Abstract
Background
Admissions are generally classified as COVID-19 hospitalizations if the patient has a positive SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test. However, because 35% of SARS-CoV-2 infections are asymptomatic, patients admitted for unrelated indications with an incidentally positive test could be misclassified as a COVID-19 hospitalization. Electronic health record (EHR)–based studies have been unable to distinguish between a hospitalization specifically for COVID-19 versus an incidental SARS-CoV-2 hospitalization. Although the need to improve classification of COVID-19 versus incidental SARS-CoV-2 is well understood, the magnitude of the problems has only been characterized in small, single-center studies. Furthermore, there have been no peer-reviewed studies evaluating methods for improving classification.
Objective
The aims of this study are to, first, quantify the frequency of incidental hospitalizations over the first 15 months of the pandemic in multiple hospital systems in the United States and, second, to apply electronic phenotyping techniques to automatically improve COVID-19 hospitalization classification.
Methods
From a retrospective EHR-based cohort in 4 US health care systems in Massachusetts, Pennsylvania, and Illinois, a random sample of 1123 SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive patients hospitalized from March 2020 to August 2021 was manually chart-reviewed and classified as “admitted with COVID-19” (incidental) versus specifically admitted for COVID-19 (“for COVID-19”). EHR-based phenotyping was used to find feature sets to filter out incidental admissions.
Results
EHR-based phenotyped feature sets filtered out incidental admissions, which occurred in an average of 26% of hospitalizations (although this varied widely over time, from 0% to 75%). The top site-specific feature sets had 79%-99% specificity with 62%-75% sensitivity, while the best-performing across-site feature sets had 71%-94% specificity with 69%-81% sensitivity.
Conclusions
A large proportion of SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive admissions were incidental. Straightforward EHR-based phenotypes differentiated admissions, which is important to assure accurate public health reporting and research.
Keywords: COVID-19, medical informatics, public health, phenotype, electronic health records, clinical research informatics, health data, SARS-CoV-2, patient data, health care
Introduction
Despite the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic and the dozens of research groups and consortia worldwide that continue to utilize clinical data available in electronic health records (EHRs), critical gaps remain in both our understanding of COVID-19 and how to accurately predict poor outcomes, including hospitalization and mortality [1-4].
One of the most prominent gaps in the field is how to distinguish hospital admissions specifically for COVID-19-related indications (eg, severe disease with respiratory failure) from an incidentally positive SARS-CoV-2 polymerase chain reaction (PCR) test in admissions for an unrelated reason (eg, a broken leg). Approximately 800,000 new SARS-CoV-2 cases are being reported daily, and approximately 150,000 patients are hospitalized with a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test [5]. Misclassification of incidental COVID-19 during hospitalizations is common [5] and raises research and public health concerns. For example, deleterious effects on health care system resource disbursement or utilization as well as on local and regional social and economic structure and function can result from inaccurate reporting of incidental cases of SARS-CoV-2.
Misclassification in research studies occurs because patients are usually considered COVID-19 patients if they have a recent positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test or the International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision (ICD-10) diagnosis code U07, which, according to guidelines, is equivalent to a positive test [6]. This approach has been used in most COVID-19 studies published to date [7,8] and is in line with Centers of Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) guidelines, which treat positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR tests as confirmed cases [9]. Given that at least 35% of SARS-CoV-2 cases are asymptomatic, patients seeking unrelated care are erroneously classified as COVID hospitalizations [10-14]. The magnitude of this misclassification has increased over time as health care systems began to be less restrictive after the second wave and elective surgeries were again performed starting in the second quarter of 2021.
A potential solution is EHR-based phenotyping, which identifies patient populations of interest based on proxies derived from EHR observations. EHR phenotypes are developed by first performing manual chart review to classify cases and then applying a machine learning or statistical reasoning method to the EHR data to create an explainable predictive model [15,16]. For example, a phenotyping study of bipolar disorder found that true bipolar disorder is correlated with a set of several EHR features [17]. Our previous work validated a “severe COVID-19” phenotype in the Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR (4CE) network using both chart review and comparison across sites [18,19]. 4CE is a diverse international network of over 300 hospitals engaged in collaborative COVID-19 research [2,20,21].
The Massachusetts Department of Public Health has recently begun using a simple phenotype to report COVID-19 hospitalizations [22,23]. Although it is based on treatment recommendations and not a gold standard, it illustrates the interest in EHR-based phenotyping for COVID-19.
In this study, we utilized EHR data from 60 hospitals across 4 US health care systems in 4CE, combined with clinical expertise, data analytics, and manual EHR chart review, to determine whether patients admitted to the hospital and who had a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test were hospitalized for COVID-19 (for-COVID-19 group) or were admitted for a different indication and simply had an incidental positive test (admitted-with-COVID-19 group).
Methods
Sites
We selected a sample of 4 4CE sites across the United States to participate in the development of our for-COVID-19 hospitalization phenotype. These sites included the Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), Mass General Brigham (MGB), Northwestern University (NWU), and the University of Pittsburgh/University of Pittsburgh Medical Center (UPITT). Each site involved at least 1 clinical expert (for chart review and manual annotation) and 1 data analytics expert (to apply various analytic filtering approaches). Eligible patients for this study were those included in the 4CE COVID-19 cohort: all hospitalized patients (pediatric and adult) with their first positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test 7 days before to 14 days after hospitalization [2].
Chart Review
Each development site randomly sampled an equal number of admissions in each quarter (BIDMC, MGB) or month (NWU, UPITT) from their cohort of SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive patients over the period of March 2020 until at least March 2021 (N=1123). Clinical experts reviewed the charts in the EHRs and recorded whether these patients were admitted for COVID-19-related reasons, as defined later. The total number of chart reviews per site was somewhat variable and determined by availability of the clinical experts. Participating sites and the number of chart reviews are listed in Table 1.
Table 1.
Participating health care systems’ overall characteristics and the number and period of chart reviews performed for this study.
| Participating site | Hospitals, n | Inpatient discharges per year, n | Number of chart reviews performed, n | Chart review time period, start date-end date |
| BIDMCa | 1 | 40,752 | 400 | March 2020-March 2021 |
| MGBb | 10 | 163,521 | 406 | March 2020-July 2021 |
| NWUc | 10 | 103,279 | 70 | March 2020-February 2021 |
| UPITTd | 39 | 369,300 | 247 | April 2020-August 2021 |
aBIDMC: Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center.
bMGB: Mass General Brigham.
cNWU: Northwestern University.
dUPITT: University of Pittsburgh/University of Pittsburgh Medical Center.
To develop chart review criteria, a 4CE subgroup met during March-July 2021. The group consists of about 20 researchers in 4CE, with a mixture of physicians, medical informaticians, and data scientists. In the process, dozens of real patient charts were considered, and edge cases were discussed until consensus was reached on the minimal chart review necessary to determine the reason a patient was hospitalized.
Based on the developed criteria, chart reviewers (1 per site, except at the BIDMC, where there were 2) classified the patients based on review of primarily the admission note, discharge summary (or death note), and laboratory values for the hospitalization. Each site had Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval to view the charts locally, and only deidentified aggregate summaries were presented to the subgroup. Each site summarized the chart reviews in a spreadsheet that was then linked to the site’s 4CE EHR data, wherein medical record numbers were replaced with 4CE’s patient pseudoidentifiers, and criteria classifications were coded as an integer. The 4CE EHR data set is a COVID-19-related subset of raw EHR data consisting of selected laboratory test, medication, and procedure categories and all available ICD-10 diagnosis codes. The data dictionary is explained in more detail in Multimedia Appendix 1. The chart review process is presented visually in steps 1-5 of Figure 1.
Figure 1.
