Significance
Until now, it was not known if, how, or why pathogenic human viruses might modulate the de novo production of the replication-dependent (RD) histone proteins that decorate their DNA genomes within infected cells. Our finding that human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) inhibits RD histone production affirms that a virus targets this fundamental cellular process. Furthermore, our revelation that HCMV induces, relocalizes, and then commandeers the stem loop–binding protein (SLBP) for a purpose other than RD histone synthesis to support productive replication illuminates the potential for other functions of this highly conserved protein. The critical nature of SLBP for HCMV infection and of RD histone synthesis for cellular DNA replication highlights this process as a target for future antiviral and chemotherapeutic interventions.
Keywords: histone, SLBP, HCMV, cell cycle, S phase
Abstract
Replication-dependent (RD) histones are deposited onto human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) genomes at the start of infection. We examined how HCMV affects the de novo production of RD histones and found that viral infection blocked the accumulation of RD histone mRNAs that normally occurs during the S phase. Furthermore, RD histone mRNAs present in HCMV-infected cells did not undergo the unique 3′ processing required for their normal nuclear export and translation. The protein that orchestrates processing in the nucleus, stem loop–binding protein (SLBP), was found predominantly in the cytoplasm, and RD histone proteins were not de novo synthesized in HCMV-infected cells. Intriguingly, however, we found that SLBP was required for the efficient synthesis and assembly of infectious progeny virions. We conclude that HCMV infection attenuates RD histone mRNA accumulation and processing and the de novo protein synthesis of the RD histones, while utilizing SLBP for an alternative purpose to support infectious virion production.
Histones are deposited onto naked DNA to produce chromatin. Most naked DNA in cells is produced by genome duplication during the DNA synthesis (S) phase of the cell cycle. The major core histone proteins (H2A, H2B, H3.1/3.2, and H4) are synthesized only during S phase and are deposited onto newly replicated DNA concomitant with its synthesis, and thus they are termed the replication-dependent (RD) histones (1). Histone deposition onto naked DNA outside of S phase occurs in a replication-independent (RI) manner (2, 3) and uses RI histone variants such as H1.0 and mH2A that are de novo synthesized throughout the cell cycle (2).
Naked herpesviral DNA introduced into nuclei upon infection rapidly becomes histone associated and chromatinized in a RI process (4–6). It is unclear whether viral genome chromatinization is a normal cellular response to naked DNA, a cellular defense against virus infection, or is orchestrated by the virus as protection from nucleases or to permit epigenetic transcriptional regulation (7, 8). However, herpesviruses actively manipulate the chromatin structure of their genomes to regulate viral transcription (9, 10). Transcription of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) immediate-early (IE) genes begins shortly after infection. The IE proteins activate the transcription of the early genes that encode proteins required for viral DNA replication, which begins around 24 h post-infection (hpi). After viral DNA replication, the late genes encoding structural proteins are transcribed, and any remaining nucleosomes are removed from the newly synthesized viral genomes before they are packaged into capsids within the nucleus (11). DNA-containing capsids leave the nucleus, acquire the viral envelope in the cytoplasm, and are released from the cell. Interestingly, both RI histone variants and RD histones are deposited onto herpesvirus genomes (4, 5, 12–17). HCMV arrests the cell cycle in early S phase, presumably because it utilizes cellular proteins expressed during this cell cycle stage for viral genome synthesis (18, 19). Early S phase is also the cell cycle position where the RD histones are synthesized (20), although it is unclear if new RD histones are produced in HCMV-infected cells.
The unique biogenesis of the RD histone mRNAs and proteins presents multiple opportunities for regulation by HCMV or other viruses. The RD histone genes lack introns, and most are present at two major clusters forming a nuclear structure called the histone locus body (1, 21). Histone loci contain multiple copies of genes for each histone protein, each with nucleotide substitutions (22). The RNA polymerase II–dependent transcription of the RD histone genes increases ∼5-fold in S phase (23). This transcriptional induction occurs upon Cdk/cyclin E–mediated phosphorylation of the nuclear protein at the ataxia telangiectasia locus, a critical histone locus body protein present only at RD histone genes (24, 25). At the end of S phase, or when DNA replication is inhibited, RD histone mRNAs are rapidly oligouridylated and degraded (26–28).
The RD histone mRNAs are the only eukaryotic mRNAs that lack poly-A tails (29). Instead, they have a 3′ stem loop structure that binds the stem loop–binding protein (SLBP) and participates in their posttranscriptional processing, stability, nuclear export, and translation (26, 30–38). Transcription of the SLBP gene is constitutive, but translation of its mRNA is induced at the G1/S border (20, 39). SLBP accumulates during S phase (39) but is rapidly degraded in G1 (39, 40) and G2 (20, 41, 42) by separate ubiquitin ligase complexes. This tight window of SLBP availability restricts RD histone synthesis to the S phase.
SLBP is imported into the nucleus through the canonical importin pathway but may also passively diffuse through nuclear pores (43). In the nucleus, SLBP cotranscriptionally associates with the stem loop in the 3′ untranslated region of RD histone mRNAs (44). Stem loop–bound SLBP stabilizes the binding of the U7 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein with the histone downstream element, and the histone cleavage complex completes the processing by cleaving the mRNA (21). SLBP remains associated, and the RD histone messenger ribonucleoprotein is exported to the cytoplasm in a process dependent on the TAP/NXF1 nuclear export factor (43). This noncanonical mRNA export method is necessitated by the lack of common export signals on either the mRNA (e.g., splice junctions or a poly(A) tail) or SLBP (e.g., a nuclear export signal). In the cytoplasm, SLBP stimulates the translation of bound RD histone mRNAs (30, 31, 34, 36, 45).
Because little is known about RD histone biogenesis during viral infections, we examined this process in HCMV-infected cells. Even though HCMV-infected cells are in S phase, we show here that RD histone protein de novo accumulation in fibroblasts productively infected with HCMV is significantly reduced compared to uninfected S phase cells. The RD histone mRNAs do not accumulate to normal S phase levels in HCMV-infected fibroblasts, and the transcripts that are present remain unprocessed. In contrast, SLBP accumulates in HCMV-infected fibroblasts but is more cytoplasmic in subcellular localization than in S phase cells. Importantly, we show that SLBP supports productive viral replication and the assembly of infectious progeny virions, processes that have both nuclear and cytoplasmic stages. We conclude that HCMV infection interferes with the synthesis of the RD histones at multiple steps but uses the SLBP to facilitate productive infection.
Results
RD Histone mRNAs Do Not Accumulate to S Phase Levels in HCMV-Infected Cells.
