Abstract
Angiopoietin-like protein 1 (ANGPTL1) is a member of the ANGPTL family that suppresses angiogenesis, cancer invasion, metastasis, and cancer progression. ANGPTL1 is down-regulated in various cancers including colorectal cancer (CRC); however, the effects and mechanisms of ANGPTL1 on liver metastasis and cancer stemness in CRC are poorly understood. In the present study, we identified that ANGPTL1 was down-regulated in CRC and inversely correlated with metastasis and poor clinical outcomes in CRC patients form the ONCOMINE database and Human Tissue Microarray staining. ANGPTL1 significantly suppressed the migration/invasion abilities, the expression of cancer stem cell (CSC) markers, and sphere formation by enhancing FOXO3a expression, which contributed to the reduction of stem cell transcription factor SOX2 expression in CRC cells. Consistently, overexpression of ANGPTL1 reduced liver metastasis, tumor growth, and tumorigenicity in tumor-bearing mice. ANGPTL1 expression was negatively correlated with CSC markers expression and poor clinical outcomes in CRC patients. Taken together, these findings demonstrate that the molecular mechanisms of ANGPTL1 in colorectal cancer stem cell progression may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for CRC.
Keywords: ANGPTL1, cancer stem cell, colorectal cancer, FOXO3a, liver metastasis, SOX2
Introduction
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a major diagnosed cancer and the third leading cause of death and disease from cancer worldwide [1]. Approximately 50% of patients with CRC developed distant metastases, and the 5-year survival rates were low in those patients [1]. Both recurrence and metastasis are two important prognosis factors for survival of colon cancer. Therefore, it is vital and urgent to investigate the genes and detailed molecular mechanisms involved in CRC tumor metastasis, which may provide novel diagnostic biomarkers for CRC. Increasing evidences have implicated that cancer stem cells (CSCs) participate in tumor initiation, metastasis, drug resistance, and tumor recurrence [2–5]. CSCs exhibit as small subpopulations of tumor cells resides in niches, which is a part of the tumor microenvironment and supports cancer cell dissemination [6]. Recent studies have reported that some cancer cells, including CRC, acquire the features of CSCs through the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT), which facilitate the invasion potential of colon cancer cells into the basement membrane and the lymph and blood vascular systems [7,8]. Due to the plasticity and capacity of CSCs, it is essential for developing the therapeutic strategies to eliminate CSCs for CRC therapy.
Angiopoietin-like protein 1 (ANGPTL1) is a member of ANGPTLs family and known as an anti-angiogenic factor as well as a tumor suppressor. Indeed, ANGPTL1 is down-regulated in several cancers, including lung [9], thyroid [10], hepatocellular carcinoma [11] and colorectal cancer [12]. ANGPTL1 is implicated in the angiogenesis [11], metastasis [13], inflammation [14], hematopoietic stem cell behavior [15], lipid metabolism [16], drug resistance [17] and cancer progression [18]. Previous studies showed that ANGPTL1 repressed EMT by inhibiting Slug expression of CRC [9], and proved that ANGPTL1 suppressed liver metastasis and prolonged overall survival in vivo of CRC [12]. In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), ANGPTL1 attenuates cancer stem cell properties and sorafenib resistance by reduction of Slug [17]. Nevertheless, the functions and detailed mechanisms of ANGPTL1 in CSC properties of CRC are yet not fully developed.
In the present study, we investigated the effects and mechanisms of ANGPTL1 on liver metastasis and cancer stemness in CRC. We demonstrate a novel mechanism in which ANGPTL1 inhibits SRY-related HMG-box (SOX)-2 (SOX2) expression by enhancing forkhead box O (FOXO)-3a (FOXO3a) expression, thereby reduces migration, invasion, liver metastasis, and cancer stemness of CRC. Furthermore, the tumorigenicity was eliminated in ANGPTL1-overexpressed tumors in vivo and ANGPTL1 expression was inversely correlated with the expression of cancer stem cell markers, and conferred better clinical outcomes in patients with CRC. These findings not only illustrate how ANGPTL1 reduces CRC metastasis and cancer stemness but provides a rationale for developing the potential therapeutic strategy of ANGPTL1 for CRC patients.
Materials and methods
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining
CRC human tissue microarrays (TMA) were purchased form SuperBioChips (Seoul, Korea), including 59 paired normal colon and rectum tissues (CDN4) and tumor tissues (CD4), and human CRC metastasis-normal tissues (CDA3). IHC staining was performed by an IHC kit (cat. no. ab64264, Abcam, Cambridge, U.K.) with the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, TMA sections were deparaffinized and rehydrated in gradient ethanol solutions. For antigen retrieval, slides were incubated with protease and blocked with protein block reagent for 10 min, and then incubated with ANGPTL1 antibody (1:100; cat. no. sc-271841, Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Dallas, TX, U.S.A.) overnight at 4 °C. Slides were applied for HRP-conjugated secondary antibody, incubated with DAB substrate, counterstained with hematoxylin, and mounted with mounting medium. Finally, slides were measured by ImageJ software with the IHC profiler plugin [19]. Two groups were analyzed: lower expression (score 0 and 1) and higher expression (score 2 and 3). The negative staining is score 0; the positive staining in ≤ 20% is score 1; the positive staining in 20%∼50% is score 2; strong staining in >50% is score 3.
Cell lines
Both SW480 and SW620 cells were grown in DMEM/F12 medium. HT-29 cells were grown in DMEM medium. American Type Culture Collection (ATCC; Manassas, VA, U.S.A.) provided these cell lines. HCT116 cell were grown in McCoy’s 5A medium and purchased from the Bioresource Collection and Research Center (BCRC, Hsinchu, Taiwan). Media were supplemented with 1% penicillin-streptomycin-Amphotericin B and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), incubated at 37°C with 5% CO2. These cells have been checked for free of mycoplasma contamination.
Immunoblotting and antibodies
Cells were lysed in RIPA lysis buffer supplemented with protease inhibitor cocktail (cat. no. 78430, Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, U.S.A.). It was then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 30 min. Protein samples were mixed with gel sample buffer, separated by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, transferred to a PVDF membrane (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, U.S.A.), blocked, incubated with primary antibodies, and secondary antibodies. The immunoreactive proteins were identified by reaction with enhanced ECL system (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, U.S.A.). The primary antibodies were used for ANGPTL1 (cat. no. sc-271841, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), SOX2 (cat. no. #3579, Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, U.S.A.), Oct4 (cat. no. #2750, Cell Signaling Technology), Nanog (cat. no. ab80892, Abcam), LGR5 (cat. no. ab273092, Abcam), CD133 (cat. no. #64326, Cell Signaling Technology), FOXO1 (cat. no. sc-11350, Santa Cruz Biotechnology), FOXO3a (cat. no. ab53287, Abcam), FOXO4 (cat. no. #9472, Cell Signaling Technology), and α-Tubulin (cat. no. T-5168; Sigma-Aldrich). The secondary antibodies for immunoblotting were obtained from Cell Signaling Technology.
Transwell migration and invasion assay
Migration and invasion abilities were assessed as previously described [20]. Briefly, cells were plated inside the upper chamber in medium without serum, and the lower chamber contained medium with 10% FBS as a chemoattractant at a 24-well plate. The 8 × 104 cells were seeded in the upper chamber and incubated for 24 h for migration assay. For invasion assay, the transwell chamber coated with Matrigel matrix (Corning Costar, Lowell, MA, U.S.A.) was used. The 1 × 105 cells were seeded in the upper chamber and incubated for 24 h. Cells were removed by cotton swabs in the upper chamber, and cells on the membrane surface of the lower chamber were fixed and stained by Crystal Violet (0.05%). The ImageJ software was used for quantification.
Sphere formation assay
Sphere formation was determined as previously described [20]. Cells were seeded on the ultra–low attachment 24-well plates (Corning Costar) with sphere formation medium, which was contained serum free culture medium, B27 supplement, recombinant human EGF (20 ng/ml), and basic FGF (10 ng/ml) for 14 days. The diameters of spheres reached 50 μm were counted.
