Abstract
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is an interface between cerebral blood and the brain parenchyma. As a gate keeper, BBB regulates passage of nutrients and exogeneous compounds. Owing to this highly selective barrier, many drugs targeting brain diseases are not likely to pass through the BBB. Thus, a large amount of time and cost have been paid for the development of BBB targeted therapeutics. However, many drugs validated in in vitro models and animal models have failed in clinical trials primarily due to the lack of an appropriate BBB model. Human BBB has a unique cellular architecture. Different physiologies between human and animal BBB hinder the prediction of drug responses. Therefore, a more physiologically relevant alternative BBB model needs to be developed. In this review, we summarize major features of human BBB and current BBB models and describe organ-on-chip models for BBB modeling and their applications in neurological complications.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier, In vitro modeling, Neurological diseases, Organ-on-a-chip
INTRODUCTION
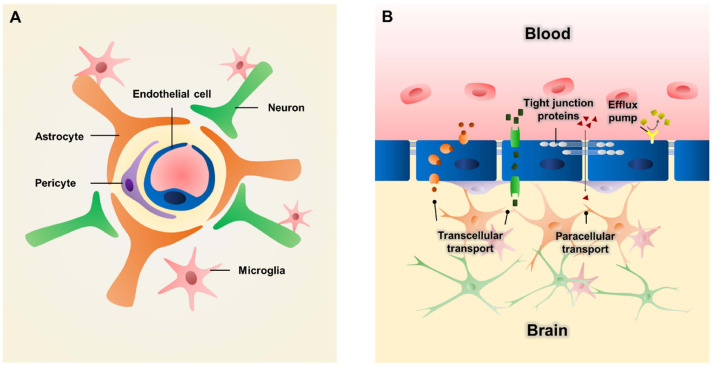
The blood-brain barrier (BBB) is a highly selective barrier in the brain. It protects the brain from exogenous substances by strictly regulating the transport of molecules from the blood vasculature into the brain. The BBB has a multicellular structure. It mainly comprises endothelial cells (ECs), pericytes, and astrocytes (1). Brain ECs are core cellular components of the BBB. They line the inner surface of cerebral blood vessels. Pericytes wrap around brain ECs and astrocytes extend their endfeet to contact with blood vessels. ECs, pericytes, and astrocytes interplay with each other to maintain the structural and functional integrity of the BBB (2). Additionally, with surrounding neurons, microglia and extracellular matrix (ECM) cooperate with BBB, forming a more functional structure called a neurovascular unit (NVU) which plays a critical role in regulating cerebral blood flow and BBB functions to maintain brain homeostasis (Fig. 1A) (3).
Fig. 1.
Schematic illustration of blood-brain barrier (BBB) structure. (A) Brain endothelial cells (ECs) are lined to form blood vessels. Pericytes wrap around the vessel and astrocytes extend endfeet to contact with ECs. Neurons and microglia cooperate with each other to form more functional neurovascular unit (NVU). (B) The barrier accounts for limited paracellular transport due to tight junction proteins (e.g., zonula occludens 1 (ZO-1) and claudin) and transcellular transport due to efflux pumps (e.g., P-glycoprotein).
As a gate-keeper, BBB protects the brain from toxic substances and pathogens (4). The barrier function results from the restriction of both paracellular and transcellular transport. The paracellular transport of ions and hydrophilic solutes is severely limited by tight junctions between adjacent ECs with proteins including zonula occludens 1 (ZO-1) and claudin (5). Transporters such as P-glycoprotein serve as efflux pumps to remove harmful agents from the brain (Fig. 1B) (6). In addition, a low level of transcytosis in cerebral ECs further increases the selectivity of the BBB (7). Owing to the presence of the BBB, the entry of many therapeutic drugs targeting human brain are prevented, as more than 98% and approximately 100% of small- and large-molecule drugs cannot cross the BBB, respectively (8).
