SUMMARY
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a highly prevalent herpesvirus linked to infectious mononucleosis and several malignancies. This paper aims to study the association between children's early life social environment at 9 months and EBV infection at 3 years of age.
Methods
We used data on children included in the UK Millennium Cohort Study. We described the social environment using area-level and material factors as well as socioeconomic position (SEP) at 9 months. EBV was measured at 3 years of age (n = 12 457).
Results
Lower rates of EBV infection were observed in children living in towns and rural areas compared with those living in cities. Lower SEP and overcrowding in the household increased the odds of being infected. Children whose parents were social tenants were more likely to be infected than homeowners. In the overall model, the strength of the association between material factors and EBV infection weakened.
Conclusions
We showed that early life material deprivation was associated with a higher risk of EBV infection among 3-year-olds. Children living in more deprived social conditions may be more likely to become EBV carriers at an earlier age.
Key words: Early infections, Epstein-Barr virus, Socioeconomic inequalities, UK
INTRODUCTION
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a ubiquitous B-lymphotropic herpesvirus, which is highly prevalent in the general population affecting more than 90% of adults. Usually, EBV is transmitted through oral fluid [1] early in life and persists as a dormant or active pathogen over the lifetime of infected individuals [2, 3]. Age at initial infection is variable and may have a differential impact on host response. Infections occurring early in life are generally asymptomatic but have been linked with some chronic diseases in later life, while EBV primary infection occurring in older childhood or adolescence often causes symptomatic disease, most commonly infectious mononucleosis [4, 5]. Early acquisition of primary EBV infection could be beneficial in the short term, contributing to the maturation of the immune system with generally mild symptoms among preadolescents [6], however, in some cases, it has been considered a possible risk factor for subsequent chronic pathologies [7–9]. As such, examining the determinants of the timing of EBV acquisition may facilitate our understanding of different health trajectories over the life course.
A number of infections in early life and adulthood have been shown to have a higher prevalence among those lower on the socioeconomic gradient. The overall nature and burden of these infections in early life may have positive or negative consequences for chronic diseases later in life [6, 10, 11]. The mechanisms involved in acquiring infections in early in life include material factors such as poorer hygiene or overcrowded living conditions [5]. Indeed, EBV acquisition itself has been linked to socioeconomic position (SEP) [7, 12–14], underlining that associations between childhood SEP and EBV infection at an early age deserve further attention as a potential mechanism of earlier primary infection among more disadvantaged groups of the population. Should early primary infection be socially patterned, this may be an interesting ‘social-to-biological’ mechanism to examine, with implications for subsequent immune function and health trajectories across the life course [15]. One set of mechanisms of interest here that may link disadvantaged socioeconomic circumstances with infection and the timing of infection, may be through the material environment, such as the area of residence, the quality of housing and family characteristics [6].
Life course epidemiology involves understanding how health is constructed through dynamic process occurring over the life span. It is a conceptual framework that allows researchers to examine how environmental factors (in the broadest sense including social, psychosocial, behavioural, physical etc.) lead to biological alterations over time [16]. In turn, these alterations may result in differential health outcomes. The social-to-biological mechanisms highlighted by such an approach may be beneficial or deleterious to subsequent health trajectories, but in both cases warrant analysis to improve our understanding of the life course processes affecting the health outcomes of different population groups. Ultimately, the environmental factors and life course stages implicated may underline potential areas for public health intervention.
