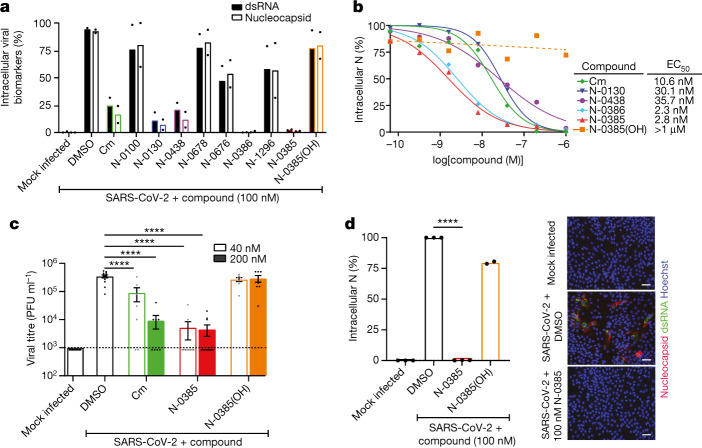
Fig. 2. Peptidomimetics active against TMPRSS2 are potent low nanomolar inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 in a human lung epithelial cell line and in human colonoids.
a, Calu-3 cells were pretreated with 100 nM of the indicated compounds followed by SARS-CoV-2 (VIDO) infection (multiplicity of infection (MOI) = 2)). Intracellular infection levels were evaluated by high-content screening of cell nuclei, dsRNA and nucleocapsid and then quantified relative to DMSO-treated cells (n = 2 independent experiments). b, Dose–response curves were generated for the lead antiviral peptidomimetic compounds in Calu-3 cells using nucleocapsid (N) staining of cells that were pretreated with the indicated compounds before infection (Cm, n = 5; N-0130, n = 5; N-0438, n = 3; N-0386, n = 4; N-0385, n = 8; N-0385(OH), n = 5). c, Plaque assays were performed using two of the experimental conditions evaluated in the dose–response analysis (40 nM and 200 nM) to determine the viral titres (amount of infectious virus) produced in cells that were pretreated with the indicated compounds before infection (n = 3 independent experiments); dotted line represents limit of detection. d, Colonoids were pretreated with 100 nM of the indicated compounds and infected with SARS-CoV-2 (MOI ≈ 1). Intracellular infection was relatively quantified using N staining. (N-0385, n = 3; N-0385(OH), n = 2). Representative fluorescent images of colonoids subjected to the indicated treatments are shown (Hoechst in blue, nucleocapsid in red and dsRNA in green). Scale bars, 50 μm. One-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction was used to determine significance in c, d; **** indicates modified P < 0.0001. Error bars, s.e.m.