacking interactions. According to a Hirshfeld surface analysis of the crystal structure, the most significant contributions to the crystal packing are from O⋯H/H⋯O (15.0%), H⋯H (14.3%), Br⋯H/H⋯Br (14.2%), C⋯H/H⋯C (10.1%), F⋯H/H⋯F (7.9%), Br⋯Br (7.2%) and Br⋯C/C⋯Br (5.8%) contacts.
1. Chemical context
Azo dyes are characterized by one or more azo groups R—N=N—R′, where R and R′ can be either alkyl, aryl or heterocyclic functional groups. Depending on the attached substituents, azo compounds have attracted attention because of their high synthetic potential for organic and inorganic chemistry and numerous useful properties. For example, azo dyes find applications in the design of functional materials attributed to smart hydrogen bonding, as self-assembled layers, photo-triggered structural switching, liquid crystals, ionophors, indicators, semiconductors, spectrophotometric reagents for determination of metal ions, catalysts, photoluminescent materials, optical recording media, spin-coating films and antimicrobial agents (Kopylovich et al., 2012 ▸; Ma et al., 2020 ▸, 2021 ▸; Mac Leod et al., 2012 ▸; Viswanathan et al., 2019 ▸). The azo-to-hydrazo tautomerism and E/Z isomerization properties of azo compounds are both crucial phenomena in the synthesis and design of new functional materials (Mahmudov et al., 2012 ▸, 2013 ▸, 2020 ▸; Mizar et al., 2012 ▸). Moreover, attachment of functional groups to the azo compounds acting as non-covalent donors or acceptors can be applied as a synthetic strategy for the improvement of the functional properties of this class of organic compounds (Gurbanov et al., 2020a ▸,b ▸; Mahmoudi et al., 2017 ▸, 2018 ▸; Shixaliyev et al., 2013 ▸, 2014 ▸).
In the above context, we have attached F, Br and NO2 groups and aryl rings to the –N=N– moiety leading to a new azo compound, (E)-1-[2,2-dibromo-1-(4-nitrophenyl)ethenyl]-2-(4-fluorophenyl)diazene, the molecular and crystal structure of which along with a Hirshfeld surface analysis are reported here.
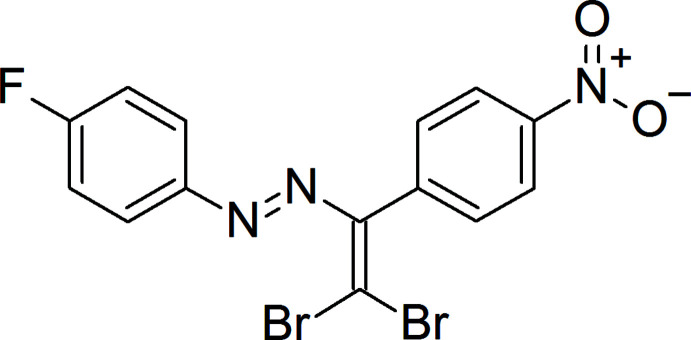
2. Structural commentary
The molecular conformation of the title compound is not planar, as seen in Fig. 1 ▸, with the 4-fluorophenyl ring and the nitro-substituted phenyl ring subtending a dihedral angle of 64.37 (10)°. The C1=C2 double bond has a small twist, with the dihedral angle between atoms C1/Br1/Br2 and C2/C3/N2 being 3.99 (10)°, possibly to minimize steric repulsion between Br2 and H. The N3/N2/C2/C1/Br1/Br2 moiety subtends dihedral angles of 63.70 (8) and 1.39 (8)° with the C3–C8 and C9–C14 rings, respectively. The aromatic ring and olefin synthon in the molecule are trans-configured with regard to the N=N double bond and are practically coplanar as revealed by the C2—N2=N3—C9 torsion angle of −178.63 (16)°. All of the bond lengths and angles in the title compound are similar to those for the related azo compounds reported in the Database survey section.
Figure 1.
