Abstract
Background
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs in one‐third of critically‐ill COVID‐19 patients. Although prior studies identified several pathways contributing to thrombogenicity, it is unknown whether this is COVID‐19‐specific or also occurs in ARDS patients with another infection.
Objective
To compare pathway activity among patients having COVID‐19 with PE (C19PE+), COVID‐19 without PE (C19PE‐), and influenza‐associated ARDS (IAA) using a targeted proteomics approach.
Methods
We exploited an existing biorepository containing daily plasma samples to carefully match C19PE+ cases to C19PE‐ and IAA controls on mechanical ventilation duration, PEEP, FiO2, and cardiovascular‐SOFA (n = 15 per group). Biomarkers representing various thrombosis pathways were measured using proximity extension‐ and ELISA‐assays. Summed z‐scores of individual biomarkers were used to represent total pathway activity.
Results
We observed no relevant between‐group differences among 22 biomarkers associated with activation of endothelium, platelets, complement, coagulation, fibrinolysis or inflammation, except sIL‐1RT2 and sST2, which were lower in C19PE‐ than IAA (log2‐Foldchange −0.67, p = .022 and −1.78, p = .022, respectively). However, total pathway analysis indicated increased activation of endothelium (z‐score 0.2 [−0.3–1.03] vs. 0.98 [−2.5–−0.3], p = .027), platelets (1.0 [−1.3–3.0] vs. −3.3 [−4.1–−0.6], p = .023) and coagulation (0.8 [−0.5–2.0] vs. −1.0 [−1.6–1.0], p = .023) in COVID‐19 patients (C19PE+/C19PE‐ groups combined) compared to IAA.
Conclusion
We observed only minor differences between matched C19PE+, C19PE‐, and IAA patients, which suggests individual biomarkers mostly reflect disease severity. However, analysis of total pathway activity suggested upregulation of some distinct processes in COVID‐19 could be etiologically related to increased PE‐risk.
Keywords: COVID‐19, influenza, pulmonary embolism, respiratory distress syndrome, thrombosis
Essentials
-
•
The COVID‐19 (C19) specific etiology of pulmonary embolism (PE) remains unknown.
-
•
Thrombosis biomarkers were compared between C19 patients with PE, without PE, and patients with influenza.
-
•
Biomarker levels were quite similar, but activity of endothelium, platelets and coagulation was higher in C19.
-
•
Individual biomarkers mostly reflect severe disease, but activity of some pathways may raise PE‐risk in C19.
Alt-text: Unlabelled Box
1. INTRODUCTION
A distinctive feature of COVID‐19 infection is hypercoagulability, characterized by high D‐dimer and fibrinogen concentrations as well as minor changes in clotting times and platelet counts.1., 2. This prothrombotic state has been coined COVID‐19 associated coagulopathy (CAC), with local microvascular thrombosis being documented by lung autopsies3 and macrovascular thrombosis observed in 10%–39% of critically‐ill patients.4., 5. Though reminiscent of disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC) in some respects, CAC typically lacks consumption coagulopathy, which suggests a distinct pathophysiology.
Excessive activation of endothelium, platelets and complement as well as formation of neutrophil extracellular traps have been reported in COVID‐19, and may drive thrombogenicity.3., 6., 7., 8., 9., 10., 11., 12., 13. However, it remains uncertain whether these findings are CAC‐specific or reflect more general features of the acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).
To advance our understanding of CAC we used a targeted proteomics approach, comparing COVID‐19 patients developing pulmonary embolism (C19PE+) to carefully matched (1) COVID‐19 patients without pulmonary embolism (C19PE‐), and (2) influenza‐associated ARDS (IAA) patients. We hypothesized that there would be upregulation of endothelial‐, platelet‐, complement‐, and pro‐coagulant pathways, and downregulation of anticoagulant and fibrinolytic pathways in COVID‐19 as compared to IAA, and that this would be more pronounced in C19PE+ compared to C19PE‐.
2. METHODS
2.1. Patients
We obtained clinical data and daily plasma samples from the Molecular Diagnosis and Risk Stratification of Sepsis (MARS) biorepository (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier NCT01905033), established in our tertiary ICU in the Netherlands from 2011 onwards. For this study, the Institutional Review Board approved an opt‐out method (protocol number 10‐056). Patients (>18 years) were eligible for the present study if they had been 1. admitted with influenza virus or SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and 2. had received invasive mechanical ventilation for at least 48 h. Immunocompromised patients (defined as a history of solid organ or stem cell transplantation, hematological malignancy, use of immunosuppressive medication, or chemotherapy or radiotherapy in the year before ICU admission) and those receiving therapeutic anticoagulation upon presentation were excluded.
