Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the various causes of death among patients with non-muscular invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC), non-metastatic muscle invasive bladder cancer (non-MMIBC) and metastatic bladder cancer (MBC) after diagnosis. Methods: With the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and Final Results database, patients diagnosed with bladder cancer from 2004 to 2015 were identified. All causes of death and the standardization mortality ratio (SMR) were analyzed. Results: A total of 111,784 NMIBC, 26,546 non-MIBC and 4,678 MBC patients were identified. For NMIBC patients, 44,638 patients died during the follow-up, including 20.57% of bladder cancer, 18% of other tumors and 61.36% of non-tumor diseases. Main causes of other tumors death were cancers from lung and bronchus [n=2,860, SMR: 1.56 (1.51-1.62)], pancreas [n=506, SMR: 1.15 (1.05-1.26)], and prostate [n=442, SMR: 0.62 (0.56-0.68)]. Main causes of non-tumor deaths were diseases of heart [n=10,007, SMR: 1.15 (1.13-1.17)], chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) [n=3,153, SMR: 1.54 (1.49-1.59)], cerebrovascular diseases [n=1,704, SMR: 0.96 (0.91-1)], alzheimers [n=1,211, SMR: 0.87 (0.82-0.92)] and diabetes mellitus [n=1,047, SMR: 1.19 (1.12-1.27)]. Among the 18829 deaths in non-MMIBC patients, 62.65% patients died of bladder cancer, 11.08% of other tumors and 26.39% of non-tumor causes. Main deaths of other cancers were tumors from lung and bronchus [n=435, SMR: 1.83 (1.66-2.01)], prostate [n=192, SMR: 2.21 (1.91-2.54)]. Main causes of non-tumor death were diseases of heart [n=1717, SMR: 1.56 (1.49-1.64)], COPD [n=561, SMR: 2.18 (2.01-2.37)], and cerebrovascular diseases [n=290, SMR: 1.28 (1.14-1.44)]. Among the 4,392 deaths of MBC patients, 3,486 (79.37%) died of bladder cancer. Main cause of other deaths included diseases of heart (n=128) and prostate cancer (n=57). Conclusion: For NMIBC patients, leading causes of death were diseases of heart, COPD, lung and bronchus cancer, cerebrovascular diseases, Alzheimer’s, and diabetes mellitus. Leading causes of deaths for non-MMIBE patients were bladder cancer, diseases of heart, COPD, lung and bronchus cancer, cerebrovascular diseases and prostate cancer. Main causes of death for MBC patients were bladder cancer itself. Our results of all causes of death and mortality risks provided useful information for bladder cancer patients.
Keywords: Bladder cancer, causes of death, SMR, SEER
Introduction
Bladder cancer ranks ninth among the most common cancers in the world, and the incidence of bladder cancer is the highest in countries in Southern Europe, Western Europe, North America, North Africa, and West Asia [1]. According to recent statistics, the number of new cases of bladder cancer in the United States in 2021 was 83,730, and the death in these cases was 17,200 [2]. Thus, it seriously threatens the life and health of patients and has also brought huge economic and social burdens.
Tumors isolated on the urothelium (Ta stage) and lamina propria (T1 stage) are considered to be non-muscle invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC). Their treatment is different from tumors of T2-4 stages which are called muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC) [3]. NMIBC represents approximately 70% of organ-confined bladder cancer. The standard treatment for NMIBC is transurethral resection of bladder tumor (TURBT) with risk-based recommendations regarding intravesical therapy [4]. Kong et al pointed out that even 20 years after the diagnosis of primary bladder cancer, the probability of death from primary bladder cancer was still observed as an important cause of death (the cancer itself was still observed as an important cause of death), but the heart and non-malignant lung causes accounted for a large proportion of deaths among long-term bladder cancer survivors [5]. Muscle-invasive bladder cancer represents the remaining 30% of local bladder disease [6]. The standard therapy for MIBC (T2-T4) is radical cystectomy (RC) with bilateral pelvic lymph node dissection (PLND) [7]. Although bladder cancer-specific deaths accounted for a relatively high proportion of MIBC, there are still a large proportion of non-bladder cancer-specific deaths [8].
Although lots of studies have evaluated the prognosis of patients with bladder cancer, most of them focused on the tumor itself and the deaths it caused. Few studies assessed other deaths during the survivorship. As other causes of death including other tumors and non-tumor causes accounted for a considerable proportion of all deaths, it’s worthy of attention. To our knowledge, there is not a study that evaluated the other causes of deaths among NMIBC, non-MIBC and MBC patients. The National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) 18 registries collected cancer data that covers approximately 28% of the United States population from 2004 to 2015 [9]. This demonstrated that the regional data reported by SEER can represent the US population and can be generalized. The general population data could be obtained from the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Therefore, we evaluated all causes of death including bladder cancer, other tumors and non-tumor causes, and calculated mortality risk of each cause comparing with the general population.
Materials and methods
Data source
Data for bladder cancer patients came from the National Cancer Institute’s Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) 18 registries. The SEER*Stat software version 8.3.9 (National Cancer Institute, USA) was utilized to access the data from the SEER database. Meanwhile, the data for the general population came from the United States CDC. Our data was de-identified and not considered as human subject research. Therefore, approval by the institutional review board was not required.
Patients
Patients who were histologically diagnosed with bladder cancer as the first primary tumor and had clear TNM stages and follow-up time were identified. The living status (alive or died), the alive time after diagnosis and detailed causes of death in these patients were clearly known. The last follow-up time was December 31, 2015. According to the definition of the National Cancer Institute, survival included any patients undergoing treatment and those after treatment [14]. We divided these patients into NMIBC, non-MMIBC and MBC according to the depth of tumor invasion and aggressiveness and classified and analyzed their causes of death.
Study variables
The following variables were collected, including age (15-44 years, 45-54 years, 55-64 years, 65-74 years and >75 years), sex (male and female), race (white, black, American Indian/Alaska Native and Asian or Pacific Islander), differentiation (grade l, ll, lll, and lV), pathology, surgical treatments (local tumor excision, partial cystectomy, radical cystectomy, other surgery, and no surgical treatments), chemotherapy (yes, no/unknown), and radiation (yes, no/unknown). The causes of deaths during the whole follow-up and different periods (<1 year, 1-5 years, 5-10 years, and >10 years after diagnosis) and related SMRs were regarded as the main outcomes.
Statistical analyses
For the baseline characteristics of patients with different stages of bladder cancer, we calculated the number of all causes of deaths stratified by age, sex, race, differentiation, pathology, treatments. The causes of death including bladder cancer, other tumors, and non-tumor were analyzed and the number of cases was calculated among patients with NMIBC, non-MMIBC and MBC. The SMR of different reasons for death were also calculated by comparing the observed number of deaths to the expected number. The expected number of deaths was based on the total number of patient-years and the incidence of the general population. The statistical significance of SMR was based on the P-value generated by the two-sided test. All these analyses were performed using SEER*Stat version 8.3.9. Pie charts of the proportion of different causes of death were drawn with Microsoft Excel 2016.
Results
Baseline characteristics
A total of 143,008 patients diagnosed with bladder cancer were extracted from the SEER database. 78.17% of all patients were with NMIBC, 18.56% with non-MMIBC, and 3.27% with MBC. 67,859 (47.45%) died during follow-up, the number of male patients exceeded that of females (75.96%), most patients were white (89.99%), transitional cell carcinoma was the main pathological type group (76.71%), but squamous cell carcinoma had the highest risk of death. 94.04% of people received surgery, 21.16% received chemotherapy, and 81.64% received radiotherapy. Among all included patients, a total of 67,859 patients (47.45%) died during the follow-up period. NMIBC deaths most occurred at 5-10 years after diagnosis (31.62%). Most deaths from non-MMIBC (38.82%) and MBC (41.55%) occurred within 1 year after diagnosis. NMIBC and non-MMIBC total number and death toll baseline information is reported in Table 1 and the information about MBC is reported in Table 2.