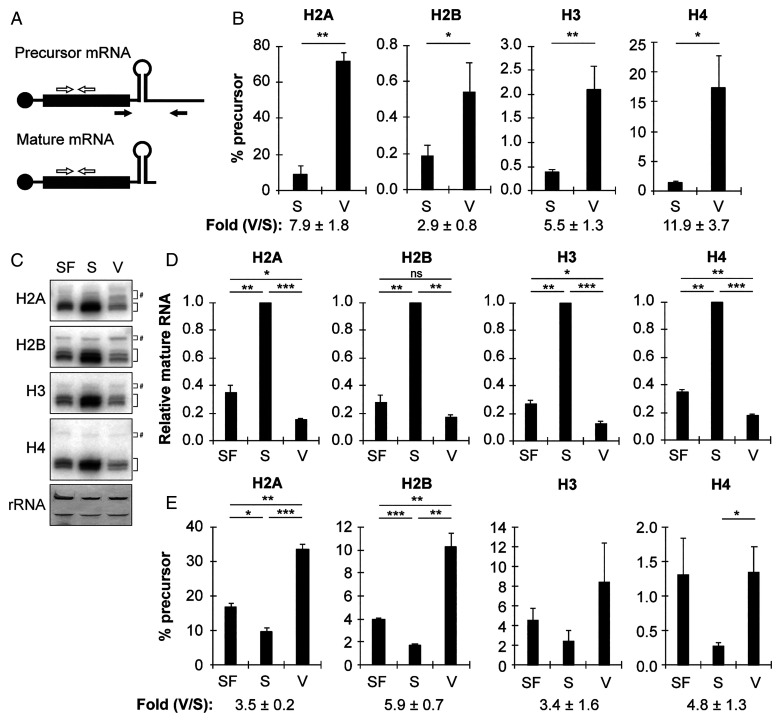
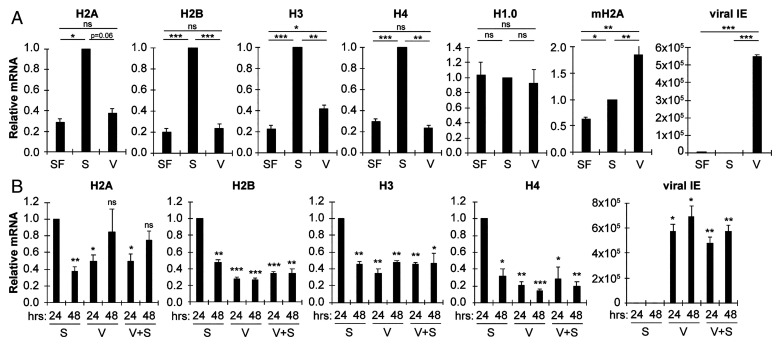
RD histone genes are transcriptionally induced in S phase (21), and HCMV infection drives serum-starved (G0) cells into S (18, 19). To determine if RD histone transcripts accumulate during HCMV infection, we designed primers for qRT-PCR to quantitate transcript levels of the coding region (see Fig. 2A) of one of the multiple genes of each core RD histone type (H2A, H2B, H3, and H4), as well as the RI histone genes H1.0 and macroH2A. We found that serum stimulation of G0 cells induced the accumulation of the RD histone mRNAs, but a productive HCMV infection did not (Fig. 1A). RI histone mRNA accumulation was similar between HCMV infection and serum stimulation (Fig. 1A). Viral IE1/2 transcript accumulation demonstrated viral infection was initiated, and viral RNAs were produced (Fig. 1A). We also found that HCMV infection was able to reduce the ability of serum to induce the accumulation of the RD histone mRNAs (Fig. 1B). We conclude that HCMV does not induce, and it reduces the serum induction of RD histone mRNA accumulation.
Fig. 2.
RD histone mRNAs are more likely to be unprocessed in HCMV-infected cells as compared to S phase cells. (A) Schematic of histone mRNA processing PCR assay. Primers in the coding region (white arrows) detect both precursor and mature RD histone mRNA transcripts, while primers downstream (black arrows) detect only unprocessed precursor mRNA. (B) Serum-starved fibroblasts were stimulated with serum for 24 h (S) or infected with HCMV (V) for 48 h and analyzed by qRT-PCR for precursor and total transcripts for the indicated histone. The ratio of precursor to total mRNA for the indicated histone (×100) is shown. The mean fold difference between infected (V) and serum-stimulated (S) ± SEM is indicated below bar graphs (n = 6). (C) Serum-starved fibroblasts were left untreated (SF) or stimulated with serum (S) for 24 h or infected with HCMV (V) for 48 h, and equal amounts of total RNA were analyzed by Northern blot with probes complementary to the open reading frame of the indicated histone. Black brackets indicate processed, mature histone RNA, while gray brackets denoted by (#) indicate slower migrating (unprocessed, misprocessed, or alternatively processed) RNA. The 28S and 18S ribosomal RNA were visualized by methylene blue staining of blotted membranes, serving as loading controls (n = 3). (D) Quantitation of mature RNA from Northern blots in (C). Levels of mature mRNA relative to serum-treated cells from the same experiment are shown (n = 3). (E) Ratio of unprocessed histone RNA to total histone RNA from the Northern blots in (C). The mean fold difference between infected (V) and serum-stimulated (S) ± SEM is indicated below bar graphs (n = 3; for H3, one replicate had no detectable unprocessed signal for any sample; thus, H3 quantitation represents n = 2). Bar graphs show the mean ± SEM from the indicated number of biological replicates.
Fig. 1.
RD histone mRNAs do not accumulate to S phase levels in HCMV-infected cells. (A) Serum-starved fibroblasts were left untreated (SF, serum-free media), stimulated with serum for 24 h (S) or infected with HCMV for 48 h (V) and analyzed by qRT-PCR for the indicated transcripts. Transcript levels were normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) levels from the same sample and are shown relative to serum-treated (S) cells from the same experiment. (B) Serum-starved fibroblasts were stimulated with serum (S) with or without infection with HCMV (V) for the indicated time and analyzed by qRT-PCR for the indicated transcripts. Transcript levels were normalized to GAPDH levels from the same sample and are shown relative to 24 h serum-stimulated cells from the same experiment. Bar graphs show the mean ± SEM from three biological replicates. Statistical significance is shown compared to 24 h serum-stimulation samples, unless otherwise indicated.
RD Histone mRNAs Are More Likely to be Unprocessed and Poly-adenylated in HCMV-Infected Cells as Compared to S Phase Cells.
