Abstract
Background
COVID-19 is associated with several risk factors such as distinct ethnicities (genetic ancestry), races, sexes, age, pre-existing comorbidities, smoking, and genetics. The authors aim to evaluate the correlation between variability in the host genetics and the severity and susceptibility towards COVID-19 in this study.
Methods
Following the PRISMA guidelines, we retrieved all the relevant articles published until September 15, 2021, from two online databases: PubMed and Scopus.
Findings
High-risk HLA haplotypes, higher expression of ACE polymorphisms, and several genes of cellular proteases such as TMPRSS2, FURIN, TLL-1 increase the risk of susceptibility and severity of COVID-19. In addition, upregulation of several genes encoding for both innate and acquired immune systems proteins, mainly CCR5, IFNs, TLR, DPPs, and TNF, positively correlate with COVID-19 severity. However, reduced expression or polymorphisms in genes affecting TLR and IFNλ increase COVID-19 severity.
Conclusion
Higher expression, polymorphisms, mutations, and deletions of several genes are linked with the susceptibility, severity, and clinical outcomes of COVID-19. Early treatment and vaccination of individuals with genetic predisposition could help minimize the severity and mortality associated with COVID-19.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, Genetic Susceptibility, Polymorphisms, COVID-19 severity, Host genetics
Abbreviations: ACE-1, angiotensin-converting enzyme 1; ACE-2, angiotensin-converting enzyme 2; ACE, Angiotensin-converting enzyme; AR, Androgen receptor; BPIFB4, BPI fold containing family B member 4; C3, Complement component 3; CCR5, C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 5; CCR9, CC motif chemokine receptor 9; COVID-19, Coronavirus disease 2019; CXCR6, Chemokine Receptor Type 6; CYP2R1, cytochrome P450 gamily 2 subfamily R member 1; DDR1, discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1; DPP, dipeptidyl peptidases; FYCO1, fyve and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1; GOLGA3, Golgin A3; HLA, Human leukocyte antigen; HNRNPK, heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K; IFI30, gamma-interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase; IFITM3, Interferon Induced Transmembrane Protein 3; IFN, interferons; IFNAR, interferon alpha and beta receptor; IL, Interleukin; KIR3DS1, Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL1; LZTFL1, Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor Like; MBL2, mannose binding lectin 2; MERS, Middle East Respiratory Syndrome; MUC5B, mucin 5B; PNPLA3, patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3; RMI1, RecQ mediated genome instability 1; SLC6A20, Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 20; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphisms; TAS2R38, taste receptor 2 member 38; TLL-1, Tolloid-Like Protein 1; TLR, Toll‐like receptor; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor-α; TNFRSF13C, TNF Receptor Superfamily Member 13C; TNFRSF1A, TNF Receptor Superfamily Member 1A; Transmembrane protease serine2, TMPRSS2; XCR1, X-C motif chemokine receptor 1; TIRAP, TIR Domain Containing Adaptor Protein; IFNλ3, interferon lambda 3
1. Introduction
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by SARS-CoV-2, mainly spreads via respiratory droplets and primarily targets the respiratory tract (Go et al., 2020, Talalaev et al., 2022). Recently, it caused a global pandemic with deleterious effects on a large scale leading to unprecedented damage and high number of deaths worldwide (Ferreira Caceres, 2022, Go et al., 2020, Hathaway et al., 2020, Sarfraz et al., 2021, Sosa et al., 2021). The severity of COVID-19 seems to be affected by various risk factors (Glotov et al., 2021). Heightened risk of COVID-19 associated mortality is seen in about 27–30% of the population suffering from arterial hypertension, 16.2% of the diabetic population, and 5.8% patients with cardiovascular issues (Glotov et al., 2021). In addition, approximately 60% of the deceased patients are reportedly males (D’Amico et al., 2021). Race and ethnicity appear to have an importance in shaping the course of the COVID-19, as individuals from the black community reportedly contributed to roughly 58 percent of COVID-19 deaths in the United States in 2020 (Millett et al., 2020). Similarly, cohort studies from the United Kingdom show that certain ethnic minorities such as South Asians were more likely to acquire COVID-19 infection and suffer from complications associated with severe infection (Mathur et al., 2021).
COVID-19 has a wide clinical range- from asymptomatic individuals to full-blown illness, with symptoms ranging from moderate to severe (Booth et al., 2021, Casanova et al., 2020). Fever, cough, myalgias, fatigue, and dyspnea are the most common symptoms seen in moderate to severe cases of COVID-19 (Huang et al., 2020) . Critical COVID-19 cases are depicted by acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and extrapulmonary manifestations affecting the cardiovascular, renal, gastrointestinal, hepatobiliary, and central nervous system, arising in 15% of COVID-19 cases (Cascella et al., 2022, Maslove et al., 2021, Yildirim et al., 2021). It takes around seven days for the patient to develop moderate to critical illness from symptom onset, receiving treatment only in the late phase of COVID-19 during hospitalization (Giammaria and Pajewski, 2020). Early treatment of high-risk patients has shown a reduction in the disease progression to a severe form of COVID-19 (Giammaria and Pajewski, 2020). Hence, identifying the populations at risk from suffering from severe complications of COVID-19 disease is crucial to reducing hospitalizations, intensive care unit (ICU) admissions, and death (Giammaria and Pajewski, 2020).
Recent research suggests that individuals with a varied expression of several genes and their alleles such as HLA, Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 (ACE-2), cellular proteases, and immune response proteins might have a genetic predisposition to severe COVID-19 (Yildirim et al., 2021).
After viral binding and entry, the SARS-COV-2 virus invades the upper and the lower respiratory tract, triggering the immune response by releasing numerous cytokines and interleukins (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8, IL-120, and IL-12), tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), and interferons (IFN) from the infected host cells (Cascella et al., 2022, Parasher, 2021). The cytokine-induced inflammatory response in the lungs and extrapulmonary tissues leads to a severe course of COVID-19 (Parasher, 2021).