Table 1.
Baseline characteristics of patients with non-muscular invasive bladder cancer (NMIBC) and non-metastatic muscle invasive bladder cancer (non-MMIBC)
| Variables | Total | <1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | 5-10 years | >10 year | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | |
| NMIBC | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 111784 | 44638 | 1.40# (1.38/1.41) | 111784 | 5230 | 1.45# (1.41/1.49) | 106181 | 11700 | 1.43# (1.4/1.45) | 93500 | 9802 | 1.40# (1.38/1.43) | 68316 | 14117 | 1.36# (1.34-1.38) | 24255 | 3789 | 1.36# (1.31-1.4) |
| Age | ||||||||||||||||||
| 15-54 years | 12617 | 1394 | 2.03# (1.93-2.14) | 12617 | 110 | 2.36# (1.94-2.85) | 12431 | 314 | 2.54# (2.27-2.84) | 11931 | 269 | 2.14# (1.9-2.42) | 9850 | 502 | 1.85# (1.69-2.02) | 4804 | 199 | 1.67# (1.45-1.92) |
| 55-64 years | 24077 | 4840 | 1.73# (1.68-1.78) | 24077 | 387 | 1.80# (1.63-1.99) | 23590 | 1079 | 1.94# (1.83-2.06) | 22251 | 1023 | 1.88# (1.77-2) | 17429 | 1764 | 1.66# (1.58-1.74) | 7372 | 587 | 1.40# (1.29-1.51) |
| 65-74 years | 33685 | 11588 | 1.50# (1.47-1.53) | 33685 | 957 | 1.50# (1.4-1.59) | 32644 | 2645 | 1.62# (1.56-1.69) | 29747 | 2511 | 1.62# (1.55-1.68) | 21895 | 4101 | 1.45# (1.4-1.49) | 7561 | 1374 | 1.28# (1.21-1.35) |
| 75-84 years | 29770 | 17497 | 1.20# (1.18-1.21) | 29770 | 1969 | 1.40# (1.33-1.46) | 27718 | 4514 | 1.27# (1.23-1.31) | 22996 | 3849 | 1.14# (1.11-1.18) | 15699 | 5740 | 1.11# (1.08-1.14) | 4137 | 1425 | 1.29# (1.22-1.36) |
| 85+ years | 11621 | 9319 | 1.52# (1.49-1.55) | 11621 | 1807 | 1.40# (1.34-1.47) | 9784 | 3148 | 1.35# (1.3-1.4) | 6562 | 2150 | 1.55# (1.49-1.62) | 3431 | 2010 | 1.93# (1.84-2.01) | 376 | 204 | 2.97# (2.58-3.41) |
| Sex | ||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 86021 | 34976 | 1.39# (1.38-1.4) | 86021 | 3855 | 1.34# (1.3-1.39) | 81904 | 9224 | 1.41# (1.39-1.44) | 71967 | 7894 | 1.43# (1.4-1.46) | 52204 | 11098 | 1.37# (1.34-1.4) | 18341 | 2905 | 1.34# (1.29-1.39) |
| Female | 25763 | 9662 | 1.42# (1.39-1.45) | 25763 | 1375 | 1.87# (1.77-1.97) | 24277 | 2476 | 1.48# (1.42-1.54) | 21533 | 1908 | 1.30# (1.24-1.36) | 16112 | 3019 | 1.33# (1.28-1.37) | 5914 | 884 | 1.41# (1.32-1.5) |
| Race | ||||||||||||||||||
| White | 101420 | 40699 | 1.37# (1.36-1.38) | 101420 | 4644 | 1.39# (1.35-1.43) | 96470 | 10617 | 1.40# (1.37-1.42) | 85023 | 8953 | 1.38# (1.35-1.41) | 62291 | 12998 | 1.34# (1.32-1.37) | 22171 | 3487 | 1.34# (1.3-1.39) |
| Black | 5440 | 2320 | 1.72# (1.65-1.79) | 5440 | 373 | 2.27# (2.04-2.51) | 5042 | 654 | 1.82# (1.68-1.96) | 4339 | 497 | 1.70# (1.56-1.86) | 3078 | 624 | 1.48# (1.37-1.61) | 1052 | 172 | 1.54# (1.32-1.79) |
| 274 | 111 | 3.60# (2.96-4.33) | 274 | 18 | 4.71# (2.79-7.44) | 255 | 25 | 2.93# (1.9-4.32) | 223 | 26 | 4.22# (2.76-6.19) | 148 | 30 | 3.12# (2.11-4.46) | 53 | 12 | 4.40# (2.27-7.68) | |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 4650 | 1508 | 1.72# (1.63-1.81) | 4650 | 195 | 1.97# (1.7-2.26) | 4414 | 404 | 1.79# (1.62-1.97) | 3915 | 326 | 1.69# (1.51-1.89) | 2799 | 465 | 1.66# (1.51-1.81) | 979 | 118 | 1.50# (1.24-1.79) |
| Differentiation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Grade I | 17233 | 6102 | 1.20# (1.17-1.24) | 17233 | 505 | 1.02 (0.93-1.11) | 16657 | 1367 | 1.16# (1.1-1.23) | 15161 | 1315 | 1.21# (1.15-1.28) | 12187 | 2182 | 1.25# (1.2-1.3) | 4981 | 733 | 1.31# (1.21-1.41) |
| Grade II | 33904 | 12445 | 1.22# (1.2-1.25) | 33904 | 1069 | 1.06 (1-1.13) | 32737 | 2721 | 1.14# (1.1-1.18) | 29730 | 2625 | 1.25# (1.21-1.3) | 21816 | 4527 | 1.27# (1.24-1.31) | 9767 | 1503 | 1.34# (1.28-1.41) |
| Grade III | 14851 | 7448 | 1.60# (1.56-1.64) | 14851 | 1044 | 1.96# (1.84-2.08) | 13757 | 1989 | 1.71# (1.63-1.78) | 11682 | 1492 | 1.49# (1.42-1.57) | 9074 | 2280 | 1.51# (1.44-1.57) | 3553 | 643 | 1.45# (1.34-1.56) |
| Grade IV | 23627 | 10430 | 1.67# (1.64-1.71) | 23627 | 1525 | 1.82# (1.73-1.91) | 22013 | 3318 | 1.82# (1.76-1.88) | 18446 | 2378 | 1.71# (1.64-1.78) | 11443 | 2666 | 1.48# (1.43-1.54) | 3359 | 543 | 1.41# (1.29-1.53) |
| T stage | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ta | 71504 | 25213 | 1.21# (1.19-1.22) | 71504 | 2154 | 0.97 (0.93-1.01) | 69140 | 6022 | 1.15# (1.12-1.18) | 62475 | 5701 | 1.24# (1.21-1.27) | 46328 | 8868 | 1.27# (1.25-1.3) | 16766 | 2468 | 1.30# (1.25-1.35) |
| Tis | 7385 | 3205 | 1.37# (1.33-1.42) | 7385 | 315 | 1.26# (1.13-1.41) | 7046 | 780 | 1.36# (1.26-1.45) | 6215 | 706 | 1.42# (1.32-1.53) | 4634 | 1107 | 1.41# (1.33-1.49) | 1753 | 297 | 1.31# (1.16-1.46) |
| T1 | 31804 | 15561 | 1.84# (1.81-1.86) | 31804 | 2524 | 2.31# (2.22-2.4) | 29146 | 4707 | 2.03# (1.97-2.09) | 24159 | 3289 | 1.78# (1.72-1.85) | 16920 | 4043 | 1.57# (1.53-1.62) | 5608 | 998 | 1.53# (1.43-1.62) |
| Pathology | ||||||||||||||||||
| Papillary transitional cell carcinoma | 92360 | 35229 | 1.32# (1.3-1.33) | 92360 | 3451 | 1.17# (1.13-1.21) | 88603 | 8967 | 1.32# (1.29-1.34) | 78818 | 7911 | 1.35# (1.32-1.38) | 57931 | 11690 | 1.33# (1.31-1.36) | 20886 | 3210 | 1.35# (1.3-1.39) |
| Transitional cell carcinoma | 16766 | 7949 | 1.76# (1.72-1.79) | 16766 | 1307 | 2.29# (2.17-2.42) | 15409 | 2352 | 1.93# (1.85-2.01) | 12913 | 1681 | 1.70# (1.62-1.78) | 9081 | 2110 | 1.51# (1.44-1.57) | 2881 | 499 | 1.43# (1.31-1.56) |
| Papillary carcinoma | 527 | 234 | 1.40# (1.22-1.59) | 527 | 24 | 1.46 (0.93-2.17) | 502 | 57 | 1.53# (1.16-1.98) | 443 | 38 | 1.19 (0.84-1.64) | 354 | 82 | 1.37# (1.09-1.7) | 181 | 33 | 1.50# (1.03-2.1) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 185 | 146 | 5.04# (4.26-5.93) | 185 | 76 | 14.33# (11.29-17.94) | 107 | 36 | 4.52# (3.17-6.26) | 69 | 14 | 2.52# (1.38-4.23) | 46 | 16 | 2.17# (1.24-3.52) | 14 | 4 | 1.46 (0.4-3.75) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 183 | 95 | 2.48# (2-3.03) | 183 | 26 | 4.77# (3.12-6.99) | 155 | 23 | 2.24# (1.42-3.37) | 132 | 25 | 3.33# (2.16-4.92) | 92 | 17 | 1.44 (0.84-2.31) | 26 | 4 | 1.18 (0.32-3.01) |
| Surgery | ||||||||||||||||||
| Local tumor excision | 102721 | 40681 | 1.37# (1.36-1.39) | 102721 | 4424 | 1.33# (1.29-1.37) | 97966 | 10690 | 1.41# (1.38-1.43) | 86393 | 8986 | 1.39# (1.36-1.42) | 63073 | 13046 | 1.36# (1.33-1.38) | 22486 | 3535 | 1.36# (1.32-1.41) |
| Cystectomy | 2428 | 947 | 1.72# (1.62-1.84) | 2428 | 127 | 2.26# (1.88-2.69) | 2286 | 232 | 1.78# (1.56-2.02) | 2027 | 207 | 1.74# (1.51-1.99) | 1502 | 312 | 1.64# (1.46-1.83) | 508 | 69 | 1.30# (1.01-1.65) |
| other | 6635 | 3010 | 1.66# (1.6-1.72) | 6635 | 679 | 3.02# (2.8-3.26) | 5929 | 778 | 1.65# (1.53-1.77) | 5080 | 609 | 1.55# (1.43-1.68) | 3741 | 759 | 1.30# (1.21-1.4) | 1261 | 185 | 1.32# (1.14-1.52) |
| Chemotherapy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 16762 | 5397 | 1.38# (1.34-1.41) | 16762 | 556 | 1.13# (1.04-1.22) | 16145 | 1650 | 1.42# (1.36-1.49) | 14317 | 1335 | 1.40# (1.33-1.48) | 9154 | 1579 | 1.40# (1.34-1.47) | 2120 | 277 | 1.43# (1.26-1.6) |
| No/Unknown | 95022 | 39241 | 1.40# (1.39-1.41) | 95022 | 4674 | 1.50# (1.46-1.55) | 90036 | 10050 | 1.43# (1.4-1.46) | 79183 | 8467 | 1.40# (1.37-1.43) | 59162 | 12538 | 1.35# (1.33-1.38) | 22135 | 3512 | 1.35# (1.31-1.4) |
| Radiation | ||||||||||||||||||
| yes | 111006 | 43999 | 1.38# (1.37-1.4) | 111006 | 5037 | 1.41# (1.37-1.45) | 105599 | 11465 | 1.41# (1.38-1.43) | 93155 | 9698 | 1.40# (1.37-1.42) | 68114 | 14026 | 1.36# (1.33-1.38) | 24200 | 3773 | 1.36# (1.31-1.4) |
| No/Unknown | 778 | 639 | 3.68# (3.4-3.98) | 778 | 193 | 5.23# (4.52-6.02) | 582 | 235 | 4.10# (3.59-4.66) | 345 | 104 | 3.04# (2.48-3.68) | 202 | 91 | 2.38# (1.92-2.92) | 55 | 16 | 2.34# (1.34-3.8) |
| non-MMIBC | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | 26546 | 18829 | 4.67# (4.6-4.73) | 26546 | 7309 | 9.62# (9.4-9.84) | 19096 | 6948 | 6.07# (5.93-6.21) | 11935 | 2159 | 2.72# (2.61-2.84) | 7808 | 1970 | 1.85# (1.77-1.93) | 2511 | 443 | 1.64# (1.49-1.8) |
| Age | ||||||||||||||||||
| 15-54 years | 2535 | 1331 | 15.54# (14.72-16.4) | 2535 | 410 | 44.62# (40.4-49.15) | 2116 | 593 | 32.27# (29.73-34.98) | 1485 | 170 | 10.96# (9.38-12.74) | 1086 | 126 | 4.20# (3.5-5) | 491 | 32 | 2.54# (1.74-3.59) |
| 55-64 years | 5496 | 3166 | 8.56# (8.26-8.86) | 5496 | 975 | 21.73# (20.38-23.13) | 4482 | 1379 | 16.01# (15.17-16.88) | 3046 | 379 | 5.35# (4.82-5.91) | 2175 | 342 | 2.75# (2.46-3.05) | 811 | 91 | 2.09# (1.68-2.57) |
| 65-74 years | 7542 | 4984 | 5.21# (5.06-5.35) | 7542 | 1652 | 13.00# (12.38-13.65) | 5849 | 1924 | 8.13# (7.77-8.5) | 3870 | 631 | 3.37# (3.11-3.65) | 2510 | 621 | 2.05# (1.89-2.22) | 777 | 156 | 1.50# (1.28-1.76) |
| 75-84 years | 7463 | 6078 | 3.43# (3.34-3.51) | 7463 | 2539 | 8.78# (8.44-9.13) | 4889 | 2041 | 4.17# (3.99-4.35) | 2802 | 678 | 1.79# (1.66-1.93) | 1713 | 682 | 1.33# (1.23-1.43) | 391 | 138 | 1.33# (1.12-1.58) |
| 85+ years | 3510 | 3270 | 3.85# (3.72-3.99) | 3510 | 1733 | 5.98# (5.7-6.27) | 1760 | 1011 | 3.22# (3.02-3.42) | 732 | 301 | 2.12# (1.89-2.37) | 324 | 199 | 2.07# (1.79-2.38) | 41 | 26 | 3.79# (2.48-5.55) |