To test if the small number of RD histone mRNAs present in HCMV-infected cells is processed, or if they remain unprocessed (including alternatively or misprocessed transcripts), we used a previously developed PCR assay (46, 47) that uses one primer set that amplifies both processed (mature) and unprocessed (precursor) mRNAs and another that amplifies only unprocessed mRNAs (Fig. 2A). The ratios of precursor-to-total mRNAs for the RD histones were significantly higher in HCMV-infected cells compared to serum-stimulated cells (Fig. 2B), indicating that their processing is decreased or altered in HCMV-infected cells. We confirmed these results with Northern blot analyses using probes derived from the entire coding region of one member of each class of RD core histone type (Fig. 2C). Consistent with the qPCR data (Fig. 1A), levels of mature RD histone mRNA were significantly induced by serum stimulation, but not HCMV infection (Fig. 2 C and D). The ratios of slower-migrating (unprocessed, misprocessed, or alternatively processed) mRNAs to total RD histone mRNAs were significantly higher in HCMV-infected cells compared to serum-stimulated cells (Fig. 2 C and E). We conclude that RD histone mRNA processing is inhibited or altered in HCMV-infected cells.
Processing of RD histone mRNAs is a prerequisite for their normal export to the cytoplasm (43). To determine where RD histone mRNAs accumulate, we biochemically fractionated S phase or HCMV-infected cells into nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions and used qRT-PCR to quantitate mRNA levels in equal percentages of the nuclear or cytoplasmic fractions. Fractionation efficiency was monitored by demonstrating the known cytoplasmic (48) mitochondrial RNA (16S) was predominantly cytoplasmic, while the known nuclear (49) long noncoding RNA (MEG3) was predominantly nuclear (although a small fraction was cytoplasmic) (SI Appendix, Fig. S1A). We found no significant differences between the fractions of cytoplasmic mRNAs for the RD histones, as well as for the actin control, between HCMV-infected and S phase cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S1A).
Our finding of RD histone mRNAs in the cytoplasm of HCMV-infected cells where RD histone mRNA processing is inhibited (Fig. 2) prompted us to determine if unprocessed (precursor) RD histone mRNAs were cytoplasmic in HCMV-infected cells. Indeed, we found substantially (preH2A, preH3) or significantly (preH2B, preH4) higher levels of unprocessed (precursor) RD histone mRNAs in the cytoplasmic fraction of HCMV-infected cells compared to uninfected cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S2B). When the processing of RD histone mRNAs is inhibited, the RD histone mRNAs can be anomalously polyadenylated and exported to the cytoplasm (50). We detected a significantly higher ratio of oligo deoxythymine-selected RD histone mRNAs in HCMV-infected cells as compared to serum-stimulated S phase cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S1C). From this series of experiments, we conclude that during HCMV infection, there is a substantial increase in the number of RD histone mRNAs that are not properly processed but are polyadenylated and accumulate in the cytoplasm.
SLBP Accumulates during HCMV Infection, but Its Subcellular Localization Is More Cytoplasm Than in S Phase Cells.
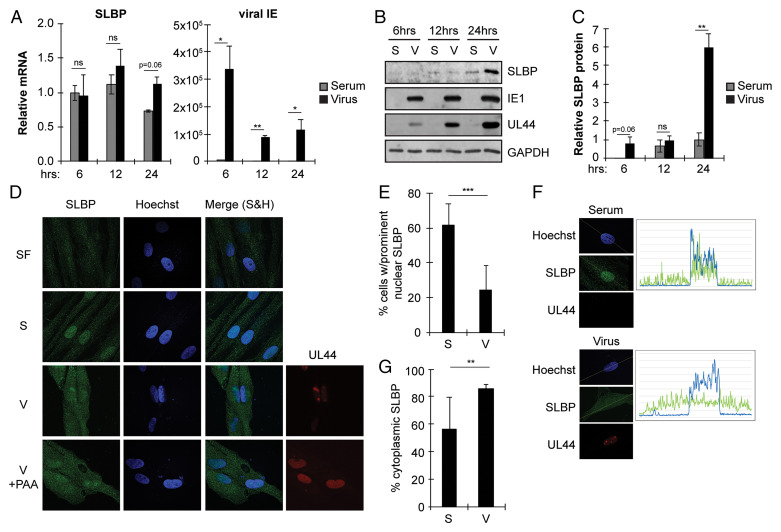
Because of the increase in unprocessed RD histone mRNAs during HCMV infection, we next examined SLBP. We found the SLBP mRNA at similar levels in serum-stimulated or HCMV-infected cells, where infection was confirmed by viral IE1/2 transcript accumulation (Fig. 3A), indicating that HCMV does not appear to regulate SLBP transcription or mRNA stability. Serum stimulation caused SLBP accumulation as expected, but HCMV infection, in the absence of serum stimulation, caused an even greater increase in SLBP levels (Fig. 3 B and C). Notably, there is a dramatic increase of SLBP in HCMV-infected cells at 24 hpi compared to serum-stimulated cells at the same time point. In S phase cells, we found SLBP in both the nucleus and the cytoplasm (Fig. 3D) as expected, and more than 60% of S phase cells contained SLBP predominantly in the nucleus (Fig. 3E). However, in HCMV-infected cells, we found SLBP more extensively in the cytoplasm (Fig. 3D), with fewer than ∼20% of HCMV-infected cells containing SLBP predominantly in the nucleus (Fig. 3E). The HCMV DNA polymerase processivity factor UL44 was imaged to confirm HCMV infection (Fig. 3D). Single-cell tracings (Fig. 3F) clearly showed SLBP concentrated in the nucleus under serum stimulation conditions, with almost 50% of the SLBP density in the nucleus (Fig. 3G). Similar tracings in HCMV-infected cells showed SLBP more evenly distributed through the cell (Fig. 3F), with less than 20% of the SLBP density in the nucleus (Fig. 3G). SLBP cytoplasmic localization during HCMV infection was not impaired by the viral DNA polymerase inhibitor phosphonacetic acid (PAA) (Fig. 3D), indicating that viral DNA replication is not required for this process. Biochemical cell fractionation followed by analysis of proteins from equal percentages of nuclear or cytoplasmic fractions by Western blot (SI Appendix, Fig. S2) also showed a higher percentage of SLBP in the cytoplasm of HCMV-infected cells than in S phase cells. We conclude that compared to S phase cells, HCMV-infected cells show an increase in SLBP steady-state protein levels and a skewing of the subcellular localization of the protein more toward the cytoplasm than the nucleus.
