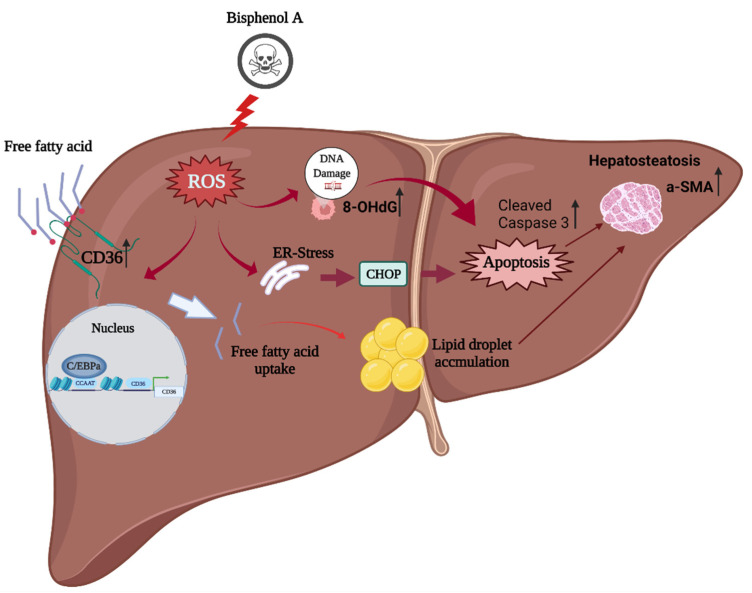
Figure 6.
The proposed mechanism of BPA coupled with a high-fat diet in enhancing ROS-induced hepatic lipid accumulation and liver fibrosis: BPA + HFCCD increases intracellular ROS production, which induces the expression of CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein α (C/EBPα) and CD36, and promotes free fatty acid uptake. BPA exposure aggravates HFCCD-induced liver damage, leading to cleaved caspase-3 activation for apoptosis, steatohepatitis, and acceleration of the fibrotic process (due to α-SMA overexpression). The figure was created using Biorender.