Abstract
Criteria for treatment-resistant depression (TRD) and partially responsive depression (PRD) as subtypes of major depressive disorder (MDD) are not unequivocally defined. In the present document we used a Delphi-method-based consensus approach to define TRD and PRD and to serve as operational criteria for future clinical studies, especially if conducted for regulatory purposes. We reviewed the literature and brought together a group of international experts (including clinicians, academics, researchers, employees of pharmaceutical companies, regulatory bodies representatives, and one person with lived experience) to evaluate the state-of-the-art and main controversies regarding the current classification. We then provided recommendations on how to design clinical trials, and on how to guide research in unmet needs and knowledge gaps. This report will feed into one of the main objectives of the EUropean Patient-cEntric clinicAl tRial pLatforms, Innovative Medicines Initiative (EU-PEARL, IMI) MDD project, to design a protocol for platform trials of new medications for TRD/PRD.
Subject terms: Diagnostic markers, Depression
Introduction
Many medications have proven efficacy in major depressive disorder (MDD) [1, 2], but frequently and even with multiple medication exposures, they fail to improve MDD symptoms [3–7]; one third of individuals do not achieve full symptomatic remission [3], and even fewer meet criteria for both symptomatic and functional remission [8]. In individuals with ineffective initial treatments, even if subsequent treatments are effective, there is a very high relapse rate while continuing the treatment; for example, in the STAR*D trial, individuals who required more treatment steps had higher relapse rates (up to 71% after the fourth step) [3].
‘Incomplete response’ is not an all-or-nothing phenomenon, but rather a continuum that ranges from partially responsive depression (PRD), to treatment-resistant depression (TRD), to ‘multi-therapy-resistant MDD (MTR-MDD)’ [9], to ‘refractory depression’, which implies an absence of response to all currently available treatments. Unfortunately, there is a lack of consensus definitions around concepts such as PRD, TRD, and ‘adequate’ treatments [10–13]. Moreover, guidelines on how to treat TRD/PRD, such as pharmacological augmentation, are not consistent [14], and evidence on effectiveness is sparse [15]. This complicates the generalizability of results from research settings to the real-world, and hinders progress in this field, as there is no uniform population for clinical and biological investigations in TRD/PRD, including clinical trials for new or repurposed medications. Importantly, regulators acknowledge that response, partial response, and non-response exist on a continuum without universally accepted definitions, but nevertheless distinguish between these conditions; indeed, treatments for TRD and PRD already have accepted regulatory paths for drug approval.
Interestingly, a recent consensus statement (including experts also participating in the present report) suggested that the terms PRD and TRD are semantically and operationally not ideal, and proposed the broader concepts of ‘difficult-to-treat depression (DTD)’ or ‘suspected DTD’ [7], described as “depression that continues to cause significant burden despite usual treatment efforts”. This concept overlaps with PRD and TRD, but introduces a more flexible, multidimensional and longitudinal definition. The authors themselves acknowledged that “what constitutes significant burden” is “subjective and likely to vary between patients”, thus implicitly involving the patient’s point of view, and also likely to vary among clinicians and raters. Indeed, the authors cautioned that this definition may not be specific and objective enough to define clinical populations for regulatory clinical trials. In a subsequent follow-up paper, they also emphasised this as a ‘model of care’ that might be useful for both individuals with MDD and clinicians, especially in averting the development of ‘therapeutic nihilism’ [16].
In this document, we use a Delphi-method-based consensus approach to define TRD and PRD and to deliver operational criteria for future clinical studies, including clinical trials conducted for regulatory purposes. We have reviewed the relevant literature and brought together a group of international experts (including clinicians, academics, researchers, employees of pharmaceutical companies, regulatory bodies representatives, and one person with lived experience (PWLE)) to discuss the current state-of-the-art and the main controversies regarding the current classification. Our specific aims are to: (1) deliver TRD/PRD definitions that could be used at a person-centred level using information that is currently routinely collected in clinical practice; (2) recommend measures and instruments that should be included in future investigations and clinical trials for TRD/PRD; and (3) indicate which are the important areas that require further research. We provide consensus recommendations and the level of agreement for each recommendation, and discuss their limitations. We balance the need of clinicians and scientists with those of regulatory authorities, and describe differences when indicated.
This initiative is part of the EU Patient-cEntric clinicAl tRial pLatforms (EU-PEARL) programme, a public-private strategic partnership funded by the Innovative Medicines Initiative (IMI) to conceptualize and lead the design of an integrated research platform (IRP), that is, an infrastructure which allows the planning and completion of platform trials (see Appendix for further information).
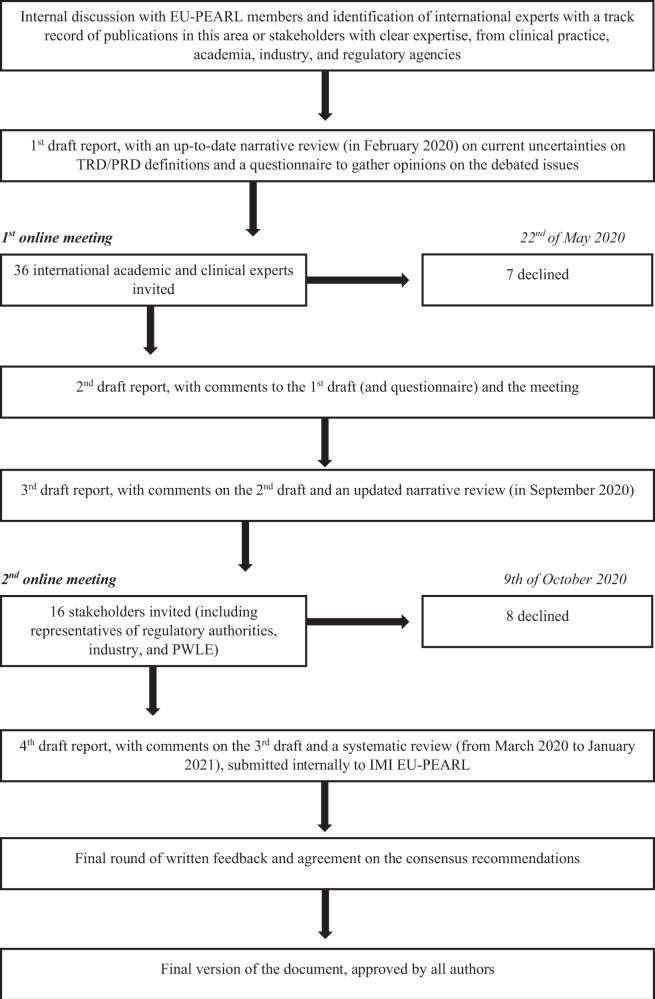
Our Delphi-method-based approach
The Delphi approach is a method of choice for developing guidelines in health research [17]. Indeed, a recent commentary to the aforementioned paper on DTD [7] specifically recommends using a Delphi approach for consensus statement in depression [18]. However, this method could be difficult to standardize, with poor reporting of findings [19, 20]. Probably the most important of these issues has been identified in the definition of consensus [21]. Therefore, we clearly defined consensus as a percentage of agreement (vs. disagreement) on a precise recommendation, and further defined strong consensus when this percentage was equal or above 95%, moderate consensus between 61 and 94%, and weak consensus between 51 and 60%. Details of our Delphi process are available in the Appendix and summarized in Fig. 1. Briefly, it consisted of: (1) identification of experts with a track record of publications in this area or stakeholders with clear expertise, from clinical practice, academia, industry, and regulatory agencies; (2) first draft report, with an up-to-date narrative review on TRD/PRD definitions (in February 2020) and a questionnaire to gather opinions on the debated issues; (3) an online consensus meeting with academics and clinicians, on the 22nd of May 2020; (4) second draft report, integrating comments to the first draft with those from the meeting, and again circulated to all contributors; (5) third draft report (with an updated narrative review, in September 2020), circulated to a different group of stakeholders, including representatives of regulatory authorities, industry, and one PWLE; (6) an online consensus meeting with stakeholders, on the 9th of October 2020, with additional stakeholders providing written feedback; (7) fourth draft report (with a systematic review of the literature published from March 2020 to January 2021), integrating stakeholders comments, which was then circulated and approved by all authors, and submitted in its entirety (approximately 28,000 words) internally to IMI EU-PEARL (available from the corresponding author on request); (8) editing of the report into this shorter version for publication, again circulated and approved by all authors. Comments to the different versions of the report were always anonymized. Methodological details of the narrative reviews and of the subsequent systematic review are presented in the Appendix.
Fig. 1. Delphi process flow diagram.
Schematic representation of the different phases of the Delphi-method-based process.
We provide a number of recommendations, each based on the view supported by the largest number of the experts, while highlighting areas of uncertainty and defining the ‘level of consensus’ on each recommendation: ‘strong’, indicating the top one-third of recommendations that had unanimous or almost unanimous (≥95%) agreement; ‘moderate’, indicating almost all the remaining two-thirds of recommendations, which had a substantial majority (61–94%); and ‘weak’, indicating the one recommendation that only reached the minimum consensus of 51%. We have summarised all the recommendations in Table 1 and Fig. 2. We suggest that: (1) recommendations with strong consensus should be immediately adopted; (2) recommendations with a moderate consensus could provide a working model for immediate implementation, but should be further confirmed by future research/discussion; and (3) recommendations with a weak consensus represent an area of uncertainty and thus require further research/discussion.
