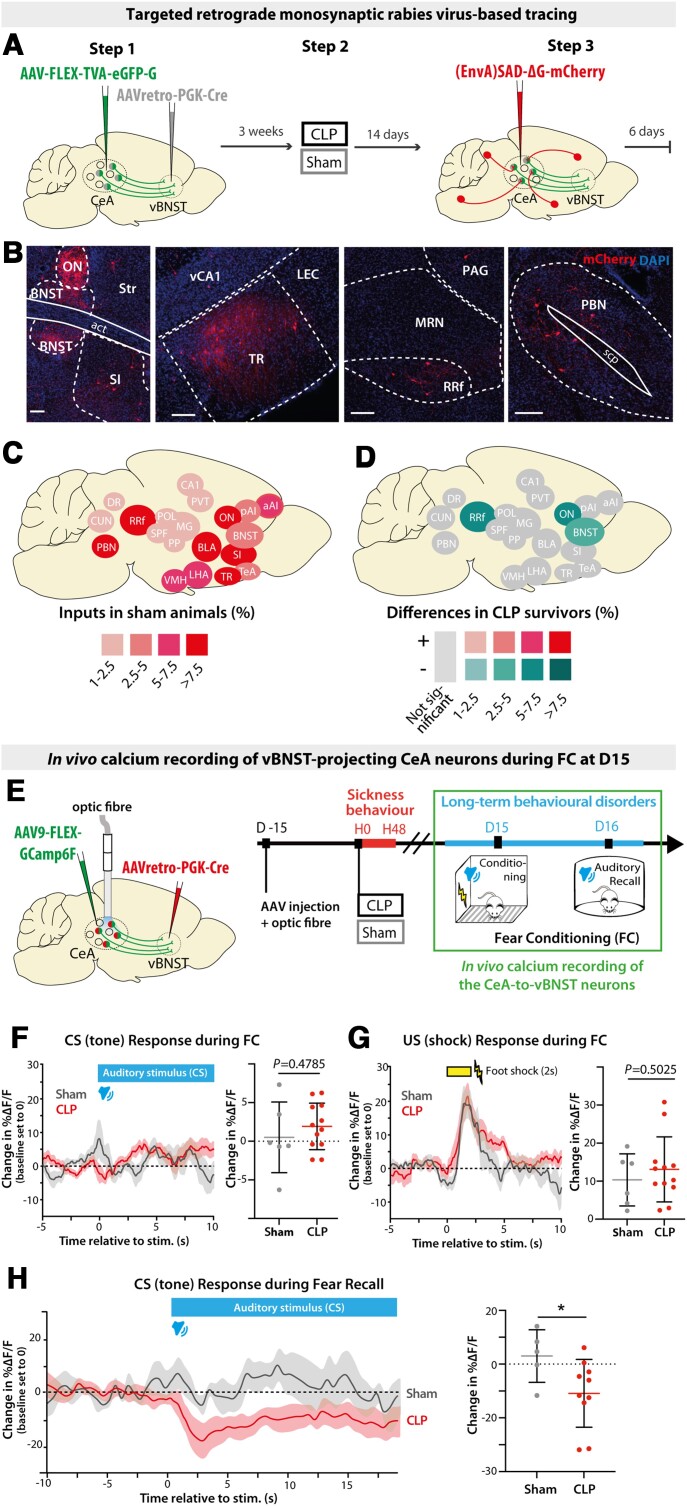
Figure 4.
CLP induces long-term alterations of synaptic connectivity and functional activity of vBNST-projecting CeA neurons. (A) Experimental design for targeting mCherry-expressing pseudotyped rabies virus to CeA neurons projecting to the vBNST in sham versus CLP survivors, 2 weeks after surgery. (B) Trans-synaptically labelled neurons in different brain regions. Scale bar = 100 μm. (C) Map of the brain regions providing the largest fraction of presynaptic neurons to the vBNST-projecting CeA neurons in sham animals (relative to the total). Regions providing <1% of total inputs are not displayed (n = 4). BNST included all BNST subdivisions except oval nucleus (ON). (D) Map of the differences in presynaptic neurons to vBNST-projecting CeA neurons in CLP survivors compared to sham survivors. Only regions showing significant difference are colour-coded (nCLP = 4, Mann–Whitney tests; BNST: *P = 0.028, ON: *P = 0.017, *RRf: P = 0.049). (E) vBNST-projecting CeA neurons were chronically recorded during fear conditioning at D15 using fibre photometry. (F and G) Averaged ΔF/F traces (baseline set to 0) showing the responses to conditioned stimulus [tone; conditioned stimulus (CS); F] and unconditional stimulus [foot shock; unconditional stimulus (US); G] during fear conditioning in CLP and sham mice (nSham = 6, nCLP = 12). Mean ΔF/F changes relative to baseline during the conditioned stimulus response (0–5 s window) and during the unconditional stimulus response (0–4 s window) showed no difference between CLP and sham mice. (H) Averaged ΔF/F traces (baseline set to 0) during fear conditioning (FC) recall exhibited a stronger inhibitory response to conditioned stimulus in CLP mice compared to sham animals (nSham = 5, nCLP = 10, *P = 0.0426). Statistics: (D and F–H) Mann–Whitney tests. Data shown as mean ± SD (except traces in F–H ± SEM). aAI = anterior agranular insular cortex; CUN = cuneiform nucleus; DR = dorsal raphe nucleus; LEC = lateral entorhinal cortex; LHA = lateral hypothalamic area; MG = medial geniculate nucleus; MRN = midbrain reticular nucleus; OV = oval nucleus; PAG = periaqueductal grey; pAI = posterior agranular insular cortex; POL = posterior limiting nucleus of the thalamus; PP = peripeduncular nucleus; RRf = retrorubral field; SPF = subparafascicular nucleus; TeA = temporal association area; TR = post-piriform transition area; vCA1 = ventral CA1; VMH = ventro-medial hypothalamic nucleus..