At the time of study, the indication and timing of CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) in our ICU was determined by the occurrence of otherwise unexplained hemodynamic deterioration, right ventricular strain, worsening P/F‐ratio and/or increasing CO2‐gap, triggering a clinical suspicion of PE. Importantly, D‐dimer and fibrinogen levels were only rarely measured. Furthermore, we assumed patients in whom no CTPA had (ever) been obtained to have no, or at least no clinically relevant, thromboembolism.
In C19PE+ patients, we analyzed a plasma samples drawn 24 h prior to a clinical suspicion of PE (t1) as well as at start of therapeutic anticoagulation (t2). We then matched these cases to C19PE‐ and IAA controls (in a 1:1:1 ratio) for positive end‐expiratory pressure (PEEP), fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2), cardiovascular sequential organ failure assessment (cSOFA) score, and number of days on mechanical ventilation at t1. Timepoint t2 in controls was determined pairwise, using an interval between t1 and t2 identical to that observed in the C19PE+ case. If multiple control subjects were eligible for a case, we used random selection.
2.2. Samples
Protein biomarkers relating to 1. endothelial activation, 2. platelet activation, 3. coagulation, 4. fibrinolysis, and 5. inflammation pathways were measured in EDTA‐plasma by proximity extension assay (PEA), using multiplex Olink Cardiometabolic and Cardiovascular‐III immunoassay‐panels (Olink Proteomics). Although these panels measured 184 proteins, an a priori subselection of 20 proteins was used for the current analysis, based on their involvement in the above‐mentioned pathways. Lastly, complement activation was assessed as an additional pathway of interest, using ELISA assays. We focused on the formation of Complement‐5‐activation markers (C5a and sC5b‐9), since these markers were previously described as being increased in COVID‐19 patients with poor outcomes.14., 15.
2.3. Statistical analysis
We used Wilcoxon‐signed rank tests to compare individual biomarkers as well as total pathway activity among cases and controls. For the latter, we summed the z‐scores of individual biomarkers within each pathway (after sign‐inversion for biomarkers having a pathway‐inhibiting function). Subsequently, we used Mann‐Whitney U tests to compare COVID‐19 (i.e., C19PE+ and C19PE‐ combined) to IAA patients (as these groups were no longer paired). Associations among biomarkers were evaluated using Spearman correlation. Benjamini‐Hochberg correction was used in all tests to decrease the false discovery rate. Data were analyzed using R (v.4.0.2).
3. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
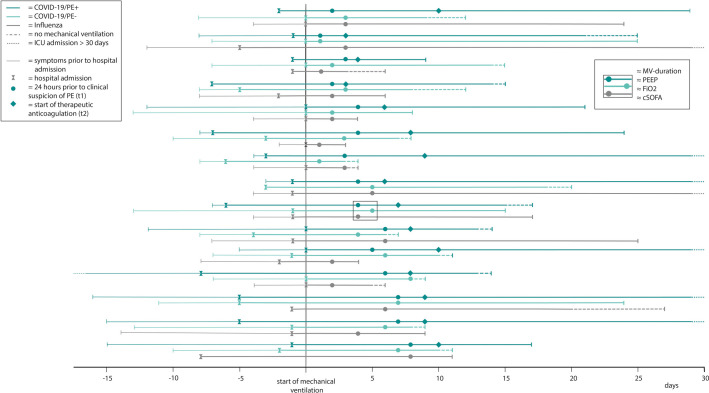
Fifteen C19PE+ cases were matched to C19PE‐ and IAA controls in a 1:1:1 ratio (Figure 1 ). For the C19PE+ cases, PE was located in the central arteries in three patients, in segmental arteries in seven patients, and in subsegmental arteries in five patients. Although matching on pre‐specified criteria was successful, IAA patients were younger compared to C19PE‐ and C19PE+ patients (median age 55 [IQR 50–64] vs. 65 [59–72] and 65 [59–69] years, respectively; p = .014), and had more often received corticosteroids prior to t1 (67% vs. 13% and 7%; p < .001). Key coagulation markers at t1 were comparable between groups, with an exception for platelet counts being lower in IAA patients (Table 1 ).
FIGURE 1.