Table 1.
Main consensus recommendations on TRD/PRD regulatory clinical trials.
| Level of consensus– Strong | % of agreement | |
| Recommendations which can be implemented within current practice | ||
| TRD and PRD definitions | ||
| 1 | A definition of TRD for clinical trials conducted for regulatory purposes is necessary. | 98% |
| Previous antidepressant treatments | ||
| 3 | TRD should be defined after a minimum of two failed treatments with <25% of improvement with adequate dosing and duration. | 96% |
| Type of medications | ||
| 10 | Discontinuation of treatment before the completion of the fourth week, without clear evidence of lack of response, should not be considered as a treatment failure for the purpose of establishing TRD/PRD. | 96% |
| Exclusion from TRD/PRD studies | ||
| 12 | A previous structured psychotherapy failing to improve MDD symptoms is not an exclusion criterion. | 100% |
| Clinical presentation | ||
| 15 | All specifiers of depression (melancholic, atypical, anxious, psychotic, mixed) should be considered within the TRD/PRD definition, except for bipolar depression. | 95% |
| Recommendations which can be implemented in future research | ||
| 21 | Future research should recognize and target different clinical phenotypes of TRD (and PRD) underpinned by a specific biological mechanism. | 100% |
| 22 | For future research, diagnostic and history-taking instruments should be implemented in clinical cohorts and electronic health records, to allow a reliable, comprehensive, and multidimensional evaluation of people with lived experience (PWLE). | 100% |
| 24 | Preferences, perspectives, and reported outcomes of PWLE should be included in future TRD (and PRD) diagnostic tools and outcome measures. | 100% |
| Level of consensus – Moderate | ||
| Recommendations which can be implemented within current practice | ||
| TRD and PRD definitions | ||
| 2 | It is important to distinguish between TRD and PRD for randomized clinical trials for new treatments. | 85% |
| Previous antidepressant treatments | ||
| 4 | PRD can be defined even after a single treatment (improvement 25 to <50%) with adequate dosing and duration. | 76% |
| 6 | It is possible to assess ineffective past/current antidepressant treatment attempts, but only if properly documented, that is, based not only on subjective recollection or standardised instruments to assess psychiatric history and previous treatments (see below), but also on clinical documentation. | 75% |
| Type of medications | ||
| 7 | To define TRD, the two antidepressant treatment failures should consist of two established (licensed) medications for MDD of different mechanisms of action. | 75% |
| 8 | A failed course of psychotherapy should not be included as one of the previous treatments required for the definition of TRD/PRD. | 78% |
| 9 | The criteria of ‘adequate dose and duration’ is the minimal effective dosage, that is, the minimal approved dosage, administered for at least four weeks. | 74% |
| Exclusion from TRD/PRD studies | ||
| 11 | Multiple-drug resistant individuals, and individuals in whom augmentation strategies failed to improve/eliminate MDD symptoms should not be excluded from TRD/PRD studies. | 93% |
| 13 | Individuals with MDD in whom deep brain stimulation (DBS) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) failed to improve/eliminate MDD symptoms should be excluded from TRD/PRD clinical studies. | 62% |
| 14 | Individuals with MDD in whom other non-continuous/non-invasive brain stimulation interventions, such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), failed to improve/eliminate MDD symptoms should not be excluded. | 88% |
| Clinical presentation | ||
| 16 | Comorbid personality disorders or other mental disorders should be excluded from TRD/PRD studies only when their onset is properly documented as independent and antecedent to the MDD diagnosis. | 79% |
| 17 | Individuals with a severe substance use disorder not currently in remission should be excluded from TRD/PRD studies, independently from the onset; in contrast, individuals with comorbid substance use disorder that is active and mild/moderate should be excluded from TRD/PRD studies only when the onset is properly documented as independent and antecedent to the MDD diagnosis. | 83% |
| Diagnostic tools and measures of outcome | ||
| 18 | Maudsley Staging Model is the preferred instrument to assess TRD/PRD status. | 69% |
| 19 | Clinician administered MADRS10 is the preferred outcome instrument to assess treatment response (and remission), together with patient-reported QIDS-SR. |
MADRS = 85% QIDS-SR = 81% |
| 20 | Criteria for remission, response, and partial response should not be relaxed in regulatory clinical trials for TRD/PRD, and shorter versions of the traditional scales, such as the HAM-D6 and the MADRS6, should not be preferred to full scales. | 92% |
| Recommendations which can be implemented in future research | ||
| 23 | Currently, no biomarker has been validated in clinical practice or in clinical trials to identify people with TRD (and PRD), or to further stratify them; however, collection of biological samples for subsequent subgroup or stratified analyses is recommended. | 91% |
| 25 | The usefulness of adherence assessment using blood levels or other methods (also in a run-in period) should be assessed through research, before deciding whether it should be implemented in future clinical trials. | 92% |
| Level of consensus – Weak | ||
| Recommendations which can be implemented within current practice | ||
| Previous antidepressant treatments | ||
| 5 | The definition of TRD should include two treatment failures both within the current episode, and the definition of PRD should include partial response to at least one treatment within the current episode; moreover, for long current episodes, only treatment failures within the last two years should be considered. | 51% |
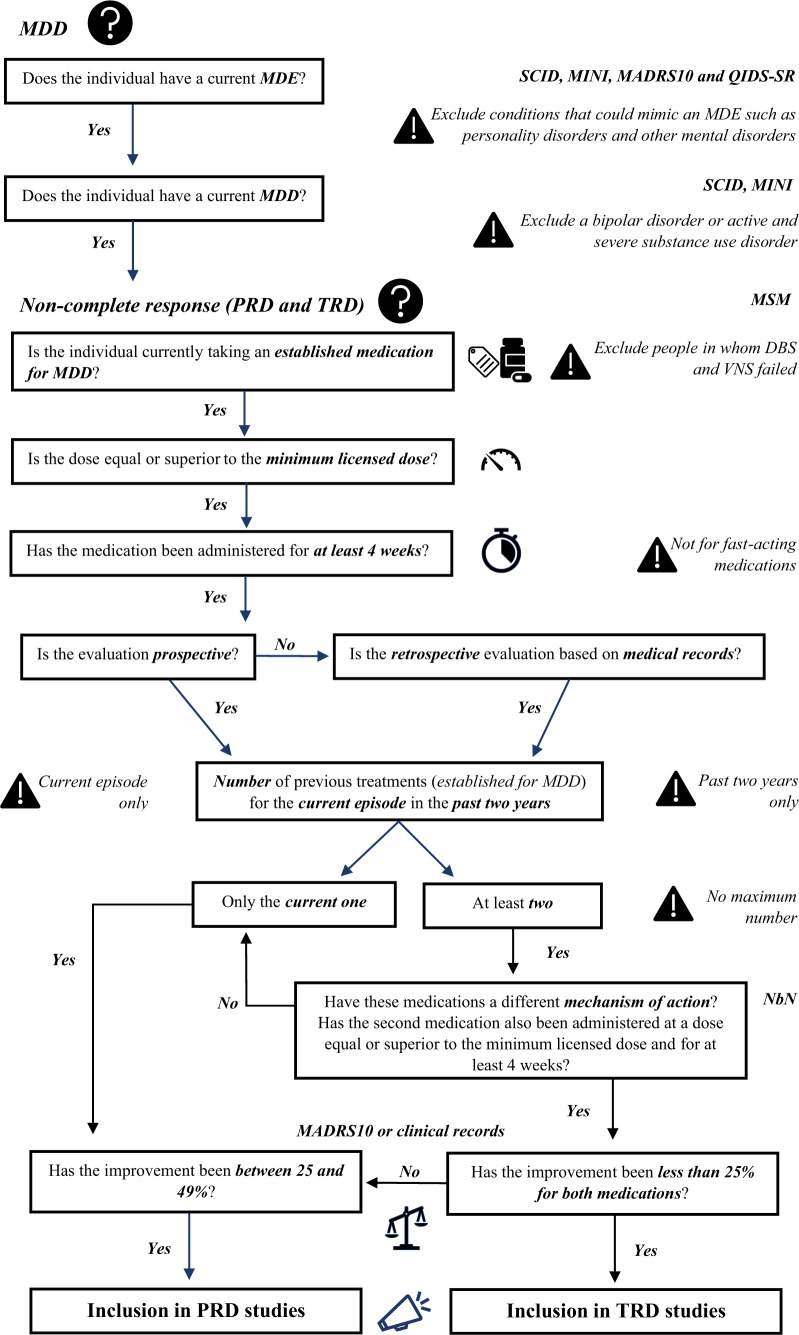
Fig. 2. Algorithm for inclusion in TRD/PRD studies.
Recommended algorithm for inclusion of participants in TRD and PRD studies based on the consensus recommendations discussed throughout the manuscript and listed in Table 1.
TRD and PRD definitions
What is lack of response?