Fig. 3.
SLBP accumulates during HCMV infection but is mislocalized. (A) Serum-starved fibroblasts were stimulated with serum (serum) or infected with HCMV (virus) for the indicated amount of time and analyzed by qRT-PCR for the indicated transcripts. Levels are shown relative to 6 h serum stimulation from the same experiment. (B) Western blots for the indicated proteins from serum-starved fibroblasts stimulated with serum (S) or infected with HCMV (V) for the indicated time. (C) Quantitation of SLBP levels from (B) normalized to GAPDH levels and shown relative to 12 h serum-stimulated samples from the same experiment. (D) Localization of SLBP in serum-starved fibroblasts left untreated (SF), stimulated with serum for 24 h (S), or infected with HCMV in the absence (V) or presence of PAA (V + PAA) for 48 h. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst. UL44 staining serves as a marker for HCMV-infected cells. (E) Percentage of cells with prominent nuclear SLBP in serum-stimulated (S) and HCMV-infected (V) cells from (D). (F) Serum-stimulated (top) and HCMV-infected (bottom) cells treated and stained as in (D) were analyzed for fluorescence distribution using Plot Profile with FIJI software. (G) Distribution of SLBP signal intensity in serum-stimulated (S) and HCMV-infected (V) cells from (D). Bar graphs show the mean ± SEM from three biological replicates.
RD Histone Protein Synthesis Is Attenuated in HCMV-Infected Cells Compared to S Phase Cells.
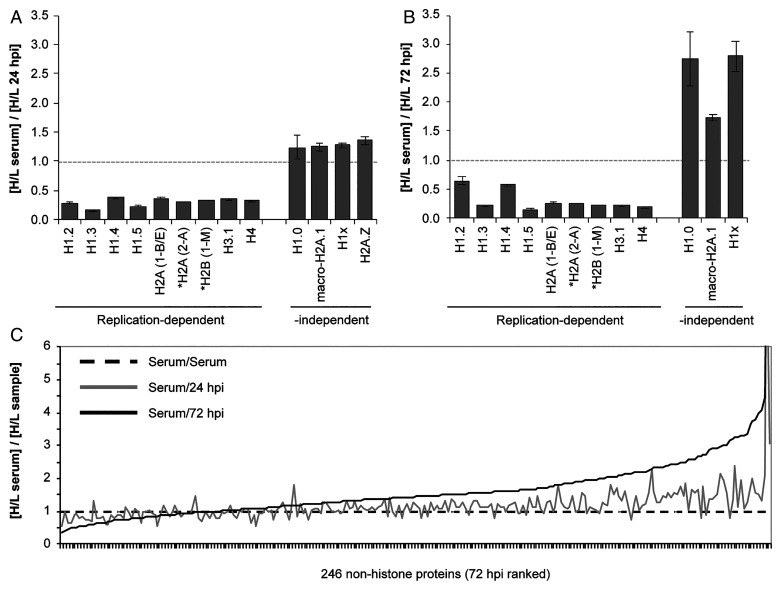
We next employed stable isotope labeling of amino acids in cell culture (SILAC) proteomics to quantitate RD histone de novo synthesis at 24 h (HCMV infection or serum stimulation) and 72 h (HCMV infection) time points. We identified and determined heavy/light (H/L) ratios for 13 histones (SI Appendix, Table S1) common among serum-stimulated, 24 hpi (Fig. 4A), and 72 hpi (Fig. 4B) samples of chromatin-associated proteins. For RD histones (22), we observed H/L ratios less than 1, indicating de novo synthesis was higher in serum-stimulated cells than during HCMV infection. In contrast, all of the RI histones (and the majority of the nonhistone proteins; Fig. 4C) showed ratios near or greater than 1, indicating similar de novo synthesis during serum stimulation and HCMV infection. Combined with the previous data, we conclude that during HCMV infection, less RD histone mRNA accumulates and less is properly processed compared to S phase cells, and the balance of SLBP subcellular localization is altered, all resulting in the inhibition of RD histone de novo protein accumulation.
Fig. 4.
RD histone protein synthesis is attenuated in HCMV-infected cells compared to S phase cells. Fibroblasts were propagated in heavy arginine and lysine for eight doublings then growth arrested in 0.5% serum for 24 h. Subsequent incubations were in light media. Histones were enriched from cells following stimulation with serum for 24 h or infection with HCMV for 24 and 72 h. Proteins were identified and quantified by liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry from technical triplicate analyses for two independent biological experiments. Protein identification required a minimum of two peptides with at least one unique peptide. Samples marked by asterisks—namely, H2A variants H2a(1-B/E) from gene H2AC4 and H2a (2-A) from H2AC18 as well as H2B variant H2B (1-M) from gene H2BC14—were identified in one biological replicate. (A) The relative H/L normalized intensity ratios are presented for RD and RI histones between serum-stimulated cells and cells infected with HCMV for 24 h. (B) Comparison as in (A) between serum-stimulated cells and cells infected with HCMV for 72 h. (C) The relative H/L ratios for the total population of proteins identified and quantified.
SLBP Is Required for the Efficient Production of Infectious HCMV Virions.
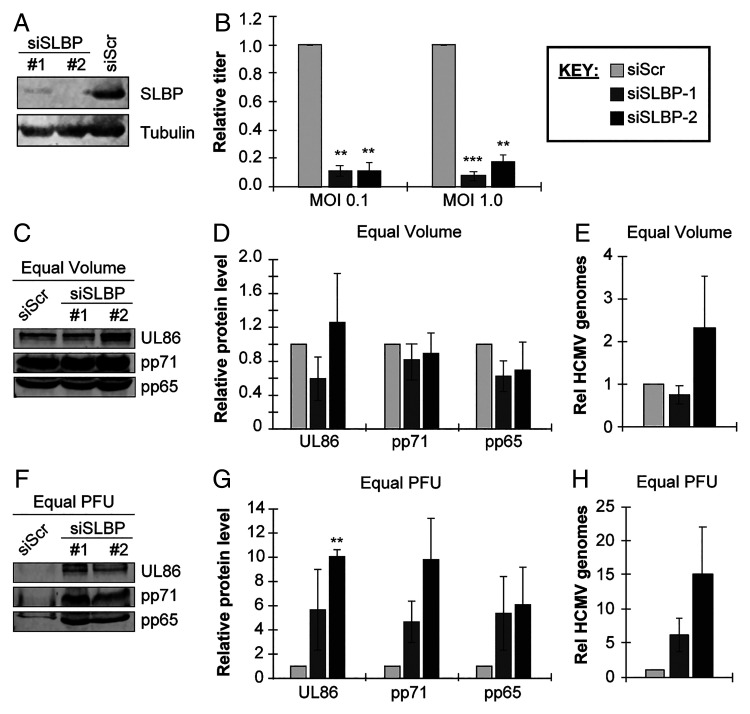
The increased accumulation of SLBP in the absence of RD histone protein production led us to ask if the protein might have an alternative function in HCMV-infected cells. We used two different small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to knock down SLBP (with a scrambled siRNA as a control), then infected cells with HCMV and assayed viral replication. Western blots confirmed SLBP knockdown (Fig. 5A). We found a ∼12-fold reduction in viral titers produced by SLBP knockdown cells at each of the two multiplicities of infection (MOI) assayed (MOI = 0.1 or MOI = 1.0) (Fig. 5B). We conclude that SLBP is required for efficient HCMV productive replication.
