Figure 12.
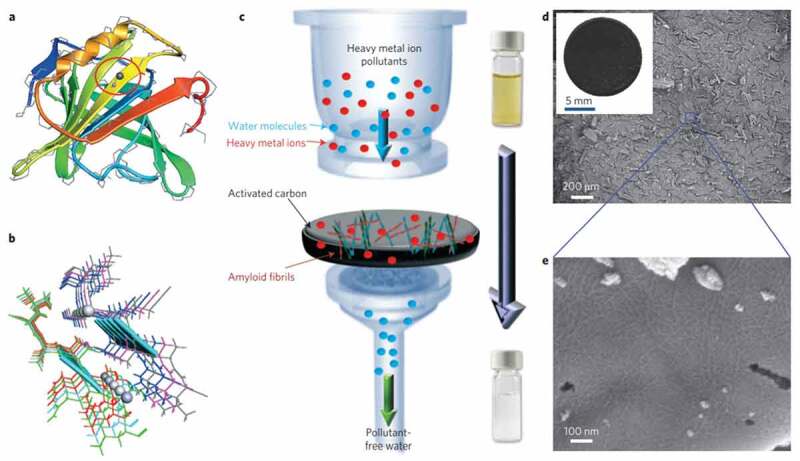
Schematic illustration of amyloid fibrils coupled with activated carbon membrane as an adsorber of heavy metal ions. (a) Structure of the β-lactoglobulin protein with the strongest heavy metal-binding motif highlighted, 121-cys, with a lead ion attached. (b) Amyloid-forming 121-cys-containing fragment (LACQCL) from β-lactoglobulin with docked Pb metal ions. (c) Schematic representation of heavy metal ion purification by amyloid–carbon adsorbers, and photographs of Na2PdCl4 solution changing color from yellow to colorless after filtration due to the adsorption of palladium heavy metal ion pollutants onto the composite membrane. (d) SEM image showing the surface of the composite membrane, with the visual aspect of the membrane shown in the inset. (e) Higher-magnification SEM image of the membrane, demonstrating the assembly of the amyloid fibrils onto the activated carbon surface [259].