In this paper, we hypothesise that early socioeconomic disadvantage influences the timing of EBV infection along a social-material pathway, which we will examine at both an ecological and individual level. We will study the association between household SEP at 9 months, including family, material and area-level factors and EBV infection at 3 years of age using a prospective, nationally representative birth cohort study from the UK.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The Millennium Cohort Study (MCS) and participants
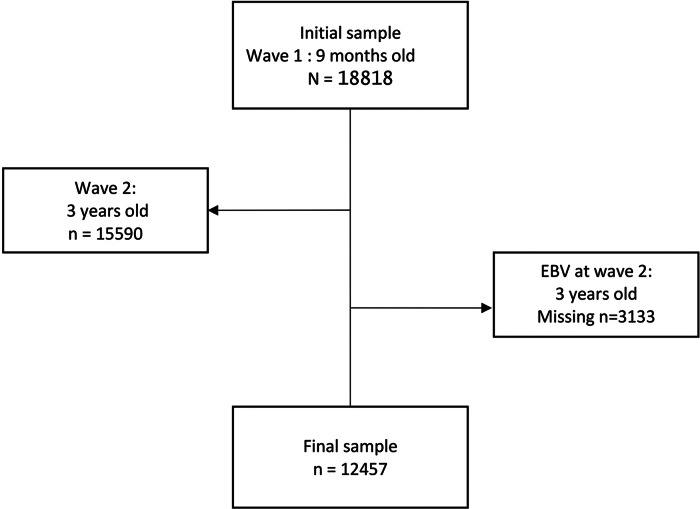
The MCS follows children born in the UK (Scotland, England, Wales and Northern Ireland) between 2000 and 2002. Data are deposited in the UK Data Archive by the Centre for Longitudinal Studies (http://www.cls.ioe.ac.uk) [17–19]. The sample is nationally representative of children living in the UK shortly after birth, a stratified clustered survey design was used. There were six waves of data collection at the time of writing: at 9 months (baseline) and then at 3, 5, 7, 11 and 14 years of age [17–19]. At baseline, 18 818 children were included [17, 19]. Our sample selection was based on individuals with data available for oral fluid at 3 years of age (wave 2) from which analyses were extracted [18, 19]. We randomly chose one child per family to satisfy the hypothesis of independence between observations. The flow chart is shown in Figure 1. The final sample size for our analyses is 12 457 children. The children's mean age at wave 2 is 3·14 (±0·20) years of age.
Fig. 1.
Flow chart.
Measures
Ethics and data
Consent was obtained from parents, by an NHS Research Ethics Committee (MREC) and approval for the collection and analysis of oral fluid samples for the presence of antibodies to EBV, varicella zoster virus (VZV) and norovirus was approved by the London MREC and registered with the Research and Development Office at the UCL Institute of Child Health [17, 18, 20].
EBV measure
We used oral fluid samples collected at 3 years of age (wave 2). Laboratory techniques based on the oral fluid samples obtained from cohort children were used to examine exposure to common infections including varicella zoster virus, EBV and norovirus [19–21]. A cut-off value of 4·74 AU (Arbitrary Units) is proposed for EBV [22] and has been used here as the definition of infection.
The samples were tested at the Health Protection Agency (HPA) for total immunoglobulin G (IgG) content and antibodies to EBV. IgG concentration has been used to test the oral fluid sample quality in MCS. A cut-off value of 2 mg/l for IgG is suggested to provide a reliable measure (IgG less than 2 mg/l dataset represents 45% of children in the MCS), however, it is recommended that total IgG concentrations below this threshold should be removed from analyses [22].
Social position and environment
Here, we describe the variables used to identify household SEP and the material environment the child is exposed to, at wave 1:
Household SEP using mother's education (Higher/Degree level|A/As/S level (UK national school exam at 17/18 years of age)|GCSE (UK national school exam at 15/16 years of age)|No qualification), equivalised income rank identifying the co-resident partners’ joint income within the equivalised income distribution, normalised between 0 and 1 (⩽0·25| > 0·25 and ⩽0·5| > 0·5 and ⩽0·75| > 0·75) [23], and parents’ highest social class. The National Statistics Socioeconomic Classification five-class version, adding a ‘never worked, absent, missing’ category is used to define the social class (I. Managerial, administrative and professional occupations|II. Intermediate occupations |III. Small employers and own account workers|IV. Lower supervisory and technical occupations|V. Semi-routine and routine occupations). The highest social class in the household was determined by the highest social class of the two co-resident partners at baseline.
Area environment: using a variable distinguishing between rural and urban contexts (Large urban|Towns|Rural). The ‘Towns’ category includes very small cities with a maximum of 10 000 residents in England and Wales while the ‘urban’ category covers a whole range of settlements from 10 000 to 7 million inhabitants. The indicator was developed for the government department concerned with rural affairs.
Home environment: in the MCS, variables describing these conditions include overcrowding (less or equal to 1·5 rooms per person; more than 1·5 rooms per person), childcare (Collective childcare; Home, Nannies, others), temperature in the baby's room (cold, very cold; very warm, warm, neither warm nor cold), damp in the home (no; yes), all available in wave 1 [4, 24].