| Sex | ||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 19317 | 13457 | 4.36# (4.29-4.44) | 19317 | 4872 | 8.57# (8.33-8.81) | 14353 | 5123 | 5.82# (5.67-5.99) | 9068 | 1619 | 2.65# (2.53-2.79) | 5958 | 1504 | 1.84# (1.75-1.93) | 1918 | 339 | 1.63# (1.46-1.81) |
| Female | 7229 | 5372 | 5.65# (5.5-5.81) | 7229 | 2437 | 12.74# (12.24-13.26) | 4743 | 1825 | 6.87# (6.56-7.2) | 2867 | 540 | 2.94# (2.7-3.2) | 1850 | 466 | 1.88# (1.71-2.06) | 593 | 104 | 1.67# (1.37-2.03) |
| Race | ||||||||||||||||||
| White | 23280 | 16527 | 4.50# (4.43-4.57) | 23280 | 6381 | 9.27# (9.05-9.5) | 16805 | 6047 | 5.81# (5.67-5.96) | 10581 | 1921 | 2.66# (2.54-2.78) | 6924 | 1783 | 1.83# (1.74-1.91) | 2220 | 395 | 1.60# (1.45-1.77) |
| Black | 1961 | 1503 | 6.63# (6.3-6.98) | 1961 | 629 | 13.42# (12.39-14.51) | 1319 | 585 | 8.63# (7.94-9.36) | 723 | 141 | 3.16# (2.66-3.73) | 465 | 120 | 2.25# (1.86-2.69) | 135 | 28 | 2.02# (1.34-2.92) |
| American Indian-Alaska Native | 106 | 76 | 15.66# (12.34-19.6) | 106 | 35 | 26.84# (18.69-37.32) | 70 | 29 | 17.21# (11.52-24.71) | 40 | 6 | 7.25# (2.66-15.77) | 24 | 6 | 6.34# (2.33-13.79) | 9 | 0 | 0 (0-41.37) |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 1199 | 723 | 5.55# (5.16-5.97) | 1199 | 264 | 11.19# (9.88-12.63) | 902 | 287 | 8.20# (7.28-9.21) | 591 | 91 | 3.59# (2.89-4.41) | 395 | 61 | 1.66# (1.27-2.14) | 147 | 20 | 2.09# (1.27-3.22) |
| Differentiation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Grade I | 316 | 196 | 3.05# (2.64-3.51) | 316 | 66 | 8.11# (6.27-10.32) | 247 | 58 | 3.86# (2.93-4.99) | 187 | 20 | 1.5 (0.92-2.32) | 146 | 41 | 1.89# (1.35-2.56) | 50 | 11 | 1.83 (0.91-3.27) |
| Grade II | 1473 | 1007 | 4.09# (3.84-4.35) | 1473 | 362 | 9.44# (8.5-10.47) | 1102 | 313 | 4.84# (4.32-5.41) | 775 | 145 | 2.99# (2.52-3.52) | 546 | 152 | 2.13# (1.8-2.49) | 197 | 35 | 1.51# (1.05-2.1) |
| Grade III | 8222 | 6220 | 4.71# (4.59-4.83) | 8222 | 2410 | 10.06# (9.66-10.47) | 5768 | 2252 | 6.46# (6.19-6.73) | 3456 | 663 | 2.66# (2.46-2.87) | 2486 | 706 | 1.87# (1.74-2.02) | 977 | 189 | 1.77# (1.53-2.04) |
| Grade IV | 14765 | 10146 | 4.67# (4.58-4.76) | 14765 | 3886 | 9.21# (8.92-9.5) | 10809 | 3889 | 6.05# (5.86-6.24) | 6802 | 1199 | 2.76# (2.61-2.92) | 4188 | 982 | 1.80# (1.69-1.91) | 1199 | 190 | 1.51# (1.3-1.74) |
| T | ||||||||||||||||||
| T2a | 4651 | 2918 | 3.57# (3.44-3.7) | 4651 | 962 | 6.52# (6.11-6.94) | 3673 | 1067 | 4.36# (4.1-4.63) | 2562 | 411 | 2.38# (2.15-2.62) | 1685 | 386 | 1.86# (1.68-2.06) | 444 | 92 | 2.01# (1.62-2.47) |
| T2b | 3899 | 2622 | 4.08# (3.93-4.24) | 3899 | 960 | 8.49# (7.96-9.05) | 2911 | 959 | 5.67# (5.31-6.04) | 1908 | 312 | 2.51# (2.24-2.81) | 1325 | 304 | 1.67# (1.49-1.87) | 486 | 87 | 1.62# (1.3-2) |
| T3a | 3016 | 2116 | 5.01# (4.8-5.23) | 3016 | 666 | 9.65# (8.93-10.41) | 2340 | 894 | 7.90# (7.39-8.44) | 1426 | 257 | 2.98# (2.63-3.37) | 939 | 249 | 2.01# (1.77-2.28) | 288 | 50 | 1.63# (1.21-2.15) |
| T3b | 1552 | 1163 | 6.48# (6.12-6.87) | 1552 | 463 | 13.38# (12.19-14.66) | 1084 | 494 | 10.17# (9.29-11.11) | 581 | 90 | 2.63# (2.11-3.23) | 371 | 97 | 1.92# (1.55-2.34) | 102 | 19 | 1.68# (1.01-2.62) |
| T4a | 3076 | 2514 | 7.19# (6.92-7.48) | 3076 | 1106 | 14.83# (13.97-15.73) | 1950 | 931 | 9.28# (8.69-9.89) | 1002 | 258 | 3.92# (3.46-4.43) | 615 | 188 | 2.16# (1.87-2.5) | 216 | 31 | 1.42 (0.96-2.01) |
| T4b | 655 | 599 | 24.19# (22.29-26.21) | 655 | 396 | 42.31# (38.24-46.69) | 252 | 167 | 23.93# (20.43-27.84) | 81 | 22 | 6.85# (4.29-10.36) | 50 | 13 | 3.23# (1.72-5.53) | 19 | 1 | 0.84 (0.02-4.71) |
| N | ||||||||||||||||||
| N0 | 22110 | 15233 | 4.17# (4.1-4.23) | 22110 | 5827 | 8.69# (8.47-8.92) | 16166 | 5371 | 5.19# (5.05-5.33) | 10613 | 1844 | 2.54# (2.43-2.66) | 7033 | 1782 | 1.82# (1.74-1.91) | 2248 | 409 | 1.66# (1.5-1.83) |
| N1 | 2066 | 1605 | 8.52# (8.11-8.95) | 2066 | 608 | 15.56# (14.35-16.85) | 1450 | 715 | 13.52# (12.55-14.55) | 720 | 164 | 4.80# (4.09-5.59) | 440 | 101 | 2.09# (1.71-2.55) | 160 | 17 | 1.21 (0.71-1.94) |
| N2 | 1823 | 1527 | 12.51# (11.89-13.15) | 1823 | 645 | 19.95# (18.44-21.55) | 1168 | 704 | 20.00# (18.55-21.53) | 449 | 114 | 5.37# (4.43-6.45) | 245 | 56 | 2.07# (1.57-2.69) | 70 | 8 | 1.27 (0.55-2.5) |
| N3 | 69 | 62 | 14.70# (11.27-18.85) | 69 | 29 | 22.08# (14.79-31.71) | 40 | 26 | 17.87# (11.67-26.18) | 14 | 5 | 6.39# (2.07-14.91) | 3 | 2 | 3 (0.36-10.85) | 0 | 0 | 0 (0-0) |
| Pathology | ||||||||||||||||||
| Transitional cell carcinoma | 14794 | 10692 | 5.02# (4.93-5.12) | 14794 | 4321 | 10.29# (9.99-10.6) | 10400 | 4026 | 6.68# (6.48-6.89) | 6252 | 1114 | 2.70# (2.54-2.86) | 4089 | 1006 | 1.82# (1.71-1.94) | 1305 | 225 | 1.58# (1.38-1.81) |
| Papillary transitional cell carcinoma | 8540 | 5761 | 3.69# (3.6-3.79) | 8540 | 1821 | 6.69# (6.39-7) | 6671 | 2166 | 4.82# (4.62-5.03) | 4435 | 814 | 2.59# (2.42-2.78) | 2921 | 778 | 1.86# (1.73-1.99) | 961 | 182 | 1.72# (1.48-1.99) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 765 | 615 | 7.66# (7.07-8.29) | 765 | 374 | 23.87# (21.51-26.41) | 385 | 147 | 7.92# (6.69-9.31) | 237 | 36 | 2.31# (1.62-3.2) | 173 | 51 | 2.12# (1.58-2.79) | 52 | 7 | 1.09 (0.44-2.24) |
| Small cell carcinoma | 421 | 317 | 6.44# (5.75-7.19) | 421 | 144 | 13.90# (11.72-16.37) | 276 | 119 | 8.74# (7.24-10.46) | 152 | 29 | 3.16# (2.11-4.53) | 95 | 22 | 1.64# (1.03-2.49) | 27 | 3 | 1.13 (0.23-3.3) |
| Transitional cell carcinoma, spindle cell | 263 | 194 | 7.43# (6.42-8.55) | 263 | 114 | 21.65# (17.86-26.01) | 147 | 55 | 7.32# (5.52-9.53) | 90 | 12 | 2.22# (1.15-3.89) | 65 | 11 | 1.72 (0.86-3.07) | 15 | 2 | 1.29 (0.16-4.65) |
| Surgery | ||||||||||||||||||
| Partial cystectomy | 1179 | 713 | 3.15# (2.92-3.39) | 1179 | 186 | 5.38# (4.64-6.21) | 991 | 279 | 4.52# (4-5.08) | 699 | 116 | 2.35# (1.94-2.81) | 477 | 107 | 1.66# (1.36-2) | 145 | 25 | 1.56# (1.01-2.3) |
| Radical cystectomy | 7360 | 4668 | 3.89# (3.78-4.01) | 7360 | 1335 | 8.81# (8.34-9.29) | 5992 | 1830 | 6.60# (6.3-6.91) | 4107 | 596 | 2.53# (2.33-2.74) | 3063 | 714 | 1.74# (1.61-1.87) | 1195 | 193 | 1.56# (1.35-1.8) |
| Other therapy | 14166 | 11294 | 5.20# (5.11-5.3) | 14166 | 5101 | 10.13# (9.85-10.41) | 8983 | 3881 | 5.75# (5.58-5.94) | 4998 | 1170 | 2.86# (2.7-3.03) | 3028 | 957 | 2.00# (1.87-2.13) | 897 | 185 | 1.77# (1.52-2.04) |
| Chemotherapy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 10905 | 7181 | 5.11# (4.99-5.23) | 10905 | 2124 | 8.11# (7.77-8.46) | 8740 | 3320 | 7.71# (7.45-7.98) | 5322 | 900 | 3.08# (2.88-3.28) | 3165 | 727 | 2.09# (1.94-2.25) | 783 | 110 | 1.54# (1.26-1.85) |
| No/Unknown | 15641 | 11648 | 4.43# (4.35-4.51) | 15641 | 5185 | 10.41# (10.13-10.7) | 10356 | 3628 | 5.08# (4.91-5.25) | 6613 | 1259 | 2.51# (2.38-2.66) | 4643 | 1243 | 1.73# (1.63-1.83) | 1728 | 333 | 1.68# (1.5-1.87) |
| Radiation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 4693 | 3858 | 5.02# (4.86-5.18) | 4693 | 1428 | 7.50# (7.12-7.9) | 3245 | 1587 | 6.15# (5.85-6.46) | 1628 | 448 | 3.02# (2.75-3.31) | 887 | 351 | 2.34# (2.1-2.6) | 182 | 44 | 1.95# (1.42-2.62) |
| No/Unknown | 21853 | 14971 | 4.58# (4.51-4.66) | 21853 | 5881 | 10.33# (10.06-10.59) | 15851 | 5361 | 6.04# (5.88-6.21) | 10307 | 1711 | 2.65# (2.53-2.78) | 6921 | 1619 | 1.77# (1.68-1.85) | 2329 | 399 | 1.61# (1.46-1.78) |
NMIBC: Non-muscular invasive bladder cancer; non-MMIBC: non-metastatic muscle invasive bladder cancer; SMR: Standard Mortality Ratio;
significant difference.
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of patients with metastatic bladder cancer
| Variables | Total | <6 m | 6 m-1 year | 1-3 years | years | >5 years | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | Patients | Deaths | SMR | |
| MBC | 4678 | 4392 | 27.13# (26.33-27.94) | 4678 | 1825 | 47.67# (45.51-49.91) | 2823 | 1193 | 37.71# (35.6-39.91) | 1616 | 1159 | 24.63# (23.24-26.09) | 426 | 153 | 7.67# (6.5-8.98) | 177 | 62 | 2.48# (1.9-3.18) |
| Age | ||||||||||||||||||
| 15-54 years | 593 | 538 | 120.08# (110.14-130.67) | 593 | 167 | 231.13# (197.4-268.96) | 420 | 155 | 207.00# (175.69-242.27) | 261 | 187 | 152.63# (131.54-176.14) | 68 | 19 | 32.74# (19.71-51.13) | 33 | 10 | 8.31# (3.98-15.28) |
| 55-64 years | 1133 | 1046 | 59.56# (56-63.28) | 1133 | 364 | 115.78# (104.19-128.3) | 766 | 310 | 100.25# (89.4-112.05) | 452 | 328 | 66.35# (59.36-73.93) | 117 | 37 | 16.78# (11.82-23.14) | 53 | 7 | 1.68 (0.67-3.45) |
| 65-74 years | 1327 | 1248 | 33.67# (31.82-35.59) | 1327 | 494 | 66.91# (61.14-73.08) | 825 | 345 | 50.55# (45.36-56.18) | 476 | 336 | 29.40# (26.34-32.71) | 133 | 55 | 11.72# (8.83-15.25) | 46 | 18 | 2.67# (1.58-4.22) |
| 75-84 years | 1156 | 1105 | 17.02# (16.03-18.05) | 1156 | 518 | 35.69# (32.69-38.9) | 631 | 286 | 22.36# (19.84-25.11) | 345 | 249 | 12.66# (11.14-14.33) | 89 | 34 | 3.95# (2.73-5.51) | 34 | 18 | 1.93# (1.14-3.04) |
| 85+ years | 469 | 455 | 12.02# (10.94-13.18) | 469 | 282 | 22.52# (19.97-25.31) | 181 | 97 | 11.85# (9.61-14.46) | 82 | 59 | 6.03# (4.59-7.78) | 19 | 8 | 2.07 (0.89-4.08) | 11 | 9 | 2.57# (1.17-4.87) |
| Sex | ||||||||||||||||||
