Abstract
The coding regions of six putative open reading frames (ORFs) identified near the phage φ31 late promoter and the right cohesive end (cos) of lactococcal bacteriophage φ31 were used to develop antisense constructs to inhibit the proliferation of phage φ31. Two middle-expressed ORFs (ORF 1 and ORF 2) and four late-expressed ORFs (ORF 3 through ORF 6) were cloned individually between the strong Lactobacillus P6 promoter and the T7 terminator (TT7) to yield a series of antisense RNA transcripts. When expressed on a high-copy-number vector from a strong promoter, the constructs had no effect on the efficiency of plaquing (EOP) or the plaque size of phage φ31. To increase the ratio of antisense RNA to the targeted sense mRNA appearing during a phage infection, the antisense cassettes containing the late-expressed ORFs (ORF 3 through ORF 6) were subcloned to pTRK360, a low-copy-number vector containing the phage φ31 origin of replication, ori31. ori31 allows for explosive amplification of the low-copy-number vector upon phage infection, thereby increasing levels of antisense RNA transcripts later in the lytic cycle. In addition, the presence of ori31 also lowers the burst size of phage φ31 fourfold, resulting in fewer sense, target mRNAs being expressed from the phage genome. The combination of ori31 and P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 resulted in a threefold decrease in the EOP of phage φ31 (EOP = 0.11 ± 0.03 [mean ± standard deviation]) compared to the presence of ori31 alone (EOP = 0.36). One-step growth curves showed that expression of anti-ORF 4H RNA decreased the percentage of successful centers of infection (75 to 80% for ori31 compared to 35 to 45% for ori31 plus anti-ORF 4H), with no further reduction in burst size. Growth curves performed in the presence of varying levels of phage φ31 showed that ori31 plus anti-ORF 4H offered significant protection to Lactococcus lactis, even at multiplicities of infection of 0.01 and 0.1. These results illustrate a successful application of an antisense strategy to inhibit phage replication in the wake of recent unsuccessful reports.
Lactococcus lactis is an industrially important member of the lactic acid bacteria used in the fermentation of many dairy products, including sour cream, buttermilk, and various cheeses, such as cheddar. Because of the nature of the cheese fermentation process, bacteriophage problems continue to appear in the dairy industry, resulting in slowed or failed fermentation tanks and substantial economic losses. Efforts to protect L. lactis from phage attack have led to the identification of several phage resistance mechanisms naturally harbored by this important microorganism. These mechanisms can be divided into four groups: blockage of phage adsorption, blockage of phage DNA injection, restriction/modification, and abortive mechanisms (for extensive reviews, see references 2, 9, 10, 18, 23, and 33). These phage defense mechanisms are often located on plasmids, many of which have been successfully transferred, separately or in combination, to other industrial strains (6, 7, 16, 20, 29, 42, 47) to provide barriers to phage proliferation. Despite advances in this arena, however, the appearance of new phages capable of overcoming these defenses continues to pose a challenge to starter culture manufacturers. In addition, the use of biotechnology to develop highly specialized strains for specific functions may exacerbate this problem, since repeated use can allow the accumulation of phages capable of attacking the strain, thereby limiting its long-term usefulness in industry (9, 23, 33).
Recent advances in the molecular biology of L. lactis and its bacteriophages have opened the door to the development of novel, recombinant phage defense mechanisms to complement the mechanisms described above. Two interesting examples of novel phage defense mechanisms involve the alteration or replacement of chromosomal elements to inhibit phage proliferation. In one case, site-specific integration was used to inactivate sequences in the NCK203 chromosome, which contributed to the emergence of new phages insensitive to certain resistance mechanisms (14, 36). Inactivation prevented the evolution and subsequent proliferation of recombinant lytic phages. In the second case, a bacteriophage receptor (pip), encoded by the L. lactis chromosome and involved in sensitivity to phages of the c2 species, was replaced with a mutated version (17). The replacement, which left no nonlactococcal DNA or antibiotic markers, resulted in a strain resistant to infection by c2 phages. In addition, phage sequences have been successfully utilized in the development of phage defense mechanisms. For example, a suicide system consisting of a phage-specific promoter from the lytic bacteriophage φ31 (φ31P) (41, 52) linked to a lethal gene (the LlaI restriction cassette) (40) was described recently (13). In this system, the infection transcriptionally activates a phage-specific, inducible promoter to express a lethal gene, thereby killing the host and destroying the phage genome. Another example is phage-encoded resistance, which provides a phage origin of replication in trans to compete with and inhibit phage replication (22, 37). This phage resistance mechanism was demonstrated with two origins of replication isolated from the P335 phages, φ50 (per50) (22) and φ31 (per31) (37). When present on a low-copy-number vector, per50 and per31 result in explosive plasmid amplification, with a concomitant reduction in phage efficiency of plaquing (EOP) (0.42 and 0.3, respectively) and plaque size (22, 37). On a high-copy-number vector, both cause a significant decrease in EOP (22, 37).
In addition to the novel phage defense systems described above, antisense technology offers another approach to exploit phage sequences in providing barriers to phage attack. Binding of antisense RNA to the target mRNA prevents translation, either by preventing ribosome loading or by destabilizing the mRNA and making it more susceptible to RNase attack (27). Naturally occurring antisense mechanisms have been described for several systems (for reviews, see references 27 and 46). Although results have been inconsistent, antisense strategies have also been used successfully to control gene expression in animals (28), plants (15), and bacteria (8). In fact, Hirashima et al. (24, 25) utilized antisense RNA directed against various regions of the maturation protein, coat protein, and replicase gene to develop a novel immune system against RNA coliphage SP proliferation. These authors found that a 30-nucleotide antisense RNA directed against the Shine-Dalgarno sequence and base pairs just upstream of the maturation protein was sufficient to almost completely inhibit this phage (25).
Previous attempts to use antisense mechanisms to protect L. lactis from bacteriophage attack, however, have yielded variable results. Using the major coat protein gene, mcp, of φF4-1, Chung et al. (5) achieved a reduction in EOP of 0.5 to 0.77, depending on the extent of the mcp gene included in the antisense construct. In contrast, Moineau et al. (35) found that the major structural proteins of the P335 phage ul36 were produced in excess, making them poor targets for antisense technology. Kim et al. (30–32) cloned an entire open reading frame (ORF) (gp51C) of unknown function from φ7-9 in an antisense orientation. When the entire coding region was used, this antisense construct resulted in a reduction in the EOP of φ7-9 to 10−2. This same EOP reduction was observed upon infection with phages related to φ7-9, which also contained this ORF. In addition, resistance to phage φ7-9 was achieved by antisense RNA directed to two ORFs immediately downstream of gp51C (gp18C and gp24C), although the resistance was far less efficient (EOP, ∼0.45) than that achieved with gp51C (32). More recently, Polzin et al. (K. M. Polzin, L. J. Collins, M. W. Lubbers, and A. W. Jarvis, Abstr. 5th Symp. Lactic Acid Bacteria, abstr. F2, 1996) used an antisense strategy to target several ORFs from the early and late regions of the prolate phage c2. The ORFs included e5, a putative subunit of DNA polymerase; e12, a putative transcription factor; l7, a major tail protein; and l12, a terminase. No inhibition was observed at low or high copy numbers for any of the constructs, even though there was some evidence that the antisense constructs lowered the expression levels of some of the ORFs. Lastly, in our laboratory, an antisense strategy was used to target the gene encoding the transcriptional activator, tac31A, of the phage φ31 late promoter (52). Although the anti-tac31A construct was able to significantly reduce expression from the phage promoter, it was not able to inhibit proliferation of φ31.
