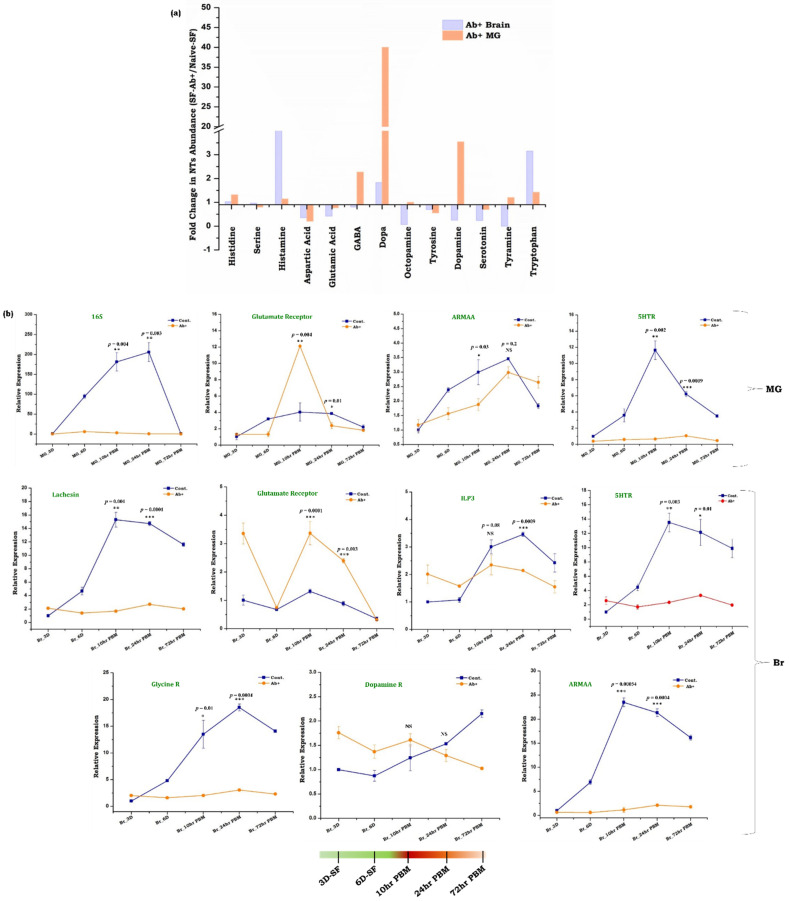
Figure 6.
Establishing Microbiome–Gut–Brain–Axis (MGB) communication in mosquitoes. (a) Absolute quantification of the neurotransmitters (NT) in the brain and gut tissues of naïve sugar-fed and antibiotic-treated mosquitoes (n = 65, N = 2) which are represented as fold-change of NT abundance when compared to naïve sugar-fed conditions. Statistically significant differences in the amount of metabolites were tested by p-values (p ≤ 0.005) that are deduced by two-way ANOVA and Tukey’s test, (n = 50, N = 2); (b) Relative expression profiling of the 16S gene to show the population of microbial flora and other neuro-transcripts in the gut and brain of naïve and antibiotic-treated mosquitoes undergoing metabolic switch. Statistical significance of differences of the respective genes in control (without antibiotic) and aseptic mosquitoes (antibiotic-treated) were tested by the t-test. p ≤ 0.0005 is indicated as ‘***’, p ≤ 0.005 is indicated as ‘**’, p ≤ 0.05 is indicated as ‘*’. (n = number of mosquitoes from which the respective tissue was dissected and pooled for each independent experiment; N = number of biological replicates).