Plasmid constructs, RNA interference, cell transfection, and virus infection assay
Full-length human ANGPTL1 was cloned into the pcDNA3.1/V5-His Topo vector (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The SOX2 small interfering RNA (siRNA) in a TriFECTa RNAi Kit was obtained from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA, U.S.A.). Cell transfection was performed with PrueFection reagent (System Biosciences, Palo Alto, CA, U.S.A.). Experiments were conducted following the manufacturer's instruction. The lentivirus ANGPTL1 short hairpin RNA (shRNA) clones (TRCN0000426666 and TRCN0000434824), FOXO3 shRNA clones (TRCN0000235488 and TRCN0000235490), pLKO.1-emptyT control clone (TRCN0000208001), and plasmids for pMD2.G and pCMV-deltaR8.91 were obtained from the National RNAi Core Facility at Academia Sinica (Taipei, Taiwan). For lentivirus preparation, HEK-293T cells were transfected with 3.5 μg plasmid DNA, 0.35 μg of envelop plasmid (pMD2.G) and 3.15 μg of package plasmid (pCMV-deltaR8.91) using PureFection reagent. The medium contained lentivirus was collected after 48 h, centrifuged at 1250 rpm for 5 min, and then the supernatant was collected. Cells were infected with medium containing lentivirus and supplemented with 8 μg/ml polybrene (cat. no. H9268, Sigma-Aldrich) for 48 h.
Animals
Male nude mice (5 weeks old) were purchased from BioLASCO (Taipei, Taiwan) and maintained in accordance with the Guide of Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care International. All animal experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at the National Taiwan University College of Medicine (Taipei, Taiwan) (IACUC No. 20200023). Animals were acclimatized and housed under pathogen-free conditions for one week before the experiments. All surgeries were carried out in an operating room at the Laboratory Animal Center of the National Taiwan University College of Medicine.
Intrasplenic injection model
The liver metastasis of CRC was evaluated by an intrasplenic injection model. The 1 × 105 cells were suspended in 50 μl PBS and gently injected into the exposed spleens of mice with a 31G needle (n = 7/ group) under anesthesia (Zoletil 50 mg/kg/Xylazine 2 mg/kg mixture, i.p.), then the peritoneum was closed with stitch. Four weeks later, the mice were killed and the liver were excised to examine and quantify the amount of liver metastasis.
Tumor xenograft animal model
For tumor growth assay, 5 × 106 tumor cells were suspended in PBS contained equal volume of Matrigel (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, U.S.A.) on ice and subcutaneously inoculated into the dorsal flanks of mice (n = 8/group). For tumorigenesis assay, the indicated number of cells were subcutaneously injected into mice (n = 8/group). Tumor volumes were detected twice a week using a caliper and calculated following the formula [(length × width × width) /2].
Statistical analysis
All data are presented as the mean ± S.D. from at least 3 independent experiments using a Prism 6 software (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, U.S.A.). The significant difference among multi-groups was analyzed by a one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. P<0.05 were statistically significant.
Results
ANGPTL1 expression was down-regulated in CRC and associated with better prognosis
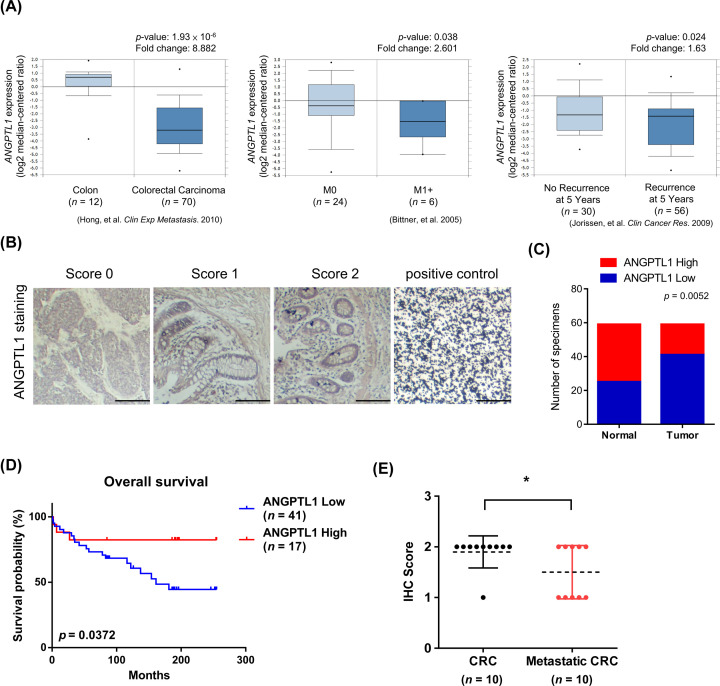
To determine the clinical significance of ANGPTL1 in CRC, we queried the ONCOMINE database to define ANGPTL1 gene expression in CRC patients (1.5-fold change, P-value < 0.05 as the threshold) and observed that ANGPTL1 was highly expressed in normal tissues, non-metastatic tissue, and associated with low recurrence in patients (Figure 1A). We also analyzed other datasets of CRC patients and found that ANGPTL1 expression was down-regulated in CRC patients and inversely correlated with poor outcomes (Table 1). Moreover, we detected ANGPTL1 expression of normal colon and CRC tissues using CRC tissue microarrays (TMAs), which contained 59 paired normal and tumor tissues, and 10 CRC tissues with or without metastasis. The different scores of ANGPTL1 were represented in Figure 1B based on IHC staining analysis. The results showed that ANGPTL1 expression levels were higher in normal colon tissues than paired CRC tissues (Figure 1C), and elevated ANGPTL1 expression had longer survival outcomes in CRC patients by Kaplan–Meier survival analysis (Figure 1D). Compared with metastatic CRC tissues, the scores of ANGPTL1 staining were higher in paired non-metastatic CRC tissues (Figure 1E). These results suggest that ANGPTL1 inversely correlates with worse prognosis in CRC patients.
Figure 1. The clinical significance of ANGPTL1 expression in colorectal cancer (CRC).
(A) The expression of ANGPTL1 negatively correlates with CRC, metastatic stage, and recurrence. ONCOMINE datasets: Hong_Colon, Bitner_Colon, and Jorissen_Colon. (B) IHC staining of ANGPTL1 in colon and CRC TMA tissues with scores of 0–3 was represented. Positive control: Carbon; scale bar: 100 μm. (C) The box plot representation of scores based on IHC staining of ANGPTL1 in 59 paired specimens of CRC and adjacent normal colon tissues. P-value was analyzed by Chi-square analysis followed by Fisher’s exact test. (D) The overall survival of 58 patients in TMA with low and high ANGPTL1 expression was analyzed by Kaplan–Meier analysis (P=0.0372). ANGPTL1 expression was grouped based on the median of the IHC score of specimens. (E) ANGPTL1 expression inversely associated with metastatic tissues compared with paired specimens of CRC tissues in TMA (n=10). *P<0.05 was obtained by paired two-tailed Student’s t-tests.
Table 1. Clinic pathological features, clinical outcomes and their association with ANGPTL1 expression in colorectal cancer datasets.
| Clinic pathological features | Datasets | Mean ANGPTL1 expression (normal tissues) | Mean ANGPTL1 expression (tumor tissues) | Fold change* | P-value† |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rectal adenocarcinoma | Gaedcke (n=65) | 1.89 | −0.77 | −6.321 | 1.44 × 10−48 |
| Kaiser (n=8) | −0.34 | −0.68 | −1.697 | 0.002 | |
| TCGA (n=60) | 4.67 | −0.30 | −21.740 | 2.42 × 10-21 | |
| Colon adenocarcinoma | Kaiser (n=41) | −0.34 | −0.92 | −2.306 | 8.84 × 10−7 |
| TCGA (n=102) | 4.67 | −0.23 | −19.706 | 4.00 × 10−19 | |
| Colorectal adenocarcinoma | Skrzypczak (n=45) | 0.50 | −0.88 | −2.945 | 1.48 × 10-7 |
| Hong (n=70) | −1.28 | −3.22 | −8.882 | 1.93 × 10-6 | |
| Recurrence at 5 years | Jorissen (n=56) | −1.1 | −1.9 | −1.630 | 0.024 |
*Fold change (Log2 median-centered intensity).