The variable and largely negative results with antisense technology are unfortunate, especially since the recent availability of several complete and partial bacteriophage genome sequences (3, 34, 45, 50) makes the design of antisense strategies a viable option. In the present study, we have used available sequence information from near the late promoter and the right cohesive end of phage φ31 (51) to develop antisense constructs in both a high-copy-number vector and a low-copy-number explosive vector containing ori31, the putative phage φ31 origin of replication. The constructs allowed us to compare the efficacy of providing high levels of antisense RNA constitutively or explosively during the appropriate time in the phage lytic cycle.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains, plasmids, and media.
The strains and plasmids used in this study are listed in Table 1. L. lactis subsp. lactis NCK203, the sensitive host for bacteriophage φ31, was propagated in M17 (Difco) supplemented with 0.5% glucose (GM17) at 30°C. When appropriate, erythromycin was added at a concentration of 2.5 μg/ml. Escherichia coli strains were grown in Luria-Bertani broth at 37°C with shaking, or on Luria-Bertani medium supplemented with 1.5% agar. When required, chloramphenicol was added at a concentration of 20 μg/ml. In E. coli, erythromycin resistance was selected on brain heart infusion agar (Difco) supplemented with 120 μg of erythromycin per ml (38).
TABLE 1.
Bacterial strains and plasmids used in this study
| Strain or plasmid | Descriptiona | Reference or source |
|---|---|---|
| E. coli | ||
| JM110 | E. coli cloning host | 54 |
| XL1-Blue | E. coli cloning host | Gibco-BRL |
| L. lactis subsp. lactis NCK203 | Sensitive host for phage φ31 | 21 |
| Plasmids | ||
| pTRK593 | Emr, high-copy-number expression vector | This study |
| pTRK594 | Emr pTRK593::P6::anti-ORF 1 | This study |
| pTRK595 | Emr pTRK593::P6::anti-ORF 1 plus ORF 2 | This study |
| pTRK596 | Emr pTRK593::P6::anti-ORF 3 | This study |
| pTRK597 | Emr pTRK593::P6::anti-ORF 4H | This study |
| pTRK598 | Emr pTRK593::P6::anti-ORF 5H | This study |
| pTRK599 | Emr pTRK593::P6::anti-ORF 6H | This study |
| pTRK600 | Emr pTRK593::P6::anti-ORF 6 | This study |
| pTRK360 | Cmr Emr pSA3 plus ori31 | 37 |
| pTRK601 | Cmr Emr pTRK360::T7 terminator | This study |
| pTRK602 | Cmr Emr pTRK601::P6::anti-ORF 3 | This study |
| pTRK603 | Cmr Emr pTRK601::P6::anti-ORF 4H | This study |
| pTRK604 | Cmr Emr pTRK601::P6::anti-ORF 5H | This study |
| pTRK605 | Cmr Emr pTRK601::P6::anti-ORF 6 | This study |
| pTRKH2 | Emr, high-copy-number cloning vector | 38 |
| pTRK606 | Emr pTRKH2::P15A102x::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 | This study |
| pTRK607 | Emr pTRKH2::P15A102x::P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 | This study |
| pTRK608 | Cmr Emr pTRK601::ORF 4H | This study |
Abbreviations: Emr, erythromycin resistance; Cmr, chloramphenicol resistance.
Bacteriophage propagation and assays.
Phage φ31 is a small, isometric, cohesive-ended, lytic lactococcal bacteriophage of the P335 species (1) with a double-stranded DNA genome of 31.9 kb. Phage φ31 was propagated on NCK203 in GM17 supplemented with 10 mM CaCl2 at 30°C. EOP assays were performed as described previously (49). Center-of-infection assays, one-step growth curves, and burst size determinations were all performed at 30°C as described previously (13, 48).
Plasmid and phage DNA isolation and molecular cloning.
Small-scale E. coli plasmid preparations were performed by the alkaline-sodium dodecyl sulfate method (44). Large-scale E. coli plasmid preparations were performed with a plasmid kit (Qiagen, Inc., Chatsworth, Calif.) according to the manufacturer's directions. Small-scale isolation of plasmids from L. lactis was as described by O'Sullivan and Klaenhammer (39), except that ethidium bromide was not used prior to phenol-chloroform extraction. Phage DNA was isolated by a large-scale protocol, as described elsewhere (43). Standard procedures were used for the DNA manipulations described in this study (44). Restriction enzymes and T4 DNA ligase were obtained from Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals (Indianapolis, Ind.) and used according to the manufacturer's instructions. All DNA used in cloning reactions was first gel purified with the QIAEX II DNA extraction kit (Qiagen, Inc.).
Bacterial transformations.
Ligations were transformed into RbCl-competent E. coli XL1-Blue. RbCl-competent E. coli cells were prepared by the procedure of Hanahan (19), modified as described by Dinsmore and Klaenhammer (11). Cells were frozen at −70°C in 100-μl aliquots and transformed by the procedure described previously for CaCl2-competent cells (44). After screening for the proper insert in E. coli, plasmids were electroporated into L. lactis by a modified procedure of Holo and Nes (26), as described previously (52).
PCR and DNA sequencing.
PCR was performed with Taq DNA polymerase (Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals) according to the manufacturer's instructions. In each case, 40 cycles were used to amplify the region of interest. Annealing temperatures were 5 to 10°C below the lowest Tm of each primer pair. To facilitate cloning of PCR products, appropriate restriction enzyme sites were designed into the 5′ ends of the primers. Primer sequences used to amplify the different ORFs described in this manuscript are shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2.
Primers used for PCR of various ORFs
| ORF | Primer
|
|
|---|---|---|
| 5′a | 3′b | |
| 1 | ATTACTCGAGGATATACCGGGAGGTAGACCAT | ATATCTGCAGTTAATCTGGCATTAATACATC |
| 1 plus tac31A | ATTACTCGAGGATATACCGGGAGGTAGACCAT | TAATCTGCAGTTACCAGAAGCCGCACATATC |
| 3 | ATATCTCGAGTGTGGAGAAAGTGAGGTGAC | GATCCTGCAGTTAAGATACATAAGAAGAC |
| 4H | GATCCTCGAGCTTAGGAGCTAAACTATGG | GTACCTGCAGTCTGACTGACGACACTTACCT |
| 5H | ATATCTCGAGGAGAGAAAGGAGCAAAAAATTGAC | GATCCTGCAGAGAAATGAGCTTCAAGAACAA |
| 6Hc | GATCCTCGAGCTGGAATTAAAGGAGCTGAA | ATATCTGCAGGTTACTATTGGCTCTTTCA |
| 6c | GATCCTCGAGCTGGAATTAAAGGAGCTGAA | ATTGCTGCAGTTATTTTTTACTTTTTAGATTC |
XhoI site is underlined.
