Summary
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the leading cause of death in the Americas and raised blood pressure accounts for over 50% of CVD. In the Americas over a quarter of adult women and four in ten adult men have hypertension and the diagnosis, treatment and control are suboptimal. In 2021, the World Health Organization (WHO) released an updated guideline for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension in adults. This policy paper highlights the facilitating role of the WHO Global HEARTS initiative and the HEARTS in the Americas initiative to catalyze the implementation of this guideline, provides specific policy advice for implementation, and emphasizes that an overarching strategic approach for hypertension control is needed. The authors urge health advocates and policymakers to prioritize the prevention and control of hypertension to improve the health and wellbeing of their populations and to reduce CVD health disparities within and between populations of the Americas.
Keywords: Hypertension, High blood pressure, Health policy, Clinical guideline, Health services, Public health, Cardiovascular disease
Introduction
In the Americas, cardiovascular diseases (CVD) are the leading cause of death, responsible for 29% of all lives lost (>2 million deaths in 2019).1, 2, 3 CVD is also the leading cause of disability in the region.1 High blood pressure (BP), is the most important reversible risk factor for CVD and death, with over 50% of CVD events and 17% of overall deaths being attributed to elevated BP in the Americas.1,4
In the America's over a quarter of women and four in ten men (aged 30–79 years) have hypertension (defined as BP ≥ 140/90 mmHg or taking antihypertensive drugs) and the rates of diagnosis, treatment and control of hypertension are suboptimal.3 Indeed, only 35% of women and 23% of men with hypertension have their BP controlled to an SBP/DBP <140/90 mmHg in Latin America and the Caribbean.3 Using the newer World Health Organization recommendations for initiation of antihypertensive pharmacotherapy, the prevalence of adults recommended for antihypertensive drug therapy is much higher, and consequently, the rates for treatment and control are much lower.3,5 In most countries in the region, the prevalence of hypertension is increasing with only modest gains in treatment and control rates since 1990.3 Although, hypertension is unlikely to have a causal link it is the most common risk associated with COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) infection and death.6
Approximately 8% of the region's healthcare spending is attributed to high blood pressure, a wise use of resources as control of hypertension reduces death and disability and is highly cost-effective or cost-saving in most settings.7 For example, the effective management of CVD risks, including hypertension, has an estimated return on investment of 3:1 in low and middle-income countries (LMIC).8
There is high variability in the prevalence of hypertension and its detection, treatment and control between countries and within important subpopulations within countries.1,3 This variability leads to large disparities in cardiovascular death and disability with large economic consequences extending from the personal to the global level.1,3,9 In part, some of this variation may be attributed to variations in guidelines and their implementation10. In the past 5–10 years, important global and regional technical documents have been produced that provide an opportunity to optimize the prevention, treatment and control of the cardiovascular disease. These documents highlight the prevention and control of hypertension.11, 12, 13, 14
This health policy manuscript was developed by a group of senior public health, global health, clinical, and hypertension experts primarily to facilitate the implementation and integration of the new WHO pharmacotherapy of hypertension guideline with other global and regional technical documents.15,16 The manuscript is also intended to be a resource to those advocating to policymakers. Firstly, we highlight the facilitating role of the Global HEARTS initiative and the HEARTS in the Americas initiative to catalyze the implementation of the WHO guideline on hypertension.11,17 Secondly, we provide suggestions for policymakers and health services managers which can also be used in advocacy by health scientists, clinicians, and organizations. Finally, the document emphasizes that beyond the WHO Hypertension guideline, a strategic approach for hypertension control is needed. Although important in the prevention and control of hypertension, the WHO pharmacotherapy of hypertension guidelines and this manuscript do not address individual lifestyle interventions to control hypertension.
