Abstract
Background
Quorum sensing (QS) system can regulate the expression of virulence factors and biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutans. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) inhibits quorum quenching (QQ), and can be used to prevent microbial biofilm. We thereby aimed to evaluate the anti-biofilm potency and anti-metabolic activity of nano-quercetin (N-QCT)-mediated aPDT against S. mutans. Also, in silico evaluation of the inhibitory effect of N-QCT on the competence-stimulating peptide (CSP) of S. mutans was performed to elucidate the impact of aPDT on various QS-regulated genes.
Methods
Cytotoxicity and intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation were assessed following synthesis and confirmation of N-QCT. Subsequently, the minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration (MBIC) of N-QCT against S. mutans and anti-biofilm effects of aPDT were assessed using colorimetric assay and plate counting. Molecular modeling and docking analysis were performed to confirm the connection of QCT to CSP. The metabolic activity of S. mutans and the expression level of various genes involved in QS were evaluated by flow cytometry and reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR, respectively.
Results
Successful synthesis of non-toxic N-QCT was confirmed through several characterization tests. The MBIC value of N-QCT against S. mutans was 128 μg/mL. Similar to the crystal violet staining, the results log10 CFU/mL showed a significant degradation of preformed biofilms in the group treated with aPDT compared to the control group (P < 0.05). Following aPDT, metabolic activity of S. mutans also decreased by 85.7% (1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT) and 77.3% (1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT), as compared to the control values (P < 0.05). In silico analysis showed that the QCT molecule was located in the site formed by polypeptide helices of CSP. The relative expression levels of the virulence genes were significantly decreased in the presence of N-QCT-mediated aPDT (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
The combination of N-QCT with blue laser as a QQ-strategy leads to maximum ROS generation, disrupts the microbial biofilm of S. mutans, reduces metabolic activity, and downregulates the expression of genes involved in the QS pathway by targeting genes of the QS signaling system of S. mutans.
Keywords: Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy, Competence-stimulating peptide, Dental caries, Quorum sensing, Streptococcus mutans
Introduction
Dental caries is a common irreversible chronic infectious disease that over time, demineralizes the tooth structure and results in progressive tooth decay [1]. The dental cariogenic pathogen Streptococcus mutans synthesizes quorum sensing (QS) signals, competence-stimulating peptides (CSP) that are sensed via a two-component signal system (ComDE) [2]. The comC gene encodes the ComC propeptide, that is processed by the ABC transporter complex, ComAB, leading to the production of 21-CSP. This 21-amino acid polypeptide is cleaved into an 18-amino acid polypeptide (18-CSP) by SepM, a membrane-localized protease. 18-CSP, activates the cytoplasmic response regulator ComE through interaction with ComD, a histidine kinase membrane-bound protein receptor. Active ComE then results in the expression of various virulence genes as a response to the development of competence [3–5]. A previous study showed that the ComD/ComE signal transduction system can regulate the expression of glucosyltransferase B/C/D (gtfB/C/D), fructosyltransferase (ftf), and glucan-binding protein B (gbpB) genes [6, 7].
S. mutans utilizes Com-dependent QS systems to coordinate a myriad of biological processes such as regulating genetic transformation, natural competence, niche adaptation during host colonization, sporulation, virulence, and biofilm formation [5]. The structure of S. mutans biofilm acts as a barrier in exposure to the chemical anti-biofilm agents and leads to increase resistance against different antimicrobial factors. It has been reported that any mechanism with the capability of inhibiting any one of the key processes in the QS signals, named quorum quenching (QQ) can be potentially used for QQ sensing and preventing microbial infections. Given that research in QS inhibitors and QQ has been progressing so rapidly in recent years, the introduction of new mechanisms of QQ is inevitable [8, 9].
According to the literature, antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) by suppression of the virulence factors of microbial pathogens is a novel approach to inhibit biofilms [10–12]. aPDT is a multi-stage process including administration of a non-toxic dye called photosensitizer (PS), harmless visible light irradiation with specific wavelengths for PS, and interaction of the excited state with oxygen. The excited PS can produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) and result in microbial cell death either by damaging the cell membrane or proteins, lipids, and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). Up to now, a variety of in vitro and in vivo aPDT studies have demonstrated a broad-spectrum of activity in favor of biofilm-eradication or substantial reduction [13].
As mentioned, one of the most important components involved in aPDT is PS. Among PS structures commonly employed in aPDT, natural products have received a lot of attention. Quercetin (QCT) as a major flavonoid, a class of secondary metabolic products of plants, possesses a wide range of pharmacological activities, including neuroprotective, antioxidant, anticancer, antimicrobial infections, and antiapoptotic applications [14]. QCT has two maximum absorption bands 380 and 258 nm [15] with a strong biological effect at micromolar concentrations after activation by light at 405 ± 10 nm.
Due to the increasing need for the effective degradation of S. mutans biofilm in dental caries, more attention in this study has been focused on the combination of nano-QCT (N-QCT) and blue laser light. Since previous studies have shown that aPDT can be a useful supplementary strategy for QS inhibitor in inducing microbicidal effect and reducing the possibility of drug resistance [16–18], the current study was designed (i) to determine the anti-biofilm potency and anti-metabolic activity of N-QCT-mediated aPDT against S. mutans, (ii) to identify in silico N-QCT with an inhibitory effect on S. mutans CSP, and (iii) to elucidate the effects of aPDT on various QS regulated genes. It was hypothesized that the combination of phototherapy and N-QCT can enhance the photosensitivity of S. mutans biofilm in response to aPDT.
Materials and methods
Synthesis of N-QCT
N-QCT was synthesized according to the study by Debnath et al. [19] with a slight modification. Briefly, QCT (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany) solution at a concentration of 3 mg/mL was prepared in 1% DMSO (Merck, Germany). Then, 30 mL of poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA, Sigma-Aldrich, Germany) 0.1% (w/v) was added and the resulting mixture was magnetically stirred at room temperature for 6 h to form a colloidal suspension. The suspension was subsequently centrifuged at 15,000 rpm for 15 min to remove free un-encapsulated QCT. The final product was transferred to a freeze-dryer to obtain a dry powder.
Characterization of synthesized N-QCT
The surface morphology of N-QCT was studied by field emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM; ZEISS, German). The size distribution profiles of nanometer-sized particles and zeta potential of N-QCT were carried out using a MALVERN Zetasizer Ver. 6.01 (Malvern Instruments, UK) at approximately 25 °C. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy was used to analyze the elemental composition of N-QCT. Also, the entrapment efficiency (EE%) and drug loading (DL%) of N-QCT were determined by an ultraviolet-visible (UV–vis) spectroscopy (Eppendorf BioSpectrometer®, Germany) at 438 nm using the following equations:
and
Absorption spectra of N-QCT
The ultraviolet-visible (UV–vis) spectra of N-QCT were scanned within the wavelength range of 300–600 nm using an UV–vis spectrophotometer.
Cytotoxicity and N-QCT induced cell survival assay
The normal human gingival fibroblast (HGF) cells (IBRC C10459) at a density of 1 × 105 cells/well were sub-cultured in a 96-well culture plate containing 200 μL of Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium (DMEM) supplemented with 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), 2 mM L-glutamine, 100 μg/mL amphotericin B, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin antibiotic solution (10,000 Unit/mL penicillin, 10 mg/mL streptomycin). The cells were incubated overnight in a humidified incubator at 37 °C with 5% CO2 and 95% air for adherence to the culture plate. Afterward, the cells were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h in presence of N-QCT at the different concentrations (128, 256, and 512 μg/mL) and cell viability was determined by MTT assay as reported previously [20].
Bacterial strain and growth conditions
The standard strain of S. mutans ATCC 35668 was cultured from single colonies in brain heart infusion (BHI) broth (Sigma-Aldrich, Germany) at 37 °C in a 5% CO2, aerobic atmosphere. Bacterial suspensions were standardized with half McFarland standard, equivalent to a suspension of 1.5 × 108 colony forming unit (CFU) per milliliter (mL).
Determination of Minimum Biofilm Inhibitory Concentration (MBIC) of N-QCT
The broth microdilution method was used for determining the MBIC dose of N-QCT against S. mutans according to Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines [21]. We used the experimental conditions of the method described by Aires et al. [22] to prepare S. mutans biofilms. Briefly, 100 μL of bacterial cells at a final concentration of 1.5 × 106 CFU/mL was added to wells of a 96-well microtiter plate which were containing two-fold N-QCT-dilutions ranging from 512 to 1.0 μg/mL in ultrafiltered buffered tryptone–yeast extract broth (UFTYE) for 3 days, at 10% CO2 and 37 °C, and exposed to 10% sucrose for 1 min, 8×/day. After incubation, the supernatant was removed and the wells were washed twice with PBS (200 μL/well) to remove planktonic and loosely bound cells. The attached bacterial cells were then stained with 0.1% crystal violet for 15 min and dissolved in 96% ethanol to remove the bound dye from the stained cells. The dye bound to biofilm was re-solubilized with 150 μL of 33% acetic acid and the optical density (OD) of each well was measured at 570 nm by a microplate reader (BioTek, Germany) [23]. The following controls were included in each MBIC test plate: 1) 0.2% chlorhexidine (CHX; positive control); 2) S. mutans in medium (negative control); 3) medium only (sterility control). MBIC was defined as the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial agent required to inhibit the formation of biofilms [21].
