Fig. 3.
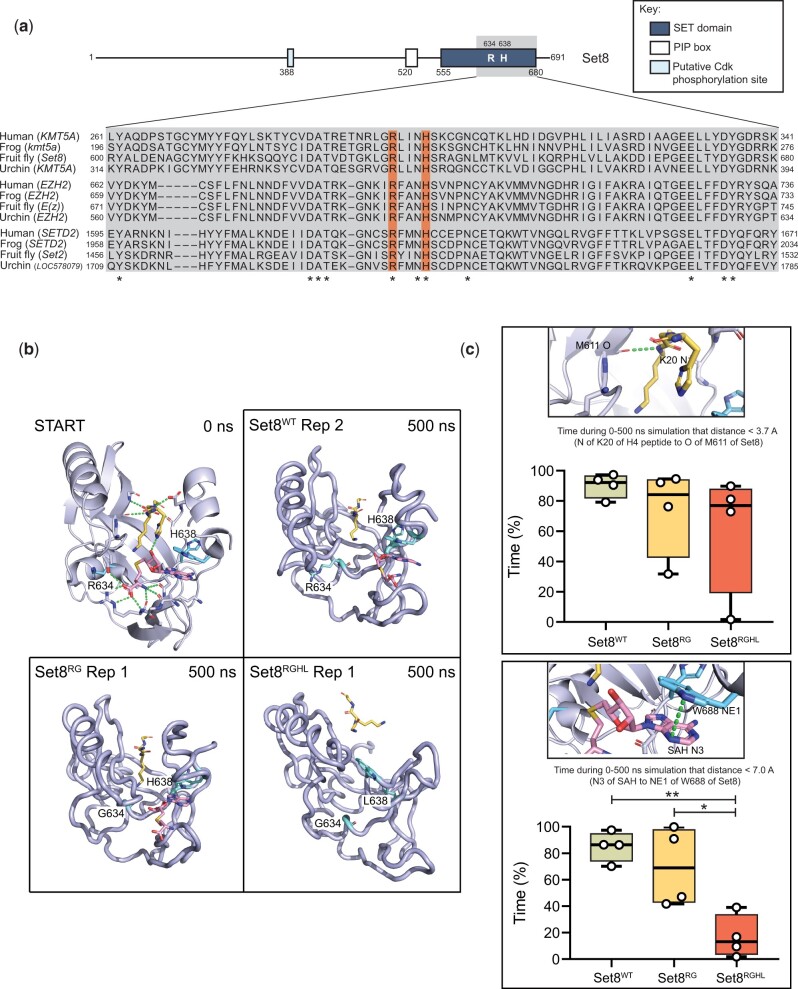
Generation Set8 proteins predicted to be catalytically inactive. a) Diagram of Set8 and conservation of the Set8 Arg634 and Leu638 residues (orange bars) among KMT5A proteins from human, frog, and sea urchin, and among other SET domain proteins from these species. Gray inset indicates region of Set8 SET domain shown in alignment. Numbers on the left and right of the gray box indicate the starting and ending amino acid positions for each protein sequence. Asterisks mark where residues are identical across all 12 proteins. b) Modeling of Set8 with SAH and peptide from H4 bound to the enzyme. Shown are representative structures after 500 ns of molecular dynamics for Set8, Arg634Gly and Arg634Gly, His638Leu mutations in Set8. Ending structures for all replicates can be found in Supplementary Fig. 4. The 10-residue H4 peptide (A-K-R-H-R-K20-V-L-R-D) is yellow, SAH is magenta, and the R/G634 and H/L638 amino acid side chains are cyan. c) Total length of time during 500 ns simulations that ligands remained in binding pocket as measured by distances between key atoms. The two distance measurements shown were selected because they were the most stable interactions between Set8 and H4 peptide and between Set8 and SAH. The selected hydrogen bond to the peptide was also the most stable interaction with the peptide and one of the last to be broken. Circles represent values from four replicate simulations. Significance was determined by a one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test. * indicates P < 0.05, ** indicates P < 0.01, and all other comparisons are not significant.