†P-value of individual dataset were obtained from the ONCOMINE database.
ANGPTL1 suppresses CRC cell malignant mobility and metastasis
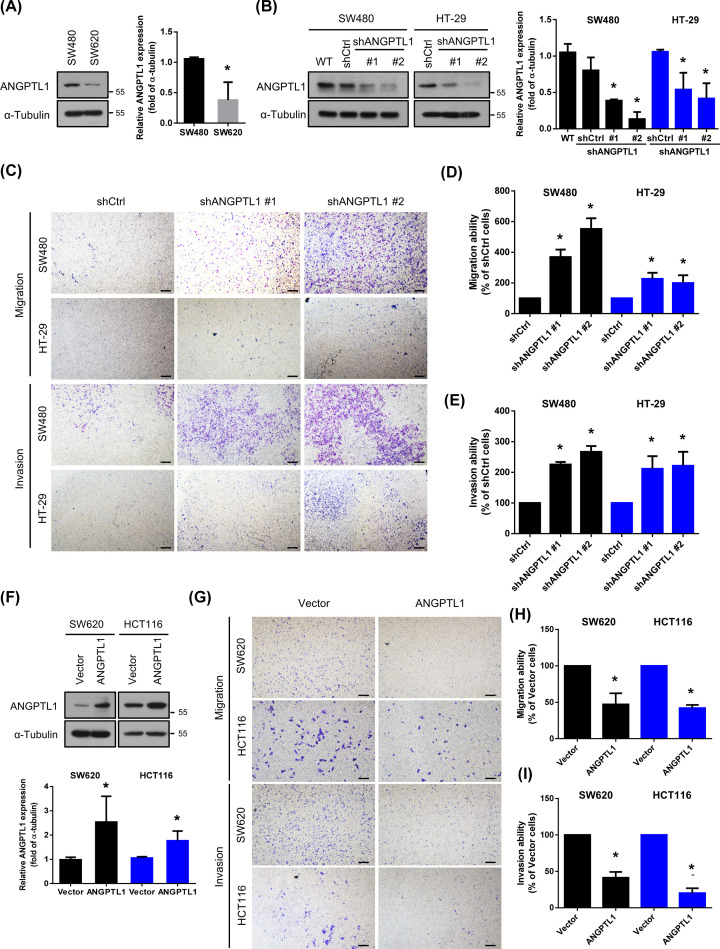
To validate the metastatic capacity of ANGPTL1 in CRC cells, we examined the expression of ANGPTL1 in both SW480 and SW620 cells. SW620 cells were derived from a lymph node metastasis of SW480 cells at the same patient [21]. Interestingly, the basal expression level of ANGPTL1 was lower in SW620 cells than SW480 cells (Figure 2A). To further determine the role of ANGPTL1 on cell mobility in vitro, we performed transwell migration and invasion assays. We knocked down ANGPTL1 in SW480 and HT-29 cells using shRNA lentivirus infection (Figure 2B), the migration and invasion abilities were significantly enhanced (Figure 2C–E). In contrast, overexpression of ANGPTL1 in highly metastatic SW620 and HCT116 cells dramatically inhibited the migration and invasion abilities in both SW620 and HCT116 cells (Figure 2F–I), implying that ANGPTL1 may suppress CRC cell mobility.
Figure 2. ANGPTL1 is required for suppression of cell mobility and metastasis in CRC.
(A) Protein expression of ANGPTL1 in CRC cells (SW480 and the metastatic cell line SW620 cells) were analyzed by Western blotting. The expression of α‐tubulin is as an internal loading control. (B) Knockdown efficiencies of ANGPTL1 in SW480 and HT-29 cells were analyzed by Western blotting. WT: wild-type cells; shCtrl: cells infected with scrambled shRNA virus; shANGPTL1: cells infected with shANGPTL1 virus. (C) Effects of ANGPTL1 inhibition on cancer cell migration and invasion for SW480 and HT-29 cells were analyzed; scale bar = 100 μm. (D,E) Quantification of migrated and invaded cells of ANGPTL1-silenced cells were presented as mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05. (F) Protein expression of ANGPTL1 in ANGPTL1-overexpressed SW620 and HCT116 cells was examined by Western blotting and quantified. (G–I) The transwell migration and invasion assays of ANGPTL1 overexpression in SW620 and HCT116 cells were determined and quantified. Results presented as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05; scale bar = 100 μm.
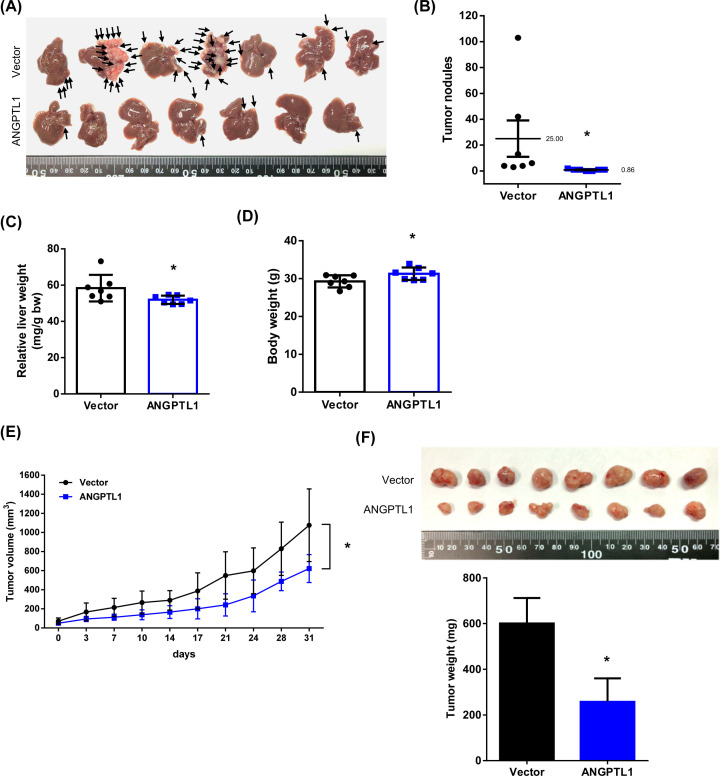
The intrasplenic injection model has been suggested to be a reliable in vivo experimental metastasis assay for testing the cancer stem cell seeding capacity or metastatic stem cell property [22]. To evaluate the potential of ANGPTL1 on metastasis of CRC in vivo, we constructed an intrasplenic injection model using injection with HCT116/Vector or HCT116/ANGPTL1 cells into the spleens of nude mice. After four weeks, the liver metastatic nodules were significantly lower in ANGPTL1-transfected mice compared with the vector control mice (Figure 3A,B). The relative liver weight (normalized with body weight) was also lower (Figure 3C), and the body weight before euthanasia was higher in ANGPTL1-transfected mice (Figure 3D). In addition, a subcutaneous xenograft model was also performed with implanting the same groups into the dorsal flanks and measured the tumor volume and weight of the resulting primary tumors. Overexpression of ANGPTL1 markedly decelerated the tumor volume and weight compared with the control groups (Figure 3E,F). Taken together, these results indicate that ANGPTL1 impedes CRC metastasis in vitro and in vivo.
Figure 3. Effects of ANGPTL1 overexpression on liver metastasis and tumor growth in CRC.