We aim to evaluate the existing pool of literature signifying the correlation between the variability of human genomic expression, the severity of COVID-19, and susceptibility to COVID-19 infection. A thorough understanding of the roleplay between different genetic factors and the progression of COVID-19 infection is crucial to develop new therapeutic options, strategies for disease prevention, and diagnostic, predictive models to anticipate severe clinical outcomes, thereby starting medical intervention during the early course of the disease, which could help in improving the clinical outcomes.
2. Methods
2.1. Search strategy
This systematic review was reported following the Preferred Reporting Item for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement (Page et al., 2021). PubMed and Scopus were systematically searched until 15th September 2021. A medical subject subheadings (MESH) term and keyword searches were performed using relevant combinations. The search strategy included terms related to COVID-19, disease susceptibility, disease severity, genetic predisposition, and specific genes associated with COVID-19, such as ACE. Citations of relevant articles and reviews were also searched for relevant articles. The exact search strategy for each electronic database is provided in the Appendix. Additionally, an updated database search was undertaken on May 5th, 2022, using the same search strategy.
2.2. Study selection
Two reviewers performed the abstract/title and full-text screening processes for the eligible articles. Any disagreements that arose during the screening were resolved independently xby a third reviewer. The following were the inclusion criteria: (1) studies available in English, (2) studies including COVID-19 patients that discussed the link between certain genes and COVID-19 disease severity or susceptibility, and (3) articles on the adult population. On the other hand, the exclusion criteria were: (1) articles in languages other than English, (2) animal studies (3) studies with overlapping data. Reviews, editorials, letters to editors, conference abstracts, and articles with incomplete results were also excluded.
2.3. Data extraction
Data were extracted onto an Excel® 2019 sheet by two authors. The extracted information included the author, year, the gene studied, the specific genetic polymorphism, sample size, and population characteristics.
2.4. Study outcomes
The primary outcome of this review was to assess the genetic risk factors that can increase the severity of COVID-19 infections and render certain individuals more susceptible to infection. Secondary outcomes included assessing if certain genes were more prevalent in specific populations.
2.5. Definitions
Mild COVID-19 disease (controls) was defined as patients who were asymptomatic or those who were symptomatic but did not develop pneumonia, while severe/critical disease was defined as patients who developed radiographical evidence of pneumonia with confirmatory COVID-19 diagnosis and required hospitalization.
3. Results
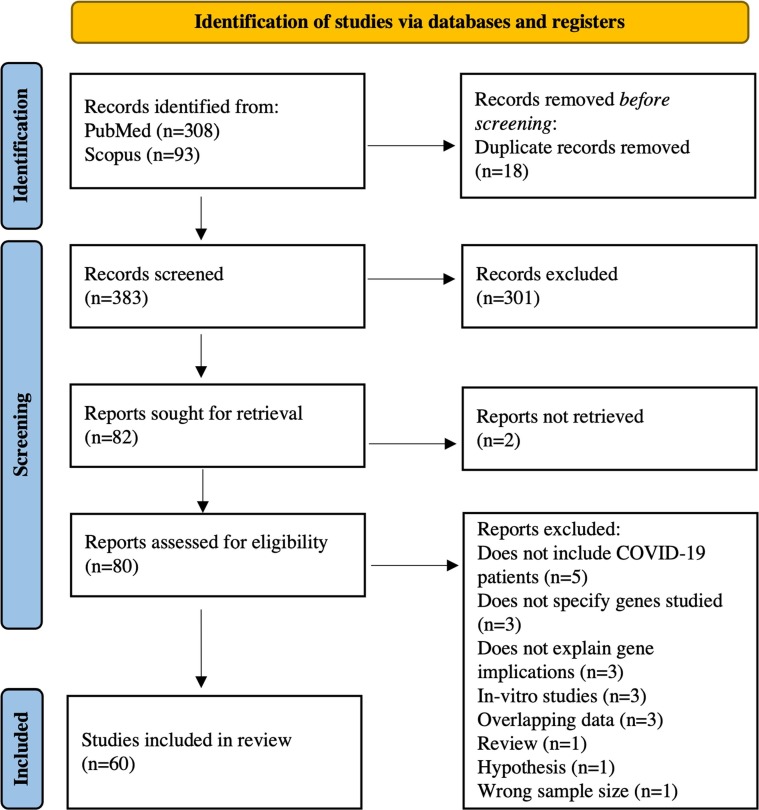
295 articles were screened from PubMed (202 articles) and Scopus (93 articles) during the initial search. Sixteen duplicate articles were removed, leaving 279 articles for the preliminary (title and abstract) screening process, of which 63 were eligible for full-text screening. 106 more articles were identified following an updated database search. Of these, 19 were eligible for full-text screening. 20 articles were excluded for reasons explained in Figure 1 . Therefore, 60 articles were included in the final qualitative analysis. The detailed screening process and reasons for article exclusion are summarized in Figure 1.
Figure 1.
The 2020 PRISMA flowchart detailing study screening and selection
This systematic review elucidates the impact of the genetic makeup of an individual or certain populations on the severity and susceptibility towards COVID-19 infection. Based on this premise, all the genes found in association with increased risk of COVID-19 severity and susceptibility are described in detail below.
4. Discussion
4.1. Angiotensin-converting enzyme
Our systematic review identified several angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) polymorphisms that affect the pathogenesis of COVID-19 infection, summarized in Table 1 . Entry of SARS-CoV-2 virus to the host cell occurs via the attachment of its S protein to ACE-2. Therefore, variations in the sequence of ACE-2 affecting its interaction with the SARS-CoV-2 virus via conformational changes in its structure or affecting the degree of its affinity to the viral S proteins, could be a genetic risk factor for the susceptibility and severity of COVID-19 infection, ultimately governing its clinical outcome. It has been observed that variations located at the proteolytic cleavage site led to soluble ACE-2 acting as a decoy receptor for the virus and decreasing virus intake by cell surface ACE-2 (Darbeheshti et al., 2021).
Table 1.
