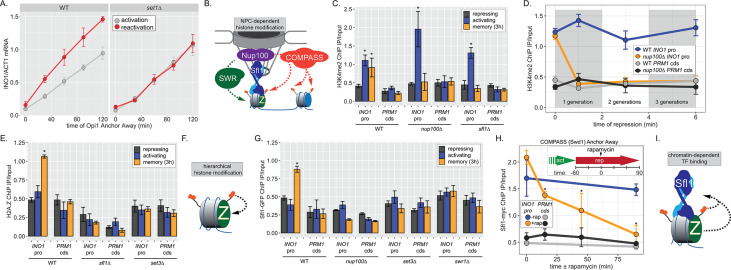
Figure 2. INO1 transcriptional memory requires a positive feedback loop.
(A) Activation and reactivation of INO1 in wild type (WT) (left) and set1∆ (right) strains upon removal of Opi1 by Anchor Away. Cells were harvested at indicated time points and INO1 mRNA was quantified relative to ACT1 mRNA by real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR) (*p-value<0.05 from one-tailed t-test comparing reactivation and activation, alternative = greater). Data for the WT strain is the same as Figure 1D and is shown for comparison. (B) Model for transcription factor (TF)-and NPC-dependent H3K4 dimethylation by COMPASS (orange circles) and SWR (Swi/Snf Related)-dependent H2A.Z incorporation (green Z). For the chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) experiments in panels C, D, E, G, and H: recovery of either the INO1 promoter or the repressed PRM1 coding sequence was quantified by RT-qPCR. The average of ≥3 replicates ± SEM is plotted (*p-value<0.05 from one-tailed t-test compared with the repressing condition, alternative = greater). (C) ChIP against H3K4me2 in WT, nup100∆, and sfl1∆ strains grown under repressing, activating, and memory (3 hr) conditions. (D) ChIP against H3K4me2 at the indicated times after switching to repressing conditions in WT and nup100∆ strains. The gray and white bars indicate doubling times. (E) ChIP against H2A.Z from WT, sfl1∆, or set3∆ strains under repressing, activating, or memory (3 hr) conditions. (F) Schematic for hierarchical relationship between H2A.Z incorporation and H3K4me2. (G) ChIP against Sfl1-GFP in WT, nup100∆, set3∆, and swr1∆ strains grown under repressing, activating, or memory (3 hr) conditions. (H) ChIP against Sfl1-myc at the indicated times ±1 µg/ml rapamycin in a Swd1 (COMPASS) Anchor Away strain, 1 hr after shifting from activating to repressing conditions. *p-value<0.05 from one-sided t-test compared with the time = 0 min time point, alternative = less. (I) Schematic of the requirement for H2A.Z incorporation and H3K4me2 for Sfl1 binding to the INO1 promoter during memory.