The global HEARTS initiative and the HEARTS in the Americas program: the CVD risk reduction approach through hypertension management
In response to the global health threat from CVD, the World Health Organization (WHO) global HEARTS Initiative supports countries strengthening actions to prevent CVD, such as enhanced tobacco control, dietary salt reduction, increasing physical activity, elimination of industrially-produced dietary trans fat, and management of CVD risks.11 From the health service side, the WHO HEARTS is a technical package that aims to strengthen primary care management of CVD and its risk factors, with hypertension being the most common and therefore main point of entry.18,19
The WHO HEARTS technical package provides support to standardize and optimize 6 essential clinical care areas, including Healthy lifestyle counseling, Evidence-based treatment of hypertension and diabetes using simple directive protocols, Access to high quality long-acting affordable medications and technology (e.g., validated automated BP devices), CVD risk assessment, Team-based care and Systems for monitoring.18
In the Americas, many asymptomatic adults do not access the health care system. For those who do, many individuals with undiagnosed hypertension are not screened and are thus unaware of their condition.3 Further, not all of those diagnosed with hypertension are treated, and a substantial proportion is undertreated and does not have their BP controlled.3 In response to the unmet need to detect, treat, and control high BP, the Pan American Health Organization (PAHO) with partner organizations and ministries of health have developed the HEARTS in the Americas initiative, a regional adaptation of the WHO HEARTS technical package, to enhance hypertension management and reduce CVD.12,13
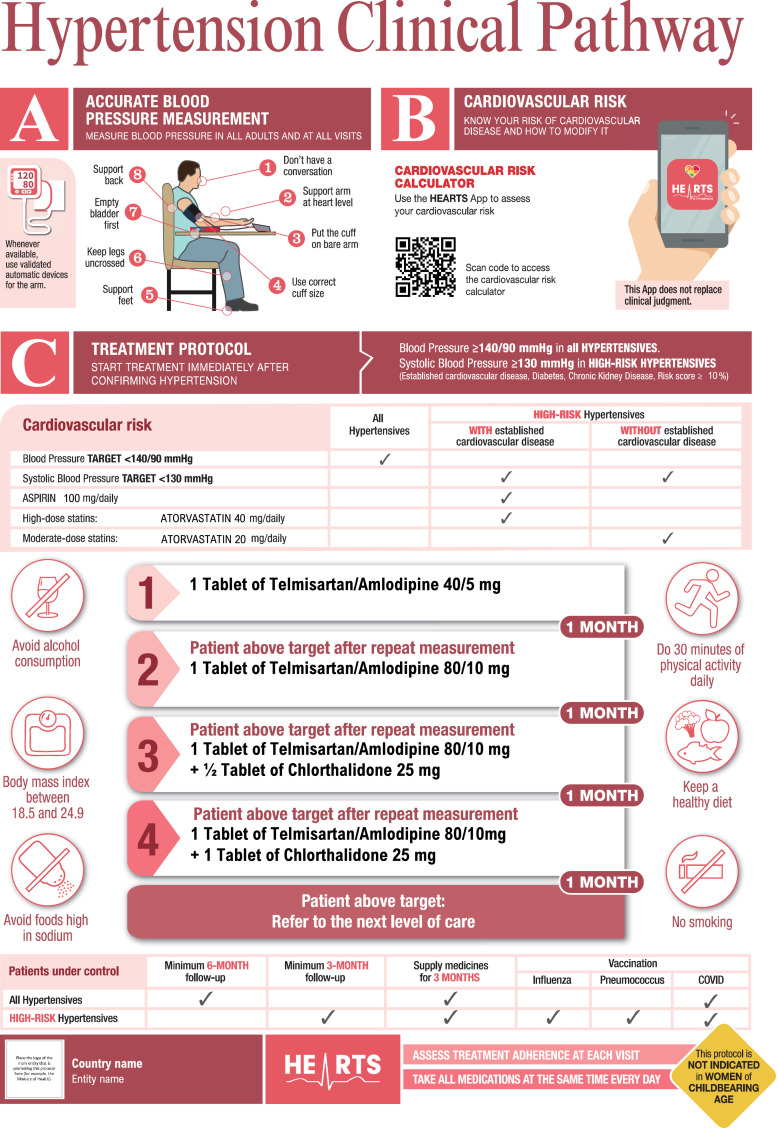
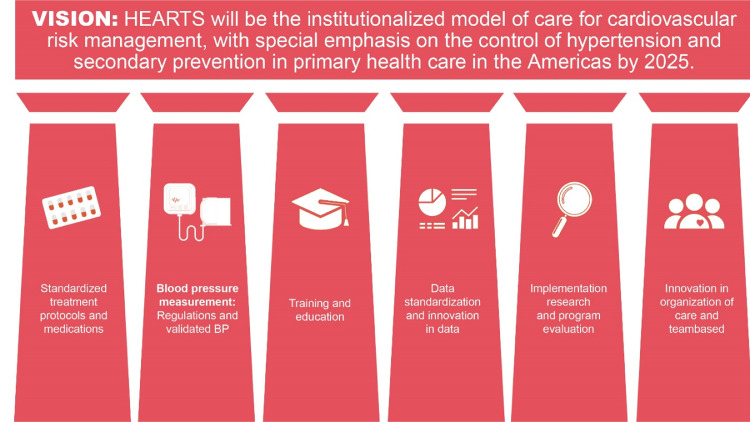
HEARTS in the Americas provides technical assistance for developing a strategic systematic public health approach to hypertension control.12,20,21 The program is focused on a hypertension treatment cascade approach that seeks to achieve increased awareness, treatment, and control of hypertension to reduce relevant ‘care gaps’.12,13,22 The pillars of the HEARTS in the Americas initiative are (1) use of standardized diagnostic and treatment protocols, (2) accurate reproducible BP measurement with recently trained and preferably certified observers who use accuracy validated automated BP devices, (3) standardized training for team-based patient-centred care, (4) standardized data collection to monitor, evaluate and report on the overall program, health regions, clinic and clinician performance, (5) the use of implementation research methods to guide program implementation and evolution and (6) innovation in patient-centred team-based health care (Figure 1).12 HEARTS in the Americas is currently being implemented in 20 countries and is the major model of care for CVD risk management in this region.17
Figure 2.