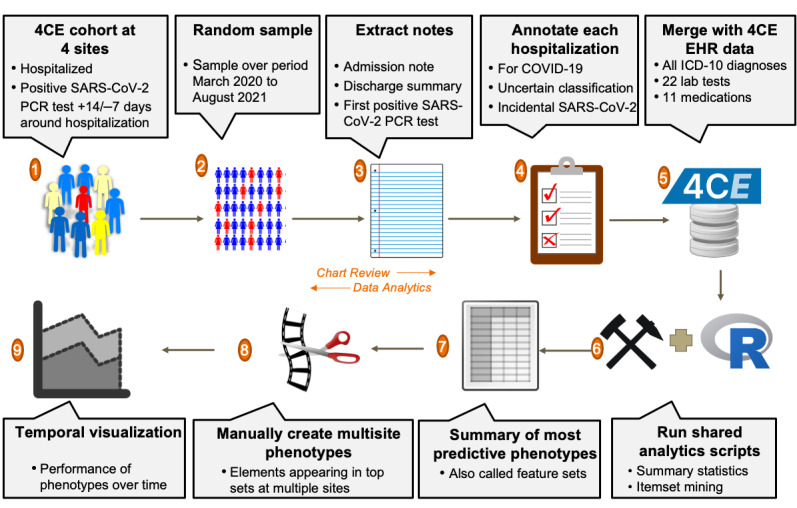
The chart review process. (1-2) At each site, an equal number of patients admitted with a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test were sampled by quarter or by month. (3-4) A chart reviewer at the site examined primarily the admission note, discharge summary (or death note), and laboratory values for the hospitalization to classify as admitted for COVID-19, incidental SARS-CoV2, or uncertain. (5-6) These classifications were then merged with 4CE EHR data for use with shared analytic scripts in R. (7-8) The top phenotypes at each site output by the data mining algorithm were summarized, and this was used to manually construct feature sets to be used across sites by selecting components that appeared in step 7 at multiple sites. (9) The performance over time of the top multisite phenotypes was visualized. 4CE: Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR; EHR: electronic health record; ICD-10: International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision; PCR: polymerase chain reaction.
We developed an R script (R Core Team) at the MGB to perform basic data summarization. This did the following: calculated chart review summary statistics, aggregated data on ICD-10 diagnosis codes used during the hospitalization to compare to the chart review classification, and generated a bubble plot that visualizes the change in proportion of hospitalizations, specifically for COVID-19, among all chart reviews over the course of the pandemic, by month. A trendline was fitted with locally estimated scatterplot smoothing (loess) regression using ggplot2 and was weighted by the number of chart reviews performed that month. Each participating health care site ran the R script on its chart-reviewed patient cohort.
Phenotypes Using Hospital System Dynamics Phenotyping
We developed an algorithm as an R script to choose phenotypes of admissions specifically for COVID-19, using established hospital dynamics measures of ordering/charting patterns in the EHRs (eg, presence of laboratory tests rather than laboratory results) [16,24]. The algorithm uses a variation of the Apriori item set–mining algorithm [25,26]. Apriori, which has been utilized in other EHR studies, uses a hill-climbing approach to find iteratively larger item sets that meet some summary statistic constraint [27,28]. Apriori, like other market basket analyses, is advantageous when the labeled data are small, because it discovers statistical properties of the underlying data, rather than developing a separate predictive model that must be evaluated. Therefore, it does not require a data split between a training and a test set, which would further limit the sample size. The original algorithm chose rules that maximized the positive predictive value (PPV) and had at least a minimum prevalence in the data set. More recent variants use other summary statistics [29] because the PPV, which measures the likelihood a positive is a true positive, is highly affected by population prevalence (which shifts dramatically over time with COVID-19). Therefore, our algorithm used sensitivity and specificity. A visual representation of our algorithm is shown in Figure 2. Item sets of size 1 are chosen that meet certain minimum prediction thresholds, and then these are combined into item sets of size 2 and again filtered by the thresholds, and so forth up to a maximum item set size.
Figure 2.
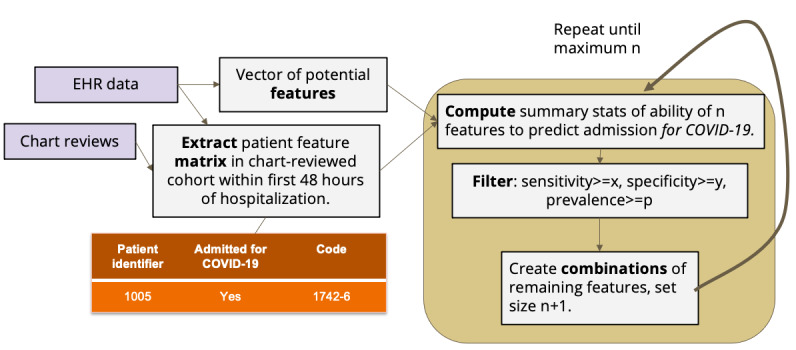
Design of the phenotyping algorithm. Predictive feature sets of iteratively larger size were selected based on their sensitivity and specificity in correctly identifying COVID-19-specific admissions using 4CE EHR data and chart reviews. We chose the following parameters after testing various thresholds at all 4 sites: AND feature sets, x=0.40, y=0.20, p=0.30; OR feature sets x=0.10, y=0.50, p=0.20; and single features: x=y=p=0. 4CE: Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR; EHR: electronic health record.
We applied our algorithm to find patterns in 4CE EHR data at each site using the presence of medications, laboratory tests, and diagnoses to select the best phenotypes. (Laboratory test results are included in the 4CE data set but were not included in this analysis, because it does not fit with the principles of hospital system dynamics [HSD].) We further compared the output at each site to see whether there were similarities (eg, transfer learning was applicable). We considered 2 cases: data that would be available in near-real time during a hospitalization (laboratory tests) and data that would be available for a retrospective analysis (including laboratory and medication facts and diagnosis codes, which are usually not coded until after discharge).
Sites exported phenotypes with sensitivity of at least 0.60, ordered by specificity in descending order. (Site B applied a slightly lower sensitivity threshold because no phenotypes with sensitivity of at least 0.60 were available.) Specificity was chosen as the sorting variable because it measures the phenotype’s ability to detect and remove incidental SARS-CoV-2 admissions—a good measure of overall performance. Sensitivity, in contrast, measures the ability to select for-COVID-19 admissions, which can be easily maximized by simply selecting all patients. Groups of phenotypes were manually summarized into conjunctive normal form by combining AND and OR phenotypes at each site, when possible, and reporting a sensitivity and specificity range for the final combined phenotype. We excluded feature sets that were more complex but with the same performance as a simpler feature set.
We also ran our phenotyping program to find the most predictive individual features at each site during every 6-month period of the pandemic, beginning January 2020. This analysis allowed us to examine the trend of HSD as the pandemic progressed.
The final piece of analysis involved selecting multisite phenotypes and plotting their performance over time. First, we selected the features that appeared at multiple sites from the best phenotypes at each site. We used these to manually construct multisite phenotypes. We optimized these using MGB data by manually adding/removing OR components based on performance, because adding too many OR components degrades the specificity. We ran these constructed phenotypes at each site to ascertain their performance characteristics.
This data-mining process can be seen visually in Figure 1, steps 6-8.
Temporal Visualization of Phenotypes
We also developed a temporal visualization used at each site (step 9 of Figure 1). The visualization shows 3 lines: a solid line showing the total number of patients in the site’s 4CE cohort (ie, admitted with a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test), a dashed line showing the total number of those patients after filtering to select patients admitted specifically for COVID-19 (ie, removing all patients who do not meet the phenotyping feature set criteria), and a dotted line showing the difference between the solid line and the dashed line (ie, patients removed from the cohort in the dashed line). Dots on the graph visualize the performance on the chart-reviewed cohort. Green dots on each line show patients who were correctly classified by the phenotype, according to the chart review. Likewise, orange dots on each line show incorrect classifications. Dot size is proportional to the number of chart reviews.
Importantly, all review and analysis were performed by local experts at each site, and only the final aggregated results were submitted to a central location for finalization. This approach is a hallmark of 4CE—keeping data close to local experts and only sharing aggregated results. It reduces regulatory complexity around data sharing and keeps those who know the data best involved in the analysis.
All our software tools were implemented as R programs. They were developed at the MGB and tested by all 4 sites. The code is available as open source [30].
Ethical Considerations
IRB approval was obtained at the BIDMC (#2020P000565), the MGB (#2020P001483), the UPITT (STUDY20070095), and the NWU (STU00212845). Participant informed consent was waived by each IRB because the study involved only retrospective data and no individually identifiable data were share outside of each site’s local study team. Site names were anonymized (to sites A, B, C, and D) to comply with hospital privacy policies. At the MGB and the BIDMC, any counts of patients were blurred with a random number +/–3 before being shared centrally. Our previous work shows that for large counts, pooling blurred counts has minimal impact on the overall accuracy of the statistics [31]. At all sites, any counts <3 were censored. All other statistics (eg, percentages, differences, CIs, P values) were preserved.