A treatment response in MDD is defined by a reduction of at least 50% in MDD severity [22] on a standardised rating scale (see below); ‘lack of response’, encompassing both TRD and PRD, is the mirror image of this definition, that is, less than 50% reduction in depression severity. TRD is further associated, in most definitions, with the ‘classic criteria’ of lack of response to at least two medications at an adequate dose and duration (see below). There is, however, much variability around the definition of TRD. In a recent systematic review, Brown et al. [12] reported that, out of 155 TRD definitions identified in the published literature, 48.4% specified at least two sequential treatment failures as a requirement. In an even more recent systematic review, Gaynes and colleagues [5] found that only 37% of intervention studies in TRD had enrolled individuals with MDD meeting the criteria of at least two failed antidepressants, and only 19% had also described failure to adequate doses and durations of treatments. In fact, the most common definition for TRD in intervention trials involved a minimum of only one previous failed treatment (48%). Thus, the majority of studies on TRD do not seem to use the ‘classic criteria’, making it difficult to pool or compare data across these TRD studies. Not surprisingly, there was a strong consensus (98%) for our first recommendation that a definition of TRD for clinical trials conducted for regulatory purposes is necessary.
Operational criteria for TRD and PRD
Based on a number of guidelines and other expert documents [22–25], in this report we adopt the definition of TRD as indicating individuals who show a reduction of less than 25% in MDD severity to at least two antidepressants, and of PRD as indicating individuals who show a reduction of between 25% and <50% in MDD severity to at least one antidepressant. This should ideally be established using prospective psychometric assessments, or at least using clinical interviews and health records to measure retrospectively the improvement in depression severity (see below).
The majority of experts, even though with moderate consensus (85%), recommended the importance of this distinction between TRD and PRD for randomized clinical trials for new treatments, especially because of the potential advantage of separating these individuals for different types of randomized controlled trials (for example, switching for TRD vs. augmentation for PRD).
Previous antidepressant treatments
Here we discuss: (1) how many previous treatments should be considered, (2) in which episode (current and/or past) and (3) the way the treatment failure or partial response should be assessed for inclusion in clinical trials (prospectively and/or retrospectively).
Number of previous treatments
The FDA guidance [26] acknowledges that no universally accepted definitions exist for TRD or PRD, and proposes that TRD studies should include people with MDD who have not responded to more than one (so, at least two) prior medications administered at an adequate dose and duration. Similarly, the EMA opts for the same definition of at least two failed treatments when considering the matter “in a clinical pragmatic view”. This same definition is confirmed as the most common in the review by Gaynes and colleagues [5], and endorsed by the DTD consensus statement by McAllister–Williams and colleagues [7], although the last document states that some individuals might be considered to have DTD even with a single treatment failure, for example when standard treatments are contraindicated. There is also an uncertainty around PRD. EMA documents do not specify a precise number of previous treatments to diagnose PRD [27], while the FDA indicates that “for adjunctive treatment, studies should include patients with partial responses to other antidepressant therapies” [26].
Consistent with the most commonly used criteria, we recommend that TRD should be defined after a minimum of two failed treatments with <25% of improvement with adequate dosing and duration (strong consensus, 96%), while PRD can be defined even after a single treatment (improvement 25 to <50%) with adequate dosing and duration (moderate consensus, 76%).
Current or past episodes
The preferred definition of TRD for clinical trials includes a current failure and a past failure, i.e., subjects are currently receiving an antidepressant and they are still depressed according to current clinician’s assessment, and they were also treated with another antidepressant in the past and showed no response based on retrospective assessment. However, it is unclear whether both of these treatments should apply to the same (current) episode or to clearly distinct episodes. Indeed, although the EMA definition of MDD [27] emphasizes the current episode for the characterisation of the disease, it does not clarify whether the two failures should both be during the current episode. Of course, it is difficult to retrospectively defining the response to an antidepressant, especially if the current episode is of long duration (years) and the previous treatment was closer to the onset of the episode.
We recommend (with weak consensus, 51%) that the definition of TRD should include two treatment failures both within the current episode, and the definition of PRD should include partial response to at least one treatment within the current episode; moreover, for long current episodes, only treatment failures within the last two years should be considered. Of note, the “minority” position was split across a continuum of different opinions ranging from those who wanted to maintain that both antidepressants should be in the same episode but within a shorter period of time (shorter than two years) to those who wanted to consider two antidepressants “life-time”; thus, our recommendation sits in the middle of these extremes.
Prospective or retrospective assessment
A related issue, particularly important for regulatory clinical trials, is whether one treatment failure should be ‘prospective within the trial’, i.e., the trial starts with an established medication for MDD at an adequate dose, and then the person is offered a new intervention only if the medication fails to improve or eliminate MDD symptoms. We acknowledge that this, while ideal, would lead to operational execution challenges within a trial, with increased complexity and burden for the sites and study participants [22].
We recommend (with moderate consensus, 75%) that it is possible to assess ineffective past/current antidepressant treatment attempts, but only if properly documented, that is, based not only on subjective recollection or standardised instruments to assess psychiatric history and previous treatments (see below), but also on clinical documentation, such as pharmacy, hospital, or other health records. This documentation can also be used to confirm some degree of adherence to the failed treatments, and to screen people with depressive symptoms for previous episodes of mania, hypomania, or sub-threshold bipolarity, since these individuals should be excluded (see below).
Adherence to treatment is a well-recognized critical issue in both clinical and research settings. Rates of adherence vary across the literature and generally are limited by different and/or restricted time periods [28]. However, people with MDD have typically high reported rates of non-adherence (up to more than 50%) [29, 30]. It is therefore vital to properly confirm the individual’s adherence in order to define non-response: many cases of TRD may not be true TRD, but, instead, represent partial or full non-adherence. However, the assessment of treatment adherence can be difficult and is often not addressed in everyday settings, or in most current studies in TRD. The most reliable method to assess adherence is to perform a blood test to measure the concentration of the medication in the plasma (which would also allow the recognition of fast and slow metabolisers), even though it may increase the participants’ burden during the trial. Although this suggestion was clearly supported by the experts, systematic use of plasma level monitoring in TRD/PRD definitions is not current practice. It is important to note that the FDA does not accept data analyses that exclude individuals not compliant to the previous treatment based on a blood dosing of the medicine. Further discussion on adherence is presented in the Appendix. However, we recommend assessing the usefulness of different methods to measure a person’s adherence for a potential (and desirable) future implementation (see Future directions).
Type of medications
Different classes and mechanisms of action
The EMA [27] mentions that the two treatment failures could be with medications of “same or different class”. Other guidelines, including the FDA guidance [26], do not make this distinction. Interestingly, the concept of ‘different mechanisms’ may overlap with ‘different classes’, although the pharmacological overlap between classes and mechanism of action is not absolute; the Neuroscience-based Nomenclature (NbN) for psychotropic agents has greatly contributed to clarify this issue [31]. Moreover, there are some geographically-relevant label limitations to the usage of some medications (see also Appendix).
We recommend (with moderate consensus, 75%) that, to define TRD, the two antidepressant treatment failures should be with two established (licensed) medications for MDD of different mechanisms of action. The two treatments could be separated by a drug free period (and there is failure to both), prescribed sequentially (switching, with failure to both), or one is prescribed as augmentation to the other (because of the first drug failing, and with the augmentation also failing).
Moreover, we also recommend (with moderate consensus, 78%) that a failed course of psychotherapy should not be included as one of the previous treatments required for the definition of TRD/PRD, but this information should be reported for staging (see below). Notably, this recommendation does not have implications for the role of psychotherapies in the treatment of TRD, and, similarly to other TRD models proposed [11], we support the use of psychotherapies as a treatment strategy for TRD in clinical practice.
Dosage and duration of antidepressants
Most studies and meta-analyses have found no benefit for antidepressant dose escalation versus staying on the minimum licensed dose, with an increased risk of side effects and discontinuation [32, 33], even if there is also evidence that higher doses may have superior efficacy [34, 35] and that higher starting doses may be associated with higher response rates [36]. In terms of ‘minimum duration’, some studies have shown that, while two weeks can be enough to observe an initial response, a stable response/remission is usually detectable after four weeks [37, 38]. However, a complete remission may not be detectable after four weeks. For example, approximately half of remitters on citalopram in level 1 of the STAR*D trial remitted between week 6 and week 14 [39]. Of note, this is different for fast-acting medications, such as esketamine [40], but these drugs are indicated for individuals that already have TRD.
We recommend (with moderate consensus, 74%) that the criteria of ‘adequate dose and duration’ is the minimal effective dosage, that is, the minimal approved dosage, administered for at least four weeks.
Interestingly, in regulatory clinical trials, participants’ discontinuation of treatments may be considered as an endpoint equivalent to a failure [41]. However, we recommend (with strong consensus, 96%) that discontinuation of treatment before the completion of the fourth week, without clear evidence of lack of response, should not be considered as a treatment failure for the purpose of establishing TRD/PRD, especially because of the difficulty in distinguishing retrospectively between non-response and intolerance.
Exclusion from TRD/PRD studies
Many people with lived experience (PWLE) who fulfil the proposed criteria for TRD may have tried many ineffective antidepressants (multi-drug resistance) or other (licensed or unlicensed) pharmacological augmentation interventions (see also Appendix). We discussed whether these individuals should be considered to have TRD which is ‘too severe’ for inclusion in clinical trials.
We recommend (with moderate consensus, 93%) that multiple-drug resistant individuals, and individuals in whom augmentation strategies failed to improve/eliminate MDD symptoms should not be excluded from TRD/PRD studies, provided the other criteria are met. We also recommend (with strong consensus, 100%) that a previous structured psychotherapy failing to improve MDD symptoms is not an exclusion criterion. Rather, all this information should be recorded for staging and for potential subgroup analyses.
