Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this systematic review was to provide an overview of current applications of 3D technologies in surgical management of tibial plateau fractures and to assess whether 3D-assisted surgery results in improved clinical outcome as compared to surgery based on conventional imaging modalities.
Methods
A literature search was performed in Pubmed and Embase for articles reporting on the use of 3D techniques in operative management of tibial plateau fractures. This systematic review was performed in concordance with the PRISMA-guidelines. Methodological quality and risk of bias was assessed according to the guidelines of the McMaster Critical Appraisal. Differences in terms of operation time, blood loss, fluoroscopy frequency, intra-operative revision rates and patient-reported outcomes between 3D-assisted and conventional surgery were assessed. Data were pooled using the inverse variance weighting method in RevMan.
Results
Twenty articles evaluating 948 patients treated with 3D-assisted surgery and 126 patients with conventional surgery were included. Five different concepts of 3D-assisted surgery were identified: ‘3D virtual visualization’, ‘3D printed hand-held fracture models’, ‘Pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plates’, ‘3D printed surgical guides’, and ‘Intra-operative 3D imaging’. 3D-assisted surgery resulted in reduced operation time (104.7 vs. 126.4 min; P < 0.01), less blood loss (241 ml vs. 306 ml; P < 0.01), decreased frequency of fluoroscopy (5.8 vs. 9.1 times; P < 0.01). No differences in functional outcome was found (Hospital for Special Surgery Knee-Rating Scale: 88.6 vs. 82.8; P = 0.23).
Conclusions
Five concepts of 3D-assisted surgical management of tibial plateau fractures emerged over the last decade. These include 3D virtual fracture visualization, 3D-printed hand-held fracture models for surgical planning, 3D-printed models for pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plates, 3D-printed surgical guides, and intra-operative 3D imaging. 3D-assisted surgery may have a positive effect on operation time, blood loss, and fluoroscopy frequency.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s00068-021-01773-2.
Keywords: Tibial plateau fracture, Three dimensional, 3D printing, Guided surgery, 3D preoperative planning, 3D virtual surgical planning
Introduction
Intra-articular fractures of the tibial plateau are usually composed of complex fracture patterns including multiple fracture fragments, which are displaced and rotated in multiple directions. Achieving normal knee alignment and an optimal reconstruction of the articular surface decreases the risk of progressive osteoarthritis [1]. However, due to the complexity of these fractures, the goals of surgery cannot always be achieved. Recently, it has been shown that up to 30% of the surgically treated tibial plateau fractures resulted in a suboptimal reduction [2]. Assessment of the fracture is essential to fully understand the fracture pattern and to choose the optimal treatment strategy. Clinical decision-making and preoperative planning is mostly based on conventional imaging modalities, including plain radiographs, two-dimensional (2D) fluoroscopy and 2D CT images [3]. With these modalities, it is difficult to fully comprehend the true extent of these injuries, since the fracture fragments are often displaced and rotated in multiple directions. 3D visualization and printing modalities have the potential to provide the physician with a better understanding of the fracture pattern and could improve treatment strategy and patient outcome [4, 5].
The growing popularity and expansion across industries providing 3D printing resources has substantially decreased costs, increased access, and led to multiple applications in orthopaedic trauma surgery [6, 7]. Early results on the clinical application of 3D printing improved levels of understanding into complex fractures for both surgeons and patients and strengthened the informed consent process [8]. Also, 3D technologies may be valuable for teaching students about fracture morphology or explaining residents about the surgical plan [9]. 3D-assisted surgery encompasses the use of 3D technology to pre-plan the operation and guide the surgeon to the planned outcome during surgery. This includes a spectrum of modalities such as 3D visualization, 3D printing and patient-specific surgical guides or implants. However, the potential advantages of 3D-assisted surgery in tibial plateau fracture management are still subject of debate.
Despite the rapid advances in technology and an increasing number of publications on the applications of 3D technologies, a comprehensive overview of the current evidence for the application of 3D-assisted surgery of tibial plateau fractures is still lacking. Therefore, the purpose of this systematic review is to provide a complete and comprehensive overview of the currently used concepts of 3D-assisted surgery in patients receiving surgical treatment for their tibial plateau fracture by including both observational and intervention studies. The aim is to answer the following clinical research questions: (1) Does the clinical application of 3D-assisted surgery for tibial plateau fractures improve intra-operative results in terms of operation time, blood loss, fluoroscopy time and intra-operative surgical revisions compared to conventional surgery? (2) Does the application of 3D-assisted surgery improve postoperative results in terms of patient functional outcome compared to conventional surgery?
Materials and methods
This systematic review was performed according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews (PRISMA) [10]. The protocol of this systematic review is registered in the international PROSPERO-database (CRD42021235524). Ethical approval was not required for this study.
Search strategy
The Pubmed and Embase libraries were searched on the 1st of February 2021 for articles published on state-of-the-art 3D technology between January 2010 until January 2021. The search string was developed in collaboration with a medical librarian. The exact search string for the different libraries is shown in the online supplementary (Appendix 1 in Supplementary file 1).
Study selection
Eligible studies for inclusion were randomized controlled trials, prospective and retrospective observational studies, descriptive studies, and case reports reporting on the use of 3D techniques in the management of tibial plateau fractures in orthopaedic trauma patients. Studies were excluded in case of: (1) paediatric fractures; (2) fracture classification studies; (3) animal or cadaveric studies; (4) review articles, letters to the editor or conference abstracts; and (5) studies in another language than English, German, French, Spanish or Dutch.
All articles were imported into Rayyan QCRI, a web-based sorting tool for systematic literature reviews [11]. The study selection was then performed in two phases: first two reviewers (NA, FIJ) independently screened the articles for eligibility based on the titles and abstracts using the Rayyan QCRI tool. Second, all articles which were considered eligible, were subsequently screened in full text by the same reviewers. Disagreement was resolved by discussion according to the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions [12].
