Figure 5.
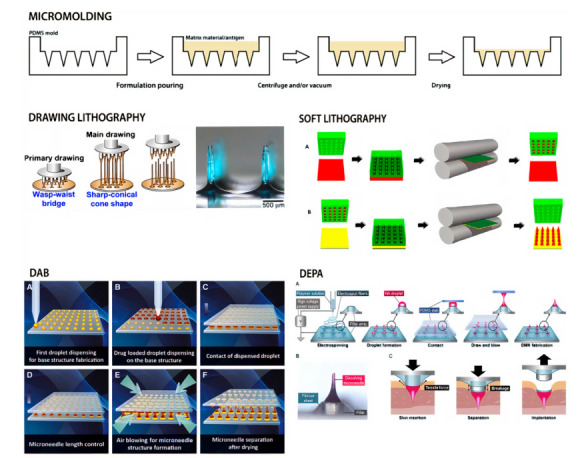
dMN manufacturing methods (taken from [277]) Micromolding with a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) mold is the most prevalent method for producing dMNs. Drawing lithography operates by extending two-dimensional polymeric material into a three-dimensional shape. Longitudinal extension of molten polymer by pillaring higher moving plate. In soft lithography, dMNs are produced by (A) heating a polymer sheet and a mold with microcavities. (B) The filled mold is then heated and placed on a flexible, water-soluble substrate. After mold detachment, a dMN patch remains on the substrate. Droplet-born air blowing (DAB) applies a (A) polymer solution and (B) a drug solution to two plates. (C) The upper plate is lowered until the droplets meet, (D)then withdrawn a distance equal to the two dMN lengths of the lower and top plates. (E) Drying the polymer solutions results in a dMN patch on each plate. (F) In addition, fabrication at moderate temperatures (4–25 degrees Celsius) minimizes medication and polymer waste. dMN on an electrospun pillar array (DEPA) is a variant of DAB. (A) The flat plate is replaced with a columnar array covered in a fibrous layer. (B) A PDMS slab is then utilized to draw and stretch polymer formulation droplets, resulting in microneedles. (C) Finally, the movement of air dries off the elongated droplets to form dissolving microneedles.