PstI site is underlined.
Since the full ORF 6 sequence was not available in our laboratory, sequence information from phage r1t (50) was used to design the 3′ primers.
RNA manipulations.
RNA was isolated from L. lactis subsp. lactis NCK203 at various times during the phage infection cycle by using TRIzol reagent (Gibco-BRL, Gaithersburg, Md.) as described by Dinsmore and Klaenhammer (11). Slot blot Northern hybridizations were performed on a Bio-Rad (Richmond, Calif.) apparatus according to the manufacturer's protocol. An equivalent amount of RNA from each time point (approximately 10 μg) was denatured and applied to a Zeta probe membrane (Bio-Rad). The RNA was UV cross-linked to the membrane with the auto-cross-link cycle of the Stratagene Stratalinker (Stratagene, La Jolla, Calif.) and then hybridized to a 32P-labeled probe at 65°C to measure ORF 4 and ORF 5 mRNA levels, or at 55°C to measure anti-ORF 4H RNA levels. The ORF 4 and ORF 5 probes used to measure levels of target, sense mRNA after phage φ31 infection were 32P-labeled by the multiprime DNA labeling system (Amersham, Piscataway, N.J.). The 72-bp oligonucleotide used to measure levels of antisense ORF 4H RNA was 32P-labeled with T4 polynucleotide kinase (Boehringer Mannheim) and [γ-32P]ATP (NEN, Boston, Mass.) per the manufacturer's instructions.
RESULTS
Construction of antisense cassettes in high-copy-number and explosive vectors.
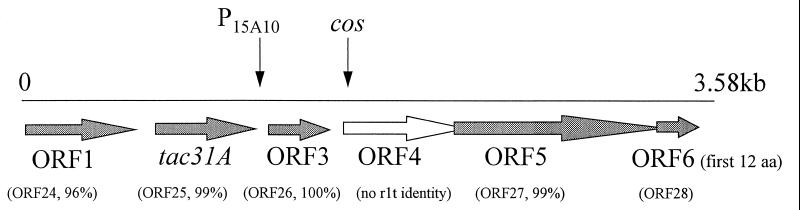
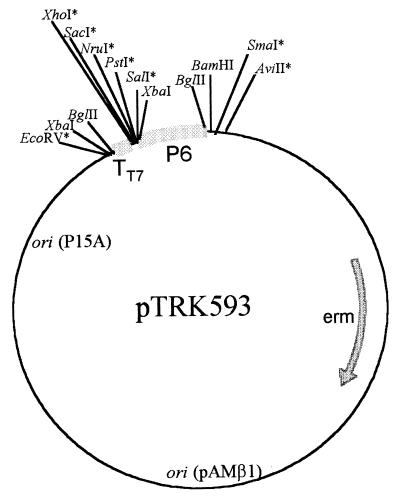
Available sequence information from near the right cohesive end of the lytic, lactococcal bacteriophage φ31 (Fig. 1) (51) was used to design antisense cassettes to act as barriers to the proliferation of phage φ31. An antisense expression vector, pTRK593 (Fig. 2), was first constructed and contained the strong, Lactobacillus P6 promoter (12) followed by the T7 terminator (TT7) in the high-copy-number vector pTRKH2 (38). Five putative ORFs and one gene (early- or middle-expressed ORF 1 and tac31A, and late-expressed ORFs 3, 4, 5, and 6) were cloned in the antisense orientation between the P6 promoter and the T7 terminator of pTRK593. The antisense constructs were prepared with either the entire coding region (anti-ORF 1, anti-ORF 1/tac31A, anti-ORF 3, and anti-ORF 6) or just part of the coding region (anti-ORF 4H, 361-bp region; anti-ORF 5H, 493-bp region; and anti-ORF 6H, 467-bp region). In all cases, the 5′ portion of each coding region, including the Shine-Dalgarno sequence, was used in an attempt to inhibit ribosome loading and negatively impact translation. The function of only two of these ORFs is known. Tac31A (formerly ORF 2 and Tac [52]) is the transcriptional activator of the phage φ31 late promoter (52). ORF 5 is highly homologous to ORF 27 of phage r1t, a putative minor structural protein (50). EOP assays were performed to measure the effectiveness of each construct in preventing phage φ31 proliferation (Table 3). The results showed that none of the antisense cassettes cloned behind a strong promoter on the high-copy-number pTRKH2-based replicon had an effect on the ability of φ31 to plaque on L. lactis subsp. lactis NCK203.
FIG. 1.
Putative ORFs identified in a 3,584-bp region near the right cohesive end of phage φ31 (51). The overlapping arrows of ORFs 4, 5, and 6 denote that the stop and start codons of these ORFs overlap each other. The extent of homology to putative ORFs of r1t (50) is shown in parentheses below each phage φ31 ORF. The positions of cos and the phage-inducible promoter, P15A10, are depicted by vertical arrows. The GenBank accession no. for this sequence is AF022773.
FIG. 2.
High-copy-number antisense expression vector pTRK593. The P6 promoter fragment (BamHI/SalI) was cloned from pLA6 (12). The T7 terminator was amplified as an XhoI-SalI fragment (restriction sites underlined in primers below) from the E. coli expression vector pET28a (Novagen, Madison, Wis.) by using a 5′ primer consisting of 5′-CTCGAGGAGAAGCCCGAAAGGAAGC-3′ and a 3′ primer consisting of 5′-GTCGACTCCGGATATAGTTCCTC-3′. The fragment was subsequently cloned into the XhoI site of the base vector pTRKH2. ∗, unique restriction site.
TABLE 3.
Comparison of the effects of expression of the various antisense cassettes from the high-copy-number vector with the effects of those from the explosive replicon on the EOP of phage φ31
| Antisense construct | EOP of phage φ31 (SD)a
|
|
|---|---|---|
| pTRKH2-based high-copy-number vector | pTRK360-based explosive replicon | |
| pTRKH2 (control) | 1.0 | — |
| pTRK360 (ori31 alone) | — | 0.36 (0.02) |
| P6::anti-ORF 1::TT7 | 0.89 (0.08) | N.T. |
| P6::anti-ORF 1 plus ORF 2::TT7 | 1.1 (0.09) | N.T. |
| P6::anti-ORF 3::TT7 | 1.3 (0.05) | 0.21 (0.04) |
| P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 | 1.1 (0.10) | 0.11 (0.03) |
| P6::anti-ORF 5H::TT7 | 1.1 (0.12) | 0.25 (0.02) |
| P6::anti-ORF 6H::TT7 | 1.2 (0.10) | N.T. |
| P6::anti-ORF 6::TT7 | 1.2 (0.11) | 0.33 (0.06) |
| anti-ORF 4H::TT7 (no P6) | N.T. | 0.29 (0.06) |
| P15A102x::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 | 1.1 (0.10) | N.T. |
| P15A102x::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 | 1.0 (0.13) | N.T. |
All EOP values were determined with L. lactis subsp. lactis NCK203 (pTRKH2) as the reference strain and are the averages of the results of at least three independent experiments. —, not applicable; N.T., not tested.