| Male | 3294 | 3074 | 25.90# (25-26.84) | 3294 | 1223 | 43.42# (41.02-45.92) | 2050 | 859 | 36.32# (33.93-38.83) | 1180 | 841 | 24.54# (22.91-26.26) | 316 | 110 | 7.88# (6.47-9.49) | 136 | 41 | 2.20# (1.58-2.99) |
| Female | 1384 | 1318 | 30.49# (28.87-32.18) | 1384 | 602 | 59.50# (54.84-64.45) | 773 | 334 | 41.82# (37.46-46.56) | 436 | 318 | 24.89# (22.23-27.78) | 110 | 43 | 7.18# (5.19-9.67) | 41 | 21 | 3.31# (2.05-5.05) |
| Race | ||||||||||||||||||
| White | 3988 | 3753 | 26.28# (25.44-27.13) | 3988 | 1535 | 46.08# (43.8-48.44) | 2428 | 1020 | 36.58# (34.37-38.9) | 1398 | 1010 | 24.25# (22.78-25.8) | 361 | 133 | 7.58# (6.34-8.98) | 147 | 55 | 2.45# (1.85-3.19) |
| Black | 479 | 454 | 34.79# (31.66-38.14) | 479 | 214 | 58.81# (51.19-67.24) | 263 | 118 | 43.39# (35.91-51.96) | 143 | 103 | 27.75# (22.65-33.65) | 40 | 15 | 12.62# (7.06-20.81) | 17 | 4 | 2.23 (0.61-5.72) |
| American Indian-Alaska Native | 17 | 16 | 24.10# (13.78-39.14) | 17 | 7 | 145.38# (58.45-299.54) | 10 | 6 | 113.06# (41.49-246.08) | 4 | 2 | 11.11# (1.35-40.14) | 2 | 0 | 0 (0-18.45) | 1 | 1 | 5.47 (0.14-30.5) |
| Asian or Pacific Islander | 194 | 169 | 31.57# (26.99-36.7) | 194 | 69 | 53.68# (41.76-67.93) | 122 | 49 | 49.84# (36.87-65.9) | 71 | 44 | 29.03# (21.1-38.98) | 23 | 5 | 4.94# (1.6-11.52) | 12 | 2 | 3.6 (0.44-12.99) |
| Differentiation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Grade I | 40 | 39 | 14.12# (10.04-19.3) | 40 | 17 | 34.78# (20.26-55.68) | 23 | 11 | 32.39# (16.17-57.96) | 12 | 9 | 16.95# (7.75-32.18) | 3 | 1 | 2.38 (0.06-13.28) | 2 | 1 | 1.02 (0.03-5.66) |
| Grade II | 187 | 169 | 17.39# (14.87-20.22) | 187 | 68 | 42.41# (32.93-53.77) | 115 | 37 | 27.05# (19.05-37.29) | 76 | 51 | 16.99# (12.65-22.34) | 23 | 5 | 2.94 (0.95-6.86) | 14 | 8 | 3.92# (1.69-7.72) |
| Grade III | 1387 | 1315 | 29.66# (28.07-31.3) | 1387 | 571 | 52.85# (48.6-57.36) | 809 | 349 | 39.77# (35.71-44.17) | 455 | 337 | 28.10# (25.18-31.26) | 113 | 44 | 9.36# (6.8-12.56) | 52 | 14 | 1.74 (0.95-2.91) |
| Grade IV | 2163 | 2021 | 25.77# (24.66-26.92) | 2163 | 763 | 42.53# (39.57-45.66) | 1389 | 582 | 38.13# (35.09-41.36) | 803 | 567 | 24.31# (22.35-26.39) | 222 | 79 | 7.60# (6.02-9.47) | 85 | 30 | 2.61# (1.76-3.73) |
| T | ||||||||||||||||||
| T0 | 27 | 26 | 31.92# (20.85-46.77) | 27 | 15 | 134.70# (75.39-222.17) | 12 | 5 | 47.23# (15.33-110.21) | 7 | 3 | 9.97# (2.06-29.12) | 4 | 3 | 23.25# (4.79-67.94) | 1 | 0 | 0 (0-22.07) |
| T1 | 613 | 572 | 20.79# (19.12-22.56) | 613 | 229 | 43.25# (37.83-49.23) | 377 | 148 | 31.41# (26.55-36.89) | 228 | 152 | 17.67# (14.97-20.71) | 73 | 33 | 8.98# (6.18-12.61) | 28 | 10 | 1.91 (0.92-3.52) |
| T2a | 318 | 289 | 22.52# (20-25.28) | 318 | 121 | 41.46# (34.4-49.54) | 195 | 79 | 34.36# (27.2-42.82) | 114 | 79 | 21.28# (16.85-26.53) | 35 | 8 | 3.82# (1.65-7.53) | 17 | 2 | 1.11 (0.13-4) |
| T2b | 432 | 405 | 21.84# (19.77-24.08) | 432 | 138 | 34.96# (29.37-41.3) | 293 | 136 | 42.62# (35.75-50.41) | 153 | 105 | 23.67# (19.36-28.66) | 44 | 16 | 7.49# (4.28-12.17) | 24 | 10 | 2.07 (0.99-3.8) |
| T3a | 204 | 180 | 16.62# (14.28-19.23) | 204 | 57 | 37.16# (28.14-48.14) | 147 | 38 | 25.09# (17.75-34.43) | 109 | 68 | 23.79# (18.47-30.16) | 36 | 14 | 8.28# (4.53-13.9) | 15 | 3 | 0.93 (0.19-2.71) |
| T3b | 201 | 181 | 19.03# (16.36-22.01) | 201 | 60 | 42.82# (32.68-55.12) | 140 | 46 | 33.46# (24.49-44.63) | 93 | 64 | 23.78# (18.31-30.37) | 28 | 5 | 3.10# (1.01-7.22) | 16 | 6 | 2.47 (0.91-5.38) |
| T4a | 733 | 697 | 38.11# (35.33-41.04) | 733 | 283 | 54.00# (47.89-60.67) | 445 | 191 | 43.25# (37.33-49.84) | 252 | 201 | 34.95# (30.28-40.13) | 48 | 14 | 7.63# (4.17-12.8) | 20 | 8 | 7.64# (3.3-15.05) |
| T4b | 325 | 313 | 41.62# (37.14-46.5) | 325 | 155 | 78.63# (66.74-92.03) | 168 | 85 | 62.27# (49.74-77) | 83 | 65 | 47.05# (36.31-59.96) | 15 | 4 | 7.39# (2.01-18.91) | 9 | 4 | 1.77 (0.48-4.53) |
| N | ||||||||||||||||||
| N0 | 2352 | 2205 | 23.71# (22.73-24.72) | 2352 | 914 | 43.43# (40.66-46.34) | 1420 | 587 | 33.30# (30.66-36.11) | 827 | 580 | 21.19# (19.5-22.99) | 236 | 88 | 7.30# (5.85-8.99) | 97 | 36 | 2.42# (1.69-3.34) |
| N1 | 661 | 623 | 30.59# (28.24-33.09) | 661 | 228 | 47.72# (41.72-54.33) | 432 | 187 | 47.54# (40.97-54.87) | 242 | 177 | 36.51# (31.33-42.3) | 58 | 20 | 8.65# (5.28-13.36) | 29 | 11 | 2.45# (1.22-4.38) |
| N2 | 879 | 802 | 31.25# (29.12-33.49) | 879 | 293 | 49.08# (43.62-55.03) | 579 | 241 | 46.48# (40.8-52.73) | 334 | 243 | 33.87# (29.75-38.41) | 84 | 20 | 6.58# (4.02-10.17) | 32 | 5 | 1.16 (0.38-2.71) |
| N3 | 36 | 36 | 72.96# (51.1-101) | 36 | 14 | 45.99# (25.14-77.16) | 22 | 13 | 103.46# (55.09-176.92) | 9 | 9 | 142.08# (64.97-269.72) | 0 | 0 | 0 (0-0) | 0 | 0 | 0 (0-0) |
| Pathology | ||||||||||||||||||
| Transitional cell carcinoma | 2541 | 2404 | 28.49# (27.36-29.65) | 2541 | 1025 | 50.65# (47.59-53.84) | 1502 | 656 | 40.68# (37.62-43.91) | 841 | 604 | 24.67# (22.74-26.72) | 219 | 84 | 7.99# (6.37-9.89) | 86 | 35 | 2.69# (1.87-3.73) |
| Papillary transitional cell carcinoma | 1098 | 1000 | 19.84# (18.62-21.1) | 1098 | 350 | 34.26# (30.76-38.04) | 740 | 270 | 28.73# (25.4-32.37) | 465 | 322 | 21.84# (19.52-24.36) | 138 | 42 | 6.49# (4.68-8.77) | 61 | 16 | 1.67 (0.95-2.71) |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 146 | 144 | 65.00# (54.82-76.53) | 146 | 89 | 124.16# (99.71-152.79) | 57 | 36 | 117.29# (82.15-162.38) | 20 | 15 | 24.67# (13.81-40.69) | 5 | 2 | 4.72 (0.57-17.06) | 3 | 2 | 12.51# (1.51-45.18) |
| Small cell carcinoma | 148 | 139 | 31.44# (26.43-37.12) | 148 | 44 | 28.72# (20.87-38.56) | 102 | 51 | 43.98# (32.75-57.83) | 50 | 41 | 34.72# (24.92-47.11) | 8 | 1 | 3.77 (0.1-21.02) | 4 | 2 | 7.03 (0.85-25.4) |
| Adenocarcinoma | 111 | 103 | 36.19# (29.54-43.89) | 111 | 44 | 61.52# (44.7-82.59) | 65 | 24 | 45.47# (29.13-67.65) | 41 | 24 | 21.85# (14-32.51) | 14 | 9 | 21.33# (9.75-40.49) | 4 | 2 | 24.22# (2.93-87.48) |
| Chemotherapy | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 2598 | 2401 | 24.38# (23.41-25.37) | 2598 | 1351 | 34.38# (32.57-36.26) | 1228 | 895 | 28.78# (26.92-30.72) | 317 | 115 | 8.66# (7.15-10.39) | 116 | 33 | 2.76# (1.9-3.87) | 30 | 7 | 2.46 (0.99-5.07) |
| No-Unknown | 2080 | 1991 | 31.40# (30.04-32.81) | 2080 | 1667 | 54.43# (51.85-57.11) | 388 | 264 | 16.55# (14.62-18.68) | 109 | 38 | 5.70# (4.03-7.82) | 61 | 20 | 2.68# (1.64-4.15) | 24 | 2 | 0.74 (0.09-2.66) |
| Radiation | ||||||||||||||||||
| Yes | 1057 | 1019 | 33.37# (31.36-35.49) | 1057 | 721 | 45.10# (41.86-48.51) | 329 | 256 | 29.42# (25.93-33.25) | 68 | 29 | 10.04# (6.72-14.42) | 25 | 11 | 4.53# (2.26-8.11) | 5 | 2 | 3.79 (0.46-13.7) |
| No/Unknown | 3621 | 3373 | 25.68# (24.82-26.56) | 3621 | 2297 | 42.59# (40.86-44.37) | 1287 | 903 | 23.55# (22.04-25.13) | 358 | 124 | 7.27# (6.04-8.66) | 152 | 42 | 2.47# (1.78-3.34) | 49 | 7 | 1.39 (0.56-2.87) |
MBC: metastatic bladder cancer; SMR: Standard Mortality Ratio;
significant difference.
Cause of death in patients with NMIBC
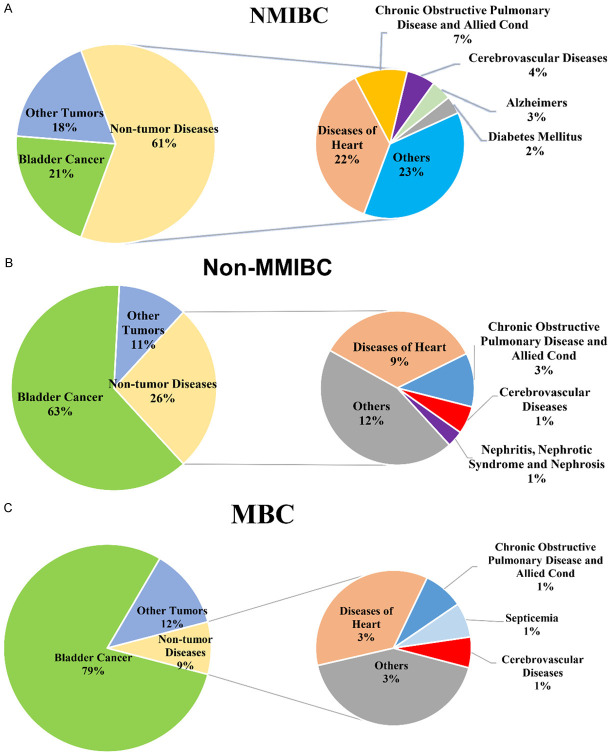
During the follow-up period, 44,638 patients died after being diagnosed with NMIBC, 9,183 (20.57%) died of bladder cancer, 8,066 (18.07%) died of other cancers (non-bladder cancer), and 27,7389 died of neoplastic disease (61.36%). The risk of dying from bladder cancer was higher than that of ordinary Americans [SMR: 31.52, 95% CI (30.88-32.17)]. The SMR of dying from bladder cancer gradually decreased over time. The risk of dying from lung and bronchial cancer was also higher than that of ordinary Americans [SMR: 1.56, 95% CI (1.51-1.62)], but on the contrary, the SMR value gradually increased with time. The risk of death of pancreas cancer [SMR: 1.15, 95% CI (1.05-1.26)], kidney and renal pelvis cancer [SMR: 1.86, 95% CI (1.66-2.07)], liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer [SMR: 1.26, 95% CI (1.13-1.41)] was significantly higher than that of the general population in the United States. The most common cause of non-cancerous death was the diseases of the heart (10007 cases, 22.42%), followed by chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and allied cond (3153 cases, 7.06%), and both were higher than the expected number of deaths, the SMR is 1.15, 95% CI (1.13-1.17) and 1.54, 95% CI (1.49-1.59). Diabetes mellitus and nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, and nephrosis were also higher than expected deaths [SMR: 1.19, 95% CI (1.12-1.27)] and [SMR: 1.18, 95% CI (1.1-1.26)]. It was worth noting that although deaths from septicemia and other infectious and parasitic diseases including HIV were higher than the general population [SMR: 1.15, 95% CI (1.05-1.25)] and [SMR: 1.21, 95% CI (1.07-1.36)], the highest risk of death was within one year after NMIBC diagnosis [SMR: 1.26, 95% CI (0.97-1.62)] and [SMR: 1.56, 95% CI (1.12-2.1)]. The risk of death from Alzheimer’s was reduced [SMR: 0.87, 95% CI (0.82-0.92)]. Cerebrovascular diseases [SMR: 0.96, 95% CI (0.91-1)], pneumonia and influenza [SMR: 0.97, 95% CI (0.91-1.05)] etc. were not statistically significant. The data of various causes of death of NMIBC patients are shown in Table 3, and their respective proportions are shown in Figure 1A.
