Abstract
The increasing multidrug-resistance in pathogenic microbes and the emergence of new microbial pathogens like coronaviruses have necessitated the discovery of new antimicrobials to treat these pathogens. The use of antibiotics began after the discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming from Penicillium chrysogenum. This has attracted the scientific community to delve deep into the antimicrobial capabilities of various fungi in general and Phoma spp. in particular. Phoma spp. such as Phoma arachidicola, P. sorghina, P. exigua var. exigua, P. herbarum, P. multirostrata, P. betae, P. fimeti, P. tropica, among others are known to produce different bioactive metabolites including polyketides, macrosporin, terpenes and terpenoids, thiodiketopiperazines, cytochalasin derivatives, phenolic compounds, and alkaloids. These bioactive metabolites have already demonstrated their antimicrobial potential (antibacterial, antifungal, and antiviral) against various pathogens. In the present review, we have discussed the antimicrobial potential of secondary metabolites produced by different Phoma species. We have also deliberated the biogenic synthesis of eco-friendly antimicrobial silver nanoparticles from Phoma and their role as potential antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: Phoma spp., Multidrug-resistance, Antibiotics, Bioactive metabolites, Silver nanoparticles
Key points
Growing multidrug-resistance and emerging pathogens need new antimicrobial drugs
Different species of Phoma produce antimicrobial metabolites
Phoma spp. are potential synthesizers of silver nanoparticles demonstrating antimicrobial activity.
Introduction
There are terrifying global reports of the multidrug-resistance in pathogens that are not responding to the available antibiotics (Wencewicz 2019). The main reasons for developing resistance by microbes include misuse and overuse of antibiotics, and environmental factors (Ghosh et al. 2020; Christaki et al. 2020). This problem of antibiotic resistance has garnered the attention of the scientific community, policymakers, and the public at large from all over the world, and it is a global health challenge (Markley and Wencewicz 2018; Hu et al. 2021).
The new and emerging diseases caused by microbes are major threat to mankind. The recent emergence of the COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 is a burning example that has devastated human life globally. The current burden of co-infections and superinfections such as mucormycosis in COVID-19 patients is also a great issue that emphasizes the discovery of new antimicrobials (Feldman and Anderson 2021). Moreover, there has been huge concern about re-emerging microbial diseases such as malaria, tuberculosis, influenza, cholera, pertussis, etc.
Unfortunately, for more than three decades, no new antibiotics have been discovered (Böttcher et al. 2021), and therefore, these facts warrant the discovery of new antibiotics and/ or search for new alternatives from natural products such as plants and microbes to tackle such a grave problem (WHO Newsletter 2020). Among the microbes, fungi play a key role in the production of antimicrobials. The serendipitous discovery of penicillin by Alexander Fleming (1929) from Penicillium notatum and P. chrysogenum is the best example (Zhu et al. 2014). Other potential antibiotics produced by fungi include cephalosporins and griseofulvin. Several species of Phoma such as P. arachidicola, P. sorghina, P. exigua var. exigua, P. herbarum, P. multirostrata, P. betae, and P. fimeti are pigment-producing (Chande et al. 1899) and some Phoma species have already demonstrated the antimicrobial potential against various fungi (Aoyagi et al. 2007; Hussain et al. 2014), bacteria (Huang et al. 2017; Chen et al. 2019) and viruses (Liu et al. 2019; Peng et al. 2020). They produce secondary metabolites with antimicrobial potential. These bioactive compounds include polyketides like anthraquinones and diphenyl ether derivatives; ergocytochalasin A, macrosporin, thiodiketopiperazines, cytochalasin derivatives, and alkaloids. The antimicrobial metabolites producing species of Phoma can be harnessed to treat various microbial pathogens.
The present review is focused on the antimicrobial potential of secondary metabolites produced by different terrestrial, marine or endophytic Phoma species. Moreover, the biogenic synthesis of eco-friendly antimicrobial silver nanoparticles produced from Phoma and their role as potential antimicrobial agents have been discussed. The review is timely as so far there is no review available on the antimicrobial nature of metabolites produced by different Phoma species.
Phoma: the producer of novel bioactive metabolites
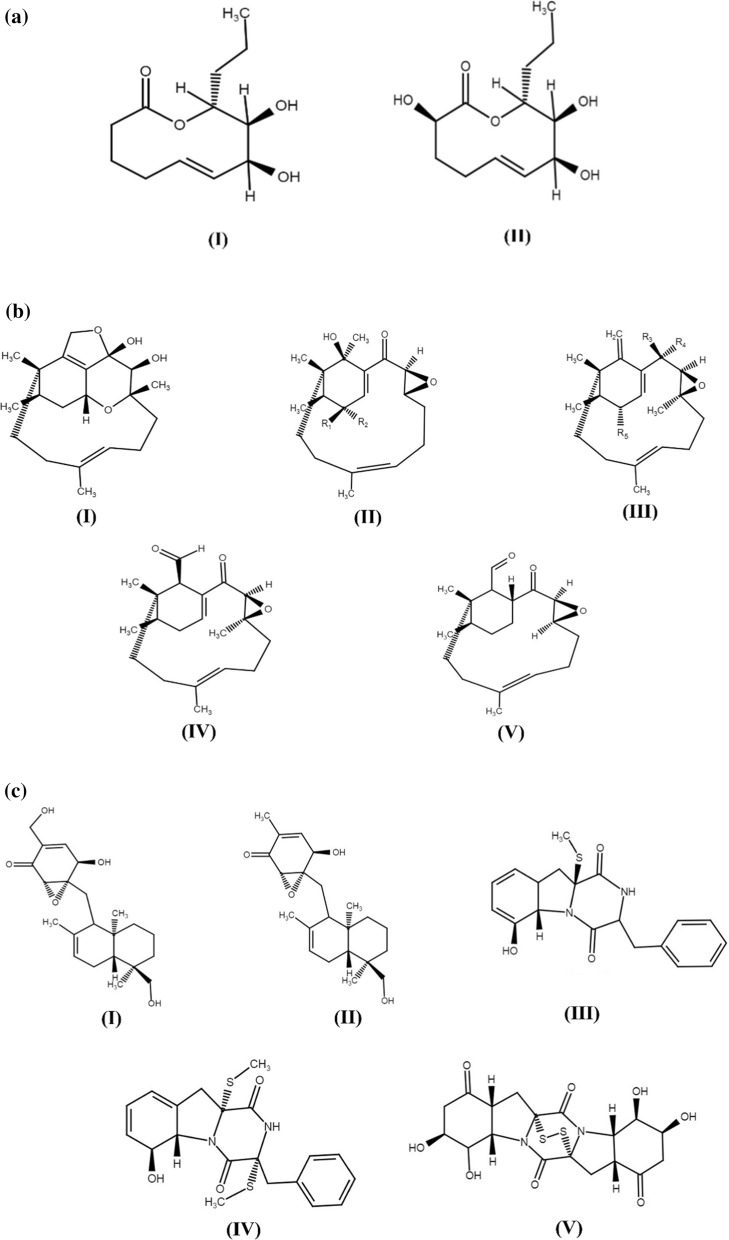
The Phoma spp. are widely distributed as pathogens of plants, animals, and humans, and also in soil, water and air (Rai 2002). The Phoma spp. secrete various metabolites that have already demonstrated antimicrobial potential (Rai et al. 2009a, b, c, 2018; Herath et al. 2009). Not only terrestrial but marine and endophytic species of Phoma are also responsible for the production of antimicrobial metabolites (Hoffman et al. 2008; Bhimba et al. 2012; Elsebai et al. 2016, 2018). A large number of metabolites with unique structures, and potential biological and pharmacological activities have been reported from the marine Phoma species particularly P. sorghina, P. herbarum, and P. tropica. These metabolites generally include lactones, quinine, diterpenes, phthalate, enolides, and anthraquinones (Fig. 1a–c). which have shown a broad range of bioactivities including antimicrobial, anticancer, radical scavenging, and cytotoxic (Rai et al. 2018, 2020). There are several reports which provide conclusive evidence that endophytic Phoma species living in plants secrete potential antimicrobial compounds (Fig. 2) (Hussain et al. 2015; Huang et al. 2017; da Silva et al. 2017; de Vries et al. 2018; Nalli et al. 2019; El-Zawawy et al. 2020; Li et al. 2020; Rai et al. 2020; Hu et al. 2021). For example, the compounds like α-tetralone derivative (3S)-3,6,7-trihydroxy-α-tetralone, together with cercosporamide, β-sitosterol, and trichodermin reported from the ethyl acetate extract of endophytic Phoma sp. (ZJWCF006) isolated from Arisaema erubescens (Wang et al., 2012). These compounds were found to be effective against the plant pathogenic fungi such as Fusarium oxysporum, Rhizoctonia solani, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Magnaporthe oryzae, and plant pathogenic bacteria including Xanthomonas campestris and X. oryzae.
