Abstract
Variations of intracellular concentrations of isocitrate and NADP+ were measured throughout all growth phases of the marine bacterium Pseudomonas nautica. The intracellular isocitrate concentration tracked the intracellular protein concentration throughout all phases of growth. It rapidly increased in early exponential phase to a maximum and fell to nearly zero in parallel with pyruvate exhaustion in the culture medium. The intracellular NADP+ and protein concentrations increased in parallel during the exponential phase but were poorly correlated. Even after carbon exhaustion, the intracellular NADP+ concentration stayed high, as did protein levels. The results demonstrated that the intracellular isocitrate concentration, but not the intracellular NADP+ concentration, was affected by the carbon availability in the culture. They also suggest that, because of its variability, isocitrate, but not NADP+, plays the larger role in the control of the respiratory CO2 production rate (RCO2). From initial rate studies, bisubstrate Michaelis constants and the dissociation constant were determined for NADP+-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) from P. nautica. These studies support the hypothesis that the mechanism of IDH’s activity involves the ordered addition of the substrates, d-isocitrate and NADP+. Furthermore, the results support the use of a bisubstrate enzyme kinetic equation to model RCO2 in P. nautica.
Heterotrophic bacteria can grow on a wide variety of carbon sources that under aerobic conditions are completely oxidized to CO2 (17). Of the decarboxylases responsible for the CO2 production, isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) is of particular interest since it controls the flow of carbon between the Krebs cycle and the glyoxylate bypass via its activation and inactivation by the bifunctional IDH kinase/phosphatase (20, 21). Thus, the activation of IDH forces the flow through the Krebs cycle, causing a decrease in the intracellular isocitrate level and an increase in the α-ketoglutarate level.
Although a few bacteria contain the NAD-IDH (EC 1.1.1.41), most have only the NADP-dependent enzyme (EC 1.1.1.42) (6, 31). The IDH reaction is expected to follow a sequential mechanism (5, 11, 44) by which both isocitrate and NADP+ bind to the enzyme to form a complex before the formation of the first product (29, 36, 39). The binding of the substrates to the enzyme may occur in a random or ordered sequence. For initial velocity (v) studies of sequential mechanisms, the Lineweaver-Burk primary plots of 1/v versus 1/isocitrate concentration at a constant NADP+ concentration or 1/v versus 1/NADP+ concentration at a constant isocitrate concentration give a family of lines with different slopes and intercepts (10, 18, 36). (For brevity’s sake, these rates are referred to as 1/isocitrate and 1/NADP+, respectively, hereafter in this work.) To differentiate between random and compulsory sequential reaction mechanisms, inhibition and isotope exchange experiments must be done (9, 18). Once defined, sequential reactions are described by the same kinetic equation that uses Michaelis constants and substrates concentrations to calculate the in vivo activity of enzymes.
Recent enzyme-based models of CO2 production and oxygen consumption in a marine bacterium, Pseudomonas nautica, revealed a deficiency in our knowledge of both the Michaelis and equilibrium constants controlling these enzymes as well as the intracellular concentrations of their substrates. Here we address this deficiency by (i) measuring the intracellular concentration of isocitrate and NADP+, the IDH substrates, and (ii) measuring the kinetic constants, Kiso and KNADP+, and the equilibrium constant, Kia. For these measurements, we used a culture of the marine bacterium P. nautica growing on pyruvate as a model. Our results demonstrated the effect of carbon availability on intracellular isocitrate and NADP+ concentrations. Also, as with many dehydrogenases, the initial velocity studies suggest an ordered sequential reaction mechanism for IDH from P. nautica.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Bacterial strain and growth conditions.
P. nautica (ATCC 27132) was grown in batch cultures on a seawater medium containing 20 mM pyruvate as the sole carbon source. Batch cultures were cultivated as described by Packard et al. (34, 35).
Bacterial enumeration and cellular fraction volume.
Flow cytometry was used to enumerate P. nautica in all growth phases. Four-milliliter samples for flow cytometric analyses were fixed by addition of 0.5 ml of formalin (final concentration, 3.7%) and held at 4°C. Cell concentrations ranged from 2.6 × 1011 to 3.4 × 1012 cells/liter. Three 1-ml subsamples were aliquoted. The pH of the suspensions was adjusted to 9 by addition of 1 N NaOH. Samples were stained for 2 h at 60°C with dichlorotriazinylfluorescein at a final concentration of 200 μg/ml (42). Cells were enumerated with a Becton Dickinson FACScan flow cytometer equipped with a 15-mW, 488-nm argon ion laser rating the measurements on the protein fluorescence (515 nm). A 100-μl sample was precisely injected into the flow cytometer by using a modular digital pump (model XL3000; Cavro Scientific Instruments Inc., Calif.). Cell abundance (C [in cells per liter]) and optical density at 550 nm (OD550) were related by the relation C = 2.05 × 10[11 + 0.882(OD550)] (n = 22). This relationship held for all growth phases with an r2 of 0.95 (P < 0.001). It is known that P. nautica cells can be considered ellipsoids of revolution with three different radii (a, b, and c), of which two are equal (11a). If one assumes a long axis, a, of 1.5 μm and small axes, b and c, of 0.7 μm (4), the volume of one cell can be calculated from the equation 4πabc/3, giving a cellular volume of 0.385 μm3 (3.85 × 10−10 μl). Then, from the OD550 at each sampling time, the volume of the cellular fraction of the culture through all growth phases was calculated and the substrate and protein concentrations were reported as intracellular concentrations.
Isocitrate and NADP+ concentration measurement. (i) Extraction.