Table 3.
Main cause of deaths for patients with non-muscular invasive bladder cancer
| Causes of deaths | Total | <1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | 5-10 years | >10 years | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | |
| All Causes of Death | 44,638 | 31,956.54 | 1.40# (1.38-1.41) | 5,230 | 3,603.88 | 1.45# (1.41-1.49) | 11,700 | 8,200.54 | 1.43# (1.4-1.45) | 9,802 | 6,982.32 | 1.40# (1.38-1.43) | 14,117 | 10,379.21 | 1.36# (1.34-1.38) | 3,789 | 2,790.58 | 1.36# (1.31-1.4) |
| All Malignant Cancers | 17,249 | 6,850.14 | 2.52# (2.48-2.56) | 2,294 | 817.43 | 2.81# (2.69-2.92) | 5,256 | 1,823.14 | 2.88# (2.81-2.96) | 3,855 | 1,508.32 | 2.56# (2.48-2.64) | 4,743 | 2,153.71 | 2.20# (2.14-2.27) | 1,101 | 547.54 | 2.01# (1.89-2.13) |
| Urinary Bladder | 9,183 | 291.34 | 31.52# (30.88-32.17) | 1,628 | 32.18 | 50.59# (48.16-53.11) | 3,215 | 74.21 | 43.33# (41.84-44.85) | 1,989 | 63.69 | 31.23# (29.87-32.64) | 1,969 | 95.46 | 20.63# (19.73-21.56) | 382 | 25.81 | 14.80# (13.35-16.36) |
| Lung and Bronchus | 2,860 | 1,831.09 | 1.56# (1.51-1.62) | 192 | 230.7 | 0.83# (0.72-0.96) | 744 | 503.37 | 1.48# (1.37-1.59) | 697 | 405.41 | 1.72# (1.59-1.85) | 980 | 557.99 | 1.76# (1.65-1.87) | 247 | 133.6 | 1.85# (1.63-2.09) |
| Pancreas | 506 | 438.9 | 1.15# (1.05-1.26) | 41 | 50.16 | 0.82 (0.59-1.11) | 135 | 114.36 | 1.18 (0.99-1.4) | 114 | 96.52 | 1.18 (0.97-1.42) | 177 | 141.02 | 1.26# (1.08-1.45) | 39 | 36.84 | 1.06 (0.75-1.45) |
| Prostate | 442 | 712.17 | 0.62# (0.56-0.68) | 34 | 83.05 | 0.41# (0.28-0.57) | 109 | 186.62 | 0.58# (0.48-0.7) | 106 | 155.89 | 0.68# (0.56-0.82) | 153 | 226.25 | 0.68# (0.57-0.79) | 40 | 60.36 | 0.66# (0.47-0.9) |
| Colon and Rectum | 440 | 591.94 | 0.74# (0.68-0.82) | 33 | 72.94 | 0.45# (0.31-0.64) | 94 | 159.97 | 0.59# (0.47-0.72) | 97 | 130.46 | 0.74# (0.6-0.91) | 172 | 182.9 | 0.94 (0.81-1.09) | 44 | 45.67 | 0.96 (0.7-1.29) |
| Kidney and Renal Pelvis | 323 | 173.7 | 1.86# (1.66-2.07) | 52 | 20.44 | 2.54# (1.9-3.34) | 91 | 45.97 | 1.98# (1.59-2.43) | 58 | 38.27 | 1.52# (1.15-1.96) | 93 | 54.98 | 1.69# (1.37-2.07) | 29 | 14.03 | 2.07# (1.38-2.97) |
| Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Duct | 314 | 248.33 | 1.26# (1.13-1.41) | 20 | 27.74 | 0.72 (0.44-1.11) | 74 | 64.23 | 1.15 (0.9-1.45) | 86 | 54.75 | 1.57# (1.26-1.94) | 103 | 80.49 | 1.28# (1.04-1.55) | 31 | 21.12 | 1.47 (1-2.08) |
| Leukemia | 273 | 314.43 | 0.87# (0.77-0.98) | 15 | 36.43 | 0.41# (0.23-0.68) | 65 | 82.27 | 0.79 (0.61-1.01) | 57 | 69.13 | 0.82 (0.62-1.07) | 110 | 100.69 | 1.09 (0.9-1.32) | 26 | 25.91 | 1 (0.66-1.47) |
| Lymphoma | 218 | 288.31 | 0.76# (0.66-0.86) | 14 | 33.98 | 0.41# (0.23-0.69) | 49 | 76.03 | 0.64# (0.48-0.85) | 48 | 63.34 | 0.76 (0.56-1) | 85 | 91.37 | 0.93 (0.74-1.15) | 22 | 23.59 | 0.93 (0.58-1.41) |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 209 | 277.4 | 0.75# (0.65-0.86) | 14 | 32.67 | 0.43# (0.23-0.72) | 48 | 73.11 | 0.66# (0.48-0.87) | 45 | 60.94 | 0.74# (0.54-0.99) | 81 | 87.95 | 0.92 (0.73-1.14) | 21 | 22.72 | 0.92 (0.57-1.41) |
| Esophagus | 203 | 201.48 | 1.01 (0.87-1.16) | 10 | 24.18 | 0.41# (0.2-0.76) | 47 | 54.12 | 0.87 (0.64-1.15) | 49 | 44.55 | 1.1 (0.81-1.45) | 74 | 62.9 | 1.18 (0.92-1.48) | 23 | 15.73 | 1.46 (0.93-2.19) |
| Myeloid and Monocytic Leukemia | 154 | 150.6 | 1.02 (0.87-1.2) | 7 | 17.03 | 0.41# (0.17-0.85) | 39 | 38.94 | 1 (0.71-1.37) | 36 | 33.05 | 1.09 (0.76-1.51) | 56 | 48.69 | 1.15 (0.87-1.49) | 16 | 12.9 | 1.24 (0.71-2.01) |
| Stomach | 144 | 129.61 | 1.11 (0.94-1.31) | 10 | 16.18 | 0.62 (0.3-1.14) | 31 | 35.31 | 0.88 (0.6-1.25) | 36 | 28.62 | 1.26 (0.88-1.74) | 52 | 39.73 | 1.31 (0.98-1.72) | 15 | 9.77 | 1.54 (0.86-2.53) |
| Brain and Other Nervous System | 142 | 133.18 | 1.07 (0.9-1.26) | 11 | 15.56 | 0.71 (0.35-1.26) | 36 | 35.21 | 1.02 (0.72-1.42) | 33 | 29.37 | 1.12 (0.77-1.58) | 57 | 42.2 | 1.35# (1.02-1.75) | 5 | 10.85 | 0.46 (0.15-1.08) |
| Acute Myeloid Leukemia | 134 | 121.68 | 1.1 (0.92-1.3) | 7 | 13.85 | 0.51 (0.2-1.04) | 36 | 31.63 | 1.14 (0.8-1.58) | 33 | 26.75 | 1.23 (0.85-1.73) | 48 | 39.2 | 1.22 (0.9-1.62) | 10 | 10.25 | 0.98 (0.47-1.79) |
| Myeloma | 125 | 149.9 | 0.83# (0.69-0.99) | 13 | 17.28 | 0.75 (0.4-1.29) | 24 | 39.08 | 0.61# (0.39-0.91) | 29 | 32.9 | 0.88 (0.59-1.27) | 48 | 48.09 | 1 (0.74-1.32) | 11 | 12.55 | 0.88 (0.44-1.57) |
| Skin excluding Basal and Squamous | 119 | 176.21 | 0.68# (0.56-0.81) | 4 | 19.99 | 0.20# (0.05-0.51) | 30 | 45.69 | 0.66# (0.44-0.94) | 28 | 38.73 | 0.72 (0.48-1.04) | 47 | 57.02 | 0.82 (0.61-1.1) | 10 | 14.78 | 0.68 (0.32-1.24) |
| Intrahepatic Bile Duct | 84 | 58.93 | 1.43# (1.14-1.76) | 5 | 6.32 | 0.79 (0.26-1.85) | 26 | 14.88 | 1.75# (1.14-2.56) | 19 | 12.94 | 1.47 (0.88-2.29) | 25 | 19.49 | 1.28 (0.83-1.89) | 9 | 5.3 | 1.7 (0.78-3.22) |
| Breast | 83 | 161.09 | 0.52# (0.41-0.64) | 4 | 18.9 | 0.21# (0.06-0.54) | 14 | 41.95 | 0.33# (0.18-0.56) | 13 | 35.22 | 0.37# (0.2-0.63) | 36 | 51.62 | 0.70# (0.49-0.97) | 16 | 13.41 | 1.19 (0.68-1.94) |
| Oral Cavity and Pharynx | 81 | 103.27 | 0.78# (0.62-0.97) | 6 | 11.88 | 0.51 (0.19-1.1) | 14 | 27.01 | 0.52# (0.28-0.87) | 11 | 22.71 | 0.48# (0.24-0.87) | 39 | 33.01 | 1.18 (0.84-1.62) | 11 | 8.66 | 1.27 (0.63-2.27) |
| Non-malignant cancer | ||||||||||||||||||
| Diseases of Heart | 10,007 | 8,709.92 | 1.15# (1.13-1.17) | 1,141 | 1,000.64 | 1.14# (1.08-1.21) | 2,417 | 2,251.26 | 1.07# (1.03-1.12) | 2,152 | 1,901.96 | 1.13# (1.08-1.18) | 3,382 | 2,802.12 | 1.21# (1.17-1.25) | 915 | 753.94 | 1.21# (1.14-1.29) |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Allied Cond | 3,153 | 2,048.61 | 1.54# (1.49-1.59) | 330 | 232.4 | 1.42# (1.27-1.58) | 735 | 528.87 | 1.39# (1.29-1.49) | 724 | 448.89 | 1.61# (1.5-1.73) | 1,093 | 663.07 | 1.65# (1.55-1.75) | 271 | 175.37 | 1.55# (1.37-1.74) |
| Cerebrovascular Diseases | 1,704 | 1,781.77 | 0.96 (0.91-1) | 206 | 201.95 | 1.02 (0.89-1.17) | 413 | 454.91 | 0.91# (0.82-1) | 348 | 387.19 | 0.90# (0.81-1) | 567 | 577.52 | 0.98 (0.9-1.07) | 170 | 160.2 | 1.06 (0.91-1.23) |
| Alzheimers | 1,211 | 1,395.89 | 0.87# (0.82-0.92) | 75 | 134.01 | 0.56# (0.44-0.7) | 225 | 326.14 | 0.69# (0.6-0.79) | 247 | 297.87 | 0.83# (0.73-0.94) | 471 | 486.9 | 0.97 (0.88-1.06) | 193 | 150.98 | 1.28# (1.1-1.47) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 1,047 | 878.31 | 1.19# (1.12-1.27) | 122 | 101.74 | 1.2 (1-1.43) | 250 | 229.57 | 1.09 (0.96-1.23) | 222 | 192.66 | 1.15# (1.01-1.31) | 365 | 280.43 | 1.30# (1.17-1.44) | 88 | 73.92 | 1.19 (0.95-1.47) |
| Accidents and Adverse Effects | 835 | 901.76 | 0.93# (0.86-0.99) | 81 | 97.87 | 0.83 (0.66-1.03) | 185 | 227.53 | 0.81# (0.7-0.94) | 202 | 196.53 | 1.03 (0.89-1.18) | 275 | 297.54 | 0.92 (0.82-1.04) | 92 | 82.29 | 1.12 (0.9-1.37) |
| Nephritis, Nephrotic Syndrome and Nephrosis | 798 | 677.88 | 1.18# (1.1-1.26) | 83 | 76.8 | 1.08 (0.86-1.34) | 188 | 174.98 | 1.07 (0.93-1.24) | 177 | 148.44 | 1.19# (1.02-1.38) | 277 | 219.44 | 1.26# (1.12-1.42) | 73 | 58.22 | 1.25 (0.98-1.58) |
| Pneumonia and Influenza | 789 | 809.41 | 0.97 (0.91-1.05) | 81 | 93.85 | 0.86 (0.69-1.07) | 192 | 210.04 | 0.91 (0.79-1.05) | 171 | 177.04 | 0.97 (0.83-1.12) | 269 | 259.33 | 1.04 (0.92-1.17) | 76 | 69.15 | 1.1 (0.87-1.38) |
| Septicemia | 516 | 450.5 | 1.15# (1.05-1.25) | 64 | 50.6 | 1.26 (0.97-1.62) | 119 | 115.53 | 1.03 (0.85-1.23) | 111 | 98.4 | 1.13 (0.93-1.36) | 169 | 146.34 | 1.15 (0.99-1.34) | 53 | 39.63 | 1.34# (1-1.75) |
| Hypertension without Heart Disease | 449 | 370.46 | 1.21# (1.1-1.33) | 52 | 38.48 | 1.35# (1.01-1.77) | 72 | 90.84 | 0.79# (0.62-1) | 106 | 80.32 | 1.32# (1.08-1.6) | 163 | 125.25 | 1.30# (1.11-1.52) | 56 | 35.57 | 1.57# (1.19-2.04) |
| Symptoms, Signs and Ill-Defined Conditions | 340 | 371.94 | 0.91 (0.82-1.02) | 43 | 41.96 | 1.02 (0.74-1.38) | 87 | 95.76 | 0.91 (0.73-1.12) | 77 | 82.39 | 0.93 (0.74-1.17) | 110 | 122.67 | 0.9 (0.74-1.08) | 23 | 29.17 | 0.79 (0.5-1.18) |
| Other Infectious and Parasitic Diseases including HIV | 274 | 226.37 | 1.21# (1.07-1.36) | 42 | 27 | 1.56# (1.12-2.1) | 76 | 60.63 | 1.25 (0.99-1.57) | 63 | 50.06 | 1.26 (0.97-1.61) | 79 | 71.21 | 1.11 (0.88-1.38) | 14 | 17.46 | 0.8 (0.44-1.35) |
| Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis | 258 | 244.6 | 1.05 (0.93-1.19) | 34 | 29.02 | 1.17 (0.81-1.64) | 74 | 65.44 | 1.13 (0.89-1.42) | 58 | 54.1 | 1.07 (0.81-1.39) | 72 | 76.61 | 0.94 (0.74-1.18) | 20 | 19.42 | 1.03 (0.63-1.59) |
Abbreviations: SMR, standardized mortality ratio; CI, confidence interval;
significant difference.