Timelines of disease state and sample timing. We analyzed plasma samples drawn at t1 and t2 for COVID‐19/PE+patients. COVID‐19/PE‐ and influenza‐associated ARDS patients were matched for positive end‐expiratory pressure (PEEP), fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2), cardiovascular sequential organ failure assessment (cSOFA) score, and number of days on mechanical ventilation at t1. Timepoint t2 in controls was determined pairwise, using an interval between t1 and t2 identical to that observed in the COVID‐19/PE+case (not shown in this figure). PE+ = patients who developed pulmonary embolism, PE‐ = patients who did not develop pulmonary embolism
TABLE 1.
Patient characteristics
| COVID/PE+ N = 15 |
COVID/PE‐ N = 15 |
Influenza N = 15 |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| CT pulmonary angiogram | |||
| Number of scans/number of patients | 22/15 | 9/5 | 4/3 |
| Dalteparin prophylactic dose, No. (%) | |||
| Once‐daily 2500 IE | 0 (0) | 2 (13) | 4 (27) |
| Once‐daily 5000 IE | 12 (80) | 12 (80) | 11 (73) |
| Twice‐daily 5000 IE | 3 (20) | 1 (7) | 0 (0) |
| Laboratory values, median (IQR) (reference range) | |||
| Platelet count, ×109/L (150–450) | 257 [216–334] | 258 [201–296] | 64 [44.5–219] |
| White blood cell count, ×109/L (4.0–10.0) | 9.6 [7.0–11.2] | 8.8 [7.2–10.1] | 9.9 [5.1–16.8] |
| Prothrombin time, sec.a (10.0–13.0) | 15.2 [14.0–15.7] | 14.5 [13.6–16.1] | 14.5 [14.0–17.0] |
| Fibrinogen, g/Lb (2.0–4.0) | 6.4 [5.8–9.3] | 7.3 [5.3–8.1] | 6.0 [4.9–8.1] |
| D‐dimer, mg/Lb (<0.5) | 3.7 [2.1–11.8] | 1.6 [1.2–3.9] | 2.1 [1.4–5.2] |
| C‐reactive protein, mg/L (0–10) | 226 [160–266] | 163 [132–240] | 169 [120–224] |
Note
Laboratory measurements were done prior to or at t1.
Abbreviations: CT, computed tomography; PE‐, patients who did not develop pulmonary embolism; PE+, patients who developed pulmonary embolism.
Missing for two COVID/PE‐ patients and one influenza patient.
Measured in 11 COVID/PE‐ and 14 influenza patients due to unavailability of biobank samples.
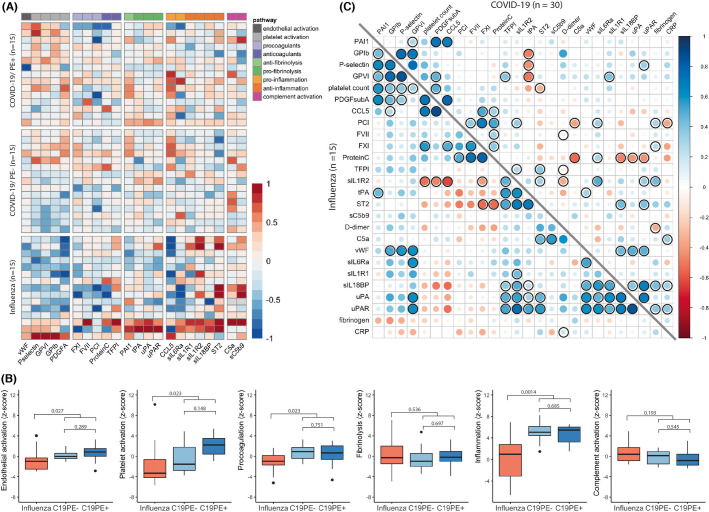
Plasma concentrations of biomarkers relating to the six thrombosis pathways of interest are shown in Figure 2A . Pairwise comparisons of individual biomarkers yielded no significant differences between C19PE+ and C19PE‐, nor between C19PE‐ and IAA, at either timepoint (t2 not shown). The only exceptions were the anti‐inflammation decoy‐receptors sIL‐1R2 and sST2, which were higher in IAA compared to C19PE‐ patients at t1 (sIL‐1R2: log2‐Fold change −0.67, p = .022; sST2: log2‐Fold change −1.78, p = .022), but not t2. Furthermore, conjoint analyses of total pathway activity at t1 yielded no relevant differences between C19PE‐ and C19PE+ cases (Figure 2B). However, we observed significant inequalities between COVID‐19 (C19PE+ and C19PE‐ groups combined) and IAA patients with regard to biomarkers related to activation of the endothelium and platelets as well as the coagulation and inflammation cascades, whereas fibrinolysis and complement activity appeared similar. Repeat analysis at t2 yielded similar findings, although observed differences in coagulation markers were not confirmed for this timepoint (data not shown).