The title molecule with the labelling scheme and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
3. Supramolecular features
In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds into layers extending parallel to (011) (Table 1 ▸; Figs. 2 ▸–4 ▸
▸). The crystal packing is consolidated by C—Br⋯π [Br1⋯Cg1 (x,
 − y, −
− y, −
 + z) = 3.6016 (9) Å, C1—Br1⋯Cg1 = 104.24 (7)°] and C—F⋯π [F1⋯Cg2 (1 − x, 1 − y, −z) = 3.5032 (17) Å, C12—F1⋯Cg2 = 92.53 (11)°] interactions, and weak π–π stacking [Cg1⋯Cg2 (x,
+ z) = 3.6016 (9) Å, C1—Br1⋯Cg1 = 104.24 (7)°] and C—F⋯π [F1⋯Cg2 (1 − x, 1 − y, −z) = 3.5032 (17) Å, C12—F1⋯Cg2 = 92.53 (11)°] interactions, and weak π–π stacking [Cg1⋯Cg2 (x,
 − y,
− y,
 + z) = 4.0788 (12) Å, slippage = 1.776 Å], where Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C3–C8 and C9–C14 rings, respectively, (Figs. 5 ▸–7 ▸
▸)].
+ z) = 4.0788 (12) Å, slippage = 1.776 Å], where Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the C3–C8 and C9–C14 rings, respectively, (Figs. 5 ▸–7 ▸
▸)].
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4⋯O2i | 0.95 | 2.47 | 3.331 (3) | 151 |
| C5—H5⋯F1ii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.150 (3) | 122 |
| C11—H11⋯O2iii | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.367 (3) | 140 |
| C14—H14⋯F1iv | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.427 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i)
 ; (ii)
; (ii)
 ; (iii)
; (iii)
 ; (iv)
; (iv)
 .
.
Figure 2.
View down [100] of the C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F interactions (dashed lines) in the title compound.
Figure 3.
View down [010] of the C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F interactions (dashed lines) in the title compound.
Figure 4.
View down [001] of the C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F interactions (dashed lines) in the title compound.
Figure 5.
View down [100] of the title compound, showing the molecular packing including C—Br⋯π and C—F⋯π interactions, as well as π–π interactions.
Figure 6.
View down [010] of the title compound, showing the molecular packing including C—Br⋯π and C—F⋯π interactions, as well as π–π interactions.
Figure 7.
View down [001] of the title compound, showing the molecular packing including C—Br⋯π and C—F⋯π interactions, as well as π–π interactions.
4. Hirshfeld surface analysis
Crystal Explorer 17.5 (Turner et al., 2017 ▸) was used to perform a Hirshfeld surface analysis and to generate the corresponding two-dimensional fingerprint plots, with a standard resolution of the three-dimensional d norm surfaces plotted over a fixed color scale of −0.1845 (red) to 1.1463 (blue) a.u. (Fig. 8 ▸). The red spots symbolize short contacts and negative d norm values on the surface corresponding to the C—H⋯O and C—H⋯F hydrogen bonds described above (Table 1 ▸). The C4—H4⋯O2 and C11—H11⋯O2 interactions, which play a key role in the molecular packing of the title compound, are responsible for the red spot that occurs around O2. The bright-red spots appearing near O2 and hydrogen atoms H4 and H11 indicate their roles as donor and/or acceptor groups in hydrogen bonding; they also appear as blue and red regions corresponding to positive and negative potentials on the Hirshfeld surface mapped over electrostatic potential (Spackman et al., 2008 ▸) shown in Fig. 9 ▸.
Figure 8.
View of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface of the title compound plotted over d norm in the range −0.1845 to 1.1463 a.u.
Figure 9.
View of the three-dimensional Hirshfeld surface of the title complex plotted over electrostatic potential energy in the range −0.0500 to 0.0500 a.u. using the STO-3 G basis set at the Hartree–Fock level of theory. The hydrogen-bond donor and acceptor groups are viewed as blue and red regions, respectively around the atoms, corresponding to positive and negative potentials.
The overall two-dimensional fingerprint plot for the title compound is given in Fig. 10 ▸ a, and those delineated into O⋯H/H⋯O, H⋯H, Br⋯H/H⋯Br, C⋯H/H⋯C, F⋯H/H⋯F, Br⋯Br and Br⋯C/C⋯Br contacts are shown in Fig.10b–h, while numerical details of the different contacts are given in Table 2 ▸. The percentage contributions to the Hirshfeld surfaces from the various interatomic contacts are compiled in Table 3 ▸. N⋯H/H⋯N, C⋯C, O⋯C/C⋯O, F⋯C/C⋯F, Br.·O/O⋯Br, N⋯C/C⋯N, N⋯O/O⋯N, N⋯N and F⋯F contacts contribute less than 5.7% to the Hirshfeld surface mapping and have little directional influence on the molecular packing (Table 3 ▸).
