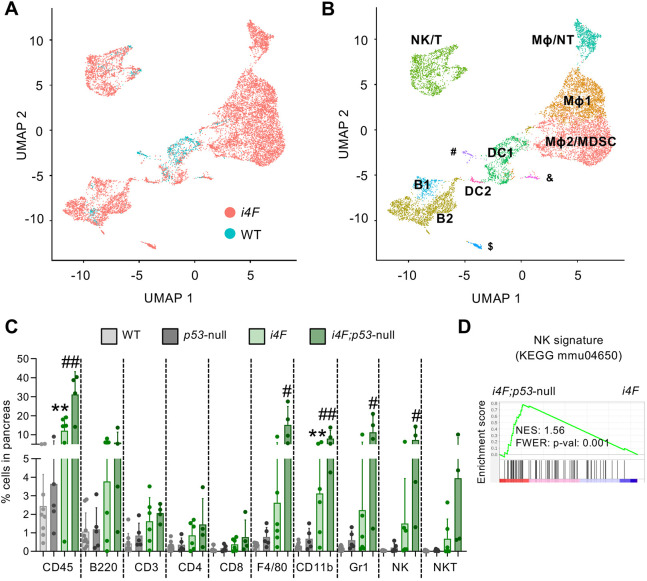
Fig. 1.
Immune cell populations infiltrate the pancreas during in vivo reprogramming. (A) UMAP plot visualizing immune cell infiltrates in the pancreas. WT (n=2) and i4F (n=3) mice were treated with doxycycline in the drinking water (1 mg/ml) for 1 week to induce partial reprogramming. (B) UMAP plot of immune cell populations. Clusters were annotated using the most-significant markers of each cluster and the FindAllMarkers function of Seurat (v3). The minor clusters correspond to endothelial cells (#), stellate cells (&) and marginal zone B cells ($). (C) Flow cytometry analysis of the main immune populations infiltrating the pancreas after WT (n=9), p53-null (n=5), i4F (n=6) and i4F;p53-null (n=4) mice were treated with doxycycline for 7 days. Cells were gated from DAPI−/CD45+ cells. Data are pooled from two independent experiments and represent mean±s.e.m. **P<0.01 (WT versus i4F) and #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 (i4F versus i4F;p53-null) evaluated using the unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test. (D) Previously published RNA-seq data generated in our laboratory (Mosteiro et al., 2016) from the pancreas of i4F and i4F;p53-null (high-reprogramming) mice were used to perform gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) against a published signature (KEGG entry: mmu04650) of NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity. B, B cells; DC, dendritic cells; Mφ, macrophages; MDSC, myeloid derived suppressor cells; NK, natural killer cells; NT, neutrophils; T, T cells.