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) and vagus nerve stimulation (VNS) are continuous treatments in which a neurostimulator (usually implanted in the chest wall) is connected to intracerebral electrodes or the left vagus nerve [42, 43]. Because of the invasiveness of these intervention, people selected for these treatments have tried an unusually large number of ineffective treatments, and thus are different from other people living with TRD [44, 45].
We recommend (with moderate consensus, 62%) that individuals with MDD in whom DBS and VNS failed to improve/eliminate MDD symptoms should be excluded from TRD/PRD clinical studies. However, we also recommend (with moderate consensus, 88%) that individuals with MDD in whom other non-continuous/non-invasive brain stimulation interventions, such as electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) or transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS), failed to improve/eliminate MDD symptoms should not be excluded.
Clinical presentation
TRD and PRD symptoms
People living with MDD have a range of symptoms specifiers (for example, with melancholic features, with atypical features, with psychotic features), as well as the presence of comorbid diagnoses (for example, comorbid anxiety, bipolar depression). Potentially, some of these symptoms may be more difficult to treat compared with others, such as MDD with anxious distress [46–49].
We recommend (with strong consensus, 95%) that all specifiers of depression (melancholic, atypical, anxious, psychotic, mixed) should be considered within the TRD/PRD definition, except for bipolar depression, which should be excluded as this is part of bipolar disorder.
Comorbidities
Individuals with a diagnosis of personality disorder (especially borderline personality disorder) frequently meet criteria for MDD, but antidepressants are unlikely to be effective and hence may mimic a non-response. Active substance users also present an increased risk of pharmacological interactions (both pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic), side effects, and mood symptoms due to the effects of the substance or of the withdrawal which may appear as a ‘phenocopy’ of MDD. However, it is important to highlight that these conditions are so frequently comorbid with depression that they cannot be routinely excluded, otherwise the proposed TRD/PRD definitions would not be generalisable to individuals seen in everyday clinics.
The FDA guidance also captures this tension between homogeneity and generalisability, stating that “investigators should seek demographically broad populations and avoid unnecessary restriction of study populations (e.g., by excluding patients with concomitant illness)” [26]. Indeed, the FDA does not explicitly take position on the inclusion or exclusion of personality disorders, and it explicitly encourages to consider people with a history of substance abuse, “although such inclusions should be weighed against concerns about diagnostic and medication effect confounders”, and further states that “patients whose substance use disorder is not at least in partial remission will likely be excluded from antidepressant trials depending on the level of particular confounding concerns”. On the other hand, the EMA document only broadly indicates that MDD occurring comorbid with other psychiatric disorders is not in the remit of the guideline [27].
We recommend (with moderate consensus, 79%) that comorbid personality disorders or other mental disorders should be excluded from TRD/PRD studies only when their onset is properly documented as independent and antecedent to the MDD diagnosis. Moreover, in accordance with the FDA guidance [26], we recommend (with moderate consensus, 83%) that individuals with a severe substance use disorder not currently in remission should be excluded from TRD/PRD studies, independently from the onset; in contrast, individuals with comorbid substance use disorder that is active and mild/moderate should be excluded from TRD/PRD studies only when the onset is properly documented as independent and antecedent to the MDD diagnosis.
Also, somatic comorbidities should be systematically recorded, but not excluded a priori; this includes conditions such as inflammatory, neuroendocrine, and metabolic diseases, which can influence the response to treatments [50–52].
Diagnostic tools and measures of outcome
We also established a consensus on the best psychometric tools to measure antidepressant response (and thus TRD/PRD status and staging) both retrospectively, to improve the way we diagnose TRD (and PRD) before entering a trial, and prospectively, as tools to use in regulatory trials. A detailed summary of the different psychometric instruments is beyond this core document and is instead presented in the Appendix.
Historical assessment of TRD/PRD status
At a minimum, assessment to define TRD should include a structured clinical interview for the diagnosis of MDD, such as the Structured Clinical Interview for DSM (SCID) [53, 54] and the Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (MINI) [55], together with a scale to assess the patient’s antidepressant history, such as the Massachusetts General Hospital Antidepressant Treatment Response Questionnaire (ATRQ) [56], and the Antidepressant Treatment History Form (ATHF) [57]. A more structured method is to use staging models [6, 58], such as the Thase and Rush method [59], the Massachusetts General Hospital Staging model (MGH-s) [22], and the more recent Maudsley Staging Model (MSM) [60], which also allows the assessment of previous antidepressant treatment failure, using the Maudsley Treatment Inventory (MTI) [10].
Among the experts, there was a substantial agreement that staging models are the preferred instrument to define TRD/PRD and assess the level of treatment-resistance, even if many experts recognize the validity of the ATRQ, often accepted in regulatory clinical trials.
We recommend (with moderate consensus, 69%) the Maudsley Staging Model as the preferred instrument. However, both the Thase and Rush and the MGH-s models are valid alternatives.
Assessment of depressive symptoms and response to antidepressant treatment
The presence and severity of depression are established through clinician-administered scales, such as the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale (HAM-D 17, 21, 24 items) [61], the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale (MADRS10) [62], and the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS) Clinician Rating (QIDS-C) [63]; or self-reported instruments, such as the Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) [64], the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 Item (PHQ-9) [65], and the QIDS Self-Report (QIDS-SR) [63]. When possible, these scales are administered before and after a specific treatment has started, but they can also be used as a single measure to determine the current severity of the depression. Although TRD/PRD definitions centre on ‘response’, the ideal treatment goal is remission, considered as the absence of a relevant MDD symptomatology as indicated by a score of ≤7 at the HAM-D17 [66] or ≤10 at the MADRS10 [67, 68].
Of note are also the Clinical Global Impression (CGI) scales, measuring psychiatric global status [69], and the Sheehan Disability Scale (SDS), assessing functional impairment [70], which are important since even responders may continue to have significant residual symptoms and functional impairment. Indeed, people with lived experience of depression often define treatment success with an emphasis on broadly-based functional outcomes rather than remission of individual symptoms, and their perspective should be included through patient-reported outcomes (PROs) such as quality of life, wellbeing, impact of symptoms, and social and occupational functioning [71].
We recommend (with moderate consensus) that the clinician administered MADRS10 is the preferred outcome instrument to assess treatment response (and remission) (85%), together with patient-reported QIDS-SR (81%). We additionally recommend (with moderate consensus, 92%) that criteria for remission, response, and partial response should not be relaxed in regulatory clinical trials for TRD/PRD and shorter versions of the traditional scales, such as the HAM-D6 and the MADRS6, should not be preferred to full scales.
The MADRS10 and QIDS-SR were chosen based solely on experts’ feedback, and not a priori selected (see also Appendix). The MADRS10 was originally developed with the precise aim to have a scale that was more sensitive to change compared with the HAM-D17, a crucial feature for clinical trials [72]. In addition, unlike the HAM-D [73], it predominately focuses on the core symptoms of depression such as sadness, tension, lassitude, pessimistic thoughts, and suicidal thoughts. This results in a higher internal consistency and a greater accuracy for the MADRS compared with HAM-D [74]. However, this is also a potential limitation of the MADRS, as it may not capture the clinical complexity of the PWLE. Most notably, individuals with MDD with non-melancholic or atypical features may present with a range of symptoms that are not captured by the MADRS. For such reason, there is a risk that MDD individuals continuing to report depressive symptoms such as irritability and anxiety may be classified as responders. The same issue may arise with a ‘short’ scale such as the QIDS-SR, which again carries the risk of omitting the measure of MDD symptoms that are not captured by standard diagnostic criteria of MDD, in contrast to far more granular self-report measures of depressive symptoms, such as the Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (IDS)-SR [75], and the Symptoms of Depression Questionnaire (SDQ) [76]. Thus, the assessment of changes in MDD severity (upon which the TRD/PRD definitions rely) should include the entirety of symptoms that an individual displays, including different (non-melancholic) MDD specifiers and symptoms not included in standard classification systems. When possible, the broadest assessment possible should be conducted, using broad-spectrum scales or checklists assessing a wide range of MDD related symptoms, such as the HAM-D28. Also, specific instruments assessing specific symptoms, such as anhedonia, motor retardation, or anxiety (for example, the Hamilton Anxiety Rating Scale (HAM-A) [77]), may be useful. Sub-analyses on specific clusters of symptoms (such as suicidal, atypical, or psychotic symptoms) could be used to generate hypotheses for future clinical trials, for medications targeted to specific symptoms or to symptoms-based subgroups of individuals. Another issue is that traditional scales address depressive symptoms in the emotional and physical clusters, with a lower attention on the cognitive ones, which may frequently remain as residual symptoms indicating poor response and thus an increased risk for relapse. Interestingly, there is evidence that a mismatch between scores in clinician-administered and self-reported scales is a poor prognostic sign [78], supporting the position endorsed in this report to have at least one score of both types of scales included, until new and more tailored instruments will be developed (see also next section and Appendix).
Future directions
This section makes recommendations that are not immediately applicable to clinical trials and highlights research gaps and new opportunities identified throughout the consultative process. Future trial sponsors may wish to incorporate one or more of these areas to expand the knowledge base. A more detailed discussion of these points is presented in the Appendix; here, we want to emphasise the main recommendations:
Future research should recognize and target different clinical phenotypes of TRD (and PRD) underpinned by a specific biological mechanism (strong, 100%).
For future research, diagnostic and history-taking instruments should be implemented in clinical cohorts and electronic health records, to allow a reliable, comprehensive, and multidimensional evaluation of the PWLE (strong, 100%).