HEARTS in the Americas suggested prototype of an integrated clinical pathway and standardized hypertension treatment algorithm*
*The medications serve as examples and can be replaced with any two medications from any of the three drug classes (ACEis/ARBs, CCBs or thiazide/thiazide-like diuretics). Start with a single-pill combination (fixed-dose combination) or two individual pills if FDC is not available.
Figure 1.
The pillars of the HEARTS in the Americas initiative.
Substantial improvements in hypertension control have been documented in preliminary analyses of pilot interventions from the program.23,24
While much of the HEARTS technical package is reflected in the 2021 WHO Guideline for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension in adults, the guideline provides updated and more specific recommendations and is an official WHO normative guideline.15,16
The 2021 WHO hypertension guideline: policy implication
In 2021, the WHO released the updated Guideline for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension in adults (WHO Guidelines).15,16 This guideline focuses on specific critical apriori questions related to (1) the BP threshold for initiation of pharmacological treatment, (2) laboratory testing, (3) how and when to use CVD risk assessment to guide the initiation of antihypertensive drugs, (4) drug classes to be used as first-line agents, (5) combinations of antihypertensive drug therapy, (6) target BP, (7) frequency of reassessment, and (8) administration of treatment by nonphysician healthcare professionals. Systematic reviews, when available, were assessed for each question, and in the absence of systematic reviews, primary research was examined. The GRADE method was used to assess the strength and certainty of recommendations. The Guideline also includes examples of standardized and simple treatment algorithms using specific drugs and doses. Notably, this new Guideline put a considerable emphasis on implementation.
We review each of eight WHO 2021 guideline recommendations (Table 1) and provide specific programmatic and policy recommendations for implementation (Table 2).
Table 1.
WHO guideline recommendations for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension in adults.
| Recommendation | Strength of recommendation/certainty of evidence |
|---|---|
| Recommendation on Blood Pressure Threshold for Initiation of Pharmacological Treatment | |
| Initiate pharmacological antihypertensive treatment of individuals with a confirmed diagnosis of hypertension and systolic blood pressure of ≥ 140 mmHg or diastolic blood pressure of ≥ 90 mmHg. | Strong / moderate to high |
| Initiate pharmacological antihypertensive treatment of individuals with existing cardiovascular disease (CVD) and systolic blood pressure of ≥ 130 mmHg. | Strong / moderate to high |
| Suggests pharmacological antihypertensive treatment of individuals without CVD but with high CVD risk, diabetes mellitus, or chronic kidney disease, and systolic blood pressure of 130–139 mmHg. | Conditional / low |
| Recommendation on Laboratory Testing | |
| Suggests obtaining tests to screen for comorbidities and secondary hypertension when starting pharmacological therapy for hypertension, but only when testing does not delay or impede starting treatment. | Conditional / low |
| Recommendation on CVD Risk Assessment | |
| Suggests CVD risk assessment at or after the initiation of pharmacological treatment for hypertension, but only where this is feasible and does not delay treatment. | Conditional / low |
| Recommendation on Drug Classes to be Used as First-Line Agents | |
Use of drugs from any of the following three classes of pharmacological antihypertensive medications as an initial treatment in those requiring pharmacological treatment:
|
Strong / high |
| Recommendation on Combination Therapy | |
| Suggests combination therapy, preferably with a single-pill combination (to improve adherence and persistence), as an initial treatment for adults with hypertension requiring pharmacological treatment. Antihypertensive medications used in combination therapy should be chosen from the following three drug classes: diuretics (thiazide or thiazide-like), ACEIs/ARBs, and long-acting dihydropyridine calcium channel blockers (CCBs). | Conditional / moderate |
| Recommendations on Target Blood Pressure | |
| Recommends a target blood pressure treatment goal of < 140/90 mmHg in all patients with hypertension without comorbidities. | Strong / moderate |
| Recommends a target systolic blood pressure treatment goal of <130 mmHg in patients with hypertension and known CVD. | Strong / moderate |
| Suggests a target systolic blood pressure treatment goal of <130 mmHg in high-risk patients with hypertension (those with high CVD risk, diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease). | Conditional / moderate |
| Recommendations on Frequency of Assessment | |
| Suggests a monthly follow up after initiation or a change in antihypertensive medications until patients reach target. | Conditional / low |
| Suggests a follow up every 3–6 months for patients whose blood pressure is under control. | Conditional / low |
| Recommendation on Treatment by Non-physician Professionals | |
| Suggests that pharmacological treatment of hypertension can be provided by nonphysician professionals such as pharmacists and nurses, if the following conditions are met: proper training, prescribing authority, specific management protocols and physician oversight. | Conditional / low |
Table 2.