ACE polymorphisms and their association with COVID-19 severity and susceptibility
| ACE gene | ACE Polymorphism | Population | Sample size | Implication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACE2 | rs2285666, rs35803318 | Italy | 7268 individuals | No correlation between ACE2 expression and disease severity based on patients’ gender. | (Asselta et al., 2020) |
| ACE | Not mentioned | Asia, Europe, North America, Australia, Africa | COVID-19 patients* | The II genotype of the ACE (which is highly prevalent in East Asians) was strongly associated with decreased COVID-19-related deaths. | (Aung et al., 2020) |
| ACE2 | rs2074192, rs2106809 | Italy | 54 symptomatic COVID-19 patients and, 50 asymptomatic | rs2074192 polymorphism of ACE2 is associated with increased severity of COVID-19 illness. | (Cafiero et al., 2021) |
| ACE1 | rs1799752 | Italy | 54 symptomatic COVID-19 patients and, 50 asymptomatic | The II genotype of the ACE1 rs1799752 polymorphism is found at a higher frequency in asymptomatic patients. | (Cafiero et al., 2021) |
| ACE | rs1799752 | Italy | 68 hospitalized patients | D/D ACE polymorphism had a significant impact on the severity of disease and the development of pulmonary embolism. | (Calabrese et al., 2021) |
| ACE1 | rs1799752 | Lebanon | 232 COVID-19 patients, 155 controls | ACE 1 I/D polymorphism was associated with a worse COVID-19 clinical outcome. | (Saad et al., 2021) |
| ACE | N/A | Turkey | 90 COVID-19 patients | ACE II genotype was prominent in asymptomatic patients and ACE D/D genotype common in patients with critical disease. | (Gunal et al., 2021) |
| ACE | rs4341, rs4343 | Spain | 128 COVID-19 patients | rs4341 and rs4343 were associated with more severe SARS-CoV-2 disease in patients with hypertension and diabetes. | (Íñiguez et al., 2021) |
| ACE, ACE2 | rs2106809, rs2285666 | Turkey | 155 COVID-19 patients | No association was observed with the severity of SARS-CoV-2 infection. | (Karakaş Çelik et al., 2021) |
| ACE1 | Not mentioned | European, Mediterranean, and the Middle East | Not mentioned | ACE D/I polymorphism was associated with increased COVID-19-related death. | (Delanghe et al., 2021) |
| ACE2 | rs4646116, rs769062069, rs776995986 | Iran | 15,000 | S331F and K26R mutations (rs4646116) could decrease the affinity of the ACE2 receptor to the viral spike protein. | (Lanjanian et al., 2021) |
| ACE | rs3730025 | Spain and Italy | Not mentioned | Variants decreasing ACE expression do not lead to increased risk of COVID-19 infection or disease severity. | (Monticelli et al., 2021) |
| ACE2 | Not mentioned | Africa | Not mentioned | Genetic variants in ACE2 may alter an individual’s variability in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and severity of the disease. | (Ortiz-Fernández and Sawalha, 2020) |
| ACE1 | Not mentioned | India | 269 COVID-19 patients | ACE1 D/D genotype was markedly higher in COVID-19 patients with severe disease. | (Verma et al., 2021) |
| ACE1 | Not mentioned | Europe and Asia | Not mentioned | ACE1 II genotype had a negative correlation with the incidence of cases and mortality rates from SARS-CoV-2 infection. | (Yamamoto et al., 2020) |
| ACE2 | rs147311723, rs142017934, rs4646140 | Africa, America, Asia, Europe | 2504 individuals | rs142017934 polymorphisms, more frequently observed in Africans, can amplify the expression of the ACE2 gene. | (Khayat et al., 2020) |
| ACE2 | rs5934250 | Africa, America, Asia, Europe | 2504 individuals | rs5934250 is found in higher frequencies in Europeans and few Africans and can minimize the expression of ACE2. | (Khayat et al., 2020) |
| ACE2 | rs2285666 | India | Not mentioned | Strong positive correlation for alternate allele (T/T-plus stand or A/A-minus strand) of ACE2 rs2285666 polymorphism, with the lower susceptibility to COVID-19 and lower case-fatality rate. | (Srivastava et al., 2020) |
| ACE2 | rs2285666 | Mexico | 481 COVID-19 patients | T allele of rs2285666 is associated with severe outcomes in COVID-19 patients. | (Martínez-Gómez et al., 2022) |
| ACE2 | rs2074192, rs1978124, rs2106809, rs2285666 | Spain | 318 COVID-19 patients | rs2074192 and rs1978124 showed a protective role in COVID-19 patients, while rs2106809 and rs2285666 were associated with severe disease. | (Sabater Molina et al., 2022) |
| ACE2 | rs2285666 | Iraq | 99 COVID-19 patients, 96 controls | No association between ACE2 rs2285666 polymorphism and risk of developing COVID-19. | (Mahmood et al., 2022) |
| ACE1 | rs1799752 | Turkey | 50 ICU patients, 50 non-ICU patients | This polymorphism did not predict COVID-19 patients requiring ICU. | (Baştuğ et al., 2022) |
ACE: Angiotensin receptor enzyme
*Number of participants was not clear
The S protein exerts an inhibitory effect on ACE-2 expression which leads to increased levels of angiotensin II and/or angiotensin 1–7 in the affected cells, which could lead to severe acute pulmonary damage by causing increased vascular permeability, inflammation, and hypoxia, thereby increasing disease severity and patient mortality (Hashemi et al., 2021). There are varying levels of expression of ACE-2 among different individuals, depending on polymorphisms of the regulatory and non-coding regions such as promoter, in ACE-2. A higher level of ACE-2 expression has been hypothesized to provide protection against severe manifestations in pediatric COVID-19 patients (Hashemi et al., 2021).
Lower expression of ACE-2 and TMPRSS2 (transmembrane protease serine 2) in the African population could perhaps explain the fewer reported cases of COVID-19 in Africa (Khayat et al., 2020, Ortiz-Fernández and Sawalha, 2020). Individuals with ACE-2 variants K31R and E37K, S331F, and K26R (rs4646116) showed decreased susceptibility to COVID-19, while individuals with K26R and T92I variants showed increased susceptibility (Lanjanian et al., 2021, Suryamohan et al., 2021).