FIGURE 2.
Levels of individual biomarkers and pathway activity at timepoint 1. (A) Heatmap of protein expression of biomarkers at t1. Light grey colored boxes represent missing data. Protein expression of all biomarkers besides C5a and sC5b‐9 was measured using proximity extension assay. Plasma concentrations of C5a and sC5b‐9 were measured using ELISA assays. (B) Summed z‐scores for thrombosis pathways at t1. Z‐scores of all biomarkers involved per thrombosis pathway (as specified in A) were summed, after sign‐inversion for biomarkers having a pathway‐inhibiting function. For endothelial activation, z‐scores for both vWF and P‐selectin were used. Differences between influenza, C19PE‐ and C19PE+ were tested using a Wilcoxon‐signed rank test. Differences between influenza and all COVID‐19 patients (i.e., C19PE+ and C19PE‐ combined) were tested using a Mann‐Whitney U test. p‐values were false discovery rate corrected. (C) Correlation matrix for the measured biomarkers, D‐dimer, fibrinogen, platelet count and CRP, at t1. Spearman correlation with false discovery rate correction was used to test significance of correlations. Correlations with FDR corrected p‐values <.05 are marked. PE+ = patients who developed pulmonary embolism, PE‐ = patients who did not develop pulmonary embolism
We observed higher circulating levels of von Willebrand Factor (vWF) and P‐selectin in COVID‐19 than IAA (Figure 2A). Both molecules are brought to the endothelial surface upon stimulation, where they can activate platelets.16 Although endothelial activation is a general feature of ARDS,17 our data suggest that it is more pronounced in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. This corroborates similar findings reported previously,7., 18. and could be the result of either excessive stimulation by pro‐inflammatory cytokines19 or direct infection of endothelial cells via the angiotensin‐converting enzyme 2 receptor.19., 20. The absence of a significant correlation between markers of inflammation and endothelial activation in our data (Figure 2C) suggests the latter.
Circulating markers of platelet activation were also higher in COVID‐19 cases compared to IAA controls (Figure 2B), which could suggest disease‐specific mechanisms. Both viruses can trigger activation through platelet Fc receptors (FcyRIIA) and IL‐6 signaling.21., 22., 23. However, SARS‐CoV‐2 may additionally stimulate the C5a‐C5aR axis,22 whereas H1N1 can activate platelets via thrombin formation independently of complement and FcyRIIA.21 Unfortunately, an apparent difference in the prevalence of thrombocytopenia at t1 (Table 1) makes it difficult to infer further mechanistic understanding from our data. Nonetheless, thrombocytes play a critical role in immunothrombosis,6 and the increased platelet activation observed here is in keeping with the higher prevalence of in situ thrombosis found in a histopathological comparison of influenza and COVID‐19‐affected lungs.13
We observed an overall more pronounced pro‐coagulant activation pattern in COVID‐19 compared to IAA (Figure 2C), which could be related to a simultaneously reduced compensatory tissue factor pathway inhibitor (TFPI) response (Figure 2A). This would confirm recent transcriptomic data suggesting that an upregulated expression of tissue factor during SARS‐CoV‐2 infection is inadequately counteracted by TFPI, resulting in a net imbalance favoring thrombosis.24 In contrast, protein C levels appeared to be well balanced with pro‐coagulant markers in C19PE+, and C19PE‐ and IAA patients, which corroborated previous data showing that there is a preserved activity of protein C, despite endothelial activation in COVID‐19.7 Plasma concentrations of the fibrinolysis initiators tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) and urokinase‐type plasminogen activator (uPA), and the fibrinolysis inhibitor plasminogen activator inhibitor (PAI‐1) were also similar among groups. High PAI‐1 levels during COVID‐19 have previously been reported,7., 25., 26. and might be associated with a hypofibrinolytic state during ARDS.27., 28. However, we did not observe a more prominent role for PAI‐1 in COVID‐19 compared to IAA. Furthermore, in C19PE+ we observed upregulation of tPA and uPA from t1 to t2 (data not shown), which would negate any depletion at t1, and implies a normal initiation of fibrinolysis. However, CAC has been described in terms of an overwhelmed fibrinolytic system,29 and our data do not contradict this. Indeed, plasminogen infusion was successful at reducing hypoxia in a small open‐label clinical trial among thirteen patients.30
We measured C5a and sC5b‐9 concentrations in plasma, which were previously found to be increased in critically‐ill COVID‐19 patients,14., 15. in order to assess the role of complement activation in COVID‐19‐related thrombosis. Compared to a healthy control population, C5a levels were 2.6–3.5‐fold increased in our study but similar across all groups. sC5b‐9 were not increased, and similarly to C5a showed no between‐group differences. Our findings contrast with a prior study reporting higher sC5b‐9 levels in patients hospitalized for COVID‐19 compared to influenza controls.14 Possibly, this discrepancy can be explained by a difference in disease severity, as our study included only mechanically ventilated patients.