Samples were taken in duplicate for NADP+ and isocitrate measurements every 2 h from inoculation to pyruvate exhaustion in the medium (14 h) and from 24 h to the end of the experiment (30 h). Aliquots of culture (5 to 50 ml, depending on the biomass) were centrifuged at 14,000 × g for 8 min at 4°C. Aliquots from the supernatant fluid were frozen for pyruvate analyses. The remainder of the supernatant fluid was decanted, and the pellets were immediately resuspended in extraction buffer consisting of 5 ml of 25 mM MOPS (morpholinepropanesulfonic acid), pH 7.9. The homogenates were acidified by the addition of 0.3 ml of 0.5 N HCl. After 10 min at room temperature, the samples were centrifuged at 15,800 × g for 2 min at 4°C. The supernatant fluid was frozen in liquid nitrogen.
(ii) Isocitrate measurement.
For isocitrate measurements, we transformed stoichiometrically all the isocitrate of the extract into NADPH by using a commercial solution of IDH and an excess of NADP+. The reaction mixture consisted of 1.4 ml of neutral extract, 0.2 ml of 250 μM NADP+ (Na salt) and 0.2 ml of commercial IDH (1.28 U/ml; EC 1.1.1.42) from porcine heart. The reaction was initiated by the addition of the enzyme. After exactly 30 min at 21°C, we added 0.12 ml of 0.2 N NaOH to stop the reaction. That particular step had to be run in glass tubes because of the effect of NaOH on plastic ones. The tubes were then incubated at 60°C for 30 min to destroy the excess NADP+ and to keep only the NADPH in the solution. The solution was then brought back to its initial pH (i.e., 7.9), and because of the very high sensitivity of NADPH to acid, the following step was very critical. We found that, in the nanomolar concentration range, the addition of a strong acid caused the destruction of all the NADPH present in the solution. Consequently, the neutralization was done with 0.12 ml of 0.2 N CH3COOH. The choice of 7.9 as the initial pH was designed to preserve the integrity of the NADPH. Since it is known that IDH is active at pH 7.9 and that our biological buffer is effective at that pH, we decided to keep the pH of the assay slightly basic, which allowed us to preserve the NADPH in the solution and did not affect the NADP+ at room temperature. The neutralized samples were assayed for NADPH using an enzyme cycling system. Blanks consisted of neutral samples treated with 0.12 ml of 1 N HCl, incubated at 21°C for 10 min, and neutralized with 0.12 ml of 1 N NaOH to destroy the NADPH. Then, knowing the volume of the cellular fraction of the culture, the intracellular isocitrate concentrations were calculated. In the final concentration data sets, the negative values of intracellular isocitrate levels observed at the beginning and the end of both experiments were considered below the detection limit of the method. Each data point represents two or four analyses. The mean standard error was 11.9% (n = 20).
(iii) NADP+ measurement.
Samples were thawed, and a known volume of supernatant was neutralized with a 0.5 N NaOH solution. The neutral samples were directly assayed for NADP+ by using an enzyme cycling system. Blanks consisted of neutral samples treated with 0.12 ml of 1 N NaOH, incubated at 60°C for 15 min, and neutralized with 0.12 ml of 1 N HCl to destroy the NADP+. From the volume of the cellular fraction of the culture, the intracellular NADP+ concentrations were calculated. Each data point represents four analyses. The mean standard error was 1.7% (n + 22).
(iv) Enzyme cycling system.
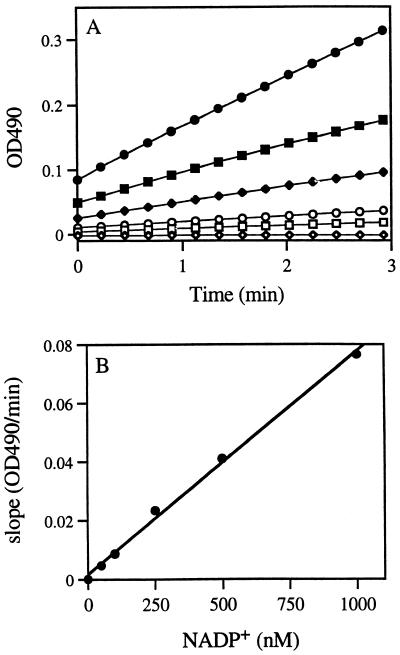
The enzymatic cycling system that we used was developed by Stephon et al. (43). The assay uses the enzymes glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.49) and diaphorase (EC 1.8.1.4) to cycle NADP+ between its oxidized and reduced forms in the presence of glucose-6-phosphate and p-iodonitrotetrazolium violet (INT). The following cycling reagents were prepared in 25 mM MOPS (pH 7.5) solution: (i) a 20 mM INT solution, (ii) a substrate solution consisting of 16 mM glucose-6-phosphate, 80 mM MgCl2, and 0.8% Triton X, and (iii) an enzyme solution containing diaphorase (88 μg/ml) and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (10 μg/ml) that was prepared on the day of use. The final assay mixture consisted of 0.7 ml of sample, 0.1 ml of substrate solution, and 0.1 ml of INT solution. The reaction was started by the addition of 0.1 ml of the enzyme solution. The assay was run in a 1-ml quartz cuvette at 21°C. The production of formazan was monitored spectrophotometrically at 490 nm for 3 min. The standard curve was constructed from measurements of the velocity of formazan formation by the enzyme cycling system starting with six different NADP+ concentrations, ranging from 0 to 1,000 nM (Fig. 1A). A curve of slopes versus NADP+ concentrations (Fig. 1B) was then used for the calculation of the NADP+ concentration in the samples. The mean standard error was 0.05%. Similarly, measurements of the velocity of formazan formation for six isocitrate concentrations, ranging from 0 to 2,000 nM, were used to construct a standard curve of slopes versus isocitrate concentrations (not shown). The mean standard error was 0.06%.
