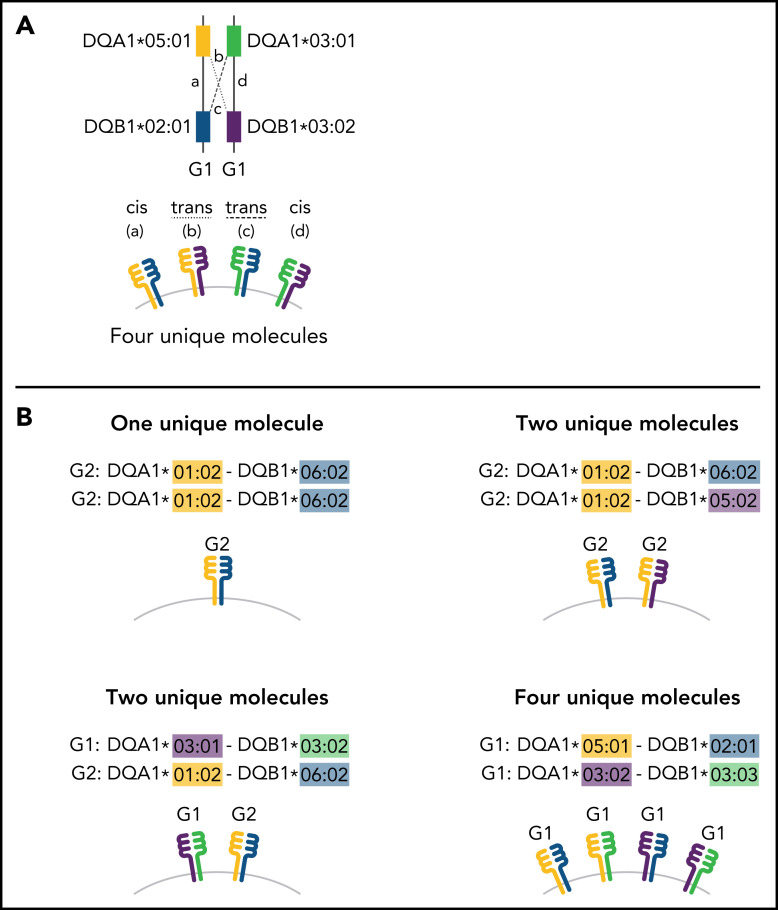
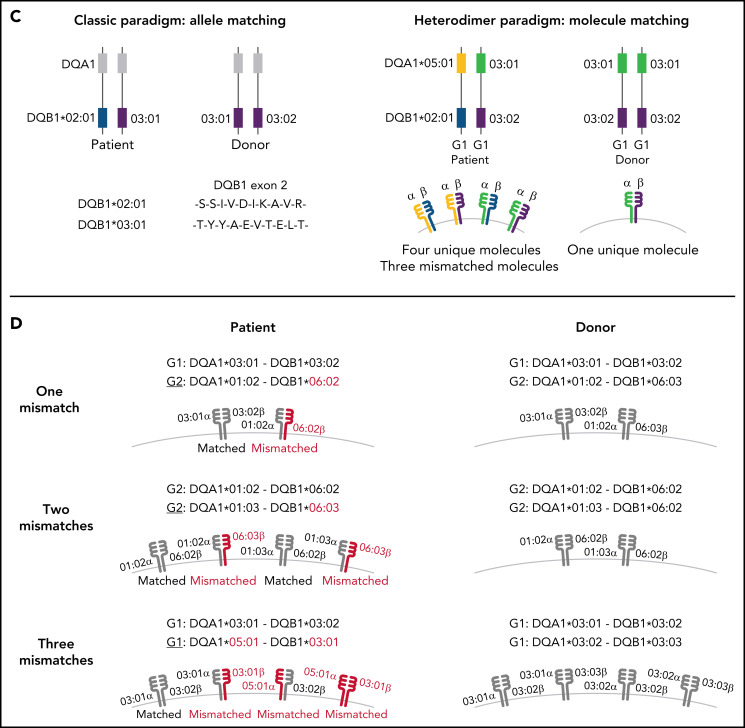
Figure 1.
Schema for HLA-DQ heterodimers. (A) HLA-DQ molecules are heterodimers composed of an α-chain protein encoded by the HLA-DQA1 allele and a β-chain protein encoded by the HLA-DQB1 allele that are coinherited on the same parental haplotype (a and d cis heterodimers). Cis encoded parental DQA1-DQB1 haplotypes define the genotype of the individual: G1G1, G1G2, and G2G2. In addition to cis heterodimer molecules, trans-heterodimer molecules (b and c) are formed by the α-chain from 1 parent with the β chain of the other parent. Stable trans-dimerization occurs between G1α (DQA1*02/03/04/05/06) and G1β (DQB1*02/03/04) and between G2α (DQA1*01) and G2β (DQB1*05/06) but not between G1α and G2β or G2α and G1β. (B) Individuals may encode up to 4 unique HLA-DQ molecules depending on DQA1-DQB1 homozygosity and G1G1, G1G2, and G2G2 genotype. G1G1 and G2G2 individuals can form trans-dimers between the DQα from 1 haplotype with the DQβ of the opposing haplotype, generating up to 4 unique molecules. Trans-dimerization cannot occur between G1α and G2β or between G2α and G1β chains; hence, G1G2 individuals have 2 unique molecules each defined by the cis-encoded parental DQA1-DQB1 haplotypes. (C) The classic paradigm for HLA-DQB1 exon 2 allele matching (left) is based on donor compatibility for amino acid residues of the parentally inherited β chains. HLA-DQB1 exon 2 matching does not interrogate HLA-DQA1 (gray) and current donor selection criteria do not include HLA-DQA1. The heterodimer model (right) incorporates sequence information from the α-chain product of DQA1 and the β-chain product of DQB1. The heterodimer paradigm describes the total number of unique molecules, the number of mismatched molecules, and the specific α- and β-protein sequences of a given molecule. (D) Transplantation from donors with 1 HLA-DQB1 allele mismatch may result in 1, 2, or 3 mismatched HLA-DQ molecules in the patient depending on homozygosity of HLA-DQA1 and DQB1 alleles in the patient and the donor and G1G1, G1G2, and G2G2 genotype. The mismatch is denoted in red.