MODELS OF THE BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER
Many BBB research studies have been conducted to resolve neurological complications (9). Development of a physiologically relevant BBB model has been a great interest as current BBB models could not represent the complexity of the human BBB. Animal models have been used in pharmaceutical development to predict drug efficacy and toxicity. They provide major human health benefits as good models to predict human physiology and pathology. The clear advantage of utilizing animals is that they provide basic biological knowledge of a living organism. Therefore, animal testing has been considered as the default and gold standard in preclinical research. It has been widely accepted for a long time. While mouse and rat are the most widely used animal models, various other animal species (e.g., zebrafish) have also been exploited as alternatives (10). Animal models have elucidated fundamental cellular architecture and morphological features, barrier permeability, and transport mechanisms (11). However, the reliability and predictability of animal testing for drug responses and physiological alterations in human have been revealed to be very low. Over 80% drugs validated in animal models have failed in human clinical trials (12) mainly due to genetic, molecular, and immunologic differences between human and other animals. Moreover, in some diseases, even pathological mechanisms are different between human and animal models (13). Additionally, ethical issues as well as high costs also hamper the use of animals (14).
To overcome these limitations of animal models, human cell-based in vitro testing methods have been adopted. As the simplest way to conduct an in vitro experiment, single cell type of ECs cultured on plastic culture dishes in two dimensions has been used to recapitulate endothelial barriers (15). Although it is simple and reproducible, this model lacks brain compartment which plays an indispensable supporting role in barrier properties (1). Associated brain components, especially astrocytes, pericytes, and neurons, need to be cultured in one culture platform to facilitate cellular interplays (16). The most widely used co-culture platform is a Transwell system. An in vitro BBB model has also been developed using the Transwell system (17). Usually, ECs are seeded on the top of the porous membrane while astrocytes, pericytes, and neurons are seeded on the opposite side of the membrane or seeded at the bottom of the well. The Transwell system offers many advantages. For example, the system enables the measurement of transendothelial resistance (TEER) and permeability assays (18). Still, it is too simple to represent the complexity and functionality of human BBB due to its two-dimensional geometry and the lack of an ECM. Thus, an innovative co-culture system needs to be developed.
Over the last decade, organoid technology which harnesses the developmental process of organogenesis has been developed to generate in vitro 3D tissue constructs to recapitulate human organs (19). BBB-like structures have been reconstituted in 3D brain organoids. For example, generated brain organoids are further added with ECs to create vascularized brain organoids (20-23). Cakir et al. developed vascular networks in cortical organoids with human embryonic stem cells overexpressing an angiogenic transcription factor human ETS variant 2 (ETV2) (23). Vascularization resulted in enhanced maturation of cortical organoid with higher growth rate and lower apoptosis. The developed vasculature in cortical organoid exhibited BBB characteristics including increased expression of tight junction markers and higher TEER value than in cortical organoid without vascularization. In another study, functional vascularization in brain organoids was induced in vivo by transplanting human brain organoids into the adult mouse brain (24). Organoid grafts integrated into the mouse brain underwent neurogenesis and vascularization, suggesting a strategy for in situ construction of BBB-like structures in brain organoids.
BLOOD-BRAIN BARRIER-ON-A-CHIP
Although animal models and recently advanced in vitro models have provided a lot of insights into BBB physiology and pathology, the complex BBB microenvironment limits current models to be effective platforms for studying neurological diseases and drug development. Fluid flow at the BBB plays an important role in maintaining barrier functions and homeostasis of the central nervous system. Shear stress generated by circulatory blood flow in the brain capillaries ranges from 5 to 23 dyn/cm2 (25). It can be applied to capillary endothelium to facilitate barrier functions and regulate transport (26-28). Fluid shear stress can also be used to regulate physiological functions in the brain parenchyma (11, 25). However, most of conventional in vitro cell culture models in static conditions cannot recapitulate such controlled fluid flow. BBB possesses a unique cellular architecture in which pericytes wrap around capillaries and astrocyte endfeet contact with capillary ECs (3). This complicated structure informing a distinctive BBB microenvironment and cell-cell interactions cannot be accurately reconstituted via conventional co-culture systems such as Transwell. Thus, a more advanced co-culture system needs to be developed.