(A) The liver metastasis of CRC was performed with an intrasplenic injection mouse model for four weeks (n = 7/group). Black arrows indicated the metastatic tumor nodules in the liver. (B) The tumor nodules were counted and analyzed by Student’s t test. (C,D) The liver and body weights were weighted; *, P<0.05. (E,F) The xenograft subcutaneous model was performed by implanted the HCT116 cells with stable expression of vector or ANGPTL1 into the dorsal flanks of nude mice. The tumor volume and tumor weight were measured. Results are represented as the mean ± S.D. *, P<0.05, compared with vector groups (N = 8/group).
ANGPTL1 diminishes the cancer stem cell (CSC) properties
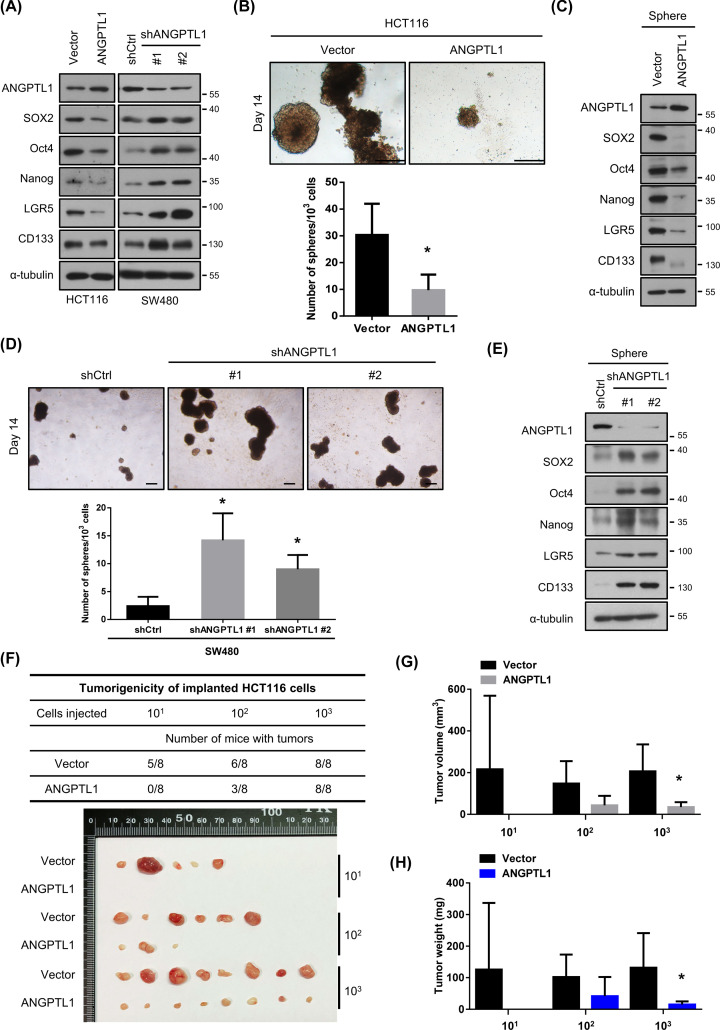
CSCs are demonstrated that can be responsible for tumor progression, drug resistance, and metastasis due to their capacity, such as self-renewing and tumorigenicity [8]. Therefore, we verified the expression of CSC markers, including SOX2, Oct4, Nanog, LGR5, and CD133. All these markers were down-regulated in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells, but dramatically induced in ANGPTL1-silenced cells (Figure 4A). Consistently, overexpression of ANGPTL1 significantly inhibited the sphere formation (Figure 4B). Of note, we further detected the expression of CSC markers of sphere cells and found that the CSC-related markers levels were decreased in ANGPTL1-overexpressed sphere cells (Figure 4C). The sphere formation ability and expression of CSC markers were also enhanced in the groups with ANGPTL1 silence (Figure 4D,E). Moreover, we observed that the expression levels of ALDH1A1, SOX2, POU5F1, and PROM1 in colorectal cancer patients were significantly and inversely correlated with ANGPTL1 expression from the ONCOMINE database (Table 2).
Figure 4. ANGPTL1 is critical for inhibition of cancer stem cell properties and tumorigenicity.
(A) The protein expression of ANGPTL1 and CSC markers in CRC cells (HCT116 and SW480) were analyzed by Western blotting. The expression of α‐tubulin is as an internal loading control. (B,D) The images of sphere formation (top) and the number of spheres in indicated cells were shown; scale bar = 100 μm. (C,E) The protein expression of ANGPTL1 and CSC markers in those sphere cells were assessed by Western blotting. The expression of α‐tubulin is as an internal loading control. (F–H) The transfected cells were subcutaneously injected with indicated cell numbers (10, 100, and 1000 cells per mice) into nude mice. The tumor incidence, tumor volume, and tumor weights were analyzed. Results are shown as the mean ± S.D. *, P<0.05, compared with their vector control cells.
Table 2. Association between stem cell markers and ANGPTL1 expression in colorectal cancer datasets.
| Stem cell markers | Datasets | Pearson correlation, r* | P-value† |
|---|---|---|---|
| ALDH1A1 | Tsuji (n=236) | −0.1806 | 0.0054 |
| Vilar (n=234) | −0.1883 | 0.0038 | |
| Watanabe (n=233) | −0.1514 | 0.0208 | |
| SOX2 | Bittner (n=373) | −0.1117 | 0.0310 |
| Kaiser (n=151) | −0.5699 | <0.0001 | |
| Skrzypczak (n=149) | −0.5540 | <0.0001 | |
| POU5F1 | Bittner (n=373) | −0.1585 | 0.0021 |
| Gaedcke (n=130) | −0.5678 | <0.0001 | |
| Hong (n=82) | −0.4263 | <0.0001 | |
| Kaiser (n=149) | −0.2560 | 0.0016 | |
| TCGA (n=237) | −0.1335 | 0.0400 | |
| Tsuji (n=231) | −0.2970 | <0.0001 | |
| Tsukamoto (n=233) | −0.2108 | 0.0012 | |
| Vilar (n=231) | −0.2532 | <0.0001 | |
| PROM1 | Bittner (n=373) | −0.1684 | 0.0011 |
| Gaedcke (n=130) | −0.1784 | 0.0423 | |
| Tsuji (n=231) | −0.4818 | <0.0001 | |
| Tsukamoto (n=233) | −0.4273 | <0.0001 | |
| Vilar (n=231) | −0.3426 | <0.0001 | |
| Watanabe (n=233) | −0.4129 | < 0.0001 |
*r, Pearson’s correlation coefficient.
†P-value for two-tailed Student’s t test of Individual dataset (ONCOMINE database).
To further explore the tumorigenicity under the presence of ANGPTL1, subcutaneous tumorigenicity model was performed in vivo. The tumor incidence (number of tumors/number of implanted cells) was dramatically repressed in the group of ANGPTL1-overexpressed HCT116 cells compared with the vector group, even in the only 10 cells with ANGPTL1-overexpression group (Figure 4F). Although the tumor incidence was not changed in 1000 cells with ANGPTL1-overexpression group compared to the vector group, the tumor volume was reduced in ANGPTL1-overexpressed tumors (Figure 4G), as well as the tumor weight was significantly decreased (Figure 4H). Collectively, these results implicate that ANGPTL1 has ability to eliminate the CSC properties of CRC.
