Abstract
COVID-19 is a highly infectious disease caused by the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus. It rapidly escalated into a global pandemic, causing more than 6 million fatalities by March 2022, a little over 2 years since its emergence in December 2019. The first peptidomimetic coronavirus main protease inhibitor, nirmatrelvir, was granted Emergency Use Authorization by the U.S. FDA on Dec 22, 2021. Less than a month after its patent application, Hoffmann La-Roche scientists filed a patent application describing azadipeptide peptidomimetic inhibitors (WO 2022/043374 A1). This patent highlight reveals the structure–activity relationship of key azadipeptide inhibitors described in the patent.
Important Compound Classes
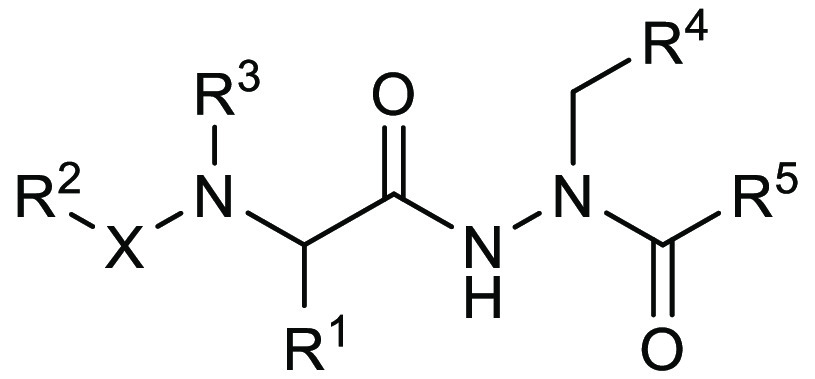
Title
Aminocarbamoyl Compounds for the Treatment of Viral Infections
Patent Publication Number
WO 2022/043374 A1
URL: https://patentscope2.wipo.int/search/en/detail.jsf?docId=WO2022043374
Publication Date
March 3, 2022
Priority Application
PCT/CN2020/111852 and PCT/CN2021/108676
Priority Date
August 27, 2020 and July 27, 2021
Inventors
Chen, J.; Liang, C.; Miao, K.; Wu, Y.; Yun, H.; Zhang, W.
Assignee Company
Hoffmann-La Roche AG, Basel.
Disease Area
COVID-19
Biological Target
SARS-CoV-2 main protease
Summary
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a highly infectious disease caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). It was first reported in China in December 2019 and was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) in March 2020. Common symptoms include sore throat, dry cough, fever, headache, fatigue, and a loss of taste or smell. Serious symptoms include breathing difficulties or shortness of breath and chest pains which can lead to death. By mid-March 2022, the WHO recorded 456 million cases and more than 6 million fatalities worldwide. On Dec 22, 2021, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) to Pfizer’s antiviral drug, nirmatrelvir, for treating COVID-19 in combination with ritonavir. The former is a peptidomimetic specifically targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro), also known as 3 chymotrypsin-like protease (3CLpro). This protease plays an essential role in viral polyprotein processing, cleaving the viral polyprotein in at least 11 sites to yield functional proteins required for the virus to survive and propagate. The drug was designed based on the natural 3CLpro polypeptide substrate recognition sequence: valine–leucine–glutamine, with an electrophilic nitrile at its C-terminus which forms a covalent bond to 3CLpro’s Cys145 thiol, resulting in its inhibition.
As a testament to the immense efforts by the global community to develop an antiviral, Hoffman-La Roche filed their patent application (WO 2022/043374 A1) less than a month after Pfizer’s patent application, describing 101 novel SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro azadipeptide inhibitors with C-terminal electrophilic halomethyl ketone warheads. Interestingly, most of the inhibitors possess a primary amide on their P1 residue side chains like natural glutamine, in contrast to the five-membered lactam found in nirmatrelvir. It is also noteworthy that 95% of the reported azapeptides were potent SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors possessing sub-micromolar IC50 values and 26% exhibited single-digit nanomolar potencies.