Figure 1.
The percentage of death reasons for patients with non-muscular invasive, non-metastatic muscular invasive and metastatic bladder cancer. A. Cause of death among patients with non-muscular invasive bladder cancer. B. Cause of death among patients with non-metastatic muscular invasive bladder cancer. C. Cause of death among patients with metastatic bladder cancer.
Cause of death in patients with non-MMIBC
Statistics showed that 18,829 patients died after the diagnosis of non-MMIBC, 11,797 (62.65%) died of bladder cancer, 2063 (10.96%) died of other cancers (non-bladder cancer), and 4969 died of non-neoplastic diseases (26.39%). Among tumorous diseases other than bladder cancer, the risk of dying of lung and bronchus [SMR: 1.83, 95% CI (1.66-2.01)] and pancreas [SMR: 1.45, 95% CI (1.15-1.8)] were higher than the general population. Unlike NMIBC, non-MMIBC has a significantly increased risk of dying from prostate cancer [SMR: 2.21, 95% CI (1.91-2.54)], and the risk of dying from kidney and renal pelvis cancer was 4 times than that of the general population [SMR: 4.28, 95% CI (3.46-5.23)], the risk of dying from ureteral cancer was 26 times than that of the general population [SMR: 26.89, 95% CI (16.64-41.1)]. Death from esophagus [SMR: 1.47, 95% CI (1.04-2.01)] and stomach [SMR: 2.00, 95% CI (1.38-2.79)] related cancer was higher than that of ordinary people, while lymphoma [SMR: 0.55, 95% CI (0.33-0.85)] and non-Hodgkin lymphoma [SMR: 0.57, 95% CI (0.35-0.88)] were much lower than ordinary people. The dominant non-neoplastic diseases were still diseases of the heart (1,717 cases, 9.12%) and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and allied cond (561 cases, 2.98%). The risk of death of cerebrovascular diseases [SMR: 1.28, 95% CI (1.14-1.44)], nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and nephrosis [SMR: 1.99, 95% CI (1.7-2.31)], diabetes mellitus [SMR: 1.35, 95% CI (1.14-1.58)], hypertension without heart disease [SMR: 1.89, 95% CI (1.52-2.33)] and other diseases, were higher than that of the general population. Infection-related diseases such as septicemia [SMR: 2.88, 95% CI (2.45-3.35)], pneumonia and influenza [SMR: 1.60, 95% CI (1.37-1.87)], other infectious and parasitic diseases including HIV [SMR: 2.64, 95% CI (2.09-3.3)], which the risk of death was much higher than that of the general population. It cannot be ignored that the risk of dying from suicide and self-inflicted injury was more than twice that of ordinary people [SMR: 2.73, 95% CI (2.11-3.46)]. The data of cause of death after non-MMIBC are shown in Table 4, and their respective proportions are shown in Figure 1B.
Table 4.
Main cause of deaths for patients with non-metastatic muscle invasive bladder cancer
| Causes of deaths | Total | <1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | 5-10 years | >10 years | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | |
| All Causes of Death | 18,829 | 4,035.71 | 4.67# (4.6-4.73) | 7,309 | 759.89 | 9.62# (9.4-9.84) | 6,948 | 1,145.04 | 6.07# (5.93-6.21) | 2,159 | 793.72 | 2.72# (2.61-2.84) | 1,970 | 1,066.89 | 1.85# (1.77-1.93) | 443 | 270.17 | 1.64# (1.49-1.8) |
| All Malignant Cancers | 13,860 | 878.05 | 15.78# (15.52-16.05) | 5,754 | 168.26 | 34.20# (33.32-35.09) | 5,629 | 256.85 | 21.92# (21.35-22.5) | 1,383 | 174.2 | 7.94# (7.53-8.37) | 942 | 225.2 | 4.18# (3.92-4.46) | 152 | 53.53 | 2.84# (2.41-3.33) |
| Urinary Bladder | 11,797 | 35.78 | 329.74# (323.82-335.75) | 5,232 | 6.5 | 805.31# (783.63-827.43) | 4,852 | 10.08 | 481.36# (467.91-495.09) | 1,065 | 7.08 | 150.41# (141.51-159.73) | 590 | 9.65 | 61.12# (56.29-66.26) | 58 | 2.47 | 23.51# (17.85-30.4) |
| Lung and Bronchus | 435 | 237.33 | 1.83# (1.66-2.01) | 45 | 46.94 | 0.96 (0.7-1.28) | 147 | 71.2 | 2.06# (1.74-2.43) | 86 | 47.15 | 1.82# (1.46-2.25) | 119 | 58.9 | 2.02# (1.67-2.42) | 38 | 13.13 | 2.89# (2.05-3.97) |
| Prostate | 192 | 87.03 | 2.21# (1.91-2.54) | 64 | 16.55 | 3.87# (2.98-4.94) | 82 | 24.95 | 3.29# (2.61-4.08) | 18 | 17.1 | 1.05 (0.62-1.66) | 23 | 22.62 | 1.02 (0.64-1.53) | 5 | 5.8 | 0.86 (0.28-2.01) |
| Kidney and Renal Pelvis | 95 | 22.19 | 4.28# (3.46-5.23) | 38 | 4.16 | 9.15# (6.47-12.55) | 29 | 6.46 | 4.49# (3-6.44) | 14 | 4.43 | 3.16# (1.73-5.31) | 11 | 5.77 | 1.91 (0.95-3.41) | 3 | 1.38 | 2.18 (0.45-6.37) |
| Colon and Rectum | 89 | 76.66 | 1.16 (0.93-1.43) | 13 | 15.25 | 0.85 (0.45-1.46) | 34 | 22.66 | 1.50# (1.04-2.1) | 10 | 15.11 | 0.66 (0.32-1.22) | 24 | 19.17 | 1.25 (0.8-1.86) | 8 | 4.48 | 1.79 (0.77-3.52) |
| Pancreas | 82 | 56.67 | 1.45# (1.15-1.8) | 13 | 10.43 | 1.25 (0.66-2.13) | 34 | 16.34 | 2.08# (1.44-2.91) | 19 | 11.32 | 1.68# (1.01-2.62) | 15 | 14.95 | 1 (0.56-1.66) | 1 | 3.63 | 0.28 (0.01-1.53) |
| Colon excluding Rectum | 75 | 63.04 | 1.19 (0.94-1.49) | 11 | 12.64 | 0.87 (0.43-1.56) | 30 | 18.66 | 1.61# (1.08-2.29) | 8 | 12.4 | 0.65 (0.28-1.27) | 19 | 15.68 | 1.21 (0.73-1.89) | 7 | 3.65 | 1.92 (0.77-3.95) |
| Liver and Intrahepatic Bile Duct | 39 | 32.44 | 1.2 (0.85-1.64) | 6 | 5.72 | 1.05 (0.38-2.28) | 8 | 9.28 | 0.86 (0.37-1.7) | 15 | 6.54 | 2.29# (1.28-3.78) | 8 | 8.76 | 0.91 (0.39-1.8) | 2 | 2.14 | 0.93 (0.11-3.37) |
| Esophagus | 38 | 25.89 | 1.47# (1.04-2.01) | 4 | 4.84 | 0.83 (0.23-2.12) | 8 | 7.63 | 1.05 (0.45-2.07) | 7 | 5.19 | 1.35 (0.54-2.78) | 15 | 6.68 | 2.25# (1.26-3.71) | 4 | 1.56 | 2.57 (0.7-6.58) |
| Stomach | 34 | 17.03 | 2.00# (1.38-2.79) | 7 | 3.39 | 2.06 (0.83-4.25) | 9 | 5.06 | 1.78 (0.81-3.38) | 8 | 3.36 | 2.38# (1.03-4.69) | 7 | 4.24 | 1.65 (0.66-3.4) | 3 | 0.98 | 3.06 (0.63-8.95) |
| Leukemia | 30 | 39.58 | 0.76 (0.51-1.08) | 1 | 7.44 | 0.13# (0-0.75) | 10 | 11.4 | 0.88 (0.42-1.61) | 5 | 7.85 | 0.64 (0.21-1.49) | 10 | 10.38 | 0.96 (0.46-1.77) | 4 | 2.51 | 1.6 (0.44-4.09) |
| Ureter | 21 | 0.78 | 26.89# (16.64-41.1) | 9 | 0.14 | 63.55# (29.06-120.63) | 7 | 0.22 | 31.78# (12.78-65.47) | 3 | 0.15 | 19.40# (4-56.71) | 1 | 0.21 | 4.75 (0.12-26.45) | 1 | 0.05 | 18.53 (0.47-103.26) |
| Breast | 20 | 22.44 | 0.89 (0.54-1.38) | 7 | 4.61 | 1.52 (0.61-3.13) | 5 | 6.58 | 0.76 (0.25-1.77) | 0 | 4.38 | 0.00# (0-0.84) | 7 | 5.58 | 1.25 (0.5-2.59) | 1 | 1.31 | 0.77 (0.02-4.27) |
| Lymphoma | 20 | 36.51 | 0.55# (0.33-0.85) | 1 | 6.97 | 0.14# (0-0.8) | 2 | 10.58 | 0.19# (0.02-0.68) | 9 | 7.22 | 1.25 (0.57-2.37) | 7 | 9.45 | 0.74 (0.3-1.53) | 1 | 2.28 | 0.44 (0.01-2.44) |
| Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma | 20 | 35.11 | 0.57# (0.35-0.88) | 1 | 6.71 | 0.15# (0-0.83) | 2 | 10.17 | 0.20# (0.02-0.71) | 9 | 6.94 | 1.3 (0.59-2.46) | 7 | 9.1 | 0.77 (0.31-1.59) | 1 | 2.2 | 0.45 (0.01-2.53) |
| Non-malignant cancer | ||||||||||||||||||
| Diseases of Heart | 1,717 | 1,097.89 | 1.56# (1.49-1.64) | 569 | 211.8 | 2.69# (2.47-2.92) | 468 | 312.58 | 1.50# (1.36-1.64) | 261 | 214.64 | 1.22# (1.07-1.37) | 320 | 286.09 | 1.12 (1-1.25) | 99 | 72.77 | 1.36# (1.11-1.66) |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Allied Cond | 561 | 256.78 | 2.18# (2.01-2.37) | 162 | 48.03 | 3.37# (2.87-3.93) | 137 | 73.21 | 1.87# (1.57-2.21) | 108 | 50.75 | 2.13# (1.75-2.57) | 122 | 67.94 | 1.80# (1.49-2.14) | 32 | 16.86 | 1.90# (1.3-2.68) |
| Cerebrovascular Diseases | 290 | 226.65 | 1.28# (1.14-1.44) | 83 | 43.8 | 1.89# (1.51-2.35) | 89 | 63.89 | 1.39# (1.12-1.71) | 38 | 44.11 | 0.86 (0.61-1.18) | 62 | 59.33 | 1.04 (0.8-1.34) | 18 | 15.52 | 1.16 (0.69-1.83) |
| Nephritis, Nephrotic Syndrome and Nephrosis | 170 | 85.62 | 1.99# (1.7-2.31) | 46 | 16.3 | 2.82# (2.07-3.76) | 41 | 24.39 | 1.68# (1.21-2.28) | 26 | 16.82 | 1.55# (1.01-2.27) | 46 | 22.47 | 2.05# (1.5-2.73) | 11 | 5.64 | 1.95 (0.97-3.49) |
| Alzheimers | 167 | 171.54 | 0.97 (0.83-1.13) | 39 | 29.63 | 1.32 (0.94-1.8) | 35 | 45.18 | 0.77 (0.54-1.08) | 27 | 33.26 | 0.81 (0.54-1.18) | 54 | 49.03 | 1.1 (0.83-1.44) | 12 | 14.44 | 0.83 (0.43-1.45) |
| Septicemia | 165 | 57.39 | 2.88# (2.45-3.35) | 80 | 10.77 | 7.43# (5.89-9.24) | 39 | 16.32 | 2.39# (1.7-3.27) | 20 | 11.31 | 1.77# (1.08-2.73) | 21 | 15.13 | 1.39 (0.86-2.12) | 5 | 3.85 | 1.3 (0.42-3.03) |
| Pneumonia and Influenza | 163 | 101.66 | 1.60# (1.37-1.87) | 50 | 20.02 | 2.50# (1.85-3.29) | 41 | 28.89 | 1.42# (1.02-1.93) | 25 | 19.78 | 1.26 (0.82-1.87) | 35 | 26.32 | 1.33 (0.93-1.85) | 12 | 6.65 | 1.8 (0.93-3.15) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 153 | 113.58 | 1.35# (1.14-1.58) | 44 | 21.52 | 2.05# (1.49-2.75) | 43 | 32.75 | 1.31 (0.95-1.77) | 32 | 22.47 | 1.42 (0.97-2.01) | 26 | 29.54 | 0.88 (0.57-1.29) | 8 | 7.3 | 1.1 (0.47-2.16) |
| Accidents and Adverse Effects | 127 | 112.61 | 1.13 (0.94-1.34) | 30 | 20.29 | 1.48 (1-2.11) | 36 | 31.64 | 1.14 (0.8-1.58) | 28 | 22.26 | 1.26 (0.84-1.82) | 22 | 30.48 | 0.72 (0.45-1.09) | 11 | 7.94 | 1.39 (0.69-2.48) |
| Hypertension without Heart Disease | 89 | 47.1 | 1.89# (1.52-2.33) | 27 | 8.48 | 3.19# (2.1-4.64) | 21 | 12.91 | 1.63# (1.01-2.49) | 11 | 9.24 | 1.19 (0.59-2.13) | 24 | 12.98 | 1.85# (1.18-2.75) | 6 | 3.48 | 1.72 (0.63-3.75) |
| Symptoms, Signs and Ill-Defined Conditions | 83 | 47.07 | 1.76# (1.4-2.19) | 33 | 9.13 | 3.61# (2.49-5.08) | 27 | 13.35 | 2.02# (1.33-2.94) | 10 | 9.27 | 1.08 (0.52-1.98) | 10 | 12.51 | 0.8 (0.38-1.47) | 3 | 2.82 | 1.06 (0.22-3.11) |
| Other Infectious and Parasitic Diseases including HIV | 78 | 29.52 | 2.64# (2.09-3.3) | 40 | 5.72 | 7.00# (5-9.53) | 18 | 8.7 | 2.07# (1.23-3.27) | 5 | 5.85 | 0.85 (0.28-1.99) | 13 | 7.52 | 1.73 (0.92-2.95) | 2 | 1.73 | 1.16 (0.14-4.19) |
| Suicide and Self-Inflicted Injury | 67 | 24.58 | 2.73# (2.11-3.46) | 24 | 4.51 | 5.32# (3.41-7.92) | 20 | 7.26 | 2.76# (1.68-4.26) | 9 | 4.96 | 1.82 (0.83-3.45) | 13 | 6.37 | 2.04# (1.09-3.49) | 1 | 1.49 | 0.67 (0.02-3.73) |
Abbreviations: SMR, standardized mortality ratio; CI, confidence interval;
significant difference.