One significant barrier to the successful use of an antisense strategy may be that expression of sufficient levels of antisense RNA is not achieved at the appropriate point in the lytic cycle to effectively compete with expression of sense RNA from the phage DNA. Attempts were therefore made to increase the ratio of antisense RNA to target mRNA by utilizing a replicon which is explosively amplified during the phage infection cycle. To accomplish this, the ORF 3, ORF 4H, ORF 5H, and ORF 6 antisense cassettes (P6::anti-ORF) were removed from the pTRK593-based vector by using AviII-XhoI or SmaI-XhoI and subcloned into the NruI-SalI site of pTRK360 containing a SalI-XhoI TT7 fragment (Fig. 2) in the SalI site (pTRK601). pTRK601 is a low-copy-number vector which contains the putative phage φ31 origin of replication, ori31 (37). These ORFs were chosen because they are expressed late in the phage infection cycle, when the highest level of antisense RNA expression would be expected due to explosive amplification of the vector copy number by phage φ31 infection. ori31 alone on the low-copy-number vector decreased the EOP of φ31 to about 0.36 and caused a marked reduction in plaque size (37). Interestingly, a combination of ori31 and P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 on the low-copy-number vector caused a further reduction in EOP to 0.11. Plaques were even more erratic in size and somewhat turbid. The ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 3::TT7 and ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 5H::TT7 constructs were not as effective, decreasing the EOP to 0.21 and 0.25, respectively, with little effect on plaque size and appearance. The ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 6::TT7 construct had no effect beyond that observed with ori31 alone.
To confirm that expression of antisense ORF 4H RNA was responsible for the observed EOP reduction of phage φ31 when combined with ori31, ORF 4H was cloned into pTRK601 in the same orientation, but without the P6 promoter. Results of EOP assays (Table 3) showed that the presence of ORF 4H DNA alone had little to no effect, other than that observed with ori31, on the proliferation of phage φ31, demonstrating that the anti-ORF 4H RNA caused the observed reduction in EOP.
Effect of antisense constructs on phage φ31 proliferation.
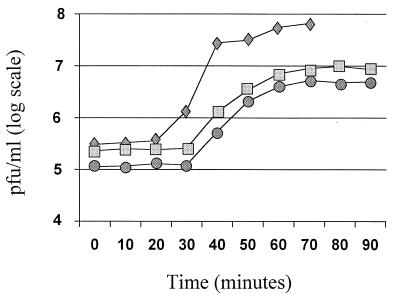
One-step growth curves were then performed to investigate the effects of the ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 construct on φ31 proliferation (Fig. 3). The presence of ori31 alone reduced the efficiency of center-of-infection formation (ECOI) by phage φ31 to 0.75 to 0.80, meaning that only 75 to 80% of the initially infected cells were able to release phages capable of plaque formation. ori31 alone also reduced the burst size fourfold, from an average of 160 phages/cell with the control to 40 phages/cell with ori31. With the ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 construct, the ECOI was further reduced to 0.35 to 0.45; only 35 to 45% of the infected cells released viable phages. There was no further reduction in burst size. ECOI assays were also performed with the ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 5H::TT7 and ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 3::TT7 constructs. In both cases, the ECOI of φ31 was reduced to approximately 0.65, a slight reduction compared to that achieved with ori31 alone.
FIG. 3.
One-step growth curves for φ31 on NCK203 (the control) (diamonds), NCK203 (pTRK360) (ori31 alone) (squares), and NCK203 (pTRK603) (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) (circles).
Levels of antisense RNA.
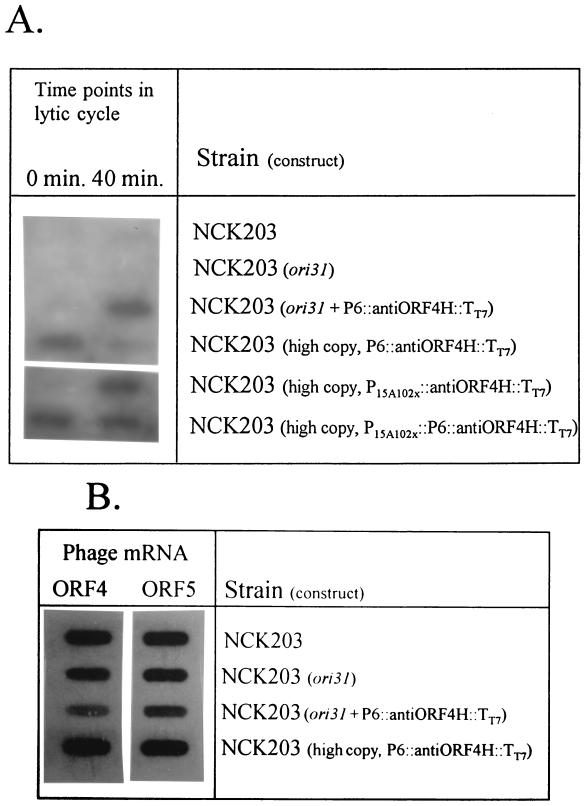
To evaluate the levels of antisense RNA generated from these constructs, Northern slot blot hybridizations were performed on RNA isolated from NCK203, NCK203 (P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) (high copy number), NCK203 (ori31), and NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) just before and 40 min after infection with phage φ31 (multiplicity of infection [MOI] = 1 to 2). The RNA was probed with a 32P-labeled 72-bp oligonucleotide (5′-TCTTGAGCGAGAAAAAGGAGATAATAATGAAAAGAATTTG TAGCATCTGTAAGCAAGAAAAAGAGCTAGATG-3′) consisting of sequences from the ORF 4H sense strand (complementary to the antisense strand). Results are shown in Fig. 4A. As expected, high levels of anti-ORF 4H RNA were generated with the high-copy-number version of P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 before phage infection. After phage infection, however, the levels of anti-ORF 4H RNA were reduced almost to background, indicating that the amount of antisense RNA available was insufficient to interfere with sense ORF 4 mRNA. In contrast, significantly greater levels of anti-ORF 4H RNA were detected with the combination of P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 and ori31 after phage infection.
FIG. 4.