Quality check and data extraction
Methodological quality and risk of bias of the included studies were independently assessed by NA and FIJ according to the guidelines of the McMaster University Occupational Therapy Evidence-Based Practice Research Group [13]. Any continued disagreements were solved during a consensus meeting with NA, FIJ and IR. The McMaster critical appraisal consists of eight categories including: (1) study purpose; (2) literature review; (3) study design; (4) study sample; (5) study outcome; (6) study intervention; (7) study results; and (8) conclusions and implications. Scores were giving with ‘yes = 1 point’, ‘no = 0 points’, ‘not addressed (NS)’, and ‘not applicable (NA)’. The total score reflects the methodological quality with a maximum score of 16 for RCTs and 14 for other designs. The definitive score is expressed as a percentage that may vary from 0 to 100%, with a higher score indicating a higher methodological quality. Scores between 90 and 100% were considered as excellent quality, studies between 75 and 89% as good quality studies and studies < 75% as moderate quality studies.
The data extraction was independently conducted (NA, FIJ) using a precompiled extraction file (Microsoft Excel version 14.0; Microsoft Inc., Redmond, WA, USA). Information on study characteristics, fracture classification, 3D technologies and outcome measures were extracted. In case data regarding the reported outcomes was missing, authors were contacted to retrieve raw data or means with their standard deviations.
Outcome measures
All parameters describing the operation were determined to assess the effect of 3D-assisted surgery on intra-operative results. These parameters include operation time, blood loss, fluoroscopy time, and the number of intra-operative revisions of the fracture reduction or implant position as a result of intra-operative 3D imaging. Second, Patient-Reported Outcome Measures (PROMs) were recorded to evaluate the effect of 3D-assisted surgery on postoperative functional outcome.
Statistical analysis
Analysis of the extracted data was performed using RevMan (version 5.4.1). Continuous variables were presented as means with standard deviation (SD) and dichotomous variables as frequencies and percentages. Continuous outcomes were pooled using the inverse variance weighting method and were presented as weighted mean difference (WMD) with the corresponding 95% confidence interval (95%CI). Heterogeneity between studies was assessed for all reported outcomes by the I2 statistic for heterogeneity. The I2 statistic was interpreted according to the benchmarks of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions, which considered < 40% as irrelevant, 30–60% as moderate heterogeneity, 50–90% as substantial heterogeneity, and > 75% as considerable heterogeneity [12]. A P value of < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Results
Search
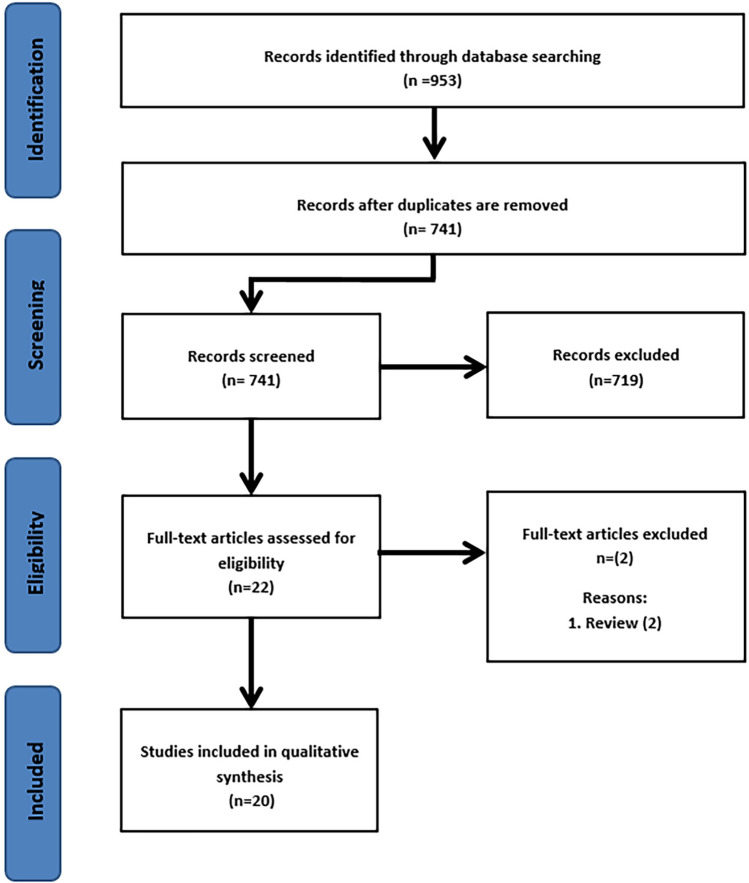
The search resulted in 953 studies, and after removal of duplicates, 741 eligible studies were screened on title and abstract. Eventually, 22 articles were included for full-text screening of which two articles were excluded [14, 15]. Twenty studies met the inclusion criteria of this systematic review [8, 16–34]. The review process is summarized in Fig. 1. There were seven prospective cohort studies [20, 21, 24, 27, 28, 32, 34], four retrospective cohort studies [16, 19, 26, 29], five case series [22, 23, 30, 31, 33], two case reports [17, 18], one descriptive study [8], and one observational study [25]. No Randomized controlled trials were found. The included studies enrolled a total of 1074 patients with a tibial plateau fracture (mean sample size 53.7; 1–559). Of all included patients, 948 received 3D-assisted tibial plateau fracture surgery and 126 had conventional surgery. There were no differences in fracture classifications between the 3D-assisted and the conventional group. The study characteristics are presented in Table 1.
Fig. 1.
Flow diagram according to PRISMA strategy
Table 1.