Cause of death in patients with MBC
A total of 4,392 patients died after the diagnosis of MBC, 3,486 deaths (79.37%) from bladder cancer, 548 deaths (12.48%) from other cancers (non-bladder cancer), and 358 deaths from non-neoplastic diseases (8.15%). Malignant tumors were the main cause of death of MBC (91.85%). Compared with non-MMIBC, the risk of dying from prostate, kidney, and renal pelvis, and ureter-related tumors was greatly increased. The SMR were 17.38, 95% CI (13.17-22.52), 31.93, 95% CI (21.54-45.58), 328.79, 95% CI (157.67-604.65). Tumors in other sites such as lung and bronchus, colon and rectum and liver were all five times higher than expected. SMR was 5.17, 95% CI (3.89-6.75), 6.08, 95% CI (3.72-9.39), 9.70, 95% CI (4.84-17.35). The spectrum of death causes of non-neoplastic diseases was like that of non-MMIBC. The risk of dying from diseases of heart, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and allied cond, cerebrovascular diseases, and other diseases was twice that of ordinary people. The SMR is 2.96, 95% CI (2.47-3.52), 2.92, 95% CI (1.97-4.17), 2.56, 95% CI (1.63-3.85), the most prominent change was that the risk of dying from septicemia, other infectious and parasitic diseases including HIV was 11 times higher than that of ordinary people, SMR is 11.11, 95% CI (7.26-16.28), 11.15, 95% CI (6.24-18.38). The related causes of death after MBC diagnosis are shown in Table 5, and their respective proportions are shown in Figure 1C.
Table 5.
Main cause of deaths for patients with metastatic bladder cancer
| Causes of deaths | Total | <6 months | 6 m-1 year | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | >5 years | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | Observed | Expected | SMR (95% CI) | |
| All Causes of Death | 4,392 | 161.9 | 27.13# (26.33-27.94) | 1,825 | 38.29 | 47.67# (45.51-49.91) | 1,193 | 31.64 | 37.71# (35.6-39.91) | 1,159 | 47.05 | 24.63# (23.24-26.09) | 153 | 19.96 | 7.67# (6.5-8.98) | 62 | 24.97 | 2.48# (1.9-3.18) |
| All Malignant Cancers | 4,034 | 37.31 | 108.13# (104.82-111.52) | 1,679 | 8.94 | 187.84# (178.96-197.04) | 1,112 | 7.6 | 146.31# (137.84-155.17) | 1,078 | 11.18 | 96.42# (90.75-102.35) | 127 | 4.33 | 29.33# (24.45-34.89) | 38 | 5.26 | 7.23# (5.11-9.92) |
| Urinary Bladder | 3,486 | 1.35 | 2,575.46# (2490.67-2662.41) | 1,431 | 0.32 | 4,509.14# (4278.51-4748.97) | 983 | 0.27 | 3,690.19# (3463.08-3928.29) | 948 | 0.39 | 2,410.45# (2259.43-2568.91) | 103 | 0.16 | 638.02# (520.77-773.78) | 21 | 0.22 | 97.64# (60.44-149.25) |
| Prostate | 57 | 3.28 | 17.38# (13.17-22.52) | 23 | 0.81 | 28.40# (18-42.61) | 11 | 0.66 | 16.78# (8.38-30.03) | 18 | 0.93 | 19.40# (11.5-30.66) | 5 | 0.38 | 13.27# (4.31-30.96) | 0 | 0.51 | 0 (0-7.25) |
| Lung and Bronchus | 54 | 10.44 | 5.17# (3.89-6.75) | 26 | 2.54 | 10.24# (6.69-15) | 13 | 2.18 | 5.97# (3.18-10.21) | 11 | 3.17 | 3.47# (1.73-6.21) | 2 | 1.18 | 1.7 (0.21-6.15) | 2 | 1.38 | 1.45 (0.18-5.24) |
| Kidney and Renal Pelvis | 30 | 0.94 | 31.93# (21.54-45.58) | 19 | 0.22 | 85.94# (51.74-134.2) | 6 | 0.19 | 31.35# (11.51-68.24) | 3 | 0.28 | 10.59# (2.18-30.95) | 0 | 0.11 | 0 (0-33.63) | 2 | 0.13 | 14.91# (1.81-53.87) |
| Colon and Rectum | 20 | 3.29 | 6.08# (3.72-9.39) | 8 | 0.8 | 9.98# (4.31-19.66) | 2 | 0.67 | 2.98 (0.36-10.77) | 7 | 0.98 | 7.15# (2.87-14.72) | 0 | 0.38 | 0 (0-9.66) | 3 | 0.45 | 6.61# (1.36-19.32) |
| Liver | 11 | 1.13 | 9.70# (4.84-17.35) | 7 | 0.25 | 27.85# (11.2-57.38) | 2 | 0.22 | 8.89# (1.08-32.13) | 2 | 0.34 | 5.81 (0.7-21) | 0 | 0.14 | 0 (0-26.41) | 0 | 0.17 | 0 (0-21.14) |
| Ureter | 10 | 0.03 | 328.79# (157.67-604.65) | 5 | 0.01 | 710.34# (230.64-1657.69) | 3 | 0.01 | 504.18# (103.97-1473.41) | 1 | 0.01 | 111.49# (2.82-621.17) | 1 | 0 | 270.84# (6.86-1509.04) | 0 | 0 | 0 (0-774.36) |
| Non-tumor diseases | ||||||||||||||||||
| Diseases of Heart | 128 | 43.28 | 2.96# (2.47-3.52) | 59 | 10.4 | 5.67# (4.32-7.32) | 23 | 8.44 | 2.73# (1.73-4.09) | 30 | 12.42 | 2.42# (1.63-3.45) | 8 | 5.32 | 1.5 (0.65-2.96) | 8 | 6.69 | 1.2 (0.52-2.36) |
| Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Allied Cond | 30 | 10.28 | 2.92# (1.97-4.17) | 9 | 2.42 | 3.72# (1.7-7.06) | 8 | 2.03 | 3.95# (1.7-7.77) | 8 | 3.03 | 2.64# (1.14-5.21) | 3 | 1.25 | 2.41 (0.5-7.03) | 2 | 1.56 | 1.28 (0.16-4.64) |
| Septicemia | 26 | 2.34 | 11.11# (7.26-16.28) | 10 | 0.56 | 17.93# (8.6-32.97) | 6 | 0.46 | 13.04# (4.79-28.39) | 6 | 0.68 | 8.78# (3.22-19.1) | 2 | 0.28 | 7.09 (0.86-25.6) | 2 | 0.36 | 5.61 (0.68-20.25) |
| Cerebrovascular Diseases | 23 | 8.97 | 2.56# (1.63-3.85) | 8 | 2.15 | 3.71# (1.6-7.32) | 7 | 1.72 | 4.07# (1.63-8.38) | 5 | 2.56 | 1.95 (0.63-4.55) | 2 | 1.13 | 1.76 (0.21-6.37) | 1 | 1.4 | 0.72 (0.02-3.98) |
| Other Infectious and Parasitic Diseases including HIV | 15 | 1.35 | 11.15# (6.24-18.38) | 5 | 0.32 | 15.77# (5.12-36.8) | 5 | 0.27 | 18.31# (5.94-42.73) | 2 | 0.4 | 4.98 (0.6-18) | 1 | 0.16 | 6.2 (0.16-34.56) | 2 | 0.19 | 10.36# (1.25-37.42) |
| Symptoms, Signs and Ill-Defined Conditions | 12 | 1.85 | 6.48# (3.35-11.33) | 9 | 0.44 | 20.49# (9.37-38.89) | 1 | 0.35 | 2.83 (0.07-15.77) | 2 | 0.53 | 3.8 (0.46-13.73) | 0 | 0.24 | 0 (0-15.55) | 0 | 0.29 | 0 (0-12.53) |
Abbreviations: SMR, standardized mortality ratio; CI, confidence interval;
significant difference.
Discussion
There are more than 80,000 new cases and 17,000 deaths each year in the United States alone [10,11]. We need to find out the important factors that cause bladder cancer and its death, and then optimize our health care system. There are many pathogenic factors of bladder cancer. The identified risk factors include smoking, being male, advanced age, white skinned, occupational exposure to certain chemicals, pelvic radiation, use of drugs such as cyclophosphamide, chronic bladder infection/irritation, schistosomiasis [12]. The main risk factor for bladder cancer is smoking. It is believed that the risk of bladder cancer for people who smoke regularly is 2.5 times that of people who do not smoke [13-15]. Advanced age is also a high-risk factor for bladder cancer. The average age at diagnosis is between 70 and 84. This is due to exposure to carcinogens, such as tobacco smoke, and the less common benzene chemicals and aromatic amines, plus age-related DNA repair ability decline [3]. Some research also showed that other related factors include diabetes, obesity, and human papillomavirus [16-18].