Organ-on-a-chip technology, a microphysiological system on which cells and tissues can be cultured, has been applied to overcome limitations of conventional in vitro BBB models. Basically, it is composed of microfluidic devices that can simulate tissue- and organ-level physiological functions (29). In the 1990s, microfluidics was developed rapidly with the introduction of poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) (30, 31), the most frequently used material for microfluidics and organ-on-a-chip. The study that cultured cells on a microfluidic chip for simula-ting organ-level function of human physiology and pathology was conducted by Shuler group in 2004 (32, 33). In that study, lung, liver, fat, and other tissue compartments called cell culture analogue (CCA) systems were connected by channels and tissue culture medium as blood surrogate was recirculated through these tissue compartments. With this system, investigators mo-deled the absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination, and potential toxicity of the chemical drugs that are mathematically simulated with a physiologically relevant pharmacokinetic model. Lung-on-a-chip introduced in 2010 by Ingber group (34) was a landmark study in the field of in vitro modeling. Since then, microfluidic devices for culturing cells have been rapidly developed, mimicking most parts of the body, especially the gut, kidney, placenta, blood-retinal barrier, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and BBB (35). Using organ-on-a-chip, several cell types can be cultured simultaneously on one chip. They can be compartmentalized in plenty of shapes with channels or membranes. Besides, channels enable the application of fluid flow, facilitating the culture of cells, especially cells requiring fluid shear stress (30). Therefore, organ-on-a-chip can offer a more physiologically relevant culture environment for BBB modeling. Despite challenges remain in transitions into drug development pipelines, organ-on-a-chip systems are not limited to academic research in laboratories. Many types of chips have already been commercialized including BBB-on-a-chip systems (35-37). Meanwhile, organ-on-a-chip technologies have attracted interest from the pharmaceutical industry and regulatory agencies, and received increasing investments (37, 38).
DESIGNS OF BBB-ON-A-CHIP
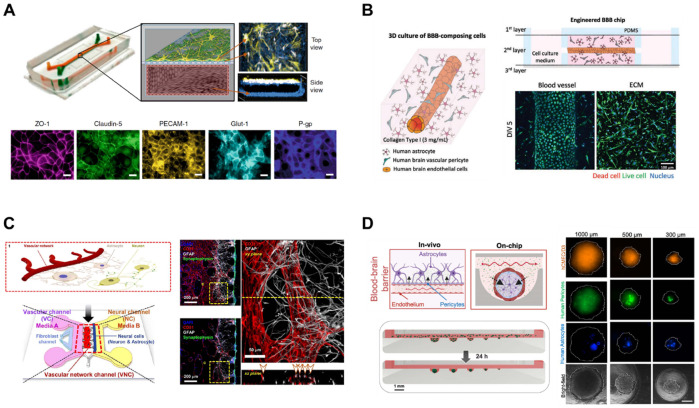
To replicate the complex structures and functions of the BBB, advances have been made for the design of BBB-on-a-chip (Fig. 2). One of the widely used BBB-on-a-chip design is the use of a porous membrane to separate chambers (39). One chamber comprises ECs and the opposite side of the chamber consists of astrocytes and pericytes (Fig. 2A). ECs can be seeded on the porous membrane or cultured to form monolayer with vascular lumen inside the chamber. Blood vessels can also be generated inside hydrogels with or without perivascular cells embedded in the hydrogel (Fig. 2B). These platforms can further recapitulate the in vivo BBB microenvironment with an ECM (40). Harnessing the inherent ability of vasculogenesis and angiogenesis, ECs can be self-organized to form vasculature (Fig. 2C). This approach mimics the vascular development in vivo, resulting in improved functionalities of the BBB (41). Recently, 3D spheroid model of BBB has been developed (Fig. 2D). 3D spheroids can mimic brain tissues by including various cell types of BBB or NVU in the spheroids. BBB spheroids can be created by assembling brain ECs, astrocytes, and pericytes with low-adherence culture techniques or microfluidic devices (42-44).
Fig. 2.
Designs of BBB-on-a-chip. (A) Porous membrane separates blood components and brain components. As an example for this type, endothelial cells (ECs) forming vascular lumen are seeded in the lower chamber, and astrocytes and pericytes are seeded on the top of the porous membrane. Adapted with permission from Park et al. (39). Copyright (2019) Springer Nature. (B) Blood vessels form inside the matrix. As an example for this type, ECs can form blood vessels inside the matrix, with astrocytes and pericytes embedded around the blood vessel. Adapted with permission from Seo et al. (40). Copyright (2021) Wiley-VCH GmbH. (C) Self-assembled vasculatures of the BBB. As an example for this type, ECs are embedded in fibrin gel and vascular networks are formed in the matrix. Neurons and astrocytes are seeded in the adjacent channel by the side of the vascular networks. Adapted with permission from Bang et al. (41). Copyright (2017) Springer Nature. (D) 3D spheroid models of the BBB. As an example for this type, the BBB spheroids are formed with ECs, astrocytes, and pericytes in low adhesive microwells. Adapted with permission from Eilenberger et al. (44). Copyright (2021) Wiley-VCH GmbH.