Study characteristics
| Study | Year | Country | Design | N | Period | 3D technology assessed | Fracture classification | Outcomes of interest |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Beisemann et al. [16] | 2019 | Germany | Retrospective cohort study | 559 | 2001–2017 | Intra-operative 3D imaging | AO/OTA: 41 B1–3 and C1-3 | Intra-operative revisions |
| Bizzotto et al.[8] | 2016 | Italy | Descriptive study | 102 (O/W 19 TPFs) | 2014–2015 | 3D printed fracture model | AO/OTA: 41 B1–3 and C1-3 | User-experience |
| Citak et al. [17] | 2010 | Germany; USA | Case report | 1 | NS | Intra-operative 3D imaging | Schatzker III | User-experience; Operation time |
| Delcogliano et al. [18] | 2020 | Switzerland; Italy | Case report | 1 | NS | Pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plate | NS | User-experience |
| Franke et al. [19] | 2016 | Germany | Retrospective cohort study | 279 (O/W 109 TPFs) | 2001–2011 | Intra-operative 3D imaging | AO/OTA: 41 C1–3 | Intra-operative revisions |
| Giannetti et al. [20] | 2016 | Italy | Prospective cohort study | 40 | NS | 3D printed fracture model vs. Conventional | Schatzker I–VI | Length of hospital stay; operation time; tourniquet time; blood loss; Rasmussen functional score |
| Guo et al. [21] | 2019 | China | Prospective cohort study | 28 | 2016–2018 | 3D printed fracture model vs. Conventional | Schatzker II, IV–VI | Operation time; blood loss; fluoroscopy time; costs; HSS Score |
| Horas et al. [22] | 2020 | Germany | Case series | 4 (O/W 1TPF) | NA | 3D printed fracture model | Moore type II | User-experience |
| Huang et al. [23] | 2018 | China | Case series | 6 | 2013–2014 | 3D Printed surgical guide | Schatzker V–VI | Screw length; screw entry point; screw direction |
| Lou et al. [24] | 2016 | China | Prospective cohort study | 72 | 2014–2015 | 3D printed fracture model vs. Conventional | Schatzker III–VI | Operation time; blood loss; no. fluoroscopy; HSS Score |
| Mishra et al. [25] | 2019 | India | Observational study | 91 (O/W 10 TPFs) | 2017–2019 | Pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plate | NS | Surgeons experience |
| Nie et al. [26] | 2019 | China | Retrospective cohort study | 13 | 2015–2016 | 3D Printed surgical guide | Schatzker V–VI | Length of screws; Operation time; Blood loss; HSS Score |
| Ozturk et al. [27] | 2020 | Turkey | Prospective cohort study | 20 | 2017–2018 | 3D printed fracture model vs. Conventional | Schatzker I, II and VI | Operation time; Blood loss; tourniquet time; no. fluoroscopy; Rasmussen score |
| Ruan et al. [28] | 2011 | China | Prospective cohort study | 30 | 2009 – 2010 | Intra-operative 3D imaging vs. conventional | Schatzker II, IV–VI | Intra-operative revisions |
| Shen et al. [29] | 2020 | China | Retrospective cohort study | 42 | 2014–2018 | 3D printed fracture model vs. conventional | Schatzker IV–VI | Operation time; blood loss; no. fluoroscopy; no. plate reshaping; Rasmussen score; HSS score |
| Suero et al. [30] | 2010 | USA; Germany | Case series | 5 | NS | 3D virtual visualization | AO/OTA: 41 B3, C1 and C3 | Planning time 3D reconstruction |
| Wang et al. [31] | 2017 | China; United Kingdom | Case series | 6 | NS | 3D printed surgical guide | Schatzker I, III and IV | Likert scale; radiographic reduction; Oxford Knee Score |
| Wu et al. [32] | 2019 | China | Prospective cohort study | 69 | 2014–2016 | 3D printed fracture model | Schatzker V–VI | Radiographic reduction; Rasmussen Clinical Functional Score; Infections |
| Yang et al. [33] | 2016 | China | Case series | 7 | 2012–2014 | 3D printed fracture model | Schatzker I–III | Operation time; blood loss; Rasmussen anatomy score; Rasmussen knee functional score |
| Zhang et al. [34] | 2015 | China | Prospective cohort study | 36 | 2011–2013 | 3D virtual visualization vs. conventional | Schatzker III | Operation time; incision length; blood loss |
TPFs tibial plateau fractures, O/W of which, NA not applicable, NS not addressed
Identified 3D applications in tibial plateau fracture surgery
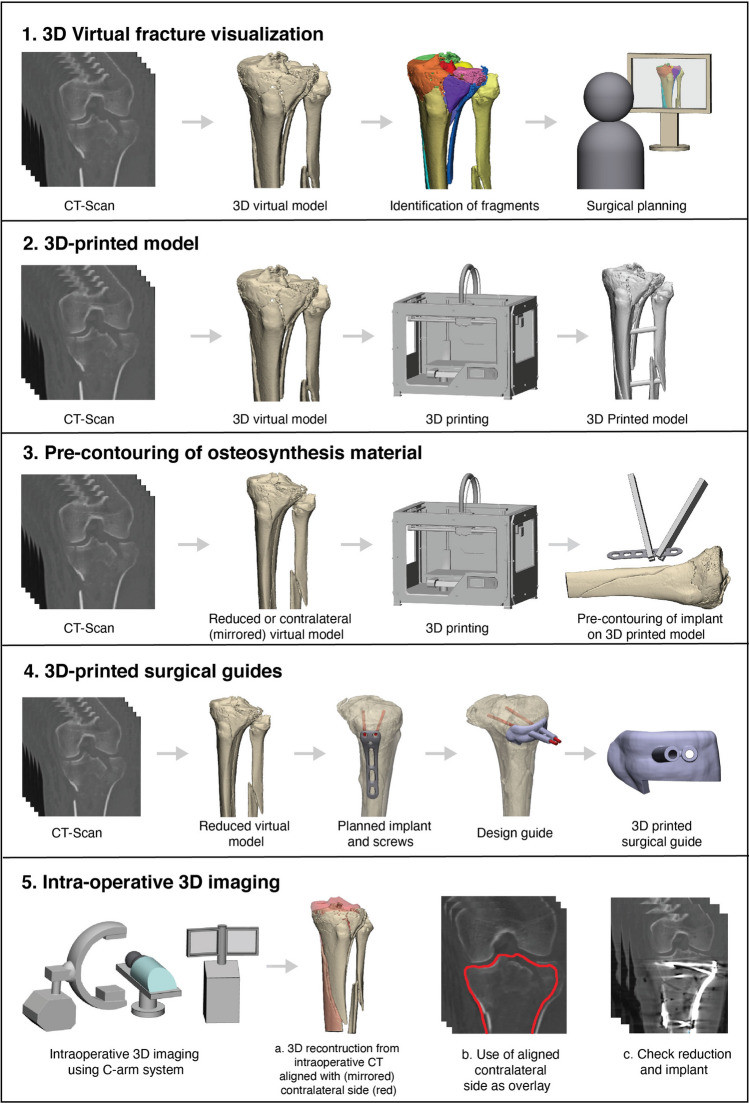
Within this search, five different concepts of 3D-assisted surgery in the management of tibial plateau fractures were identified over the past decade: ‘3D virtual fracture visualization’, ‘3D printed hand-held models’, ‘Pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plates’, ‘3D printed surgical guides’ and ‘Intra-operative 3D imaging’. Figure 2 depicts a representation of these concepts.