HEARTS in the Americas. Policies and programs recommended to support the WHO guideline recommendations for the pharmacological treatment of hypertension in adults.
| 2021 WHO guideline recommendation category15,16 | HEARTS in the Americas key programmatic and policy recommendations. |
|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
During the last several years, non-governmental organizations such as Resolve to Save Lives,33 World Heart Federation,34 Lancet Commission on Hypertension,35 and the World Hypertension League (WHL)4 have also produced position statements and ‘calls to action’ on the clinical management of hypertension at a population level (Table 3). These non-governmental positions complement the new WHO hypertension guideline by helping to identify and address barriers to hypertension control and by aligning health care professionals with the need for systematic public health approaches to control hypertension. However, in addition to the health system change, the introduction of new guidelines requires clinicians to change practice to implement the recommendations and change may be resisted by some. That is why these guidelines were developed by the WHO with stakeholder and expert engagement, including from the Americas, and they are strongly supported by NGO's that are leading work in this area, including RTSL and the WHL.
Table 3.
Some international non-governmental organization websites, statements and positions relevant to population hypertension control.
| Innitiative | Refs. |
|---|---|
| Resolve to Save Lives. | 28,31 |
| World Heart Federation Roadmap for Hypertension – a 2020 Update. | 29 |
| World Hypertension League and partners São Paulo call to action for the prevention and control of high blood pressure. | 4 |
| The Lancet Commission on Hypertension call to action and a life course strategy to address the global burden of high blood pressure on current and future generations. | 30 |
| Lancet commission on hypertension position statements on the global improvement of accuracy standards for devices that measure blood pressure and optimizing observer performance of clinic blood pressure measurement. | 27,32 |
Beyond the WHO hypertension guideline, a strategic approach for hypertension control is needed
While the WHO Guidelines focus on drug treatment, the authors recognize the fundamental importance of universal access to health care and the role of resilient and primary care-oriented health systems for the inclusive and equitable implementation of this Guideline. Thus, for this Guideline to be successfully implemented, it must be integrated into a public health systems approach, such as the HEARTS in Americas initiative. For example, implementation is likely to require policy to change the capacity, accessibility, affordability, and quality of primary care and drug treatments. To facilitate WHO Guideline implementation, all countries of the America's should prioritize implementing the HEARTS in Americas Initiative. Countries that are participating in the HEARTS in Americas initiative should urgently scale access to their full population. A broader societal approach is also needed for hypertension prevention and control, including policy change to improve nutrition, reduce salt intake, eliminate industrially-produced trans fat, facilitate physical activity, and reduce tobacco use.
In keeping with the substantial economic and disease burden of CVD, and with attention to the voluntary World Health Assembly target to reduce uncontrolled BP by 25% by the year 2025, all national governments should have hypertension control as a national health priority. For example, in the US, the Surgeon General has declared hypertension control a national priority.37 Any such action should have allocated a budget compatible with achieving the population BP control target, a strategic and operational plan, and a governmental - non-governmental technical working group to oversee the implementation.9 The monitoring and evaluation framework for hypertension initiatives developed by the PAHO and WHL outlines the key features of a hypertension strategy and operational plan.38 The framework provides detailed qualitative and quantitative indicators that can be used in developing and monitoring initiatives for hypertension control.