Our study used a matched case‐control design to minimize distorting effects of disease severity and duration when comparing COVID‐19 to IAA. We believe this approach helped us to place previously published data on CAC in the context of more ubiquitous features of ARDS. It is important to note that we classified cases based on pulmonary CT angiography (which was performed upon clinical suspicion of PE only), and that misclassification of controls who actually had clinically unsuspected macrovascular thrombosis may thus have occurred. Also, microthrombosis is a prevalent autopsy finding in COVID‐19, which may have further clouded potential differences between C19PE‐ and C19PE+ cases in our study.
In summary, we adopted a targeted proteomics approach to identify disease‐specific pathophysiological pathways contributing to CAC. After controlling for differences in ARDS severity and duration, we observed no major differences in individual biomarkers between COVID‐19 patients with pulmonary embolism, COVID‐19 patients without pulmonary embolism and patients with influenza‐associated ARDS. This suggests that these biomarkers mostly reflect disease severity, rather than drive macrovascular thromboembolism. However, total pathway activation of endothelium and platelets as well as the coagulation and inflammation cascades were significantly more pronounced in COVID‐19 than influenza‐associated ARDS patients, suggesting that these pathways could be etiologically linked to PE‐risk in these patients.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTION
Emma Rademaker collected the clinical data, selected and matched the patient cohort, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. Dennis J. Doorduijn and Suzan H. M. Rooijakkers performed the ELISA experiments. Julia Drylewicz supervised the statistical analyses. Albert Huisman and Imo Hoefer supervised experiments. Nuray Kusadasi, Lennie P.G. Derde, Marc J. M. Bonten, and Coen Maas provided consultation on the research question and design of the study. Olaf L. Cremer supervised the study and finalized the research question and design of the study. All authors critically reviewed the manuscript.
Footnotes
Manuscript Handled by: Tetsumei Urano
Final decision: Tetsumei Urano, 08 February 2022
REFERENCES
- 1.Panigada M., Bottino N., Tagliabue P., et al. Hypercoagulability of COVID‐19 patients in intensive care unit: a report of thromboelastography findings and other parameters of hemostasis. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1738–1742. doi: 10.1111/jth.14850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Tang N., Bai H., Chen X., Gong J., Li D., Sun Z. Anticoagulant treatment is associated with decreased mortality in severe coronavirus disease 2019 patients with coagulopathy. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1094–1099. doi: 10.1111/jth.14817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Ackermann M., Verleden S.E., Kuehnel M., et al. Pulmonary vascular endothelialitis, thrombosis, and angiogenesis in Covid‐19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383:120–128. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2015432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Middeldorp S., Coppens M., van Haaps T.F., et al. Incidence of venous thromboembolism in hospitalized patients with COVID‐19. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:1995–2002. doi: 10.1111/jth.14888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Goligher E.C., Bradbury C.A., McVerry B.J., et al. Therapeutic anticoagulation with heparin in critically Ill patients with Covid‐19. N Engl J Med. 2021;385:777–789. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2103417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nicolai L., Leunig A., Brambs S., et al. Immunothrombotic dysregulation in COVID‐19 pneumonia is associated with respiratory failure and coagulopathy. Circulation. 2020;142:1176–1189. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.120.048488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goshua G., Pine A.B., Meizlish M.L., et al. Endotheliopathy in COVID‐19‐associated coagulopathy: evidence from a single‐centre, cross‐sectional study. Lancet Haematol. 2020;7:e575–e582. doi: 10.1016/s2352-3026(20)30216-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Manne B.K., Denorme F., Middleton E.A., et al. Platelet gene expression and function in patients with COVID‐19. Blood. 2020;136:1317–1329. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020007214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hottz E.D., Azevedo‐Quintanilha I.G., Palhinha L., et al. Platelet activation and platelet‐monocyte aggregate formation trigger tissue factor expression in patients with severe COVID‐19. Blood. 2020;136:1330–1341. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020007252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Middleton E.A., He X.Y., Denorme F., et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps contribute to immunothrombosis in COVID‐19 acute respiratory distress syndrome. Blood. 