Fig. 2.
Schematic overview of the different concepts of 3D-assisted surgery in tibial plateau fractures
3D virtual fracture visualization
Two studies reported about the use of 3D virtual visualization of the fracture before surgery [30, 34]. Suero et al. used the VoXim software (IVS Solutions AG, Chemnitz, Germany) to create a 3D reconstruction of the fracture from which the surgeon determined the surgical plan [30], whereas Zhang et al. used the Mimics software (Materialise, Leuven, Belgium) to determine a preoperative plan in which the reduction procedure was simulated [34]. Using the 3D software, the required elevation of the depressed articular surface was measured and the surgical procedure was virtually planned.
3D-printed hand-held models
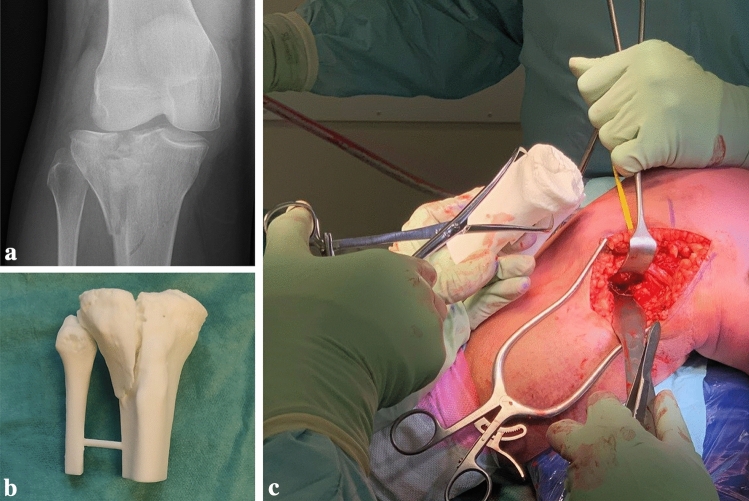
The majority of the studies reported on the use of 3D-printed models of tibial plateau fractures [8, 20–22, 24, 27, 29, 32, 33]. In these studies, a 3D-printed model of the fractured tibial plateau was used to determine the surgical plan and to guide the surgeon during surgery (Fig. 3). Furthermore, the 3D-printed models were found to be useful for educating residents and students, and to inform patients about their injury [8].
Fig. 3.
a Fluoroscopy of an intra-articular fracture of the tibial plateau. b 3D-printed han-held model of the tibial plateau fracture. c Intra-operative fracture assessment using the 3D-printed hand-held model
Pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plates
Two studies reported on the use of pre-contoured osteosynthesis plates [18, 25] using either a 3D-printed contralateral mirrored tibia or a virtually reduced fracture model. Using the printed models, implants were (pre-)operatively bended for optimized fitting along the contour of the proximal tibia.
3D printed surgical guides
Three studies described the use of 3D-printed surgical guides [23, 26, 31]. In two studies, the directions of the screws were virtually predetermined. A surgical guide was designed to translate the predetermined screw trajectories to the actual surgical procedure [23, 26]. Another application of a surgical guide was found in the operative correction of a malunited tibial plateau fracture by Wang et al. [31]. First the osteotomy was performed using a guide, which helped the surgeon to perform the (virtually) predetermined osteotomy. Secondly, a reduction guide was applied to help the surgeon to reduce the fragment to its original anatomical position.
Intra-operative 3D imaging
Four studies reported on the use of intra-operative 3D images [16, 17, 19, 28]. These studies investigated the use of an intra-operative 3D imaging system, which was used to verify whether the achieved surgical reduction was satisfactory. Using this technology, the surgeon was able to make prompt perioperative decisions based on 3D instead of 2D fluoroscopy images. In case of dissatisfaction with the articular reduction or the position of the screws or implant, the surgeon could decide instantly during the operation to perform a revision.
Effect of 3D-assisted surgery on clinical outcome
To answer the first research question, the effect of 3D-assisted surgery on intra-operative results in terms of operation time, blood loss, fluoroscopy time and intra-operative revisions was assessed. The second research question concerns the effect of 3D-assisted surgery on post-operative results in terms of functional outcome.