BBB-ON-A-CHIPS FOR VARIOUS APPLICATIONS
Various neurological diseases are known to be associated with BBB (45-47). Brain disease can affect the BBB by disrupting tight junctions. Chronic BBB malfunction is also related to the development of multiple neurological disorders. The following sections discuss applications of BBB-on-a-chip in Alzheimer’s disease, ischemic stroke, infectious disease, brain cancer, and transport mechanism studies.
Alzheimer’s disease models
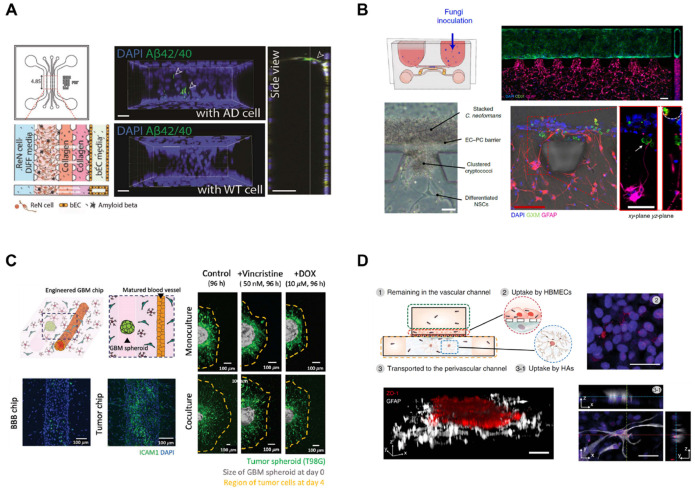
BBB disruption and impairment of barrier functions are associated with various neurological disorders and neurodegenerative diseases (48). In Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the decreased expression of tight junction proteins increases the BBB permeability and the efflux pathway through receptor-mediated trans-cytosis, the major mechanism of beta-amyloid (Aβ) clearance across the BBB, is disrupted (49). Animal models are not suit-able for human AD modeling due to their different genetic profiles and pathophysiology. The accumulation of Aβ and hyper-phosphorylated tau is observed in animals, but they cannot be considered as AD models since other biological features of human AD, such as neurofibrillary tangle pathology and sporadic forms of AD, are not exhibited in animal models (50, 51). Thus, pre-clinical results from animal models rarely translate into humans (52). Shin et al. (53) have developed a microfluidic model which comprises BBB components, including a tube-shaped brain EC monolayer and AD microenvironment (Fig. 3A). A unique AD pathological microenvironment has been developed by culturing human-origin neural progenitors expressing familial AD (FAD) mutations in 3D. Major AD pathologies were recapitulated with extracellular deposition of amyloid plaques and tauopathy followed by BBB impairment as observed in AD patients, such as elevated BBB permeability, decreased expression of tight junctions and adherens junctions, and increased levels of reactive oxygen species and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) (e.g., MMP-2). More importantly, Aβ deposition was observed at the surface of the abluminal side of brain ECs.
Fig. 3.
Various applications of BBB-on-a-chip. (A) Alzheimer’s disease (AD) can be modeled with BBB-on-a-chip. For example, AD-mimicking microenvironment can be reconstituted on the BBB-on-a-chip. Pathological features such as beta-amyloid (Aβ) deposition can be observed at the BBB. Adapted with permission from Shin et al. (53). Copyright (2019) WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim. (B) Infectious disease model in an NVU chip. For example, infection of Cryptococcus neoformans has been modeled in a BBB-on-a-chip and neurotropism of the fungus has been elucidated with a multi-organ chip design. Adapted with permission from Kim et al. (59). Copyright (2021) Springer Nature. (C) Brain cancer can be recapitulated with co-culture of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) in BBB-on-a-chip to observe different drug responses based on the interaction of the BBB with brain cancer. Adapted with permission from Seo et al. (40). Copyright (2021) Wiley-VCH GmbH. (D) Transport mechanisms are better studied using BBB-on-a-chip. For example, lipoprotein receptor-mediated transcytosis can be demonstrated with the introduction of high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-mimetic nanoparticles to BBB-on-a-chip. Adapted with permission from Ahn et al. (64). Copyright (2020) Springer Nature.
