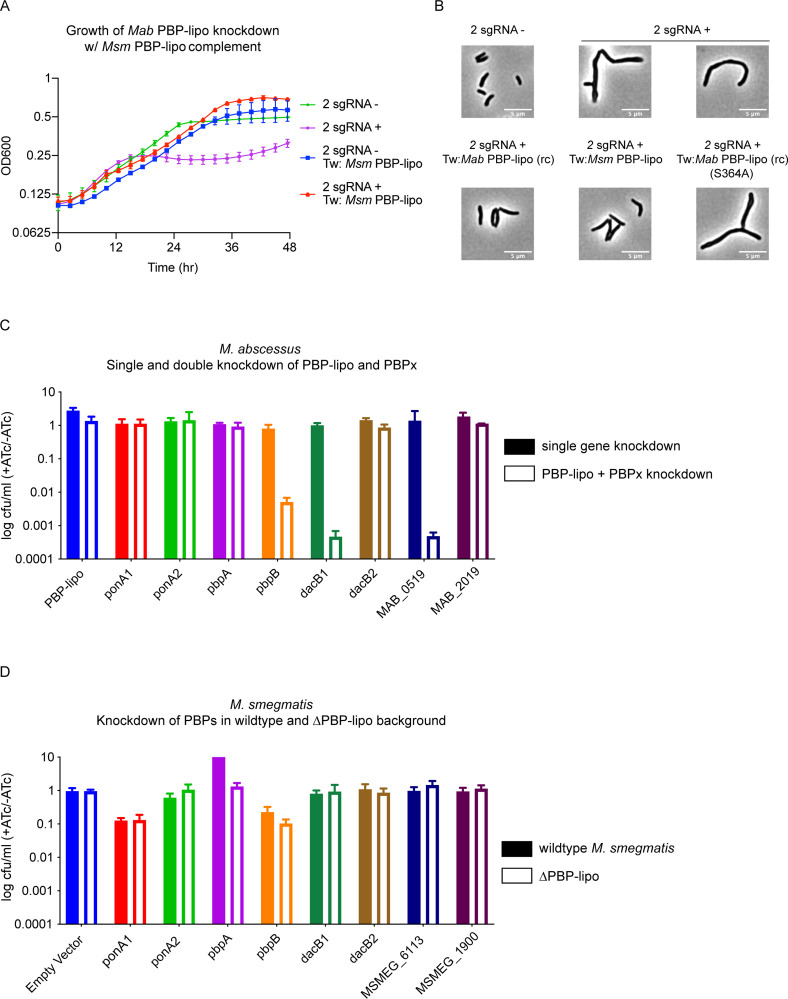
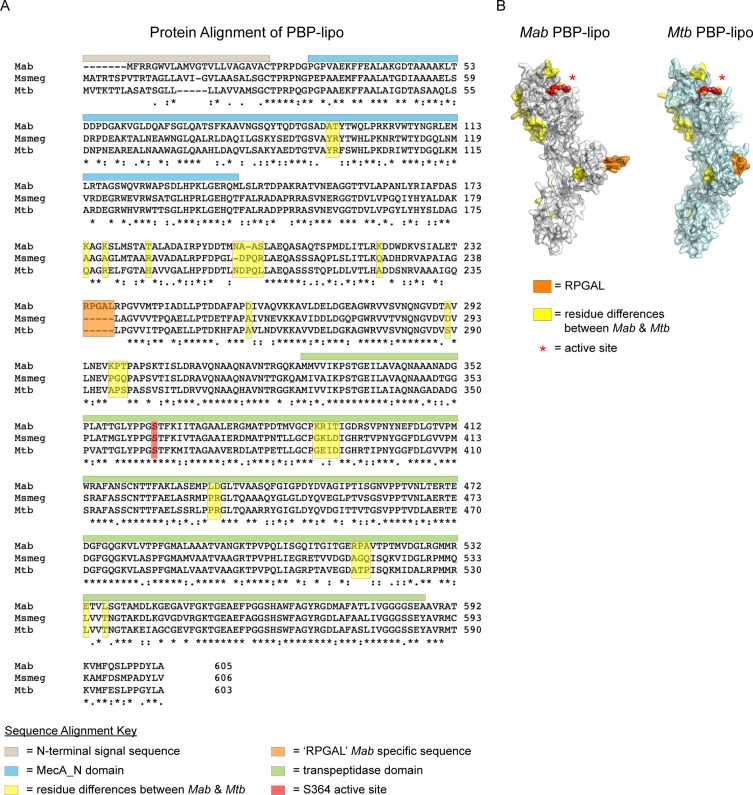
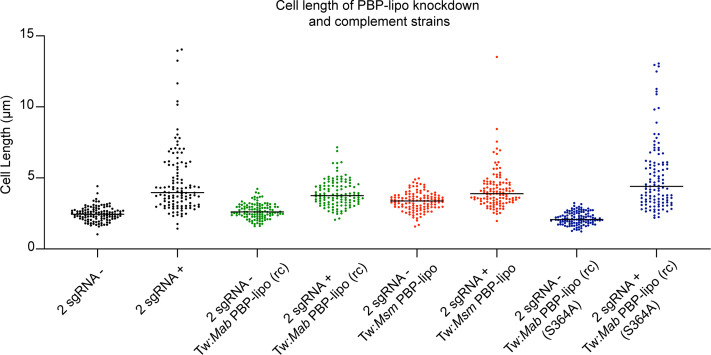
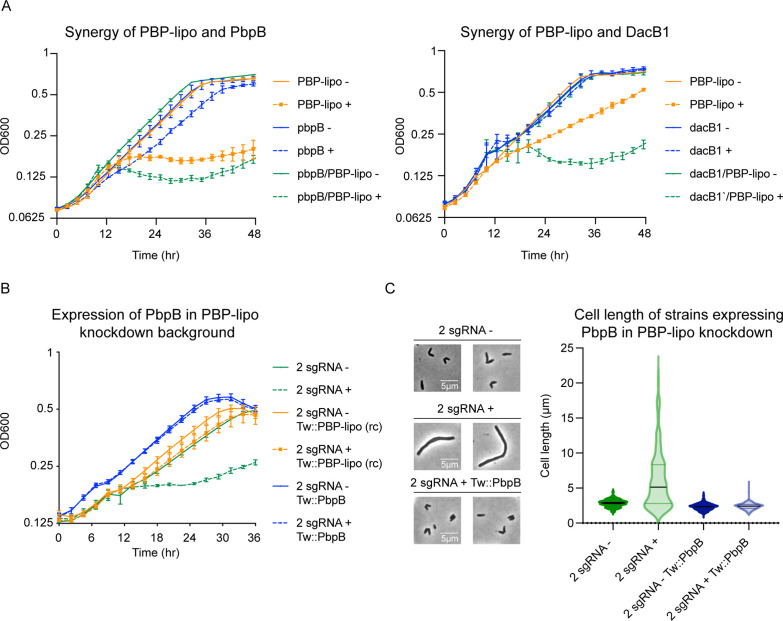
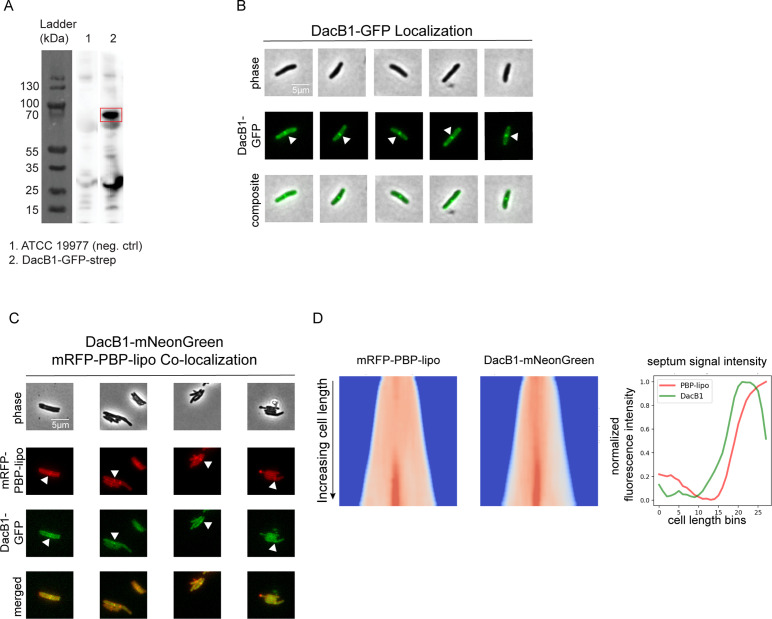
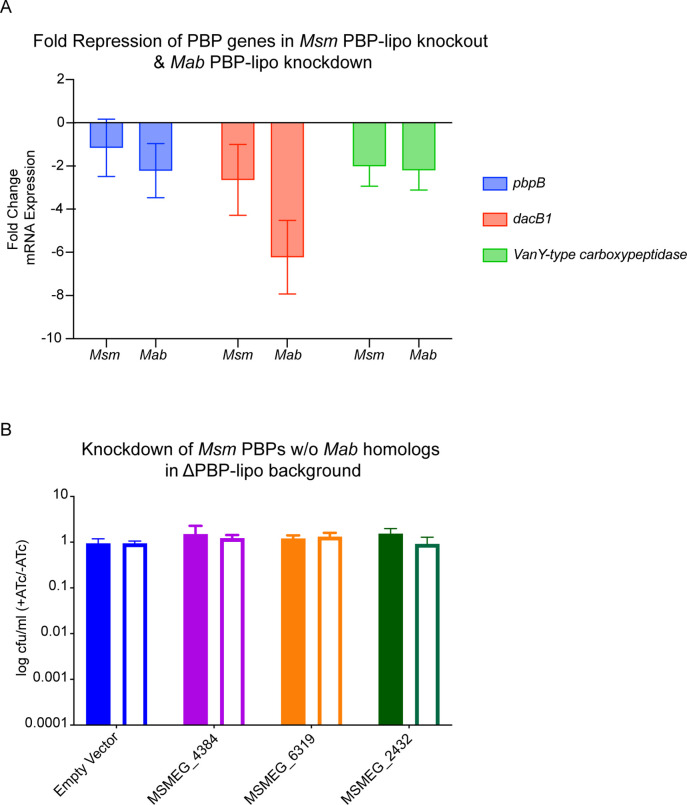
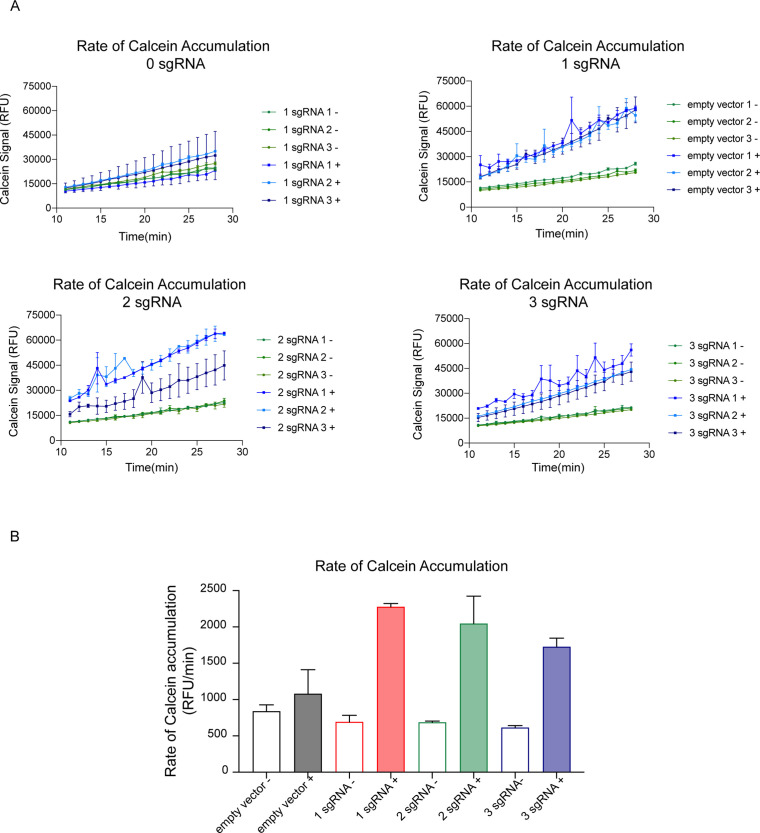
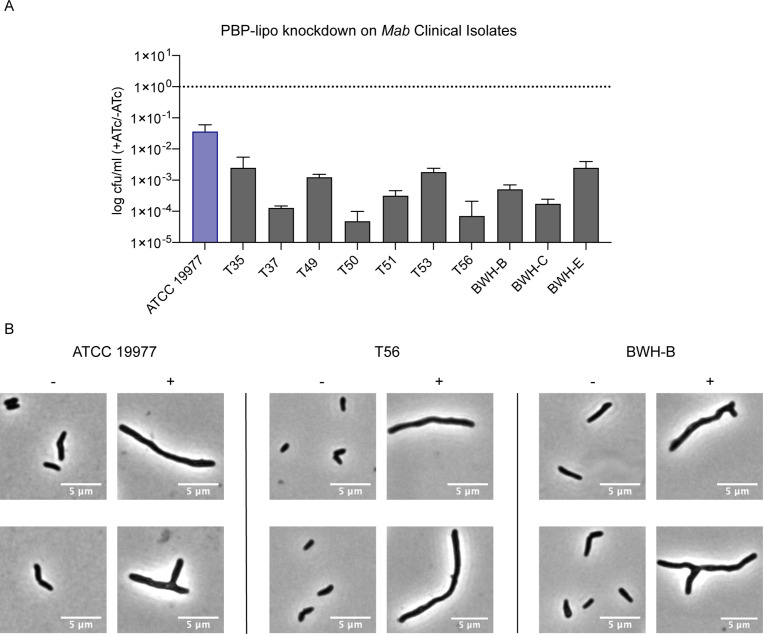
Figure 6. Penicillin-binding protein and hypothetical lipoprotein (PBP-lipo) network in Mycobacterium abscessus (Mab) does not exist in Mycobacterium smegmatis (Msm).
(A) Growth curve of 2 sgRNA strain targeting PBP-lipo and 2 sgRNA strain constitutively expressing PBP-lipoMsm. (B) Microscopy images of 2 sgRNA and PBP-lipo complement strains. (C) Genetic synergy of PBP-lipo with other PBPs in Mab. Solid bar represents colony forming unit (CFU) of strains where a single PBP was knocked down. Open bar represents strains where PBP-lipo was knocked down in combination with the listed PBP. (D) Genetic synergy of PBPs and PBP-lipo in Msm. CRISPRi plasmids carrying sgRNAs targeting each of the PBPs in Msm were transformed into wildtype Msm (closed bar) and the ΔPBP-lipo mutant (open bar).