Operation time
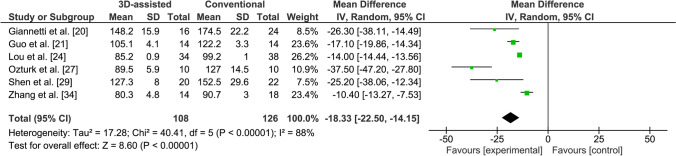
Six studies reported on operation time [20, 21, 24, 27, 29, 34], including one excellent quality, one good quality and four moderate quality studies (Appendix 2 in Supplementary file 2). Five studies reported that surgery assisted by a 3D-printed hand-held model of the fracture led to a significantly shorter operation time in comparison with conventional surgery [20, 21, 24, 27, 29]. Zhang et al. reported that the use of a preoperative 3D virtual model resulted in a significantly reduced operation time compared to conventional surgery [34]. The operation time was significantly shorter for the 3D-assisted group in comparison with the conventional group weighted mean difference (WMD) 18.3 min, 95% CI −22.5 to −14.5) (Fig. 4). The heterogeneity was considerable within these studies (I2 = 88%).
Fig. 4.
Forest plot for the operation time (min)
Blood loss
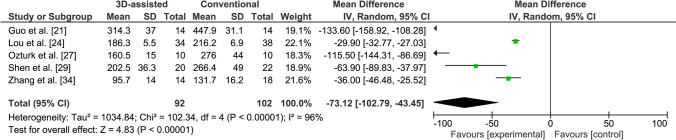
Six studies reported on blood loss [20, 21, 24, 27, 29, 34]. However, Giannetti et al. did not report the standard deviation and was, therefore, excluded from further analysis [20], leaving five studies, including one excellent quality study and four moderate quality studies. Four studies reported that 3D-printed model-assisted fracture surgery led to significantly less blood loss in comparison with conventional surgery [21, 24, 27, 29]. Zhang et al. reported that the use of a preoperative 3D virtual model resulted in significantly less blood loss compared to conventional surgery [34]. The blood loss was significantly less in the 3D-assisted group in comparison with the conventional group (WMD 73.1 ml, 95% CI −102.8 to −43.5) (Fig. 5). The heterogeneity was considerable within these studies (I2 = 96%).
Fig. 5.
Forest plot for the blood loss (ml)
Fluoroscopy frequency
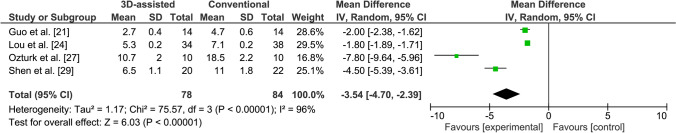
Four studies reported on the frequency of use of fluoroscopy [21, 24, 27, 29], including one study of excellent quality and three of moderate quality. The use of fluoroscopy was significantly reduced in the 3D-assisted group in comparison with the conventional group (WMD 3.5 times used, 95% CI −4.7 to −2.4) (Fig. 6). The heterogeneity was considerable within these studies (I2 = 96%).
Fig. 6.
Forest plot for the fluoroscopy frequency (number of shots)
Intra-operative revision rates
Three studies reported on immediate intra-operative revision rates resulting from intra-operative 3D imaging [16, 19, 28], including two good quality and one moderate study. These articles reported on a total of 698 patients of which 183 (26.2%) patients had an instant intra-operative revision of the fracture reduction or implant position as a result of intra-operative 3D imaging (Table 2).
Table 2.
Study outcomes
| Measure | Study | 3D technology | Groups | Outcome | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3D (N) | Conventional (N) | 3D | Conventional | P value | |||
| Operation results | |||||||
| Operation time (min) | Giannetti et al. [20] | 3D printed fracture models | 16 | 24 | 148.2 ± 15.9 | 174.5 ± 22.2 | 0.041* |
| Mean ± SD | Guo et al.[21] | 3D printed fracture models | 14 | 14 | 105.1 ± 4.1 | 122.2 ± 3.3 | < 0.05* |
| Lou et al.[24] | 3D printed fracture models | 34 | 38 | 85.2 ± 0.9 | 99.2 ± 1.0 | < 0.001* | |
| Ozturk et al. [27] | 3D printed fracture models | 10 | 10 | 89.5 ± 5.9 | 127 ± 14.5 | < 0.05* | |
| Shen et al.[29] | 3D printed fracture models | 20 | 22 | 127.3 ± 8.0 | 152.5 ± 29.6 | 0.001* | |
| Zhang et al.[34] | 3D virtual visualization | 14 | 18 | 80.3 ± 4.8 | 90.7 ± 3 | < 0.001* | |
| Blood loss (ml) | Guo et al.[21] | 3D printed fracture models | 14 | 14 | 314.3 ± 37.0 | 447.9 ± 31.1 | < 0.05* |
| Mean ± SD | Lou et al.[24] | 3D printed fracture models | 34 | 38 | 186.3 ± 5.5 | 216.2 ± 6.9 | 0.013* |
| Ozturk et al. [27] | 3D printed fracture models | 10 | 10 | 160.5 ± 15 | 276 ± 44 | < 0.05* | |
| Shen et al.[29] | 3D printed fracture models | 20 | 22 | 202.5 ± 36.3 | 266.4 ± 49.0 | 0.001* | |
| Zhang et al.[34] | 3D virtual visualization | 14 | 18 | 95.7 ± 14.0 | 131.7 ± 16.2 | < 0.001* | |
| Fluoroscopy frequency (number of times) | Guo et al.[21] | 3D printed fracture models | 14 | 14 | 2.7 ± 0.4 | 4.7 ± 0.6 | < 0.05* |
| Lou et al.[24] | 3D printed fracture models | 34 | 38 | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | < 0.001* | |
| Ozturk et al. [27] | 3D printed fracture models | 10 | 10 | 10.7 ± 2 | 18.5 ± 2.2 | < 0.05* | |
| Shen et al.[29] | 3D printed fracture models | 20 | 22 | 6.5 ± 1.1 | 11 ± 1.8 | 0.001* | |
| Intra-operative revision rates resulting from 3D imaging (%) | Beisemann et al.[16] | Intra-operative 3D imaging | 559 | – | 148 (26.5%) | – | – |
| Franke et al.[19] | Intra-operative 3D imaging | 109 | – | 29 (27%) | – | – | |
| Ruan et al.[28] | Intra-operative 3D imaging | 30 | – | 6 (20%) | – | – | |
| PROMs | |||||||
| Hospital for Special Knee | Lou et al.[24] | 3D printed fracture models | 34 | 38 | 90.0 ± 0.3 | 85.0 ± 0.4 | < 0.001* |
| Surgery (HSS) score | Shen et al.[29] | 3D printed fracture models | 20 | 22 | 86.1 ± 7.7 | 79.1 ± 6.8 | 0.003* |
| Hospital for Special Knee Surgery (HSS): Excellent and good rate (%) | Guo et al.[21] | 3D printed fracture models | 14 | 14 | 92.9 | 85.7 | 0.54 |
*Significant
Patient-reported functional outcome
Three studies reported on functional outcome [21, 24, 29], of which one was of excellent quality. All studies used the Hospital for Special Surgery (HSS) scoring system. The HSS scoring system is based on a total of 100 points. A HSS score of ≥ 85 points is considered excellent, 70–84 points is good, 60–69 points is fair, and ≤ 59 points is poor [35]. Two studies reported the actual HSS score [24, 29], whereas another study provided the rating of the score [21]. The weighted HSS score was 88.6 (86.1–90) in the 3D-assisted group and 82.8 (79.1–85) in the conventional group. Guo et al. reported no relevant differences in HSS score between 3D printing assisted and conventional surgery [21].