Currently, no biomarker has been validated in clinical practice or in clinical trials to identify subjects with TRD (and PRD), or to further stratify them; however, collection of biological samples for subsequent subgroup or stratified analyses is recommended (moderate, 91%).
Preferences, perspectives, and reported outcomes of PWLE should be included in future TRD (and PRD) diagnostic tools and outcome measures (strong, 100%).
The usefulness of adherence assessment using blood levels or other methods (also in a run-in period) should be assessed through research, before deciding whether it should be implemented in future clinical trials (moderate, 92%).
Limitations and conclusions
While we discuss many points of debate in the Appendix, here we want to acknowledge the main limitations of this report.
First, the recommendations are based on experts’ and stakeholders’ clinical and professional judgement, supported by research and clinical evidence, but without any hard and objective validation. Second, our recommendations try to strike a balance between being ‘too broad’ and being ‘too narrow’, with the aim to identify ‘clinically homogenous’ samples, based on a pragmatic and non-aetiologically-based approach; still, we cannot exclude that significant phenotypic or biological heterogeneity is present within the defined TRD/PRD samples, and future research will allow to define this inherent variability, if any, in clinical features, biomarkers, and clinical response. Third, the opposite risk is also present: that we define groups so narrowly that the findings are not generalisable to the larger population of PWLE in clinical settings, and do not translate into better care; however, maintaining narrow definitions may help avoiding overmedicalisation and may prevent the lowering of the threshold above which treatments which are specific for TRD are offered to patients, as a recent commentary on this topic highlighted [18].
In terms of theoretical limitations, some of our contributors have argued that the proposed TRD/PRD definitions are unhelpful from a clinical and a conceptual perspective, as they arbitrarily apply thresholds on a continuum, and are influenced by the different healthcare systems. Moreover, TRD and PRD concepts are based upon a conceptualisation of depression as an episodic illness with good inter-episode recovery, while many individuals with MDD have a chronic illness with waxing and waning course; this might create difficulties when trying to accurately identify the beginning and end of the current/previous episodes, in order to define response to the antidepressants. Finally, we recognise that, according to our recommendations, individuals with MDD with an ineffective (<25%) single antidepressant trial are not defined as either TRD or PRD; as in standard clinical practice, these subjects should be prescribed a second antidepressant before a decision can be made on their TRD status.
Notwithstanding these limitations (and the points of uncertainties further discussed in the Appendix), this report offers clear and consistent definitions of TRD/PRD for regulatory clinical trials and for clinical and biological studies more broadly, agreed among a large group of experts including clinicians, academics, industry, regulatory agencies, and PWLE. Our ultimate ambition is to advance tailored treatments and a truly ‘precision medicine’ approach for MDD, which in turn will finally help to deliver better care for people suffering from this severely challenging illness, which remains too often ineffectively treated.
Disclaimer
This document reflects the majority views of the experts. Authorship reflects having been part of the process and accepting the consensus statements without necessarily personally endorsing every single recommendation (see level of consensus). Also, the views expressed in this article are the personal views of the author(s) and may not be understood or quoted as being made on behalf of or reflecting the position of the regulatory agency/agencies or organisations with which the author(s) is/are employed/affiliated. This publication reflects only the authors’ view, and the JU is not responsible for any use that may be made of the information it contains.
Supplementary information
Acknowledgements
The EU-PEARL Project has received funding from the Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking (JU) under grant agreement No 853966. The JU receives support from the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme and EFPIA and CHILDREN’S TUMOR FOUNDATION, GLOBAL ALLIANCE FOR TB DRUG DEVELOPMENT NON-PROFIT ORGANISATION, SPRINGWORKS THERAPEUTICS INC.
Author contributions
LS and CMP are principal authors with full access to all of the data in this consensus report and are responsible for writing all the different versions of the manuscript. CW, MK and all the authors involved within the EUPEARL project (GA-H, FB, LCG, WRC, HDS, SMG, WJGH, VJM, EMa, HM, EMe, CO, GP-F, SPo, MES, EvdK, KW, YF, JAR-Q, AJS) contributed to the conception and design of the work, data acquisition, and initial drafting of the manuscript, or reviewed the final version of the document as part of the EU-PEARL project. All other authors contributed substantially to the writing of the manuscript and the consensus recommendations. All the authors expressed their preferences on the final recommendations. All authors contributed to the critical revision of the manuscript for intellectual content, and all are responsible for the content of this consensus paper.
Competing interests
LS reports grant from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. CW reports grant from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. MK reports grant from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. IMA has nothing to disclose. BA reports personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees and non-financial support from Janssen-Cilag, personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Eli Lilly, outside the submitted work; and has served on the advisory board of Janssen-Cilag. VA reports personal fees from Astra-Zeneca, personal fees from Gilead Sciences, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Neuraxpharm, personal fees from Otsuka, personal fees from Sanofi/Genzyme, personal fees from Servier, grants from European Union- Horizon 2020, grants from Medical Faculty Muenster- Interdisciplinary Center for Clinical Research, outside the submitted work; and Has served on Advisory Boards for Allergan, Astra-Zeneca, Janssen, Lundbeck, Neuraxpharm, Otsuka, Sanofi/Genzyme, Servier and Trommsdorff. MB reports grants from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), grants from European Commission, grants from Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung (BMBF), personal fees from Aristo, personal fees from GH Research, personal fees from Hexal, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Janssen-Cilag, personal fees from Neuraxpharm, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees from Sandoz, personal fees from Shire International, personal fees from Sunovion, personal fees from Takeda, outside the submitted work. BTB reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees from Servier, personal fees from Bristol Myers Squibb, personal fees from Otsuka, personal fees from LivaNova, personal fees from Janssen-Cilag, outside the submitted work. PB reports personal fees from Allergan, personal fees from Eisai, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Otsuka, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Pierre Fabre Médicaments, personal fees from Takeda, outside the submitted work; and Expert testimony was provided on behalf of Allergan, Bristol Myers Squibb and Otsuka. AJC reports personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Livanova, personal fees from Allergan, personal fees from NICE, grants from Medical Research Council (UK), grants from Wellcome Trust (UK), grants from National Institute for Health Research (UK), grants from Protexin Probiotics International Ltd., outside the submitted work. PJC has a patent for Ebselen in treatment-resistant depression pending. TGD has nothing to disclose. AF reports grants and personal fees from Angelini, grants and personal fees from Apsen, grants and personal fees from Boheringer Ingelheim, grants and personal fees from Daiichi Sankyo, grants and personal fees from Doc Generici, grants and personal fees from Glaxo Smith Kline, grants and personal fees from Italfarmaco, grants and personal fees from Lundbeck, grants and personal fees from Janssen, grants and personal fees from Mylan, grants and personal fees from Neuraxpharm, grants and personal fees from Otsuka, grants and personal fees from Pfizer, grants and personal fees from Recordati, grants and personal fees from Sanofi Aventis, grants and personal fees from Sunovion, grants and personal fees from Vifor, outside the submitted work. INF has nothing to disclose. UH reports personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Servier, personal fees from Medice, outside the submitted work. ADK reports grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceuticals, grants from Axsome Pharmaceutics, grants from Reveal Biosensors, grants from The Ray and Dagmar Dolby Family Fund, grants from National Institutes of Health, personal fees from Adare, personal fees from Axsome Therapeutics, personal fees from Big Health, personal fees from Eisai, personal fees from Evecxia, personal fees from Ferring Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Galderma, personal fees from Harmony Biosciences, personal fees from Idorsia, personal fees from Jazz Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Millenium Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Merck, personal fees from Neurocrine Biosciences, personal fees from Neurawell, personal fees from Pernix, personal fees from Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Sage, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees from Harmony, outside the submitted work. ML has nothing to disclose. RHM-W reports personal fees from Janssen-Cilag, personal fees from LivaNova, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from P1 Vital Ltd, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Sage Therapeutics, personal fees from Sunovian, non-financial support from MagStim, grants from AstraZeneca, personal fees from My Tomorrows, personal fees from OCM Communications s.n.c, personal fees from Syntropharma, outside the submitted work. RSM reports grants from CIHR, grants from GACD, grants from Chinese National Natural Research Foundation, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Purdue, personal fees from Pfizer, personal fees from Otsuka, personal fees from Allergan, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees from Neurocrine, personal fees from Sunovion, personal fees from Eisai, personal fees from Minerva, personal fees from Intra-Cellular, personal fees from Abbvie, other from AltMed, outside the submitted work. AM-L reports personal fees from Agence Nationale de la Recherche, personal fees from American Association for the Advancement of Science, personal fees from Brain Mind Institute, personal fees from Brainsway, personal fees from Catania International Summer School of Neuroscience (CISSN), personal fees from Daimler und Benz Stiftung, personal fees from Fondation FondaMental, personal fees from Janssen-Cilag GmbH, personal fees from Lundbeck A/S, personal fees from Lundbeck Int. Neuroscience Foundation, personal fees from MedinCell, personal fees from Sage Therapeutics, personal fees from Techspert.io, personal fees from Thieme Verlag, personal fees from von Behring Röntgen Stiftung, personal fees from BAG Psychiatrie Oberbayern, personal fees from Biotest AG, personal fees from Forum Werkstatt Karlsruhe, personal fees from International Society of Psychiatric Genetics, personal fees from Brentwood, personal fees from Klinik für Psychiatrie und Psychotherapie Ingolstadt, personal fees from Lundbeck SAS France, personal fees from med Update GmbH, personal fees from Merz-Stiftung, personal fees from Siemens Healthineers, outside the submitted work. AHM reports personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, outside the submitted work. CBN reports grants from National Institutes of Health (NIH), personal fees from ANeuroTech (division of Anima BV), personal fees from Taisho Pharmaceutical, Inc, personal fees from Takeda, personal fees from Signant Health, personal fees from Sunovion Pharmaceuticals, Inc, personal fees from Janssen Research & Development