RNA slot blot hybridizations. (A) Levels of anti-ORF 4H RNA produced before (time, 0 min) and after (time, 40 min) phage φ31 infection of L. lactis subsp. lactis NCK203 carrying the various anti-ORF 4H constructs on the high-copy-number vector or the explosive vector. The rows for NCK203 and NCK203 (ori31) show the low levels of nonspecific binding of the 72-bp anti-ORF 4H probe at 55°C. (B) Northern slot blot hybridizations to measure the levels of ORF 4 and ORF 5 mRNA obtained 40 min after phage φ31 infection of L. lactis subsp. lactis NCK203 carrying the various anti-ORF 4H constructs on the high-copy-number vector versus those of that carrying the explosive vector. In all cases, no ORF 4 or ORF 5 mRNA was detected before phage infection (data not shown).
To determine the effect of anti-ORF 4H RNA on expression of ORF 4 target mRNA from the φ31 genome, the RNA was also probed with a 32P-labeled ORF 4 PCR fragment. This fragment was amplified from the 3′ end of the gene (primers 5′-CATATTCTTATGGAAATGTAGTTC-3′ and 5′-TCAGTCAATTTTTTGCTCCT-3′) so that only sense ORF 4 mRNA, and not the anti-ORF 4H RNA generated from the plasmid, would be detected. Figure 4B shows that, while ori31 alone reduced the level of ORF 4 target mRNA somewhat, a combination of ori31 with P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 significantly reduced the level of target ORF 4 mRNA expressed by the phage. In comparison, the high-copy-number version of anti-ORF 4H did not significantly impact the levels of ORF 4 mRNA produced after phage infection. The same results were obtained when the RNA was probed with a 32P-labeled ORF 5 PCR fragment. It was not possible to determine whether or not this reduction in sense mRNA was due to an antisense effect, or to a decrease in the number of available phages in the population.
New high-copy-number constructs utilizing the phage φ31 late promoter, P15A10.
The RNA slot blot data indicated that antisense RNA levels with the P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 high-copy-number construct were reduced at the end of the phage φ31 lytic cycle. Two new constructs were made in an attempt to increase antisense RNA levels throughout the lytic cycle without using ori31. In the first construct, the P6 promoter was replaced with an 888-bp mutated version of the phage φ31 late promoter P15A10, which contains tac31A and the promoter features (41, 52). In the mutated version, designated P15A102x, a small inverted repeat downstream of the transcription start sites was eliminated by site-directed mutagenesis, resulting in a twofold increase in promoter activity. This promoter is constitutive due to the presence of tac31A, but is further induced upon phage infection (41, 52). The second construct combined both promoters (P15A102x::P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) in an attempt to maintain high levels of antisense RNA before phage infection and throughout the lytic cycle. RNA slot blots (Fig. 4A) confirmed that higher anti-ORF 4H RNA levels were present at the end of the lytic cycle, but neither construct was able to inhibit phage proliferation (Table 3). Therefore, the combination of ori31 and anti-ORF 4H RNA expression is essential to the observed reduction in EOP.
Efficiency of the ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 phage defense system.
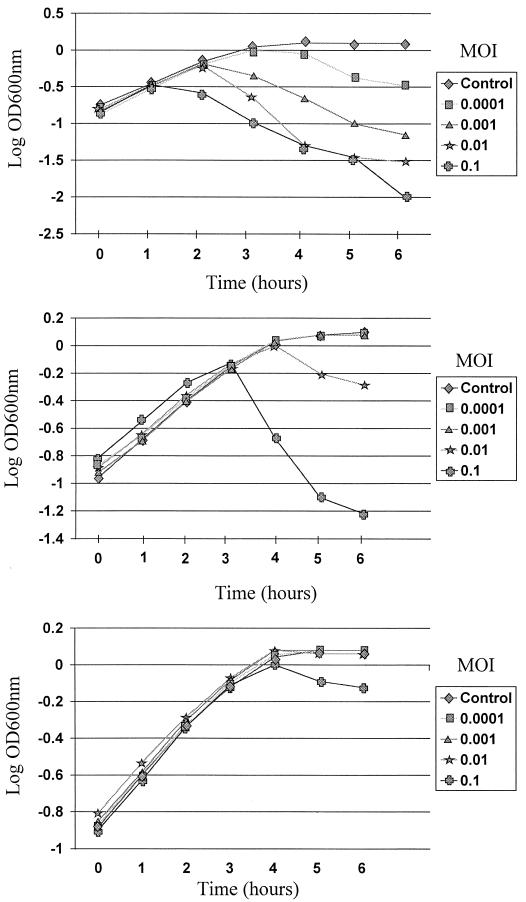
To determine the efficiency of this antisense mechanism, growth curves for NCK203, NCK203 (ori31), and NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) were measured in the presence of varying levels of phage φ31 (MOIs of 0.0001, 0.001, 0.01, and 0.1). Phage φ31 lysed the NCK203 culture at each MOI within 5 h or less (Fig. 5, top). Both ori31 and ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 provided NCK203 with significant protection against φ31, especially at the lower MOIs of 0.0001 and 0.001, where no lysis was observed after 5 to 6 h of growth. Substantially more protection against φ31 proliferation was achieved with ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 at the higher MOI levels of 0.01 and 0.1 (Fig. 5, middle and bottom). Little to no lysis occurred at an MOI of 0.01, while lysis was significantly delayed at an MOI of 0.1 compared to that observed with NCK203 with ori31 alone. Levels of phage (PFU per milliliter) in the culture supernatants were also monitored every hour from each sample (MOI, 0.01). Phage levels with ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 were reduced at least 10-fold compared to those of NCK203 (ori31) cultures and 50- to 100-fold compared to those of NCK203 cultures over the course of growth (data not shown).
FIG. 5.
Effect of varying levels of phage φ31 on the growth of NCK203 (top), NCK203 (ori31) (middle), and NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) (bottom). The strains were propagated in GM17, with 10 mM CaCl2 and erythromycin (2.5 μg/ml) when required, to an optical density at 600 nm (OD600nm) of ≈0.15 before the addition of phage φ31.
Isolation of ori31r recombinant phages.