A hypertension strategy can be mainly based on the WHO HEARTS technical package. Best practices that are included in the model can be adapted to the national context (health care structure, resources, culture, etc.).4,18,34,35,39 The strategy should be iterative when implemented, improving in design as local lessons demonstrate more effective approaches. National and regional capacity building should be continuous and based on implementation research concepts/resources and regular program review. The program should have short-term and long-term targets for hypertension control and focus on enhancing the quality of care provided.
Systematic implementation of the WHO guideline globally would likely reduce the current disparities in death and disability resulting from disparate thresholds for treatment and control in national hypertension programs. However, guidelines need to be adapted by countries when implemented to ensure they meet the specific needs of their populations. WHO Guideline is but one approach to achieve the common goal of preventing and reducing CVD and eliminating health inequities. Other institutions and organizations will have suggestions for implementing these and other guidelines based on national and local contexts. The additional input is welcomed and encouraged to control this critical public health problem. We also acknowledge that all guidelines, including those of the WHO, need clinicians to consider the context of the specific patient (e.g., drug allergy, indications for other treatments, patient autonomy, etc.) in implementing recommendations.
Additional policies to address barriers to hypertension control
There are many barriers to hypertension control at the patient, provider, and health systems level.34,35 Hence there is a need to reassess the overall policy approach to enhance primary care delivery using a systematic public health patient-centred approach. The preceding sections outlined fundamental programmatic changes essential to implementing the WHO Hypertension Guideline. Additional critical areas for policy change to overcome some of the barriers are listed in Table 4.
Table 4.
Some barriers to and policies that could enhance hypertension control.
| Barrier | Policies and programs to address barrier |
|---|---|
| Lack of knowledge, behaviors and skills of people with and at risk for hypertension | Programs that enhance public health literacy, skills and behavior change related to hypertension (e.g., the US national plan to improve health literacy).35 |
| Inequity in access to affordable, high quality, easily accessible care and treatment | Ensure adequate resource allocation to ensure easy access to high quality affordable services for underserved populations and include marginalized populations in the design and implementation of programs. Establish monitoring frameworks that assess and report outcomes on underserved subgroups and modify programs to address inequitable outcomes. |
| Lack of knowledge, behaviors and skills of health care professionals | Restructure training programs for all health care professionals (undergraduate and continuing health care education) to be competency based and emphasize team-based patient-centered public health approaches with quality-of-care monitoring to screening, diagnosis, treatment, and control of non-communicable diseases, including hypertension. PAHO has a standardized and very successful hypertension education program for the primary health care team.36 |
| The health system is designed for acute care and is centered around health care professionals | Evolve the health care system and its infrastructure to deliver high-quality primary care that is easily accessible (e.g., home-based care, worksite, community centers) and affordable (preferably free or low cost).37 Utilize technology to make care more effective and efficient (e.g., smart phones, telemedicine) |
| Lack of screening for and diagnosis of hypertension | Develop a national hypertension screening program to detect the vast majority of people with hypertension. Screening sites should include community resources and examples include old age care homes, dentist offices, blood donation sites, shopping centers, community centers, fire stations, places of worship and barber shops. Resources are available to aid the development of hypertension screening programs.38,39 |
| Suboptimal quality of care | Develop a quality-of-care culture using protocols to report performance to the overall program as well as clinics and clinicians. Develop recognition awards for clinics and clinicians with high performance (e.g., Million Hearts Hypertension Control Champions).40 |
| Lack of program monitoring | Build monitoring and evaluation indicators into the hypertension control program. A PAHO-WHL monitoring, and evaluation framework outlines the key indicators. 33 Regularly report progress to the program and, where appropriate, clinics and clinicians. |
| Lack of adherence to treatment and clinic visits | In training programs emphasize improving adherence to treatments and visits. Some strategies like ensuring treatment regimes in protocols are affordable and straightforward, use of single pill drug combinations, 90-to-120-day prescriptions when targets are met, blister packs, health care professional monitoring of adherence, follow-up of patients who miss appointments, engagement of families in the treatment plan, provision of standardized information on hypertension with individualized written instruction where appropriate, can help to improve adherence.41 |
| Inaccurate BP devices | Develop regulations to only allow the sale of accuracy validated devices for clinical use (including home and ambulatory BP devices)*.26,27 |
| Inaccurate assessment of BP | Ensure those screening for hypertension and those diagnosing hypertension use an accuracy validated automated BP device and have been trained and certified to use the device. There is a standardized PAHO-WHL online training program42,43 and a list of validated automated blood pressure measuring devices44 at the HEARTS in the Americas webpage.17 |
| Lack of identification of people whose blood pressure is high or normal only when outside the clinic setting (e.g., white coat hypertension and masked hypertension)** | Where feasible and affordable, encourage the use of out-of-clinical office BP readings (i.e., community, home or ambulatory) to confirm the diagnosis and monitor BP control.45,46 Ambulatory blood pressure devices are designed to take many blood pressure readings at regular intervals in people who follow their usual daily routines. Home blood pressures are those taken in a home environment, while community blood pressures refer to readings taken outside the home and clinical office (e.g., a pharmacy). |
*an accuracy validated automated BP device has passed accepted national or international accuracy standards testing by an independent group of investigators.26,27
⁎⁎white coat hypertension is a clinical condition where a person only has high blood pressure in the clinical office and normal blood pressure outside the clinical office. Masked hypertension is a clinical condition where a person has high blood pressure outside the clinical office and normal blood pressure in the clinical office.