FOXO3a is involved in ANGPTL1-regulated cell mobility
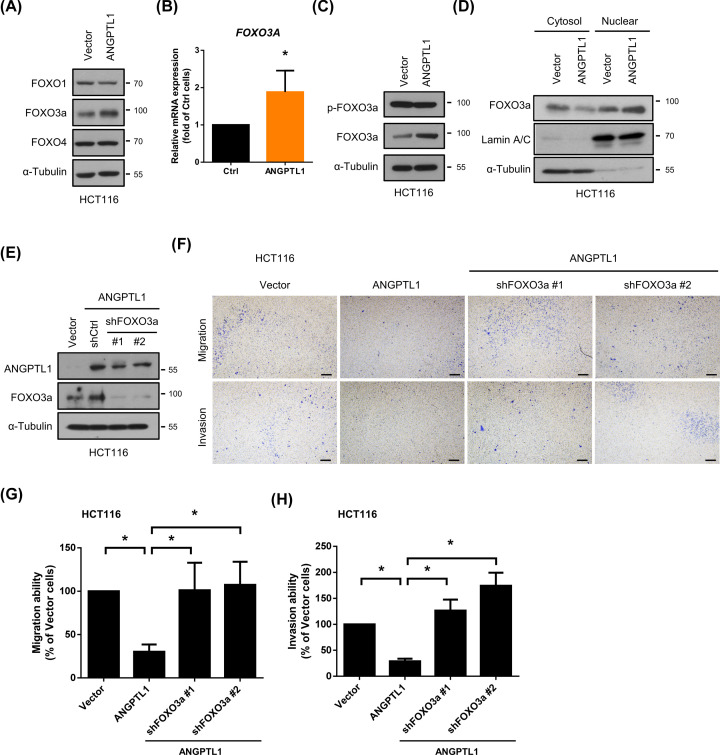
It has been well known that FOXO family, including FOXO1, FOXO3a, and FOXO4, regulates cancer development, tumorigenesis, metabolism, and metastasis [23–27]. According to the potential antitumor activity of FOXO members in several cancers, we subsequently examined the expression of FOXO1, FOXO3a, and FOXO4. As shown in Figure 5A, only the expression of FOXO3a was up-regulated in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells but not FOXO1 nor FOXO4. We further examined the mRNA expression of FOXO3a and found that the FOXO3a mRNA expression was also increased in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells (Figure 5B). Since the transcriptional activity of FOXO3a is determined by nuclear translocation of FOXO3a, which can be inhibited with phosphorylation by kinases, the phosphorylation of FOXO3a was examined. The results showed that the FOXO3a phosphorylation was not significantly higher in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells than vector control cells (Figure 5C, fold = 1.13; P=0.5456). Moreover, nuclear and cytosol fractions were examined to verify the nuclear translocation of FOXO3a under ANGPTL1 overexpression. The expression of FOXO3a in the nucleus was induced in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells (Figure 5D), suggesting that ANGPTL1 not only enhanced FOXO3a mRNA expression but also nuclear translocation. To further confirm the role of FOXO3a in ANGPTL1-regulated cell mobility, the depletion of FOXO3a in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells was examined by Western blotting (Figure 5E). FOXO3a depletion markedly abolished the ANGPTL1-reduced cell migration and invasion abilities (Figure 5F–H). These results suggest that ANGPTL1 inhibits CRC cell motility through up-regulation of FOXO3a expression.
Figure 5. ANGPTL1 suppressed cell migration and invasion through FOXO3a induction in HCT116 cells.
(A) The protein expression of FOXO family was assessed by Western blotting. The expression of α‐tubulin used as an internal loading control. (B) The mRNA expression of FOXO3 was analyzed using RT-PCR analysis. GAPDH was used as reference gene; *, P<0.05 (C) The p-FOXO3a and FOXO3a expression in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells was performed. The expression of α‐tubulin is as an internal loading control. (D) The expression of FOXO3a in the nucleus and cytosol was assessed by Western blotting. The expression of Lamin A/C used as nuclear internal loading control and α‐tubulin as a cytosol internal loading control. (E) The knockdown efficiencies of FOXO3a were analyzed. The expression of α‐tubulin is as an internal loading control. (F–H) Both migration and invasion abilities were examined and quantified. Results are shown as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05, compared with indicated cells; scale bar = 100 μm.
Down-regulation of SOX2 through the ANGPTL1-up-regulated FOXO3a pathway
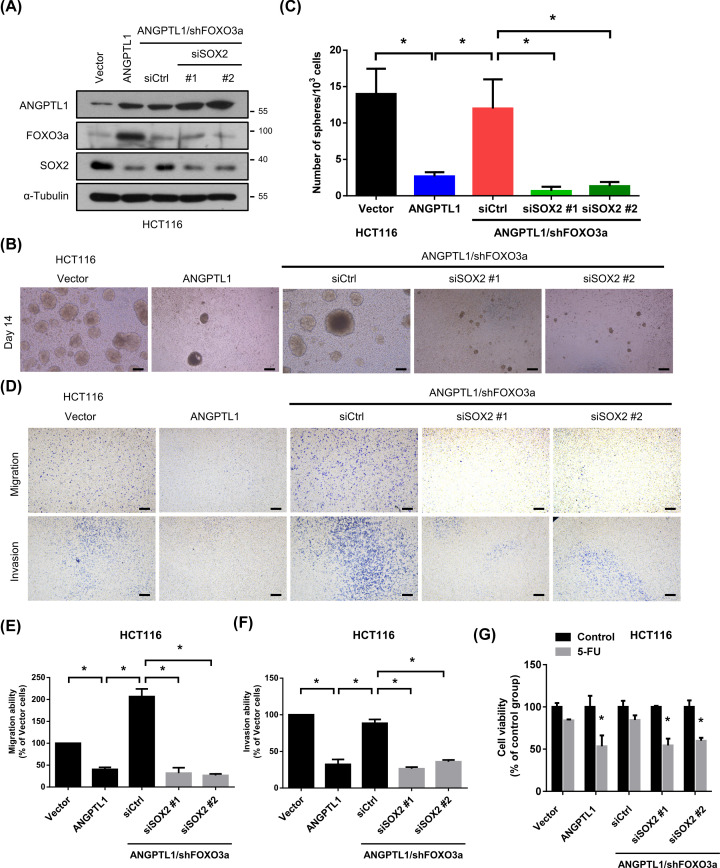
SOX2, a member of the SRY-related HMG-box (SOX) family, is one of the critical CSC transcription factors and directly inhibited by FOXO3a in neck squamous cell carcinoma [28]. We hypothesized that the mechanism of ANGPTL1-regulated CRC metastasis and cancer stemness may be through FOXO3a/SOX2 axis. As the results, the expression of SOX2 was reduced in ANGPTL1-overexpressed cells, while knockdown of FOXO3a restored the expression of SOX2 (Figure 6A). To further investigate the role of SOX2 in ANGPTL1/FOXO3a-suppressed metastasis and cancer stemness, we genetically silenced SOX2 using siRNA transfection. Suppression of SOX2 in ANGPTL1/shFOXO3a cells significantly reduced the sphere formation compared with the ANGPTL1/shCtrl group (Figure 6B,C), and the FOXO3a knockdown-induced cell migration and invasion abilities were also abolished (Figure 6D–F). Due to CSCs participate in tumor initiation, metastasis, drug resistance, and tumor recurrence, we investigated the effects of ANGPTL1-FOXO3a-SOX2 signaling on chemosensitivity, such as 5-fluorouracil (5-FU). We found that the inhibition of FOXO3a significantly reduced ANGPTL1-mediated sensitivity to 5-FU, but this effect was reversed by inhibition of SOX2 (Figure 6G), suggesting that ANGPTL1-FOXO3a-SOX2 signaling positively regulated the sensitization to 5-FU in colorectal cancer cells.
Figure 6. ANGPTL1-FOXO3a signaling pathway mediated cell motility and cancer stem cell properties via SOX2 inhibition in HCT116 cells.
(A) The inhibition efficiencies of SOX2 by siRNA transfection were determined by Western blotting. The expression of α‐tubulin is as an internal loading control. (B,C) The effects of SOX2 suppression on sphere formation abilities were analyzed and quantified. Bars presented as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, compared to indicated cells; scale bar = 100 μm. (D–F) The migration and invasion abilities of SOX2-silenced cells were measured in transwell assay. Results are represented as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05, compared with indicated cells; scale bar = 100 μm. (G) The cell viability of SOX2-silenced cells was analyzed using MTT assay after treatment with 5-FU (10 μM) for 24 h. Results are represented as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05, compared with indicated cells.
