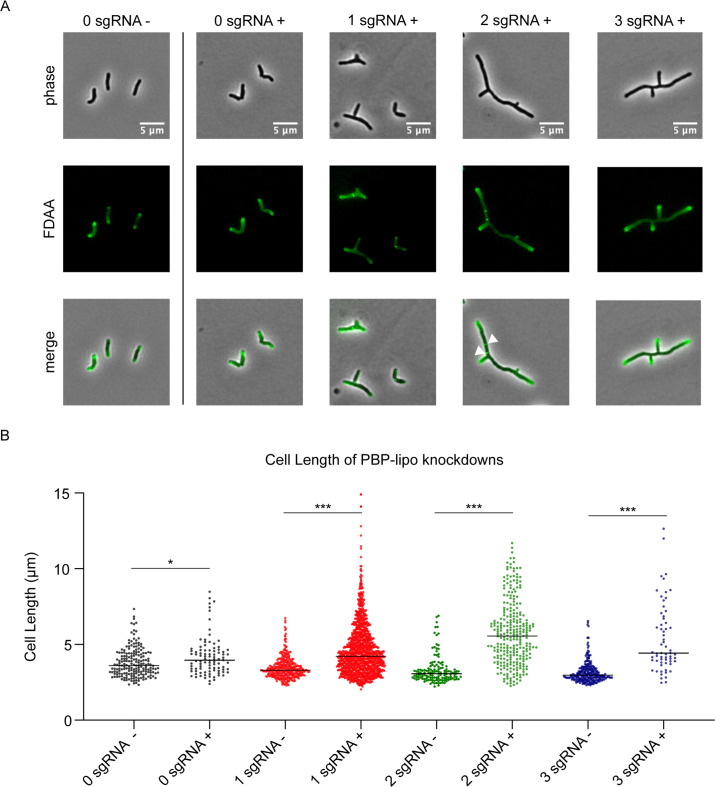
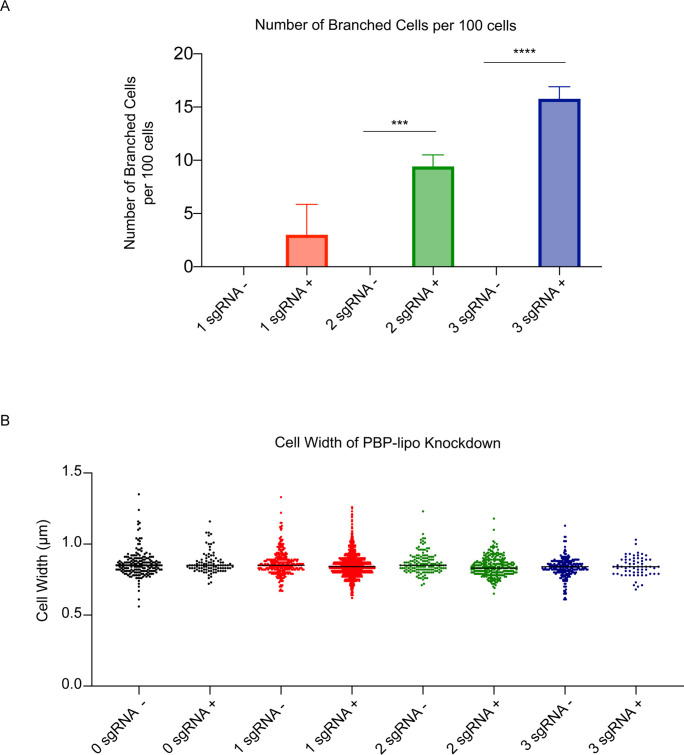
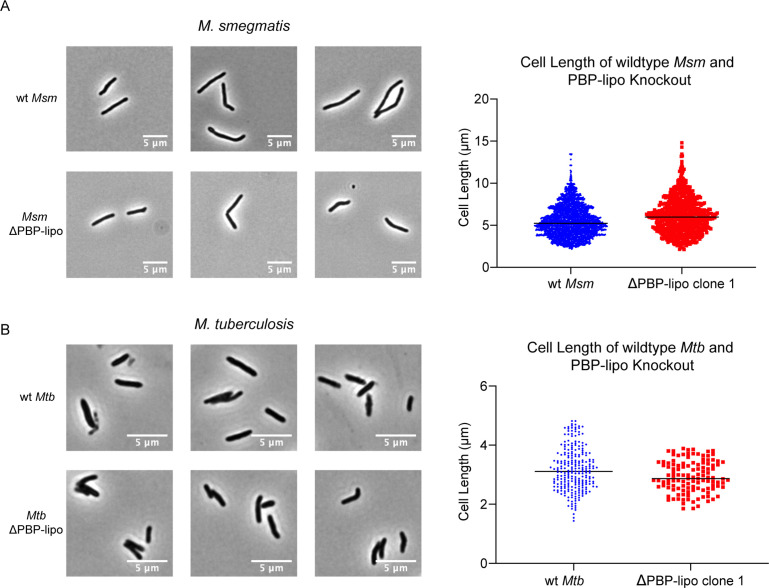
Figure 4. Knockdown of penicillin-binding protein and hypothetical lipoprotein (PBP-lipo) disrupts cell morphology.
(A) Microscopy images of PBP-lipo knockdown cultures. Mycobacterium abscessus (Mab) strains carrying CRISPRi plasmids with either 0, 1, 2, or 3 sgRNAs targeting PBP-lipo. Arrows indicate sites of multiple septa formation. (B) Cell lengths of uninduced and induced strains. Measurements were obtained by GEMATRIA and MOMIA image analysis pipelines (Zhu et al., 2021). Student’s t test used to calculate the statistical difference in mean cell lengths. ***p<0.0001, *p<0.05.