Our review found that ACE-1 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNP) rs4341 and rs4343 were linked to severe infection in hypertensive, dyslipidemic, and type 2 diabetic patients. rs2074192 (ACE-2) and rs1799752 (ACE-1) variants, and rs699 (AGT) SNP were also hypothesized to predict the clinical outcome of patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 (Cafiero et al., 2021, Íñiguez et al., 2021). However, we found just one study assessing the rs1799752 polymorphism of ACE-1 receptor which showed no association with ICU admission of severe COVID-19 patients (Baştuğ et al., 2022).
The mutations in the D allele of ACE-1 lead to high levels of serum ACE-1, increasing the severity of COVID-19 and a higher risk of development of pulmonary embolism in these patients (Calabrese et al., 2021, Hashemi et al., 2021, Verma et al., 2021). ACE D/I polymorphism was associated with increased COVID-19 mortality (Saad et al., 2021, Yamamoto et al., 2020, Delanghe et al., 2021). Conversely, the presence of the ACE-2 rs2285666 in the Indian population whereas rs2074192 and rs1978124 variants in the Spanish population demonstrated a protective effect by lowering the risk of susceptibility and mortality rate (Sabater Molina et al., 2022, Srivastava et al., 2020). However, other studies revealed that ACE I/D, DD, ACE-2 receptor rs2106809, and rs2285666 polymorphisms had no associations with COVID-19 severity (Asselta et al., 2020, Aung et al., 2020, Karakaş Çelik et al., 2021, Mahmood et al., 2022).
4.2. Human leukocyte antigen (HLA)
HLA haplotypes and variants identified to play an important role in SARS-CoV-2 infection are summarized in Table 2 . HLA alleles are highly polymorphic with the presence of different HLA alleles, generating varied immune responses against COVID-19, thus leading to a diverse spectrum of disease susceptibilities and severities. HLA are however accompanied by linkage disequilibrium. Hence, additional genes in the proximity of HLA could also influence for the course of the disease (Pisanti et al., 2020, Yung et al., 2021).
Table 2.
HLA locus and their association with COVID-19 severity and susceptibility
| HLA locus | HLA allele/haplotype | Population | Sample size | Implication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA‐A, ‐C, ‐B, and ‐DRB1 | HLA‐DRB1*09:01 | Japan | 178 COVID-19 patients | HLA‐DRB1*09:01 was strongly associated with increased severity of COVID‐19 illness. | (Anzurez et al., 2021) |
| HLA-A, -B, -C, -DQB1, -DRB1 | Not mentioned | Israel | 6,413 COVID-19 patients and 66,499 controls | No association was reported with risk for infection or illness severity. | (Ben Shachar et al., 2021) |
| HLA-DRB1, -DQB1 | HLA-DRB1*03, HLA-DRB1*15, DRB1*15 ∼ DQB1*05, DRB1*15/DRB1*04, HLA- DRB1*04 | Iran | 144 COVID-19 patients | HLA-DRB1*03 was notably higher in severely ill patients. HLA-DRB1*04 was determined to be a protective factor against the development of severe forms of the disease. Frequencies of HLA-DRB1*15, DRB1*15 ∼ DQB1*05, and DRB1*15/DRB1*04 were lower in COVID-19 patients. |
(Ebrahimi et al., 2021) |
| HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 | HLA- DRB1*04:01, HLA- DQA1*01:01‐DQB1*05:01‐DRB1*01:01 | England | 147 COVID-19 patients | Compared to the asymptomatic group, frequencies of HLA-DRB1*04:01 allele and the haplotype. HLA-DQA1*01:01‐DQB1*05:01‐DRB1*01:01 were drastically lower in severe COVID-19 patients. |
(Langton et al., 2021) |
| HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DRB1 | HLA-A*02:05, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-C*07:01, HLA-DRB1*03:01, HLA-DRB1*08 | Italy | 182 patients, 619 controls | HLA-A*02:05, B*58:01, C*07:01, DRB1*03:01 haplotype could protect against COVID-19. HLA-DRB1*08 allele was associated with the highest risk for severe COVID-19 illness. |
(Littera et al., 2020) |
| HLA-A, HLA-B, HLA-C, HLA-DRB1 and HLA-DQB1 | HLA-A*32, HLA-A*03, HLA-B*39, HLA-C*16, HLA-A*11, HLA-C*01, HLA-DQB1*04 | Spain | 3886 healthy controls, 72 COVID-19 patients | Lower frequency of HLA-A*32 in COVID-19 patients compared to controls, and higher frequency of HLA-A*03, HLA-B*39, and HLA-C*16 in COVID-19 patients compared to controls. The presence of HLA-A*11, HLA-C*01, and HLA-DQB1*04 was linked with an increased risk for COVID-19-related death. |
(Lorente et al., 2021) |
| HLA-A, -B, -C and -DRB1 | HLA-A*01:01 g-B*08:01 g-C*07:01 g-DRB1*03:01 g, HLA-A*02:01 g-B*18:01 g-C*07:01 g-DRB1*11:04 g | Italy | N/A | The presence of HLA-A*01:01 g-B*08:01 g-C*07:01 g-DRB1*03:01 g was positively associated with risk of COVID-19 infection and death. The haplotype HLA-A*02:01 g-B*18:01 g-C*07:01 g-DRB1*11:04 g could offer protection against COVID-19 infection. |
(Pisanti et al., 2020) |
| HLA‐A, ‐B, ‐C, ‐DPB1, ‐DQB1, ‐DRB1 | HLA-A*2:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-A*24:02 | Worldwide | N/A | The presence of HLA-A*2:01 may predispose an individual to an increased risk for COVID-19 infection. | (Tomita et al., 2020) |
| HLA class I and class II | HLA-I C*04:01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-DPA1*02:02 | USA | 100 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, and 26 controls | HLA-I C*04:01 and A*11:01 were significantly associated with poor outcomes in COVID-29 infection. HLA-DPA1*02:02 was discovered to be at a higher frequency COVID-19-positive patients |
(Warren and Birol, 2021) |
| HLA-C | rs143334143 | Europe and USA | 435 symptomatic COVID-19 patients | rs143334143 strongly correlated to increased COVID-19 illness severity. | (Weiner et al., 2021) |
| HLA-B | Not mentioned | China | 190 COVID-19 patients | Strong positive correlation between the B22 serotype and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection. | (Yung et al., 2021) |
| HLA-C | HLA-C*04:01 | Armenia | 299 COVID-19 patients | HLA-I C*04:01 was significantly associated with a more severe COVID-19 disease. | (Hovhannisyan et al., 2022) |
HLA: Human leukocyte antigen
A study of 190 unrelated Chinese patients found a strong relation between the B22 serotype and COVID-19 (Yung et al., 2021). HLA-DRB1*08 allele was associated with the highest risk for severe COVID-19 illness in Sardinian patients (Littera et al., 2020). HLA-DPA1*02:02 was also found to be linked to higher susceptibility to COVID-19 but did not seem to affect the risk of hospitalization (Warren and Birol, 2021). The presence of HLA-A*11, HLA-C*01, HLA-A*11:01, HLA-C*04:01, HLA-C rs143334143, DQA1*01:02, HLA-DRB1*03 and HLA-DQB1*04 were associated with higher mortality (Ebrahimi et al., 2021, Hovhannisyan et al., 2022, Lorente et al., 2021, Weiner et al., 2021). In a study of 178 Japanese COVID-19 patients, the risk for severe infection was noted to be increased in the presence of the DRB1*09:01 allele compared to pre-existing comorbid conditions like diabetes, hypertension, or cardiovascular diseases (Anzurez et al., 2021).