Housing tenure was categorised as follows: Owner; Rent privately; Social housing; Other.
Statistical analysis
First, descriptive and bivariate statistics by EBV infection were carried out using the χ2 test. We selected variables linked to EBV with a P-value inferior to 0·20. Second, to study the association between environmental variables and EBV infection, odds ratios (OR and 95% confidence intervals (CI)) were estimated using logistic regression. We compared different models to distinguish between the area-level environment and individual-level characteristics:
Model 1: adjusted for household SEP (mother's education, equivalised income and parents’ social class)
Model 2: model 1 plus area environment variables (Urban Rural morphology)
Model 3: model 2 plus home environment variables (overcrowding, temperature in the baby's room)
Model 4: model 3 plus housing tenure. Housing tenure is considered separately as potentially capturing different facets of the material environment compared to an exterior variable with a different nature of overcrowding and temperature in the baby room.
All models were adjusted for IgG concentration, age and sex. Sensitivity analyses were performed on data with IgG > 2 only and showed no differences (Table S1 in Supplementary Materials). In addition, different cut-offs were used in sensitivity analyses, not changing our substantive findings (Table S2 in Supplementary Materials). Finally, a sensitivity analysis introducing the different variables in a different order (from the area-level environment to individual-level characteristics) have been carried out (Table S3 in Supplementary Materials).
All multivariate analyses were adjusted for survey weights accounting for the sampling framework and attrition between data collection waves and item non-response [25]. All analyses were performed using R version 3.2.5.
RESULTS
Descriptive and bivariate statistics are presented in Tables 1 and 2. EBV infection affected 17·16% children at the age of 3. The bivariate analysis of the different variables is given in Table 2. Children from households with a higher social class, higher equivalised income and whose mother had a higher educational level were significantly less likely to be infected with EBV. Regarding the home environment variables, children who lived in rented accommodation, in overcrowded homes, who slept in a cold/very cold room at 9 months, were significantly more likely to be infected. Finally, living in a larger towns or cities was significantly related to a higher rate of infection. Older child age, that only varies within the year around fieldwork, was also associated with an increased proportion of EBV infections.
Table 1.
Description of EBV units
| Variables | Description |
|---|---|
| EBV units (AU/ml) | n = 12 457 |
| Mean (s.d.) | 4·8 (10·7) |
| EBV units (AU/ml) | n = 12 457 |
| ⩽4·74, n (%) | 10 320 (82·84) |
| >4·74, n (%) | 2137 (17·16) |
Table 2.
Descriptive statistics for EBV ⩽ 4·74 and EBV > 4·74
| Variables | EBV ⩽ 4·74 n (%) (N = 10 320) | EBV > 4·74 n (%) (N = 2137) | P value Σ2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age mean (s.d.) | 3·13 (0·20) | 3·16 (0·23) | <0·001 |
| Sex | n = 10 320 | n = 2137 | 0·186 |
| Boy | 5260 (50·97) | 1055 (49·37) | |
| Girl | 5060 (49·03) | 1082 (50·63) | |
| Parents social class | n = 10 320 | n = 2137 | <0·001 |
| I | 4293 (41·60) | 741 (34·67) | |
| II | 1208 (11·71) | 250 (11·70) | |
| III | 687 (6·66) | 156 (7·30) | |
| IV | 913 (8·85) | 197 (9·22) | |
| V | 2121 (20·55) | 519 (24·29) | |