Conclusion
The HEARTS in the Americas initiative is aligned with the PAHO Strategy for Universal Access to Health and Universal Health Coverage and the PAHO approach for universal primary health care.47,48 HEARTS in the Americas provides a state-of-the-art, systematic public health approach to controlling hypertension with a focus on primary health care. Likewise, the new WHO Guideline provides added value with updated thresholds and approaches for treating and controlling hypertension.16
There has been significant progress to improve hypertension control in the HEARTS in the Americas interventions. Outside of high-income global regions, Latin America and the Caribbean countries have higher hypertension control rates than other global regions.3,12,24 However, success is still largely within national pilot programs and in many countries, hypertension control is not yet a health system priority and it remains underfunded, despite all clinical interventions, antihypertensive drug therapy has arguably the most substantial evidence that it reduces death and disability and has a favourable return on investment. So, the opportunities are now more promising than ever to utilize hypertension control to enhance population health and eliminate related health inequities. Countries can take advantage of these opportunities by setting a high priority to control hypertension as a model for other NCD management and implement transformative policies.
The authors urge health policymakers to reexamine and upgrade the priority for the prevention and control of hypertension to improve the health and wellbeing of their populations and to reduce health disparities within and between populations of the Americas. We further urge health advocates and health organizations to utilize the opportunities provided by the recently released World Health Organization hypertension pharmacological treatment guideline and the HEARTS in the Americas Initiative to activate policymakers and to create the political will to improve the control of the top global and regional risk for death, uncontrolled blood pressure.
Contributors
PO conceived the idea and guided the document development. NRCC drafted the first draft manuscript. All authors reviewed and revised the manuscript and approved the final version.
Declaration of interests
NRCC reports personal fees from Resolve to Save Lives (RTSL), the Pan American Health Organization, and the World Bank outside the submitted work; and support for attending meetings from Resolve to Save Lives (RTSL), the Pan American Health Organization, and World Health Organization. He is also an unpaid advisor to the board of the World Hypertension League. The following authors declare no financial COI. PO, MPB, AR, VI, SYA,JC, ER, PKW, JWB, MGJ PO is a staff member of the Pan American Health Organization. AR and NRCC are international consultants in the same organization. However, authors alone are responsible for the views expressed in this publication, and they do not necessarily represent those of the Pan American Health Organization.
Footnotes
Editor note: The following translations in Portuguese and Spanish are provided by the authors. Our editorial processes have only been applied to the original article in English, which should serve as reference for this work. https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/55964 (Portuguese) https://doi.org/10.26633/RPSP.2022.55; https://iris.paho.org/handle/10665.2/55963 (Spanish) https://doi.org/10.26633/RPSP.2022.54.
References
- 1.Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation. GBD compare/Viz Hub. 2022; published online. http://vizhub.healthdata.org/gbd-compare/. Accessed 26 Feb 2022.