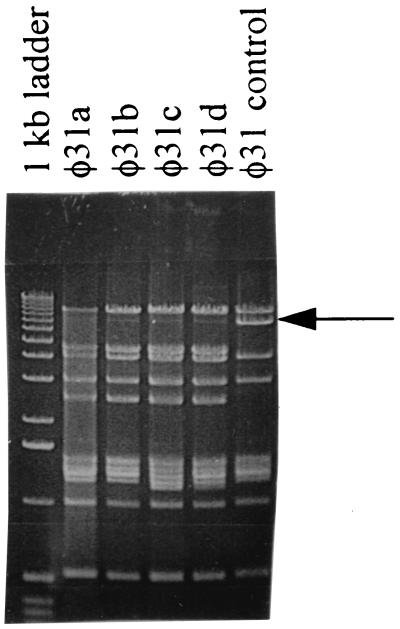
One problem encountered with the use of ori31, especially when provided on a high-copy-number vector, has been the emergence of ori31-resistant (ori31r) recombinant phages (14, 37). We investigated how readily ori31r phages emerged against the low-copy-number ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 construct. In one experiment, four small plaques of φ31 formed on NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) and two small plaques formed on NCK203 (low-copy-number ori31) were picked and analyzed. EOP assays showed that the phages from each of the plaques remained sensitive to both ori31 and ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 (data not shown). This result was not unexpected in that low-copy-number presentations of ori31 fail to select for resistant recombinant phages (37). In a second experiment, phage φ31 broth lysates were prepared with high MOIs (MOI, >2) on both NCK203 (ori31) and NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7). These lysates were then used to prepare a second set of lysates in the same manner. Interestingly, a significant number of ori31r phages [large plaques on NCK203 (ori31)] had emerged by the second pass through both NCK203 (ori31) and NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) when high MOIs were used. Characterization of genomic DNA from four of these phages isolated on NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7) by restriction analysis (Fig. 6) showed that all four had different restriction patterns from the parent phage, φ31. Interestingly, the φ31 restriction fragment encoding ori31 (E. Durmaz and T. R. Klaenhammer, Abstr. 6th Symp. Lactic Acid Bacteria, abstr. F28, 1999) was no longer present. This is likely due to a recombinational exchange of phage φ31 with host DNA (14, 37; Durmaz and Klaenhammer, Abstr. 6th Symp. Lactic Acid Bacteria) that replaces ori31 with a new origin of replication. Details of the exchange process and composition of the sequences recovered by the recombinant phages are forthcoming in another study (Durmaz and Klaenhammer, Abstr. 6th Symp. Lactic Acid Bacteria). To date, however, no anti-ORF 4Hr phages have been recovered.
FIG. 6.
HindIII restriction analysis of genomic DNA from four ori31r recombinant or mutant phages (labeled φ31a to φ31d) isolated on NCK203 (ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7). The arrow marks the band in phage φ31 containing ori31.
DISCUSSION
In this study, sequence information from a region near the late promoter and the right cohesive end of phage φ31 (51) was used to develop antisense constructs in both a high-copy-number vector and a low-copy-number explosive vector containing ori31, the putative phage φ31 origin of replication. When expressed from a strong promoter on a high-copy-number vector, none of the putative coding regions used in the antisense constructs was able to inhibit the proliferation of phage φ31. One significant barrier to the successful use of the high-copy-number strategy appeared to be that the levels of antisense RNA product expressed by the cell were not high enough to effectively compete with expression of sense mRNA generated during phage infection. Indeed, when anti-ORF 4H RNA levels were measured 40 min after phage infection, few transcripts were detected for the high-copy-number constructs (Fig. 4A). Increasing levels of anti-ORF 4H RNA later in the lytic cycle by using the phage-inducible φ31 late promoter to drive antisense expression on the high-copy-number vector also had no effect on EOP or plaque size (Table 3). These results are similar to those obtained by Chen et al. (4), who found that use of the powerful T7 promoter to drive expression of ribozyme RNA targeted to a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene did not improve the efficiency of the ribozyme in inhibiting chloramphenicol acetyltransferase activity.
To increase the ratio of antisense RNA to sense mRNA generated in the course of the phage infection, the P6::anti-ORF::TT7 cassettes were combined with ori31 on a low-copy-number vector. Upon phage infection, ori31 acts as an alternative phage origin and allows for explosive amplification of the vector, thereby increasing the dose of antisense RNA remarkably. ORFs from the late region were therefore considered the best targets since explosive expression of antisense RNA would occur in the middle and later parts of the lytic cycle. The higher level of expression which can be achieved using the explosive amplicon was clearly illustrated in previous work with a gene for β-galactosidase (lacZ.st) as a reporter (41). Significantly greater levels of β-galactosidase activity were obtained during phage φ31 infection when the P15A10 promoter::lacZ.st cassette was present on the low-copy-number vector containing ori31 rather than on a high-copy-number vector alone (2,100 Miller units versus 700 Miller units, respectively [41]). In addition to the increased dose of antisense RNA (Fig. 4A), ori31 also results in a fourfold decrease in the burst size of phage φ31, effectively lowering the levels of target sense mRNA expressed by the phage (Fig. 4B). This combination of effects (increased antisense RNA and decreased target phage RNA) retarded phage development and proved more effective than antisense constructs on the high-copy-number vector.
Successful phage inhibition with the ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 construct prompted studies into its mechanism of action. One-step growth curves showed that ori31 itself reduced the burst size fourfold, while slightly reducing the ECOI to 0.75 to 0.80. When combined with P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7, no further reduction in burst size was observed. However, the ECOI was reduced to 0.35 to 0.45, meaning only 35 to 45% of the phages could form infective centers. Therefore, while ori31 effectively decreased the number of phages released per infected cell, the antisense RNA decreased the efficiency at which phage φ31 could form infective centers in the first place. The combination of the two mechanisms was more effective than either of them alone.
While anti-ORF 4H RNA was clearly the most effective at inhibiting the proliferation of phage φ31 when combined with ori31, the mechanism behind its ability to reduce the ECOI of phage φ31 is unknown. In addition to the translation initiation region (Shine-Dalgarno and start codon), the 5′ end of the ORF 4H fragment used in the antisense construct contained the phage φ31 right cohesive end (cos). However, ORF 4H DNA alone, without the P6 promoter, had little effect on the EOP of phage φ31, confirming that the expression of anti-ORF 4H RNA was responsible for the observed phenotype, and not the presence of the cos site. ORF 4, whose function has not been determined, may encode a protein which is more critical to the development of phage φ31 than the other targets tried (ORF 3, ORF 5H, and ORF 6), or a protein which is produced in lower amounts. Therefore, decreasing its expression level below a certain threshold in a percentage of cells may have resulted in fewer centers of infection. Alternatively, since anti-ORF 4H is targeted to a polycistronic mRNA, the expression of one or more critical ORFs downstream of ORF 4 may have been affected, thereby inhibiting phage development. This explanation at first seems unlikely, since ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 3::TT7, ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 5H::TT7, and ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 6::TT7, all of which are targeted to the same polycistronic mRNA, had only a small effect, if any, on the EOP of phage φ31. However, the possibility exists that anti-ORF 4H RNA may have been better able to interact with the target mRNA, either because it was more stable or because its target was more accessible. Whichever the case, the results presented here illustrate the importance of targeting several different ORFs to determine which will be most effective at inhibiting phage proliferation. This is especially true when the function of many of the putative ORFs identified during sequencing remains unknown.