Fig. 5.
SLBP is required for the efficient production of infectious HCMV virions. (A) Serum-starved fibroblasts were transfected with one of two different siRNAs against SLBP (siSLBP #1 or #2) or a scrambled nontargeting control siRNA (siScr). Lysates were analyzed by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. Tubulin serves as a loading control. (B) siRNA-transfected cells were infected with HCMV strain AD169 at an MOI = 0.1 (left) or 1.0 (right) for 6 d, after which cell-free and cell-associated progeny virus was collected and quantitated by plaque assay on naïve fibroblasts. Titers are shown relative to control siRNA-transfected cells from the same experiment. (C) Serum-starved fibroblasts were transfected as in (A), then infected at an MOI = 1.0 for 6 d, after which cell-free and cell-associated progeny virus was collected and quantitated by plaque assay on naive fibroblasts. Equal volume of collected virus from each condition was analyzed for virion proteins by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. (D) Quantitation of Western blot in (C), shown relative to siScr samples from the same experiment. (E) Encapsidated viral genomic DNA was isolated from equal volumes of virus derived from experiments described in (C) and quantified by qPCR for UL122/123. Results are plotted relative to siScr samples from the same experiment. (F) Based on the determined titers of virus collected in (C), equal PFUs of each virus stock were analyzed for virion proteins by Western blot with the indicated antibodies. (G) Quantitation of Western blot in (F), plotted relative to siScr samples from the same experiment. (H) Encapsidated viral genomic DNA was isolated from equal PFUs of virus derived from experiments described in (C) and quantified by qPCR for UL122/123. Results are plotted relative to siScr samples from the same experiment. Bar graphs show the mean ± SEM from three biological replicates.
We next examined multiple steps of productive viral replication (MOI = 1.0) to determine which are impaired when SLBP is knocked down with siRNAs (SI Appendix, Fig. S3A), causing productive replication to be inhibited (SI Appendix, Fig. S3B). We found no differences in viral genomic DNA accumulation between control and SLBP knockdown cells (SI Appendix, Fig. S3C). We also found no difference between representative IE (IE1; SI Appendix, Fig. S3D), early (UL44; SI Appendix, Fig. S3E), or late (pp28; SI Appendix, Fig. S3F) transcript or protein (SI Appendix, Fig. S3 G–J) accumulation between control and SLBP knockdown cells. Similar results were obtained after infection at a lower multiplicity (MOI = 0.1) (SI Appendix, Fig. S4). We conclude that SLBP is not required for the synthesis and accumulation of viral proteins or nucleic acids.
In SLBP knockdown cells, there is a ∼12-fold decrease in infectious HCMV titers (Fig. 5B) but no defects in the accumulation of viral nucleic acids or proteins (SI Appendix, Figs. S3 and S4). Therefore, we hypothesized that SLBP was required for virion assembly or infectivity. To test this hypothesis, we analyzed viral particles harvested from control or SLBP knockdown cells infected with HCMV (MOI = 1.0) by Western blot (Fig. 5 C and D). We found little difference in the amounts of the major capsid protein (UL86) or tegument proteins pp71 and pp65 in equal volumes of virion preparations from control or SLBP knockdown cells. Furthermore, we found little difference in the amount of micrococcal nuclease-resistant (encapsidated) viral genomic DNA in equal volumes of virion preparations from control or SLBP knockdown cells (Fig. 5E). Similar results were obtained after infection at a lower multiplicity (MOI = 0.1) (SI Appendix, Fig. S5 A–C). We conclude that similar numbers of viral particles are assembled in control and SLBP knockdown cells and, thus, that SLBP knockdown does not affect overall virion particle assembly.
However, when we analyzed an equal number of plaque-forming units (PFUs) from the same virion preparations, we found substantially higher levels of virion proteins (UL86, pp71, pp65) (Fig. 5 F and G) and encapsidated viral genomic DNA (Fig. 5H) in virions produced in SLBP knockdown cells compared to virions representing the same number of PFUs produced in control cells infected at an MOI = 1.0. Similar results were obtained after infection at a lower multiplicity (MOI = 0.1) (SI Appendix, Fig. S5 D–F). We conclude that the HCMV virions released from SLBP knockdown cells are less infectious than those released from control cells. In total, we conclude that HCMV impairs the ability of SLBP to promote RD histone synthesis (Fig. 6A) while utilizing the protein to ensure the infectivity of its progeny virions (Fig. 6B).
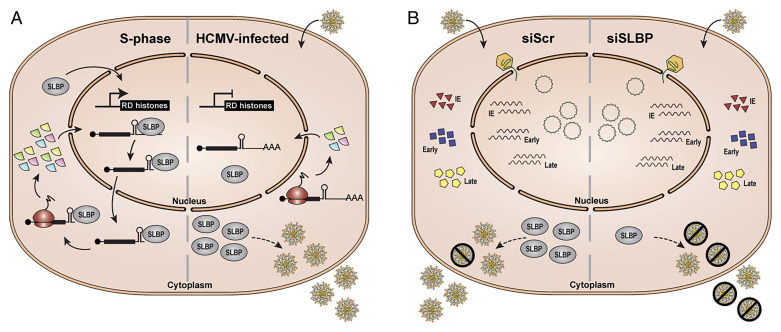
Fig. 6.