Ischemic stroke models
In ischemic stroke, inadequate supply of blood leads to neurological pathologies where BBB is disrupted, resulting in the breakdown of tight junctions and ionic shifts in the brain (54, 55). However, drugs validated in animal models have failed in clinical trials probably because of physiological and patholog-ical differences between human and animals (56). Lyu et al. (57) have created a microfluidic ischemic stroke model. A functional NVU model consisting of human brain microvascular ECs, pericytes, astrocytes, microglia, and neurons was established in the microfluidic device. An ischemic condition was developed by supplying 2% O2 with depletion of serum and glucose for 24 hours to recapitulate the peri-infarct zone of ischemic injury. The developed BBB chip was tested for evalua-ting neurorestorative efficacy of various types of stem cells to investigate the influence of stem cells during disease progression and recovery processes.
Infectious disease models
Bacteria and viruses can enter the BBB via receptor-mediated active transport or because of an increase of barrier permeability (58). The infection of pathogens can also be recapitulated in a functional BBB model. Kim et al. (59) have developed a microfluidic NVU model using human neural stem cells, brain microvascular ECs, and brain vascular pericytes in a brain-relevant 3D matrix which comprises collagen and hyaluronic acid. The microfluidic NVU chip with BBB structure was applied to model the BBB penetration of Cryptococcus neoformans, a fungal pathogen that causes fatal meningoencephalitis (Fig. 3B). The microfluidic chip was cultured in a unidirectional flow driven by stepwise gravity without syringes or tubing, thus enabling high throughput culture of chips. Cryptococcus neoformans can penetrate the BBB without changes in tight junctions, proposing transcytosis-mediated transport of Cryptococcus neoformans. Furthermore, neurotropism of Cryptococcus neoformans was recapitulated in a multi-organ chip design. More recently, coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) infection has been modeled in a microfluidic BBB device. Buzhdygan et al. (60) have used a 3D microfluidic model of BBB consisting of brain ECs injected into a channel created by mixing multiple hydrogels on a microfabricated device. SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins are then introduced to the model, showing significant influences on barrier functions. The spike proteins can trigger immune responses and elevate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and adhesion molecules to disrupt the BBB integrity and increase barrier permeability.
Brain cancer models
Pharmaceutical treatments for brain cancer are limited because of the poor BBB penetration of drugs and the aggressiveness of primary brain tumors as well as the occurrence of metastatic brain tumors from various primary sites (61). Additionally, tumors can interact with the surrounding microenvironment including cellular and noncellular components to resist therapeutics. Thus, more effective in vitro brain tumor platforms including blood vessels are required (62). Seo et al. (40) have engineered a BBB-on-a-chip to replicate the brain tissue-specific microenvironment using human astrocytes and brain vascular pericytes embedded in a 3D hydrogel matrix (Fig. 3C). A monolayer of human brain ECs formed blood vessel inside the matrix and recapitulated the glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) microenvironment by adding GBM spheroids to the matured BBB model to predict drug responses.
Transport mechanism study
Poor BBB penetration of pharmaceutical drugs is one of the major issues in neurological disease treatments (63). Thus, BBB targeting studies have been conducted to deliver drugs across the BBB (9). Park et al. (39) have established a BBB-on-a-chip with human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived brain microvascular endothelium forming a vascular lumen in the lower channel separated by a porous membrane with primary human brain astrocytes and primary human pericytes seeded on the top of the porous membrane. During differentiation, cells were exposed to hypoxia, resulting in increased endothelial barrier functionality. Ahn et al. (64) have developed a BBB-on-a-chip with human brain microvascular ECs seeded on the top of the porous membrane and human brain vascular pericytes seeded on the opposite side of the membrane (Fig. 3D). Importantly, human astrocytes were seeded in 3D in the opposite side of the membrane to highlight the contribution of astrocytes to BBB pathology with decreased reactive gliosis as well as astro-cytic network due to their extending endfeet contacting blood vessels and polarized expression of aquaporin-4 (AQP4) near the vasculature. High-density lipoprotein-mimetic nanoparticles were then introduced to demonstrate the distinct BBB penetration through lipoprotein receptor-mediated transcytosis. More recently, Eilenberger et al. (44) have demonstrated a microfluidic multi-size spheroid array to generate BBB spheroids composed of human brain ECs, human primary pericytes, and astrocytes with various spheroid sizes for studying size-dependent compound uptake. With consequential altered cell responses according to spheroid size, anticancer drug toxicity assessment and better prediction of penetration across the BBB were accomplished.
