Table 4.
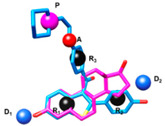
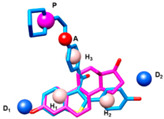
The alignment of best hypotheses pharmacophoric features (A: hydrogen-bond acceptor, D: hydrogen bond donor, R: ring feature, H: hydrophobic feature, P: positive ionizable feature) against 1ERR (blue) and 1ERE (pink). Scores of the different parameters (the upper part) and PLS statistical parameters (the lower part) of the top two hypotheses.
| ADDRRRP.11 | ADDHHHP.13 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||||||||
| HID a | S b | S-I c | P-H d | S e | V f | VOL g | SE h | M i | A j | I k |
| ADDRRRP.11 | 3.741 | 0.967 | 6.429 | 0.81 | 0.991 | 0.426 | 2.678 | 17 | 9.52 | 1.751 |
| ADDHHHP.13 | 3.743 | 0.963 | 6.432 | 0.83 | 0.993 | 0.431 | 2.674 | 17 | 9.30 | 1.755 |
| PLSF l | r 2 m | SD n | F o | P p | Stability q | q 2 LOO r | q 2 LSO s | q 2 YS LOO t | q 2 YS LSO u | |
| ADDRRRP.11 | 5 | 0.949 | 0.264 | 61.3 | 4.38e−15 | 0.971 | 0.825 | 0.627 | −0.234 | −0.247 |
| ADDHHHP.13 | 5 | 0.951 | 0.257 | 61.4 | 4.41e−15 | 0.977 | 0.826 | 0.659 | −0.241 | −0.258 |
a Hypothesis identification; b Survival score; c Survival-inactives score; d Post-hoc—the result of rescoring; e Site score—an RMDS value for the site points superimposition in an alignment to the pharmacophore of the structures that contribute to this hypothesis; f Vector alignment score; g Volume of the contributing structures’ overlap when aligned on the pharmacophore; h Selectivity—the fraction of molecules matching the hypothesis regardless of their potency; i Matches—number of actives that match the hypothesis; j Activity—Activity of the reference ligand (pIC50); k Inactive—Survival score of inactives; l PLS factor, i.e., N/5, where N is the number of ligands present in the training set; m Conventional square-correlation coefficient. n Standard deviation of regression; o Ratio of the model variance to the observed activity variance; p Significance level of variance ratio; q Stability of the model predictions to changes in the training set composition; r Cross-validation correlation coefficient using the leave-one-out (LOO) method. s Cross-validation correlation coefficient using the leave-some-out (LSO) method with 5 random groups; t Average cross-validation correlation coefficient using the leave-one-out (LOO) method obtained after Y-scrambling process. u Average cross-validation correlation coefficient using the leave-some-out (LSO) method with 5 random groups obtained after the Y-scrambling process.