- 2.Martinez R., Soliz P., Mujica O.J., et al. The slowdown in the reduction rate of premature mortality from cardiovascular diseases puts the Americas at risk of achieving SDG 3.4: a population trend analysis of 37 countries from 1990 to 2017. J Clin Hypertens. 2020;22:1296–1309. doi: 10.1111/jch.13922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Zhou B., Carrillo-Larco R.M., Danaei G., et al. Worldwide trends in hypertension prevalence and progress in treatment and control from 1990 to 2019: a pooled analysis of 1201 population-representative studies with 104 million participants. Lancet. 2021;398:957–980. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)01330-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Campbell N.R.C., Schutte A.E., Varghese C.V., et al. São Paulo call to action for the prevention and control of high blood pressure: 2020. J Clin Hypertens. 2019;21(12):1744–1752. doi: 10.1111/jch.13741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fan W.G., Xie F., Wan Y.R., Campbell N.R.C., Su H. The impact of changes in population blood pressure on hypertension prevalence and control in China. J Clin Hypertens. 2020;22:150–156. doi: 10.1111/jch.13820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ferat L.R., Forrest R., Sehmi K., et al. Preventing the next pandemic: the case for investing in circulatory health-a global coalition for circulatory health position paper. Glob Heart. 2021;16(1):66. doi: 10.5334/gh.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Gaziano T.A., Bitton A., Anand S., Weinstein M.C. The global cost of nonoptimal blood pressure. J Hypertens. 2009;27(7):1472–1477. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0b013e32832a9ba3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2018. Saving Lives, Spending Less: a Strategic Response to Noncommunicable Diseases. (WHO/NMH/NVI/18.8). Licence: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO. [Google Scholar]
- 9.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2014. Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Disease 2014. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Sudharsanan N., Theilmann M., Kirschbaum T.K., et al. Variation in the proportion of adults in need of BP-lowering medications by hypertension care guideline in low- and middle-income countries: a cross-sectional study of 1,037,215 individuals from 50 nationally representative surveys. Circulation. 2021;143:991–1001. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.051620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2016. Global Hearts Initiative, Working Together to Promote Cardiovascular Health. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Campbell N.R.C., Ordunez P., Giraldo G., et al. WHO HEARTS: a global program to reduce cardiovascular disease burden: Experience implementing in the Americas and opportunities in Canada. Can J Cardiol. 2021;37(5):744–755. doi: 10.1016/j.cjca.2020.12.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ordunez P., Martinez R., Niebylski M.L., Campbell N.R. Hypertension prevention and control in Latin America and the Caribbean. J Clin Hypertens. 2015;17(7):499–502. doi: 10.1111/jch.12518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ordunez P., Campbell N. Global health metrics and non-communicable diseases: the case of hypertension. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2015;3(10):763. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(15)00319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2021. Guideline for the Pharmacological Treatment of Hypertension in Adults. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Al-Makki A., DiPette D., Whelton P.K., et al. Hypertension pharmacological treatment recommendations in adults. A World Health Organization guidelines executive summary. Hypertension. 2022;79:293–301. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.121.18192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pan American Health Organization . Pan American Health Organization; 2021. HEARTS in the Americas. https://www.paho.org/en/hearts-americas (accessed Oct 4 2021) [Google Scholar]
- 18.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2016. HEARTS: Technical Package for Cardiovascular Disease Management in Primary Health Care. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kessner D.M., Kalk C.E., Singer J. Assessing health quality-the case for tracers. NEJM. 1973;288(4):189–194. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197301252880406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ordunez P., Luciani S., Barojas A., Fitzgerald J., Hennis A.J. A public health approach to hypertension. Lancet. 2015;385(9980):1833. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60924-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.DiPette D.J., Goughnour K., Zuniga E., et al. Standardized treatment to improve hypertension control in primary health care: the HEARTS in the Americas initiative. J Clin Hypertens. 2020;22:2285–2295. doi: 10.1111/jch.14072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Patel P., Ordunez P., DiPette D., et al. Improved blood pressure control to reduce cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality: the standardized hypertension treatment and prevention project. J Clin Hypertens. 2016;18:1284–1294. doi: 10.1111/jch.12861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Valdés González Y., Campbell N.R.C., Pons Barrera E., et al. Implementation of a community-based hypertension control program in Matanzas, Cuba. J Clin Hypertens. 2020;22(2):142–149. doi: 10.1111/jch.13814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2020. Improving Hypertension Control in 3 Million People: Country Experiences of Programme Development and Implementation. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pan American Health Organization . HEARTS in the Americas: Protocols and Medications. Pan American Health Organization; 2020. HEARTS in the Americas: protocols and medications.https://www.paho.org/en/hearts-americas/hearts-americas-protocols-and-medications Accessed 18 Aug 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Resolve to Save Lives, Links Community. LINKS is a global community for cardiovascular health. 2022; published online. https://resolvetosavelives.org/cardiovascular-health/links. Accessed 25 Sept 2021.