Discussion
The rationale for applying 3D technology in tibial plateau fracture surgery is that it may optimize preoperative planning, potentially improves fracture reduction and eventually benefits the patients’ recovery. This systematic review aimed to provide an overview of the current concepts of 3D-assisted tibial plateau fracture surgery and their relation to clinical outcome. The search was not limited to study design, which provides a complete overview of all 3D applications for tibial plateau fracture surgery published over the last decade. Five different concepts of 3D-assisted surgery were identified including ‘3D virtual visualization’, ‘3D printed hand-held models’, ‘Pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plates’, ‘3D printed surgical guides’, and ‘Intra-operative 3D imaging’. Pooled analysis of studies, concerning mainly the use of 3D-printed models, showed to have a positive effect on operation time, blood loss, and fluoroscopy frequency.
This review revealed that the majority of the studies (nine) used 3D-printed hand-held fracture models in clinical practice. Converting a CT-scan into a hand-held 3D-printed model could provide valuable insights for the pre-operative planning of the fracture reduction and fixation. Care should be taken regarding the soft tissue injuries which cannot be taken into account in the 3D model. These models could be sterilized and used in theatre to guide the surgeon during the operation. From an educational perspective, these models allow surgical trainees to accurately plan the surgery ahead of time, and subsequently discuss their plan with a senior. Moreover, a 3D-printed model may help in providing patient information during clinical consultation [8]. One could argue that most of these benefits could also be achieved with only 3D virtual visualization of the fracture [36]. Besides that it saves the cost of printing (€ 50 -100,- for a proximal tibia), it is instantly available and has no environmental impact. Yet, in this review only two articles were identified that described the use of a 3D virtual model for surgical planning [30, 34]. It should be noted that 3D visualization and printing itself has a learning curve, and it takes time to become familiar with the software. Virtual preoperative planning and discussing a new case may easily take up to two hours, of which a significant part is spent on the process of segmenting the CT-scan into a 3D model, virtually reducing the fracture fragments, and predetermining the implant positions.
Several of the identified 3D concepts go beyond 3D visualization and focus on translating a predetermined plan to the operative procedure itself. Pre-contouring the osteosynthesis plate on a 3D-printed model of either the mirrored contralateral side or the reduced fracture site might improve implant fitting. Implant pre-contouring showed beneficial results in acetabular fracture surgery regarding decrease in operation time and improved fracture reduction [37]. Moreover, good implant fitting in tibial plateau fracture surgery could reduce the need for elective implant removals due to optimal fitting of bulky plates. This technology was described in two of the included articles which also showed potential improvement in operation time, fracture reduction and patient outcome [18, 25]. These studies, however, were pilot studies and, therefore, limited to small case series. The full potential of this technique should therefore be further explored.
The use of 3D-printed surgical guides should be considered another 3D technique, which aims at translating a pre-operative plan to the patient [23, 26, 31]. Three case series introduced this concept for tibial plateau fractures and showed that 3D-printed guides may help the surgeon to accurately adhere to the pre-determined surgical plan. 3D-printed surgical guides are widely used in clinical practice and have been successfully applied in neurosurgery, dental surgery, spinal surgery and maxillofacial surgery [38]. In spinal surgery for instance, the use of 3D-printed drill guides led to accurate vertebral screw insertion with a mean deviation of 1.4 mm and 6.7° from the planned entry point and screw trajectory, respectively [39].
Several studies assessed the use of intra-operative 3D imaging to verify fracture reduction, implant position, and screw trajectories and lengths. These studies showed instant intra-operative revision rates up to 27% as a consequence of the 3D imaging [16, 19, 28]. However, these studies evaluated only the intra-operative acts resulting from the 3D imaging and not the clinical outcome. Downsides of this technique are the radiation exposure and increased operation time, where in more than 70% of the patients the intra-operative 3D imaging did not lead to any adjustments in the achieved surgical reduction. It should therefore be evaluated which fractures might benefit from this technique, and which not.
