Abstract
The present research aims to propose a simple and accurate technique for the analysis of Rifaximin in the presence of its stress degradation products and analysis of degradation products by LC-MS/MS analysis. Rifaximin was submitted to forced degradation under the acid hydrolysis condition as prescribed by the ICH. The extract was prepared by firstly treated with HCl and heated about 4 to 8 h. The filtrate was collected and separated using dichloromethane followed by evaporation in rotary evaporator to obtain a solid crude extract which was then stored under refrigeration at -80 °C. Liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF-MS/MS) was utilized to identify products in the drug sample. The data processing results revealed the presence of 9 products in the degraded sample of Rifaximin. This data article contains the m/z [M + H +] values, molecular formula, retention times and the comprehensive list of m/z values detected during the LC- QTOF- MS/MS analysis.
Keywords: Analysis LCMS/MS-QTOF, Stress degradation, Bruker
Graphical abstract
Specifications table
| Subject Area | Pharmacy |
| More specific subject area | Pharmaceutical Chemistry |
| Type of data How Data was acquired | Tables and Figures Data was acquired using liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS) through a Phenomenex Jupitor 5μm C18 300Å 5.0×100mm coupled to a CompactTM Q-TOF(Bruker daltonics,Bremen, Germany) |
| Data format Experimental factors | Analyzed data Products of drug was forced degraded with dichloromethane and concentrated at 65 °C |
| Experimental features | Identified products profiling in acid degradation was performed |
| Method Name | LC- QTOF-MS/MS analysis |
| Name and reference of original method | Data of the products obtained using LC- QTOF-MS/MS analysis and the comprehensive list of detected products is available in Table 3 |
| Resource availability | The active rifaximin was complementary provided by Hilton Pharma Pvt Ltd; acid degradation of rifaximin, LC-QTOF-MS/MS analysis and data processing was done at the H.E.J research Institute of Chemistry, University of Karachi |
| Related research article | Mahadik, M., Bhusari, V.,Kulkarni, M., & Dhaneshwar, S.LCUV and LCMS evaluation of stress degradation behavior of tenatoprazole. Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis. 50(2009),787-793 [1] |
Method details
Collection and preparation of acid degraded products
About 1 gm of Rifaximin drug was collected from Hilton Pharma Pvt Ltd. The drug sample was immediately transferred to the laboratory after collection and stored in refrigerator. About 200 mg of sample was taken and dissolve in 200 mL of methanol. Added 200 mL of 0.1 M HCl in it and transferred it in a round bottom flask using a parallel synthesizer i-e, using condenser fitted with chiller and heating mental. The solution was refluxed for about 4 to 8 h at 60 °C. Then after 4–8 h cool down at room temperature and transferred the solution in a separating funnel. Added 50 mL of dichloromethane, shake it well until the layer separated then collected lower layer. The process was repeated by 3 times to collect the layer. Then the filtrate was transferred into a round bottom flask and evaporate it on a rotary evaporator, and collected the dry product after evaporation. The resulting solid crude was then kept in frozen storage at -80 °C.
Base Peak Chromatogram ofRifaximinstandard solution.
Data
Figure 1 shows the base peak chromatogram of Rifaximin solution which was obtained by analyzing acid degraded sample of rifaximin using LC-QTOF-MS/MS. The data of 9 proposed products which includes the measured m/z [M + H+] values, calculated m/z, retention time (RT min) detected during the LC-QTOF-MS/MS analysis are available in the table A.
Fig. 1.
Base peak chromatogram (BPC) of the acid degraded rifaximin solution.
Degraded products profiling by LC-QTOF-MS/MS
Products profiling of the drug solution was done by using LC-QTOF- MS/MS in positive mode (ESI+). The analysis was done firstly by dissolving 1 mg of the drug powder in 1 mL of analytical grade methanol followed by sonicating for 05 min, and finally centrifuge for 10 min at 12,000 RPM. A sample injection volume of 5 mL was used for chromatographic separation of analytes in reverse phase ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography (RP- UHPLC) through a Zorbax Eclipse plus C-18 column 1.8 µm with dimensions of 2.1 mm (internal diameter), 50 mm (length). The analytical run was set at 20 mins. The flow profile of the mobile phase is shown in Table 1. Other parameters of the LC- QTOF-MS/MS system [2], [3] are summarized in Table 2.
Table 3.
Data analysis for products profiling was done using Bruker Compass Data Analysis software version 4.4 (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany).
| S.No | Experimental m/z | Measured mass | RT(min) | Ion Formula | Bruker data analysis peak |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 01- | 767.12 | 767.01 | 0.1 | C42H44N3O11 |  |
| 02- | 724.23 | 724.31 | 0.1 | C40H41N3O10 |  |
| 03- | 643.32 | 643.52 | 0.1 | C36H40N3O8 | 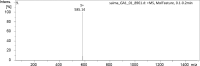 |
| 04- | 585.14 | 585.44 | 0.1 | C34H38N3O6 |  |
| 05- | 567.13 | 567.12 | 0.1 | C34H36N3O5 |  |
| 06- | 560.11 | 560.20 | 0.2 | C34H29N3O5 |  |
| 07- | 485.11 | 485.12 | 6.3 | C30H16N2O5 |  |
| 08- | 349.13 | 349.30 | 6 | C24H16N2O |  |
| 09- | 180.10 | 180.01 | 5.6 | C13H9N |  |
Table 1.
Isocratic and gradient flow profiles of the mobile phase.
| Time (minutes) | Flow (µL/minute) | Solvent% |
|---|---|---|
| 0–1 | 300 | 10 |
| 1–5 | 300 | 70 |
| 5–9 | 300 | 90 |
| 9–20 | 300 | 10 |
Table 2.
Parameters of the LC- QTOF-MS/MS system.
| Acquisition | Parameter |
|---|---|
| Source type | Electrospray-ionization |
| Ion polarity | Positive |
| Scan | 50–1500 m/z |
| Set capillary | 4500 V |
| Set end plate offset | +500V |
| Set nebulizer | 2.8 bar |
| Set dry heater | 300 °C |
| Set dry gas | 10/minute |
Ethics statements
No any ethical statement.
CRediT author statement
Dr Syed Ghulam Musharraf: Conceptualization, Methodology; Saima Yaseen Baig: Software, Data curation, Writing- Original draft preparation; Saima Yaseen Baig, Dr Arfa Akram, Dr Mehwish Wajidi: Visualization, Investigation; Dr Ghulam Musharraf, Dr Arfa Akram: Supervision; Saima Yaseen Baig, Dr Nargis tabassum: Software, Validation; Syed Muhammad Zaki Shah, Nemat Nazir: Writing- Reviewing and Editing.
Declaration of Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Third World Centre for Chemical Sciences, International Center for Chemical and Biological Sciences, University of Karachi.
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Contributor Information
Saima Baig Yaseen, Email: saimabaig@hotmail.com.
Arfa Akram, Email: arfa.akram@fuuast.edu.pk.
References
- 1.Mahadik M., Bhusari V., Kulkarni M., Dhaneshwar S. LC–UV and LC–MS evaluation of stress degradation behaviour of tenatoprazole. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009;50:787–793. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2009.06.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Won J.Y., Son S.Y., Lee S., Singh D., Lee S., Seok Lee J. Strategy for screening of antioxidant compounds from two ulmaceae species based on liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Molecules. 2018;23:1e15. doi: 10.3390/molecules23071830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kudzani Lukhanyo, Maya Vuyo. The LC-QTOF-MS/MS analysis data of detected metabolites from the crude extract of Datura stramonium leaves. Data Brief. 2019;25 doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2019.104094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