- 27.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2017. HEARTS Technical Package for Cardiovascular Disease Management in Primary Health Care: Evidence-Based Treatment Protocols; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- 28.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2018. HEARTS Technical Package for Cardiovascular Disease Management In Primary Health Care: Implementation Guide; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sánchez R.A., Boggia J., Peñaherrera E., et al. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring over 24 h: a Latin American Society of Hypertension position paper-accessibility, clinical use and cost effectiveness of ABPM in Latin America in year 2020. J Clin Hypertens. 2020;22(4):527–543. doi: 10.1111/jch.13816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pan American Health Organization . Pan American Health Organization; 2021. How to Optimize the Use of CVD Risk Evaluation. https://www.paho.org/cardioapp/web/#/optimizerisk. Accessed 4 Oct 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 31.Pan American Health Organization . Pan American Health Organization; 2021. PAHO Strategic Fund.https://www.paho.org/en/paho-strategic-fund Accessed 4 Oct 2021. [Google Scholar]
- 32.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; Geneva: 2020. WHO Technical Specifications for Automated Non-Invasive Blood Pressure Measuring Devices with Cuff; pp. 1–68. [Google Scholar]
- 33.Resolve to save lives. Resolve to save lives. 2022; published online 2022. https://www.resolvetosavelives.org/. Accessed 4 Oct 2017.
- 34.Jeemon P., Severin T., Balanbanova D., et al. World heart federation roadmap for hypertension-a 2020 update. Glob Heart. 2021;16(1):63. doi: 10.5334/gh.1066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Olsen M.H., Angell S.Y., Asma S., et al. A call to action and a lifecourse strategy to address the global burden of raised blood pressure on current and future generations: the Lancet Commission on Hypertension. Lancet. 2016;388(10060):2665–2712. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31134-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Padwal R., Campbell N.R.C., Schutte A.E., et al. Optimizing observer performance of clinic blood pressure measurement: a position statement from the lancet commission on hypertension group. J Hypertens. 2019;37:1737–1745. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.U.S. Department of Health and Human Services . Department of Health and Human Services; Washington, DC: U.S: 2020. The Surgeon General's Call to Action to Control Hypertension; pp. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Campbell N.R.C., Ordunez P., DiPette D.J., et al. Monitoring and evaluation framework for hypertension programs. A collaboration between the Pan American Health Organization and World Hypertension League. J Clin Hypertens. 2018;20:984–990. doi: 10.1111/jch.13307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Campbell N.R.C., Niebylski M. Prevention and control of hypertension: developing a global agenda. Current Opinion in Cardiology. 2014;29(4):324–330. doi: 10.1097/HCO.0000000000000067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.US. Department of Health and Human Services, Office of Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. National action plan to improve health literacy. 2010;published online 2010. https://health.gov/our-work/national-health-initiatives/health-literacy/national-action-plan-improve-health-literacy. Accessed 26 Feb 2022
- 41.Pan American Health Organization . Pan American Health Organization; 2020. HEARTS in the Americas: Virtual Courses.https://www.paho.org/en/hearts-americas/hearts-americas-virtual-courses Accessed 18 Aug 2020. [Google Scholar]
- 42.World Health Organization . World Health Organization; 2021. Primary Health Care. https://www.who.int/health-topics/primary-health-care#tab=tab_1 (accessed Oct 4, 2021) [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mangat B.K., Campbell N., Mohan S., et al. Resources for blood pressure screening programs in low resource settings: A guide from the world hypertension league. J Clin Hypertens. 2015;17(6):418–420. doi: 10.1111/jch.12499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Beaney T., Burrell L.M., Castillo R.R., et al. May measurement month 2018: a pragmatic global screening campaign to raise awareness of blood pressure by the international society of hypertension. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:2006–2027. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Barbosa E.C.D., Ramirez A., Beaney T., et al. May measurement month 2017: Latin America. J Hypertens. 2020;38(6):1183–1188. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Million Hearts. Hypertension control champions. 2021;published online March 23, https://millionhearts.hhs.gov/partners-progress/champions/index.html. Accessed 4 Oct 2021.
- 47.53rd Directing council, 66th session of the regional committee of WHO for the Americas. Strategy for universal access to health and universal health coverage. 2014; published online Oct 2. https://www.paho.org/hq/dmdocuments/2014/CD53-R14-e.pdf. Accessed 4 Oct 2021.
- 48.57th Directing Council, 71st Session of the regional committee of WHO for the AMERICAS. Primary health care for universal health. 2019; published online July 19. https://iris.paho.org/bitstream/handle/10665.2/51630/CD57-INF-5-e.pdf?sequence=1&isAllowed=y. Accessed 4 Oct 2021.