| Never worked – absent – missing | 1098 (10·64) | 274 (12·82) | |
| Equivalised income | n = 10 053 | n = 2075 | <0·001 |
| >0·75 and ⩽1 | 2902 (28·87) | 509 (24·53) | |
| >0·5 and ⩽0·75 | 3465 (34·47) | 662 (31·90) | |
| >0·25 and ⩽0·5 | 2713 (26·99) | 658 (31·71) | |
| ⩽0·25 | 973 (9·68) | 246 (11·86) | |
| Mother education | n = 9850 | n = 2035 | <0·001 |
| Higher/degree | 2894 (29·38) | 526 (25·85) | |
| A/As/S level | 959 (9·74) | 195 (9·58) | |
| GCSE | 4366 (44·32) | 878 (43·14) | |
| No qualification | 1631 (16·56) | 436 (21·43) | |
| Housing tenure | n = 9864 | n = 2040 | <0·001 |
| Own | 6258 (63·44) | 1116 (54·71) | |
| Rent privately | 803 (8·14) | 176 (8·63) | |
| Social housing | 2269 (23·00) | 585 (28·68) | |
| Other | 534 (5·41) | 163 (7·99) | |
| Number of room per person | n = 9869 | n = 2041 | <0·001 |
| No overcrowding | 7334 (74·31) | 1388 (68·01) | |
| Overcrowding | 2535 (25·69) | 653 (31·99) | |
| Childcare | n = 10 073 | n = 2090 | 0·423 |
| Home/nanny/others | 8949 (88·84) | 1870 (89·47) | |
| Crèche | 1124 (11·16) | 220 (10·53) | |
| Damp | n = 9860 | n = 2040 | 0·376 |
| No | 8567 (86·89) | 1757 (86·13) | |
| Yes | 1293 (13·11) | 283 (13·87) | |
| Temperature in baby's room | n = 9887 | n = 2041 | 0·103 |
| Warm/very warm/neither warm nor cold | 9278 (93·84) | 1895 (92·85) | |
| Cold/very cold | 609 (6·16) | 146 (7·15) | |
| Rural Urban environment | n = 9887 | n = 2041 | <0·001 |
| Large Urban | 7423 (75·08) | 1650 (80·84) | |
| Towns | 1334 (13·49) | 214 (10·49) | |
| Rural | 1130 (11·43) | 177 (8·67) |
In Table 3, we report unadjusted and adjusted odds ratio resulting from the logistic regression models (1–4). In the first model, only parent social class was still associated with an increased odds of being infected. Children whose parents belong to class V were more likely to be infected than those whose parents belong to class I (OR = 1·24 (1·02–1·50)). In the second model, we added the area-level covariate. The association between parent social class and EBV infection remained significant (OR = 1·23 (1·01–1·49)). Though not statistically significant, the odds of being infected with EBV were lower for respondents living in less urbanised settings Children who lived in towns and rural areas were less likely to be infected than those who lived in urban areas (OR = 0·81 (0·65–1·02) and OR = 0·84 (0·68–1·05), respectively). In the third model, we added home environment covariates. Children from overcrowded homes had a higher odds of being infected (OR = 1·14 (1·10–1·31)), this association approached significance. The association between parent social class and being EBV infected was slightly weakened (OR = 1·21 (0·99–1·47)) and lost significance between model 2 and 3. The effect of area-level variable remained unchanged. In our fully adjusted model we added home environment variables, observing that children whose parents rent from a social landlord (OR = 1·16 (0·98–1·38)) or in ‘other’ category (OR = 1·35 (1·07–1·70)) were more likely to be infected than those whose parents were home owners. The effect of overcrowding was reduced (OR = 1·10 (0·96–1·27)) and the effect of area-level variable remains unchanged.
Table 3.
Univariate and multivariate Logistic regression models for EBV ⩾ 4·74 vs. <4·74, adjusted for household socio-economic position (Model 1), Model 1 plus area environment (Model 2), Model 2 plus home environment (overcrowding, temperature in the baby room) (Model 3), Model 3 plus housing tenure (Model 4)