Figure 10.
The full two-dimensional fingerprint plots for the title compound, showing (a) all interactions, and delineated into (b) O⋯H / H⋯O, (c) H⋯H, (d) Br⋯H / H⋯Br, (e) C⋯H / H⋯C, (f) F⋯H / H⋯F, (g) Br⋯Br and (h) Br⋯C / C⋯Br interactions. The d i and d e values are the closest internal and external distances (in Å) from given points on the Hirshfeld surface.
Table 2. Summary of short interatomic contacts (Å) in the title compound.
| Contact | Distance | Symmetry operation |
|---|---|---|
| C1⋯Br2 | 3.6060 | −x,
 + y,
+ y,
 − z
− z
|
| Br1⋯Br1 | 3.7247 | −x, 1 − y, −z |
| H4⋯O2 | 2.47 |
x,
 − y, −
− y, −
 + z
+ z
|
| H7⋯Br2 | 3.08 | −x, 1 − y, 1 − z |
| F1⋯H5 | 2.54 | 1 − x,
 + y,
+ y,
 − z
− z
|
| C12⋯F1 | 3.3310 | 1 − x, 2 − y, −z |
| H14⋯F1 | 2.49 |
x,
 − y,
− y,
 + z
+ z
|
| O2⋯H11 | 2.58 | x, y, 1 + z |
| H13⋯O2 | 2.69 | 1 − x, 1 − y, 1 − z |
| C12⋯C12 | 3.5050 | 1 − x, 1 − y, −z |
Table 3. Percentage contributions of interatomic contacts to the Hirshfeld surface for the title compound.
| Contact | Percentage contribution |
|---|---|
| O⋯H/H⋯O | 15.0 |
| H⋯H | 14.3 |
| Br⋯H/H⋯Br | 14.2 |
| C⋯H/H⋯C | 10.1 |
| F⋯H/H⋯F | 7.9 |
| Br⋯Br | 7.2 |
| Br.·C/C⋯Br | 5.8 |
| N⋯H/H⋯N | 5.7 |
| C⋯C | 4.2 |
| O⋯C/C⋯O | 4.0 |
| F⋯C/C⋯F | 3.1 |
| Br.·O/O⋯Br | 2.7 |
| N⋯C/C⋯N | 2.1 |
| N⋯O/O⋯N | 2.0 |
| N⋯N | 1.0 |
| F⋯F | 0.8 |
5. Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.42, update of September 2021; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) for the (E)-1-(2,2-dichloro-1-phenylethenyl)-2-phenyldiazene moiety resulted in 27 hits. Eight compounds are closely related to the title compound, viz. those with CSD refcodes GUPHIL (I) (Özkaraca et al., 2020 ▸), HONBUK (II) (Akkurt et al., 2019 ▸), HONBOE (III) (Akkurt et al., 2019 ▸), HODQAV (IV) (Shikhaliyev et al., 2019a ▸), XIZREG (V) (Atioğlu et al., 2019 ▸), LEQXOX (VI) (Shikhaliyev et al., 2018a ▸), LEQXIR (VII) (Shikhaliyev et al., 2018b ▸) and PAXDOL (VIII) (Çelikesir et al., 2022 ▸).