FIG. 1.
Calibration curve for NADP+ analyses. (A) Formazan formation time courses by the enzyme cycling reaction with starting NADP+ concentrations of 0 (◊), 50 (□), 100 (○), 250 (⧫), 500 (■), and 1000 (•) nM. (B) The standard curve was obtained by plotting the slopes of these velocity curves against the NADP+ concentrations. The regression equation was slope = 7.6 × 10−5 NADP+ + 1.6 × 10−3 (r2 = 1.0; n = 24), where slope was measured as change in OD490 per minute and NADP was measured in nanomoles.
Pyruvate measurements.
The pyruvate concentration in the culture medium was determined by using the enzyme lactate dehydrogenase (LDH; EC 1.1.1.27). We adapted a clinical method largely used in blood analysis (26) to fit our needs. In this method, LDH catalyzes the transformation of the pyruvate into lactate and uses NADH as a second substrate. The determination was done by measuring the absorbance at 339 nm (OD339) of the reaction mixture before and after the reaction. The difference between the two values is directly proportional to the pyruvate concentration in the sample. The assay was carried out in quartz cuvettes at 21°C. We mixed 0.7 ml of sample or standard solution and 0.1 ml of 1.1-mg/ml NADH. Then, a first reading of the OD339 was taken. Next, LDH (0.2 ml of an 8-U/ml solution) was added; 15 min later, a second reading of the OD339 was taken. The LDH solution was prepared daily, as were the pyruvate solutions. For the standard curve, a pyruvate-free culture medium was prepared and autoclaved. A 200 μM solution of pyruvate (Na salt) was then prepared in this culture medium. The standard curve ranged from 0 to 100 μM pyruvate. The assay was performed as described above. Plots of the variation of OD339 versus pyruvate were always linear, with r2 values of >0.99. Although the slope of the standard curve varied from day to day, the mean and standard deviation of eight determinations was 381.5 ± 112.8 OD339/μM. Each data point represents the mean of four analyses; the mean standard error was 3.7% (n = 33).
Protein measurement and calculation.
Protein in the bacterial pellet was analyzed by the Lowry method (27) as described by Berdalet et al. (2). The OD550 and protein were related by the regression equation protein (in milligrams liter−1) = 258.1(OD550) − 11.5 (n = 21). This relationship held for all culture phases with an r2 of 0.98. In the present study, the protein concentration in the cultures was determined by using this regression equation. Then, knowing the volume of the cellular fraction of the culture, the intracellular protein concentrations were calculated.
Kinetic constant determination. (i) Sample preparation.
Two different cultures were sampled in early stationary phase. Twenty microliters of culture was centrifuged at 10,000 × g for 15 min at 4°C. The supernatant fluid was decanted, and the pellets were resuspended in 40 ml of 25 mM MOPS (pH 7.5) containing lysozyme (162 μg/ml) (2). The samples were mixed well and frozen in liquid nitrogen. The thawed homogenates were kept on ice during the IDH assays. The IDH activity in the homogenates was stable at 0°C for 120 min.
(ii) Enzyme kinetics.
IDH assays were carried out as described by Berdalet et al. (2). The reaction was initiated by the addition of NADP+. Initial IDH activity was measured with six different concentrations of d-isocitrate and NADP+, leading to a six-by-six data matrix. The final NADP+ concentration in the assay ranged from 200 to 10 μM, and the final d-isocitrate concentration ranged from 200 to 20 μM. The assays for each set of concentrations were performed in triplicate. Initial velocities were evaluated from the slopes of the progress curves within the first 90 s of the reaction. Each data point represents the mean of three analyses. The mean standard error was 2.7% (n = 68).
(iii) Linearization of the data.
The data were linearized by the double-reciprocal transformation of Lineweaver and Burk (25). Primary plots (1/v versus 1/d-isocitrate) patterns were used to confirm the sequential reaction mechanism of IDH from P. nautica. The Km and dissociation constant for isocitrate were determine from the secondary plots of y intercepts and slopes against 1/NADP+ plots. The inversion of the data matrix allowed the determination of the dissociation constant for NADP+.
(iv) Nonlinear procedure.
It is known that without the appropriate weighting factor, double-reciprocal transformation may convert the lowest, most imprecise velocity measurements into the largest values and thereby give them the greatest weight. To overcome this problem, Km and dissociation constant values for NADP+ and isocitrate were also estimated by fitting each data set to the bisubstrate Michaelis-Menten model, by using an interative nonlinear least-squares method (Enzfitter; Biosoft, United Kingdom) (22). Following the notation of Cleland (7), the bisubstrate equation for a bi-bi mechanism is v = VAB/(KiaKb + KaB + KbA + AB), where A is the first binding substrate concentration, B is the second binding substrate concentration, v is the velocity, V is the maximum velocity, Kia is the apparent dissociation constant of the E · A binary complex (E · A ↔ E + A), and Ka and Kb are the Michaelis constants for A and B. The Kia values were obtained by considering alternatively NADP+ and isocitrate as the first binding substrate in the fitting procedure. Finally, when substrate inhibition patterns were observed in a data set, the outlier observations were ignored for Km estimation.
RESULTS
Time profiles.
In order to fulfil the deficiency of knowledge about intracellular substrate concentrations, time courses of intracellular isocitrate, NADP+, protein, and pyruvate in the bacterial cultures during three experiments were determined (Fig. 2 and 3).