Fig. 1.
a Chemical structures of bioactive compounds recovered from P. herbarum. (I) Herbarumin I and (II) Herbarumin II. b Chemical structures of bioactive metabolites isolated from marine Phoma species. (I) Phomactin A. (II) Phomactin B (R1 = H; R2 = OH) & B1 (R1 = OH; R2 = H). (III) Phomactin B2 (R3 & R4 = O; R5 = OH). (IV) Phomactin C. (V) Phomactin D. c Chemical structures of bioactive metabolites obtained from marine Phoma sp. (I) Epoxyphomalin A. (II) Epoxyphomalin B; and from Phoma sp. OUCMDZ-1847. (III) Phomazine A. (IV) Phomazine B. (V) Phomazine C (Rai et al. 2018) reprinted with permission
Fig. 2.
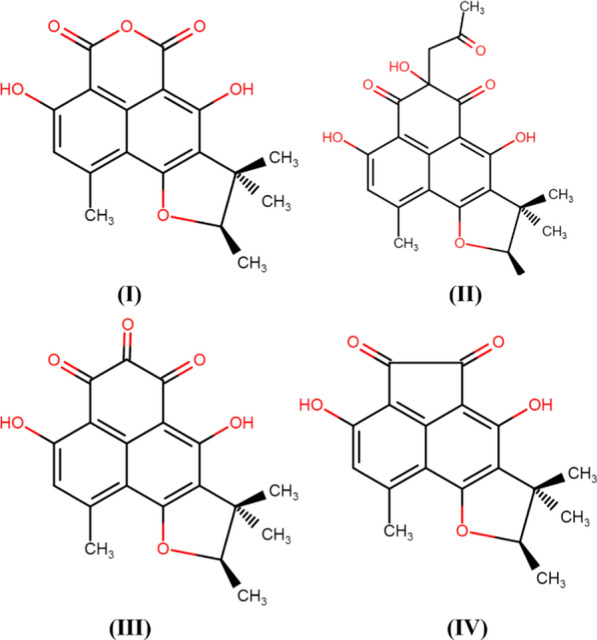
Phytochemicals identified from an endophytic Phoma sp. (I) Sclerodin, (II) 8,9-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-1,8,8,9-tetramethyl-5-(2-oxopropyl)-4H-phenaleno[1,2-b]furan-4,6(5H)-dione, (III) Atrovenetinone, and (IV) Sclerodione. Reprinted from Hussain et al. (2015) under Creative Common Rights Licence
Many species of Phoma have demonstrated remarkable antimicrobial activities. For example, Hussain et al. (2014) isolated phomafuranol (I), phomalacton (II), (3R)-5-hydroxymellein (III), and emodin (IV) (Fig. 3) from the ethyl acetate fractions of Phoma spp. recovered from Fucus serratus. which demonstrated potential inhibitory activities including antibacterial, antifungal, and antialgal.
Fig. 3.
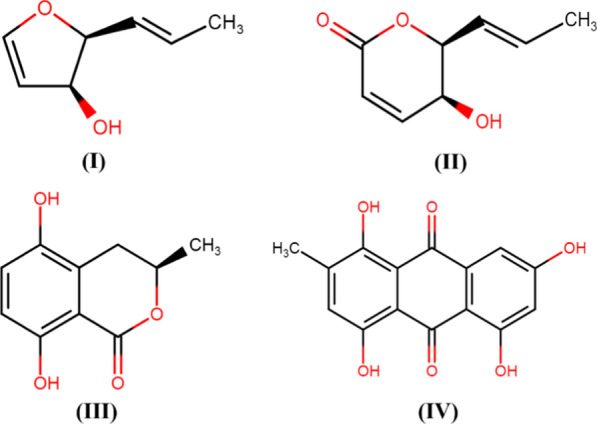
Structures of compounds isolated from Phoma sp. (I) phomafuranol, (II) phomalacton, (III) (3R)-5-hydroxymellein, and (IV) emodin (Hussain et al. 2014)—redrawn using free access MedChem Designer 5.5
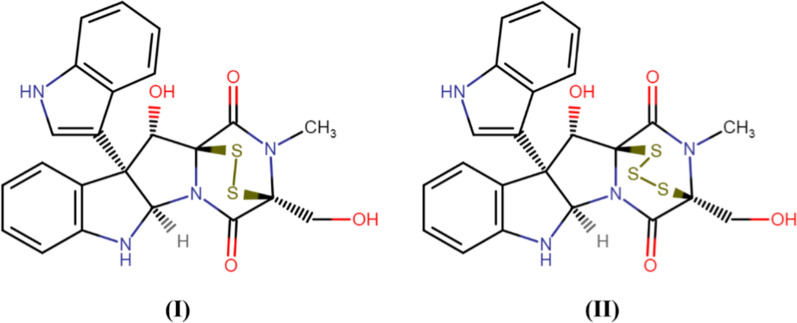
Arora et al. (2016) screened endophytes isolated from Glycyrrhiza glabra and reported the presence of Phoma spp. which was closely related to P. cucurbitacearum. Further, the authors isolated two thiodiketopiperazine derivatives (Fig. 4) from the extract of this species of Phoma which showed remarkable antibacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus and S. pyogene Moreover, these compounds significantly inhibited the biofilm formation ability of both the pathogens singly and in combination with ciprofloxacin and ampicillin in a synergistic way. Endophytic Phoma spp. (URM 7221) isolated from the leaves of Schinus terebinthifolius effectively inhibited S. aureus, MRSA, B. subtilis, and E. faecalis (de Silva et al., 2017). The potential of Phoma sp. was attributed to the production of phenolic compounds and steroids.