Human saliva collection
Whole saliva samples were collected from a healthy volunteer after overnight fasting and pooled into sterile bottles. The collected saliva was then centrifuged at 8000 rpm for 15 min at 4 °C, sterilized using a syringe filter with a 0.22 μm pore size, and coated onto wells of the 96-well microtiter plates for biofilm formation assays [6].
Biofilm formation and treatment procedure
The coated plates with saliva were incubated at 4 °C for 60 min and were washed twice with sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) followed by air drying for 30 min. The overnight culture of S. mutans was then inoculated in a semi-defined biofilm medium (BM) [24] containing a final concentration of 18 mM glucose and 2 mM sucrose (BMGS) [25]. Bacterial suspensions (100 μL) were added to the wells and the microtiter plates were incubated for 72 h at 37 °C in the presence of 5% CO2 to form the mature biofilms. Finally, the formed biofilms in the experimental groups were treated with experimental groups as follow:
-
A.
N-QCT: The 96-well microtiter plate containing preformed S. mutans biofilms was treated with 200 μL of N-QCT at sub-MBIC doses in the dark at room temperature for 5 min. The biofilm structures were washed twice with 200 μL of PBS to remove the planktonic bacterial cells.
-
B.
Blue laser: The preformed S. mutans biofilms were exposed to a blue laser (Laser Diode, ASHA, Iran) at a wavelength of 405 ± 10 nm (according to the wavelength obtained from UV-Vis) and output intensity of 150 mW/cm2 for 60 s.
The polystyrene microplate has 0% and less than 10% light absorption and reflection, respectively, at wavelengths between 400 and 1000 nm [26, 27]. The absorbance value of polystyrene microplate wells containing distilled water is the same as the empty ones [28] which reveals the advantage of applying polystyrene microplate for absorbance measurements in the visible light region of the spectrum including 405 ± 10 nm which was used in the current study [28]. To prevent beam reflection from the table top and transmission of light to wells around the test wells during irradiation in blue laser and aPDT groups, sheets of black paper were used under the microplates and filled the neighboring test wells with methylene blue, respectively. The probe of the laser was fixed 2 mm above the top surface of the microplate by a stand [29].
-
III.
aPDT: The preformed S. mutans biofilms were treated by sub-MBIC doses of N-QCT similar to group A and were then exposed with a blue laser similar to group B.
-
IV.
Positive control: 200 μL of 0.2% chlorhexidine (CHX) was added to S. mutans biofilms and incubated at room temperature for 5 min.
-
V.
Negative control: 200 μL of normal saline was added to S. mutans biofilms and incubated for 5 min at room temperature.
Measurement of intracellular ROS generation
The generation of intracellular ROS following each treatment was evaluated using fluorescent2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) method as follows [30]:
N-QCT
The 96-well microtiter plate containing preformed S. mutans biofilms was treated with 200 μL of N-QCT at sub-MBIC doses in the dark at room temperature for 5 min. The biofilm structures were washed twice with 200 μL of PBS to remove the planktonic bacterial cells. The biofilm cells were then incubated with 10 μM DCFH-DA (200 μL) for 1 h. The fluorescence intensity of DCF was then quantified with excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 530 nm, respectively.
Blue laser
ROS detections following irradiation were carried out in 1 × 1 × 3 cm glass cuvettes containing preformed S. mutans biofilms. The biofilm structures were washed twice with 2000 μL of PBS to remove the planktonic bacterial cells. After treatment of S. mutans biofilms with 10 μM DCFH-DA for 1 h. The blue laser probe stood on the top surface of the cuvette. This permitted irradiation during the acquisition of a fluorescence signal in real-time. The blue laser was switched on immediately before the beginning of fluorescence acquisition. The fluorescence intensity of DCF was then quantified with excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 530 nm, respectively.
aPDT
ROS detections following photodynamic reaction were carried out after treatment S. mutans biofilms with sub-MBIC doses of N-QCT similar to the N-QCT group and were then exposed with a blue laser similar to the blue laser group as mentioned above.
Positive and negative control groups
ROS assessment was performed in the positive control and negative control groups as in the N-QCT group, except that 0.2% CHX and sterile normal saline were used instead of N-QCT in the positive and negative control groups, respectively.
Assessment of biofilm viable cells by colony count
Media was removed from all wells after treatment of S. mutans biofilms according to the experimental design described. The formed biofilms were washed twice with PBS (200 μL). Next, 100 μL of sterile normal saline solution was added to wells containing biofilm, and the biofilm cells were suspended by vigorous pipetting. The suspended biofilm was transferred to a new microtiter plate followed by 5-fold dilutions prepared in BHI broth. Immediately, 10 μL of each well-containing dilution series were cultured onto BHI agar and the plates were incubated at 37 °C for 24 h. Eventually, the log10 CFU/mL were determined as the previous study [31]. Bactericidal activity was defined as a reduction of at least ≥3 log10 (99.9%) of the bacterial count (CFU/mL) in the original inoculum [32]. The percentage of microbial cell reduction after each treatment was calculated using the following equation:
P: is the percent reduction.
L: is the log reduction.
Assessment of biofilm biomass by colorimetric assay
After treatment of S. mutans biofilms based on the study groups, the microtiter plates were lightly washed twice with 200 μL/well of PBS to remove planktonic and loosely bound cells. The remaining cells were then stained with 0.1% crystal violet as described above, and the OD of the suspensions was measured spectrophotometrically at 570 nm.
Assessment of metabolic activity of biofilm cells by flow cytometry
Mature S. mutans biofilms were prepared, treated as described above, and resuspended. After that, 100 μL of biofilm suspensions were transferred to the microtubes and mixed with 10 μL of Syto9 (20 μM) for 15 min, and later, 10 μL of 800 μM propidium iodide (PI) for 5 min. Then, samples were immediately processed and analyzed by flow cytometry (Becton Dickinson, USA). The sample was excited at 488 nm and the emission was registered using the FITC channel for Syto 9 (530/30) and PerCP channel (670/LP) for PI [33]. The biofilm cell viability was reported in percentage in relation with the control cells (untreated biofilm cells) [34].
In silico analysis of CSP in S. mutans
Molecular modeling and in silico characterization of the structural subunit of CSP were evaluated. The amino acid sequences for the virtual search were selected using the CSP of sequence CAL29411.1. Alignment with a Protein Basic Local Alignment Search Tool-NCBI (BLAST-P) was conducted in Protein Data Bank (PDB) entries to retrieve and find similar sequences to CSP. Physicochemical properties of CSP were performed using UniProt. STRING (http://string-db.org) quantitatively assimilated the protein-protein interactions (PPI) network and ranked their significance or validity as targets.
Docking analysis
The two-dimensional structure of QCT was downloaded from the PubChem database. The Surflex-Dock program was used to build the interaction model between QCT and CSP and SwissDock was used to study the binding orientation of QCT into the CSP structure. Best protein-ligands complexes were selected according to the scoring function of the SwissDock fitness score.
Quantification of gene expression using reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR)
Immediately after treatment, the cells were pelleted by centrifugation and total RNA extraction was performed using the super RNA extraction Kit (AnaCell, Iran). Total RNA (150 ng) was reverse transcribed in a 10 μL cDNA reaction volume RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Thermo Scientific GmbH, Germany) based on the manufacturer’s instructions following the deletion of residual genomic DNA using RNase-free DNase I treatment (Thermo Scientific GmbH, Germany). The gene-specific primers designed using Primer3Plus software version 4.0 (http://bioinfo.ut.ee/primer3/) are listed in Table 1. The normalization of RT-qPCR data was carried out using the 16S rRNA gene as an internal control. Distilled water was used as a negative control in this study. RT-qPCR was conducted using Line-GeneK Real-Time PCR Detection System and Software (Bioer Technology, Hangzhou, China), with control and standard as described previously [35]. Fold differences in mRNA expression were determined using Livak and Schmittgen [36] method and down- and upregulation were considered significant when the relative expression was decreased or increased ≥ two-folds.
Table 1.