Results
Chart Review
The final chart review criteria are shown in Table 2. (See the Methods section for details.) Across the 4 sites, 764 (68%) of 1123 patients were admitted for COVID-19, 292 (26%) patients were admitted with incidental SARS-CoV-2, and 67 (6%) were uncertain (Table 3). The 4 sites included the BIDMC, the MGB, the UPITT, and the NWU. A site-by-site breakdown, both overall and by individual criteria, is also shown in Table 3. A demographic characterization of the chart-reviewed cohort at each site is shown in Table 4. Plots of the proportion of hospitalizations specifically for COVID-19 among all chart reviews by month over the course of the pandemic are shown in Figure 3. Finally, Tables 5 and 6 show the top 10 ICD-10 diagnoses that were assigned to patients with a date in the first 48 hours after admission in for-COVID-19 versus incidental-COVID-19 groups. In all results, each site is labeled with a random but consistent letter (A, B, C, or D) to comply with hospital privacy policies.
Table 2.
Summary of the chart review criteria developed by the 4CEa subgroup of physicians, medical informaticians, and data scientists.
| Chart-reviewed classification | Criteria |
| Admitted specifically for COVID-19 | Symptoms on admission were attributable to COVID-19, and clinicians admitted patients for COVID-19-related care. The symptoms included:
|
| Admitted incidentally with COVID-19 | The admission history was unlikely to be related to COVID-19, and clinicians did not specifically admit the patient for COVID-19-related care. This admission could be due to:
|
| Uncertain | Symptoms on admission may have been related to COVID-19, and clinicians considered COVID-19 exacerbation during hospitalization. The symptoms included:
|
a4CE: Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHRb.
bEHR: electronic health record.
Table 3.
Proportion of chart-reviewed patients admitted specifically for COVID-19 vs admitted with incidental SARS-CoV-2, overall and stratified by site, with a detailed criteria breakdown. A detailed breakdown at site D could not be included, because their process did not record the specific criteria for each classification. Note that cells with 0% are still included to show all the chart review criteria.
| Category | Site A (N=406), n (%) | Site B (N=70), n (%) | Site C (N=247), n (%) | Site D (N=400), n (%) | Overall (N=1123), n (%) | |
| Admitted specifically for COVID-19 | 764 (68) | |||||
|
|
All | 288 (71) | 59 (84) | 180 (73) | 240 (60) | N/Aa |
|
|
Respiratory insufficiency | 202 (50) | 36 (51) | 128 (52) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Blood clot | 6 (1) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Hemodynamic changes | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Other symptomatic COVID-19 | 71 (18) | 19 (27) | 47 (20) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Not admitted for COVID-19 but developed 1 of the above criteria | 8 (2) | <3 (<5) | 5 (2) | N/A | N/A |
| Admitted incidentally with COVID-19 | 292 (26) | |||||
|
|
All | 85 (20) | 9 (13) | 54 (22) | 144 (36) | N/A |
|
|
Full-term labor | 18 (4) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Procedure | 8 (2) | <3 (<5) | 9 (4) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Trauma | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Other not COVID-19 | 50 (13) | 6 (9) | 44 (18) | N/A | N/A |
| Uncertain | 67 (6) | |||||
|
|
All | 33 (8) | <3 (<5) | 10 (4) | 16 (4) | N/A |
|
|
Immune dysfunction | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Early labor | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Liver dysfunction | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Graft failure | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | <3 (<5) | N/A | N/A |
|
|
Other possible COVID-19 | 31 (8) | <3 (<5) | 10 (4) | N/A | N/A |
aN/A: not applicable.
Table 4.
Demographic characterization of the chart-reviewed cohort by site. For each row, the count and percentage (in parentheses) at each site are shown. Two sites did not report Hispanic/Latino. N values for each site are shown in the header; these might not exactly match the summation of each category due to blurring requirements.
| Category | Site A (N=406), n (%) | Site B (N=70), n (%) | Site C (N=247), n (%) | Site D (N=400), n (%) | |
| Age (years) | |||||
|
|
0-25 | 14 (4) | 11 (14) | 4 (1) | 11 (3) |
|
|
26-49 | 95 (23) | 15 (21) | 26 (10) | 76 (18) |
|
|
50-69 | 138 (35) | 22 (31) | 99 (40) | 135 (33) |
|
|
70-79 | 72 (17) | 9 (13) | 59 (24) | 90 (22) |
|
|
80+ | 83 (20) | 13 (18) | 59 (24) | 81 (19) |
| Race | |||||
|
|
Asian | 8 (2) | 2 (3) | 5 (2) | 17 (4) |
|
|
Black | 60 (14) | 9 (13) | 58 (23) | 97 (24) |
|
|
Hispanic/Latino | 21 (6) | N/Aa | N/A | 55 (14) |
|
|
White | 78 (19) | 50 (71) | 179 (72) | 173 (42) |
|
|
No information | 230 (58) | 8 (11) | 5 (2) | 61 (14) |
| Sex | |||||
|
|
Male | 200 (50) | 42 (60) | 121 (49) | 188 (47) |
|
|
Female | 200 (50) | 28 (40) | 126 (51) | 211 (52) |
aN/A: not applicable.
Figure 3.
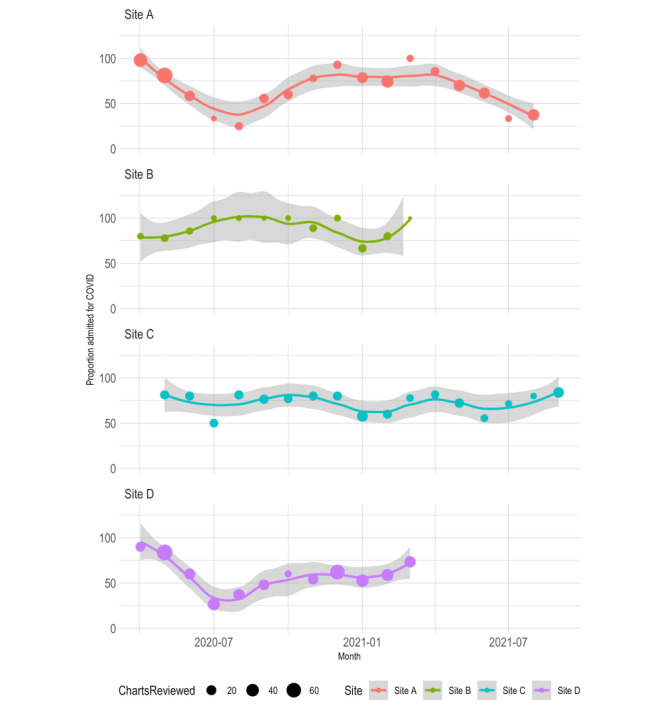
Chart-reviewed proportion of admissions specifically for COVID-19 among all chart reviews by month at each site. The bubble size shows the relative number of patient chart reviews performed that month. The trendline was weighted by bubble size and was performed using locally weighted least squares (loess) regression. Note that the y axis and 95% CI limits extend above 100%.
Table 5.
Top 10 ICD-10a diagnoses among patients’ charts reviewed as admitted specifically for COVID-19, with the proportion of patients with each diagnosis at each site. Each patient might have multiple diagnoses, and therefore, the sum might be greater than 100%.
| ICD-10 diagnosis | Site A (N=288), n (%) | Site B (N=59), n (%) | Site C (N=180), n (%) | Site D (N=240), n (%) |
| U07.1 Covid-19 | 265 (92) | 54 (92) | 145 (80) | 226 (95) |
| J12.89 Other Viral Pneumonia | 125 (44) | 24 (41) | 64 (35) | 173 (70) |
| I10 Essential (Primary) Hypertension | 113 (39) | 16 (27) | 74 (41) | 89 (37) |
| J96.01 Acute Respiratory Failure With Hypoxia | 75 (26) | 20 (34) | 56 (31) | 139 (58) |
| E78.5 Hyperlipidemia, Unspecified | 79 (28) | 4 (7) | 69 (38) | 108 (46) |
| N17.9 Acute Kidney Failure, Unspecified | 74 (25) | 4 (7) | 40 (22) | 94 (39) |
| K21.9 Gastro-Esophageal Reflux Disease Without Esophagitis | 64 (22) | <3 (<3) | 57 (31) | 65 (26) |
| Z87.891 Personal History of Nicotine Dependence | 56 (18) | <3 (<3) | 44 (24) | 66 (27) |
| R09.02 Hypoxemia | 81 (29) | 15 (25) | 21 (12) | 43 (17) |
| J12.82 Pneumonia due to COVID-19 | 72 (25) | 12 (20) | 39 (22) | 35 (15) |
aICD-10: International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision.