Fig. 4.
Thiodiketopiperazine derivatives, Compound I and II, from Phoma sp. (Arora et al. (2016); Redrawn using free access MedChem Designer 5.5
In another study, Chen et al. (2019) reported that Phoma species SYSU-SK-7 inhabiting endophytically in mangrove plant Kandelia candel contains polyketides that have shown significant activity against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Staphylococcus aureus followed by Candida albicans. Recently, Peng and his colleagues (2020) reported ergocytochalasin A from P. multirostrata which was found as an endophyte in Parasenecio albus. The bioactive compound demonstrated strong activity against different pathogenic viruses including Human dengue virus type 3 (DV3), influenza A virus (H1N1), and respiratory syncytial virus (RSV).
Secondary metabolites are responsible for antimicrobial activity
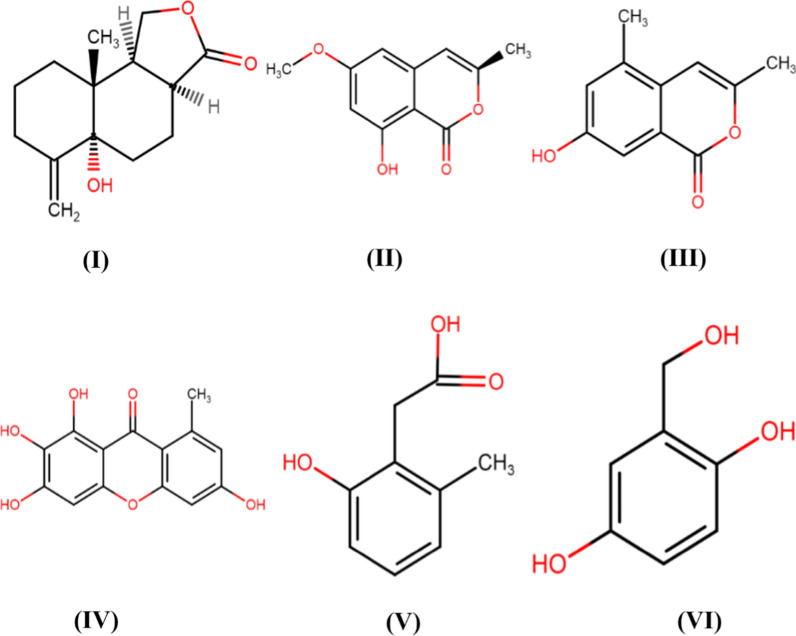
The secondary metabolites such as anthraquinones are secreted by Phoma spp. including P. herbarum, P. exigua var. exigua, P. sorghina, P. macrostoma, P. glomerata, P. macdonaldii, P. tracheiphila, P. multirostrata, P. proboscis, and P. foveata, etc. (Rai et al. 2009a, b, c, 2021a, b). As shown in Fig. 5, the different bioactive secondary metabolites reported from Phoma spp include. α-Pyrone derivatives (Sang et al. 2017), isocoumatins (Hussain et al. 2014; Shi et al. 2017); anthraquinones and xanthones (Xia et al. 2015; Liu et al. 2019); thiodiketopiperazines, phomazines (Arora et al. 2016); cytochalasin derivatives (Peng et al. 2020), and diphenyl ether derivatives (Sumilat et al. 2017), tetrasubstituted furopyrans, chenopodolans E (Evidente et al. 2016), xyloketals and chromones (Kim et al. 2018), meroterpenoids and diterpenoids (Xu et al. 2016), alkaloids such as phomapyrrolidones (Wijeratne et al. 2013), polyketides, phomaketides (Li et al. 2020) produced by different Phoma spp. A detailed account of different Phoma spp., secondary bioactive compounds, and antimicrobial activities have been given in Table 1.
Fig. 5.
Bioactive compounds recovered from both culture of an endophytic Phoma sp. isolated from the roots of Aconitum vilmorinianum, (I) Phomanolide, (II) (–)-6-methoxymellein, (III) 7-hydroxy-3, 5-dimethyl-isochromen-1-one, (IV) Norlichexanthone, (V) 6-methylsalicylic acid, and (VI) Gentisyl alcohol (Liu et al. 2019) Redrawn using free access MedChem Designer 5.5
Table 1.