LLC, personal fees from Magstim, Inc, personal fees from Navitor Pharmaceuticals, Inc, personal fees from Intra-Cellular Therapies, Inc, personal fees and other from EMA Wellness, personal fees from Acadia Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from Axsome, personal fees from Sage, personal fees from BioXcel Therapeutics, personal fees from Silo Pharma, personal fees from XW Pharma, personal fees from Neuritek, personal fees from Engrail Therapeutics, personal fees from Brain and Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF), personal fees and other from Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA), personal fees from Skyland Trail, personal fees from Signant Health, personal fees from Laureate Institute for Brain Research (LIBR), Inc, personal fees from Magnolia CNS, other from Gratitude America, other from Xhale Smart, Inc, other from Xhale, other from Seattle Genetics, other from Antares, other from BI Gen Holdings, Inc, other from Corcept Therapeutics Pharmaceuticals Company, from null, outside the submitted work; In addition, CBN has a patent Method and devices for transdermal delivery of lithium (US 6, 375, 990B1) issued, and a patent Method of assessing antidepressant drug therapy via transport inhibition of monoamine neurotransmitters by ex vivo assay (US 7, 148, 027B2) issued. CN reports personal fees from Johnson/Janssen-Cilag, outside the submitted work. DN reports personal fees from British National Formulary, personal fees from Ranvier, personal fees from Opiant, personal fees from COMPASS Pathways, personal fees from AWAKN, personal fees from Psyched Wellness, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from BMS/Otsuka, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Takeda, grants from Wellcome Trust, MRC, other from P1vital, other from Awakn, other from Psyched Wellness, other from Equasy Enterprises, other from Alcarelle, outside the submitted work; and Expert witness related to psychotropic drugs in several legal cases. Edited/written more than 34 books, some purchased by pharmaceutical companies. SPa reports grants from R21 NIMH (R21DA042271-01), outside the submitted work. LP reports personal fees from University of Modena and Reggio Emilia, personal fees from University of Miami, personal fees from EDRA-LSWR Publishing Company, personal fees from Inpeco SA Total Lab Automation Company, personal fees from VeraSci, Durham, USA, personal fees from AbbVie USA, personal fees from Acadia USA, personal fees from BCG Switzerland, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, personal fees from Compass Pathways, personal fees from Ferrer Spain, personal fees from Gedeon-Richter, Hungary, personal fees from Johnson & Johnson USA, personal fees from NeuroCog Trials USA, personal fees from Novartis-Gene Therapies, Switzerland, personal fees from Otsuka USA, personal fees from Pfizer Global USA, personal fees from PharmaMar Spain, personal fees from Relmada USA, personal fees from Takeda USA, personal fees from Vifor Switzerland, outside the submitted work. BWJHP reports grants from Boehringer Ingelheim, grants from Janssen Research, outside the submitted work. AFS reports personal fees from Axsome, personal fees and other from Delpor, personal fees and other from NeuraWell, personal fees from ANeuroTech, personal fees from Signant, personal fees from Otsuka, personal fees from EMA Wellness, personal fees and other from Owl Insights, personal fees and other from Alto, personal fees and other from Verso, personal fees from Compass, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Tris, personal fees from Schwabe, personal fees from Boehringer Ingelheim, personal fees from McKinsey, other from Corcept, other from Merck, other from Seattle Genetics, other from XHale, other from Intersect, other from Epiodyne, outside the submitted work. RCS reports grants from Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, grants and personal fees from Allergan, grants from Assurex Health, grants from Avanir Pharmaceuticals, grants and personal fees from Cerecor, Inc, personal fees from Clintara LLC, grants from Genomind, grants and personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceutica, personal fees from Medtronic, Inc., grants from Novartis, Inc., personal fees from Pfizer, Inc., grants and personal fees from Otsuka Pharmaceuticals, grants and personal fees from Acadia Pharmaceuticals, grants from Alkermes, PLC, grants and personal fees from Takeda Pharmaceuticals, grants from NeuroRx Inc., outside the submitted work. LNY reports personal fees from Alkermes, grants and personal fees from Allergan, personal fees from CANMAT, grants and personal fees from CIHR, grants and personal fees from Dainippon Sumitomo, grants and personal fees from Intracellular Therapies, grants and personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Merck, personal fees from Otsuka, personal fees from Sanofi, personal fees from Sunovion, outside the submitted work. AHY reports personal fees from King’s College London, personal fees from Sumitomo Dainippon Pharma, grants from MRC (UK), grants from Wellcome Trust (UK), grants from NIHR (UK), outside the submitted work; and Principal Investigator in the Restore-Life VNS registry study funded by LivaNova. Principal Investigator on ESKETINTRD3004: “An Open-label, Long-term, Safety and Efficacy Study of Intranasal Esketamine in Treatment-resistant Depression.” Principal Investigator on “The Effects of Psilocybin on Cognitive Function in Healthy Participants.” Principal Investigator on “The Safety and Efficacy of Psilocybin in Participants with Treatment-Resistant Depression (P-TRD)”. RZ reports personal fees from The London Depression Institute, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Depsee Ltd, personal fees from Scients Institute, Palo Alto, outside the submitted work; and Co-Investigator on a LivaNova Funded observational study of Vagus Nerve Stimulation for Depression. Collaborated with EMIS PLC for a study. Affiliated with the D’Or Institute of Research and Education, Rio de Janeiro. GA reports personal fees from BfArM (Federal Institute for Drugs and Medical Devices), personal fees from EMA (No money, honoraria or other kind of compensation paid for services rendered. Only travel and accommodation expenses are covered together with travel allowance from EMA), personal fees from University of Thessaly (Greece) and University of Nicosia (Cyprus) (Honoraria for lectures in Postgraduate Program) outside the submitted work. FB-D has nothing to disclose. CF reports personal fees and other from GSK, outside the submitted work. MH reports personal fees from BfArM, personal fees from EMA (No money, honoraria or other kind of compensation paid for services rendered. Only travel and accommodation expenses are covered together with travel allowance from EMA), personal fees from Forum-Institut, outside the submitted work. TL reports personal fees from Massachusetts General Hospital Clinical Trials Network and Institute, personal fees from Acadia, personal fees from Alairion, personal fees from Antares, personal fees from Aptinyx, personal fees from Arbor, personal fees from AxsomeBetterLife, personal fees from Biohaven, personal fees from Cadent, personal fees from Cereval, personal fees from Cingulate, personal fees from Corteyxme, personal fees from Eleusis, personal fees from Emerald Lake Safety, personal fees from Greenwich, personal fees from Harmony, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Karuna, personal fees from KemPharm, personal fees from LB Pharmaceuticals, personal fees from LevoTx, personal fees from MAPS, personal fees from Merck, personal fees from Minerva, personal fees from Neurocrine Biosciences, personal fees from Neuronetics, personal fees from Noema, personal fees from Novartis Pharma AG, personal fees from Novartis US, personal fees from Praxis Biosciences, personal fees from Promentis, personal fees from Tonix, personal fees from Vallon, personal fees from Waypoint, outside the submitted work. F-LM reports personal fees from HUS Helsinki University Hospital, non-financial support from European Patients’ Forum, outside the submitted work. KS has nothing to disclose. AT has nothing to disclose. GA-H reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study; grants from European Union’s Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Program (grant agreement no.728018), outside the submitted work. FB reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. LC-G reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. WRC reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. HDS reports non-financial support from EU-PEARL Project, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Janssen, outside the submitted work. SMG reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Almirall SA, personal fees from Celgene, personal fees from Forum für Medizinische Fortbildung (FomF), personal fees from Mylan GmbH, non-financial support from GAIA Group, grants from Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft, grants from German Federal Ministry of Health, grants from National Multiple Sclerosis Society, outside the submitted work. WJGH reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. VJM reports non-financial support from EU-PEARL Project, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Novartis Pharma AG, outside the submitted work. EMa reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Janssen-Cilag, outside the submitted work. JM reports non-financial support from EU-PEARL Project, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Janssen, outside the submitted work. EMe reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. CO reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Ferring, personal fees from Janssen, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from SAGE Therapeutics, personal fees from Fortbildungskolleg, personal fees from Limes Klinikgruppe, personal fees from Medical Tribune, grants from German Research Foundation (OT 209/7-3; 14-1, EXC 2049), grants from German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (KS2017-067), grants from Berlin Institute of Health (B3010350), outside the submitted work. GP-F reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. SPo reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. MES reports non-financial support from EU-PEARL Project, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Janssen Pharmaceutica NV, other from Johnson & Johnson, other from Novartis Inc., outside the submitted work. EvdK reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. KW reports non-financial support from EU-PEARL Project, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Janssen R&D LLC, other from Johnson & Johnson, outside the submitted work. YF reports non-financial support from EU-PEARL Project, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Novartis Pharma AG, outside the submitted work. JAR-Q reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study; personal fees and non-financial support from Eli-Lilly, personal fees and non-financial support from Janssen-Cilag, personal fees from Novartis, personal fees and non-financial support from Shire, personal fees and non-financial support from Takeda, personal fees from Bial, personal fees and non-financial support from Shionogi, personal fees from Lundbeck, personal fees from Almirall, personal fees from Braingaze, personal fees from Sincrolab, personal fees and non-financial support from Medice, personal fees and non-financial support from Rubió, personal fees from Raffo, personal fees from Actelion, personal fees from Ferrer, personal fees from Oryzon, personal fees from Roche, personal fees from Psious, outside the submitted work. AJS reports non-financial support from EU-PEARL Project, during the conduct of the study; personal fees from Johnson & Johnson, outside the submitted work (employee and own stock in the company). CMP reports grants from European Commission (IMI2 853966), during the conduct of the study. Additional funding has been provided by UK National Institute of Health Research (NIHR) Biomedical Research Centre at South London and Maudsley NHS Trust and King’s College London. He is also funded by a NIHR Senior Investigator Award. He has received research or consultation funding from Johnson & Johnson and Boehringer Ingelheim, as well as research funding from the Medical Research Council (UK) and the Wellcome Trust for research on depression and inflammation as part of two large consortia that also include Johnson & Johnson, GSK and Lundbeck.