Antisense RNA may act at two different levels to negatively impact translation of the gene of interest (27). First, binding of antisense RNA to the translation initiation region may inhibit ribosome binding and subsequent translation of the message. This inhibition may also affect downstream coding regions if they are translationally coupled to the gene of interest. Second, binding of the antisense RNA may destabilize the mRNA, making it more susceptible to degradation by double-stranded RNases. Due to lack of antibodies to ORF 4 and ORF 5 gene products, the first scenario was not studied. However, some evidence does exist that anti-ORF 4H RNA may negatively impact the stability of the late mRNA containing ORF 4. As shown in Fig. 4B, the levels of both ORF 4 and ORF 5 mRNA expressed from the phage genome during infection were decreased when ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 was present. At this point, however, it is difficult to determine whether or not this decrease in mRNA is due to the antisense mechanism or to a general decrease in the number of phages present. When early- or middle-expressed ORF 1 mRNA levels were measured in a similar manner to that described for Fig. 4B, no decrease in ORF 1 mRNA levels during phage infection was observed (data not shown), even in the presence of ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7. This result suggests that reduction in ORF 4 and ORF 5 mRNA may be due at least in part to the destabilization of the late RNA transcript containing these overlapping ORFs. Further work is needed to elucidate this mechanism.
While the success of the ori31 plus P6::anti-ORF 4H::TT7 is an exciting step forward, there remain several serious challenges to overcome in the use of antisense strategies. First, as is the case for a number of the novel phage defense mechanisms in the literature, this strategy is specific for a particular phage. Since it requires both a phage φ31 origin and coding region, it would not be effective against the heterogenous population of phages which attack L. lactis. Second, few of the lactococcal phage origins, which have been identified by genome sequencing, have been shown to be as effective as ori31 or ori50 in providing phage defense or in allowing explosive replication when present on a vector (3, 53). Lastly, the appearance and subsequent proliferation of recombinant or mutant phages no longer sensitive to ori31 would limit the longevity of this phage defense system in practice, since ori31 phages were no longer inhibited by anti-ORF 4H RNA presented as the sole defense mechanism.
Despite these drawbacks, this antisense strategy has the potential to play a significant role in the arsenal of phage defense mechanisms available for L. lactis. In addition to phage origins, antisense constructs could possibly be combined with any other phage defenses that affect phage replication and/or burst size to increase the ratio of antisense RNA to target phage mRNA. The availability of a number of abortive systems which affect phage replication and/or burst size may therefore extend the utility of this strategy or other RNA-targeted strategies, such as ribozyme technology. Also, the combination of antisense constructs which target ORFs from different phases in the phage lytic cycle may prove more productive than a single antisense construct. Availability of sequencing data and the recent intense research into the molecular biology of the lactococcal bacteriophages will surely identify targets that are fairly conserved within a phage species, thereby making antisense strategies more broadly applicable.
In conclusion, we have developed an effective phage defense strategy which combines antisense technology with an explosive replicon to deliver an enhanced ratio of antisense RNA to sense mRNA at the appropriate time in the phage lytic cycle. These findings are significant, not only because they represent another hurdle to phage proliferation, but also because they offer clues in the design of more potent antisense strategies or other strategies that target RNA.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This research was supported by the Southeast Dairy Foods Research Center (project no. 5-54201 and 5-45835-06369); Rhodia, Inc.; and the USDA—NRICGP under project number 97-35503-4368.
We thank Martin Kullen, Evelyn Durmaz, and Soren Madsen for helpful discussions and for critical reading of the manuscript.
Footnotes
Paper no. FSR99-19 of the Department of Food Science, Southeast Dairy Foods Research Center, North Carolina State University, Raleigh.
REFERENCES
- 1.Alatossava T, Klaenhammer T R. Molecular characterization of three small isometric-headed bacteriophages which vary in their sensitivity to the lactococcal phage resistance plasmid pTR2030. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991;57:1346–1353. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.5.1346-1353.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Allison G E, Klaenhammer T R. Phage resistance mechanisms in lactic acid bacteria. Int Dairy J. 1998;8:207–226. [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chandry P S, Moore S C, Boyce J D, Davidson B E, Hillier A J. Analysis of the DNA sequence, gene expression, origin of replication and modular structure of the Lactococcus lactis lytic bacteriophage sk1. Mol Microbiol. 1997;26:49–64. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2958.1997.5491926.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chen H, Ferbeyre G, Cedergren R. Efficient hammerhead ribozyme and antisense RNA targeting in slow ribosome Escherichia coli mutant. Nat Biotechnol. 1997;15:432–435. doi: 10.1038/nbt0597-432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Chung D K, Chung S K, Batt C A. Antisense RNA directed against the major capsid protein of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris bacteriophage F4-1 confers partial resistance to the host. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1992;37:79–83. doi: 10.1007/BF00174207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Coakley M, Fitzgerald G F, Ross R P. Application and evaluation of the phage resistance- and bacteriocin-encoding plasmid pMRC01 for the improvement of dairy starter cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1997;63:1434–1440. doi: 10.1128/aem.63.4.1434-1440.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Coffey A, Fitzgerald G F, Daly C. Identification and characterization of a plasmid encoding abortive infection from Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis UC811. Neth Milk Dairy J. 1989;43:229–244. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Coleman J, Green P J, Inouye M. The use of RNAs complementary to specific mRNAs to regulate the expression of individual bacterial genes. Cell. 1984;37:429–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Daly C, Fitzgerald G F, Davis R. Biotechnology of lactic acid bacteria with special reference to bacteriophage resistance. Antonie Leeuwenhoek. 1996;70:99–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00395928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Dinsmore P K, Klaenhammer T R. Bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus. Mol Biotechnol. 1995;4:297–313. doi: 10.1007/BF02779022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dinsmore P K, Klaenhammer T R. Molecular characterization of a genomic region in a Lactococcus bacteriophage that is involved in its sensitivity to the phage defense mechanism AbiA. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:2949–2957. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.9.2949-2957.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Djordjevic G M, Bojovic B, Miladinov N, Topisorovic L. Cloning and molecular analysis of promoter sequences isolated from the chromosomal DNA of Lactobacillus acidophilus ATCC 4356. Can J Microbiol. 1997;43:61–69. doi: 10.1139/m97-009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Djordjevic G M, O'Sullivan D J, Walker S A, Conkling M A, Klaenhammer T R. Triggered-suicide system designed for bacteriophage defense of Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1997;179:6741–6748. doi: 10.1128/jb.179.21.6741-6748.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Durmaz E, O'Sullivan D J, Klaenhammer T R. Site-specific chromosomal disruptions of Lactococcus lactis NCK203 prevent the appearance of new recombinant lytic phage φ31.1. J Dairy Sci. 1995;78(Suppl.):109. . (Abstract D42.) [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ecker J, Davis R. Inhibition of gene expression in plant cells by expression of antisense RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:5372–5376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Forde A, Daly C, Fitzgerald G F. Identification of four phage resistance plasmids from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris HO2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1999;65:1540–1547. doi: 10.1128/aem.65.4.1540-1547.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Garbutt K C, Kraus J, Geller B L. Bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis engineered by replacement of a gene for a bacteriophage receptor. J Dairy Sci. 1997;80:1512–1519. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Garvey P, van Sinderen D, Twomey D P, Hill C, Fitzgerald G. Molecular genetics of bacteriophage and natural defense systems in the genus Lactococcus. Int Dairy J. 1995;5:905–949. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983;166:557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Harrington A, Hill C. Construction of a bacteriophage-resistant derivative of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis 425A by using the conjugal plasmid pNP40. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991;57:3405–3409. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3405-3409.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hill C, Pierce K, Klaenhammer T R. The conjugative plasmid pTR2030 encodes two bacteriophage defense mechanisms in lactococci, restriction/modification (R/M) and abortive infection (HSP+) Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989;55:2416–2419. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2416-2419.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hill C, Miller L A, Klaenhammer T R. Cloning, expression, and sequence determination of a bacteriophage fragment encoding bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1990;172:6419–6426. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6419-6426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hill C. Bacteriophage and bacteriophage resistance in lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1993;12:87–108. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hirashima A, Sawake S, Inokuchi Y, Inouye M. Engineering of the mRNA-interfering complementary RNA immune system against viral infection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1986;83:7726–7730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Hirashima A, Sawaki S, Mizuno T, Houba-Herin N, Inouye M. Artificial immune system against viral infection involving antisense RNA targeted to the 5′-terminal noncoding region of coliphage SP RNA. J Biochem. 1989;106:163–166. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Holo H, Nes I F. High-frequency transformation, by electroporation, of Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris grown with glycine in osmotically stabilized media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989;55:3119–3123. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.12.3119-3123.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Inouye M. Antisense RNA: its functions and applications in gene regulation—a review. Gene. 1988;72:25–34. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90124-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Izant J, Weintraub H. Inhibition of thymidine kinase gene expression by anti-sense RNA: a molecular approach to genetic analysis. Cell. 1984;36:1007–1115. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90050-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Kelly W, Dobson J, Jorck-Ramberg D, Fitzgerald G, Daly C. Introduction of bacteriophage resistance plasmids into commercial Lactococcus starter strains. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 1990;87:P63. . (Abstract.) [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kim J H, Batt C A. Identification of a nucleotide sequence conserved in Lactococcus lactis bacteriophages. Gene. 1991;98:95–100. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90109-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim J H, Batt C A. Antisense RNA mediated bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991;57:1039–1045. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1109-1113.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Kim S G, Bor Y-C, Batt C A. Bacteriophage resistance in Lactococcus lactis ssp. lactis using antisense ribonucleic acid. J Dairy Sci. 1992;75:1761–1767. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(92)77935-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Klaenhammer T R, Fitzgerald G F. Bacteriophage and bacteriophage resistance. In: Gasson M J, de Vos W M, editors. Genetics and biotechnology of lactic acid bacteria. Glasgow, United Kingdom: Blackie Academic and Professional; 1994. pp. 106–168. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Lubbers M W, Waterfield N R, Beresford T P J, LePage R W F, Jarvis A W. Sequencing and analysis of the prolate-headed lactococcal bacteriophage c2 and identification of the structural genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1995;61:4348–4356. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.12.4348-4356.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Moineau S, Durmaz E, Pandian S, Klaenhammer T R. Differentiation of two abortive mechanisms by using monoclonal antibodies directed toward lactococcal bacteriophage capsid proteins. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993;59:208–212. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.1.208-212.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Moineau S, Pandian S, Klaenhammer T R. Evolution of a lytic bacteriophage via DNA acquisition from the Lactococcus lactis chromosome. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1994;60:1832–1841. doi: 10.1128/aem.60.6.1832-1841.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.O'Sullivan D J, Hill C, Klaenhammer T R. Effect of increasing the copy number of bacteriophage origins of replication, in trans, on incoming-phage proliferation. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993;59:2449–2456. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2449-2456.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.O'Sullivan D J, Klaenhammer T R. High and low copy number Lactococcus shuttle cloning vectors with features for clone screening. Gene. 1993;137:227–231. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90011-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.O'Sullivan D J, Klaenhammer T R. Rapid mini-prep isolation of high-quality plasmid DNA from Lactococcus and Lactobacillus spp. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1993;59:2730–2733. doi: 10.1128/aem.59.8.2730-2733.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.O'Sullivan D J, Zagula K, Klaenhammer T R. In vivo restriction by LlaI is encoded by three genes, arranged in an operon with llaIM, on the conjugative Lactococcus plasmid pTR2030. J Bacteriol. 1995;177:134–143. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.1.134-143.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.O'Sullivan D J, Walker S A, West S G, Klaenhammer T R. Development of an expression strategy using a lytic phage to trigger explosive plasmid amplification and gene expression. Bio/Technology. 1996;14:82–87. doi: 10.1038/nbt0196-82. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.O'Sullivan D, Coffey A, Fitzgerald G F, Hill C, Ross R P. Design of a phage-insensitive lactococcal dairy starter via sequential transfer of naturally occurring conjugative plasmids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998;64:4618–4622. doi: 10.1128/aem.64.11.4618-4622.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Raya R R, Kleeman E G, Luchansky J B, Klaenhammer T R. Characterization of the temperate bacteriophage φadh and plasmid transduction in Lactobacillus acidophilus ADH. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989;55:2206–2213. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2206-2213.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Sambrook J, Fritsch E F, Maniatis T. Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. 2nd ed. Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 1989. [Google Scholar]
- 45.Schouler C, Ehrlich S D, Chopin M-C. Sequence and organization of the lactococcal prolate-headed bIL67 phage genome. Microbiology. 1994;140:3061–3069. doi: 10.1099/13500872-140-11-3061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Simons R W. Naturally occurring antisense RNA control—a brief review. Gene. 1988;72:35–44. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90125-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sing W D, Klaenhammer T R. Conjugal transfer of bacteriophage resistance determinants on pTR2030 into Streptococcus cremoris strains. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986;51:1264–1271. doi: 10.1128/aem.51.6.1264-1271.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Sing W D, Klaenhammer T R. Characteristics of phage abortion conferred in lactococci by the conjugal plasmid pTR2030. J Gen Microbiol. 1990;136:1807–1815. [Google Scholar]
- 49.Terzaghi B, Sandine W E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975;29:807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.van Sinderen D, Karsens H, Kok J, Terpstra P, Ruiters M H J, Venema G, Nauta A. Sequence analysis and molecular characterization of the temperate lactococcal bacteriophage r1t. Mol Microbiol. 1996;19:1343–1355. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1996.tb02478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Walker S A, Dombroski C S, Klaenhammer T R. Common elements regulating gene expression in temperate and lytic bacteriophages of Lactococcus species. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1998;64:1147–1152. doi: 10.1128/aem.64.3.1147-1152.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Walker S A, Klaenhammer T R. Molecular characterization of a phage-inducible middle promoter and its transcriptional activator from the lactococcal bacteriophage φ31. J Bacteriol. 1998;180:921–931. doi: 10.1128/jb.180.4.921-931.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Waterfield N R, Lubbers M W, Polzin K M, Le Page R W F, Jarvis A W. An origin of DNA replication from Lactococcus lactis bacteriophage c2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1996;62:1452–1453. doi: 10.1128/aem.62.4.1452-1453.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yanisch-Perron C, Vieira J, Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33:103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]