Primer sequence for RT-qPCR analysis of various genes in S. mutans
| Gene | Primer Sequence (5′–3′) | Product size (bp)a |
|---|---|---|
| comA | ||
| Forward | TTGTTGGCGCAAAACAATAA | 174 |
| Reverse | AATGGTTTCCATCCCATTGA | |
| comB | ||
| Forward | CCAGTCCAAACCGTCAGACT | 164 |
| Reverse | GCTGCTTTCCTTGTCTTTCG | |
| comDE | ||
| Forward | ACAATTCCTTGAGTTCCATCCAAG | 81 |
| Reverse | TGGTCTGCTGCCTGTTGC | |
| gtfB | ||
| Forward | TGTTGTTACTGCTAATGAAGAA | 103 |
| Reverse | GCTACTGATTGTCGTTACTG | |
| 16S rRNA | ||
| Forward | CCTACGGGAGGCAGCAGTAG | 121 |
| Reverse | CAACAGAGCTTTACGATCCGAAA | |
abp base pair
Statistical analysis
All experiments were repeated at least three times. Data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey post hoc test using Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS) software version 25.0. All data are expressed as means ± standard deviation (SD), and P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
Confirmation of N-QCT synthesis
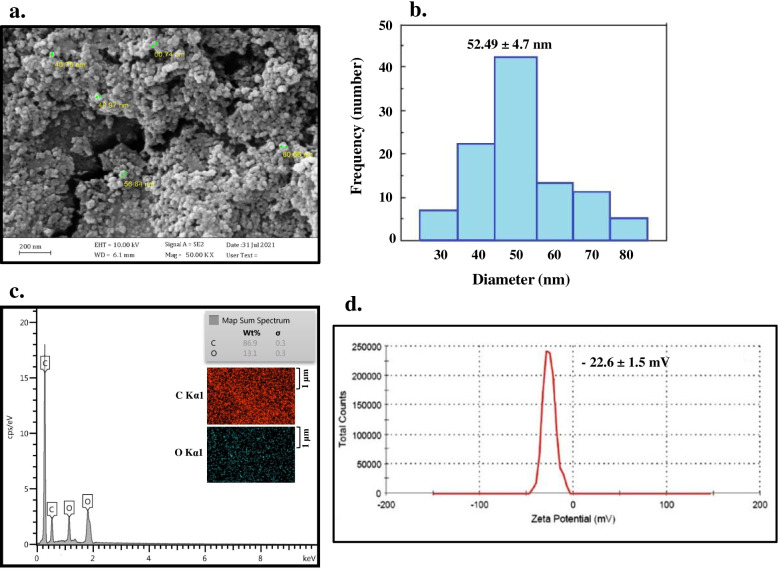
N-QCT had a spherical morphology with an average diameter of 52.49 ± 4.7 nm (Fig. 1a). The hydrodynamic size of the N-QCT was within 30-80 nm as observed from dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurement (Fig. 1b). Appearances of characteristic Kα lines of C and O in the context of the sample confirmed the presence of N-QCT (Fig. 1c). The average surface charge of N-QCT was − 22.6 ± 1.5 mV (Fig. 1d). Additionally, the EE and DL capacity ranged from 74.12 to 88.25% and from 5.36 to 17.20%, respectively.
Fig. 1.
Characterization of synthesized nano-QCT (N-QCT): a Field emission scanning electron microscope (FESEM) image (Scale bar = 2 μm), b The size distribution profile of N-QCT, c Elemental mapping of N-QCT
The UV–vis spectrum of N-QCT is presented in Fig. 2. Accordingly, the absorption wavelength of N-QCT was found to be 405 nm.
Fig. 2.
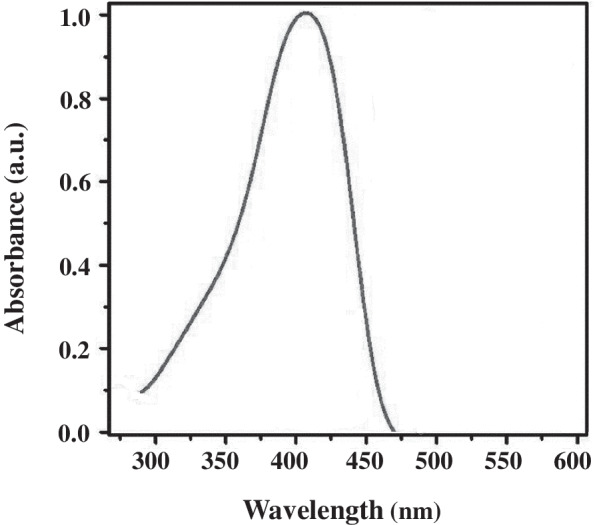
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy of N-QCT
Effect of N-QCT on cell viability
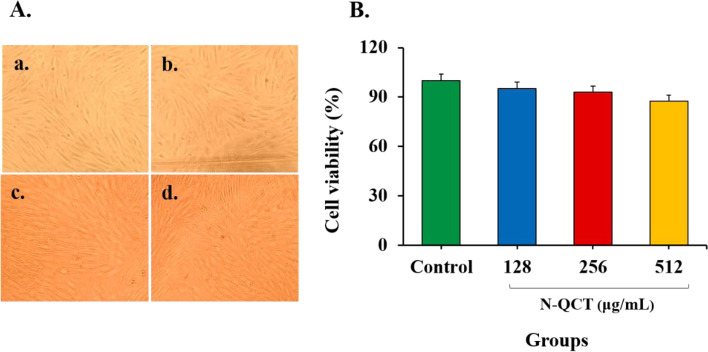
The functional effect of N-QCT on HGF as normal fibroblast cells was investigated using the MTT assay. According to the data, treatment of the cells with 128, 256, and 512 μg/mL of N-QCT for 24 h had a non-considerable adverse effect on HGF cells (P > 0.05; Fig. 3).
Fig. 3.
Effects N-QCT on cell viability of human gingival fibroblast cells: A Inverted light microscope images of treated cells with varying concentrations of N-QCT (magnification × 40); a Control (Untreated cells), b 128 μg/mL, c 256 μg/mL, and d 512 μg/mL, B. The mean percentage viability versus concentrations of N-QCT using MTT assay
MBIC of N-QCT
N-QCT at 128-512 μg/mL concentrations statistically reduced S. mutans biofilm when compared to untreated biofilm cells (P < 0.05; Fig. 4), whereas there was no significant effect on the biofilm destruction when N-QCT was decreased from 64 to 1.0 μg/mL. According to the findings, at least a concentration of 128 μg/mL of N-QCT as MBIC was required to destroy the increasing growth of the biofilm.
Fig. 4.
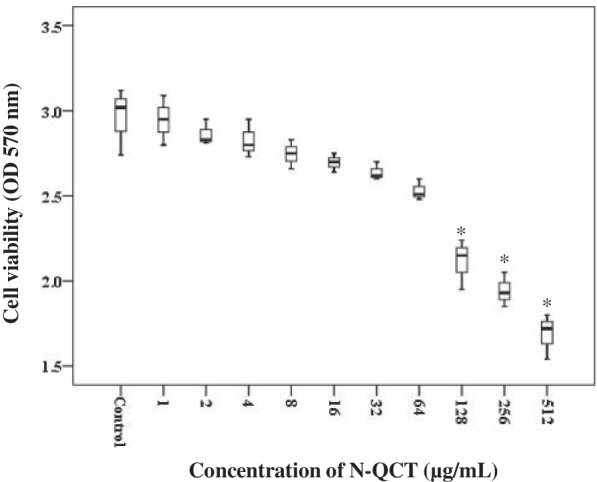
Anti-biofilm effect of N-QCT at the different concentrations against S. mutans. *Significantly different from the control group (no treatment), P < 0.05
Generation of intracellular ROS
N-QCT at 1/2× MBIC (64 μg/mL) and 1/4 × MBIC (32 μg/mL), as well as blue laser irradiation led to an increase in ROS levels compared to the non-treated cells (1.52-, 1.23-, and 1.35-folds, respectively). Maximum ROS production was observed in the aPDT groups (Fig. 5), with application of 1/2× and 1/4× MBIC of N-QCT leading to 2.75- and 2.24-fold higher ROS production, compared to control cells (untreated cells; P < 0.05).
Fig. 5.