Table 6.
Top 10 ICD-10a diagnoses among patients’ charts reviewed as admitted with incidental COVID-19, with the proportion of patients with each diagnosis at each site. Each patient might have multiple diagnoses, and therefore, the sum might be greater than 100%.
| ICD-10 diagnosis | Site A (N=85), n (%) | Site B (N=9), n (%) | Site C (N=54), n (%) | Site D (N=144), n (%) |
| U07.1 Covid-19 | 63 (74) | 5 (56) | 40 (73) | 122 (85) |
| N17.9 Acute Kidney Failure, Unspecified | 12 (14) | <3 (<11) | 12 (22) | 24 (17) |
| E11.22 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Diabetic Chronic Kidney Disease | 5 (6) | <3 (<11) | 7 (13) | 23 (15) |
| E11.9 Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Without Complications | 12 (11) | <3 (<11) | 4 (7) | 14 (11) |
| D64.9 Anemia, Unspecified | 13 (19) | <3 (<11) | 5 (9) | 10 (6) |
| E87.2 Acidosis | 8 (6) | <3 (<11) | <3 (<5) | 12 (10) |
| J12.89 Other Viral Pneumonia | <3 (<2) | <3 (<11) | 4 (7) | 15 (12) |
| J96.01 Acute Respiratory Failure With Hypoxia | 6 (8) | <3 (<11) | 4 (7) | 13 (8) |
| D69.6 Thrombocytopenia, Unspecified | 5 (7) | <3 (<11) | 6 (11) | 12 (7) |
| N18.6 End-Stage Renal Disease | 6 (7) | <3 (<11) | 5 (9) | 6 (5) |
aICD-10: International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision.
Phenotypes Using Hospital System Dynamics
Each site ran our HSD program to choose phenotypes of patients admitted for COVID-19 versus patients admitted incidentally with COVID-19. The input of the program includes the chart-reviewed classifications and patient-level EHR data on the presence of 22 selected laboratory test types, 11 selected medication categories, 12 procedure categories, and all ICD-10 diagnosis codes that are dated within 48 hours of admission. This resulted in 1880 distinct features across all sites. (See Multimedia Appendix 1 for more information on the data dictionary.) The program selected 135 feature sets across all sites using these features. These were manually reduced to 32 (23.7%) by selecting the most predictive and removing duplicates and near-duplicates. These are summarized in Table 7, divided into phenotypes that use data that could be available immediately (“real time”) and phenotypes using all data available after discharge (“retrospective”). We also reported the prevalence at each site among all SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive hospitalizations (not just among chart-reviewed patients), which is the proportion of patients meeting the criteria of the feature sets.
Table 7.
Top phenotyping feature sets by specificity, with a sensitivity of at least 0.60 for detecting admissions specifically for COVID-19. The table is grouped into feature sets involving potentially real-time data (laboratory tests) and all available data (presence of laboratory tests, medications, and diagnosis codes). Note that laboratory test results are not included in the feature sets. Ranges are shown in the summary statistics because multiple rules with similar performance were summarized using conjunctive normal form.
| Phenotyping feature set | Site | Sensitivity | Specificity | Prevalence (%) | |
| “Real-time” phenotypes (laboratory tests only) | |||||
|
|
CRPa AND (Total Bilirubin OR Ferritin OR LDHb) AND (Lymphocyte Count OR Neutrophil Count) AND Cardiac Troponin | D | 0.65-0.72 | 0.85 | 67-71 |
|
|
Ferritin AND LDH AND Cardiac Troponin AND (INRc OR PTTd OR Lymphocyte Count OR Neutrophil Count) | D | 0.62-0.69 | 0.85 | 67-71 |
|
|
CRP AND (LDH AND/OR Ferritin) AND Cardiac Troponin | A | 0.67-0.70 | 0.89-0.90 | 72-77 |
|
|
Procalcitonin OR D-dimer OR CRP OR Cardiac Troponin OR Ferritin | A | 0.63-0.87 | 0.73-0.85 | 65-85 |
|
|
Any 2 of: Procalcitonin, LDH, CRP | B | 0.56-0.58 | 0.67 | 63-67 |
|
|
D-dimer OR Ferritin OR CRP | C | 0.26-0.37 | 0.86-0.93 | 54-58 |
| “Retrospective” phenotypes (laboratory tests, medications, and diagnosis codes) | |||||
|
|
Total bilirubin AND (Ferritin OR LDH OR Lymphocyte Count OR Neutrophil Count) AND diagnosis of Other Viral Pneumonia (J12.89) | D | 0.62-0.64 | 0.92 | 46-48 |
|
|
Diagnosis of: Other Viral Pneumonia (J12.89) OR Acute Respiratory Failure with Hypoxia (J96.01) OR Anemia (D64.9) | D | 0.70-0.74 | 0.82-0.88 | 50-63 |
|
|
Diagnosis of: Other Viral Pneumonia (J12.89) OR Supplemental Oxygen (severe) | D | 0.75 | 0.82 | 61 |
|
|
CRP AND (LDH OR Ferritin) AND Cardiac Troponin | A | 0.70 | 0.89 | 74-77 |
|
|
Remdesivir OR Procalcitonin OR Other Viral Pneumonia (J12.89) OR Nonspecific Abnormal Lung Finding (R91.8) OR Shortness of Breath (R06.02) OR Other COVID Disease (J12.82) | A | 0.68-0.72 | 0.85-0.95 | 58-74 |
|
|
Hypoxemia (R09.02) OR Other Coronavirus as Cause of Disease (B97.29) OR Shortness of Breath (R06.02) OR Pneumonia (unspecified organism) (J18.9) OR Acute Respiratory Failure with Hypoxia (J96.01) OR Nonspecific Abnormal Lung Finding (R91.8) | B | 0.63-0.68 | 0.89-0.99 | 54-67 |
|
|
D-dimer OR ferritin OR CRP OR Other Viral Pneumonia (J12.89) OR Acute Respiratory Failure with Hypoxia (J96.01) | C | 0.71-0.75 | 0.79-0.86 | 52-58 |
aCRP: C-reactive protein.
bLDH: lactate dehydrogenase.
cINR: international normalized ratio.
dPTT: partial thromboplastin time.
We examined the top individual features over time at all sites. In the first half of 2020, a diagnosis of “Other Viral Pneumonia” (J12.89) was the only strong predictor of an admission specifically for COVID-19 across all 4 sites. In the second half of 2020, the phenotyping algorithm began selecting laboratory tests, including C-reactive protein (CRP), troponin, ferritin, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). In addition, the diagnosis “Other Coronavirus as Cause of Disease” (B97.29) began to be used at site B. By 2021, remdesivir and the diagnosis “Pneumonia due to COVID-19” (J12.82) additionally came into widespread use and became predictive of admissions specifically for COVID at site A.
Temporal Visualization of Phenotypes
We manually constructed 5 multisite phenotypes from elements in Table 7 that appeared at multiple sites. These were evaluated at each site: 2 variations of multisite diagnoses, 2 variations of all multisite features, and top laboratory tests. OR rules were favored due to better applicability across data sets (because of different coding practices at different sites), except for laboratory tests where the top pair of tests had high prevalence at every site. The best-performing phenotypes in each category are shown with their performance characteristics in Table 8, with the top single phenotype at each site in italics. In Figure 4, we plotted the performance of the top phenotype at each site (the boldfaced rows in Table 8) using the temporal phenotype visualization described in the Methods section. (The top phenotype involved all data types at every site except site C, where diagnoses alone performed better.)
Table 8.
The best multisite phenotyping feature sets and their overall performance characteristics. The multisite phenotypes were derived from Table 7 by selecting components of phenotypes that appeared at multiple sites.
| Phenotyping Feature Set | Description | Sensitivity, specificity |
| Other Viral Pneumonia OR Acute Respiratory Failure with Hypoxia OR Shortness of Breath OR Abnormal Lung Finding | Retrospective phenotype: Diagnoses mentioned in top feature sets at >1 site |
|
| CRPa AND Ferritin | Real-time phenotype: Laboratory tests mentioned in top feature sets at all 4 sites |
|
| Remdesivir OR Oxygen (severe) OR Dx of Other Viral Pneumonia | Retrospective phenotype: All items mentioned at multiple sites in OR feature sets |
|
aCRP: C-reactive protein.
bThe top-performing phenotype at each site is italicized.