Antimicrobial activity of Phoma metabolites
| Species | Compound | Activity | Host plant/Source | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phoma sp. | Sclerodione |
Antifungal: Eurotium repens Ustilago violacea |
Hussain et al. (2015) | |
| 8,9-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-1,8,8,9-tetramethyl-5-(2-oxopropyl)-4H-phena-leno[1,2-b]furan-4,6(5H)-dione | Antifungal: Mycotypha microspora | Hussain et al. (2015) | ||
| Atrovenetinone |
Antifungal: Fusarium oxysporum E. repens Ustilago violacea |
Hussain et al. (2015) | ||
| sclerodin; 8,9-dihydro-3,5,7-trihydroxy-1,8,8,9-tetramethyl-5-(2-oxopropyl)-4H-phenaleno[1,2-b]furan-4,6(5H)-dione, atrovenetinone; and sclerodione | Antibacterial: Bacillus megaterium | Hussain et al. (2015) | ||
| Phoma sp. | 4-acetylpyrenophorol |
Antibacterial: E. coli, B. megaterium Antifungal: Microbotryum violaceum Antialgal: Chlorella fusca |
Lycium intricatum |
Zhang et al. (2008) |
|
4α-acetyldihyd- ropyrenophorin |
||||
| cis-dihydropyrenophorin | ||||
| tetrahydropyrenophorin | ||||
|
7α-acetyl- seco-dihydropyrenophorin |
||||
| seco-dihydropyrenophorin |
Antibacterial: E. Coli, B. megaterium Antifungal: M. violaceum |
|||
|
seco-dihydropyrenopho- rin-1,4-lactone |
||||
| pyrenophorin |
Antifungal: Microbotryum violaceum Antialgal: C. fusca |
|||
|
4,4⬘- diacetylpyrenophorol |
||||
| Phoma sp. URM 7221 |
Antibacterial: S. aureus, B. subtilis |
Schinus terebinthifolius | da Silva et al. (2017) | |
| Phoma sp. | viridicatol, tenuazonic acid, alternariol, and alternariol monomethyl ether |
Antifungal: Fusarium graminearum, F lateritium, F. sporotrichioides, F avenaceum, Trichoderma longibrachiatum, Aspergillus flavus and Alternaria alternata |
Eleusine coracana | Mousa et al. (2015) |
| Phoma sp. | Phomodione | Antifungal: Pythium ultimum, Sclerotinia sclerotiorum, Rhizoctonia solani | Saurauia scaberrinae | Hoffman et al. (2008) |
| Antibacterial: S. aureus, E. coli | ||||
| Phoma herbarum VB7 | Phalate derivates |
Antibacterial: Vibrio cholerae, Micrococcus luteus, Salmonella thyphi, S aureus |
Mangrove leaves | Bhimba et al. (2012) |
| Phoma sp. | polyketide derivatives | Antibacterial: E. coli, B. subtilis, Mycobacterium phlei,S. aureus | Ectyplasia perox | Elsebai et al. (2016) |
| Phoma multirostrata PUTY3 | Crude extract | Antibacterial: Pseudomonas aeruginosa | Carica papaya | Ahmed and Sarma (2020) |
| Phoma medicaginis | Crude extract | Antibacterial: S. aureus, E. coli, P. aeruginosa | Mikania cordata | Jayatilake and Munasinghe (2020) |
| Phoma hedericola | Antibacterial: B. subtilis, Bacillus licheniformis, Micrococcus luteus, P. aeruginosa | Calotropis procera | Juyal et al. (2017) | |
| Phoma sorghina, Phoma exigua, Phoma herbarum, Phoma fimeti | pigments | Antibacterial:S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, B. subtilis and Proteus vulgaris | Kadu (2021) | |
| Phoma moricola | (3S)-3, 6, 7-trihydroxy-α-tetralone | Antibacterial: E. coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, P. vulgaris, P. aeruginosa, Salmonella typhimurium, Staphylococcus aureus, and Streptococcus faecalis | Withania somnifera | Roshan and Mohana (2021) |
| Antifungal: Alternaria brassicicola, A. geophila, Aspergillus flavus, A. fumigatus, A. ochraceus, A. tamarii, A. terreus, Curvularia tetramera, F. oxysporum, F. lateritium, F. equiseti, F. udum, verticillioides, Penicillium citrinum, P. expansum | ||||
| Phoma sp. | flavipucine | Antifungal:Phytophthora infestans | Salsola oppositifolia | Loesgen et al. (2011) |
| Phoma herbarum | Ethyl acetate extract | Antibacterial: Bacillus cereus | Urospermum picroides | El-Zawawy et al. (2020) |
| Phoma sp.135 | cryptophomic acid, cryptodiol, cryptotriol | Antibacterial:E. coli, B. subtilis, Mycobacterium phlei, S. aureus | Marine-derived | Elsebai et al. (2018) |
| Phoma sp. L28 |
7-(γ,γ)-dimethylallyloxymacrosporin, macrosporin, 7-methoxymacrosporin, tetrahydroaltersolanol B, altersolanol L, ampelanol |
Antifungal: Colletotrichum musae, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium graminearum, Penicillium italicum, F. oxysporum. f. sp. lycopersici Rhizoctonia solani |
mangrove | Huang et al. (2017) |
| macrosporin |
Antifungal: F. graminearum |
|||
| Phoma sp. JS752 | barceloneic acid C | Antibacterial: Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus pseuditermedius | Phragmites communis | Xia et al. (2015) |
| Phoma macrostoma | macrooxazole C |
Antibacterial: B. subtilis Antifungal: Mucor hiemalis |
Circium arvense | Matio Kemkuignou et al. (2020) |
|
macrocidin A macrooxazole B, macrooxazole C, macrocidin Z |
Antibacterial:S. aureus | |||
| Phoma herbarum YG5839 | tyrosine derivative, terezine derivatives |
Antifungal: F. oxysporum, F. graminearum, P. italicum, Colletotrictum gloeosporioides, Colletotrichum musae |
marine-sponge-derived | Hu et al. (2021) |
| Phoma eupatorii 8082 | Antifungal: Phytophthora infestans | De Vries et al. (2018) | ||
| Phoma multirostrata XJ-2–1 | Ergocytochalasin A | Antiviral: Human dengue virus type 3 (DV3), influenza A virus (H1N1), respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) | Peng et al. (2020) | |
| Phoma sp. | Phomalacton, (3R)-5-hydroxymellein, emodin | Antibacterial: Microbotryum violaceum, Bacillus megaterium | Fucus serratus | Hussain et al. (2014) |
| Phoma sp. WF4 |
Viridicatol, tenuazonic acid, alternariol, alternariol monomethyl ether ( |
Antifungal: F. graminearum | Eleusine coracana | Mousa et al. (2015) |
| Phoma sp. | Phomapyrrolidones A, B and C | Antibacterial: Mycobacterium tuberculosis | Saurauia scaberrinae | Wijeratne et al. (2013) |
| Phoma sp. | 4-hydroxymellein | Antibacterial: B. subtilis | Cinnamomum mollissimum | Santiago et al. (2014) |
| 4,8-dihydroxy-6-methoxy-3-methyl-3,4-dihydro-1H-isochromen-1-one | Antifungal: Aspergillus niger | |||
| Phoma sp. |
Thiodiketopiperazine deriva- tives |
Antibacterial: S. aureus, Streptococcus pyogenes |
Glycyrrhiza glabra | Arora et al. (2016) |
| Phoma sp. | phomafungin | Antifungal: Candida albicans, Aspergillus fumigatus, Trichophyton mentagrophytes | Africa and the Indian and Pacific Ocean islands | Herath et al. (2009) |
Several members of the genus Phoma are well-known to produce a wide range of antimicrobials that are specific to the target organisms (bacteria, fungi, and viruses). P. exigua var. exigua produces antibiotic E and cytochalasin B (Boerema and Howeler 1967), P. pigmentivora produces LL-D253alpha (McIntyre et al. 1984), P. lingam (Tode) Desm. yields phomenoic acid and phomenolactone which are antibacterial and antifungal compounds (Topgi et al. 1987). In addition, there are other bioactive compounds reported from Phoma spp. For example, a well-known anti-infective agent squalestatin was reported from a Phoma spp. (Dawson et al. 1992); antitumor compound fusidienol A from another Phoma spp. (Singh et al. 1997), and Yamaguchi et al. (2002) isolated the bioactive compound FOM-8108 which inhibited neutral sphingomyelinases.
Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles by Phoma spp. and its antimicrobial efficacy
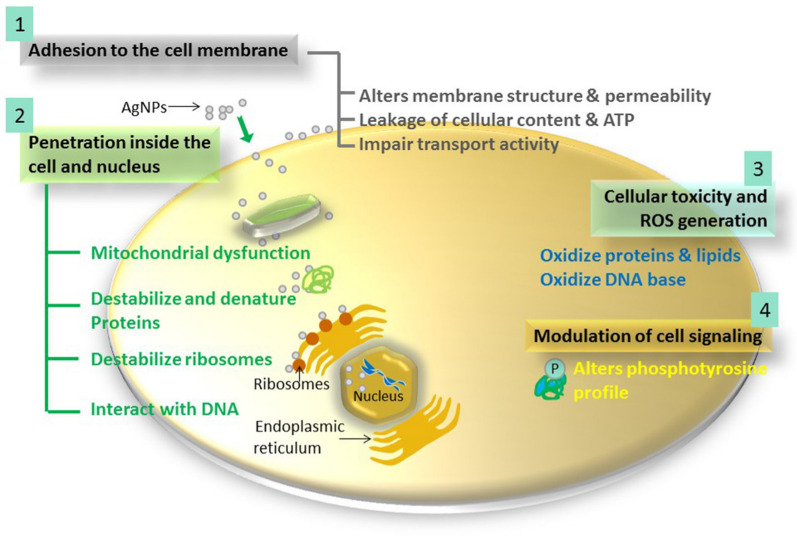
As discussed earlier, Phoma species are known to produce a wide range of metabolites that have already shown antimicrobial activity (Rai et al. 2009a). Some of the metabolites may not directly reveal the antimicrobial potential but can be used for the fabrication of silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) which also demonstrated remarkable antimicrobial potential. AgNPs are well known as a new generation of antimicrobials (Rai et al., 2009b). An elaborative account of multiple modes of action of AgNPs is reviewed by Dakal et al. (2016) and a schematic representation of the same is given in Fig. 6.
Fig. 6.
The four most prominent routes of antimicrobial action of AgNPs. 1. AgNPs adhere to microbial cell surface and results in membrane damage and altered transport activity; 2. AgNPs penetrate inside the microbial cells and interact with cellular organelles and biomolecules, and thereby, affect respective cellular machinery; 3. AgNPs cause increase in ROS inside the microbial cells leading to cell damage and; 4. AgNPs modulate cellular signal system ultimately causing cell death.
Reproduced from Dakal et al. (2016) under the Creative Commons Attribution Licence (CC BY)
Phoma species are capable of extracellular synthesis of spherical AgNPs and silver nanorods. Extracellular synthesis of nanoparticles by Phoma spp. offer an advantage of obtaining large quantities of AgNPs at a rapid rate and in a relatively pure state. Furthermore, the extracellular synthesis of AgNPs by Phoma spp. would make the process simple and easier for downstream processing; fungal broths can be easily filtered by filter press of similar simple equipment, thus making it a cost-effective process (Gade et al., 2010). Moreover, the fabrication of AgNPs by Phoma spp. is a green and eco-friendly approach as no toxic chemicals, high temperature, or pressure are used for the synthesis (Gade et al., 2014; Rai et al. 2021a, b).
In a study, the fabrication of AgNPs by P. glomerata (MTCC-2210) was reported by Birla et al. (2009). Authors also reported the combined activity of commercial antibiotics and AgNPs synthesised from Phoma spp. by testing against E. coli JM-103 (ATCC-39403) and S. aureus (ATCC-25923) on Muller–Hinton agar plates. Commercial antibiotics like ampicillin (10 µg), gentamycin (10 µg), kanamycin (30 µg), streptomycin (10 µg) and vancomycin (30 µg) were used in the study. The comprehensive fold increases in area were observed for ampicillin, streptomycin, and vancomycin. Thus, the combined activity observed was better in E. coli than S. aureus. Whereas the disc diffusion analysis of only AgNPs showed better activity against S. aureus as compared to E. coli. In another study, the AgNPs synthesised from P. gardinae (ITCC 4554) showed antimicrobial activity against human pathogenic bacteria and fungi (Rai et al., 2015a). Authors evaluated the activity of AgNPs against C. albicans, S. choleraesuis, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and E. coli. The AgNPs were found to be most effective against E. coli followed by S. aureus, C. albicans, S. choleraesuis, and P. aeruginosa as compared with antibiotics. Further extracellular synthesis of AgNPs by P. capsulatum, P. putaminum, and P. citri was reported by Rai and co-workers (2015b). The AgNPs syjthesised from these Phoma spp. showed potential antimicrobial activity against Aspergillus niger, C. albicans, S. choleraesuis, P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, and E. coli. The least minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.85 μg/ml was shown by AgNPs synthesized from P. citri against S. choleraesuis. AgNPs fabricated using Phoma spp. is not only reported for antibacterial and antifungal activity but also demonstrated antiviral potential. Some Phoma spp. isolated from the infected plants and identified on the basis of morphological and molecular characteristics were used for the fabrication of AgNPs. This demonstrated a significant decrease in replication efficiency for Herpes Simplex Virus (HSV)-1 and human parainfluenza virus (HPIV) type-3, and a minor effect on the replication of HSV-2 at a concentration of 10 mg/ml (Gaikwad et al. 2013). Further, the authors reported that AgNPs ability to control viral infectivity was most likely attributed to the size and zeta potential of the fabricated AgNPs, which interfere with virus and cell interaction, thereby blocking viral entry into the cell.
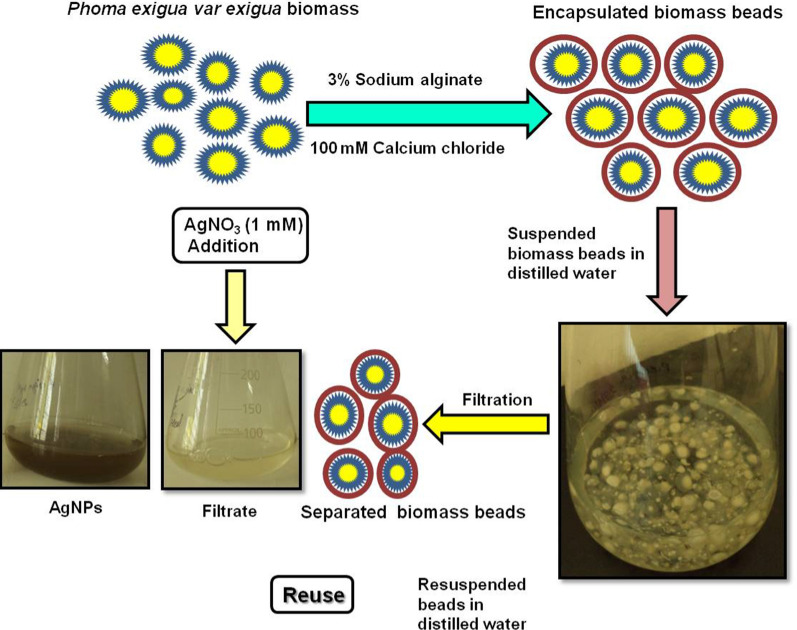
Shende et al. (2017) synthesised AgNPs using immobilized biomass of the P. exigua var. exigua. This process was found to be a simple, fast, large-scale, and efficient route for the synthesis of AgNPs, without disintegration of calcium alginate beads in the medium for ten batch cycles. The immobilization of P. exigua biomass leads to the development of a method for the continuous synthesis of AgNPs. Moreover, this large-scale synthesis process could be a boon to the commercial fabrication of AgNPs which will be required due to the application of AgNPs in a large number of commercial products. The AgNPs thus produced also demonstrated antibacterial activity against E. coli and S. aureus. Graphical illustration of P. exigua var. exigua biomass immobilization process and AgNPs fabrication is given in Fig. 7.