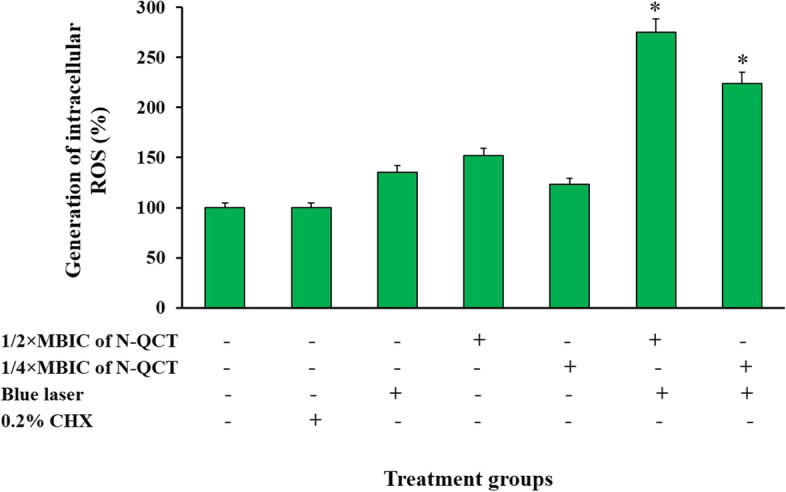
Effects of different treatment groups on the production of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) in S. mutans. *Significantly different from the control group (no treatment), P < 0.05
Anti-biofilm effects of treatment groups against S. mutans biofilms
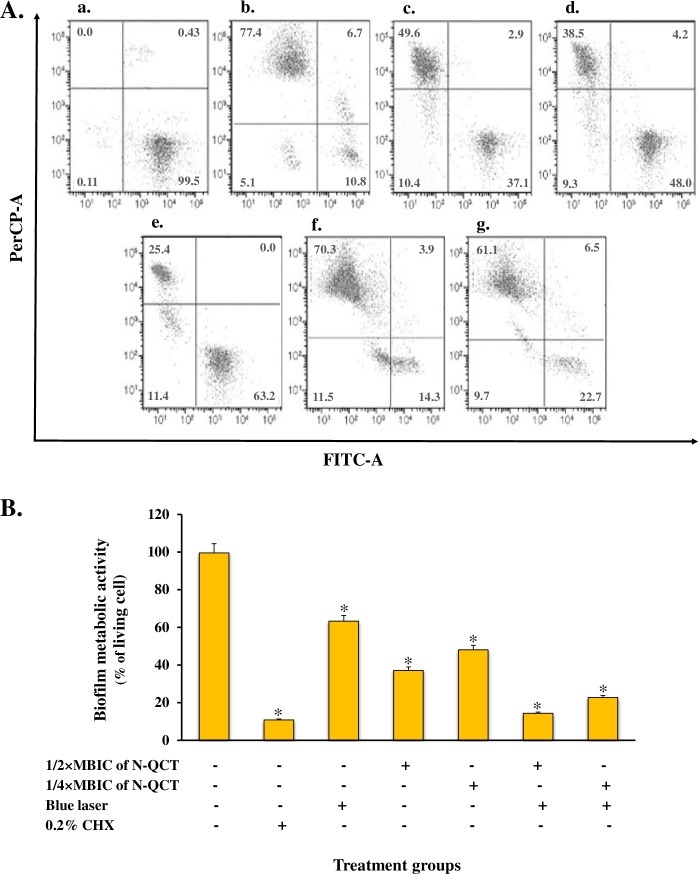
Significant degradation of preformed biofilms was observed in the group treated with aPDT using sub-MBIC doses of N-QCT plus irradiation of blue laser for 60 s (P < 0.05; Fig. 6). Although the preformed biofilms treated with 1/2× and 1/4× MBIC of N-QCT and blue laser also showed similar results with decreased cell viability, the rate of biofilm degradation was not considerable (P > 0.05). Also, the results showed no significant differences between aPDT using 1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT and 0.2% CHX in biofilm inhibition (P > 0.05).
Fig. 6.
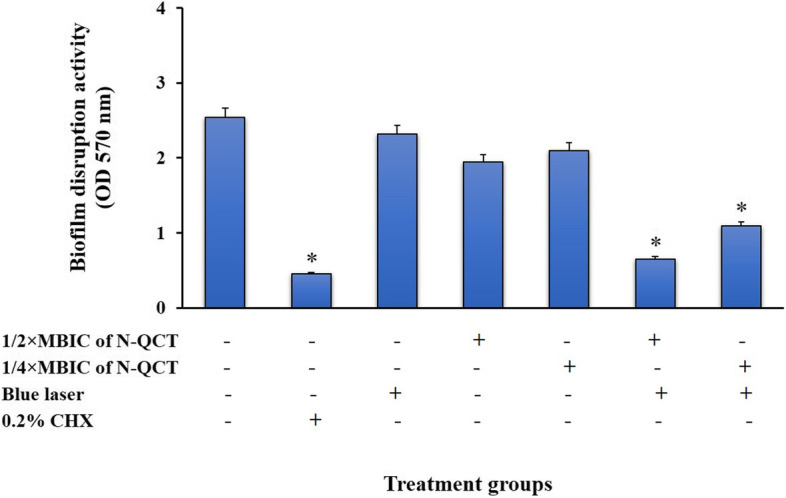
Biofilm disruption effects of different treatment groups against S. mutans. *Significantly different from the control group (no treatment), P < 0.05
The crystal violet staining of the biofilms also confirmed the log10 CFU/mL results. As shown in Fig. 7, a dense biofilm matrix was seen in the control group, while dead cells increased in the biofilm matrix treated with aPDT (both concentrations) and 0.2% CHX (P < 0.05).
Fig. 7.
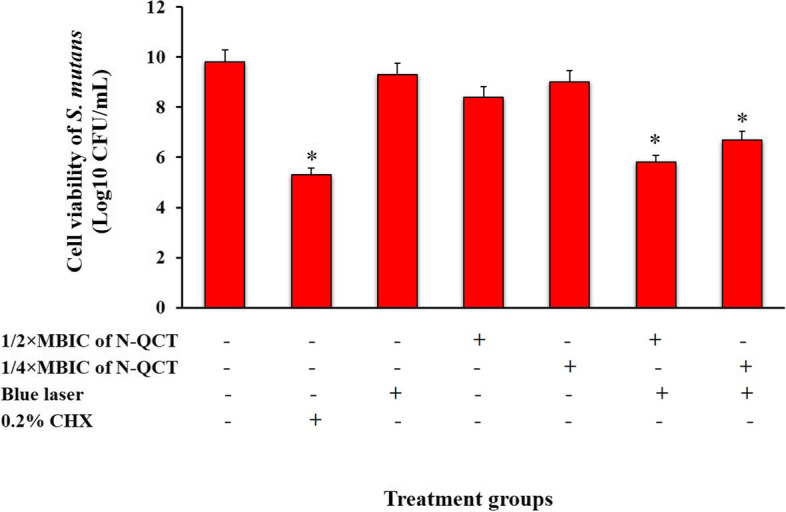
Effect of different treatment groups on cell viability of S. mutans. *Significantly different from the control group (no treatment), P < 0.05
Also, Log10 CFU/mL reduction and percent reduction following each treatment were shown in Table 2. Our results demonstrated that there was a significant reduction in cell viability of S. mutans following aPDT groups using 1/2× and 1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT, and 0.2% CHX (P > 0.05).
Table 2.
Log10 CFU/mL, Log10 CFU/mL reduction, and percent reduction of treated S. mutans biofilm following each treatment
| Groups | Log10 CFU/mL | Log10 CFU/mL reduction | Percent reduction (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 9.8 | – | – |
| 0.2% CHX | 5.3 | −4.5 | 99.99 |
| Blue laser | 9.3 | −0.5 | 68.41 |
| 1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT | 8.4 | −1.4 | 96.11 |
| 1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT | 9 | −0.8 | 84.22 |
| aPDT using 1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT | 5.8 | −4.0 | 99.99 |
| aPDT using 1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT | 6.7 | −3.1 | 99.92 |
Biofilm metabolic activity of S. mutans by flow cytometry
Flow cytometry was employed to measure metabolic activity in treated S. mutans biofilms. Figure 8A depicts the differentiation of live and dead cell populations as individual dot plots. All treatment groups significantly reduced the biofilm metabolic activity in S. mutans (P < 0.05). As demonstrated in Fig. 8B, both aPDT groups were more efficient in reducing S. mutans metabolic activity compared to the other treatment groups (Fig. 8B). The percentage of living cells was 14.3 ± 1.73% and 22.7 ± 2.45% in cells treated with laser plus 1/2× and 1/4 × MBICs of N-QCT, respectively. Blue laser irradiation also showed anti-metabolic activity compared to the control group but it was less than that observed in the N-QCT groups at 1/2 × MBIC (37.1 ± 2.06% live cells) and 1/4 × MBIC (48.0 ± 3.00% live cells) Fig. 8B).
Fig. 8.
Effect of different treatment groups on biofilm metabolic activity in S. mutans; A measured by flow cytometry: a Untreated biofilm cells, b 0. 2% CHX, c N-QCT at 1/2 × MBIC, d N-QCT at 1/4 × MBIC, e Blue laser light, f aPDT using 1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT, and g aPDT using 1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT. B Percentage of biofilm living cells. *Significantly different from the control group (no treatment), P < 0.05
Molecular modeling and docking analysis
The sequence similarity and coverage results on CSP displayed that it is similar to the protein structure with accession number 2JHQ. The total score for protein alignment between CSP and 2JHQ was 62.4, with 95 and 28.89% query cover and identity, respectively. Basic information obtained from CSP at the NCBI GenBank database showed that it has 46 amino acids and its estimated structure weight and theoretical pI were 5211.06 Da and 9.70, respectively. The amino acid compositions of CSP are: Ala (A) 2.2%; Arg (R) 4.3%; Asn (N) 4.3%; Asp (D) 4.3%; Cys (C) 0.0%; Gln (Q) 2.2%; Glu (E) 6.5%; Gly (G) 8.7%; His (H) 0.0%; Ile (I) 8.7%; Leu (L) 13.0%; Lys (K) 13.0%; Met (M) 2.2%; Phe (F) 10.9%; Pro (P) 0.0%; Ser (S) 10.9%; Thr (T) 8.7%; Trp (W) 0.0%; Tyr (Y) 0.0%; and Val (V) 0.0%. The results obtained from UniProt revealed that CSP had 8 positively charged residues (Arg + Lys) and 5 negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu) with an aliphatic index of 86.96. Also, the instability index (II) and grand average of hydropathicity value were 20.99 and − 0.224, respectively. These results classify the protein as stable.
The PPI network of CSP was constructed. The main connected component including 10 nodes was formed. As shown in Fig. 9, each node is distinguishable from the other nodes based on degree value. Whenever the protein score is closer to 1.0 is an indication that this protein is near to CSP. The properties of each node based on analysis of the PPI network are tabulated in Table 3.