Our research data showed that the mortality and risk of death of female patients with bladder cancer were higher than that of males. The same research showed that although the incidence of bladder cancer was three times higher in men, women’s outcomes consistently appeared to be worse [19,20]. The most common clinical manifestation of bladder cancer was hematuria, but hematuria in women was usually attributed to infection, leading to delays in the diagnosis of bladder cancer, resulting in women’s cancer specificity and worse overall survival rates [21]. Recent studies have shown that, compared with men, the effects of hormone receptor and genome differences in certain bladder cancers on women may also be part of the reasons [22]. Regarding race, although the number of white patients was the largest and then black skinned people were second to them, the risk of death of blacks was often higher than that of whites. Some scholars had put forward the same view that bladder cancer affected whites twice as much as blacks or Hispanics, but black patients were more likely to be diagnosed at an advanced stage [23]. This may not only reflect genetic differences, but also socioeconomic differences [1]. In NMIBC, we found that there was no significant difference in the SMR between patients with chemotherapy and non-chemotherapy. While radiotherapy can significantly reduce SMR, for non-MMIBC and MBC, neither radiotherapy nor chemotherapy can reduce SMR. Therefore, we look forward to seeking better therapies, such as surgery combined with neoadjuvant chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy, to improve the survival rate of patients [23].
The most common cause of non-neoplastic deaths from bladder cancer was heart diseases. Studies have shown that cancer patients faced a higher risk of death from cardiovascular diseases throughout their lives. The death rate of cardiovascular diseases in cancer patients was 2-6 times that of the general population on average [24]. This may be due to the long-term use of chemotherapeutics, which has dose-dependent cardiotoxicity, leading to cardiomyopathy and heart failure [25,26]. In addition, other high-risk diseases such as diabetes, nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and nephrosis, diabetes mellitus disease, etc. can change the body’s metabolic state and hemodynamics, thereby increasing the burden on the heart. The risk of death from cardiovascular disease was obviously throughout the entire process of cancer treatment, including the early and late follow-up. Considering such serious and persistent consequences, reactive management methods that only work when clinical manifestations and complications occur were no longer applicable. On the contrary, we advocate a proactive approach, which begins before any cancer treatment is given and lasts for a lifetime thereafter. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease was the second largest non-tumor cause of death after heart diseases. At the same time, lung cancer and bronchial cancer were the most common non-bladder cancer malignancies after diagnosis of bladder cancer. Bladder cancer has such a significant impact on the lungs, but the reason is still unknown. Another noteworthy point was that the risk of death from septicemia, other infectious and parasitic diseases including HIV was much higher than that of the general population, especially in non-MMIBC and MBC. This may be caused by using chemotherapy drugs causing bone marrow suppression and reduced white blood cell production which is related to the dysfunction of the immune system. Studies have shown that the main suicide patients were male, white, diagnosed with lung cancer, head, neck cancer, testicular cancer, bladder cancer and Hodgkin’s lymphoma, which had the highest SMR (>5-10) [27]. A study found that the suicide rate of bladder cancer patients in British Columbia is 2.71 times that of the general population (95% credible interval 2.02, 3.62) [28]. Men, the elderly, unmarried status, whites, and non-localized diseases were risk factors for suicide [26]. Interestingly, the median time from diagnosis to suicide was 43 months [25], which emphasizes the necessity of providing long-term survival support and basic psychological encouragement for patients with bladder cancer.
Compared with the general population, patients with bladder cancer were at a higher risk of dying from other non-neoplastic diseases. High-risk patients should not consider intensive treatment of bladder cancer, nor should they undergo intensive medical management during and after treatment. Therefore, our research on non-cancerous causes of death may help clinicians individualize the risk characteristics of specific early death events, thereby contributing to more individualized clinical decision-making and survival planning. In addition, the survival time and causes of death for patients were also affected to a certain extent by their lifestyle. It was estimated that 30-40% of cancers can achieve primary prevention by changing lifestyle and environmental risk factors known to be associated with cancer morbidity. An active lifestyle can also contribute to tertiary prevention of cancer and reduce cancer mortality [30]. A healthy lifestyle, including avoiding smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, active exercise, avoiding harmful alcohol consumption and maintaining a healthy diet are the best strategies for preventing and treating cancer and other major non-communicable diseases [31]. Previous studies have shown that physical exercise can reduce the risk and mortality of breast cancer, colon cancer and bladder cancer [32]. Drinking more water and increasing the intake of vegetables and fruits could prolong the survival time of patients with bladder cancer. Vegetables and fruits contain many micronutrients and phytochemicals that may prevent or inhibit carcinogenicity, thereby prolonging the survival of patients with bladder cancer [33]. However, bladder cancer patients have physical discomfort, reduced exercise, loss of appetite and other conditions, the pursuit of the healthiest lifestyle is not ideal. Given the low proportion of people with healthy lifestyles in many countries, creating an environment more conducive to behavioral change should be a priority for public health worldwide.
There were some limitations in our study. Firstly, we used AJCC TNM 6th edition staging (2004-2015) to distinguish NMIBC, non-MMIBC and MBC, but these classifications are not the same as the current version. Therefore, the results of this study can’t fully represent the current staging results. Secondly, the treatment information of patients in this database was incomplete. The database only provided radiotherapy and chemotherapy records, but not detailed treatment information. For non-MMIBC and MBC patients, the treatments varied greatly which had important impacts on the survival time and the death reasons. Our results might be influenced by this missing information. Therefore, high-quality studies are needed in the future to explore the main causes of deaths and related risk of deaths compared with general population.
In summary, during the follow-up period after diagnosis, deaths caused by non-bladder cancer accounted for a considerable proportion of patients with bladder cancer, especially NMIBC and non-MMIBC. Heart disease and other malignant tumors accounted for the largest number of deaths from non-bladder cancer. Other important non-cancer causes of death include chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, nephritis, nephrotic syndrome and nephrosis, diabetes mellitus, sepsis and other infectious diseases, and suicide. Our findings will help guide bladder cancer patients about their future health and life managements.
Disclosure of conflict of interest
None.
References
- 1.Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 2017;71:96–108. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2016.06.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Fuchs HE, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2021. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:7–33. doi: 10.3322/caac.21654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lenis AT, Lec PM, Chamie K, Mshs MD. Bladder cancer: a review. JAMA. 2020;324:1980–1991. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.17598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tse J, Singla N, Ghandour R, Lotan Y, Margulis V. Current advances in BCG-unresponsive non-muscle invasive bladder cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2019;28:757–770. doi: 10.1080/13543784.2019.1655730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Kong J, Diao X, Diao F, Fan X, Zheng J, Yan D, Huang J, Qin H, Lin T. Causes of death in long-term bladder cancer survivors: a population-based study. Asia Pac J Clin Oncol. 2019;15:e167–e174. doi: 10.1111/ajco.13156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kirkali Z, Chan T, Manoharan M, Algaba F, Busch C, Cheng L, Kiemeney L, Kriegmair M, Montironi R, Murphy WM, Sesterhenn IA, Tachibana M, Weider J. Bladder cancer: epidemiology, staging and grading, and diagnosis. Urology. 2005;66:4–34. doi: 10.1016/j.urology.2005.07.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Smith ZL, Christodouleas JP, Keefe SM, Malkowicz SB, Guzzo TJ. Bladder preservation in the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer (MIBC): a review of the literature and a practical approach to therapy. BJU Int. 2013;112:13–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11762.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ghandour R, Singla N, Lotan Y. Treatment options and outcomes in nonmetastatic muscle invasive bladder cancer. Trends Cancer. 2019;5:426–439. doi: 10.1016/j.trecan.2019.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. www.seer.cancer.gov.
- 10.Richters A, Aben KKH, Kiemeney LALM. The global burden of urinary bladder cancer: an update. World J Urol. 2020;38:1895–1904. doi: 10.1007/s00345-019-02984-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34. doi: 10.3322/caac.21551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bellmunt J. Bladder cancer. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2015;29:xiii–xiv. doi: 10.1016/j.hoc.2014.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Cumberbatch MG, Rota M, Catto JW, La Vecchia C. The role of tobacco smoke in bladder and kidney carcinogenesis: a comparison of exposures and meta-analysis of incidence and mortality risks. Eur Urol. 2016;70:458–466. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.06.042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Freedman ND, Silverman DT, Hollenbeck AR, Schatzkin A, Abnet CC. Association between smoking and risk of bladder cancer among men and women. JAMA. 2011;306:737–745. doi: 10.1001/jama.2011.1142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Park S, Jee SH, Shin HR, Park EH, Shin A, Jung KW, Hwang SS, Cha ES, Yun YH, Park SK, Boniol M, Boffetta P. Attributable fraction of tobacco smoking on cancer using population-based nationwide cancer incidence and mortality data in Korea. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:406. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Sun JW, Zhao LG, Yang Y, Ma X, Wang YY, Xiang YB. Obesity and risk of bladder cancer: a dose-response meta-analysis of 15 cohort studies. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0119313. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0119313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Zhu Z, Wang X, Shen Z, Lu Y, Zhong S, Xu C. Risk of bladder cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: an updated meta-analysis of 36 observational studies. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:310. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-13-310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li N, Yang L, Zhang Y, Zhao P, Zheng T, Dai M. Human papillomavirus infection and bladder cancer risk: a meta-analysis. J Infect Dis. 2011;204:217–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Uhlig A, Seif Amir Hosseini A, Simon J, Lotz J, Trojan L, Schmid M, Uhlig J. Gender specific differences in disease-free, cancer specific and overall survival after radical cystectomy for bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Urol. 2018;200:48–60. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2017.11.150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Liu S, Yang T, Na R, Hu M, Zhang L, Fu Y, Jiang H, Ding Q. The impact of female gender on bladder cancer-specific death risk after radical cystectomy: a meta-analysis of 27,912 patients. Int Urol Nephrol. 2015;47:951–958. doi: 10.1007/s11255-015-0980-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Dobruch J, Daneshmand S, Fisch M, Lotan Y, Noon AP, Resnick MJ, Shariat SF, Zlotta AR, Boorjian SA. Gender and bladder cancer: a collaborative review of etiology, biology, and outcomes. Eur Urol. 2016;69:300–310. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2015.08.037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Hurst CD, Alder O, Platt FM, Droop A, Stead LF, Burns JE, Burghel GJ, Jain S, Klimczak LJ, Lindsay H, Roulson JA, Taylor CF, Thygesen H, Cameron AJ, Ridley AJ, Mott HR, Gordenin DA, Knowles MA. Genomic subtypes of non-invasive bladder cancer with distinct metabolic profile and female gender bias in KDM6A mutation frequency. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:701–715. e707. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2017.08.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.DeGeorge KC, Holt HR, Hodges SC. Bladder cancer: diagnosis and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:507–514. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sturgeon KM, Deng L, Bluethmann SM, Zhou S, Trifiletti DM, Jiang C, Kelly SP, Zaorsky NG. A population-based study of cardiovascular disease mortality risk in US cancer patients. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:3889–3897. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Klaassen Z, Goldberg H, Chandrasekar T, Arora K, Sayyid RK, Hamilton RJ, Fleshner NE, Williams SB, Wallis CJD, Kulkarni GS. Changing trends for suicidal death in patients with bladder cancer: a 40+ year population-level analysis. Clin Genitourin Cancer. 2018;16:206–212. e201. doi: 10.1016/j.clgc.2017.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Mohamed NE, Chaoprang Herrera P, Hudson S, Revenson TA, Lee CT, Quale DZ, Zarcadoolas C, Hall SJ, Diefenbach MA. Muscle invasive bladder cancer: examining survivor burden and unmet needs. J Urol. 2014;191:48–53. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2013.07.062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zaorsky NG, Zhang Y, Tuanquin L, Bluethmann SM, Park HS, Chinchilli VM. Suicide among cancer patients. Nat Commun. 2019;10:207. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-08170-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Klaassen Z, DiBianco JM, Jen RP, Harper B, Yaguchi G, Reinstatler L, Woodard C, Moses KA, Terris MK, Madi R. The impact of radical cystectomy and urinary diversion on suicidal death in patients with bladder cancer. J Wound Ostomy Continence Nurs. 2016;43:152–157. doi: 10.1097/WON.0000000000000188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhai M, Tang C, Li M, Chen X, Jin Y, Ying X, Tang Z, Wang X, Wu Y, Sun C, Chen K, Guo X. Short-term mortality risks among patients with non-metastatic bladder cancer. BMC Cancer. 2020;20:1148. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07655-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Friedenreich CM, Ryder-Burbidge C, McNeil J. Physical activity, obesity and sedentary behavior in cancer etiology: epidemiologic evidence and biologic mechanisms. Mol Oncol. 2021;15:790–800. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.12772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhang YB, Pan XF, Chen J, Cao A, Zhang YG, Xia L, Wang J, Li H, Liu G, Pan A. Combined lifestyle factors, incident cancer, and cancer mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Br J Cancer. 2020;122:1085–1093. doi: 10.1038/s41416-020-0741-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.McTiernan A, Friedenreich CM, Katzmarzyk PT, Powell KE, Macko R, Buchner D, Pescatello LS, Bloodgood B, Tennant B, Vaux-Bjerke A, George SM, Troiano RP, Piercy KL. Physical activity in cancer prevention and survival: a systematic review. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2019;51:1252–1261. doi: 10.1249/MSS.0000000000001937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Kwan ML, Garren B, Nielsen ME, Tang L. Lifestyle and nutritional modifiable factors in the prevention and treatment of bladder cancer. Urol Oncol. 2019;37:380–386. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2018.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]