CONCLUSION
The high selectivity of the BBB has hampered the therapeutical treatment for neurological diseases. In addition, inappropriate in vivo and in vitro models have led to the requirement of a novel in vitro BBB model. Organ-on-a-chip has been employed to better recapitulate the human in vivo microenvironment to facilitate the prediction of drug responses. BBB-on-a-chip has also been developed rapidly over the last decade. Various disease modeling and transport mechanism studies have been implemented using BBB-on-a-chip. In future studies, BBB-on-a-chip is expected to develop more clinically relevant models using patient-derived stem cells and integration of analyzing sensors.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by Samsung Research Funding & Incubation Center of Samsung Electronics (Project Number SRFC-TC2003-03).
Footnotes
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors have no conflicting interests.
REFERENCES
- 1.Abbott NJ, Patabendige AA, Dolman DE, Yusof SR, Begley DJ. Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2010;37:13–25. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2009.07.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Obermeier B, Daneman R, Ransohoff RM. Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med. 2013;19:1584–1596. doi: 10.1038/nm.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Abbott NJ, Ronnback L, Hansson E. Astrocyte-endothelial interactions at the blood-brain barrier. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:41–53. doi: 10.1038/nrn1824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Huber JD, Egleton RD, Davis TP. Molecular physiology and pathophysiology of tight junctions in the blood-brain barrier. Trends Neurosci. 2001;24:719–725. doi: 10.1016/S0166-2236(00)02004-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Abbott NJ. Blood-brain barrier structure and function and the challenges for CNS drug delivery. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2013;36:437–449. doi: 10.1007/s10545-013-9608-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schinkel AH. P-Glycoprotein, a gatekeeper in the blood-brain barrier. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 1999;36:179–194. doi: 10.1016/S0169-409X(98)00085-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.De Bock M, Van Haver V, Vandenbroucke RE, Decrock E, Wang N, Leybaert L. Into rather unexplored terrain-transcellular transport across the blood-brain barrier. Glia. 2016;64:1097–1123. doi: 10.1002/glia.22960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Pardridge WM. The blood-brain barrier: bottleneck in brain drug development. NeuroRx. 2005;2:3–14. doi: 10.1602/neurorx.2.1.3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Banks WA. From blood-brain barrier to blood-brain interface: new opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2016;15:275–292. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2015.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Geldenhuys WJ, Allen DD, Bloomquist JR. Novel models for assessing blood-brain barrier drug permeation. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2012;8:647–653. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2012.677433. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hajal C, Le Roi B, Kamm RD, Maoz BM. Biology and models of the blood-brain barrier. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2021;23:359–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-082120-042814. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Van Norman GA. Limitations of animal studies for predicting toxicity in clinical trials: is it time to rethink our current approach? JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2019;4:845–854. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2019.10.008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Dawson TM, Golde TE, Lagier-Tourenne C. Animal models of neurodegenerative diseases. Nat Neurosci. 2018;21:1370–1379. doi: 10.1038/s41593-018-0236-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Akhtar A. The flaws and human harms of animal experimentation. Camb Q Healthc Ethics. 2015;24:407–419. doi: 10.1017/S0963180115000079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bowman PD, Ennis SR, Rarey KE, Betz AL, Goldstein GW. Brain microvessel endothelial cells in tissue culture: a model for study of blood-brain barrier permeability. Ann Neurol. 1983;14:396–402. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Rauh J, Meyer J, Beuckmann C, Galla HJ. Development of an in vitro cell culture system to mimic the blood-brain barrier. Prog Brain Res. 1992;91:117–121. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)62325-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stone NL, England TJ, O'Sullivan SE. A novel transwell blood brain barrier model using primary human cells. Front Cell Neurosci. 2019;13:230. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2019.00230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.inivasan B, Sr, Kolli AR, Esch MB, Abaci HE, Shuler ML, Hickman JJ. TEER measurement techniques for in vitro barrier model systems. J Lab Autom. 2015;20:107–126. doi: 10.1177/2211068214561025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Clevers H. Modeling development and disease with organoids. Cell. 2016;165:1586–1597. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.05.082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pham MT, Pollock KM, Rose MD, et al. Generation of human vascularized brain organoids. Neuroreport. 