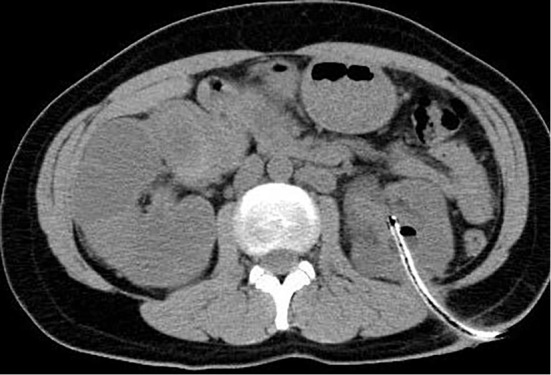
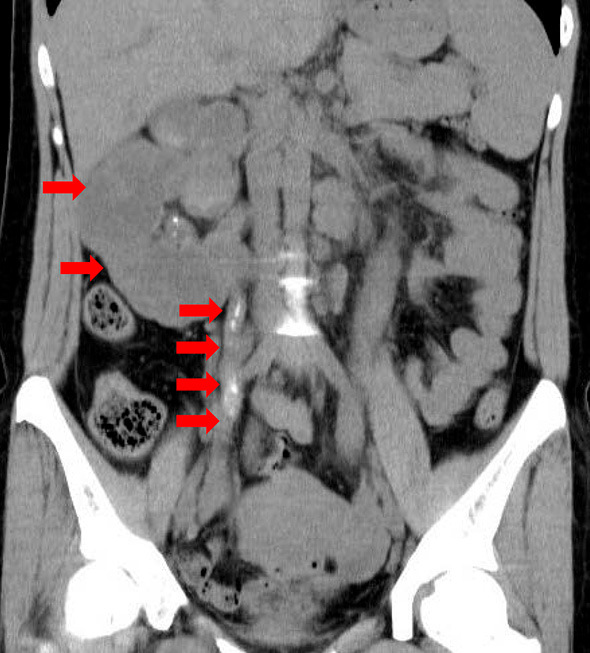
A 39-year-old Philippine woman visited our hospital to initiate hemodialysis. Her past-medical history showed a 6-year history of bilateral polycystic hydroureterropathy, and she had previously undergone left renal fistula construction due to urinary stenosis. Computed tomography of the abdomen showed the presence of bilateral polycystic hydroureterropathy with right ureter calcification (Picture 1, 2). Although the results of a QuantiFERON-TB Gold In-tube assay were positive, the results of an acid-fast culture and polymerase-chain-reaction (PCR) testing of urine specimens from the left renal fistula for Mycobacterium tuberculosis were negative. Therefore, we approached the right ureter pathway using stenting and thereby obtained a few drops of urine, which showed a positive PCR and culture finding for M. tuberculosis. She was thereafter treated with anti-M. tuberculosis drugs for 6 months, however, her renal dysfunction did not recover. Approximately 1-5% of all patients admitted for the initiation of hemodialysis are associated with M. tuberculosis infection (1). This case emphasized the importance of obtaining timely specimens since any delay in making an accurate diagnosis of renal and urinary tuberculosis may lead to the development of renal insufficiency.
Picture 1.
Picture 2.
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI).
References
- 1. Daher E de F, da Silva GB Jr, Barros EJG. Renal tuberculosis in the modern era. Am J Trop Med Hyg 88: 54-64, 2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


