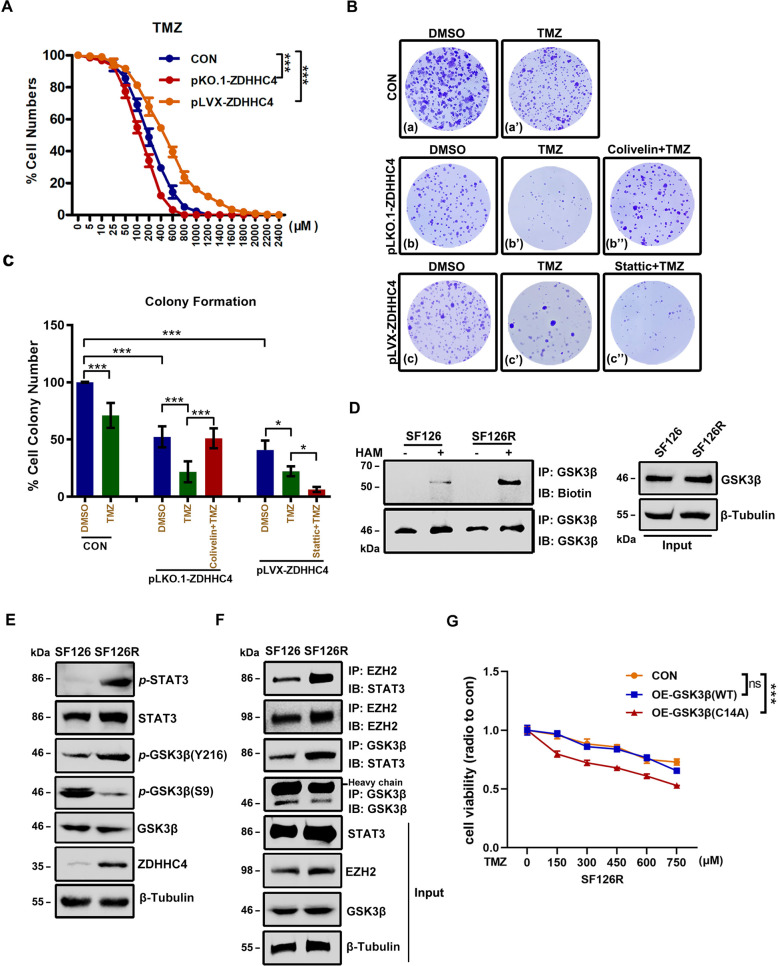
Fig. 3. GSK3β palmitoylation regulates GBM TMZ-resistance.
A Growth curve describing the effect of ZDHHC4 expression on TMZ inhibition in GBM cells. SF126 cells with overexpression or knockout of ZDHHC4 were treated with different concentrations of TMZ. B Representative image of colony formation in the SF126 cell lines 14 days after different treatments. For the control group, DMSO and TMZ were used. For the pLKO.1-ZDHHC4 group, DMSO, TMZ, and TMZ + Colivelin were used. For the pLVX-ZDHHC4 group, DMSO, TMZ, and TMZ + Stattic were used. Colonies were stained using crystal violet. C The number of clones stained by crystal violet in each dish in Figure B is calculated. Con-DMSO group was set at 100%. D ABE analysis of GSK3β palmitoylation in SF126 and SF126R cells. E Western blot analysis of GSK3β and STAT3 phosphorylation in SF126 and SF126R cells. F Immunoprecipitation analysis of the STAT3 binding capacity of GSK3β and EZH2 in SF126 and SF126R cells. G CCK-8 assay was used to detect the effect of GSK3β (C14A) mutant on TMZ killing SF126R cells. Data are shown as means ± SD (n = 3). P-values were determined by two-tailed Student’s t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.