In the crystal of (I), molecules are linked into inversion dimers via short halogen⋯halogen contacts [Cl1⋯Cl1 = 3.3763 (9) Å, C16—Cl1⋯Cl1 = 141.47 (7)°] compared to the van der Waals radius sum of 3.50 Å for two chlorine atoms. No other directional contacts could be identified, and the shortest aromatic ring centroid separation is greater than 5.25 Å. In the crystals of (II) and (III), molecules are linked through weak X⋯Cl contacts [X = Cl for (II) and Br for (III)], C—H⋯Cl and C—Cl⋯π interactions into sheets lying parallel to (001). In the crystal of (IV), molecules are stacked in columns parallel to [100] via weak C—H⋯Cl hydrogen bonds and face-to-face π–π stacking interactions. The crystal packing is further consolidated by short Cl⋯Cl contacts. In (V), molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds into zigzag chains running parallel to [001]. The crystal packing also features C—Cl⋯π, C—F⋯π and N—O⋯π interactions. In (VI), C—H⋯N and short Cl⋯Cl contacts are observed, and in (VII), C—H⋯N and C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds and short Cl⋯O contacts occur. In the crystal of (VIII), molecules are linked into chains running parallel to [001] by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The crystal packing is consolidated by C—F⋯π interactions and π–π stacking interactions, and short Br⋯O [2.9828 (13) Å] contacts are also observed.
6. Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was synthesized according to a reported method (Akkurt et al., 2019 ▸; Atioğlu et al., 2019 ▸; Maharramov et al., 2018 ▸; Özkaraca et al., 2020 ▸; Shikhaliyev et al., 2018a ▸,b ▸, 2019a ▸,b ▸). A 20 ml screw-neck vial was charged with dimethyl sulfoxide (10 ml), (E)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-(4-nitrobenzylidene)hydrazine (1 mmol), tetramethylethylenediamine (295 mg, 2.5 mmol), CuCl (2 mg, 0.02 mmol) and CBr4 (4.5 mmol). After 1–3 h (until TLC analysis showed complete consumption of the corresponding Schiff base), the reaction mixture was poured into a 0.01 M HCl solution (100 ml, pH = 2–3), and extracted with dichloromethane (3 × 20 ml). The combined organic phase was washed with water (3 × 50 ml), brine (30 ml), dried over anhydrous Na2SO4 and concentrated in vacuo using a rotary evaporator. The residue was purified by column chromatography on silica gel using appropriate mixtures of hexane and dichloromethane (v/v 3/1–1/1). Light-orange solid (yield 52%); m.p. 377 K. Analysis calculated for C14H8Br2FN3O2 (M = 429.04): C 39.19, H 1.88, N 9.79; found: C 39.17, H 1.85, N 9.76%. 1H NMR (300MHz, CDCl3) δ 7.36–7.14 (8H, Ar–H). 13C NMR (75MHz, CDCl3) δ 164.35, 153.13, 152.46, 133.69, 133.24, 131.74, 127.98, 127.89, 127.75, 127.42, 119.07, 89.02. ESI–MS: m/z: 430.06 [M + H]+. Crystals suitable for X-ray analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution.
7. Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 4 ▸. All H atoms were positioned geometrically [C—H = 0.95 Å] and refined using a riding model with U iso(H) = 1.2U eq(C). The maximum electron density in the final difference map is located 0.75 Å from atom Br1, while the minimum electron density is located 0.72 Å from Br2.
Table 4. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C14H8Br2FN3O2 |
| M r | 429.05 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 100 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 16.0658 (2), 7.0329 (1), 12.7934 (2) |
| β (°) | 96.8470 (6) |
| V (Å3) | 1435.21 (4) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 5.67 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.37 × 0.21 × 0.08 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Bruker AXS D8 QUEST, Photon III detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015 ▸) |
| T min, T max | 0.415, 0.747 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 44165, 4177, 3809 |
| R int | 0.102 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.703 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.034, 0.096, 1.05 |
| No. of reflections | 4177 |
| No. of parameters | 199 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 2.00, −1.04 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004388/wm5642sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004388/wm5642Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2168678