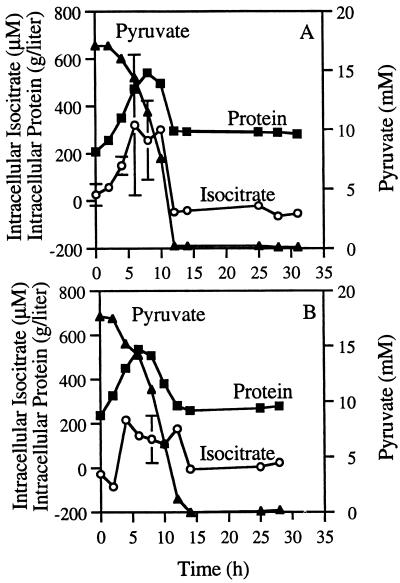
FIG. 2.
Replicates of 1-day time course experiments showing intracellular isocitrate concentration and concentrations of bacterial protein and pyruvate in the culture medium. The error bars on the isocitrate data points represent the standard deviation (A) or the range (B). When no bar is evident, the deviation is smaller than the size of the symbol. The standard deviation for all pyruvate data points is smaller than the size of the symbol.
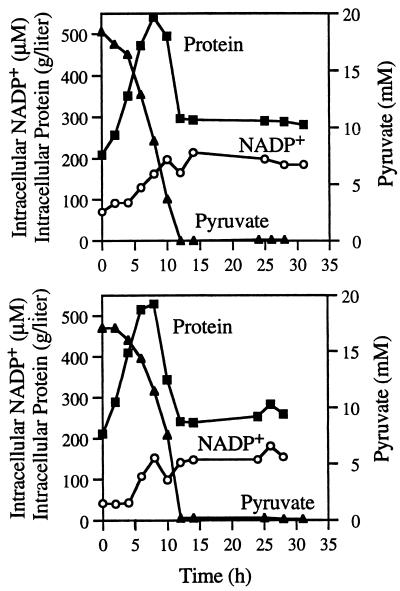
FIG. 3.
Replicates of 1-day time course experiments showing intracellular NADP+ concentration and concentrations of bacterial protein, and pyruvate in the culture medium. No error bars are shown for the NADP+ or pyruvate data points because the standard deviations for these and are always smaller than the size of the symbol.
(i) Pyruvate and protein.
Pyruvate and protein concentrations in the culture were used as indexes of the culture’s biomass. The pyruvate in the culture medium in the three experiments decreased from an average initial level of 17.7 mM to nearly 0 mM after 12 h. The intracellular protein concentration increased from ∼175 g/liter (based on cell volume) at the beginning of the experiment to a maximum of ∼450 g/liter during the exponential growth phase. Then, when approximately half the pyruvate was consumed, the protein level started to fall. When the pyruvate was exhausted, the protein reached a level of about 200 g/liter that stayed constant until the end of the experiment. These time courses described the growth phases of the cultures.
(ii) Intracellular isocitrate.
We expected the intracellular isocitrate concentration to be affected by the carbon source availability. Basic features of the isocitrate time course were identified in preliminary experiments but were quantified only in the two final experiments (Fig. 2). The features are characterized by low levels of intracellular isocitrate during the first 2 h of the experiment, by a rapid increase during the exponential growth phase, by a maximum concentration of about 300 μM (based on cell volume) which lasted as long as pyruvate was not depleted, and finally by low or undetectable levels after pyruvate became exhausted. Intracellular isocitrate exhaustion is clearly a characteristic of old cultures. These general features of the intracellular isocitrate time course tracked the intracellular protein time course throughout all phases of growth. The correlation was described by the following regression equation: isocitrate concentration = 1.07(protein concentration) − 203.5 (n = 17; r2 = 0.79). The intracellular isocitrate concentration was clearly affected by the exhaustion of pyruvate in the culture medium.
(iii) Intracellular NADP+.
NADP+ is a substrate of IDH that can also be involved in other intracellular enzyme reactions. The general features of the NADP+ and the isocitrate time courses were different. The intracellular NADP+ concentration increased from about 50 μM (based on cell volume) at the beginning of the exponential growth to about 200 μM at the end of the same growth phase (Fig. 3). After pyruvate exhaustion in the culture medium, the NADP+ concentration stayed constant until the end of the experiment. In exponential growth, the intracellular NADP+ concentration and the intracellular protein concentration increased in parallel but were poorly correlated. Then, in late exponential and early stationary phase, the intracellular NADP+ concentration stayed high while the intracellular protein concentration diminished. Nevertheless, the intracellular NADP+ concentration and the pyruvate concentration were related by the following polynomial equation: NADP+ concentration = −0.78(pyruvate concentration)2 + 6.98(pyruvate concentration) + 171.0 (n = 21). This relationship held for all growth phases, with an r2 of 0.84. The intracellular NADP+ concentration did not decrease when the pyruvate became exhausted in the culture.
Kinetic studies. (i) Lineweaver-Burk plot.
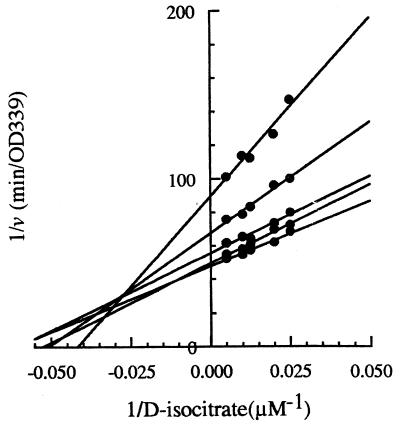
To determine the kinetic constants, Kiso, KNADP+, and the Kia values, Lineweaver-Burk plots were first constructed. These double-reciprocal plots of 1/v versus 1/d-isocitrate at various fixed NADP+ concentrations gave a family of straight lines of different slopes and intercepts which intersected at a common point in the second quadrant of the diagram (Fig. 4). In two independent experiments, values of the Michaelis constants for NADP+ and for d-isocitrate were calculated (Table 1). These were obtained by plotting the Y intercepts of the plots for 1/v versus 1/d-isocitrate and 1/v versus 1/NADP+ against those for 1/NADP+ or 1/d-isocitrate, respectively (not shown). KNADP+ values determined from two experiments were not significantly different (P < 0.01), but the determinations of Kiso (Table 1) gave two significantly different values (P < 0.01). The apparent dissociation constants (Kia) were also determined for both enzyme-substrate complexes (Table 1). These are single values and were obtained by plotting the slopes of the plots for 1/v versus 1/d-isocitrate and 1/v versus 1/NADP+ against 1/NADP+ or 1/d-isocitrate, respectively (not shown).
