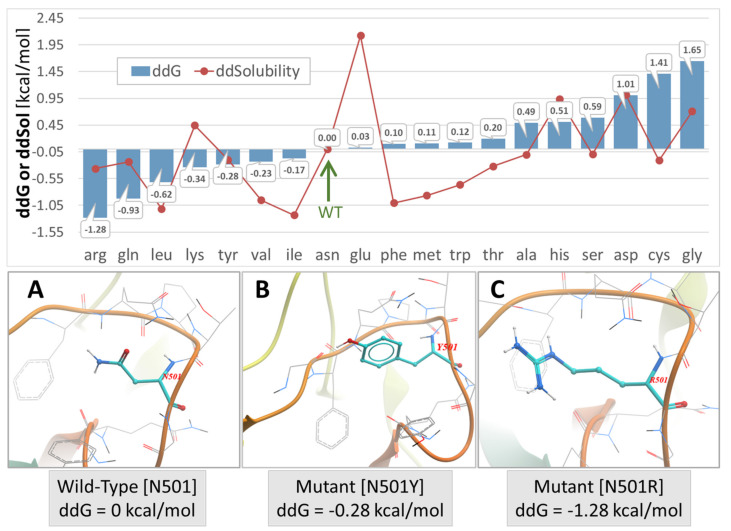
Figure 4.
Upper Panel: S-protein (Swiss Model #05) stability expressed by change in ddG or free-energy of solubility (ddSol) plotted as a function of mutation type (amino acid substitution) at the N501x locus of PDB 7KGK. The calculated free-energy values for each mutation are expressed relative to the wild-type N501, which was assigned a value of zero. Lower values of ddG and ddSol correspond to increased protein stability. Thus, an Asn to Arg substitution at the N501 locus resulted the largest enhancement of protein stability (−1.28 kcal/mol). The green arrow indicates the wild-type N501 S-protein. Lower Panel: (A) Asn conformation at the wild-type N501 locus. (B) Mutant N501Y conformation. (C) Mutant N501R conformation. All conformers were modeled directly from the 6LZG x-ray structure using ICM-Chemist-Pro (Molsoft, LLC, San Diego, CA, USA). Atom Colors: cyan = carbon; blue = nitrogen; red/orange tubes = protein backbone.