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors’ contributions are as follows. Conceptualization, NQS, MA and AB; synthesis, NAM and GVB; X-ray analysis, ZA, VNK and MA; writing (review and editing of the manuscript) ZA, MA and AB; funding acquisition, NQS, NAM and GVB; supervision, NQS, MA and AB.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C14H8Br2FN3O2 | F(000) = 832 |
| Mr = 429.05 | Dx = 1.986 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 16.0658 (2) Å | Cell parameters from 9926 reflections |
| b = 7.0329 (1) Å | θ = 3.2–33.2° |
| c = 12.7934 (2) Å | µ = 5.67 mm−1 |
| β = 96.8470 (6)° | T = 100 K |
| V = 1435.21 (4) Å3 | Plate, light red |
| Z = 4 | 0.37 × 0.21 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker AXS D8 QUEST, Photon III detector diffractometer | 4177 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed X-Ray tube | 3809 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.102 |
| Detector resolution: 7.31 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 30.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| φ and ω shutterless scans | h = −22→22 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Krause et al., 2015) | k = −9→9 |
| Tmin = 0.415, Tmax = 0.747 | l = −17→17 |
| 44165 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.034 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.096 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0647P)2 + 0.5442P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 4177 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 199 parameters | Δρmax = 2.00 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −1.04 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.07857 (2) | 0.35922 (3) | 0.08663 (2) | 0.01718 (8) | |
| Br2 | 0.02778 (2) | 0.28084 (3) | 0.31239 (2) | 0.02246 (8) | |
| C1 | 0.10911 (13) | 0.3752 (3) | 0.23267 (15) | 0.0143 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.18336 (12) | 0.4450 (3) | 0.27612 (15) | 0.0135 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.20411 (12) | 0.4693 (3) | 0.39184 (15) | 0.0131 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.26892 (13) | 0.3653 (3) | 0.44734 (16) | 0.0151 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.301935 | 0.282209 | 0.410651 | 0.018* | |
| C5 | 0.28537 (13) | 0.3827 (3) | 0.55606 (16) | 0.0148 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.329792 | 0.313645 | 0.594394 | 0.018* | |
| C6 | 0.23537 (13) | 0.5033 (3) | 0.60701 (15) | 0.0141 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.17169 (13) | 0.6115 (3) | 0.55419 (16) | 0.0158 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.139047 | 0.694455 | 0.591491 | 0.019* | |
| C8 | 0.15669 (12) | 0.5958 (3) | 0.44533 (15) | 0.0143 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.114268 | 0.670850 | 0.407127 | 0.017* | |
| N1 | 0.24975 (12) | 0.5135 (2) | 0.72236 (14) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.19544 (12) | 0.5861 (2) | 0.76893 (13) | 0.0259 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.31534 (11) | 0.4454 (2) | 0.76654 (12) | 0.0245 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.23866 (11) | 0.4967 (2) | 0.20300 (13) | 0.0153 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.31074 (11) | 0.5492 (3) | 0.24360 (14) | 0.0165 (3) | |
| C9 | 0.36346 (12) | 0.6039 (3) | 0.16716 (15) | 0.0144 (3) | |
| C10 | 0.33917 (13) | 0.6020 (3) | 0.05795 (16) | 0.0158 (4) | |
| H10 | 0.285307 | 0.556049 | 0.030764 | 0.019* | |
| C11 | 0.39360 (14) | 0.6669 (3) | −0.00982 (16) | 0.0177 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.377788 | 0.667540 | −0.083780 | 0.021* | |
| C12 | 0.47214 (14) | 0.7314 (3) | 0.03294 (17) | 0.0185 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.49862 (14) | 0.7325 (3) | 0.13950 (18) | 0.0203 (4) | |
| H13 | 0.553030 | 0.776322 | 0.165862 | 0.024* | |
| C14 | 0.44330 (14) | 0.6675 (3) | 0.20716 (17) | 0.0186 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.459864 | 0.666418 | 0.280965 | 0.022* | |
| F1 | 0.52527 (9) | 0.7950 (2) | −0.03383 (11) | 0.0261 (3) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.01901 (12) | 0.01931 (12) | 0.01257 (11) | 0.00170 (7) | −0.00084 (8) | −0.00163 (6) |