Figure 4.
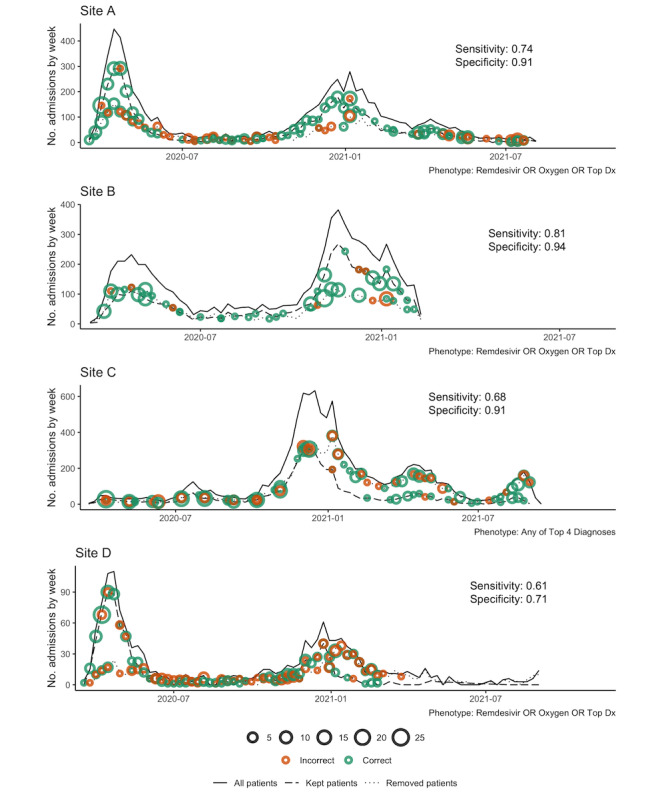
Performance of the top phenotyping feature sets (Table 7) over time at each site. The y axis is the number of admissions per week, the x axis is the week, and overall sensitivity and specificity are shown on each figure panel. Solid lines show the total number of weekly admissions for patients with a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test. Dashed lines show the number of weekly admissions after filtering to select patients admitted specifically for COVID-19 (ie, removing all patients who do not meet the phenotyping feature set criteria). The dotted line shows the difference between the solid line and the dashed line (ie, patients removed from the cohort in the dashed line). Green dots indicate correct classification by the phenotype according to chart review. Orange dots indicate incorrect classification. The dot size is proportional to the number of chart reviews. PCR: polymerase chain reaction.
Discussion
Principal Results and Analysis
The COVID-19 pandemic has lasted for over 2 years, with multiple waves worldwide. Although hospital systems have been cyclically overwhelmed by patients seeking care for COVID-19, as health care systems began to open up before the second wave, elective surgeries were again performed starting in the later part of 2020, and especially in the second quarter of 2021, many approached the health care system for health issues (eg, accidents, strokes) while incidentally infected with SARS-CoV-2 [32]. This, along with the high false-positive rate of SARS-CoV-2 PCR tests in some situations [33-36], has led to increasing numbers of misclassified patients in analyses of COVID-19 characteristics and severity. This could be creating significant detection and reporting bias, leading to erroneous conclusions [10-13]. This study presents a multi-institutional characterization of 1123 hospitalized patients either incidentally infected with SARS-CoV-2 or specifically hospitalized for COVID-19 in 4 health care systems across multiple waves using consensus-based chart review criteria. Overall, we found that 764 (68%) of 1123 patients who tested SARS-CoV-2 positive were hospitalized because of COVID-19 but with significant variation during each wave of the pandemic.
We applied an item set–mining approach and established HSD principles to phenotype SARS-CoV-2 PCR-positive patients who were admitted specifically for COVID-19 by using data on charting patterns (eg, presence of laboratory tests within 48 hours of admission) rather than results (eg, laboratory results) [16,37]. HSD examines health care process data about a hospitalization, such as ordering/charting patterns, rather than the full data set. For example, to study severely ill patients, an HSD approach might select patients with a high total number of laboratory tests on the day of admission. This could be an indirect measure of clinical suspicion of disease complexity or severity. Previous work shows that proxies such as the total number of laboratory tests on the day of admission or the time of day of laboratory tests can be highly predictive of disease course [24,37]. Our methods sorted out who was treated for COVID-19 automatically, over time, with specificities above 0.70, even for some phenotypes discovered at a single site and applied to all 4. We focused on specificity because the goal was to remove false positives (ie, incidental SARS-CoV-2) from the cohort.
Our chart review protocol illustrates that patients who were admitted and had a positive SARS-CoV-2 PCR test were more likely to be admitted specifically for COVID-19 when disease prevalence was high (at least prior to Omicron). However, during periods in which health care systems were less restrictive (ie, resumed routine surgeries), a secondary measure/phenotype was critical for accurately classifying admissions specifically for SARS-CoV-2 infection.
As expected, we observed a lower proportion of hospitalizations specifically for COVID-19 in the summer months when disease prevalence was lower (Figure 3). One would expect this because there were fewer overall admissions as hospitals were recovering from the previous wave.
As expected, the top chart review criteria (Table 3) were respiratory insufficiency in admissions specifically for COVID-19 and other for incidental and uncertain admissions with SARS-CoV-2. Surprisingly, 10%-20% of patients admitted with incidental SARS-CoV-2 were diagnosed with pneumonia, respiratory failure, or acute kidney injury (Tables 5 and 6). This could reflect data collection issues, where some systems might repeat past problems automatically at hospital admission. In the case of codes for acute kidney injury, further investigation is needed to determine whether SARS-CoV-2-associated acute kidney injury (including COVID-19-associated nephropathy) occurs in patients we otherwise classified as having incidental admissions [38].
Health care systems are beginning to explore phenotyping feature sets to report admissions specifically for COVID-19. Starting January 2022 in Massachusetts, hospitals began reporting the number of for-COVID-19 hospitalizations as the count of admitted patients with both a SARS-CoV-2-positive test and a medication order for dexamethasone [22,23]. This simple phenotype was designed by the Massachusetts Department of Public Health as a first attempt, and it was based only on treatment recommendations for moderate-to-severe COVID-19 with hypoxia. It was not validated against a gold standard. Nonetheless, it illustrates the interest in EHR-based phenotyping for COVID-19.
Phenotypes with diagnosis codes tended to be the best-performing predictors of admissions, specifically for COVID-19. This could be because diagnosis codes represent either a clinically informed conclusion or a justification for ordering a test (implying the clinician suspected COVID-19). However, diagnoses are less prevalent in the population than laboratory tests and might not cover the entire population of admissions for COVID-19. Further, diagnoses early in hospitalization also do not always reflect the patient’s eventual diagnosis or hospital-related complications that are more accurately reflected in discharge diagnoses. There was also some heterogeneity in the diagnoses used at different sites (eg, B97.29 “Other Coronavirus as Cause of Disease” was a top predictor only at site B). In addition, the presence of laboratory tests is useful for real-time detection systems because diagnosis codes usually are assigned after discharge. Clusters of tests for inflammatory markers (eg, LDH, CRP, and ferritin) appeared across most sites as predictive of hospitalizations, specifically for COVID-19, which fits intuitively because an underlying systemic pathophysiological mechanism of SARS-CoV-2 is thought to be an inflammatory process [39,40], and guidelines therefore have encouraged health care providers to check inflammatory markers on COVID-19 admissions [41,42]. Many of these inflammatory laboratory tests are not routinely ordered on all hospitalized patients and would therefore be expected to help distinguish COVID-19 from other diseases. However, laboratory protocol differences across sites may have reduced generalizability for this metric.
Our methods generated pairs of items using OR and groups of up to 4 using AND logical operators. Our feature sets were somewhat vulnerable to the problem that specificity decreases when multiple elements are combined with OR, although, in general, OR feature sets performed better across sites because they could be designed to choose the top-performing elements at each site.
In addition to site differences, we also found changing disease management patterns over time. At the start of the pandemic, the only predictive phenotype was a pneumonia diagnosis. As standard COVID-19 order recommendations began to appear, laboratory orders became more consistent and predictive. Next, remdesivir began to be administered regularly. Finally, COVID-19-specific ICD-10 codes began to appear.