Fig. 7.
Graphical illustration of Phoma exigua var. exigua biomass immobilization process and AgNPs fabrication (Shende et al. 2017), reprinted with permission
It is evident from the above reports that the different Phoma spp. possess tremendous ability to reduce the inorganic metal ions to nanoparticles in general and AgNPs in particular, which is due to the extracellular secretions of metabolites by Phoma spp. Consequently, the metabolites secreted by the Phoma spp. can be harnessed and explored for the synthesis of nanoparticles of different sizes and shapes. In near future, the possibility of utilizing antimicrobial metabolites secreted by Phoma spp. for the fabrication of AgNPs cannot be overlooked, since these metabolites can be used with AgNPs synergistically which will provide the solution to the increasing drug resistance problem worldwide.
Conclusions
Antimicrobial resistance and the entry of new fatal microbes like Coronavirus have made the researchers to seriously think about searching for new strategies to combat the global problem. Thus, there is a high demand for new antibiotics for difficult-to-treat bacteria and other pathogenic microbes. In this context, various fungi including Phoma offers antimicrobial metabolites. Various species of Phoma particularly pigment-producing species such as P. arachidicola, P. sorghina, P. exigua var. exigua, P. herbarum, P. multirostrata, P. betae, and P. fimeti have already demonstrated their potential against pathogenic fungi, bacteria, and viruses. Moreover, several species of Phoma have been studied for the production of bioactive compounds such as polyketides, ergocytochalasin A, macrosporin, thiodiketopiperazines, terpenes, terpenoids, and alkaloids which have shown their antimicrobial potential. These antimicrobial metabolites of Phoma spp. are not only terrestrial but also include marine and endophytic spp. dwelling in medicinal plants. Moreover, some Phoma species are also known to synthesize silver nanoparticles extracellularly which have already proven to be the new generation of antimicrobials. Such a process of nanoparticle synthesis is eco-friendly, economically viable and a greener approach without the use of harmful chemicals and high pressure and temperature. These nanoparticles can also be utilized as nanocarriers for the slow and sustained delivery of antimicrobial drugs. Finally, more thorough research is required to screen different species of Phoma from extreme environments to find out potential antibiotic producers.
Acknowledgements
Mahendra Rai is thankful to the Polish National Agency for Academic Exchange (NAWA) for financial support (Project No. PPN/ULM/2019/1/00117/A/DRAFT/00001) to visit the Department of Microbiology, Nicolaus Copernicus University, Toruń, Poland.
Author contributions
MR conceived and designed the review. BZ contributed substantially, AG and PI co-wrote the manuscript. MR critically revised the mss. All authors read and approved the manuscript.
Funding
Not applicable.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- Ahmed T, Sarma VV. Attenuation of quorum sensing associated virulence factors and biofilm formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa pao1 by Phoma multirostrata puty3, a saprophytic fungus, isolated from Carica papaya. IJPSR. 2020;11(7):3268–3284. doi: 10.13040/IJPSR.0975-8232.11(7).3268-84. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi A, Yano T, Kozuma S, Takatsu T. Pleofungins, novel inositol phosphorylceramide synthase inhibitors, from Phoma sp. SANK 13899. II. Structural elucidation. J Antibiot. 2007;60(2):143–152. doi: 10.1038/ja.2007.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arora P, Wani ZA, Nalli Y, Ali A, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S. Antimicrobial potential of thiodiketopiperazine derivatives produced by Phoma sp., an endophyte of Glycyrrhiza glabra Linn. Microb Ecol. 2016;72(4):802–812. doi: 10.1007/s00248-016-0805-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhimba BV, Pushpam AC, Arumugam P, Prakash S. Phthalate derivatives from the marine fungi Phoma herbarum VB7. Int J Biol Pharma Res. 2012;3(4):507–512. [Google Scholar]
- Birla SS, Tiwari VV, Gade AK, Ingle AP, Yadav AP, Rai MK. Fabrication of silver nanoparticles by Phoma glomerata and its combined effect against Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus. Lett App Micro. 2009;48:173–179. doi: 10.1111/j.1472-765X.2008.02510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boerema GH, Howeler LH. Phoma exigua desm and its varieties. Persoonia. 1967;5:15–28. [Google Scholar]
- Böttcher L, Gersbach H, Wernli D. Restoring the antibiotic R&D market to combat the resistance crisis. Sci Public Policy. 2021 doi: 10.1093/scipol/scab067. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chande A, Kövics GJ, Sandhu SS, Rai MK. Morphological and genetic differentiation among four pigment producing Indian species of Phoma (Saccardo, 1899). Indian J Microbiol. 50(Suppl 1):110–6. Doi: 10.1007/s12088-010-0067-0. Epub 2010 Nov 25. PMID: 22815582; PMCID: PMC3396407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Chen Y, Yang W, Zou G, Chen S, Pang J, She Z. Bioactive polyketides from the mangrove endophytic fungi Phoma sp. SYSU-SK-7. Fitoterapia. 2019;139:104369. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2019.104369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christaki E, Marcou M, Tofarides A. Antimicrobial resistance in bacteria: mechanisms, evolution, and persistence. J Mol Evol. 2020;88(1):26–40. doi: 10.1007/s00239-019-09914-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dakal TC, Kumar A, Majumdar RS, Yadav V. Mechanistic basis of antimicrobial actions of silver nanoparticles. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:1831. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.01831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson MJ, Farthing JE, Marshall PS, Middleton RF, O’Neill MJ, Shuttleworth A, Stylli C, Tait RM, Taylor PM, Wildman HG, Buss AD, Langley D, Hayes MV. The squalestatins, novel inhvolibitors of squalene synthase produced by a species of Phoma. J Antibiotics. 1992;45:639–647. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.45.639. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Vries S, von Dahlen JK, Schnake A, Ginschel S, Schulz B, Rose LE. Broad-spectrum inhibition of Phytophthora infestans by fungal endophytes. FEMS Micro Ecol. 2018;94(4):fiy037. doi: 10.1093/femsec/fiy037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsebai MF, Ghabbour HA, Legrave N, Fontaine-Vive F, Mehiri M. New bioactive chlorinated cyclopentene derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Phoma sp. Med Chem Res. 2018;27(8):1885–1892. doi: 10.1007/s00044-018-2201-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Elsebai MF, Fontaine-Vive F, Mehiri M. New derivatives from the marine-derived fungus Phoma. sp isolated from the sponge Ectyplasia ferox. Biol Mar Mediterr. 2016;23(1):312. [Google Scholar]
