In the article titled “Role of Baicalin in Anti-Influenza Virus A as a Potent Inducer of IFN-Gamma” [1], there appears to be an image duplication in Figure 1, as raised on PubPeer [2]. In Figure 1(c), the panel showing the 100x + untreated mice inadvertently duplicated the panel showing the 100x + 2.0 g/kg BA-treated mice.
Figure 1.
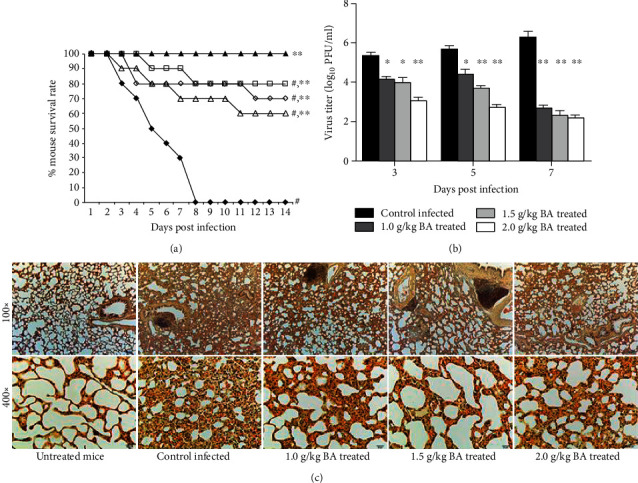
Antiviral activity of BA in treating A/PR/8/34-infected mice. Mice were inoculated with virus intranasally and treated with BA at the indicated concentration every 24 h for 14 days. Each group consists of 10 mice. (a) Survival rate of mice was observed in the next two weeks. ▲: untreated mice; ●: control A/PR/8/34-infected mice; ∆: 1.0 g/kg BA-treated mice; ○: 1.5 g/kg BA-treated mice; □: 2.0 g/kg BA-treated mice. (b) Lungs of mice were homogenized separately, diluted, and centrifuged on the third, fifth, and seventh day after infection, and the EID50s were determined using 10-day chick embryo. (c) Lungs of mice were removed and examined pathologically using HE staining on the seventh day after infection. #Levels of significance of P < 0.05 against untreated mice; ∗P < 0.05 against control infected mice; ∗∗P < 0.01 against control infected mice.
The corrected figure, as approved by the editorial board, is shown below.
References
- 1.Chu M., Xu L., Zhang M.-b., Chu Z.-y., Wang Y.-d. Role of baicalin in anti-influenza virus A as a potent inducer of IFN-gamma. BioMed Research International . 2015;2015:11. doi: 10.1155/2015/263630.263630 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Valida G. Role of baicalin in anti-influenza virus A as a potent inducer of IFN-gamma. 2019. https://pubpeer.com/publications/78D9F9DB59726ACFD6FA4BA2D6C860 .