Overall, we found that an informatics-informed phenotyping approach successfully improved classification of for-COVID-19 versus incidental SARS-CoV-2-positive admissions, although generalizability was a challenge. Although some transfer learning is apparent (ie, a few phenotypes performed well across sites), local practice and charting patterns reduced generalizability. Specifically, phenotypes involving only laboratory tests did not perform well at site C, because the prevalence of these laboratory tests was low in the overall EHR data. This could be due to a data extraction or mapping issue in the underlying data warehouse. Site D had lower performance than other sites on the cross-site rules but not on the site-specific rules, perhaps highlighting less typical clinician treatment patterns.
Any of the multisite phenotypes developed here could be implemented as a cohort enhancement tool in hospital systems or data research networks, and the laboratory-only phenotypes (“CRP and Ferritin”) could be used for real-time corrections in reporting. However, because of the changing nature of COVID-19 and practice and coding variation across sites, these phenotypes should be used primarily as a starting point. It is important to run the phenotyping algorithm on each individual site’s data to tweak the rules to optimize them for each implementation.
Limitations
Although the current data start at the beginning of the pandemic, they do not include the current Omicron wave nor much of the Delta wave. We believe that the techniques introduced here (if not the phenotypes themselves) will be applicable to these variants, and we are planning future studies to validate this.
Our phenotypes demonstrated some transfer learning but not enough to create a single phenotype applicable to all sites. Technically, our system used machine learning at individual sites, but results were manually aggregated across sites. Emerging techniques for federated learning [43] might reduce the manual work required and increase the complexity of possible cross-site phenotype testing.
Finally, an inherent weakness of EHR-based research is that EHR data do not directly represent the state of the patient, because some observations are not recorded in structured data and some entries in the EHR are made for nonclinical reasons (eg, to justify the cost of a test or to ensure adequate reimbursement for services). This is common to all EHR research efforts, and we mitigated this limitation by developing chart-verified phenotypes.
Conclusion
At 4 health care systems around the United States over an 18-month period starting in March 2020, we developed and applied standardized chart review criteria to characterize the correct classification of hospitalization specifically for COVID-19 as compared to incidental hospitalization of a patient with a positive SARS-CoV-2 test or ICD-10 code. Then we applied HSD and frequent item set mining to electronic phenotyping to generate phenotypes specific to hospitalizations for COVID-19, and we showed how patterns changed over the course of the pandemic. Application of this approach could improve public health reporting, health care system resource disbursement, and research conclusions.
Acknowledgments
We would like to additionally thank Trang Le, PhD, for her assistance in developing the temporal phenotype visualization R script; Karen Olson, PhD, for her knowledge of the R programming language and insights into the topic of this study; Margaret Vella for her administrative coordination; and Isaac Kohane, MD, PhD, for convening, leading, and guiding the Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by electronic health record (4CE).
We would like to express our gratitude to all group members of the Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR (4CE) for their contribution to the study [Multimedia Appendix 2].
JSM is supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Library of Medicine (NLM) T15LM007092. MM is supported by NIH/National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (NCATS) UL1TR001857. AMS is supported by NIH/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) K23HL148394 and L40HL148910 and NIH/NCATS UL1TR001420. GMW is supported by NIH/NCATS UL1TR002541, NIH/NCATS UL1TR000005, NIH/NLM R01LM013345, and NIH/National Human Genome Research Institute (NHGRI) 3U01HG008685-05S2. WY is supported by NIH T32HD040128. KBW is supported by NIH/NHLBI R01 HL151643-01. YL is supported by NIH/NCATS U01TR003528 and NLM 1R01LM013337. GSO is supported by NIH U24CA210867 and P30ES017885. SV is supported by NCATS UL1TR001857. JHH is supported by NCATS UL1-TR001878. ZX is supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) R01NS098023 and NINDS R01NS124882. SNM is supported by NCATS 5UL1TR001857-05 and NHGRI 5R01HG009174-04.
The study sponsors played no role in defining or designing the study, nor did they play any role in collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; or in the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Abbreviations
- 4CE
Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR
- BIDMC
Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center
- CRP
C-reactive protein
- EHR
electronic health record
- HSD
hospital system dynamics
- ICD-10
International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision
- IRB
Institutional Review Board
- INR
international normalized ratio
- LDH
lactate dehydrogenase
- MGB
Mass General Brigham
- NWU
Northwestern University
- PCR
polymerase chain reaction
- PPV
positive predictive value
- UPITT
University of Pittsburgh/University of Pittsburgh Medical Center
4CE data dictionary. 4CE: Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR. EHR: electronic health record.
List of group members of the Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR (4CE).
Data Availability
All data analysis code developed for this study is available under the Mozilla Public License v2 with a health care disclaimer.
The electronic health record (EHR) data sets analyzed during this study cannot be made publicly available due to regulations for protecting patient privacy and confidentiality. These regulations also prevent the data from being made available upon request from the authors. Any questions about the data set can be directed to the corresponding author.
Footnotes
Authors' Contributions: JGK and SNM conceptualized and designed the study. ZHS, GAB, JGK, and SNM conceptualized and designed the chart review process. JGK, ZHS, MRH, CJK, JSM, MM, MJS, ACP, GMW, WY, YL, SV, ZX, and GAB contributed to data collection (of electronic health record [EHR] data or chart reviews). JGK, ZHS, MRH, CJK, JSM, MM, MJS, ACP, AMS, GMW, WY, PA, KBW, GSO, SV, JHH, ZX, GAB, and SNM contributed to data analysis or interpretation. JGK, ZHS, MRH, CJK, MM, HE, AMS, GMW, PA, KBW, YL, GSO, JHH, ZX, GAB, and SNM contributed to drafting and revision of the manuscript. SNM contributed to grant funding. All authors approved the final draft of the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest: The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. JGK reports a consulting relationship with the i2b2-tranSMART Foundation through Invocate, Inc. CJK reports consulting for the University of California, Berkeley; the University of Southern California (USC), and the University of California, San Francisco (UCSF). AMS reports funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH)/National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK) R01DK127208, NIH/National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI) R01HL146818, and institutional pilot awards from the Wake Forest School of Medicine. GMW reports consulting for the i2b2-tranSMART Foundation. PA reports consulting for the Cincinnati Children’s Hospital Medical Center (CCHMC) and Boston Children’s Hospital (BCH). ZX has received research support from the NIH, the Department of Defense, and Octave Biosciences and has served on the scientific advisory board for Genentech/Roche. SNM reports professional relationships with the Scientific Advisory Board for Boston University, the Universidad de Puerto Rico, the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), the University of Massachusetts Medical School (UMMS), and the Kenner Family Research Fund.
References
- 1.Haendel MA, Chute CG, Bennett TD, Eichmann DA, Guinney J, Kibbe WA, Payne PRO, Pfaff ER, Robinson PN, Saltz JH, Spratt H, Suver C, Wilbanks J, Wilcox AB, Williams AE, Wu C, Blacketer C, Bradford RL, Cimino JJ, Clark M, Colmenares EW, Francis PA, Gabriel D, Graves A, Hemadri R, Hong SS, Hripscak G, Jiao D, Klann JG, Kostka K, Lee AM, Lehmann HP, Lingrey L, Miller RT, Morris M, Murphy SN, Natarajan K, Palchuk MB, Sheikh U, Solbrig H, Visweswaran S, Walden A, Walters KM, Weber GM, Zhang XT, Zhu RL, Amor B, Girvin AT, Manna A, Qureshi N, Kurilla MG, Michael SG, Portilla LM, Rutter JL, Austin CP, Gersing KR, N3C Consortium The National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C): rationale, design, infrastructure, and deployment. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021 Mar 01;28(3):427–443. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocaa196. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32805036 .5893482 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Brat GA, Weber GM, Gehlenborg N, Avillach P, Palmer NP, Chiovato L, Cimino J, Waitman LR, Omenn GS, Malovini A, Moore JH, Beaulieu-Jones BK, Tibollo V, Murphy SN, Yi SL, Keller MS, Bellazzi R, Hanauer DA, Serret-Larmande A, Gutierrez-Sacristan A, Holmes JJ, Bell DS, Mandl KD, Follett RW, Klann JG, Murad DA, Scudeller L, Bucalo M, Kirchoff K, Craig J, Obeid J, Jouhet V, Griffier R, Cossin S, Moal B, Patel LP, Bellasi A, Prokosch HU, Kraska D, Sliz P, Tan ALM, Ngiam KY, Zambelli A, Mowery DL, Schiver E, Devkota B, Bradford RL, Daniar M, Daniel C, Benoit V, Bey R, Paris N, Serre P, Orlova N, Dubiel J, Hilka M, Jannot AS, Breant S, Leblanc J, Griffon N, Burgun A, Bernaux M, Sandrin A, Salamanca E, Cormont S, Ganslandt T, Gradinger T, Champ J, Boeker M, Martel P, Esteve L, Gramfort A, Grisel O, Leprovost D, Moreau T, Varoquaux G, Vie J, Wassermann D, Mensch A, Caucheteux C, Haverkamp C, Lemaitre G, Bosari S, Krantz ID, South A, Cai T, Kohane IS. International electronic health record-derived COVID-19 clinical course profiles: the 4CE consortium. NPJ Digit Med. 2020;3:109. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00308-0. doi: 10.1038/s41746-020-00308-0.308 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Murphy SN, Weber G, Mendis M, Gainer V, Chueh HC, Churchill S, Kohane I. Serving the enterprise and beyond with informatics for integrating biology and the bedside (i2b2) J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2010;17(2):124–30. doi: 10.1136/jamia.2009.000893. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/20190053 .17/2/124 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Visweswaran S, Samayamuthu MJ, Morris M, Weber GM, MacFadden D, Trevvett P, Klann JG, Gainer VS, Benoit B, Murphy SN, Patel L, Mirkovic N, Borovskiy Y, Johnson RD, Wyatt MC, Wang AY, Follett RW, Chau N, Zhu W, Abajian M, Chuang A, Bahroos N, Reeder P, Xie D, Cai J, Sendro ER, Toto RD, Firestein GS, Nadler LM, Reis SE. Development of a coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) application ontology for the Accrual to Clinical Trials (ACT) network. JAMIA Open. 2021 Apr;4(2):ooab036. doi: 10.1093/jamiaopen/ooab036. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/34113801 .ooab036 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Khullar D. Do the Omicron Numbers Mean What We Think They Mean? The New Yorker. 2022. Jan 16, [2022-01-25]. https://www.newyorker.com/magazine/2022/01/24/do-the-omicron-numbers-mean-what-we-think-they-mean .