Fig. 9.
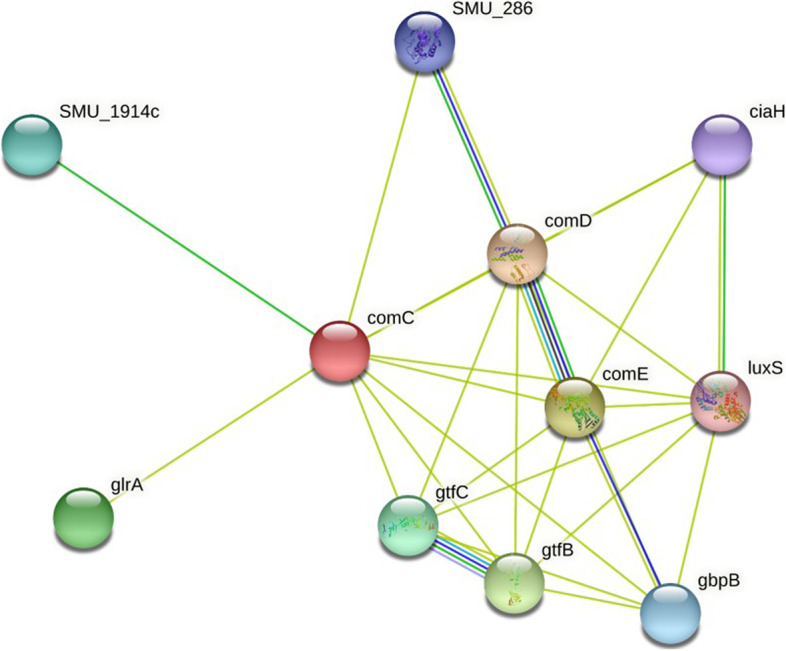
The PPI network of CSP protein identified in S. mutans
Table 3.
The list of the properties of key nodes based on the PPI network analysis
| Nodes | Predicted functional partners | Neighborhood | Gene Fusion | Co-occurrence | Co-expression | Experiments | Databases | Textmining | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| comD | Two-component system, lyttr family, sensor histidine kinase agrc; Putative histidine kinase of the competence regulon | * | 0.750 | ||||||
| comE | Putative response regulator of the competence regulon, come; Response regulator of the competence regulon ComE | * | 0.750 | ||||||
| gtfB | Glucosyltransferase-i; Production of extracellular glucans, that are thought to play a key role in the development of the dental plaque because of their ability to adhere to smooth surfaces and mediate the aggregation of bacterial cells and food debris | * | 0.711 | ||||||
| glrA | ABC-2 type transport system ATP-binding protein | * | 0.585 | ||||||
| gtfC | Glucosyltransferase-si; Production of extracellular glucans, that are thought to play a key role in the development of the dental plaque because of their ability to adhere to smooth surfaces and mediate the aggregation of bacterial cells and food debris | * | 0.516 | ||||||
| SMU_1914c | Hypothetical protein; Uncharacterized protein | * | 0.442 | ||||||
| gbpB | Peptidoglycan dl-endopeptidase cwlo; Putative secreted antigen GbpB/SagA putative peptidoglycan hydrolase | * | 0.429 | ||||||
| SMU_286 | Atp-binding cassette, subfamily c, bacteriocin exporter | * | 0.429 | ||||||
| ciaH | Two-component system, ompr family, sensor histidine kinase ciah; Putative histidine kinase sensor CiaH | * | 0.428 | ||||||
| luxS | Putative autoinducer-2 production protein luxs; Involved in the synthesis of autoinducer 2 (AI-2) which is secreted by bacteria and is used to communicate both the cell density and the metabolic potential of the environment. The regulation of gene expression in response to changes in cell density is called quorum sensing. Catalyzes the transformation of S-ribosylhomocysteine (RHC) to homocysteine (HC) and 4,5-dihydroxy-2,3-pentadione (DPD) | * | 0.428 |
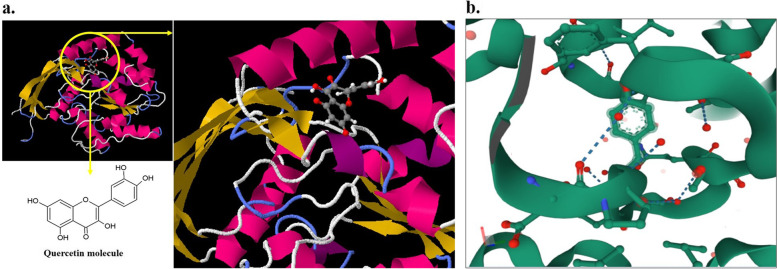
The molecular docking analysis was performed using SwissDock. The lowest binding free energy docked conformation of the best cluster was selected and analyzed. The best docking results are given in Fig. 10. As shown in Fig. 8a, the QCT molecule was located in the site formed by polypeptide helices. Figure 8b shows that the QCT molecule was adjacent to some residues in the hydrophobic cavity; oxygen atoms 7 and 10 in QCT formed hydrogen bonds with two hydrogen atoms in Tyr66 and Gly109. In addition, hydrogen atoms 6, 9, and14 formed hydrogen bonds with Ala 78, Arg177, and His 202, respectively.
Fig. 10.
Molecular modeling of QCT-bound CSP. The residues of CSP and QCT are represented using a ball-and-tinctorial stick physical model: a Binding site of QCT in CSP, b Conformation of QCT in the binding site of CSP. The bonds between the ligand and the protein are presented by blue dashed lines
Gene expression profiling using RT-qPCR
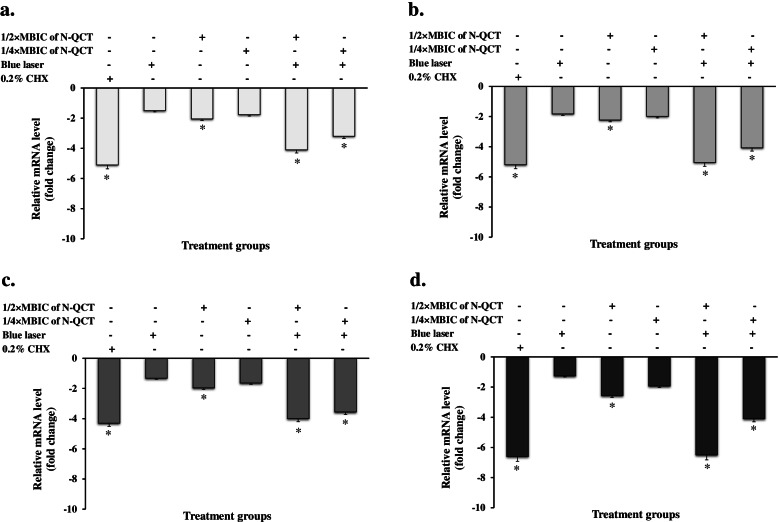
Gene expression analysis using RT-qPCR in S. mutans revealed that the aPDT groups downregulated the QS signals-related genes. As shown in Fig. 11, 1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT plus blue laser could decrease the gene expression levels of comA, comB, comDE, and gtfB by 4.1-, 5.05-, 4.0-, and 6.5-fold, respectively (P < 0.05). Also, a 3.2-, 4.08-, 3.56-, and 4.1-fold reduction in the expression of comA, comB, comDE, and gtfB genes was observed in the biofilm cells treated with aPDT using 1/4× MBIC of N-QCT-treated (P < 0.05). In contrast, 1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT, 1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT, and blue laser alone did not show any significant effect on the expression of QS genes of S. mutans biofilm. (P > 0.05). It is noteworthy that there is no significant difference in the reduction of genes expression between aPDT and 0.2% CHX groups (P > 0.05).
Fig. 11.
Effect of different treatment groups on the expression of various genes involved in quorum sensing of S. mutans: a comA, b comB, c comDE, and d gtfB. *Significantly different from the control group (no treatment), P < 0.05
Discussion
Many microorganisms in dental plaque biofilm deposited on the tooth surface have been found to be associated with dental caries [37]. Extensive investigations showed that S. mutans was considered as a primary etiologic agent responsible for dental caries due to its ability to form biofilm and to provide adhesion of bacteria to each other and to the tooth enamel [38, 39]. So, the inhibition of S. mutans biofilm formation or degradation/dispersal of a formed biofilm could be the main target to forestall dental caries. Using hand or rotary instruments not only leads to incomplete removal of the caries and insufficient elimination of residual microorganisms but can also cause damage to the pulp, resulting in pain and weakening of the tooth structure [40]. On the other hand, chemical antimicrobial agents can cause various side effects and lead to the emergence of antimicrobial resistance due to overdose and prolonged administration. Therefore, in recent years, plant-derived natural products, as anti-biofilm agents, have been considered to be an appealing option for overcoming virulence biofilm characters [41].