| Br2 | 0.02126 (13) | 0.02844 (14) | 0.01798 (12) | −0.00940 (8) | 0.00360 (8) | 0.00113 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0179 (9) | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0121 (8) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0173 (8) | 0.0111 (8) | 0.0124 (8) | 0.0016 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0007 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0144 (8) | 0.0131 (8) | 0.0118 (8) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0022 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0176 (9) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0124 (8) | 0.0025 (7) | 0.0038 (7) | 0.0002 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0165 (8) | 0.0144 (8) | 0.0134 (8) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0013 (7) | 0.0020 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0196 (9) | 0.0124 (8) | 0.0105 (8) | −0.0044 (7) | 0.0027 (7) | −0.0002 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0197 (9) | 0.0124 (8) | 0.0159 (9) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0052 (7) | −0.0017 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0156 (8) | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0142 (8) | 0.0016 (7) | 0.0023 (7) | 0.0000 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0122 (7) | 0.0147 (8) | −0.0054 (6) | 0.0037 (6) | −0.0008 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0394 (9) | 0.0243 (8) | 0.0159 (7) | 0.0010 (7) | 0.0107 (7) | −0.0038 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0325 (9) | 0.0245 (8) | 0.0150 (7) | −0.0041 (7) | −0.0029 (6) | 0.0020 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0182 (8) | 0.0141 (7) | 0.0139 (7) | 0.0018 (6) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0002 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0192 (8) | 0.0158 (8) | 0.0148 (7) | 0.0010 (6) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0005 (6) |
| C9 | 0.0172 (9) | 0.0133 (8) | 0.0128 (8) | 0.0019 (7) | 0.0026 (7) | −0.0002 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0179 (9) | 0.0154 (8) | 0.0140 (8) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0012 (7) | −0.0010 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0212 (9) | 0.0184 (9) | 0.0132 (8) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | −0.0007 (7) |
| C12 | 0.0194 (9) | 0.0183 (9) | 0.0188 (9) | −0.0006 (7) | 0.0062 (8) | 0.0009 (7) |
| C13 | 0.0168 (9) | 0.0232 (10) | 0.0205 (10) | −0.0025 (8) | 0.0012 (8) | −0.0018 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0198 (9) | 0.0217 (9) | 0.0140 (9) | −0.0006 (8) | 0.0004 (7) | −0.0017 (7) |
| F1 | 0.0239 (7) | 0.0354 (8) | 0.0202 (6) | −0.0064 (6) | 0.0081 (5) | 0.0037 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| Br1—C1 | 1.878 (2) | N1—O1 | 1.225 (2) |
| Br2—C1 | 1.872 (2) | N1—O2 | 1.232 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.347 (3) | N2—N3 | 1.266 (2) |
| C2—N2 | 1.412 (3) | N3—C9 | 1.421 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.488 (3) | C9—C14 | 1.397 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.395 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.405 (3) |
| C3—C8 | 1.402 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.380 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.390 (3) | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C11—C12 | 1.390 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.384 (3) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C12—F1 | 1.354 (2) |
| C6—C7 | 1.385 (3) | C12—C13 | 1.379 (3) |
| C6—N1 | 1.468 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.390 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.389 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | ||
| C2—C1—Br2 | 123.06 (15) | O1—N1—O2 | 123.97 (19) |
| C2—C1—Br1 | 123.08 (15) | O1—N1—C6 | 118.25 (18) |
| Br2—C1—Br1 | 113.85 (10) | O2—N1—C6 | 117.77 (17) |
| C1—C2—N2 | 114.61 (17) | N3—N2—C2 | 114.84 (17) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 122.32 (17) | N2—N3—C9 | 112.81 (17) |
| N2—C2—C3 | 123.05 (17) | C14—C9—C10 | 120.10 (19) |
| C4—C3—C8 | 120.02 (18) | C14—C9—N3 | 115.55 (18) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 120.73 (17) | C10—C9—N3 | 124.33 (18) |
| C8—C3—C2 | 119.23 (17) | C11—C10—C9 | 119.98 (19) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.28 (18) | C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.9 | C10—C11—C12 | 118.29 (19) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.27 (18) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.9 | C12—C11—H11 | 120.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.9 | F1—C12—C13 | 118.6 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 122.93 (18) | F1—C12—C11 | 118.07 (19) |
| C5—C6—N1 | 118.21 (18) | C13—C12—C11 | 123.3 (2) |