FIG. 4.
Bisubstrate kinetic initial rate studies for the determination of kinetic constants. NADP+ levels are 10, 25, 50, 100, and 200 μM. The slope of each line is defined by (Kiso + KiaKNADP+/NADP+)/V. Each intercept is defined by (1 + KNADP+/NADP+)/V. Each x intersect is equal to −1/Kia.
TABLE 1.
Kinetic constants of NADP-IDH from P. nautica
| Procedurea | Experimentb |
Km (μM) for:
|
Kia (μM) for:
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NADP+ | d-Isocitrate | NADP+c | d-Isocitrated | ||
| Lineweaver-Burk | PnPy1504 | 24.0 ± 1.5 (2)e | 15.2 ± 0.3 (2) | 62.4 (1) | 32.0 (1) |
| PnPy1801 | 24.7 ± 5.7 (2) | 6.3 ± 0.9 (2) | 24.3 (1) | 7.7 (1) | |
| Enzfitter | PnPy1504 | 25.0 ± 2.2 (10) | 14.7 ± 0.8 (10) | 55.0 ± 4.9 (5) | 29.3 ± 6.6 (5) |
| PnPy1801 | 27.3 ± 5.4 (16) | 6.6 ± 1.4 (16) | 41.5 ± 12.2 (9) | 13.6 ± 16.3 (7) | |
Kinetic constants were determined by the graphical Lineweaver-Burk method and by a nonlinear regression data analysis program (Enzfitter).
Determinations were done on homogenates from two exponentially growing cultures of P. nautica on pyruvate.
Dissociation constants determined when considering NADP+ as the first binding substrate.
Dissociation constants determined when considering d-isocitrate as the first binding substrate.
Numbers in parentheses represent the number of data used to calculate the average values. Data shown are average ± range for an n of 2 and average ± standard deviation for an n of ≥5.
(ii) Nonlinear procedure.
Since the accuracy of kinetic constant determination may depend on the data distribution and the error of the measurements, kinetic constants were also determined by a nonlinear least-squares procedure (Table 1). Estimated values of KNADP+ for two separate cultures were not significantly different (P < 0.01), but the Kiso values were different (P < 0.01). The apparent dissociation constant of the IDH-NADP+ complex (Table 1) was significantly higher (P < 0.01) than KNADP+. However, the apparent dissociation constant of the IDH-isocitrate complex was significantly higher (P < 0.01) than the Kiso of the PnPy1801 experiment whereas it was not significantly higher (P < 0.01) than the Kiso of the PnPy1504 experiment.
DISCUSSION
Time courses of intracellular intermediary metabolites throughout the different growth phases of a bacterial culture are rare, and to our knowledge this is the first determination of intracellular isocitrate and NADP+ concentrations over all growth phases of a bacterial culture.
Time profiles of intracellular isocitrate, NADP+, and protein concentrations.
Reports of intracellular isocitrate concentrations in acetate-grown cultures of Escherichia coli (14, 15) revealed constant concentrations of about 600 μM (based on cell volume) during the exponential growth phase when acetate was plentiful. In our experiments, we found that, when P. nautica was grown on pyruvate, the intracellular pool of isocitrate increased rapidly to ∼300 μM (based on cell volume) and stayed constant as long as the culture was C sufficient (Fig. 2). The discrepancy between our maximum isocitrate concentrations and the reported ones may have been due to strain differences but also to the different metabolic pathways involved in acetate and pyruvate utilization. In fact, it has been demonstrated that during growth on acetate, carbon flow through the glyoxylate bypass is facilitated by maintenance of a high intracellular level of isocitrate (32). On the other hand, pyruvate is known to activate IDH phosphatase, the enzyme responsible for the activation of IDH (16, 17), and a high IDH activity affects the distribution of the carbon flow through the glyoxylate bypass and the Krebs cycle. Furthermore, it contributes to maintaining a lower intracellular isocitrate concentration in pyruvate-growing cells than in acetate-growing ones.
Nowhere in the literature can we find time course analyses of intracellular isocitrate during the transition from exponential to stationary growth phase in bacterial cultures. Our time course observations covered all bacterial growth phases. The low intracellular isocitrate concentration found in the first 2 h of our experiments could be explained as a metabolic adjustment of cells from a poor environment being freshly inoculated into a rich one (Fig. 2) (28). The different lag phases observed in our cultures probably reflect the age of the mother cultures that were used for the inoculations.
During exponential growth, our P. nautica cultures accumulated high concentrations of isocitrate and intracellular protein (Fig. 2). In a similar fashion, the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum accumulated intracellular nitrate and protein when growing exponentially in an N-sufficient batch culture (12). The internal nitrate in the diatom persisted until the external nitrogen supply (NO3, NO2, and NH4) was depleted. Our P. nautica cultures were supplied with enough carbon (60 mM [based on culture volume]) to saturate the internal isocitrate pool during exponential growth, but when pyruvate became exhausted, the intracellular isocitrate level and the intracellular protein concentration decreased precipitously. In a previous study of P. nautica growing on pyruvate, a similar diminution of the respiratory CO2 production rate (RCO2) during pyruvate exhaustion was observed (34). These results confirm that intracellular isocitrate concentration is affected by the availability of carbon and may play a major role in the control of RCO2.