2018;29:588–593. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000001014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Qian X, Song H, Ming GL. Brain organoids: advances, applications and challenges. Development. 2019;146:dev166074. doi: 10.1242/dev.166074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shi Y, Sun L, Wang M, et al. Vascularized human cortical organoids (vOrganoids) model cortical development in vivo. PLoS Biol. 2020;18:e3000705. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000705.66f6d290c2f84ede886185d58cd7368f [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cakir B, Xiang Y, Tanaka Y, et al. Engineering of human brain organoids with a functional vascular-like system. Nat Methods. 2019;16:1169–1175. doi: 10.1038/s41592-019-0586-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mansour AA, Goncalves JT, Bloyd CW, et al. An in vivo model of functional and vascularized human brain organoids. Nat Biotechnol. 2018;36:432–441. doi: 10.1038/nbt.4127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Wang X, Xu B, Xiang M, et al. Advances on fluid shear stress regulating blood-brain barrier. Microvasc Res. 2020;128:103930. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2019.103930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.van der Meer AD, Poot AA, Feijen J, Vermes I. Analyzing shear stress-induced alignment of actin filaments in endothelial cells with a microfluidic assay. Biomicrofluidics. 2010;4:11103. doi: 10.1063/1.3366720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Xu H, Li Z, Yu Y, et al. A dynamic in vivo-like organotypic blood-brain barrier model to probe metastatic brain tumors. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36670. doi: 10.1038/srep36670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang YI, Abaci HE, Shuler ML. Microfluidic blood-brain barrier model provides in vivo-like barrier properties for drug permeability screening. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2017;114:184–194. doi: 10.1002/bit.26045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Bhatia SN, Ingber DE. Microfluidic organs-on-chips. Nat Biotechnol. 2014;32:760–772. doi: 10.1038/nbt.2989. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Duffy DC, McDonald JC, Schueller OJ, Whitesides GM. Rapid prototyping of microfluidic systems in poly(dimethylsiloxane) Anal Chem. 1998;70:4974–4984. doi: 10.1021/ac980656z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Xia Y, Whitesides GM. Soft lithography. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1998;37:550–575. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980316)37:5<550::AID-ANIE550>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Viravaidya K, Sin A, Shuler ML. Development of a microscale cell culture analog to probe naphthalene toxicity. Biotechnol Prog. 2004;20:316–323. doi: 10.1021/bp0341996. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sin A, Chin KC, Jamil MF, Kostov Y, Rao G, Shuler ML. The design and fabrication of three-chamber microscale cell culture analog devices with integrated dissolved oxygen sensors. Biotechnol Prog. 2004;20:338–345. doi: 10.1021/bp034077d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Huh D, Matthews BD, Mammoto A, Montoya-Zavala M, Hsin HY, Ingber DE. Reconstituting organ-level lung functions on a chip. Science. 2010;328:1662–1668. doi: 10.1126/science.1188302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Zhang B, Korolj A, Lai BFL, Radisic M. Advances in organ-on-a-chip engineering. Nat Rev Mater. 2018;3:257–278. doi: 10.1038/s41578-018-0034-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Zhang B, Radisic M. Organ-on-a-chip devices advance to market. Lab Chip. 2017;17:2395–2420. doi: 10.1039/C6LC01554A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ma C, Peng Y, Li H, Chen W. Organ-on-a-chip: a new paradigm for drug development. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2021;42:119–133. doi: 10.1016/j.tips.2020.11.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Reardon S. 'Organs-on-chips' go mainstream. Nature. 2015;523:266. doi: 10.1038/523266a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Park TE, Mustafaoglu N, Herland A, et al. Hypoxia- enhanced blood-brain barrier chip recapitulates human barrier function and shuttling of drugs and antibodies. Nat Commun. 2019;10:2621. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10588-0.83253cf0aed94f3c93f14d16e82efff7 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Seo S, Nah SY, Lee K, Choi N, Kim HN. Triculture model of in vitro BBB and its application to study BBB‐associated chemosensitivity and drug delivery in glioblastoma. Adv Funct Mater. 2021;32:2106860. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202106860. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Bang S, Lee SR, Ko J, et al. A low permeability microfluidic blood-brain barrier platform with direct contact between perfusable vascular network and astrocytes. Sci Rep. 2017;7:8083. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-07416-0.9009db61c1c64367b7ec14eb53e64c00 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Urich E, Patsch C, Aigner S, Graf M, Iacone R, Freskgard PO. Multicellular self-assembled spheroidal model of the blood brain barrier. Sci Rep. 2013;3:1500. doi: 10.1038/srep01500. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Cho CF, Wolfe JM, Fadzen CM, et al. Blood-brain-barrier spheroids as an in vitro screening platform for brain-penetrating agents. Nat Commun. 