| C7—C6—N1 | 118.85 (17) | C12—C13—C14 | 118.0 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 118.38 (18) | C12—C13—H13 | 121.0 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.8 | C14—C13—H13 | 121.0 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.8 | C13—C14—C9 | 120.3 (2) |
| C7—C8—C3 | 120.04 (18) | C13—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.0 | C9—C14—H14 | 119.8 |
| C3—C8—H8 | 120.0 | ||
| Br2—C1—C2—N2 | 175.66 (13) | C7—C6—N1—O1 | 14.3 (3) |
| Br1—C1—C2—N2 | −3.1 (3) | C5—C6—N1—O2 | 14.4 (3) |
| Br2—C1—C2—C3 | −5.6 (3) | C7—C6—N1—O2 | −166.82 (18) |
| Br1—C1—C2—C3 | 175.56 (14) | C1—C2—N2—N3 | −175.03 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 115.8 (2) | C3—C2—N2—N3 | 6.3 (3) |
| N2—C2—C3—C4 | −65.7 (3) | C2—N2—N3—C9 | −178.63 (16) |
| C1—C2—C3—C8 | −63.1 (3) | N2—N3—C9—C14 | 178.57 (18) |
| N2—C2—C3—C8 | 115.5 (2) | N2—N3—C9—C10 | 0.4 (3) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | 1.7 (3) | C14—C9—C10—C11 | −1.4 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −177.12 (18) | N3—C9—C10—C11 | 176.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.8 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −2.1 (3) | C10—C11—C12—F1 | −179.95 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6—N1 | 176.62 (18) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | 0.5 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 1.0 (3) | F1—C12—C13—C14 | 179.7 (2) |
| N1—C6—C7—C8 | −177.77 (17) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −0.7 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C3 | 1.5 (3) | C12—C13—C14—C9 | −0.1 (3) |
| C4—C3—C8—C7 | −2.9 (3) | C10—C9—C14—C13 | 1.2 (3) |
| C2—C3—C8—C7 | 175.96 (18) | N3—C9—C14—C13 | −177.1 (2) |
| C5—C6—N1—O1 | −164.51 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4···O2i | 0.95 | 2.47 | 3.331 (3) | 151 |
| C5—H5···F1ii | 0.95 | 2.54 | 3.150 (3) | 122 |
| C11—H11···O2iii | 0.95 | 2.58 | 3.367 (3) | 140 |
| C14—H14···F1iv | 0.95 | 2.49 | 3.427 (3) | 169 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (ii) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (iii) x, y, z−1; (iv) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2.
Funding Statement
This work was performed under the support of the Science Development Foundation under the President of the Republic of Azerbaijan (grant No. EIF-BGM-4-RFTF-1/2017–21/13/4).
References
- Akkurt, M., Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Suleymanova, G. T., Babayeva, G. V., Mammadova, G. Z., Niyazova, A. A., Shikhaliyeva, I. M. & Toze, F. A. A. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 1199–1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Atioğlu, Z., Akkurt, M., Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Suleymanova, G. T., Bagirova, K. N. & Toze, F. A. A. (2019). Acta Cryst. E75, 237–241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2018). APEX3 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Çelikesir, S. T., Akkurt, M., Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Mammadova, N. A., Suleymanova, G. T., Khrustalev, V. N. & Bhattarai, A. (2022). Acta Cryst. E78, 404–408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (2012). J. Appl. Cryst. 45, 849–854.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Gurbanov, A. V., Kuznetsov, M. L., Demukhamedova, S. D., Alieva, I. N., Godjaev, N. M., Zubkov, F. I., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2020a). CrystEngComm, 22, 628–633.
- Gurbanov, A. V., Kuznetsov, M. L., Mahmudov, K. T., Pombeiro, A. J. L. & Resnati, G. (2020b). Chem. Eur. J. 26, 14833–14837. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Kopylovich, M. N., Mac Leod, T. C. O., Haukka, M., Amanullayeva, G. I., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2012). J. Inorg. Biochem. 115, 72–77. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Krause, L., Herbst-Irmer, R., Sheldrick, G. M. & Stalke, D. (2015). J. Appl. Cryst. 48, 3–10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z., Mahmudov, K. T., Aliyeva, V. A., Gurbanov, A. V., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2021). Coord. Chem. Rev. 437, 213859.
- Ma, Z., Mahmudov, K. T., Aliyeva, V. A., Gurbanov, A. V. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2020). Coord. Chem. Rev. 423, 213482.
- Mac Leod, T. C., Kopylovich, M. N., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2012). Appl. Catal. Gen. 439–440, 15–23.