Prior to this investigation, the intracellular NADP+ concentration in P. nautica was predicted to fall as the carbon source was depleted (34). The observed time courses of intracellular NADP+ concentration showing high levels of NADP+ in senescence (Fig. 3) refute this prediction. In a subsequent study of the activity of the respiratory electron transfer system (ETS) in P. nautica, a similar fall in the concentrations of NADPH and NADH was predicted (35). Since in a C-sufficient bacterial culture NADP+ is used and NADPH is produced (via the Krebs cycle) (23, 28), it is unlikely that the concentrations of both NADP+ and NADPH would fall as the culture passed from exponential growth to senescence. These two concentrations would, however, fall if the combined pool of the oxidized and reduced forms of NAD fell or if IDH and ETS were separated in different compartments of the bacterial cell. In view of the decreasing availability of the Krebs cycle intermediates during a depletion of the external carbon source, it is more likely that the time courses of the two pyridine nucleotides are the inverse (mirror image) of each other, with NADP+ increasing and NADPH decreasing in a bacterial culture.
Respiratory enzyme activities (IDH and ETS) have been shown to increase during the exponential growth phase and to plateau at the end of this phase in marine bacterial cultures grown on different carbon sources (2, 34, 35, 40). During C starvation, these enzymes were not cannibalized to fill other needs of the cells. They were kept metabolically active but in alert status (34). In our experiments, the NADP+ time profiles followed the pattern of the respiratory enzyme activities throughout all bacterial growth phases. NADP+ was not degraded during C depletion, indicating that it remained available for metabolism and primed for substrate availability. The high intracellular NADP+ concentration in the stationary phase argued for the constitutivity of NADP+ in P. nautica, even if intracellular protein concentration and intracellular NADP+ concentration were not related throughout all phases of the bacterial cultures. Thus, these observations reveal that the intracellular NADP+ concentration is not affected by C starvation conditions. They also suggest that NADP+ is not limiting for the IDH reaction during the stationary phase and plays a limited role in the control of RCO2 in P. nautica.
Michaelis-Menten and dissociation constants.
The simplicity of the single-substrate Michaelis-Menten equation facilitates the estimation of the Km values for every substrate of an enzyme, but it cannot be used to determine the dissociation constant, Kia. This explains why bisubstrate enzyme kinetic studies and Kia determinations are rare in the literature. Our bisubstrate Km estimations of IDH from P. nautica ranged from 25 to 27 μM for NADP+ and from 6.6 to 15 μM for isocitrate. These values fall in the range of Km values determined by simple or bisubstrate Michaelis-Menten kinetics in other bacteria that varied from 6.0 to 54 μM for NADP+ and from 3.3 to 74 μM for isocitrate (Table 2) (6). In spite of the fact that the Kiso values in the two cultures were significantly different, they were always lower than the KNADP+ values. This observation suggests that IDH from P. nautica has a higher affinity for isocitrate than for NADP+ and confirms that the isocitrate concentration is most likely to control the IDH reaction rate.
TABLE 2.
Bacterial NADP-IDH Michaelis-Menten constants based on single-substrate and bisubstrate reaction equations
| Bacterial strain |
Km (μM) for:
|
Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|
| NADP+ | Isocitrate | ||
| Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120 | 9.3 | 4.2 | 30 |
| Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803 | 6.0 | 5.7 | 31 |
| Rhodomicrobium vannielii | 2.5 | 3.3 | 24 |
| Thermoleophilum minutum YS-4 | 48 | 33 | 33 |
| Thermus thermophilus HB8 | 6.3 | 8.8 | 13 |
| Mycobacterium phlei | 53 | 74 | 19 |
| Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides | 7.0 | 8.7 | 5 |
| Bacillus subtilis | 27 | 9.1 | 37 |
| Escherichia coli | 37 | 16 | 38 |
| Acinetobacter sp. | 54 | 26 | 41 |
| Azotobacter vinelandii | 20 | 17 | 44 |
| Azotobacter vinelandii | 18 | 36 | 1 |
| Escherichia coli S113 | 17 | 11 | 11a |
| Pseudomonas nautica | 25–27 | 6.6–15 | This studya |
In these studies, the kinetic constants determinations were based on a bisubstrate enzyme reaction equation.
It is well known that, for a sequential mechanism, the primary reciprocal plots may intersect above, on, or below the horizontal axis, depending on the magnitude of the ratio Kia/Ka (18). In fact, when Kia is higher than Ka, the reciprocal plots intersect in the second quadrant above the horizontal axis. If we consider isocitrate as the substrate A, Kia becomes Kiiso and KA becomes Kiso. Then, in our two experiments, we find that Kiiso is always higher than Kiso (Table 1) and that the ratio Kiiso/Kiso varies from 2.0 to 2.1. On the other hand, if we consider NADP+ as the substrate A, Kia becomes KiNADP+ and KA becomes KNADP+. Similarly, we find that KiNADP+ is always higher than KNADP+ (Table 1) and that the ratio KiNADP+/KNADP+ varies from 1.5 to 2.2. These findings are consistent with the fact that the intersection points of the family of 1/v versus 1/d-isocitrate plots presented in Fig. 4 and 1/v versus 1/NADP+ plots (not shown) are always above the horizontal axis.
Kinetic reaction mechanism.