2017;8:15623. doi: 10.1038/ncomms15623.66ff86f13d85438c93395cad172f6fbe [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Eilenberger C, Rothbauer M, Selinger F, et al. A microfluidic multisize spheroid array for multiparametric screening of anticancer drugs and blood-brain barrier transport properties. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2021;8:e2004856. doi: 10.1002/advs.202004856.938deb758c2a4b7988008b2945c6c720 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rosenberg GA. Neurological diseases in relation to the blood-brain barrier. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2012;32:1139–1151. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2011.197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Schoknecht K, Shalev H. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in brain diseases: clinical experience. Epilepsia. 2012;53 Suppl 6:7–13. doi: 10.1111/j.1528-1167.2012.03697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Daneman R. The blood-brain barrier in health and disease. Ann Neurol. 2012;72:648–672. doi: 10.1002/ana.23648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sweeney MD, Sagare AP, Zlokovic BV. Blood-brain barrier breakdown in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2018;14:133–150. doi: 10.1038/nrneurol.2017.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yoon JK, Kim J, Shah Z, Awasthi A, Mahajan A, Kim Y. Advanced human BBB-on-a-chip: a new platform for Alzheimer's disease studies. Adv Healthc Mater. 2021;10:e2002285. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202002285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Drummond E, Wisniewski T. Alzheimer's disease: experimental models and reality. Acta Neuropathol. 2017;133:155–175. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1662-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Golaszewska A, Bik W, Motyl T, Orzechowski A. Bridging the gap between Alzheimer's disease and Alzheimer's-like diseases in animals. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:1664. doi: 10.3390/ijms20071664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Cummings J, Feldman HH, Scheltens P. The "rights" of precision drug development for Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019;11:76. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0529-5.7b081af0310247768e61591dd9bd27e5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Shin Y, Choi SH, Kim E, et al. Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in a 3D in vitro model of Alzheimer's disease. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2019;6:1900962. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yang C, Hawkins KE, Dore S, Candelario-Jalil E. Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2019;316:C135–C153. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00136.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Wang Y, Cai Y. Obtaining human ischemic stroke gene expression biomarkers from animal models: a cross-species validation study. Sci Rep. 2016;6:29693. doi: 10.1038/srep29693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Xiong Y, Mahmood A, Chopp M. Animal models of traumatic brain injury. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2013;14:128–142. doi: 10.1038/nrn3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lyu Z, Park J, Kim KM, et al. A neurovascular-unit-on-a-chip for the evaluation of the restorative potential of stem cell therapies for ischaemic stroke. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5:847–863. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00744-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Chaudhuri JD. Blood brain barrier and infection. Med Sci Monit. 2000;6:1213–1222. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Kim J, Lee KT, Lee JS, et al. Fungal brain infection modelled in a human-neurovascular-unit-on-a-chip with a functional blood-brain barrier. Nat Biomed Eng. 2021;5:830–846. doi: 10.1038/s41551-021-00743-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Buzhdygan TP, DeOre BJ, Baldwin-Leclair A, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alters barrier function in 2D static and 3D microfluidic in-vitro models of the human blood-brain barrier. Neurobiol Dis. 2020;146:105131. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2020.105131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kim Y, Stolarska MA, Othmer HG. The role of the microenvironment in tumor growth and invasion. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 2011;106:353–379. doi: 10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2011.06.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kim HN, Habbit NL, Su CY, et al. Microphysiological systems as enabling tools for modeling complex-ity in the tumor microenvironment and accelerating cancer drug development. Adv Funct Mater. 2019;29:1807553. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201807553. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Pardridge WM. Blood-brain barrier delivery. Drug Discov Today. 2007;12:54–61. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2006.10.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Ahn SI, Sei YJ, Park HJ, et al. Microengineered human blood-brain barrier platform for understanding nanoparticle transport mechanisms. Nat Commun. 2020;11:175. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13896-7.95fd2b9d6594462fac69a3cba4e9f50b [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]