- 6.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ICD-10-CM Official Coding and Reporting Guidelines. National Center for Health Statistics. 2020. [2022-04-29]. https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/icd/COVID-19-guidelines-final.pdf .
- 7.Bennett TD, Moffitt RA, Hajagos JG, Amor B, Anand A, Bissell MM, Bradwell KR, Bremer C, Byrd JB, Denham A, DeWitt PE, Gabriel D, Garibaldi BT, Girvin AT, Guinney J, Hill EL, Hong SS, Jimenez H, Kavuluru R, Kostka K, Lehmann HP, Levitt E, Mallipattu SK, Manna A, McMurry JA, Morris M, Muschelli J, Neumann AJ, Palchuk MB, Pfaff ER, Qian Z, Qureshi N, Russell S, Spratt H, Walden A, Williams AE, Wooldridge JT, Yoo YJ, Zhang XT, Zhu RL, Austin CP, Saltz JH, Gersing KR, Haendel MA, Chute CG, National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C) Consortium Clinical characterization and prediction of clinical severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection among US adults using data from the US National COVID Cohort Collaborative. JAMA Netw Open. 2021 Jul 01;4(7):e2116901. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16901. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.16901 .2781923 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Al-Aly Z, Xie Y, Bowe B. High-dimensional characterization of post-acute sequelae of COVID-19. Nature. 2021 Jun;594(7862):259–264. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03553-9.10.1038/s41586-021-03553-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.National Notifiable Diseases Surveillance System (NNDSS), Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) 2021 Case Definition. 2021. [2022-04-29]. https://ndc.services.cdc.gov/case-definitions/coronavirus-disease-2019-2021/
- 10.Sah P, Fitzpatrick MC, Zimmer CF, Abdollahi E, Juden-Kelly L, Moghadas SM, Singer BH, Galvani AP. Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Aug 24;118(34):e2109229118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2109229118. https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2109229118?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3dpubmed .2109229118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Buitrago-Garcia D, Egli-Gany D, Counotte MJ, Hossmann S, Imeri H, Ipekci AM, Salanti G, Low N. Occurrence and transmission potential of asymptomatic and presymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infections: a living systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Med. 2020 Sep;17(9):e1003346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1003346. https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.1003346 .PMEDICINE-D-20-02690 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Fisman DN, Tuite AR. Asymptomatic infection is the pandemic's dark matter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2021 Sep 21;118(38):e2114054118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2114054118. https://www.pnas.org/doi/abs/10.1073/pnas.2114054118?url_ver=Z39.88-2003&rfr_id=ori:rid:crossref.org&rfr_dat=cr_pub%3dpubmed .2114054118 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cohen JB, D'Agostino McGowan L, Jensen ET, Rigdon J, South AM. Evaluating sources of bias in observational studies of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin II receptor blocker use during COVID-19: beyond confounding. J Hypertens. 2021 Apr 01;39(4):795–805. doi: 10.1097/HJH.0000000000002706. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33186321 .00004872-202104000-00028 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Garrett N, Tapley A, Andriesen J, Seocharan I, Fisher LH, Bunts L, Espy N, Wallis CL, Randhawa AK, Ketter N, Yacovone M, Goga A, Bekker L, Gray GE, Corey L. High rate of asymptomatic carriage associated with variant strain omicron. medRxiv. 2022 Jan 14; doi: 10.1101/2021.12.20.21268130. doi: 10.1101/2021.12.20.21268130. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yu S, Ma Y, Gronsbell J, Cai T, Ananthakrishnan AN, Gainer VS, Churchill SE, Szolovits P, Murphy SN, Kohane IS, Liao KP, Cai T. Enabling phenotypic big data with PheNorm. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2018 Jan 01;25(1):54–60. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocx111. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29126253 .4590261 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Hripcsak G, Albers DJ. Next-generation phenotyping of electronic health records. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2013 Jan 01;20(1):117–21. doi: 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-001145. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/22955496 .amiajnl-2012-001145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Castro VM, Minnier J, Murphy SN, Kohane I, Churchill SE, Gainer V, Cai T, Hoffnagle AG, Dai Y, Block S, Weill SR, Nadal-Vicens M, Pollastri AR, Rosenquist JN, Goryachev S, Ongur D, Sklar P, Perlis RH, Smoller JW, International Cohort Collection for Bipolar Disorder Consortium Validation of electronic health record phenotyping of bipolar disorder cases and controls. Am J Psychiatry. 2015 Apr;172(4):363–72. doi: 10.1176/appi.ajp.2014.14030423. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/25827034 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Klann JG, Estiri H, Weber GM, Moal B, Avillach P, Hong C, Tan ALM, Beaulieu-Jones BK, Castro V, Maulhardt T, Geva A, Malovini A, South AM, Visweswaran S, Morris M, Samayamuthu MJ, Omenn GS, Ngiam KY, Mandl KD, Boeker M, Olson KL, Mowery DL, Follett RW, Hanauer DA, Bellazzi R, Moore JH, Loh N-HW, Bell DS, Wagholikar KB, Chiovato L, Tibollo V, Rieg S, Li ALLJ, Jouhet V, Schriver E, Xia Z, Hutch M, Luo Y, Kohane IS, Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR (4CE) (CONSORTIA AUTHOR) Brat GA, Murphy SN. Validation of an internationally derived patient severity phenotype to support COVID-19 analytics from electronic health record data. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2021 Jul 14;28(7):1411–1420. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocab018. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33566082 .6132348 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.4CE: Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR. [2022-04-29]. https://covidclinical.net/
- 20.Weber GM, Zhang HG, L'Yi S, Bonzel C, Hong C, Avillach P, Gutiérrez-Sacristán A, Palmer NP, Tan ALM, Wang X, Yuan W, Gehlenborg N, Alloni A, Amendola DF, Bellasi A, Bellazzi R, Beraghi M, Bucalo M, Chiovato L, Cho K, Dagliati A, Estiri H, Follett RW, García Barrio N, Hanauer DA, Henderson DW, Ho Y, Holmes JH, Hutch MR, Kavuluru R, Kirchoff K, Klann JG, Krishnamurthy AK, Le TT, Liu M, Loh NHW, Lozano-Zahonero S, Luo Y, Maidlow S, Makoudjou A, Malovini A, Martins MR, Moal B, Morris M, Mowery DL, Murphy SN, Neuraz A, Ngiam KY, Okoshi MP, Omenn GS, Patel LP, Pedrera Jiménez M, Prudente RA, Samayamuthu MJ, Sanz Vidorreta FJ, Schriver ER, Schubert P, Serrano Balazote P, Tan BW, Tanni SE, Tibollo V, Visweswaran S, Wagholikar KB, Xia Z, Zöller D, Kohane Is, Cai T, South Am, Brat Ga. International changes in COVID-19 clinical trajectories across 315 hospitals and 6 countries: retrospective cohort study. J Med Internet Res. 2021 Oct 11;23(10):e31400. doi: 10.2196/31400. https://www.jmir.org/2021/10/e31400/ v23i10e31400 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kohane IS, Aronow BJ, Avillach P, Beaulieu-Jones BK, Bellazzi R, Bradford RL, Brat GA, Cannataro M, Cimino JJ, García-Barrio N, Gehlenborg N, Ghassemi M, Gutiérrez-Sacristán A, Hanauer DA, Holmes JH, Hong C, Klann JG, Loh NHW, Luo Y, Mandl KD, Daniar M, Moore JH, Murphy SN, Neuraz A, Ngiam KY, Omenn GS, Palmer N, Patel LP, Pedrera-Jiménez M, Sliz P, South AM, Tan ALM, Taylor DM, Taylor BW, Torti C, Vallejos AK, Wagholikar KB, Consortium For Clinical Characterization Of COVID-19 By EHR (4CE) Weber GM, Cai T. What every reader should know about studies using electronic health record data but may be afraid to ask. J Med Internet Res. 2021 Mar 02;23(3):e22219. doi: 10.2196/22219. https://www.jmir.org/2021/3/e22219/ v23i3e22219 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fatima S. Mass. Hospitals Will Begin Reporting Primary vs. Incidental COVID-19 Admissions on Monday, DPH Says. The Boston Globe. 2022. [2022-01-26]. https://www.bostonglobe.com/2022/01/06/nation/teachers-union-accuses-state-gross-incompetence-questions-swirl-around-masks-distributed-school-staff/
- 23.Bebinger M. State Changes COVID Reporting to Distinguish between Primary and Incidental Hospital Cases. WBUR. 2022. [2022-01-26]. https://www.wbur.org/news/2022/01/21/massachusetts-primary-incidental-coronavirus-grouping .