| Characteristic | Univariate OR (95% CI)a | Model 1a (95% CI) | Model 2a (95% CI) | Model 3a (95% CI) | Model 4a (95% CI) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1 (1,1)*** | 1 (1,1)** | 1 (1,1)* | 1 (1,1)* | 1 (1,1)* |
| Sex | |||||
| Boy | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| Girl | 1·07 (0·98–1·18)† | 1·06 (0·96,1·18) | 1·06 (0·95,1·18) | 1·06 (0·95,1·18) | 1·06 (0·95,1·17) |
| Income | |||||
| >0·75 and ⩽1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| >0·5 and ⩽0·75 | 1·02 (0·89–1·17)† | 0·95 (0·82–1·09) | 0·94 (0·82–1·09) | 0·93 (0·80–1·08) | 0·92 (0·79–1·07) |
| >0·25 and ⩽0·5 | 1·30 (1·13–1·51)*** | 1·10 (0·93–1·31) | 1·10 (0·92–1·31) | 1·07 (0·90–1·28) | 1·02 (0·85–1·24) |
| ⩽0·25 | 1·26 (1·06–1·51)* | 1·00 (0·80–1·26) | 1·00 (0·79–1·25) | 0·97 (0·77–1·22) | 0·91 (0·71–1·16) |
| Mother education | |||||
| Higher/degree | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| A/As/S level | 1·18 (0·97–1·44)† | 1·13 (0·93–1·38) | 1·14 (0·93–1·39) | 1·14 (0·93–1·39)† | 1·13 (0·93–1·39) |
| GCSE | 1·14 (0·98–1·32)° | 1·04 (0·88–1·22) | 1·03 (0·88–1·22) | 1·03 (0·87–1·21) | 1·02 (0·87–1·20) |
| No qualification | 1·46 (1·22–1·74)*** | 1·20 (0·98–1·47)° | 1·18 (0·96–1·44)† | 1·16 (0·94–1·42)† | 1·14 (0·92–1·40) |
| Parent social class | |||||
| I | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| II | 1·19 (0·99–1·43)* | 1·13 (0·92–1·38) | 1·12 (0·92–1·37) | 1·11 (0·91–1·36) | 1·10 (0·90–0.34) |
| III | 1·29 (1·03–1·61)* | 1·13 (0·89–1·44) | 1·14 (0·90–1·45) | 1·11 (0·88–1·41) | 1·10 (0·87–1·40) |
| IV | 1·16 (0·96–1·40)† | 1·11 (0·90–1·36) | 1·11 (0·90–1·36) | 1·09 (0·89–1·34) | 1·06 (0·87–1·31) |
| V | 1·38 (1·18–1·6)*** | 1·24 (1·02–1·50)* | 1·23 (1·01–1·49)* | 1·21 (0·99–1·47)° | 1·15 (0·94–1·41)† |
| Never worked – absent – missing | 1·39 (1·13–1·71)** | 1·24 (0·96–1·61)† | 1·22 (0·94–1·58)† | 1·20 (0·92–1·55)† | 1·14 (0·88–1·48) |
| Urban rural area | |||||
| Large Urban | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| Towns | 0·78 (0·62–0·98)* | 0·81 (0·65–1·02)° | 0·81 (0·65–1·02)° | 0·82 (0·65–1·03)° | |
| Rural | 0·80 (0·65–0·99)* | 0·84 (0·68–1·05)† | 0·84 (0·68–1·05)† | 0·84 (0·67–1·05)† | |
| Number of room per person | |||||
| No overcrowding | 1 | 1 | 1 | ||
| Overcrowding | 1·28 (1·13–1·45)*** | 1·14 (1·00–1·31)° | 1·10 (0·96–1·27)† | ||
| Temperature in the baby's room | |||||
| Very warm/warm/neither warm nor cold | 1 | 1 | |||
| Very cold/cold | 1·06 (0·85–1·32) | 0·99 (0·79–1·25) | 0·98 (0·78–1·24) | ||
| Housing tenure | |||||
| Own | 1 | 1 | |||
| Rent privately | 1·17 (0·95–1·43)† | 1·05 (0·84–1·31) | |||
| Social housing | 1·39 (1·21–1·58)*** | 1·16 (0·98–1·38)° | |||
| Other | 1·53 (1·24–1·89)*** | 1·35 (1·07–1·70)* |
***P ⩽ 0.001, **P ⩽ 0.01, *P ⩽ 0.05, °P < 0.10 and †P < 0.20.
Adjusted for IgG and for sample weights and MCS complex survey design.
DISCUSSION
We observed that early household SEP was associated with early EBV infection through a material pathway, in particular via area-level and household environment variables. We observed an association between living in a large urban area, household overcrowding and living in rented accommodation (specifically renting from the local authority, housing tenure association) and being infected with EBV by the age of 3. However, the effects of urban residence and overcrowding were reduced when we adjusted for housing tenure, which may indicate that housing quality linked to the built environment within the household is a determinant of early EBV infection above area-level factors and the effects of overcrowding.