According to the literature, QCT with broad-spectrum antimicrobial effects has been also used to prevent and treat various infectious bacterial diseases. Qin et al. [42] found that QCT inhibited Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, and Pseudomonas aeruginosa with minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 0.0061, 0.0242, and 0.0121 μmol/mL, respectively. In another study, Wang et al. [14] evaluated the bacteriostatic effect of QCT as an antibiotic alternative on four kinds of bacteria in vitro. They reported QCT had significant antibacterial activity against E. coli, Salmonella enterica Typhimurium, S. aureus, and P. aeruginosa with MICs of 0.0082, 0.0072, 0.0068, and 0.0085 μmol/mL, respectively. Nevertheless, QCT generally exhibits low bioavailability due to its poor aqueous solubility. To address this problem, various promising approaches, such as pharmaceutical nanotechnology have been developed that can effectively improve the bioavailability of QCT by enhancing its solubility, dissolution rate and permeability, and/or delivering them directly to their physiological targets [43]. In the present study, we used 1% of DMSO for the preparation of the N-QCT solution. However, in vitro studies have shown a lower solubility of quercetin. Kakran et al. [44] have shown the saturation solubility of coarse QCT was extremely low being only 2.84 ± 0.03 μg/mL while forming nanostructure enhanced the saturation solubility of QCT approximately nine times to 25.59 ± 1.11 μg/mL. The saturation solubility of the QCT-nanostructure is persistent and remains almost the same for seven days [44]. Usually, the existence of micrometer-sized crystals (acting as nuclei for crystallization) causes the saturation solubility to decrease by re-crystallization (growth of microcrystals being present). In the N-QCT structures, the microcrystals are present in a limited amount or absent, and hence, the saturation solubility remains unchanged. This is favorable for oral administration [44].
In this study, after confirmation of the synthesized N-QCT properties, its cytotoxic effect was investigated. We used MTT assay to determine the potential toxicity of N-QCT on the HGF cell line and found no cytotoxic effect. In addition, the biofilm inhibitory concentration of N-QCT against S. mutans biofilm was evaluated and according to the results, both minimum (128 μg/mL) and maximum (512 μg/mL) biofilm inhibitory concentrations, decreased the biofilms of S. mutans by 28.7 and 43.2%, respectively.
Several investigations evaluated the anti-cancer effects of QCT by reducing the cell viability of different cancer cell lines during aPDT [45–49]. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that has determined the effects of N-QCT-mediated aPDT on S. mutans biofilm. We calculated the MBIC of N-QCT (128 μg/mL) and assessed the effectiveness of its 1/2 and 1/4 values alone and in combination with blue laser on S. mutans biofilm. It was found that aPDT using 1/2× and 1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT disrupted the biofilm by 74.40 and 57.08%, respectively probably due to intracellular ROS generation.
In microbial cells ROS are produced by oxidative phosphorylation involves the transport of protons across the inner cell membrane by means of the electron-transport chain that occurs during the processes of respiration in normal metabolisms and under exogenous stress conditions. ROS has a dual role; whether they will act as signaling or harmful factors depends on the balance between ROS production and disposal at the right place and time. ROS are intrinsic to cellular functioning including cell homeostasis and signaling and are present at stationary and low levels in microbial cells. On the other hand, ROS as a highly reactive chemical agent can cause irreversible damage to DNA, oxidize and modify some cellular components, and prevent their original functions. Oxygen toxicity can arise both from the inefficient elimination of ROS by the antioxidant system and uncontrolled production [50]. Our results suggest that ROS over natural production in S. mutans cells following N-QCT-based aPDT reduces metabolic activity, preformed biofilms, and relative expression levels of the virulence genes, which is a feasible avenue to reducing S. mutans population as a main cariogenic bacterium.
Although the biofilms cells treated with sub-MBIC doses of N-QCT and blue laser alone showed decreased cell viability, the rate of biofilm disruption was not significant. In addition, we investigated the biofilm metabolic activity of treated S. mutans bacteria using flow cytometry. All treatment groups significantly reduced the biofilm metabolic activity of S. mutans; however, the reduction was more prominent in the aPDT groups. These results are consistent with those of previous studies in which aPDT was reported to exhibit an inhibitory effect on the metabolic activity of S. mutans. We showed that N-QCT had the ability to produce ROS, which probably led to the significant inhibition of the microbial metabolic activity.
The current study showed a discrepancy between metabolic activity and log10 CFU/mL as a tool for assessing cell proliferation so that a 4 log (40%) reduction was observed in 1/2 × MBIC of N-QCT treated with the light group, whereas only 80% were metabolically inactive in flow cytometry. The results of the current study are consistent with a report in which daunorubicin led to cell detachment but not to fragmentation of cells and they continued to convert MTT to formazan resulting in an apparent overestimation of cell viability when applying MTT. However, MTT was originally developed to measure chemical reagent cytotoxicity, but the literature review shows that mainly metabolic assays including MTT were used to quantify proliferative activities but such assays may not accurately reflect proliferation due to non-linear and miscorrelating changes in metabolic activity and cell number over time in culture. The obvious limitation of metabolic assays is that cellular metabolic activity varies greatly throughout the growth cycle of cells [51]. Tetrazolium salt-based assays including MTT do not measure the cell number of viable cells in a culture or their growth, but more a set of enzyme activities, that are related in various ways to the cellular metabolism.
In a major MTT-based cytotoxicity study [52], daunorubicin led to cell detachment but not to fragmentation of cells; however, the treated cells continued to reduce MTT to formazan resulting in an overestimation of cell viability. This disadvantage is common in vitro cell-based assays, warranting precise interpretation of the results. It could therefore be useful to monitor the cell counting including colony counting (CFU/ml) or live/dead staining procedure as a visual confirmation of cell viability in addition to the metabolic assay to validate the results.
On the other hand, generally metabolic activity is higher in actively proliferating microbial cells under optimal growth conditions when compared with treated cells. Reduction in microbial cell metabolic activity is the use of a defense mechanism to withstand sub-lethal external stress doses; surviving cells grow in the presence of the sub-lethal stress doses. This phenotype of the microbial cells is not inherited, and cells revert to the wild-type phenotype once the stress is removed. Microbial cells with reduced metabolic activity produce fewer targets of stress and can continue their viability. After an initial die-off of the microbial population following treatment, surviving cells (are known as persister cells) with a slowly increasing population density due to their reduction of metabolic activity [53]. Furthermore, persister cells are a subpopulation of bacteria within a larger antimicrobial agents-susceptible population that display decreased susceptibility to microbicidal agents through mechanisms involving metabolic repression [54]. Kwan et al. [55] have confirmed this evidence by demonstrating that persister cells reduce proton motive force, transcription, and translation, as well as Shah et al. [56], revealed reduced metabolic activity in persister cells using green fluorescent protein as a reporter under the control of a ribosomal promoter.
One of the most important advantages of successful aPDT targeting is the localization of the PS in the target site. For this purpose, molecular modeling and docking analysis were performed to confirm the connection of QCT to CSP. In silico findings showed that CSP is a stable protein with both positively and negatively charged residues. On the other hand, we found that the QCT molecule was located in the site formed by polypeptide helices of CSP, and oxygen and hydrogen atoms formed hydrogen bonds with CSP residues.
As previously proven, the biofilm formation in S. mutans is regulated by a QS signaling system that moderates the expression of virulence factors in a cell density-dependent manner [2, 57–59]. Therefore, inhibition of this system results in the reduction of S. mutans biofilm development and can consequently decrease the cariogenic process. Hence, disruption of S. mutans QS system has been proposed as a new anti-biofilm infection approach. Using QQ is considered to be one of the most promising methods for disrupting the QS systems and attenuating bacterial virulence [60, 61]. As Mion et al. [60] reported, QQ not only constitutes an interesting therapeutic strategy to fight against bacterial infections but also restricts the consequences of antibiotic resistance. It has been suggested that aPDT can be applied as a useful QQ strategy in enhancing the microbicide effects and in reducing drug resistance [16–18, 62, 63].
Our study examined the effect of QQ of S. mutans via aPDT on various QS-regulated genes. The QS pathway in S. mutans encompasses several genetic loci such as comCDE and comAB. The genes evaluated in this study are reported to be involved in the QS of S. mutans that further affect major virulence factors like biofilm formation. We found that the groups treated with blue laser plus 1/2× and 1/4 × MBIC of N-QCT, significantly downregulated the QS signal-related genes (comA, comB, and comDE). There was also a reduction in gtfB expression which is a gene involved in biofilm formation of S. mutans. The findings of the current investigation suggest that aPDT with a minimum concentration of N-QCT along with blue laser irradiation has the ability to perform QQ and through generation of large amounts of intracellular ROS is able to disrupt the microbial biofilm, reduce the metabolic activity of S. mutans, and downregulate the expression of genes associated with the QS signal system. Further studies are required to achieve a better understanding of QQ in microbe-microbe and host-pathogen interactions.