The main research questions concerned the effects of 3D-assisted surgery of tibial plateau fractures on intra- and postoperative outcomes. Surgery assisted by 3D visualization or prints resulted in improved intra-operative results in terms of operation time, blood loss and frequency of fluoroscopy. This is in line with previous findings regarding the use of 3D printing techniques in orthopaedic trauma fracture care [5, 38]. 3D technology provides the surgeon the ability to extensively prepare the surgery. This benefits the workflow in the operating room leading to a reduction in operation time and the frequency of fluoroscopy. A possible explanation for the decrease in blood loss could be the efficiency during the operation and a smaller incision size due to improved preoperative planning. Zhang et al. showed that the 3D-assisted group had a significant smaller incision length [34]. Studies included in this review indicate that 3D-assisted surgery might improve functional outcome. It could be hypothesized that 3D-assisted surgery leads to improved preoperative planning and eventually better reduction of the fracture. This assumption is still a matter of debate since no post-operative CTs were available in any of the studies. The effect of the 3D technique on the fracture reduction should, therefore, be further assessed.
This review has some strengths and some limitations. First, this review provides a clinically question-driven overview about the ongoing debate whether these advanced 3D technologies contribute to operation results and patient-recovery. To present a complete overview of the stare-of-the-art 3D technologies applied for tibial plateau fracture surgery we were forced to not restrict our search to solely RCTs. Inevitably, the included studies therefore encompass a wide range of study designs including case series, observational studies and retro- and prospective cohort studies. Due to the wide range of the methodological quality and heterogeneity between these studies, the pooled analysis of operation time (I2 = 88%), blood loss (I2 = 96%) and fluoroscopy frequency (I2 = 96%) should be interpret with caution. Moreover, some studies suffered from a limited sample size. Lastly, different concepts of 3D technologies were aggregated under the term “3D-assisted surgery”. However, the studies used for the pooled analysis mainly concerned the use of 3D-printed models and 3D virtual visualization. This hampers the generalizability of the results and therefore these should be interpreted with caution. High-quality randomized controlled trials for each of the 3D application are, therefore, recommended to fully explore the potential benefits of these rapid developing advanced technologies.
Conclusion
Over the last decade, five different concepts of 3D-assisted surgical management of tibial plateau fractures emerged: ‘3D virtual visualization’, ‘3D printed hand-held models’, ‘Pre-contouring of osteosynthesis plates’, ‘3D printed surgical guides’, and ‘Intra-operative 3D imaging’. Several studies indicate that 3D-assisted surgery had a positive effect on operation time, blood loss, frequency of fluoroscopy, and functional outcome. However, 3D technologies also come with a price in preparation time and production costs (i.e. software, materials, printing devices). The potential benefits should be further investigated in high-quality studies before widespread clinical use.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Acknowledgements
We thank the central medical library of the University Medical Center Groningen for their support setting up the search strategy.
Author contributions
This study represents a great deal of effort, resources and dedication of the authors. All the authors have contributed materially to the elements below: study design: NA, IR, JK, MW, JPdV, and FIJ. Literature search: NA, IR, and FIJ. Analysed data: NA, IR, FIJ. Initial draft: NA, IR, FIJ. Critically revised the work: KtD, JD, HH, JK, MW, and JPdV.
Funding
The authors declare that there is no funding source.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Availability of data and material
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
- 1.Parkkinen M, Madanat R, Mustonen A, Koskinen SK, Paavola M, Lindahl J. Factors predicting the development of early osteoarthritis following lateral tibial plateau fractures: mid-term clinical and radiographic outcomes of 73 operatively treated patients. Scand J Surg. 2014 doi: 10.1177/1457496914520854. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Meulenkamp B, Martin R, Desy NM, Duffy P, Korley R, Puloski S, et al. Incidence, risk factors, and location of articular malreductions of the Tibial Plateau. J Orthop Trauma. 2017 doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000000735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Mthethwa J, Chikate A. A review of the management of Tibial Plateau fractures. Musculoskelet Surg. 2018 doi: 10.1007/s12306-017-0514-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Assink N, Kraeima J, Slump CH, ten Duis K, de Vries JPPM, Meesters AML, et al. Quantitative 3D measurements of Tibial Plateau fractures. Sci Rep. 2019 doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50887-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Xiong L, Li X, Li H, Chen Z, Xiao T. The efficacy of 3D printing-assisted surgery for traumatic fracture: a meta-analysis. Postgrad Med J. 2019 doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2019-136482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Wixted CM, Peterson JR, Kadakia RJ, Adams SB. Three-dimensional printing in orthopaedic surgery: current applications and future developments. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2021 doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-20-00230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lal H, Patralekh MK. 3D printing and its applications in orthopaedic trauma: a technological marvel. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.07.022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bizzotto N, Tami I, Santucci A, Adani R, Poggi P, Romani D, et al. 3D-printed replica of articular fractures for surgical planning and patient consent: a two years multi-centric experience. 3D Print Med. 2016 doi: 10.1186/s41205-016-0006-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weidert S, Andress S, Suero E, Becker C, Hartel M, Behle M, et al. 3D-Druck in der unfallchirurgischen Fort- und Weiterbildung. Unfallchirurg. 2019 doi: 10.1007/s00113-019-0650-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Moher D, Liberati A, Tetzlaff J, Altman DG, Altman D, Antes G, et al. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. PLoS Med. 2009 doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ouzzani M, Hammady H, Fedorowicz Z, Elmagarmid A. Rayyan—a web and mobile app for systematic reviews. Syst Rev. 2016 doi: 10.1186/s13643-016-0384-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. Cochrane Book Ser. 2008 doi: 10.1002/9780470712184. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Law M, Stewart D, Pollock N, Letts L, Bosch J, Westmoreland M. Guidelines for critical review form—quantitative studies. Quant Rev Form Guidel. 1998 doi: 10.1088/1751-8113/44/8/085201. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Jinsihan N, Jin G. Recent developments of 3D-printing technique assisted surgery in the management of complex fractures. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2018 doi: 10.1109/ICCONS.2018.8662981. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Xie L, Chen C, Zhang Y, Zheng W, Chen H, Cai L. Three-dimensional printing assisted ORIF versus conventional ORIF for tibial plateau fractures: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Surg. 2018 doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2018.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Beisemann N, Keil H, Swartman B, Schnetzke M, Franke J, Grützner PA, et al. Intraoperative 3D imaging leads to substantial revision rate in management of tibial plateau fractures in 559 cases. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019 doi: 10.1186/s13018-019-1286-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Citak M, Citak M, Suero EM, O’Loughlin PF, Hüfner T, Krettek C. Navigated reconstruction of a tibial plateau compression fracture post-virtual reconstruction. A case report. Knee. 2011 doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2010.04.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Delcogliano M, Marin R, Deabate L, Previtali D, Filardo G, Surace MF, et al. Arthroscopically assisted and three-dimensionally modeled minimally invasive rim plate osteosynthesis via modified anterolateral approach for posterolateral tibial plateau fractures. Knee. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.knee.2020.02.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Franke J, Vetter SY, Beisemann N, Swartman B, Grϋtzner PA, Schnetzke M. 3-D-Sicherheit bei gelenknahen Osteosynthesen. Unfallchirurg. 2016 doi: 10.1007/s00113-016-0228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Giannetti S, Bizzotto N, Stancati A, Santucci A. Minimally invasive fixation in tibial plateau fractures using an pre-operative and intra-operative real size 3D printing. Injury. 2017 doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Guo C, Zhang Y, Yang L, Zhu Q, Zou S. The application and operation-effect analysis for complex tibial plateau fractures with 3D printing technique. Int J Clin Med. 2019 doi: 10.4236/ijcm.2019.103010. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Horas K, Hoffmann R, Faulenbach M, Heinz SM, Langheinrich A, Schweigkofler U. Advances in the preoperative planning of revision trauma surgery using 3D printing technology. J Orthop Trauma. 2020 doi: 10.1097/BOT.0000000000001708. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Huang H, Hsieh MF, Zhang G, Ouyang H, Zeng C, Yan B, et al. Improved accuracy of 3D-printed navigational template during complicated tibial plateau fracture surgery. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2015 doi: 10.1007/s13246-015-0330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Lou Y, Cai L, Wang C, Tang Q, Pan T, Guo X, et al. Comparison of traditional surgery and surgery assisted by three dimensional printing technology in the treatment of tibial plateau fractures. Int Orthop. 2017 doi: 10.1007/s00264-017-3445-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Mishra A, Verma T, Vaish A, Vaish R, Vaishya R, Maini L. Virtual preoperative planning and 3D printing are valuable for the management of complex orthopaedic trauma. Chin J Traumatol Engl Ed. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2019.07.006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nie W, Gu F, Wang Z, Wu R, Yue Y, Shao A. Preliminary application of three-dimension printing technology in surgical management of bicondylar tibial plateau fractures. Injury. 2019 doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2018.12.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ozturk AM, Suer O, Derin O, Ozer MA, Govsa F, Aktuglu K. Surgical advantages of using 3D patient-specific models in high-energy tibial plateau fractures. Eur J Trauma Emerg Surg. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s00068-020-01378-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ruan Z, Luo C, Feng D, Zhang C, Zeng B. Intraoperative three-dimensional imaging in tibial plateau fractures with complex depressions. Technol Heal Care. 2011 doi: 10.3233/THC-2011-0613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shen S, Wang PZ, Li XY, Han X, Tan HL. Pre-operative simulation using a three-dimensional printing model for surgical treatment of old and complex tibial plateau fractures. Sci Rep. 2020 doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63219-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Suero EM, Hüfner T, Stübig T, Krettek C, Citak M. Use of a virtual 3D software for planning of tibial plateau fracture reconstruction. Injury. 2010 doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2009.10.053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wang H, Newman S, Wang J, Wang Q, Wang Q. Corrective osteotomies for complex intra-articular tibial plateau malunions using three-dimensional virtual planning and novel patient-specific guides. J Knee Surg. 2018 doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1605563. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Wu W, yong, Xu W guo, Wan C you, Fang M, Preoperative plan with 3D printing in internal and external fixation for complex tibial plateau fractures. Orthop Surg. 2019 doi: 10.1111/os.12466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Yang P, Du D, Zhou Z, Lu N, Fu Q, Ma J, et al. 3D printing-assisted osteotomy treatment for the malunion of lateral tibial plateau fracture. Injury. 2016 doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2016.09.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Zhang H, Li Z, Xu Q, Zhang Y, Xu K, Ma X. Analysis for clinical effect of virtual windowing and poking reduction treatment for Schatzker III tibial plateau fracture based on 3D CT data. Biomed Res Int. 2015 doi: 10.1155/2015/231820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of The Knee Society clinical rating system. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1989 doi: 10.1097/00003086-198911000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Spek RWA, Schoolmeesters BJA, Oosterhoff JHF, Doornberg JN, van den Bekerom MPJ, Jaarsma RL, Eygendaal D, IJpma F; Traumaplatform 3D Consortium. 3D-printed handheld models do not improve recognition of specific characteristics and patterns of three-part and four-part proximal humerus fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2021. 10.1097/CORR.0000000000001921. Online ahead of print. PMID: 34427569 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Huang JH, Liao H, Tan XY, Xing WR, Zhou Q, Zheng YS, et al. Surgical treatment for both-column acetabular fractures using pre-operative virtual simulation and three-dimensional printing techniques. Chin Med J (Engl) 2020 doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Tack P, Victor J, Gemmel P, Annemans L. 3D-printing techniques in a medical setting: a systematic literature review. Biomed Eng Online. 2016 doi: 10.1186/s12938-016-0236-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pijpker PAJ, Kraeima J, Witjes MJH, Oterdoom DLM, Vergeer RA, Coppes MH, et al. Accuracy of patient-specific 3D-printed drill guides for pedicle and lateral mass screw insertion. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2021 doi: 10.1097/brs.0000000000003747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.