- El-Zawawy N, Metwally M, El-Salam A. Antitumor and antimicrobial activities of endophytic fungi obtained from Egyptian Urospermum picroides. Int J Cancer Biomed Res. 2020;4(3):187–199. [Google Scholar]
- Evidente M, Cimmino A, Zonno MC, Masi M, Santoro E, Vergura S, Evidente A. Chenopodolans E and F, two new furopyrans produced by Phoma chenopodiicola and absolute configuration determination of chenopodolan B. Tetrahedron. 2016;72(51):8502–8507. doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2016.11.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman C, Anderson R. The role of co-infections and secondary infections in patients with COVID-19. Pneumonia. 2021;13:5. doi: 10.1186/s41479-021-00083-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gade AK, Ingle AP, Whiteley C, Rai M. Mycogenic metal nanoparticles: progress and applications. Biotech Lett. 2010;32(5):593–600. doi: 10.1007/s10529-009-0197-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gade AK, Gaikwad SC, Duran N, Rai MK. Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Phoma glomerata. Micron. 2014;59:52–59. doi: 10.1016/j.micron.2013.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaikwad S, Ingle A, Gade A, Rai M, Falanaga A, Incoronato N, Galdiero S, Galdiero M. Antiviral activity of mycosynthesized silver nanoparticles against herpes simplex virus and human parainfluenza virus type 3. Int J Nanomed. 2013;8:4303–4314. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S50070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D, Veeraraghavan B, Elangovan R, Vivekanandan P. Antibiotic resistance and epigenetics: more to it than meets the eye. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2020;64(2):e02225–19. doi: 10.1128/AAC.02225-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herath K, Harris G, Jayasuriya H, Zink D, Smith S, Vicente F, et al. Isolation, structure and biological activity of phomafungin, a cyclic lipodepsipeptide from a widespread tropical Phoma sp. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17(3):1361–1369. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2008.12.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman AM, Mayer SG, Strobel GA, Hess WM, Sovocool GW, Grange AH, et al. Purification, identification and activity of phomodione, a furandione from an endophytic Phoma species. Phytochemistry. 2008;69(4):1049–1056. doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2007.10.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Z, Gopal JV, Liu L, Gao Z. Tyrosine and terezine derivatives from the marine-sponge-derived fungus Phoma herbarum YG5839. Nat Prod Res. 2021 doi: 10.1080/14786419.2021.1892671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang S, Xu J, Li F, Zhou D, Xu L, Li C. Identification and antifungal activity of metabolites from the mangrove fungus Phoma sp. L28. Chem Nat Comp. 2017;53(2):237–240. doi: 10.1007/s10600-017-1961-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain H, Kock I, Harrasi AA, Rawahi AA, Abbas G, Green IR, Shah A, Badshah A, Saleem M, Draeger S, Schulz B, Krohn K. Antimicrobial chemical constituents from endophytic fungus Phoma sp. Asian Pac J Trop Med. 2014;7:699–702. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60119-X. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hussain H, John M, Al-Harrasi A, Shah A, Hassan Z, Abbas G, Rana UA, Green IR, Schulz B, Krohn K. Phytochemical investigation and antimicrobial activity of an endophytic fungus Phoma sp. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2015;27:92–95. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2014.08.001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jayatilake PL, Munasinghe H. Antimicrobial activity of cultivable endophytic and rhizosphere fungi associated with “mile-a-minute,” Mikania cordata (Asteraceae) BioMed Res Int. 2020 doi: 10.1155/2020/5292571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juyal P, Shrivastava V, Mathur A. Antimicrobial activity of Endophytes from aerial and non aerial parts of Calotropis procera against Pathogenic microbes. Int J Scient Res Pub. 2017;7(7):590–596. [Google Scholar]
- Kadu P. Antimicrobial activity of Phoma species against pathogenic bacteria. J Sci Res. 2021 doi: 10.37398/JSR.2021.650211. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kim JW, Ko W, Kim E, Kim GS, Hwang GJ, Son S, Jeong MH, Hur JS, Oh H, Ko SK, Jang JH. Anti-inflammatory phomalichenones from an endolichenic fungus Phoma sp. J Antibiot. 2018;71:753–756. doi: 10.1038/s41429-018-0058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li HT, Liu T, Yang R, Xie F, Yang Z, Yang Y, Zhou H, Ding ZT. Phomretones A-F, C 12 polyketides from the co-cultivation of Phoma sp YUD17001 and Armillaria sp. RSC Adv. 2020;10:18384–18389. doi: 10.1039/D0RA02524K. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu SS, Jiang JX, Huang R, Wang YT, Jiang BG, Zheng KX, Wu SH. A new antiviral 14-nordrimane sesquiterpenoid from an endophytic fungus Phoma sp. Phytochem Lett. 2019;29:75–78. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2018.11.005. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Loesgen S, Bruhn T, Meindl K, Dix I, Schulz B, Zeeck A, Bringmann G. (+)-Flavipucine, the missing member of the pyridione epoxide family of fungal antibiotics. Eur J Org Chem. 2011 doi: 10.1002/ejoc.201100284. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Markley JL, Wencewicz TA. Tetracycline-inactivating enzymes. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:1058. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.01058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matio Kemkuignou B, Treiber L, Zeng H, Schrey H, Schobert R, Stadler M. Macrooxazoles A-D, new 2, 5-disubstituted oxazole-4-carboxylic acid derivatives from the plant pathogenic fungus Phoma macrostoma. Molecules. 2020;25(23):5497. doi: 10.3390/molecules25235497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mclntyre CR, Simpson TJ, Trimble LA, Vederas JC. Biosynthesis of LL-D253a in Phoma pigmentivora: incorporation of 13C, 2H, and 18O enriched precursors. J Chem Soc Chem Comm. 1984;11:706–709. doi: 10.1039/c39840000706. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mousa WK, Schwan A, Davidson J, Strange P, Liu H, Zhou T, et al. An endophytic fungus isolated from finger millet (Eleusine coracana) produces anti-fungal natural products. Front Micro. 2015;6:1157. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.01157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nalli Y, Arora P, Khan S, Malik F, Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S, Gupta V, Ali A. Isolation, structural modification of macrophin from endophytic fungus Phoma macrostoma and their cytotoxic potential. Med Chem Res. 2019;28:260–266. doi: 10.1007/s00044-018-2281-y. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- WHO Newsletter. (17 Jan, 2020) Lack of new antibiotics threatens global efforts to contain drug-resistant infections. https://www.who.int/news/item/17-01-2020-lack-of-new-antibiotics-threatens-global-efforts-to-contain-drug-resistant-infections.