In RT-qPCR, CHX was used as a treatment (positive) control. The current study demonstrated that there is no significant difference in the reduction of genes expression between N-QCT mediated aPDT and CHX groups, which indicates N-QCT mediated aPDT is as effective as CHX in reducing virulence genes expression without CHX́ s side effects. CHX was introduced in dentistry in 1954 as a broad-spectrum microbicide effective against Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria [64]. However, it requires a high concentration of 0.2% to achieve effective results. Application of CHX has been limited due to many of its side effects including teeth staining, calculus buildup, and metallic aftertaste. Therefore, an antimicrobial strategy that robustly reduces or eliminates the microbial biofilms, while maintaining their biocompatibility, is highly desirable. The results of the current study showed that the effect of N-QCT mediated aPDT is as effective as the CHX in reducing genes expression and considering that aPDT is more bio-compatible, it can be considered an adjunctive treatment. We acknowledge that further evaluation of the antimicrobial activity of N-QCT mediated aPDT against additional common cariogenic bacteria, such as lactobacillus spp., will strengthen our study findings.
Conclusion
Collectively, the data of the present study show that the combination of blue laser and N-QCT at low concentrations, target genes involved in the QS pathway of S. mutans making it a favorable QQ strategy. N-QCT-based aPDT may provide a potential adjuvant treatment to the currently used anti-biofilm approaches to prevent the incidence of dental caries.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- aPDT
Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy
- CFU
Colony forming unit
- CSP
Competence-stimulating peptide
- MBIC
Minimum biofilm inhibitory concentration
- N-QCT
Nano-quercetin
- PS
Photosensitizer
- QCT
Quercetin
Quorum quenching
- QS
Quorum sensing
Authors’ contributions
MP and AB contributed to the study design and provided funding. MP, BR, and RMM collaborated on the synthesis of nanoparticles. MP performed the experiments contributed to the performed the experiments and analyzed the data. MP wrote the manuscript. MA, SE, and AB collaborated on the scientific writing of the manuscript. MP, MA, SE, BR, and AB reviewed the analyses and the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Availability of data and materials
All data of this study are included in the manuscript. All figures are original images and have been used for the first time in this study. The primary datasets used during the current study in the section of in silico analysis about competence stimulating peptide (CSP) and quercetin (QCT) are available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/115312774 and https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5280459, respectively.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All methods were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations. All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of Tehran University of Medical Sciences (Application No. IR.TUMS.MEDICINE.REC.1400.089). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects and/or their legal guardian(s).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
There is no competing interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Rezvaneh sadat Miri Mousavi, Email: rezvanehmoosavi@gmail.com.
Abbas Bahador, Email: abahador@sina.tums.ac.ir.
References
- 1.Frencken JE, Sharma P, Stenhouse L, Green D, Laverty D, Dietrich T. Global epidemiology of dental caries and severe periodontitis–a comprehensive review. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44:S94–105. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Medapati MR, Singh N, Bhagirath AY, Duan K, Triggs-Raine B, Batista EL, Jr, Chelikani P. Bitter taste receptor T2R14 detects quorum sensing molecules from cariogenic Streptococcus mutans and mediates innate immune responses in gingival epithelial cells. FASEB J. 2021;35(3):e21375. doi: 10.1096/fj.202000208R. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yang Y, Cornilescu G, Tal-Gan Y. Structural characterization of competence-stimulating peptide analogues reveals key features for ComD1 and ComD2 receptor binding in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Biochemistry. 2018;57(36):5359–5369. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.8b00653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bikash CR, Tal-Gan Y. Identification of highly potent competence stimulating peptide-based quorum sensing activators in Streptococcus mutans through the utilization of N-methyl and reverse alanine scanning. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2019;29(6):811–814. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2019.01.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Bikash CR, Hamry SR, Tal-Gan Y. Structure–activity relationships of the competence stimulating peptide in Streptococcus mutans reveal motifs critical for membrane protease SepM recognition and ComD receptor activation. ACS Infect Dis. 2018;4(9):1385–1394. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Suzuki Y, Nagasawa R, Senpuku H. Inhibiting effects of fructanase on competence-stimulating peptide-dependent quorum sensing system in Streptococcus mutans. J Infect Chemother. 2017;23(9):634–641. doi: 10.1016/j.jiac.2017.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Bikash CR, Tal-Gan Y. Structure activity relationship study of the XIP quorum sensing pheromone in Streptococcus mutans reveal inhibitors of the competence Regulon. ACS Chem Biol. 2020;15(10):2833–2841. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.0c00650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tang K, Zhang XH. Quorum quenching agents: resources for antivirulence therapy. Mar Drugs. 2014;12(6):3245–3282. doi: 10.3390/md12063245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hemmati F, Salehi R, Ghotaslou R, Samadi Kafil H, Hasani A, Gholizadeh P, Nouri R, Ahangarzadeh RM. Quorum quenching: a potential target for Antipseudomonal therapy. Infect Drug Resist. 2020;13:2989–3005. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S263196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Warrier A, Mazumder N, Prabhu S, Satyamoorthy K, Murali TS. Photodynamic therapy to control microbial biofilms. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2021;33:102090. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.102090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Antunes M, de Melo WC, Celiešiūtė-Germanienė R, Šimonis P, Stirkė A. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) for biofilm treatments. Possible synergy between aPDT and pulsed electric fields. Virulence. 2021;12(1):2247–2272. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1960105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nikinmaa S, Alapulli H, Auvinen P, Vaara M, Rantala J, Kankuri E, Sorsa T, Meurman J, Pätilä T. Dual-light photodynamic therapy administered daily provides a sustained antibacterial effect on biofilm and prevents Streptococcus mutans adaptation. PLoS One. 2020;15(5):e0232775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0232775. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Golmohamadpour A, Bahramian B, Khoobi M, Pourhajibagher M, Barikani HR, Bahador A. Antimicrobial photodynamic therapy assessment of three indocyanine green-loaded metal-organic frameworks against enterococcus faecalis. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2018;23:331–338. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2018.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wang S, Yao J, Zhou B, Yang J, Chaudry MT, Wang M, Xiao F, Li Y, Yin W. Bacteriostatic effect of quercetin as an antibiotic alternative in vivo and its antibacterial mechanism in vitro. J Food Prot. 2018;81(1):68–78. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-17-214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Catauro M, Papale F, Bollino F, Piccolella S, Marciano S, Nocera P, Pacifico S. Silica/quercetin sol–gel hybrids as antioxidant dental implant materials. Sci Technol Adv Mater. 2015;16:1–11. doi: 10.1088/1468-6996/16/3/035001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Abdulrahman H, Misba L, Ahmad S, Khan AU. Curcumin induced photodynamic therapy mediated suppression of quorum sensing pathway of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: an approach to inhibit biofilm in vitro. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2020;30:101645. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.101645. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sun Y, Qin H, Yan Z, Zhao C, Ren J, Qu X. Combating biofilm associated infection in vivo: integration of quorum sensing inhibition and photodynamic treatment based on multidrug delivered hollow carbon nitride sphere. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29(14):1808222. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201808222. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pourhajibagher M, Mahmoudi H, Rezaei-Soufi L, Alikhani MY, Bahador A. Potentiation effects of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy on quorum sensing genes expression: a promising treatment for multi-species bacterial biofilms in burn wound infections. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2020;1(30):101717. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2020.101717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Debnath K, Jana NR, Jana NR. Quercetin encapsulated polymer nanoparticle for inhibiting intracellular polyglutamine aggregation. ACS Appl Bio Mater. 2019;2(12):5298–5305. doi: 10.1021/acsabm.9b00518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Lee Y, Ahn JS, Yi YA, Chung SH, Yoo YJ, Ju SW, Hwang JY, Seo DG. Cytotoxicity of four denture adhesives on human gingival fibroblast cells. Acta Odontol Scand. 2015;73(2):87–92. doi: 10.3109/00016357.2014.954266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. 29th ed. CLSI supplement M100. Wayne: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2019.