On the contrary, certain HLA variants such as HLA-A*02:05, HLA-B*58:01, HLA-C*07:01, and HLA- DRB1*03:01 are thought to be protective against critical COVID-19 infection (Ebrahimi et al., 2021, Langton et al., 2021, Littera et al., 2020, Lorente et al., 2021, Pisanti et al., 2020, Tomita et al., 2020). Higher frequencies of activating B-telomeric KIR3DS1 (Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor 3DL1) in HLA-B*15:01 were linked to less severe infection (Bernal et al., 2021). However, other studies reported no link between HLA and SARS-CoV-2 infection (Ben Shachar et al., 2021, de Sousa et al., 2020). Of importance, Ben Shachar et al., studied the association of various HLA loci and severity of COVID-19 severity and in 6,413 COVID-19 positive Israeli patients, largest patient population among included studies, and revealed that was no association between COVID-19 severity and several HLA loci (Ben Shachar et al., 2021).
A major limitation in studying the HLA loci is that various methodologies can be utilized which can affect the observed results. The studies included used a utilized a variety of different methodologies and used different sources of their DNA samples (peripheral blood or nasopharyngeal samples). Therefore, larger genome-wide association studies and whole-genome sequencing among different populations are still required to understand the association between specific HLA loci and COVID-19 disease course. A recent study using whole genome sequencing in 7,491 critically COVID-19 hospitalized in the UK showed that only HLA-DRB1*04:01 reached genome-wide significance (Kousathanas et al., 2022) which as previously mentioned is thought to be protective against severe COVID-19 infection (Langton et al., 2021).
These results suggest that HLA typing could play an important role in predicting the course of COVID-19 disease in certain populations and could help stratify patients infected with SARS-CoV-2. Other genes that are implicated in the progression of COVID-19 infection and disease severity are described in Table 3 .
Table 3.
Candidate genes, their polymorphisms and their association with COVID-19 severity and susceptibility in select populations
| Gene | Polymorphism | Population | Sample size | Implication | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3p21.31 cluster | rs11385942 | Spain and Italy | 1980 | The 3p21.31 cluster was observed in patients with respiratory failure. | (The Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group, 2020) |
| Androgen receptor | Not mentioned | European males | 1178 | Androgen receptors with shorter polyQ alleles offered protection against severe COVID-19 in Italian males. | (Baldassarri et al., 2021) |
| BPIFB4 | LAV-BPIFB4 | Italy | 171, 64 with COVID-19 | Values of BPIFB4 were markedly lower in COVID-19-positive individuals as compared with negative patients. BPIFB4 levels in plasma are negatively correlated with SARS-CoV-2 illness severity. |
(Ciaglia et al., 2021) |
| Complement 3 | Complement 3 (S) | European, Mediterranean, and the Middle East | Not mentioned | C3 was associated with increased COVID-19-related death. | (Delanghe et al., 2021) |
| CCR5 | rs9845542, rs12639314, rs35951367, rs34418657 | Europe | 6406 hospitalized COVID-19 patients and 902,088 controls | rs9845542, rs12639314, rs35951367 polymorphisms were associated with severe COVID-19 illness and low CCR5 expression | (Cantalupo et al., 2021) |
| CCR5 | rs333 | Czech Republic | 416 | Δ32 deletion in the CCR5, most found in Caucasians, could offer protection against COVID-19 illness. | (Hubacek et al., 2021) |
| TLL-1 | rs4618569 | Egypt | 141 patients, 100 controls | The A allele of the TLL-1 rs17047200 variant is associated with poor clinical outcomes. | (Agwa et al., 2021) |
| GOLGA3, DPP7, TMPRSS2 | rs12329760 in TMPRSS2 | China | 332 | The rs12329760 variant in TMPRSS2 was less prevalent in severe SARS-CoV-2 patients. Loss of function mutation in DPP7 and GOLGA3 was observed in severe COVID-19 disease. |
(Wang et al., 2020) |
| IFI30 | rs11554159 | Spain and Italy | N/A | IFI30 polymorphisms may be a risk factor to acquiring severe COVID-19 disease | (Monticelli et al., 2021) |
| MEFV | rs3743930 | Spain and Italy | N/A | Deleterious variants in MEFV could affect the severity of COVID-19. | (Monticelli et al., 2021) |
| IFITM3 | rs12252, rs34481144 | Germany | 239 patients with COVID-19 and 253 controls. | There was no association between these polymorphisms and severity of COVID-19 illness. | (Schönfelder et al., 2021) |
| IFITM3 | rs12252 | China | 80 | Presence of the rs12252 variant of the IFITM3 correlated with a more critical COVID-19 infection. | (Zhang et al., 2020) |
| LZTFL1, XCR1, CCR9, FYCO1, SLC6A20, CXCR6, HNRNPK, RMI1, IFNAR2, ABO | rs9976829 in IFNAR2- IL10RB | Italy and Spain | 1,610 COVID-19 patients and 2,205 controls | All genes were strongly associated with risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection. A 16% higher chance of having SARS-CoV-2 in subjects with the G allele of rs9976829. |
(Ma et al., 2021) |
| MBL2 | rs1800450 | N/A | 284 patients, 100 control | Reduced MBL2 levels correlated with a more severe COVID-19 clinical course. | (Medetalibeyoglu et al., 2021) |