- Peng X, Duan F, He Y, Gao Y, Chen J, Chang J, Ruan H. Ergocytochalasin A, a polycyclic merocytochalasan from an endophytic fungus Phoma multirotrata XJ-2-1. Org Biomol Chem. 2020;18(21):4056–4062. doi: 10.1039/D0OB00701C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Deshmukh P, Gade A, Ingle A, Kövics GJ, Irinyi L. Phoma Saccardo: distribution, secondary metabolite production and biotechnological applications. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2009;35:182–196. doi: 10.1080/10408410902975992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Yadav AP, Gade AK. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotech Adv. 2009;27(1):76–82. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2008.09.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Deshmukh P, Gade A, Ingle A, Kövics GJ, Irinyi L. Phoma saccardo: Distribution, secondary metabolite production and biotechnological applications. Crit Rev Micro. 2009;35(3):182–196. doi: 10.1080/10408410902975992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Ingle AP, Gade A, Duran N. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles by Phomagardeniae and in vitro evaluation of their efficacy against human disease-causing bacteria and fungi. IET Nanobiotec. 2015;9(2):71–75. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2014.0013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Gade A, Zimowska B, Ingle AP, Ingle P. Marine-derived Phoma-the gold mine of bioactive compounds. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018;102:9053–9066. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Ingle AP, Trzcińska-Wencel J, Wypij M, Bonde S, Yadav A, Kratošová G, Golińska P. Biogenic silver nanoparticles: what we know and what do we need to know? Nanomaterials. 2021;11:2901. doi: 10.3390/nano11112901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Zimowska B, Shinde S, Tres MV. Bioherbicidal potential of different species of Phoma: opportunities and challenges. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2021;105:3009–3018. doi: 10.1007/s00253-021-11234-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Ingle AP, Gade AK, Duarte MCT, Duran N. Three Phoma spp. synthesised novel silver nanoparticles that possess excellent antimicrobial efficacy. IET Nanobiotech. 2015;9(5):280–287. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2014.0068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M, Gade A, Zimowska B, Ingle AP, Ingle P. Harnessing the potential of novel bioactive compounds produced by endophytic Phoma spp.—biomedical and agricultural applications. Acta Sci Pol Hortorum Cultus. 2020;19(6):31–45. doi: 10.24326/asphc.2020.6.3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rai M (2002) Diversity and biotechnological applications of Indian species of Phoma. In: Rao GP, Manoharachari C, Bhat DJ, Rajak RC, Lakhanpal TN, eds. Frontiers of fungal diversity in India (Prof Kamal Festscrift) 179–204, pp 906. International Book Distributing Co., Lucknow, India
- Roshan AB, Mohana DC. Antimicrobial and antimycotoxigenic activities of (3s)-3, 6, 7-trihydroxy-α-tetralone isolated from endophytic Phoma moricola. Pharma Innov J. 2021;10(7):852–860. [Google Scholar]
- Sang XN, Chen SF, Chen G, An X, Li SG, Lu XJ, Pei YH. Two pairs of enantiomeric α-pyrone dimers from the endophytic fungus Phoma sp. YN02-P-3. RSC Adv. 2017;7:1943–1946. doi: 10.1039/C6RA26319D. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago C, Sun L, Munro MHG, Santhanam J. Polyketide and benzopyran compounds of an endophytic fungus isolated from Cinnamomum mollissimum: biological activity and structure. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed. 2014;4(8):627–632. doi: 10.12980/APJTB.4.2014APJTB-2014-0030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shende S, Gade A, Rai M. Large-scale synthesis and antibacterial activity of fungal-derived silver nanoparticles. Env Chem Lett. 2017;15(3):427–434. doi: 10.1007/s10311-016-0599-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shi T, Qi J, Shao CL, Zhao DL, Hou XM, Wang CY. Bioactive diphenyl ethers and isocoumarin derivatives from a gorgonian-derived fungus Phoma sp. (TA07–1) Mar Drugs. 2017;15:146. doi: 10.3390/md15060146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- da Silva GBPG, Silvino KF, Bezerra JDP, de Farias TGS, de Araújo JM, Stamford TLM. Antimicrobial activity of Phoma sp URM 7221: an endophyte from Schinus terebinthifolius Raddi (Anacardiaceae) Afr J Micro Res. 2017;11(1):1–7. doi: 10.5897/AJMR2016.8326. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Singh SB, Ball RG, Zink DL, Monaghan RL, Polishook JD, Sanshez M, Pelaez F, Silverman KC, Lingham RB. Fusidienol—A: a novel Ras farnesyl- protein—transferase inhibitor from Phoma sp. J Org Chem. 1997;62(21):7485–7488. doi: 10.1021/jo9708304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumilat DA, Yamazaki H, Kanno SI, Saito R, Watanabe Y, Namikoshi M. Biphenyl ether derivatives with protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory activity from the freshwater fungus Phoma sp. J Antibiot. 2017;70(3):331–333. doi: 10.1038/ja.2016.147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topgi RS, Devys M, Bousquet JF, Kollmann A, Barbier M (1987) Phomenoic acid phomenolactone, antifungal substances from Phoma lingam (Tode) Desm.: kinetics of their biosynthesis, with an optimization of the isolation procedures. Appl Environ Microbiol 53(5): 966-968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Wang LW, Xu BG, Wang JY, Su ZZ, Lin FC, Zhang CL, Kubicek CP. Bioactive metabolites from Phoma species, an endophytic fungus from the Chinese medicinal plant Arisaema erubescens. App Micro Biotech. 2012;93(3):1231–1239. doi: 10.1007/s00253-011-3472-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wencewicz TA. Crossroads of antibiotic resistance and biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 2019;431(18):3370–3399. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.06.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wijeratne EK, He H, Franzblau SG, Hoffman AM, Gunatilaka AL. Phomapyrrolidones A-C, antitubercular alkaloids from the endophytic fungus Phoma sp. NRRL 46751. J Nat Prod. 2013;76:1860–1865. doi: 10.1021/np400391p. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xia X, Kim S, Bang S, Lee HJ, Liu C, Park CI, Shim SH. Barceloneic acid C, a new polyketide from an endophytic fungus Phoma sp. JS752 and its antibacterial activities. J Antibiotics. 2015;68(2):139–141. doi: 10.1038/ja.2014.116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu JB, Fan YY, Gan LS, Zhou YB, Li J, Yue JM. Cephalotanins A-D, Four norditerpenoids represent three highly rigid carbon skeletons from Cephalotaxus sinensis. Chem Eur J. 2016;22:14648–14654. doi: 10.1002/chem.201603373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi YM, Masuma R, Uchida R, Arai M, Tomoda H, Omura S. Phoma sp. FOM-8108, a producer of gentisylquinones, isolated from sea sand. Mycoscience. 2002;43(2):127–133. doi: 10.1007/S102670200019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang W, Krohn K, Egold H, Draeger S, Schulz B (2008) Diversity of antimicrobial pyrenophorol derivatives from an endophytic fungus, Phoma sp. 10.1002/ejoc.200800404
- Zhu H, Sandiford SK, van Wezel GP. Triggers and cues that activate antibiotic production by actinomycetes. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2014;41(2):371–386. doi: 10.1007/s10295-013-1309-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]