A major concern in the construction of an enzyme kinetics-based model of RCO2 is the choice of the correct equation for the IDH reaction. Studies of the kinetic mechanism of the bacterial NADP+-IDH have proposed a sequential reaction mechanism involving the random or ordered addition of substrates (5, 11, 44). Accordingly, a sequential reaction mechanism was chosen as the basis of the IDH model of RCO2 (34). The sequential nature of the IDH reaction becomes obvious from the family of lines of different slopes and intercepts presented in Fig. 4. This plot does not allow us to differentiate between the random and the compulsory mechanism but it does allow us to conclude that the IDH reaction is sequential and that the equation used to build the enzyme kinetics-based model of RCO2 in P. nautica was appropriate (34).
It is known that, at high concentrations, substrates may often act as dead-end inhibitors of the enzymatic reaction in which they are involved (8) and form an abortive binary complex with the enzyme. In an ordered mechanism, one of the binary complexes, E · A or E · B, is expected to be abortive. In our initial rate study, NADP+ caused a detectable substrate inhibition at concentrations higher than 200 μM when isocitrate concentrations were lower than 40 μM (not shown). This inhibition pattern could be explained by the formation of an abortive binary complex between IDH and NADP+ (E · NADP+) under these conditions. As a result, a sequential ordered mechanism with isocitrate binding first most likely defines the reaction mechanism of IDH from P. nautica. This hypothesis still needs to be verified with a substrate analogue and by product inhibition studies, and until this is done, it is important to report both dissociation constants that are given in Table 1. Nevertheless, the finding that Kiso is always higher than KNADP+ is more consistent with an ordered than with a random reaction mechanism and supports the hypothesis.
Comparison of linear and nonlinear procedures.
The selection of a fitting method should be based on the data distribution, the level of error, and the variability or constancy of error (3). The distribution of our data is such that all data points are higher than the Km and fall in the low and constant error category described by Berges et al. (3). The comparison of our Km determinations using the Lineweaver-Burk and a nonlinear method of the type of Cleland-Wilkinson confirms the observations of Berges et al. (3). Both methods gave identical results. Nevertheless, we observed a high sensitivity of the nonlinear method to initial parameter estimates. This problem was raised before (3) and still needs to be addressed.
Conclusion.
This study presents the first determination of intracellular isocitrate and NADP+ concentrations over all growth phases of a bacterial culture. The results demonstrate that the time course of intracellular isocitrate concentration in P. nautica is affected by the availability of carbon in the culture whereas the time course of the intracellular NADP+ concentration is not. They also suggest that isocitrate plays a major role in the control of RCO2. The high intracellular NADP+ concentration in stationary phase argues for the constitutivity of NADP+ in P. nautica and suggests that NADP+ plays a limited role in the control of RCO2. The Lineweaver-Burk primary plots presented here clearly establish the sequential nature of the reaction mechanism of IDH from P. nautica, but the order of binding of the substrates has not been determined. Finally, the low Kiso values observed suggest a higher affinity of IDH for isocitrate than for NADP+, confirming that the isocitrate concentration is most likely to control the IDH reaction rate.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by the Department of Fisheries and Ocean of Canada.
We thank L. St-Amand for her support and encouragement, R. Gagnon for his technical assistance, M. Fournier and Y. Morin for use of their flow cytometer, and M. Denis for valuable comments.
REFERENCES
- 1.Barrera C R, Jurtshuk P. Characterization of the highly active isocitrate (NADP+) dehydrogenase of Azotobacter vinelandii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970;220:416–429. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90273-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Berdalet E, Packard T T, Lagacé B, Roy S, St-Amand L, Gagné J-P. CO2 production, O2 consumption, isocitrate dehydrogenase and electron transport system activities in the marine bacterium Pseudomonas nautica. Aquat Microb Ecol. 1995;9:211–217. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Berges J A, Montagnes D J S, Hurd C L, Harrison P J. Fitting ecological and physiological data to rectangular hyperbolae: a comparison of methods using Monte Carlo simulations. Mar Ecol Prog Ser. 1994;114:175–183. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bonin P, Gilewicz M, Bertrand J C. Denitrification by a marine bacterium Pseudomonas nautica strain 617. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1987;138:371–383. doi: 10.1016/0769-2609(87)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Budzygon B E, Braginski J E, Chung A E. Isocitrate dehydrogenase from Rhodopseudomonas spheroides: kinetic mechanism and further characterization. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973;159:400–408. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Chen R-D, Gadal P. Structure, functions and regulation of NAD and NADP dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase in higher plants and in other organisms. Plant Physiol Biochem. 1990;28:411–427. [Google Scholar]
- 7.Cleland W W. The kinetics of enzyme-catalyzed reactions with two or more substrates or products. I. Nomenclature and rate equations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963;67:104–137. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91800-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cleland W W. Steady state kinetics. In: Boyer P D, editor. The enzymes. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1970. pp. 1–65. [Google Scholar]
- 9.Copeland R A. A practical introduction to structure, mechanisms, and data analysis. New York, N.Y: VCH Publishers Inc.; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Cornish-Bowden A, Wharton C W. Enzyme kinetics. Washington, D.C: IRL Press; 1988. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dean A M, Koshland D E J. Kinetic mechanism of Escherichia coli isocitrate dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1993;32:9302–9309. doi: 10.1021/bi00087a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11a.Denis, M. (University of Aix-Marseille II). Personal communication.