| MUC5B | rs35705950 | Europe | 4124 cases and 20,465 controls | rs35705950 offered protection against COVID-19 in patients with pulmonary fibrosis. | (Fadista et al., 2021) |
| PNPLA3, TLL-1 | PNPLA3 rs738409, TLL-1 rs17047200, | Italy | 383 | Polymorphisms of PNPLA3 and TLL-1 were markedly associated with severe COVID-19 disease and worse outcomes. | (Grimaudo et al., 2021) |
| TAS2R38 | Not mentioned | USA | 1935, 265 tested positive | T2Rs may protect against illness by SARS-CoV-2. | (Barham et al., 2021) |
| DDR1 | rs17047200 | Egypt | 141 patients, 100 controls | The AG genotype of the DDR1 rs4618569is associated with poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients. | (Agwa et al., 2021) |
| TLR3 | rs3775291 | Spain and Italy | N/A | A missense mutation in TLR3 (rs3775291) is associated with severe disease. | (Monticelli et al., 2021) |
| TLR7 | rs189681811, rs147244662, rs149314023, rs200146658, rs5743781 | Italy | 79 cases, 77 controls |
TLR7 variants were found in 2.1% of males with severe disease, while none were found in asymptomatic males. Lower TLR7 expression was observed in COVID-19 patients. |
(Fallerini et al., 2021) |
| TMPRSS2 | rs2298659, rs17854725, rs12329760, rs3787950 | Italy | 3984 | Exonic variant (p.Val160Met) and two haplotypes in TMPRSS2 showed substantial disparities between East Asians and Italians, showing increased levels of TMPRSS2 in Italians, leading to increased susceptibility to infection. | (Asselta et al., 2020) |
| TMPRSS2 | N/A | Africa | N/A | Genetic variants in TMPRSS2 may alter an individual’s variability in susceptibility to COVID-19 infection and disease severity. | (Ortiz-Fernández and Sawalha, 2020) |
| TNFRSF1A | rs767455 | Mexico | 102 patients, 25 controls | This polymorphism is associated with increased COVID-19 disease severity. | (Palacios et al., 2021) |
| TNFRSF13C | p.His159Tyr | Italy | 500 | p.His159Tyr variant of TNFRSF13C was notably increased in patients with severe illness compared to asymptomatic patients. | (Russo et al., 2021) |
| Vitamin D (DHCR7/NADSYN1), CYP2R1 | Vitamin D (DHCR7/NADSYN1) rs12785878, CYP2R1 rs10741657 | Serbia | 120 males | The presence of CYP2R1 and DHCR7/NADSYN1 correlated with COVID-19 increased illness severity in adults. | (Kotur et al., 2021) |
| IFNλ3 | rs12979860, rs8099917, rs12980275 | Iran | 750 patients with COVID-19 | Frequency of these favorable variants was significantly higher in patients who survived from COVID-19 infection. | (Rahimi et al., 2021) |
| IFNλ4 | rs368234815 | Iran | 750 COVID-19 positive patients | Higher frequency of this variant was present in patients who survived from COVID-19 infection. | (Rahimi et al., 2021) |
| TMPRSS2 | rs2070788 | India | 393 COVID-19 patients | rs2070788 may lead to worse clinical outcomes in COVID-19 patients. | (Pandey et al., 2022) |
| TIRAP | rs8177374 | Netherlands | 116 COVID-19 patients | Carriers of rs8177374 could be associated with a significantly lower COVID-19 mortality. | (Traets et al., 2022) |
| TMPRSS2 | rs17854725/rs75603675/rs12329760/rs4303795 | Iran | 288 COVID-19 patients | These polymorphisms were associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection and severe disease. | (Rokni et al., 2022) |
| IL-6 | rs1800795, rs1800796, rs1800797 | Iran | 175 COVID-19 patients, 171 controls | No significant differences in severity of COVID-19 disease in patients with these polymorphisms. | (Falahi et al., 2022) |
| TMPRSS2/MX1 (21q22.3) locus | rs3787946, rs9983330, rs12329760, rs2298661, rs9985159 | Italy | 6,406 COVID-19 patients, 902,088 controls | These polymorphisms showed an association with severe COVID-19 disease. | (Andolfo et al., 2021) |
BPIFB4: BPI fold containing family B member 4, CCR5: CC motif chemokine receptor 5, CCR9: CC motif chemokine receptor 9, CXCR6: C-X motif chemokine receptor 6, DPP7: dipeptidyl peptidase 7, DDR1: discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1, GOLGA3: Golgin A3, TMPRSS2: transmembrane protease, serine 2, IFI30: gamma-interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase, SLC6A20: solute carrier family 6 member 20, LZTFL1: human leucine zipper transcription factor like 1, XCR1: X-C motif chemokine receptor 1, FYCO1: fyve and coiled-coil domain-containing protein 1, TLR3: toll like receptor 3, TLR7: toll like receptor 7, IFNAR2: interferon alpha and beta receptor subunit 2, IFNλ3: interferon lambda 3, IFNλ3: interferon lambda 3, MUC5B: mucin 5B, HNRNPK: heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein K, IFITM3: interferon induced transmembrane protein 3, RMI1: RecQ mediated genome instability 1, MBL2: mannose binding lectin 2, PNPLA3: patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3, TLL1: tolloid like 1, TAS2R38: taste receptor 2 member 38, TNFRSF13C: TNF receptor superfamily member 13C, TNFRSF1A: TNF receptor superfamily member 1A, CYP2R1: cytochrome P450 gamily 2 subfamily R member 1, TIRAP: TIR Domain Containing Adaptor Protein
4.3. Cellular proteases
4.3.1. Transmembrane protease serine 2
TMPRSS2 is an androgen-responsive gene and a key agent in prostate cancer, driving ETS-family oncogene expression (Stopsack et al., 2020), which is why males are expected to have higher TMPRSS2 expression; however, recent literature suggests that estrogen also can upregulate it (Asselta et al., 2020).