Footnotes
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41380-021-01381-x.
References
- 1.Cipriani A, Furukawa TA, Salanti G, Chaimani A, Atkinson LZ, Ogawa Y, et al. Comparative efficacy and acceptability of 21 antidepressant drugs for the acute treatment of adults with major depressive disorder: a systematic review and network meta-analysis. Lancet. 2018;391:1357–66. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32802-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Otte C, Gold SM, Penninx BW, Pariante CM, Etkin A, Fava M, et al. Nature disease primer: Major Depressive Disorder. Nature Publishing Group. 2016. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, et al. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: A STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry. 2006;163:1905–17. doi: 10.1176/ajp.2006.163.11.1905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.McIntyre RS, Filteau MJ, Martin L, Patry S, Carvalho A, Cha DS, et al. Treatment-resistant depression: Definitions, review of the evidence, and algorithmic approach. J Affect Disord. 2014;156:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2013.10.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Gaynes BN, Lux L, Gartlehner G, Asher G, Forman‐Hoffman V, Green J, et al. Defining treatment‐resistant depression. Depression Anxiety. 2019;37:134–45. doi: 10.1002/da.22968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Salloum NC, Papakostas GI. Staging treatment intensity and defining resistant depression: Historical overview and future directions. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 2019, 80. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 7.McAllister-Williams RH, Arango C, Blier P, Demyttenaere K, Falkai P, Gorwood P, et al. The identification, assessment and management of difficult-to-treat depression: An international consensus statement. J Affect Disord. 2020;267:264–82. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2020.02.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Sheehan DV, Harnett-Sheehan K, Spann ME, Thompson HF, Prakash A. Assessing remission in major depressive disorder and generalized anxiety disorder clinical trials with the discan metric of the Sheehan disability scale. Int Clin Psychopharmacol. 2011;26:75–83. doi: 10.1097/YIC.0b013e328341bb5f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.McAllister-Williams RH, Christmas DMB, Cleare AJ, Currie A, Gledhill J, Insole L, et al. Multiple-therapy-resistant major depressive disorder: A clinically important concept. Br J Psychiatry. 2018;212:274–8. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2017.33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Fekadu A, Donocik JG, Cleare AJ. Standardisation framework for the Maudsley staging method for treatment resistance in depression. BMC Psychiatry. 2018, 18. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 11.Conway CR, George MS, Sackeim HA. Toward an evidence-based, operational definition of treatment-resistant depression: When Enough is enough. JAMA Psychiatry Am Med Assoc. 2017;74:9–10. doi: 10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.2586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Brown S, Rittenbach K, Cheung S, McKean G, MacMaster FP, Clement F. Current and Common Definitions of Treatment-Resistant Depression: Findings from a Systematic Review and Qualitative Interviews. Can J Psychiatry SAGE Publ Inc. 2019;64:380–7. doi: 10.1177/0706743719828965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Howes OD, Thase ME, Pillinger T. Treatment resistance in psychiatry: state of the art and new directions. Mol Psychiatry 2021. 2021;13:1–15. doi: 10.1038/s41380-021-01200-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Taylor RW, Marwood L, Oprea E, Deangel V, Mather S, Valentini B, et al. Pharmacological Augmentation in Unipolar Depression: A Guide to the Guidelines. International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology. 2021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Strawbridge R, Carter B, Marwood L, Bandelow B, Tsapekos D, Nikolova VL, et al. Augmentation therapies for treatment-resistant depression: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Psychiatry. 2019;214:308–308. doi: 10.1192/bjp.2018.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.McAllister-Williams RH, Arango C, Blier P, Demyttenaere K, Falkai P, Gorwood P, et al. Reconceptualising treatment-resistant depression as difficult-to-treat depression. The Lancet. Psychiatry. 2021;8:14–15. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30516-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Moher D, Schulz KF, Simera I, Altman DG. Guidance for developers of health research reporting guidelines. PLoS Med. 2010;7:e1000217. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cosgrove L, Naudet F, Högberg G, Shaughnessy AF, Cristea IA. Reconceptualising treatment-resistant depression as difficult-to-treat depression. The Lancet. Psychiatry. 2021;8:11–3. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(20)30416-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Humphrey-Murto S, de Wit M. The Delphi method—more research please. J Clin Epidemiol Elsevier USA. 2019;106:136–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.10.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Grant S, Booth M, Khodyakov D. Lack of preregistered analysis plans allows unacceptable data mining for and selective reporting of consensus in Delphi studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2018;99:96–105. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.03.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Diamond IR, Grant RC, Feldman BM, Pencharz PB, Ling SC, Moore AM, et al. Defining consensus: A systematic review recommends methodologic criteria for reporting of Delphi studies. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014;67:401–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2013.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fava M. Diagnosis and definition of treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;53:649–59. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(03)00231-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hirschfeld RMA, Montgomery SA, Aguglia E, Amore M, Delgado PL, Gastpar M, et al. Partial response and nonresponse to antidepressant therapy: Current approaches and treatment options. J Clin Psychiatry. 2002;63:826–37. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v63n0913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kennedy SH, Lam RW, McIntyre RS, Tourjman SV, Bhat V, Blier P, et al. Canadian Network for Mood and Anxiety Treatments (CANMAT) 2016 clinical guidelines for the management of adults with major depressive disorder: Section 3. Pharmacological Treatments. Canadian Journal of Psychiatry. 2016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 25.Jackson WC, Papakostas GI, Rafeyan R, Trivedi MH. Recognizing Inadequate Response in Patients With Major Depressive Disorder. The Journal of clinical psychiatry. 2020, 81. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Food and Drug Administration. Major Depressive Disorder: Developing Drugs for Treatment, Guidance for Industry’, DRAFT GUIDANCE. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER), Revision 1. 2018.
- 27.European Medicines Agency. Guideline on clinical investigation of medicinal products in the treatment of depression. EMA/CHMP/185423/2010 Rev 2. 2013.