Model for RD histone synthesis and SLBP function in S phase versus HCMV-infected cells. (A) During S phase (left), RD histone transcription is induced, and SLBP binds to RD histone mRNAs, facilitating their processing, nuclear export, and translation resulting in de novo RD histone protein production. In contrast, during HCMV infection (right), RD histone transcripts do not accumulate, and the transcripts that are present remain largely unprocessed and a fraction are polyadenylated, resulting in inhibition of de novo RD histone protein synthesis. SLBP accumulates in the cytoplasm and promotes the production of infectious virions through an unknown mechanism. (B) Knockdown of SLBP (siSLBP; right) does not globally affect viral transcript or protein accumulation, viral genome replication, or the amount of virions produced compared to infection of control cells (siScr; left). However, in the absence of SLBP, the virions that are produced are less infectious, resulting in a higher particle-to-PFU ratio.
Discussion
In this study, we found that RD histone mRNAs do not accumulate to normal S phase levels in HCMV-infected cells (Figs. 1 and 2), perhaps because of a lack of transcriptional induction. Alternatively, because RD histone mRNAs are degraded when cellular DNA replication is inhibited (26, 31), they may be degraded during HCMV infection because productive viral infection inhibits cellular DNA replication (18). It seems likely that the RD histone mRNAs are not efficiently processed (Fig. 2) because SLBP subcellular localization is skewed toward the cytoplasm (Fig. 3), resulting in an inhibition of de novo RD histone protein synthesis (Fig. 4). What is unclear is why the subcellular localization of SLBP in HCMV-infected cells is more cytoplasmic than in S phase cells. SLBP is imported into the nucleus through the canonical importin-dependent pathway (43), which appears to be active in HCMV-infected cells, after both de novo synthesis and dissociation from the RD histone mRNP complex. Determining whether cytoplasmic SLBP in HCMV-infected cells is associated with RD histone mRNAs or other RNAs might help clarify which stage of SLBP trafficking is altered.
SLBP accumulates in HCMV-infected cells to a level that exceeds that found in our S phase cultures (Fig. 3). When cellular DNA replication is inhibited during the S phase, SLBP levels remain stable and may slightly increase, and the protein remains in the nucleus (51). As S phase is prolonged in HCMV-infected cells, we may simply be observing the natural accumulation of SLBP. Alternatively, HCMV may be actively stabilizing the protein to support the accumulation of infectious progeny virions (Fig. 5).
This positive role for SLBP during HCMV infection (Fig. 5) may reveal how and why HCMV synchronizes cells and replicates most efficiently in the early S phase (18). Mechanisms through which HCMV stimulates the cell cycle are well established (18, 52, 53), but the mechanisms through which it arrests cells in early S phase are less understood (54–57). The appropriation of SLBP, perhaps for a unique purpose, may be the proximal cause of HCMV-mediated cell cycle arrest in early S phase. The current dogma proposes that DNA viruses including HCMV drive quiescent cells into the S phase, in part by inactivating the retinoblastoma (Rb) tumor suppressor, in order to accumulate the macromolecules and enzymes required for viral DNA synthesis. However, the Rb protein plays an unidentified positive role during HCMV infection (58, 59), and the accumulation of deoxyribonucleotides for DNA synthesis does not appear to explain why HCMV induces cell cycle progression (60). Our revelation that SLBP localization and function is modulated during HCMV productive replication presents an opportunity to revisit the role of cell cycle modulation during DNA virus infections.
Questions remain as to how SLBP promotes virion infectivity, as well as what function of SLBP is required. While SLBP did not substantially affect the virion packaging of the viral DNA genome or any of the proteins we analyzed, global and unbiased quantitative approaches may reveal more subtle defects in virion composition (RNAs, proteins, or lipids) in the absence of SLBP that could be explored for their role in promoting virion infectivity. Imaging approaches could compare the architecture of DNA-containing capsids and complete virions produced in control and SLBP-deficient cells. How any observed defects in composition or architecture may affect virion stability, binding to the cell surface, or intracellular trafficking (during entry or egress) would then need to be determined. Interestingly, SLBP is required for efficient HCMV infectious progeny accumulation despite the fact that during an HCMV infection, SLBP does not appear to perform its only known function (supporting RD histone biosynthesis). A mutational analysis of SLBP could reveal which function of SLBP (e.g., RNA binding, specific protein–protein interactions, nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling) facilitates HCMV infection. Finally, as viruses are expert manipulators of cellular proteins and pathways, studying the role of SLBP during HCMV infection may reveal a previously unknown cellular function or functions of this protein.
Materials and Methods
Cells and Viruses.
For serum starvation, de-identified human foreskin fibroblasts were seeded at 1.2 × 104 cells/cm2 in medium containing 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). After 24 h, media were removed, and cells were washed twice with phosphate-buffered saline and refed with low-serum media (0.1% FBS) for 48 h. Serum stimulation was performed by addition of media containing 10% FBS for 24 h. Unless otherwise indicated, cells were infected with HCMV strain AD169 at an MOI of 1.0 pfu/cell in low-serum media (resulting in ∼60–70% of cells being infected, based on UL44 expression by 48 hpi).
Western Blots and Immunofluorescence.
For Western blot, cells were lysed in sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) lysis buffer (1% SDS, 2% b-mercaptoethanol), and equivalent amounts of total protein were analyzed by Western blot as previously described (61). For immunofluorescence, cells were cultured and infected on glass coverslips and fixed and stained as previously described (61). Images were acquired using a Nikon confocal laser scanning microscope with Prairie View Software, and images were processed and analyzed using FIJI software (62).
DNA and RNA Analysis.
Total DNA or total RNA was isolated from cells using an total DNA or total RNA minikit (IBI Scientific). For qRT-PCR, equal amounts of RNA were treated with double-stranded DNA specific endonuclease (dsDNase) and converted to complementary DNA (cDNA) using the Maxima H Minus Supermix with dsDNase system (ThermoScientific). Equal amounts of DNA and cDNA were analyzed by qPCR as previously described (63). For Northern blots, equal amounts of total RNA were used for Northern blot analysis with probes derived from the entire open reading frame of histone genes.
siRNA Transfection.
Serum-starved fibroblasts were transfected with ON-TARGETplus siRNAs (Dharmacon) targeting SLBP (siSLBP#1: J-012286–07, CGGCUGACUUUGAGACAGA; siSLBP#2: J-012286–08, GACAGAAGCAGAUCAACUA) or a nontargeting control (siScr: D-001810-10) at 20 pmol of siRNA per one million cells by electroporation using an Amaxa Human Dermal Nucleofector Kit (Lonza cat. no. VPD-1001) according to the manufacturer’s directions.
Quantification of Histones Using Mass Spectrometry.
Changes in histone levels were determined using SILAC and mass spectrometry. Cells were cultured in heavy (H) SILAC media and then either infected or serum stimulated in light (L) SILAC media. Histones were isolated using a histone purification kit (Active Motif, Carlsbad, CA) and analyzed by mass spectrometry as previously described (64).