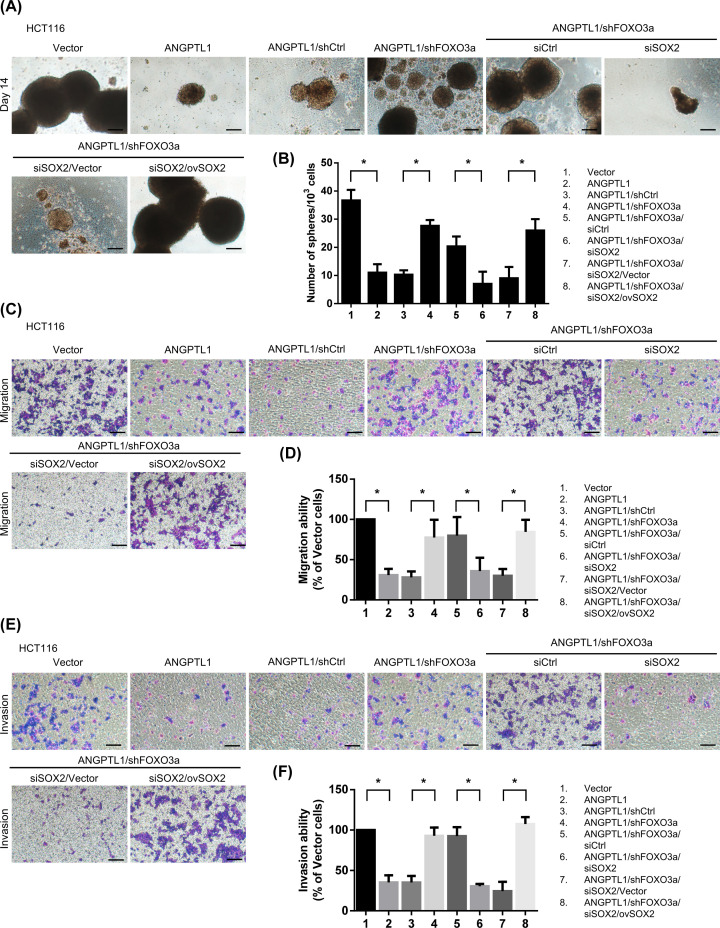
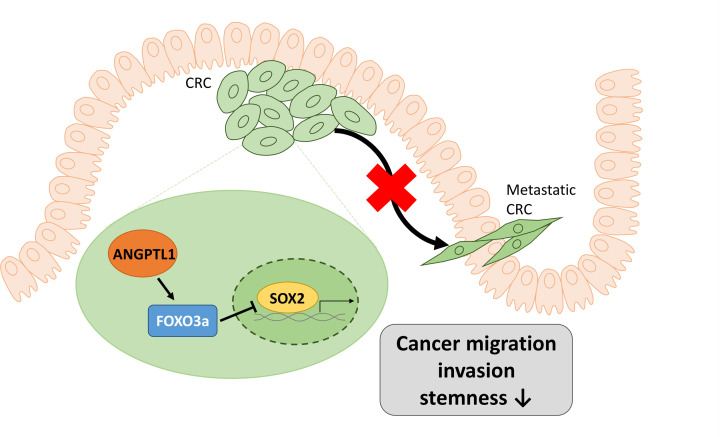
To further confirm the role of SOX2 in CRC stemness and metastasis, we overexpressed the expression of SOX2 in ANGPTL1/shFOXO3a/siSOX2-transfected HCT116 cells and evaluated these effects. Overexpression of SOX2 in ANGPTL1/shFOXO3a/siSOX2-transfected HCT116 cells significantly enhanced the sphere formation, and the migration/invasion abilities were also markedly restored in overexpressed SOX2 cells (Figure 7), suggesting that the expression of SOX2 played a vital role in ANGPTL1-regulated CRC stemness and metastasis. Taken together, these results suggest that ANGPTL1-up-regulated FOXO3a expression may inhibit metastasis and cancer stemness through the suppression of SOX2 in CRC cells (Figure 8).
Figure 7. Restored SOX2 expression enhanced the ANGPTL1-FOXO3a-mediated cancer stemness and metastasis.
(A,B) The sphere formation abilities in SOX2 re-overexpression were analyzed and quantified. Bars presented as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05, compared to indicated cells; scale bar: 100 μm. (C–F) The migration and invasion abilities of SOX2 re-overexpression in cells were measured in transwell assay. Results are represented as the mean ± S.D. of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05, compared with indicated cells; scale bar: 100 μm.
Figure 8. A schematic model illustrating the transcriptional reduction of SOX2 by ANGPTL1 through the induction of FOXO3a in CRC, and how this affects cancer stemness and metastasis.
Discussion
Accumulating studies have clarified that ANGPTL1 inhibits angiogenesis, tumor growth, and metastasis, yet the mechanisms are diverse in different cancer types, including lung cancer [29], HCC [17], and CRC [12,30]. In lung cancer, ANGPTL1 suppressed cell motility through interaction with integrin α1β1 and reduction of Slug, then elicited mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET) [29]. Another study also reported that ANGPTL1 interacted with integrin α1β1 and repressed the Src/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway to attenuate the HCC angiogenesis and metastasis [11]. Beside the integrin pathway, ANGPTL1 also impeded MET activation and downstream signaling, which contributed to overcome sorafenib resistance in HCC [17]. In CRC, ANGPTL1 suppressed EMT by inhibition of Slug [31] and repressed metastasis via microRNA-138 regulation [12]. A recent study has shown that exosomal ANGPTL1 retards liver metastasis using an intrasplenic injection mouse model by regulation the secretion of Kupffer cells in the liver [30]. Another study showed that intrasplenic injection of tumor cells allowed the maximum expression of the metastatic ability and disseminate to liver [32]. These studies suggested that the intrasplenic injection model could be used to investigate the role of ANGPTL1 in liver metastasis. Consistent with these previous studies, we found that ANGPTL1 suppressed CRC cell migration and invasion in vitro, and inhibited tumor growth and liver metastasis in vivo. However, in this model, CRC cells were injected into the circulation without the process of extravasation. The cecal wall injection model may be a better choice. It may be considered conducting this model for liver metastasis in the future.
During cancer initiation and metastasis, CSCs have been considered to participate in the process and modulate the tumor microenvironment. The cross-talk between endothelial cells and tumor cells or CSCs promotes EMT and angiogenesis [33,34]. A previous study has found that metastatic breast cancer cells maintain the signature of the distinct stem-like cells, including the gene expression of stem cells, EMT, survival, and dormancy [35]. The Yamanaka factors, including Sox2, Oct3/4, c-Myc, and Klf4 are established in the induced pluripotent stem (iPS) cells, leading to tumorigenesis [36,37]. Highly expression of SOX2 has been identified in CRC cells and patients, and associated with poor prognosis [38]. SOX2 promotes CSCs properties through β-catenin and transcriptional regulation of Beclin1 in CRC [39]. Inhibition of Oct4 diminished the self-renewal of colorectal cancer stem cells via EMT and positively correlated with TNM stage, lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis of CRC patients [40]. Nanog, another pluripotency-related transcription factor, has been shown to modulate the stemness [41] and facilitate the proliferation, invasion, and EMT [42] in CRC. Moreover, ANGPTL1 has been reported to inhibit the expression of CSCs markers and sphere formation by suppressing Slug in HCC [17]. However, there are no studies that have evaluated the role of ANGPTL1 in the regulation of stemness in CRC. Thus, in this study, we demonstrate that ANGPTL1 can suppress the expression of CSCs markers and sphere formation in vitro and tumorigenesis in vivo of CRC.