Recent evidence revealed that the cleavage and activation of SARS-CoV-2 S protein during membrane fusion is a function of TMPRSS2 along with cathepsin L and furin (Hoffmann et al., 2020). A recent analysis identified several SNPs could affect the function and structural composition of TMPRSS2, with rs2070788, rs9974589, rs17854725, rs75603675, rs12329760, rs4303795, and rs7364083 types being associated with increased severity of the disease and rs77675406, rs713400, rs112657409, and rs11910678 polymorphisms causing upregulation of the TMPRSS2 (Asselta et al., 2020, Irham et al., 2020, Paniri et al., 2021, Rokni et al., 2022). A study performed by Andolfo et al identified five common variants at locus 21q22.3 within TMPRSS2 and near the MX1 and revealed that higher frequencies of this variants were linked to more severe COVID-19 disease in the Italian population (Andolfo et al., 2021).
TMPRSS2 expression could vary among different populations. A study demonstrated that the East Asian population presented the highest expression of TMPRSS2, and the African population had the lowest (Ortiz-Fernández and Sawalha, 2020). In contrast, a study from Italy showed lower expression of TMPRSS2 in Asians than Italians, explaining the higher susceptibility towards COVID-19 in Italians (Asselta et al., 2020). Exonic variant p.Val160Met (rs12329760) has the highest allele frequency in the European population (∼25%), whereas p.Val197Met missense variant (rs12329760) studies showed an increased allelic frequency in the East Asian population (Hou et al., 2020, Wang et al., 2020). A recent study reported that both isoforms were associated with a reduction in TMPRSS2 stability and binding capacity with ACE-2, thus reducing the risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection (Wang et al., 2020). Finally, the potential increased risk of infection among populations with Down syndrome is highly suggestive of a relation with the TMPRSS2 locus (Hou et al., 2020).
4.3.2. Furin
Furin is a calcium-dependent serine endoprotease that is predominantly found in T-cells to maintain peripheral immune tolerance (Takeda, 2022). TMPRSS2 and furin play are involved in the proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 by cleaving the S protein from the S1/S2 site of SARS-CoV-2 (Bestle et al., 2020, Hoffmann et al., 2020). Furin’s role is especially noteworthy concerning the delta variant, as a mutation in D614G in the delta variant enhances the cleavability of S1/S2 domains by furin (Takeda, 2022).
Furin might increase the risk of acquiring COVID-19 infection in certain populations. It has been hypothesized that diabetic patients have increased levels of plasmatic furin, explaining their vulnerability to a severe course of COVID-19 (Fernandez et al., 2018, Muniyappa and Gubbi, 2020). Another study revealed that the conversion of the FURIN to allelic type GG mediated by CRISPR/Cas9 showed a decrease in the alveolar and neuronal expression of furin, reducing SARS-CoV-2 infectivity (Dobrindt et al., 2020).
Certain FURIN mutations could exist in different ethnicities explaining the differences in the prevalence of COVID-19 infections worldwide. A study in the Italian population showed that individuals with the c.893G > A, (p.Arg298Gln) missense mutation of FURIN have the highest frequency of contracting severe COVID-19 resulting in death, compared to the general European population (Latini et al., 2020).
4.3.3. Tolloid-like protein 1
Our results imply that the A allele of the Tolloid-Like Protein 1 (TLL-1) rs17047200 variant is linked with poor COVID-19 outcomes. TLL-1 is a protein-encoding gene located on 4q32.3, responsible for astacin-like, zinc-dependent, metalloprotease expression (Sieron et al., 2019). An in-silico analysis found that TLL-1 protease acted on several S1/S2 cleavage sites (Grimaudo et al., 2021). This leads to the idea that this protein might be involved in S protein cleavage (Grimaudo et al., 2021). In a study on the intronic variant rs17047200 (A > T) of TLL-1, it was determined that the homozygotes TT has a higher risk of infection and severe manifestation of SARS-CoV2 infection (Grimaudo et al., 2021). Conversely, another study stated that the AA genotype has a higher incidence of the disease, higher comorbidities risk, and ventilation necessity (Agwa et al., 2021).
4.4. Immune system genes
4.4.1. Toll-like receptors
Toll‐like receptors (TLRs) recognize pathogen-associated molecular patterns and are highly active during times of infection (Lim and Staudt, 2013). Various evidence suggests that TLR could play an essential role in cytokine activation in COVID-19 (Zheng et al., 2021). TLR3, located on 4q35.1, encodes for the TLR3 protein, also known as CD283, that recognizes double-stranded (ds) viral RNA, therefore being a key factor for activation and sensitization of the innate immune system (Lim and Staudt, 2013). Our review suggests that a missense mutation in TLR3 (rs3775291) leads to a complicated course of COVID-19. Additionally, an in silico analysis showed that the rs73873710 polymorphism was associated with lower expression of the TLR3, whereas the rs3775290 and rs3775291 variants enhanced the TLR3 expression, which led to increased recognition of the SARS-CoV-2 dsRNA genome and a more severe immune response (Teimouri et al., 2020). Another four TLR3 variants (p.Ser339fs, p.Pro554Ser, p.Trp769* and p.Met870Val) are also associated with severe evolution and complications of COVID-19 pneumonia (Darbeheshti et al., 2021).