- 24.Agniel D, Kohane IS, Weber GM. Biases in electronic health record data due to processes within the healthcare system: retrospective observational study. BMJ. 2018 Apr 30;361:k1479. doi: 10.1136/bmj.k1479. http://www.bmj.com/lookup/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=29712648 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Agrawal R, Imieliński T, Swami A. Mining association rules between sets of items in large databases. Proceedings of the 1993 ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data; 1993; New York, NY. 1993. Jun, pp. 207–216. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Agrawal R, Srikant R. Fast Algorithms for Mining Association Rules. IBM Almaden Research Center; [2022-04-29]. https://citeseerx.ist.psu.edu/viewdoc/download?doi=10.1.1.40.7506&rep=rep1&type=pdf . [Google Scholar]
- 27.Wright A, Chen ES, Maloney FL. An automated technique for identifying associations between medications, laboratory results and problems. J Biomed Inform. 2010 Dec;43(6):891–901. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2010.09.009. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1532-0464(10)00141-3 .S1532-0464(10)00141-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Klann JG, Szolovits P, Downs SM, Schadow G. Decision support from local data: creating adaptive order menus from past clinician behavior. J Biomed Inform. 2014 Apr;48:84–93. doi: 10.1016/j.jbi.2013.12.005. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1532-0464(13)00196-2 .S1532-0464(13)00196-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Adamo J. Data Mining for Association Rules and Sequential Patterns: Sequential and Parallel Algorithms. Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: Springer Science & Business Media; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 30.Klann J. Jeff Klann’s 4CE-Related Tools Github. [2022-03-16]. https://github.com/jklann/jgk-i2b2tools .
- 31.Klann JG, Joss M, Shirali R, Natter M, Schneeweiss S, Mandl KD, Murphy SN. The ad-hoc uncertainty principle of patient privacy. AMIA Jt Summits Transl Sci Proc. 2018;2017:132–138. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/29888058 . [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.CMS Releases Recommendations on Adult Elective Surgeries, Non-Essential Medical, Surgical, and Dental Procedures During COVID-19 Response. CMS Newsroom. 2020. [2022-04-29]. https://www.cms.gov/newsroom/press-releases/cms-releases-recommendations-adult-elective-surgeries-non-essential-medical-surgical-and-dental .
- 33.Lan L, Xu D, Ye G, Xia C, Wang S, Li Y, Xu H. Positive RT-PCR test results in patients recovered from COVID-19. JAMA. 2020 Apr 21;323(15):1502–1503. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.2783. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32105304 .2762452 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wu J, Liu X, Liu J, Liao H, Long S, Zhou N, Wu P. Coronavirus disease 2019 test results after clinical recovery and hospital discharge among patients in China. JAMA Netw Open. 2020 May 01;3(5):e209759. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.9759. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.9759 .2766230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Skittrall JP, Wilson M, Smielewska AA, Parmar S, Fortune MD, Sparkes D, Curran MD, Zhang H, Jalal H. Specificity and positive predictive value of SARS-CoV-2 nucleic acid amplification testing in a low-prevalence setting. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Mar;27(3):469.e9–469.e15. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.10.003. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1198-743X(20)30614-5 .S1198-743X(20)30614-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Mina MJ, Peto TE, García-Fiñana M, Semple MG, Buchan IE. Clarifying the evidence on SARS-CoV-2 antigen rapid tests in public health responses to COVID-19. Lancet. 2021 Apr 17;397(10283):1425–1427. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00425-6. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/33609444 .S0140-6736(21)00425-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Weber GM, Kohane IS. Extracting physician group intelligence from electronic health records to support evidence based medicine. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e64933. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064933. https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0064933 .PONE-D-11-22167 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Batlle D, Soler MJ, Sparks MA, Hiremath S, South AM, Welling PA, Swaminathan S, COVID-19ACE2 in Cardiovascular‚ Lung‚ Kidney Working Group Acute kidney injury in COVID-19: emerging evidence of a distinct pathophysiology. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Jul;31(7):1380–1383. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020040419. https://jasn.asnjournals.org/cgi/pmidlookup?view=long&pmid=32366514 .ASN.2020040419 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y, Zhang L, Fan G, Xu J, Gu X, Cheng Z, Yu T, Xia J, Wei Y, Wu W, Xie X, Yin W, Li H, Liu M, Xiao Y, Gao H, Guo L, Xie J, Wang G, Jiang R, Gao Z, Jin Q, Wang J, Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. Lancet. 2020 Feb 15;395(10223):497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0140-6736(20)30183-5 .S0140-6736(20)30183-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Guan W, Ni Z, Hu Y, Liang W, Ou C, He J, Liu L, Shan H, Lei C, Hui DSC, Du B, Li L, Zeng G, Yuen K, Chen R, Tang C, Wang T, Chen P, Xiang J, Li S, Wang J, Liang Z, Peng Y, Wei L, Liu Y, Hu Y, Peng P, Wang J, Liu J, Chen Z, Li G, Zheng Z, Qiu S, Luo J, Ye C, Zhu S, Zhong N, China Medical Treatment Expert Group for Covid-19 Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. 2020 Apr 30;382(18):1708–1720. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2002032. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32109013 . [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kim A, Gandhi RT. COVID-19: Management in Hospitalized Adults. UpToDate. 2022. [2022-04-29]. https://www.uptodate.com/contents/covid-19-management-in-hospitalized-adults?search=covid-19%20admission%20management&source=covid19_landing&usage_type=main_section .
- 42.Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Interim Clinical Guidance for Management of Patients with Confirmed Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) [2022-02-04]. https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/hcp/clinical-guidance-management-patients.html .
- 43.Pfitzner B, Steckhan N, Arnrich B. Federated learning in a medical context: a systematic literature review. ACM Trans Internet Technol. 2021 Jun;21(2):1–31. doi: 10.1145/3412357. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
4CE data dictionary. 4CE: Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR. EHR: electronic health record.
List of group members of the Consortium for Clinical Characterization of COVID-19 by EHR (4CE).
Data Availability Statement
All data analysis code developed for this study is available under the Mozilla Public License v2 with a health care disclaimer.
The electronic health record (EHR) data sets analyzed during this study cannot be made publicly available due to regulations for protecting patient privacy and confidentiality. These regulations also prevent the data from being made available upon request from the authors. Any questions about the data set can be directed to the corresponding author.