- Maharramov, A. M., Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Suleymanova, G. T., Gurbanov, A. V., Babayeva, G. V., Mammadova, G. Z., Zubkov, F. I., Nenajdenko, V. G., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2018). Dyes Pigments, 159, 135–141.
- Mahmoudi, G., Afkhami, F. A., Castiñeiras, A., García-Santos, I., Gurbanov, A., Zubkov, F. I., Mitoraj, M. P., Kukułka, M., Sagan, F., Szczepanik, D. W., Konyaeva, I. A. & Safin, D. A. (2018). Inorg. Chem. 57, 4395–4408. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Mahmoudi, G., Zaręba, J. K., Gurbanov, A. V., Bauzá, A., Zubkov, F. I., Kubicki, M., Stilinović, V., Kinzhybalo, V. & Frontera, A. (2017). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 4763–4772.
- Mahmudov, K. T., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C., Glucini, M., Renzi, M., Gabriel, K. C. P., Kopylovich, M. N., Sutradhar, M., Marchetti, F., Pettinari, C., Zamponi, S. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2012). Inorg. Chem. Commun. 22, 187–189.
- Mahmudov, K. T., Gurbanov, A. V., Aliyeva, V. A., Resnati, G. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2020). Coord. Chem. Rev. 418, 213381.
- Mahmudov, K. T., Kopylovich, M. N., Haukka, M., Mahmudova, G. S., Esmaeila, E. F., Chyragov, F. M. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2013). J. Mol. Struct. 1048, 108–112.
- Mizar, A., Guedes da Silva, M. F. C., Kopylovich, M. N., Mukherjee, S., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2012). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 2305–2313.
- Özkaraca, K., Akkurt, M., Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Askerova, U. F., Suleymanova, G. T., Mammadova, G. Z. & Shadrack, D. M. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1251–1254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015a). Acta Cryst. A71, 3–8.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015b). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Ahmadova, N. E., Gurbanov, A. V., Maharramov, A. M., Mammadova, G. Z., Nenajdenko, V. G., Zubkov, F. I., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2018a). Dyes Pigments, 150, 377–381.
- Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Ahmadova, N. E., Gurbanov, A. V., Maharramov, A. M., Mammadova, G. Z., Nenajdenko, V. G., Zubkov, F. I., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2018b). Dyes Pigments, 150, 377–381.
- Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Kuznetsov, M. L., Maharramov, A. M., Gurbanov, A. V., Ahmadova, N. E., Nenajdenko, V. G., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2019a). CrystEngComm, 21, 5032–5038.
- Shikhaliyev, N. Q., Kuznetsov, M. L., Maharramov, A. M., Gurbanov, A. V., Ahmadova, N. E., Nenajdenko, V. G., Mahmudov, K. T. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2019b). CrystEngComm, 21, 5032–5038.
- Shixaliyev, N. Q., Gurbanov, A. V., Maharramov, A. M., Mahmudov, K. T., Kopylovich, M. N., Martins, L. M. D. R. S., Muzalevskiy, V. M., Nenajdenko, V. G. & Pombeiro, A. J. L. (2014). New J. Chem. 38, 4807–4815.
- Shixaliyev, N. Q., Maharramov, A. M., Gurbanov, A. V., Nenajdenko, V. G., Muzalevskiy, V. M., Mahmudov, K. T. & Kopylovich, M. N. (2013). Catal. Today, 217, 76–79.
- Spackman, M. A., McKinnon, J. J. & Jayatilaka, D. (2008). CrystEngComm, 10, 377–388.
- Spek, A. L. (2020). Acta Cryst. E76, 1–11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Turner, M. J., McKinnon, J. J., Wolff, S. K., Grimwood, D. J., Spackman, P. R., Jayatilaka, D. & Spackman, M. A. (2017). CrystalExplorer17. The University of Western Australia.
- Viswanathan, A., Kute, D., Musa, A., Mani, S. K., Sipilä, V., Emmert-Streib, F., Zubkov, F. I., Gurbanov, A. V., Yli-Harja, O. & Kandhavelu, M. (2019). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 166, 291–303. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004388/wm5642sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989022004388/wm5642Isup2.hkl
CCDC reference: 2168678
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report