Key Structures
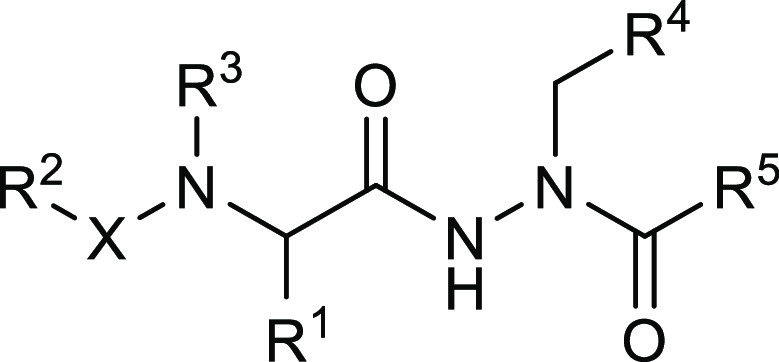
The inventors described 101 novel structures with their synthesis procedures. Key exemplified structures and their 3CLpro IC50 values are shown in the table below.
Biological Assay
SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro IC50 values were determined in a biochemical SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro fluorescence resonance energy transfer assay, where the exemplified compounds were challenged with a fluorogenic peptide substrate, FAM-KTSAVLQSGFRKMEK-TAMRA, in the presence of SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro.
Biological Data
The SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro IC50 data of key inhibitors are summarized in the
following table.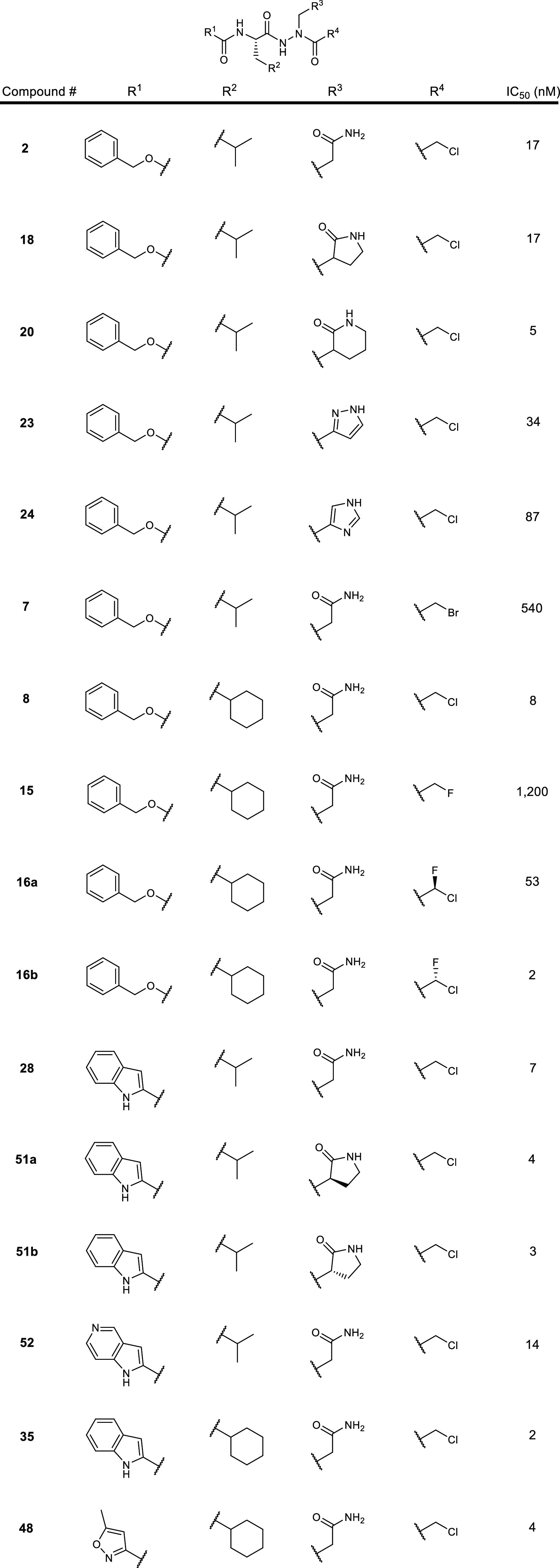
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (ASTAR), Singapore, for funding this patent review.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Recent Review Articles. References
- Banerjee R.; Perera L.; Tillekeratne L. M. V. Potential SARS-CoV-2 main protease inhibitors. Drug Discovery Today. 2021, 26, 804. 10.1016/j.drudis.2020.12.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chia C. S. B. Novel Nitrile Peptidomimetics for Treating COVID-19. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022, 13, 330. 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.2c00030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