Data Presentation and Statistical Analysis.
Unless otherwise indicated, all bar graphs represent the mean ± SEM from at least three biological replicates. Blots and micrographs shown are representative images from at least three biological replicates. Statistical significance was calculated by two-tailed Student’s t test with *: P < 0.05, **: P < 0.01, ***: P < 0.001, ns: P > 0.1.
Please see SI Appendix for a more detailed description of the materials and methods.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We thank Satoko Iwahori for advice regarding SLBP localization, William Marzluff for the SLBP antibody and valuable suggestions, and the members of the Kalejta lab for helpful comments on the work and manuscript. This work was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants AI130089 and AI139180 to R.F.K. and AI083281 to S.S.T. D.M.C. was supported by a Friends of MCW Minority Scholarship. M.D.S. was supported by a John J. Kopchick Molecular and Cellular Biology Research Fellowship. P.A. is an investigator of the Morgridge Institute for Research and director of the John and Jeanne Rowe Center for Research in Virology and gratefully acknowledges their support. The funders had no role in study design, data collection and interpretation, or the decision to submit the work for publication.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
This article is a PNAS Direct Submission.
This article contains supporting information online at https://www.pnas.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1073/pnas.2122174119/-/DCSupplemental.
Data Availability
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.
References
- 1.Jaeger S., Barends S., Giegé R., Eriani G., Martin F., Expression of metazoan replication-dependent histone genes. Biochimie 87, 827–834 (2005). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Maze I., Noh K.-M., Soshnev A. A., Allis C. D., Every amino acid matters: Essential contributions of histone variants to mammalian development and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 259–271 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Venkatesh S., Workman J. L., Histone exchange, chromatin structure and the regulation of transcription. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 178–189 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nitzsche A., Paulus C., Nevels M., Temporal dynamics of cytomegalovirus chromatin assembly in productively infected human cells. J. Virol. 82, 11167–11180 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Albright E. R., Kalejta R. F., Canonical and variant forms of histone H3 are deposited onto the human cytomegalovirus genome during lytic and latent infections. J. Virol. 90, 10309–10320 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Oh J., Fraser N. W., Temporal association of the herpes simplex virus genome with histone proteins during a lytic infection. J. Virol. 82, 3530–3537 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Saffert R. T., Kalejta R. F., Promyelocytic leukemia-nuclear body proteins: Herpesvirus enemies, accomplices, or both? Future Virol. 3, 265–277 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Knipe D. M., Cliffe A., Chromatin control of herpes simplex virus lytic and latent infection. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 6, 211–221 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kristie T. M., Dynamic modulation of HSV chromatin drives initiation of infection and provides targets for epigenetic therapies. Virology 479-480, 555–561 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Reeves M., Sinclair J., Regulation of human cytomegalovirus transcription in latency: Beyond the major immediate-early promoter. Viruses 5, 1395–1413 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Nevels M., Nitzsche A., Paulus C., How to control an infectious bead string: Nucleosome-based regulation and targeting of herpesvirus chromatin. Rev. Med. Virol. 21, 154–180 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chiu Y.-F., Sugden A. U., Sugden B., Epstein-Barr viral productive amplification reprograms nuclear architecture, DNA replication, and histone deposition. Cell Host Microbe 14, 607–618 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Conn K. L., Schang L. M., Chromatin dynamics during lytic infection with herpes simplex virus 1. Viruses 5, 1758–1786 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kutluay S. B., Triezenberg S. J., Regulation of histone deposition on the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome during lytic infection. J. Virol. 83, 5835–5845 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Oh J., Ruskoski N., Fraser N. W., Chromatin assembly on herpes simplex virus 1 DNA early during a lytic infection is Asf1a dependent. J. Virol. 86, 12313–12321 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Placek B. J., et al. , The histone variant H3.3 regulates gene expression during lytic infection with herpes simplex virus type 1. J. Virol. 83, 1416–1421 (2009). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zalckvar E., et al. , Nucleosome maps of the human cytomegalovirus genome reveal a temporal switch in chromatin organization linked to a major IE protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 110, 13126–13131 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kalejta R. F., Shenk T., Manipulation of the cell cycle by human cytomegalovirus. Front. Biosci. 7, d295–d306 (2002). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Spector D. H., Human cytomegalovirus riding the cell cycle. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. (Berl.) 204, 409–419 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Whitfield M. L., et al. , Stem-loop binding protein, the protein that binds the 3′ end of histone mRNA, is cell cycle regulated by both translational and posttranslational mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 4188–4198 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Marzluff W. F., Koreski K. P., Birth and death of histone mRNAs. Trends Genet. 33, 745–759 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Marzluff W. F., Gongidi P., Woods K. R., Jin J., Maltais L. J., The human and mouse replication-dependent histone genes. Genomics 80, 487–498 (2002). [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wang Z. F., Whitfield M. L., T. C. Ingledue, 3rd, Dominski Z., Marzluff W. F., The protein that binds the 3′ end of histone mRNA: A novel RNA-binding protein required for histone pre-mRNA processing. Genes Dev. 10, 3028–3040 (1996). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Ma T., et al. , Cell cycle-regulated phosphorylation of p220(NPAT) by cyclin E/Cdk2 in Cajal bodies promotes histone gene transcription. Genes Dev. 14, 2298–2313 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ye X., Wei Y., Nalepa G., Harper J. W., The cyclin E/Cdk2 substrate p220(NPAT) is required for S-phase entry, histone gene expression, and Cajal body maintenance in human somatic cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 8586–8600 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kaygun H., Marzluff W. F., Translation termination is involved in histone mRNA degradation when DNA replication is inhibited. Mol. Cell. Biol. 25, 6879–6888 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Mullen T. E., Marzluff W. F., Degradation of histone mRNA requires oligouridylation followed by decapping and simultaneous degradation of the mRNA both 5′ to 3′ and 3′ to 5′. Genes Dev. 22, 50–65 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F., The stem-loop structure at the 3′ end of histone mRNA is necessary and sufficient for regulation of histone mRNA stability. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 4557–4559 (1987). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Marzluff W. F., Wagner E. J., Duronio R. J., Metabolism and regulation of canonical histone mRNAs: Life without a poly(A) tail. Nat. Rev. Genet. 