2020;136:1169–1179. doi: 10.1182/blood.2020007008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Magro C., Mulvey J.J., Berlin D., et al. Complement associated microvascular injury and thrombosis in the pathogenesis of severe COVID‐19 infection: a report of five cases. Transl Res. 2020;220:1–13. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2020.04.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gao T., Hu M., Zhang X., et al. Highly pathogenic coronavirus N protein aggravates lung injury by MASP‐2‐mediated complement over‐activation. medRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.03.29.20041962. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Nicolai L., Leunig A., Brambs S., et al. Vascular neutrophilic inflammation and immunothrombosis distinguish severe COVID‐19 from influenza pneumonia. J Thromb Haemost. 2021;19:574–581. doi: 10.1111/jth.15179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Ma L., Sahu S.K., Cano M., et al. Increased complement activation is a distinctive feature of severe SARS‐CoV‐2 infection. Science Immunology. 2021;6:eabh2259. doi: 10.1126/sciimmunol.abh2259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Carvelli J., Demaria O., Vély F., et al. Association of COVID‐19 inflammation with activation of the C5a–C5aR1 axis. Nature. 2020;588:146–150. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2600-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Pober J.S., Sessa W.C. Evolving functions of endothelial cells in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:803–815. doi: 10.1038/nri2171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zimmerman G.A., Albertine K.H., Carveth H.J., et al. Endothelial activation in ARDS. Chest. 1999;116:18s–24s. doi: 10.1378/chest.116.suppl_1.18s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Juneja G.K., Castelo M., Yeh C.H., et al. Biomarkers of coagulation, endothelial function and fibrinolysis in critically‐ill patients with COVID‐19: a single‐centre prospective longitudinal study. J Thromb Haemost. 2021;19(6):1546–1557. doi: 10.1111/jth.15327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Perico L., Benigni A., Casiraghi F., Ng L.F.P., Renia L., Remuzzi G. Immunity, endothelial injury and complement‐induced coagulopathy in COVID‐19. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2021;17:46–64. doi: 10.1038/s41581-020-00357-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Varga Z., Flammer A.J., Steiger P., et al. Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID‐19. Lancet. 2020;395:1417–1418. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(20)30937-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Boilard E., Paré G., Rousseau M., et al. Influenza virus H1N1 activates platelets through FcγRIIA signaling and thrombin generation. Blood. 2014;123:2854–2863. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-515536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Apostolidis S.A., Sarkar A., Giannini H.M., et al. Signaling through FcγRIIA and the C5a–C5aR pathway mediates platelet hyperactivation in COVID‐19. bioRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.05.01.442279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Levi M., van der Poll T. Inflammation and coagulation. Crit Care Med. 2010;38:S26–S34. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3181c98d21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.FitzGerald E.S., Chen Y., Fitzgerald K.A., Jamieson A.M. Lung epithelial cell transcriptional regulation as a factor in COVID‐19‐associated coagulopathies. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021;64:687–697. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0453OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zuo Y., Warnock M., Harbaugh A., et al. Plasma tissue plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor‐1 in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients. Sci Rep. 2021;11:1580. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80010-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nougier C., Benoit R., Simon M., et al. Hypofibrinolytic state and high thrombin generation may play a major role in SARS‐COV2 associated thrombosis. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:2215–2219. doi: 10.1111/jth.15016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bertozzi P., Astedt B., Zenzius L., et al. Depressed bronchoalveolar urokinase activity in patients with adult respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1990;322:890–897. doi: 10.1056/nejm199003293221304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ware L.B., Matthay M.A., Parsons P.E., Thompson B.T., Januzzi J.L., Eisner M.D. Pathogenetic and prognostic significance of altered coagulation and fibrinolysis in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1821–1828. doi: 10.1097/01.Ccm.0000221922.08878.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Medcalf R.L., Keragala C.B., Myles P.S. Fibrinolysis and COVID‐19: a plasmin paradox. J Thromb Haemost. 2020;18:2118–2122. doi: 10.1111/jth.14960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Wu Y., Wang T., Guo C., et al. Plasminogen improves lung lesions and hypoxemia in patients with COVID‐19. QJM. 2020;113:539–545. doi: 10.1093/qjmed/hcaa121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]