- 12.Dortch Q. Effect of growth conditions on accumulation of internal nitrate, ammonium, amino acids, and protein in three marine diatoms. J Exp Mar Biol Ecol. 1982;61:243–264. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Eguchi H, Wakagi T, Oshima T. A highly stable NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase from Thermus thermophilus HB8: purification and general properties. Biochem Biophys Acta. 1989;990:133–137. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(89)80024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.El-Mansi E M T, Nimmo H G, Holms W H. The role of isocitrate in control of the phosphorylation of isocitrate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli ML308. FEBS Lett. 1985;183:251–255. [Google Scholar]
- 15.El-Mansi E M T, Nimmo H G, Holms W H. Pyruvate metabolism and the phosphorylation state of isocitrate dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. J Gen Microbiol. 1986;132:797–806. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-3-797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Gálvez S, Gadal P. On the function of the NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase isoenzymes in living organisms. Plant Sci. 1995;105:1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Holms W H. The central metabolic pathways of Escherichia coli: relationship between flux and control at a branch point, efficiency of conversion to biomass, and excretion of acetate. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1986;28:69–105. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152828-7.50004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kuby S A. A study of enzymes. I. Enzyme catalysis, kinetics, and substrate binding. Boston, Mass: CRC Press Inc.; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kuldeep R, Dhariwal R, Venkitasubramanian T A. NADP-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase of Mycobacterium phlei ATCC 354. J Gen Microbiol. 1987;133:2457–2460. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-9-2457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.LaPorte D C, Koshland D E J. A protein with kinase and phosphatase activities involved in regulation of tricarboxylic acid cycle. Nature. 1982;300:458–460. doi: 10.1038/300458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.LaPorte D C, Thorness P E, Koshland J D E. Compensatory phosphorylation of isocitrate dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:10563–10568. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Leatherbarrow R J. Use of nonlinear regression to analyze enzyme kinetic data: application to situations of substrate contamination and background subtraction. Anal Biochem. 1990;184:274–278. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90680-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lehninger A L, Nelson D L, Cox M M. Principles of biochemistry. New York, N.Y: Worth Publishers; 1993. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Leyland M L, Kelly D J. Purification and characterization of a monomeric isocitrate dehydrogenase with dual coenzyme specificity from the photosynthetic bacterium Rhodomicrobium vannielli. Eur J Biochem. 1991;202:85–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lineweaver H, Burk D. The determination of enzyme dissociation constants. J Am Chem Soc. 1934;56:658–666. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lowry O H, Passonneau J V. A flexible system of enzymatic analysis. New York, N.Y: Academic Press; 1972. [Google Scholar]
- 27.Lowry O H, Rosebrough N J, Farr A L, Randall R J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mandelstam J, McQuillen K, Dawes I. Biochemistry of bacterial growth. London, United Kingdom: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1982. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mathews C K, van Holde K E. Biochemistry. Redwood City, Calif: The Benjamin/Cummings Publishing Company; 1990. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Muro-Pastor M I, Florencio F J. Purification and properties of NADP-isocitrate dehydrogenase from the unicellular cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Eur J Biochem. 1992;203:99–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb19833.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Muro-Pastor M I, Florencio F J. NADP+-isocitrate dehydrogenase from the cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. strain PCC 1720: purification and characterization of the enzyme and cloning, sequencing, and disruption of the icd gene. J Bacteriol. 1994;176:2718–2726. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.9.2718-2726.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nimmo G A, Nimmo H G. The regulatory properties of isocitrate dehydrogenase kinase and isocitrate dehydrogenase phosphatase from Escherichia coli and the roles of these activities in the control of isocitrate dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1984;141:409–414. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08206.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Novotny J F, Perry J J. Characterization of a heat-stable NADP-dependent isocitrate dehydrogenase from the obligate thermophile Thermoleophilum minutum YS-4. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1991;35:461–465. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Packard T, Berdalet E, Blasco D, Roy S O, St-Amand L, Lagacé B, Lee K, Gagné J-P. CO2 production predicted from isocitrate dehydrogenase activity and bisubstrate enzyme kinetics in the marine bacterium Pseudomonas nautica. Aquat Microb Ecol. 1996;11:11–19. [Google Scholar]
- 35.Packard T T, Berdalet E, Blasco D, Roy S O, St.-Amand L, Lagacé B, Lee K, Gagné J-P. Oxygen consumption in the marine bacterium, Pseudomonas nautica predicted from ETS activity and bisubstrate enzyme kinetics. J Plankton Res. 1996;18:1819–1835. [Google Scholar]
- 36.Palmer T. Understanding enzymes. New York, N.Y: Ellis Horwood Limited; 1991. [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ramaley R F, Hudock M O. Purification and properties of isocitrate dehydrogenase (NADP) from Thermus aquaticus YT-1, Bacillus subtilis-168 and Chlamidomonas reinhardtii-Y-2. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973;315:22–36. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90125-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Reeves H C, Daumy G O, Lin C C, Houston M. NADP+-specific isocitrate dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972;258:27–39. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90964-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ricard J. Cinétique et mécanismes d’action des enzymes. Paris, France: Doin Éditeurs; 1973. [Google Scholar]
- 40.Roy, S. O., T. T. Packard, E. Berdalet, and L. St-Amand. The impact of acetate, pyruvate, and physiological state on the respiration and RQ in Pseudomonas nautica. Aquat. Microb. Ecol., in press.
- 41.Self C H, Weitzman P D J. The isocitrate dehydrogenases of Acinetobacter lwoffi. Separation and properties of two nicotinamide-adenine dinucleotide phosphate-linked isoenzymes. Biochem J. 1972;130:211–219. doi: 10.1042/bj1300211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sherr B F, Sherr E B, Fallon R D. Use of monodispersed, fluorescently labeled bacteria to estimate in situ protozoan bacterivory. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987;53:958–965. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.958-965.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Stephon R L, Niedbala R S, Schray K J, Heindel N D. An enzymatic cycling procedure for β-NADP+ generated by 3′-phosphodiesterase, 2′:3′-cyclic nucleotide. Anal Biochem. 1992;202:6–9. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(92)90197-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Wicken J S, Chung A E, Franzen J S. Isocitrate dehydrogenase from Azotobacter vinelandii. Order of substrate addition and product release. Biochem. 1972;11:4766–4788. doi: 10.1021/bi00775a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]