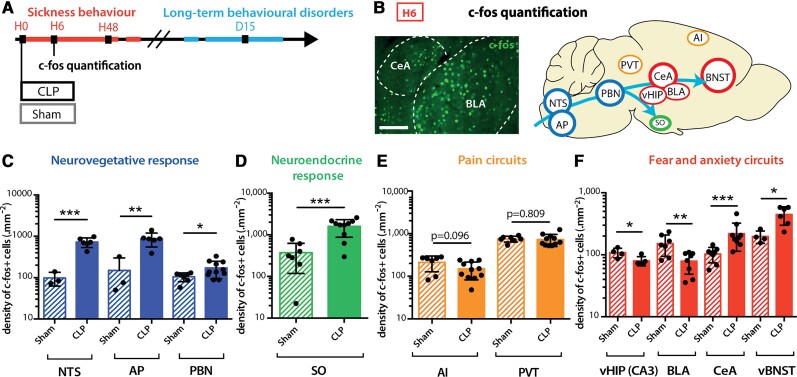
Figure 2.
CLP induced transient brain activation. (A and B) Neuronal activation marker c-fos was quantified at H6 post-surgery. Scale bar = 200 μm. (C and D) H6 c-fos quantification showed transient neuronal activation in CLP compared to sham mice in areas involved in the neurovegetative response [C; NTS: nsham = 3, nCLP = 6, ***P = 0.0009; area postrema (AP): nsham = 3, nCLP = 6, **P = 0.0089; PBN: nsham = 7, nCLP = 12, *P = 0.0255] and the neuroendocrine system [D; supra-optic nucleus (SO): nsham = 7, nCLP = 10, ***P = 0.0003]. (E) At H6, CLP showed no effect on the activation of pain related areas compared to the sham group ([agranular insular area (AI), paraventricular nucleus of the thalamus (PVT) nsham = 7, nCLP = 11]. (F) CLP-induced c-fos expression variations at H6 in areas involved in fear and anxiety circuits [ventral hippocampus (vHIP) cornu ammonis 3 (CA3): nsham = 4, nCLP = 5, *P = 0.0328; BLA: nsham = 7, nCLP = 8, **P = 0.0079; CeA: nsham = 8, nCLP = 9, ***P = 0.0006; vBNST: nsham = 4, nCLP = 6, *P = 0.0121)]. Statistics: (C–F) Mann–Whitney test or unpaired t-test. Data shown as mean ± SD.