- 22.Aires CP, Sassaki GL, Santana-Filho AP, Spadaro AC, Cury JA. Baccharis dracunculifolia-based mouthrinse alters the exopolysaccharide structure in cariogenic biofilms. Int J Biol Macromol. 2016;84:301–307. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.12.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Margaritova Zaharieva M, Dimitrov Kroumov A, Dimitrova L, Tsvetkova I, Trochopoulos A, Mihaylov Konstantinov S, et al. Micellar curcumin improves the antibacterial activity of the alkylphosphocholines erufosine and miltefosine against pathogenic Staphyloccocus aureus strains. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2019;33(1):38–53. doi: 10.1080/13102818.2018.1533792. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Loo CY, Corliss DA, Ganeshkumar N. Streptococcus gordonii biofilm formation: identification of genes that code for biofilm phenotypes. J Bacteriol. 2000;182(5):1374–1382. doi: 10.1128/JB.182.5.1374-1382.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wen ZT, Yates D, Ahn SJ, Burne RA. Biofilm formation and virulence expression by Streptococcus mutans are altered when grown in dual-species model. BMC Microbiol. 2010;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-10-111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Pourhajibagher M, Boluki E, Chiniforush N, Pourakbari B, Farshadzadeh Z, Ghorbanzadeh R, Aziemzadeh M, Bahador A. Modulation of virulence in Acinetobacter baumannii cells surviving photodynamic treatment with toluidine blue. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2016;15:202–212. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2016.07.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Butun S, Aydin K. Structurally tunable resonant absorption bands in ultrathin broadband plasmonic absorbers. Opt Express. 2014;22(16):19457–19468. doi: 10.1364/OE.22.019457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Abedi M, Cohan RA, Ardestani MS, Davami F. Comparison of polystyrene versus cycloolefin microplates in absorbance measurements in the UV/VIS region of the spectrum. J Shahrekord Univ Med Sci. 2019;21(3):110–113. doi: 10.34172/jsums.2019.19. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nemezio MA, de Souza Farias SS, Borsatto MC, Aires CP, Corona SAM. Effect of methylene blue-induced photodynamic therapy on a Streptococcus mutans biofilm model. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2017;20:234–237. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2017.10.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zhang XF, Shen W, Gurunathan S. Biologically synthesized gold nanoparticles ameliorate cold and heat stress-induced oxidative stress in Escherichia coli. Molecules. 2016;21(6):1–18. doi: 10.3390/molecules21060731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pourhajibagher M, Bahador A. Synergistic biocidal effects of metal oxide nanoparticles-assisted ultrasound irradiation: antimicrobial sonodynamic therapy against Streptococcus mutans biofilms. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2021;35:102432. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2021.102432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Zadrazilova I, Pospisilova S, Pauk K, Imramovsky A, Vinsova J, Cizek A, Jampilek J. In vitro bactericidal activity of 4- and 5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-[1-oxo-1-(phenylamino)alkan-2-yl]benzamides against MRSA. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:349534. doi: 10.1155/2015/349534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Veloz JJ, Alvear M, Salazar LA. Evaluation of alternative methods to assess the biological properties of propolis on metabolic activity and biofilm formation in Streptococcus mutans. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019;2019:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2019/1524195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kouidhi B, Zmantar T, Bakhrouf A. Anti-cariogenic and anti-biofilms activity of Tunisian propolis extract and its potential protective effect against cancer cells proliferation. Anaerobe. 2010;16(6):566–571. doi: 10.1016/j.anaerobe.2010.09.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Pourhajibagher M, Monzavi A, Chiniforush N, Monzavi MM, Sobhani S, Shahabi S, et al. Real-time quantitative reverse transcription-PCR analysis of expression stability of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans fimbria-associated gene in response to photodynamic therapy. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2017;18:78–82. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2017.02.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2− ΔΔCT method. Methods. 2001;25(4):402–408. doi: 10.1006/meth.2001.1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Yu OY, Zhao IS, Mei ML, Lo EC, Chu CH. Dental biofilm and laboratory microbial culture models for Cariology research. Dent J (Basel) 2017;5(2):21. doi: 10.3390/dj5020021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tang X, Kudo Y, Baker JL, LaBonte S, Jordan PA, McKinnie SM, Guo J, Huan T, Moore BS, Edlund A. Cariogenic Streptococcus mutans produces tetramic acid strain-specific antibiotics that impair commensal colonization. ACS Infect Dis. 2020;6(4):563–571. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.9b00365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Niu JY, Yin IX, Wu WK, Li QL, Mei ML, Chu CH. Antimicrobial peptides for the prevention and treatment of dental caries: a concise review. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;122:105022. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2020.105022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Farges JC, Alliot-Licht B, Renard E, Ducret M, Gaudin A, Smith AJ, Cooper PR. Dental pulp defence and repair mechanisms in dental caries. Mediat Inflamm. 2015;2015:1–8. doi: 10.1155/2015/230251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Chen X, Daliri EB, Kim N, Kim JR, Yoo D, Oh DH. Microbial etiology and prevention of dental caries: exploiting natural products to inhibit cariogenic biofilms. Pathogens. 2020;9(7):569. doi: 10.3390/pathogens9070569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Qin XR, Zhang MJ, Gao XN, Lin Y, Li MA, Si-Yi HE. Study on the antibacterial activity of quercetin. Chem Bioengineer. 2009;26(4):55–57. [Google Scholar]
- 43.Zhao J, Yang J, Xie Y. Improvement strategies for the oral bioavailability of poorly water-soluble flavonoids: an overview. Int J Pharm. 2019;570:118642. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2019.118642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Kakran M, Shegokar R, Sahoo NG, Shaal LA, Li L, Müller RH. Fabrication of quercetin nanocrystals: comparison of different methods. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2012;80(1):113–121. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2011.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Sahyon HAE, Ramadan ENM, Althobaiti F, Mashaly MMA. Anti-proliferative effects of the combination of Sulfamethoxazole and Quercetin via caspase3 and NFkB gene regulation: an in vitro and in vivo study. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol. 2022;395(2):227–246. doi: 10.1007/s00210-021-02174-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Alhakamy NA, Fahmy UA, Eldin SMB, Ahmed OAA, Aldawsari HM, Okbazghi SZ, et al. Scorpion Venom-Functionalized Quercetin Phytosomes for Breast Cancer Management: In Vitro Response Surface Optimization and Anticancer Activity against MCF-7 Cells. Polymers (Basel) 2021;14(1):93. doi: 10.3390/polym14010093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Ezzati M, Yousefi B, Velaei K, Safa A. A review on anti-cancer properties of Quercetin in breast cancer. Life Sci. 2020;248:117463. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Tang SM, Deng XT, Zhou J, Li QP, Ge XX, Miao L. Pharmacological basis and new insights of quercetin action in respect to its anti-cancer effects. Biomed Pharmacother. 2020;121:109604. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Reyes-Farias M, Carrasco-Pozo C. The anti-Cancer effect of Quercetin: molecular implications in Cancer metabolism. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(13):3177. doi: 10.3390/ijms20133177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Hong Y, Zeng J, Wang X, Drlica K, Zhao X. Post-stress bacterial cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019;116(20):10064–10071. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1901730116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Quent VM, Loessner D, Friis T, Reichert JC, Hutmacher DW. Discrepancies between metabolic activity and DNA content as tool to assess cell proliferation in cancer research. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14(4):1003–1013. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2010.01013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hamid R, Rotshteyn Y, Rabadi L, Parikh R, Bullock P. Comparison of alamar blue and MTT assays for high through-put screening. Toxicol In Vitro. 2004;18(5):703–710. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2004.03.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kaldalu N, Hauryliuk V, Tenson T. Persisters-as elusive as ever. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016;100(15):6545–6553. doi: 10.1007/s00253-016-7648-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Brauner A, Fridman O, Gefen O, Balaban NQ. Distinguishing between resistance, tolerance and persistence to antibiotic treatment. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2016;14(5):320–330. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.34. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kwan BW, Valenta JA, Benedik MJ, Wood TK. Arrested protein synthesis increases persister-like cell formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2013;57(3):1468–1473. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02135-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Shah D, Zhang Z, Khodursky A, Kaldalu N, Kurg K, Lewis K. Persisters: a distinct physiological state of E. coli. BMC Microbiol. 2006;6:53–59. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-6-53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Senadheera D, Cvitkovitch DG. Quorum sensing and biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans. 2008. pp. 178–188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rued BE, Covington BC, Bushin LB, Szewczyk G, Laczkovich I, Seyedsayamdost MR, Federle MJ. Quorum sensing in Streptococcus mutans regulates production of Tryglysin, a novel RaS-RiPP antimicrobial compound. mBio. 2021;12(2):e02688–e02620. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02688-20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Yuan K, Hou L, Jin Q, Niu C, Mao M, Wang R, Huang Z. Comparative transcriptomics analysis of Streptococcus mutans with disruption of LuxS/AI-2 quorum sensing and recovery of methyl cycle. Arch Oral Biol. 2021;127:105137. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2021.105137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Mion S, Rémy B, Plener L, Chabrière É, Daudé D. Quorum sensing et quorum quenching : Comment bloquer la communication des bactéries pour inhiber leur virulence ? [Quorum sensing and quorum quenching: how to disrupt bacterial communication to inhibit virulence?] Med Sci (Paris) 2019;35(1):31–38. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2018310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Zhang W, Fan X, Li J, Ye T, Mishra S, Zhang L, Chen S. Exploration of the quorum-quenching mechanism in pseudomonas nitroreducens W-7 and its potential to attenuate the virulence of Dickeya zeae EC1. Front Microbiol. 2021;12:1–10. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.694161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Pourhajibagher M, Chiniforush N, Bahador A. Antimicrobial action of photoactivated C-Phycocyanin against enterococcus faecalis biofilms: attenuation of quorum-sensing system. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther. 2019;28:286–291. doi: 10.1016/j.pdpdt.2019.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rezaie P, Pourhajibagher M, Chiniforush N, Hosseini N, Bahador A. The effect of quorum-sensing and efflux pumps interactions in Pseudomonas aeruginosa against photooxidative stress. J Lasers Med Sci. 2018;9(3):161. doi: 10.15171/jlms.2018.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Horner C, Mawer D, Wilcox M. Reduced susceptibility to chlorhexidine in staphylococci: is it increasing and does it matter? J Antimicrob Chemother. 2012;67(11):2547–2559. doi: 10.1093/jac/dks284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
All data of this study are included in the manuscript. All figures are original images and have been used for the first time in this study. The primary datasets used during the current study in the section of in silico analysis about competence stimulating peptide (CSP) and quercetin (QCT) are available at https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/protein/115312774 and https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/5280459, respectively.