FOXO3a is a tumor suppressor and involved in the regulation of CSCs properties, metastasis, and cancer progression in various cancers [43–45]. Overexpression of FOXO3a reduced the transcriptional expression of SOX2 by directly binding on SOX2 promoter region and subsequent impeded the CSCs properties in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma [28]. In breast cancer, DNMT1 down-regulated FOXO3a expression, thereby induced the expression of FOXM1/SOX2, contributed to promote the cancer stemness and tumorigenicity [46]. In this study, our results suggest that FOXO3a drives the inhibition of SOX2 and reduction of the sphere formation and cell motility in CRC under ANGPTL1 regulation. We also found that ANGPTL1 not only enhanced FOXO3a mRNA expression but also triggered the nuclear translocation of FOXO3a. These findings can also help for completing the knowledge of FOXO3a in cancer stemness in various types of cancers. However, the detailed mechanism for ANGPTL1-regulated FOXO3a expression still needs to be further investigation in future research.
Conclusion
Our findings uncover a novel mechanism of ANGPTL1/FOXO3a/SOX2 axis that suppresses cancer migration, invasion, and stemness in CRC. We also demonstrate the clinical significance of ANGPTL1 that there is a clinically inverse association between CSCs markers and ANGPTL1 in CRC patients. These results figure out the important roles of ANGPTL1 in the CRC stemness and progression and may provide a potential target to develop therapeutic strategies or novel prognosis markers for colorectal cancer patients. However, the limitation of this study is lack of the evidence of ANGPTL1-FOXO3a-SOX2-mediated cancer stemness in animal model. It may be possible in the future to analyze the in vivo ANGPTL1-FOXO3a-SOX2-mediated cancer stemness.
Clinical perspectives
Previous studies have shown that ANGPTL1 plays a crucial role in cancer progression by suppressing cancer cell proliferation and motility in various cancers. However, there may have undefined functions and molecular mechanisms involved in the tumor progression mediated by ANGPTL1. Thus, this study was aimed to identify the role of ANGPTL1 in metastasis, cancer stemness, and the molecular mechanisms of colorectal cancer.
We found for the first time that ANGPTL1 significantly suppressed the cancer migration, invasion, and stemness by enhancing FOXO3a expression, which reduced the stem cell transcription factor SOX2 expression in CRC.
This study demonstrates the detail molecular mechanism of ANGPTL1 suppresses cancer migration, invasion, and stemness in colorectal cancer cells. Furthermore, define the biological significance of ANGPTL1 may provide more potential targets to develop the anticancer therapeutic strategies or novel prognosis markers for colorectal cancer patients.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgements
We thank the National RNAi Core Facility (Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan) for providing specific shRNAs and the results shown here are in part based on data generated from the ONCOMINE database.
Abbreviations
- ANGPTL1
angiopoietin-like protein 1
- CRC
colorectal cancer
- CSC
cancer stem cell
- EMT
epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- FBS
fetal bovine serum
- FOXO3a
forkhead box O-3a
- IHC
immunohistochemistry
- shRNA
short hairpin RNA
- siRNA
small interfering RNA
- SOX2
SRY-related HMG-box-2
- TMA
tissue microarrays
Contributor Information
Meei-Ling Sheu, Email: mlsheu@nchu.edu.tw.
Shing-Hwa Liu, Email: shinghwaliu@ntu.edu.tw.
Data Availability
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The full uncropped and unedited versions of the representative Western blot images are listed in the Supplementary Figure.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Funding
This study was funded in part by grants from the Ministry of Science and Technology of Taiwan [grant numbers MOST-106-2320-B-005-001-MY3; MOST107-2314-B-002-251] and the Teh-Tzer Study Group for Human Medical Research Foundation [grant numbers B1081007 and B1101008].
CRediT Author Contribution
Ting-Yu Chang: Data curation, Formal analysis, Validation, Investigation, Visualization, Methodology, and Writing—original draft. Kuo-Cheng Lan: Resources, Funding acquisition, Validation, and Writing—review & editing. Chen-Yuan Chiu: Resources, Funding acquisition, and Validation. Meei-Ling Sheu: Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Validation, and Writing—review & editing. Shing-Hwa Liu: Resources, Supervision, Funding acquisition, Validation, and Writing—review & editing.
References
- 1.Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Fuchs H.E. and Jemal A. (2022) Cancer statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin. 72, 7–33 10.3322/caac.21708 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gonzalez-Villarreal C.A., Quiroz-Reyes A.G., Islas J.F. and Garza-Trevino E.N. (2020) Colorectal cancer stem cells in the progression to liver metastasis. Front. Oncol. 10, 1511 10.3389/fonc.2020.01511 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mani S.A., Guo W., Liao M.J., Eaton E.N., Ayyanan A., Zhou A.Y.et al. (2008) The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell 133, 704–715 10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.027 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Diehn M., Cho R.W., Lobo N.A., Kalisky T., Dorie M.J., Kulp A.N.et al. (2009) Association of reactive oxygen species levels and radioresistance in cancer stem cells. Nature 458, 780–783 10.1038/nature07733 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Phi L.T.H., Sari I.N., Yang Y.G., Lee S.H., Jun N., Kim K.S.et al. (2018) Cancer stem cells (CSCs) in drug resistance and their therapeutic implications in cancer treatment. Stem. Cell Int. 2018, 5416923 10.1155/2018/5416923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Quante M., Tu S.P., Tomita H., Gonda T., Wang S.S., Takashi S.et al. (2011) Bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the mesenchymal stem cell niche and promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell 19, 257–272 10.1016/j.ccr.2011.01.020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Fumagalli A., Oost K.C., Kester L., Morgner J., Bornes L., Bruens L.et al. (2020) Plasticity of Lgr5-negative cancer cells drives metastasis in colorectal cancer. Cell Stem Cell 26, 569.e7–578.e7 10.1016/j.stem.2020.02.008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Frank M.H., Wilson B.J., Gold J.S. and Frank N.Y. (2021) Clinical implications of colorectal cancer stem cells in the age of single-cell omics and targeted therapies. Gastroenterology 160, 1947–1960 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.12.080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kuo T.C., Tan C.T., Chang Y.W., Hong C.C., Lee W.J., Chen M.W.et al. (2017) Angiopoietin-like protein 1 suppresses SLUG to inhibit cancer cell motility. J. Clin. Invest. 127, 402 10.1172/JCI91882 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sun R., Yang L., Hu Y., Wang Y., Zhang Q., Zhang Y.et al. (2020) ANGPTL1 is a potential biomarker for differentiated thyroid cancer diagnosis and recurrence. Oncol. Lett. 20, 240 10.3892/ol.2020.12103 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Yan Q., Jiang L., Liu M., Yu D., Zhang Y., Li Y.et al. (2017) ANGPTL1 interacts with integrin alpha1beta1 to suppress HCC angiogenesis and metastasis by inhibiting JAK2/STAT3 signaling. Cancer Res. 77, 5831–5845 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0579 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen H., Xiao Q., Hu Y., Chen L., Jiang K., Tang Y.et al. (2017) ANGPTL1 attenuates colorectal cancer metastasis by up-regulating microRNA-138. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 36, 78 10.1186/s13046-017-0548-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Xu Y., Liu Y.J. and Yu Q. (2004) Angiopoietin-3 inhibits pulmonary metastasis by inhibiting tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 64, 6119–6126 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1054 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Carbone C., Piro G., Merz V., Simionato F., Santoro R., Zecchetto C.et al. (2018) Angiopoietin-like proteins in angiogenesis, inflammation and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 19, 431 10.3390/ijms19020431 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhang C.C., Kaba M., Ge G., Xie K., Tong W., Hug C.et al. (2006) Angiopoietin-like proteins stimulate ex vivo expansion of hematopoietic stem cells. Nat. Med. 12, 240–245 10.1038/nm1342 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kersten S. (2005) Regulation of lipid metabolism via angiopoietin-like proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 33, 1059–1062 10.1042/BST0331059 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chen H.A., Kuo T.C., Tseng C.F., Ma J.T., Yang S.T., Yen C.J.et al. (2016) Angiopoietin-like protein 1 antagonizes MET receptor activity to repress sorafenib resistance and cancer stemness in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 64, 1637–1651 10.1002/hep.28773 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Endo M. (2019) The roles of ANGPTL families in cancer progression. J. UOEH 41, 317–325 10.7888/juoeh.41.317 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Varghese F., Bukhari A.B., Malhotra R. and De A. (2014) IHC Profiler: an open source plugin for the quantitative evaluation and automated scoring of immunohistochemistry images of human tissue samples. PLoS ONE 9, e96801 10.1371/journal.pone.0096801 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Chang T.Y., Wu C.T., Sheu M.L., Yang R.S. and Liu S.H. (2021) CARMA3 promotes colorectal cancer cell motility and cancer stemness via YAP-mediated NF-κB activation. Cancers 13, 5946 10.3390/cancers13235946 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hewitt R.E., McMarlin A., Kleiner D., Wersto R., Martin P., Tsokos M.et al. (2000) Validation of a model of colon cancer progression. J. Pathol. 192, 446–454 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Dafflon C., Santamaría-Martínez A. and Ordóñez-Morán P. (2020) An intrasplenic injection model for the study of cancer stem cell seeding capacity. Method. Mol. Biol. (Clifton, N.J.) 2171, 293–302 10.1007/978-1-0716-0747-3_20 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Pan S., Deng Y., Fu J., Zhang Y., Zhang Z., Ru X.et al. (2018) Decreased expression of ARHGAP15 promotes the development of colorectal cancer through PTEN/AKT/FOXO1 axis. Cell Death Dis. 9, 673 10.1038/s41419-018-0707-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Bullock M.D., Bruce A., Sreekumar R., Curtis N., Cheung T., Reading I.et al. (2013) FOXO3 expression during colorectal cancer progression: biomarker potential reflects a tumour suppressor role. Br. J. Cancer 109, 387–394 10.1038/bjc.2013.355 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Liu L., Yan X., Wu D., Yang Y., Li M., Su Y.et al. (2018) High expression of Ras-related protein 1A promotes an aggressive phenotype in colorectal cancer via PTEN/FOXO3/CCND1 pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 37, 178 10.1186/s13046-018-0827-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Liu X., Zhang Z., Sun L., Chai N., Tang S., Jin J.et al. (2011) MicroRNA-499-5p promotes cellular invasion and tumor metastasis in colorectal cancer by targeting FOXO4 and PDCD4. Carcinogenesis 32, 1798–1805 10.1093/carcin/bgr213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sun Y., Wang L., Xu X., Han P., Wu J., Tian X.et al. (2021) FOXO4 inhibits the migration and metastasis of colorectal cancer by regulating the APC2/beta-Catenin axis. Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 9, 659731 10.3389/fcell.2021.659731 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Chen Y., Zhao H., Liang W., Jiang E., Zhou X., Shao Z.et al. (2022) Autophagy regulates the cancer stem cell phenotype of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma through the noncanonical FOXO3/SOX2 axis. Oncogene 41, 634–646 10.1038/s41388-021-02115-7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kuo T.C., Tan C.T., Chang Y.W., Hong C.C., Lee W.J., Chen M.W.et al. (2013) Angiopoietin-like protein 1 suppresses SLUG to inhibit cancer cell motility. J. Clin. Invest. 123, 1082–1095 10.1172/JCI64044 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Jiang K., Chen H., Fang Y., Chen L., Zhong C., Bu T.et al. (2021) Exosomal ANGPTL1 attenuates colorectal cancer liver metastasis by regulating Kupffer cell secretion pattern and impeding MMP9 induced vascular leakiness. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 40, 21 10.1186/s13046-020-01816-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Fan H., Huang L., Zhuang X., Ai F. and Sun W. (2019) Angiopoietin-like protein 1 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer cells via suppress Slug expression. Cytotechnology 71, 35–44 10.1007/s10616-018-0259-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kozlowski J.M., Fidler I.J., Campbell D., Xu Z.L., Kaighn M.E. and Hart I.R. (1984) Metastatic behavior of human tumor cell lines grown in the nude mouse. Cancer Res. 44 8, 3522–3529 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Galan-Moya E.M., Le Guelte A., Lima Fernandes E., Thirant C., Dwyer J., Bidere N.et al. (2011) Secreted factors from brain endothelial cells maintain glioblastoma stem-like cell expansion through the mTOR pathway. EMBO Rep. 12, 470–476 10.1038/embor.2011.39 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lu J., Ye X., Fan F., Xia L., Bhattacharya R., Bellister S.et al. (2013) Endothelial cells promote the colorectal cancer stem cell phenotype through a soluble form of Jagged-1. Cancer Cell 23, 171–185 10.1016/j.ccr.2012.12.021 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Minn A.J., Gupta G.P., Siegel P.M., Bos P.D., Shu W., Giri D.D.et al. (2005) Genes that mediate breast cancer metastasis to lung. Nature 436, 518–524 10.1038/nature03799 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Takahashi K. and Yamanaka S. (2006) Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 126, 663–676 10.1016/j.cell.2006.07.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ohnishi K., Semi K., Yamamoto T., Shimizu M., Tanaka A., Mitsunaga K.et al. (2014) Premature termination of reprogramming in vivo leads to cancer development through altered epigenetic regulation. Cell 156, 663–677 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Takeda K., Mizushima T., Yokoyama Y., Hirose H., Wu X., Qian Y.et al. (2018) Sox2 is associated with cancer stem-like properties in colorectal cancer. Sci. Rep. 8, 17639 10.1038/s41598-018-36251-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Zhu Y., Huang S., Chen S., Chen J., Wang Z., Wang Y.et al. (2021) SOX2 promotes chemoresistance, cancer stem cells properties, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by beta-catenin and Beclin1/autophagy signaling in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 12, 449 10.1038/s41419-021-03733-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhou J.M., Hu S.Q., Jiang H., Chen Y.L., Feng J.H., Chen Z.Q.et al. (2019) OCT4B1 Promoted EMT and Regulated the Self-Renewal of CSCs in CRC: Effects Associated with the Balance of miR-8064/PLK1. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 15, 7–20 10.1016/j.omto.2019.08.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Zhang J., Espinoza L.A., Kinders R.J., Lawrence S.M., Pfister T.D., Zhou M.et al. (2013) NANOG modulates stemness in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene 32, 4397–4405 10.1038/onc.2012.461 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Meng H.M., Zheng P., Wang X.Y., Liu C., Sui H.M., Wu S.J.et al. (2010) Over-expression of Nanog predicts tumor progression and poor prognosis in colorectal cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 9, 295–302 10.4161/cbt.9.4.10666 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Smit L., Berns K., Spence K., Ryder W.D., Zeps N., Madiredjo M.et al. (2016) An integrated genomic approach identifies that the PI3K/AKT/FOXO pathway is involved in breast cancer tumor initiation. Oncotarget 7, 2596–2610 10.18632/oncotarget.6354 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Prabhu V.V., Allen J.E., Dicker D.T. and El-Deiry W.S. (2015) Small-molecule ONC201/TIC10 targets chemotherapy-resistant colorectal cancer stem-like cells in an Akt/Foxo3a/TRAIL-dependent manner. Cancer Res. 75, 1423–1432 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-3451 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chiu C.F., Chang Y.W., Kuo K.T., Shen Y.S., Liu C.Y., Yu Y.H.et al. (2016) NF-kappaB-driven suppression of FOXO3a contributes to EGFR mutation-independent gefitinib resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 113, E2526–E2535 10.1073/pnas.1522612113 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Liu H., Song Y., Qiu H., Liu Y., Luo K., Yi Y.et al. (2020) Downregulation of FOXO3a by DNMT1 promotes breast cancer stem cell properties and tumorigenesis. Cell Death Differ. 27, 966–983 10.1038/s41418-019-0389-3 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. The full uncropped and unedited versions of the representative Western blot images are listed in the Supplementary Figure.