- 28.Keyloun KR, Hansen RN, Hepp Z, Gillard P, Thase ME, Devine EB. Adherence and Persistence Across Antidepressant Therapeutic Classes: A Retrospective Claims Analysis Among Insured US Patients with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD) CNS Drugs. 2017;31:421–32. doi: 10.1007/s40263-017-0417-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.ten Doesschate MC, Bockting CLH, Schene AH. Adherence to continuation and maintenance antidepressant use in recurrent depression. J Affect Disord. 2009;115:167–70. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2008.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ho SC, Chong HY, Chaiyakunapruk N, Tangiisuran B, Jacob SA. Clinical and economic impact of non-adherence to antidepressants in major depressive disorder: A systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2016;193:1–10. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2015.12.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Frazer A, Blier P. A Neuroscience-based Nomenclature (NbN) for psychotropic agents. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2016;19:pyw066. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyw066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Cleare A, Pariante CM, Young AH, Anderson IM, Christmas D, Cowen PJ, et al. Evidence-based guidelines for treating depressive disorders with antidepressants: A revision of the 2008 British Association for Psychopharmacology guidelines. J Psychopharmacol 2015. 2015;29:459–525. doi: 10.1177/0269881115581093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Furukawa TA, Salanti G, Cowen PJ, Leucht S, Cipriani A. No benefit from flexible titration above minimum licensed dose in prescribing antidepressants for major depression: systematic review. Acta Psychiatr Scandinavica. 2020;141:401–9. doi: 10.1111/acps.13145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Hieronymus F, Nilsson S, Eriksson E. A mega-Analysis of fixed-dose trials reveals dose-dependency and a rapid onset of action for the antidepressant effect of three selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6:e834–e834. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Jakubovski E, Varigonda AL, Freemantle N, Taylor MJ, Bloch MH. Systematic review and meta-analysis: Dose-response relationship of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors in major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry. 2016;173:174–83. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2015.15030331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Papakostas GI, Charles D, Fava M. Are typical starting doses of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors sub-optimal? A meta-analysis of randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, dose-finding studies in major depressive disorder. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2010;11:300–7. doi: 10.3109/15622970701432528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Szegedi A, Jansen WT, Van Willigenburg APP, Van Der Meulen E, Stassen HH, Thase ME. Early improvement in the first 2 weeks as a predictor of treatment outcome in patients with major depressive disorder: A meta-analysis including 6562 patients. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70:344–53. doi: 10.4088/JCP.07m03780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kelley ME, Dunlop BW, Nemeroff CB, Lori A, Carrillo-Roa T, Binder EB, et al. Response rate profiles for major depressive disorder: Characterizing early response and longitudinal nonresponse. Depression Anxiety. 2018;35:992–1000. doi: 10.1002/da.22832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Warden D, Ritz L, et al. Evaluation of Outcomes With Citalopram for Depression Using Measurement-Based Care in STAR*D. Implic Clin Pract. 2006;163:28–40. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.163.1.28. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.McIntyre RS, Rosenblat JD, Nemeroff CB, Sanacora G, Murrough JW, Berk M, et al. Synthesizing the Evidence for Ketamine and Esketamine in Treatment-Resistant. Depression: Int Expert Opin Available Evid Implement. 2021;178:383–99. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2020.20081251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pradier MF, McCoy TH, Hughes M, Perlis RH, Doshi-Velez F. Predicting treatment dropout after antidepressant initiation. Transl Psychiatry. 2020;10:60. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-0716-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Bauer M, Severus E, Köhler S, Whybrow PC, Angst J, Möller HJ. World Federation of Societies of Biological Psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for biological treatment of unipolar depressive disorders. part 2: Maintenance treatment of major depressive disorder-update 2015. World Journal of Biological Psychiatry. 2015. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Dandekar MP, Fenoy AJ, Carvalho AF, Soares JC, Quevedo J. Deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: an integrative review of preclinical and clinical findings and translational implications. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:5. doi: 10.1038/mp.2018.2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Holtzheimer PE, Husain MM, Lisanby SH, Taylor SF, Whitworth LA, McClintock S, et al. Subcallosal cingulate deep brain stimulation for treatment-resistant depression: a multisite, randomised, sham-controlled trial. The Lancet. Psychiatry. 2017;4:839–49. doi: 10.1016/S2215-0366(17)30371-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rush AJ, Siefert SE. Clinical issues in considering vagus nerve stimulation for treatment-resistant depression. Exp Neurol. 2009;219:36–43. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2009.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Souery D, Oswald P, Massat I, Bailer U, Bollen J, Demyttenaere K, et al. Clinical factors associated with treatment resistance in major depressive disorder: Results from a European multicenter study. J Clin Psychiatry. 2007;68:1062–70. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v68n0713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Rush AJ, Wisniewski SR, Warden D, Luther JF, Davis LL, Fava M, et al. Selecting among second-step antidepressant medication monotherapies: Predictive value of clinical, demographic, or first-step treatment features. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 2008;65:870–80. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.65.8.870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bartova L, Dold M, Kautzky A, Fabbri C, Spies M, Serretti A, et al. Results of the European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression (GSRD) — basis for further research and clinical practice. World J Biol Psychiatry. 2019;20:427–48. doi: 10.1080/15622975.2019.1635270. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Braund TA, Palmer DM, Williams LM, Harris AWF. Characterising anxiety in major depressive disorder and its use in predicting antidepressant treatment outcome: An iSPOT-D report. Aust NZ J Psychiatry. 2019;53:782–93. doi: 10.1177/0004867419835933. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Juruena MF, Pariante CM, Papadopoulos AS, Poon L, Lightman S, Cleare AJ. The role of mineralocorticoid receptor function in treatment-resistant depression. J Psychopharmacol. 2013;27:1169–79. doi: 10.1177/0269881113499205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Strawbridge R, Arnone D, Danese A, Papadopoulos A, Herane Vives A, Cleare AJ. Inflammation and clinical response to treatment in depression: A meta-analysis. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol. 2015;25:1532–43. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Pan LA, Martin P, Zimmer T, Segreti AM, Kassiff S, McKain BW, et al. Neurometabolic disorders: Potentially treatable abnormalities in patients with treatment-refractory depression and suicidal behavior. Am J Psychiatry. 2017;174:42–50. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2016.15111500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.First, MB, Spitzer, RL, Gibbon M, and Williams JBW. Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR Axis I Disorders. New York State Psychiatric Institute. 2002.
- 54.First MB, Williams JBW, Karg RS, Spitzer RL. Structured clinical interview for DSM-5 research version. American Psychiatric Association, Washington DC. 2015.
- 55.Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E, et al. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): The development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. In: Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 1998. [PubMed]
- 56.Chandler GM, Iosifescu DV, Pollack MH, Targum SD, Fava M. Validation of the massachusetts general hospital Antidepressant Treatment History Questionnaire (ATRQ) CNS Neurosci Therapeutics. 2010;16:322–5. doi: 10.1111/j.1755-5949.2009.00102.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sackeim HA. The definition and meaning of treatment-resistant depression. J Clin Psychiatry. 2001;62:10–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ruhé HG, Van Rooijen G, Spijker J. Peeters FPML, Schene AH. Staging methods for treatment resistant depression. A systematic review. J Affect Disord. 2012;137:35–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2011.02.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Thase ME, Rush AJ. When at first you don’t succeed: Sequential strategies for antidepressant nonresponders. In: Journal of Clinical Psychiatry. 1997. [PubMed]
- 60.Fekadu A, Wooderson S, Donaldson C, Markopoulou K, Masterson B, Poon L, et al. A multidimensional tool to quantify treatment resistance in depression: The Maudsley staging method. J Clin Psychiatry. 2009;70:177–84. doi: 10.4088/JCP.08m04309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Hamilton M. A rating scale for depression. J Neurol, Neurosurg, psychiatry. 1960;23:56–62. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.23.1.56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry. 1979;134:382–9. doi: 10.1192/bjp.134.4.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Ibrahim HM, Carmody TJ, Arnow B, Klein DN, et al. The 16-item Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology (QIDS), clinician rating (QIDS-C), and self-report (QIDS-SR): A psychometric evaluation in patients with chronic major depression. Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54:573–83. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3223(02)01866-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Beck AT, Ward CH, Mendelson M, Mock J, Erbaugh J. An Inventory for Measuring Depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1961;4:561–71. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1961.01710120031004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JBW. The PHQ-9: Validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16:606–13. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1497.2001.016009606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Frank E, Prien RF, Jarrett RB, Keller MB, Kupfer DJ, Lavori PW, et al. Conceptualization and rationale for consensus definitions of terms in major depressive disorder: Remission, recovery, relapse, and recurrence. Arch Gen Psychiatry. 1991;48:851–5. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.1991.01810330075011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Hawley CJ, Gale TM, Sivakumaran T. Defining remission by cut off score on the MADRS: Selecting the optimal value. J Affect Disord. 2002;72:177–84. doi: 10.1016/S0165-0327(01)00451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Zimmerman M, Posternak MA, Chelminski I. Defining remission on the montgomery-asberg depression rating scale. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65:163–8. doi: 10.4088/JCP.v65n0204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Guy W. Rating Clinician-rated | Clinical Global Impression (CGI). ECDEU Assessment Manual for Psychopharmacology. 1976.
- 70.Leon AC, Olfson M, Portera L, Farber L, Sheehan DV. Assess Psychiatr Impairment Prim Care Sheehan Disabil Scale. 1997;27:93–105. doi: 10.2190/T8EM-C8YH-373N-1UWD. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Deshpande P, Bl Sudeepthi, Rajan S, Abdul Nazir C. Patient-reported outcomes: A new era in clinical research. Perspect Clin Res. 2011;2:137–44. doi: 10.4103/2229-3485.86879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Montgomery SA, Asberg M. A new depression scale designed to be sensitive to change. Br J Psychiatry. 1979;134:382–9. doi: 10.1192/bjp.134.4.382. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Bagby RM, Ryder AG, Schuller DR, Marshall MB. The Hamilton Depression Rating Scale: Has the gold standard become a lead weight? Am J Psychiatry Am Psychiatr Publ. 2004;161:2163–77. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.161.12.2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Uher R, Farmer A, Maier W, Rietschel M, Hauser J, Marusic A, et al. Measuring depression: Comparison and integration of three scales in the GENDEP study. Psychological Med. 2008;38:289–300. doi: 10.1017/S0033291707001730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Trivedi MH, Rush AJ, Ibrahim HM, Carmody TJ, Biggs MM, Suppes T, et al. The Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology, Clinician Rating (IDS-C) and Self-Report (IDS-SR), and the Quick Inventory of Depressive Symptomatology, Clinician Rating (QIDS-C) and Self-Report (QIDS-SR) in public sector patients with mood disorders: a psychometric evaluation. Psychological Med. 2004;34:73–82. doi: 10.1017/S0033291703001107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Pedrelli P, Blais MA, Alpert JE, Shelton RC, Walker RSW, Fava M. Reliability and validity of the Symptoms of Depression Questionnaire (SDQ) CNS Spectr. 2014;19:535–46. doi: 10.1017/S1092852914000406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Hamilton M. The assessment of anxiety states by rating. Br J Med Psychol. 1959;32:50–5. doi: 10.1111/j.2044-8341.1959.tb00467.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Dunlop BW, Li T, Kornstein SG, Friedman ES, Rothschild AJ, Pedersen R, et al. Concordance between clinician and patient ratings as predictors of response, remission, and recurrence in major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2011;45:96–103. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2010.04.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.