9, 843–854 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Cakmakci N. G., Lerner R. S., Wagner E. J., Zheng L., Marzluff W. F., SLIP1, a factor required for activation of histone mRNA translation by the stem-loop binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 1182–1194 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Choe J., et al. , Rapid degradation of replication-dependent histone mRNAs largely occurs on mRNAs bound by nuclear cap-binding proteins 80 and 20. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 1307–1318 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Dominski Z., Zheng L. X., Sanchez R., Marzluff W. F., Stem-loop binding protein facilitates 3′-end formation by stabilizing U7 snRNP binding to histone pre-mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 3561–3570 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Fan J., et al. , ALYREF links 3′-end processing to nuclear export of non-polyadenylated mRNAs. EMBO J. 38, e99910 (2019). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gorgoni B., et al. , The stem-loop binding protein stimulates histone translation at an early step in the initiation pathway. RNA 11, 1030–1042 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.von Moeller H., et al. , Structural and biochemical studies of SLIP1-SLBP identify DBP5 and eIF3g as SLIP1-binding proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 41, 7960–7971 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sànchez R., Marzluff W. F., The stem-loop binding protein is required for efficient translation of histone mRNA in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 7093–7104 (2002). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.DeLisle A. J., Graves R. A., Marzluff W. F., Johnson L. F., Regulation of histone mRNA production and stability in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Mol. Cell. Biol. 3, 1920–1929 (1983). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Lyons S. M., et al. , A subset of replication-dependent histone mRNAs are expressed as polyadenylated RNAs in terminally differentiated tissues. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 9190–9205 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Djakbarova U., Marzluff W. F., Köseoğlu M. M., Translation regulation and proteasome mediated degradation cooperate to keep stem-loop binding protein low in G1-phase. J. Cell. Biochem. 115, 523–530 (2014). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Dankert J. F., Pagan J. K., Starostina N. G., Kipreos E. T., Pagano M., FEM1 proteins are ancient regulators of SLBP degradation. Cell Cycle 16, 556–564 (2017). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Dankert J. F., et al. , Cyclin F-mediated degradation of SLBP limits H2A.X accumulation and apoptosis upon genotoxic stress in G2. Mol. Cell 64, 507–519 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Koseoglu M. M., Graves L. M., Marzluff W. F., Phosphorylation of threonine 61 by cyclin a/Cdk1 triggers degradation of stem-loop binding protein at the end of S phase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 28, 4469–4479 (2008). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Erkmann J. A., et al. , Nuclear import of the stem-loop binding protein and localization during the cell cycle. Mol. Biol. Cell 16, 2960–2971 (2005). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Battle D. J., Doudna J. A., The stem-loop binding protein forms a highly stable and specific complex with the 3′ stem-loop of histone mRNAs. RNA 7, 123–132 (2001). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ling J., Morley S. J., Pain V. M., Marzluff W. F., Gallie D. R., The histone 3′-terminal stem-loop-binding protein enhances translation through a functional and physical interaction with eukaryotic initiation factor 4G (eIF4G) and eIF3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22, 7853–7867 (2002). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Gruber J. J., et al. , Ars2 promotes proper replication-dependent histone mRNA 3′ end formation. Mol. Cell 45, 87–98 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brodersen M. M. L., et al. , CRL4(WDR23)-mediated SLBP ubiquitylation ensures histone supply during DNA replication. Mol. Cell 62, 627–635 (2016). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Chatre L., Ricchetti M., Large heterogeneity of mitochondrial DNA transcription and initiation of replication exposed by single-cell imaging. J. Cell Sci. 126, 914–926 (2013). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Cabili M. N., et al. , Localization and abundance analysis of human lncRNAs at single-cell and single-molecule resolution. Genome Biol. 16, 20 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Narita T., et al. , NELF interacts with CBC and participates in 3′ end processing of replication-dependent histone mRNAs. Mol. Cell 26, 349–365 (2007). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Whitfield M. L., et al. , SLBP is associated with histone mRNA on polyribosomes as a component of the histone mRNP. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, 4833–4842 (2004). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Hume A. J., et al. , Phosphorylation of retinoblastoma protein by viral protein with cyclin-dependent kinase function. Science 320, 797–799 (2008). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Kalejta R. F., Bechtel J. T., Shenk T., Human cytomegalovirus pp71 stimulates cell cycle progression by inducing the proteasome-dependent degradation of the retinoblastoma family of tumor suppressors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 23, 1885–1895 (2003). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Kalejta R. F., Brideau A. D., Banfield B. W., Beavis A. J., An integral membrane green fluorescent protein marker, Us9-GFP, is quantitatively retained in cells during propidium iodide-based cell cycle analysis by flow cytometry. Exp. Cell Res. 248, 322–328 (1999). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Lu M., Shenk T., Human cytomegalovirus UL69 protein induces cells to accumulate in G1 phase of the cell cycle. J. Virol. 73, 676–683 (1999). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Murphy E. A., Streblow D. N., Nelson J. A., Stinski M. F., The human cytomegalovirus IE86 protein can block cell cycle progression after inducing transition into the S phase of permissive cells. J. Virol. 74, 7108–7118 (2000). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wiebusch L., Asmar J., Uecker R., Hagemeier C., Human cytomegalovirus immediate-early protein 2 (IE2)-mediated activation of cyclin E is cell-cycle-independent and forces S-phase entry in IE2-arrested cells. J. Gen. Virol. 84, 51–60 (2003). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.VanDeusen H. R., Kalejta R. F., The retinoblastoma tumor suppressor promotes efficient human cytomegalovirus lytic replication. J. Virol. 89, 5012–5021 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.VanDeusen H. R., Kalejta R. F., Deficiencies in cellular processes modulated by the retinoblastoma protein do not account for reduced human cytomegalovirus replication in its absence. J. Virol. 89, 11965–11974 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Kuny C. V., Kalejta R. F., Human cytomegalovirus can procure deoxyribonucleotides for viral DNA replication in the absence of retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation. J. Virol. 90, 8634–8643 (2016). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Albright E. R., Kalejta R. F., Myeloblastic cell lines mimic some but not all aspects of human cytomegalovirus experimental latency defined in primary CD34+ cell populations. J. Virol. 87, 9802–9812 (2013). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Schindelin J., et al. , Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 9, 676–682 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lee S. H., Albright E. R., Lee J.-H., Jacobs D., Kalejta R. F., Cellular defense against latent colonization foiled by human cytomegalovirus UL138 protein. Sci. Adv. 1, e1501164 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Carter D. M., Westdorp K., Noon K. R., Terhune S. S., Proteomic identification of nuclear processes manipulated by cytomegalovirus early during infection. Proteomics 15, 1995–2005 (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All study data are included in the article and/or SI Appendix.