As in other studies [12, 26], our work showed that having parents with a low SEP (income, education, occupation) was related to EBV infection in early childhood, however, this relationship is likely to operate through the material living conditions within the household, as captured by overcrowding and housing tenure. Our findings are in line with the observation that poor housing quality and dense living conditions influence the transmission of EBV [4, 5, 26, 27]. Recent studies in the USA reported this link in older children [12, 27]. In our study, household tenure acts as a proxy for the quality and condition of the housing in which the children were living in early life. This is strongly correlated with overcrowding, where social housing tenants may share their living spaces with many individuals in a small space [27, 28]. The relationship between the two variables means that the relative contribution of each is hard to disentangle [29]. Thus, the variables may be capturing a general material environment effect, or each variable may represent a separate route for infection, overcrowding through proximity to others and housing tenure through poorer housing conditions such as dilapidated buildings.
Our results also showed that, in our large, nationally representative sample, living in a large urban area may influence early EBV infection. The nature of urban dwelling, including constant contact with others through public transport and living in smaller shared spaces may be an ideal environment for exposure to viruses such as EBV. Few studies reported this association and in very different environmental contexts such as among Nepalese children [30].
We also observed that the risk of EBV infection increased with age, this is to be expected since children's opportunities for being exposed to- and becoming infected with- the virus increases with their exposure to the environment over time [12]. The age at which children become infected may be an important factor to take into account especially as the variation of age in the sample is limited to a few months within a year [5]. Research suggests that the timing of infections may be important for immune system maturation, and affect immune function over the lifecourse [31]. We have shown that disadvantaged social conditions may ‘get under the skin’ leading to EBV infection early in life, which has been linked to immune system disorders [15, 32] and a sensitivity to adult health outcomes. It is important to understand the social patterning of early life exposures to get to grips with mechanisms involved in the social-to-biological transition.
The main limitation of our study is the definition of ‘large urban areas’ which is different in England and Wales, Scotland and Northern Ireland. Moreover, due to a lack of availability of variables, we could not include a number of important factors in our model, such as nutritional behaviours, or other factors that could affect EBV infection. Another limitation is our lack of repeated measures of EBV, which would allow us to examine the timing of infection in more detail. Finally, through our hypothesis-driven approach, we attributed specific mechanisms to overcrowding and housing tenure, which may, in fact, capture the same general effect of the material environment.
CONCLUSION AND NEXT STEPS
Our work suggests that the household material environment may be a pathway to early infection by the EBV. This social patterning of early infection may be an important mechanism for understanding subsequent host susceptibility or resistance to disease, as well as lifecourse pathways to social differences in health. Future work building on these results to examine the link between socially-patterned early infection and subsequent health outcomes may provide valuable information on social-to-biological mechanisms over the lifecourse.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded by the European Commission as part of the Lifepath project (H2020 grant number 633666).
DECLARATION OF INTEREST
None.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268817002515.
click here to view supplementary material
REFERENCES
- 1.Wolf H, Bogedain C, Schwarzmann F. Epstein-Barr virus and its interaction with the host. Intervirology 1993; 35(1–4): 26–39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.De-The G, et al. Sero-epidemiology of the Epstein-Barr virus: preliminary analysis of an international study – a review. IARC Scientific Publications 1975; 11(2): 3–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cohen JI. Epstein-Barr virus infection. The New England journal of medicine 2000; 343(7): 481–492. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Evans AS. The spectrum of infections with Epstein-Barr virus: a hypothesis. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 1971; 124(3): 330–337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hsu JL, Glaser SL. Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignancies: epidemiologic patterns and etiologic implications. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 2000; 34(1): 27–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zajacova A, Dowd JB, Aiello AE. Socioeconomic and race/ethnic patterns in persistent infection burden among U.S. adults. The Journals of Gerontology Series A, Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences 2009; 64A(2): 272–279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Condon LM, et al. Age-specific prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus infection among Minnesota children: effects of race/ethnicity and family environment. Clinical Infectious Diseases 2014; 59(4): 501–508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Piriou E, et al. Early age at time of primary Epstein-Barr virus infection results in poorly controlled viral infection in infants from Western Kenya: clues to the etiology of endemic Burkitt lymphoma. Journal of Infectious Diseases 2012; 205(6): 906–913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Slyker JA, et al. Clinical and virologic manifestations of primary Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection in Kenyan infants born to HIV-infected women. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2013; 207(12): 1798–1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dowd JB, Aiello AE, Alley D. Socioeconomic disparities in the seroprevalence of cytomegalovirus infection in the US population: NHANES III. Epidemiology and Infection 2009; 137(01): 58–65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.McQuillan GM, et al. Racial and ethnic differences in the seroprevalence of 6 infectious diseases in the United States: data from NHANES III, 1988–1994. American Journal of Public Health 2004; 94(11): 1952–1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dowd JB, et al. Seroprevalence of Epstein-Barr virus infection in U.S. children ages 6–19, 2003–2010. PLoS ONE 2013; 8(5): e64921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Ferres M, et al. Seroprevalence of Epstein Barr virus infection in a healthy population of Santiago de Chile. Revista medica de Chile 1995; 123(12): 1447–1452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jansen MA, et al. Determinants of ethnic differences in cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus, and herpes simplex virus type 1 seroprevalence in childhood. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 2016; 170: 126–134, e121–e126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Chabay PA, Preciado MV. EBV primary infection in childhood and its relation to B-cell lymphoma development: a mini-review from a developing region. International Journal of Cancer 2013; 133(6): 1286–1292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kelly-Irving M, Tophoven S, Blane D. Life course research: new opportunities for establishing social and biological plausibility. International Journal of Public Health 2015; 60(6): 629–630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Connelly R, Platt L. Cohort profile: UK Millennium Cohort Study (MCS). International Journal of Epidemiology 2014; 43(6): 1719–1725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Anon. University of London. Institute of Education. Centre for Longitudinal Studies. (2012). Millennium Cohort Study: Second Survey, 2003–2005: Oral Fluid Collection Bioassay Data. [data collection]. UK Data Service. SN: 6993, 10.5255/UKDA-SN-6993-1. [DOI]
- 19.Anon. University of London. Institute of Education. Centre for Longitudinal Studies. (2017). Millennium Cohort Study: First Survey, 2001–2003. [data collection]. 12th Edition. UK Data Service. SN: 4683, 10.5255/UKDA-SN-4683-4. [DOI]
- 20.Bartington SE, et al. Feasibility of collecting oral fluid samples in the home setting to determine seroprevalence of infections in a large-scale cohort of preschool-aged children. Epidemiology and Infection 2009; 137(2): 211–218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Anon. University of London. Institute of Education. Centre for Longitudinal Studies. (2017). Millennium Cohort Study: Second Survey, 2003–2005. [data collection]. 9th Edition. UK Data Service. SN: 5350, 10.5255/UKDA-SN-5350-4. [DOI]
- 22.Townsend C, et al. Technical report on the Millennium Cohort Study biomedical data enhancement study of infections and later allergies. UK Data Service, http://doc.ukdataservice.ac.uk/doc/6993/mrdoc/pdf/mcs2_oral_fluid_data_collection.pdf.2012.
- 23.McLeod CB, et al. Income inequality, household income, and health status in Canada: a Prospective Cohort Study. American Journal of Public Health 2003; 93(8): 1287–1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hsu JL, Glaser SL. Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignancies: epidemiologic patterns and etiologic implications. Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology 2000; 34(1): 27–53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Plewis I. Non-response in a birth Cohort study: the case of the Millennium Cohort Study. International Journal of Social Research Methodology 2007; 10(5): 325–334. [Google Scholar]
- 26.Sumaya CV, et al. Seroepidemiologic study of Epstein-Barr virus infections in a rural community. The Journal of Infectious Diseases 1975; 131(4): 403–408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Crowcroft NS, et al. Epidemiology of Epstein-Barr virus infection in pre-adolescent children: application of a new salivary method in Edinburgh, Scotland. Journal of Epidemiology and Community Health 1998; 52(2): 101–104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Baker MG, et al. Collaborating with a social housing provider supports a large cohort study of the health effects of housing conditions. BMC Public Health 2016; 16: 159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gray A. Definitions of Crowding and the Effects of Crowding on Health. A Literature Review Prepared for the Ministry of Social Policy. 2001.
- 30.Worthman CM, Panter-Brick C. Homeless street children in Nepal: use of allostatic load to assess the burden of childhood adversity. Development and Psychopathology 2008; 20(1): 233–255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Dowd JB, Zajacova A, Aiello A. Early origins of health disparities: burden of infection, health, and socioeconomic status in U.S. children. Social Science & Medicine 2009; 68(4): 699–707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Schaub B, Lauener R, von Mutius E. The many faces of the hygiene hypothesis. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 2006; 117(5): 969–977; quiz 978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0950268817002515.
click here to view supplementary material