TLR7 is located on Xp22.2 and is a key factor in recognizing single-strand RNAs (via uridine or guanosine) and enhancing the host immune response (Zhang et al., 2016). The outcome of our study establishes a link between variable expression of TLR7 polymorphisms (rs189681811, rs147244662, rs149314023, rs200146658, rs5743781) and severe COVID-19. In addition, we found reduced expression of the TLR7 in COVID-19 positive males. Likewise, another study identified two mutations in males with severe COVID-19 - a missense variant (c.2383G > T; p.[Val795Phe]) and a deletion variant (c.2129_2132del; p.[Gln710Argfs*18]), attributing the decreased number of IFN production to the lower expression of TLR7 (van der Made et al., 2020). These deficiencies significantly impact males due to hemizygosity on the X chromosome (Kotsev et al., 2021). Furthermore, TIRAP corresponds to the TLR/IL-1 receptor complex. TIRAP promotes the induction of transduction signaling pathways, that lead to the release of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF- α through the NF-κβ pathway. The rs8177374 polymorphism of the TIRAP (TIR Domain Containing Adaptor Protein) has been shown to reduce the COVID-19 related mortality (Traets et al., 2022).
4.4.2. Interferons
IFNs are specialized cytokines with essential antiviral functions that are secreted in response to various inflammatory stimuli and are classified into three distinct subgroups: type I, type II, and type III (R. R. Goel et al., 2021). Our review suggests interferons and their receptors are heavily implicated in COVID-19 disease, especially polymorphisms in genes that affect IFNλ (type III) expression.
This review’s findings suggest that both IFNλ 3 and 4 are potential markers for severe COVID-19. IFNλ3 rs12979860 CC and rs368234815 TT variants were associated with higher efficiency in clearing RNA viruses (Grimaudo et al., 2021). Similar results were noted with rs8099917, rs12980275 variants of IFNλ3 (Rahimi et al., 2021). However, in a study on the rs12979860 variant, the CC genotype was associated with a remarkably increased susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection (Agwa et al., 2021). Controversially, the TC genotype was linked with higher mortality and a more severe course of disease (Agwa et al., 2021). However, there seems to be a discrepancy in the effects of IFNλ4 polymorphisms on the course of COVID-19. Additionally, The polymorphism at the rs368234815 TT/ΔG locus, resulted in a reduced expression of IFNλ4, seemingly increasing the risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 and was linked to a higher viral load due to a reduction in viral clearing (Amodio et al., 2020). However, rs368234815 was discovered to have a protective function against COVID-19, as the patients' survival rate was reported to be higher (Rahimi et al., 2021).
Interferon-α/β receptors (IFNAR), formed by IFNAR1 and IFNAR2, bind to type 1 IFNs to induce the production of large amounts of protective IFNα (Hashemi et al., 2021). IFNAR2 variant rs2236757, which results in lower expression of type 1 IFNs, was found in patients with critical COVID-19 infection ( The GenOMICC Investigators et al., 2021). In another study, the p.Trp73Cys, p.Ser422Arg and p.Pro335del variants of IFNAR1, and p.Glu140fs variant of IFNAR2 were also present in patients with critical COVID-19 infections, further corroborating the link between serious COVID-19 disease and dysregulations of type I IFNs (Zhang et al., 2020).
Another IFN inducible gene associated with the abysmal aftermath of COVID-19 is gamma-interferon-inducible lysosomal thiol reductase (IFI30). IFI30 plays an important protective role against SARS-CoV-2 viruses (Monticelli et al., 2021). The IFI30 rs11554159 polymorphism is linked with increased susceptibility and severe outcome of COVID-19 due to high viral charge (Monticelli et al., 2021). Moreover, Interferon Induced Transmembrane Protein 3 (IFITM3) polymorphisms were also associated with a higher disease burden and a greater risk of acquiring SARS-CoV-2 infection (Gómez et al., 2021, Iyer et al., 2020, Kotsev et al., 2021, Zhang et al., 2020). However, a study showed that there was no association between the rs12252 and rs34481144 variants of IFITM3 and SARS-CoV-2 severity German patients with COVID-19 (Schönfelder et al., 2021).
4.4.3. Complement component (C3)
The findings of this review suggest a correlation between age, C3 levels and the course of COVID-19 infection could exist. In a univariate analysis, C3 levels were elevated in young patients with severe COVID-19 infection. However, in the general population, it showed no statistically significant difference. The same results were observed in a multivariable analysis. However, critically low levels were associated with higher mortality overall (Cheng et al., 2021). This might explain the risk of severe COVID-19 and associated mortality in the elderly due to immunosenescence lowering the activity of C3 (Cheng et al., 2021).
4.4.4. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptors
TNF Receptor Superfamily Member 1A (TNFRSF1A) binds to TNF- α, playing a vital role in the inflammatory cascade (Iyer et al., 2020). This review indicates that polymorphism rs767455 of TNFRSF1A is associated with a severe progression of COVID-19 (Palacios et al., 2021). Another receptor implicated with severe COVID-19 is TNF Receptor Superfamily Member 13C (TNFRSF13C) which contributes to B-cell survival (Smulski and Eibel, 2018). A rare variant, p.His159Tyr variant of TNFRSF13C, was drastically more frequent in severe cases (n = 38) compared to asymptomatic patients (n = 375) (Russo et al., 2021). This mutation was associated with a gain of function and significantly increased NF-kb1 and NF-kb2 activation (Russo et al., 2021).
4.5. Chromosome 3p21.31
C-C Motif Chemokine Receptor 5 (CCR5) located on 3p21.31 is highly expressed in macrophages and T cells, serving as a co-receptor for macrophage-tropic viruses and plays an important role COVID-19 infection (Ray et al., 2020). The rs9845542, rs12639314, rs34418657, and rs35951367 variants of CCR5 were associated with severe COVID-19 illness (Cantalupo et al., 2021). Our results pointed out that the Δ32 deletion within CCR5 leads to reduced expression of CCR5, playing a protective role against COVID-19 infection (Hippisley-Cox et al., 2020, Hubacek et al., 2021). Our results showed that the CCR5Δ32 allele is present in 11.4 % of the Czech population (Hubacek et al., 2021). This allele has a predilection for Northern-European Caucasians (16%), whereas approximately 5% of Southern Europeans were carriers and Asian and African populations were devoid of this deletion (Hippisley-Cox et al., 2020).
The findings of this review suggest that the younger population carrying a GA allele of the rs11385942 variant were prone to severe COVID-19 infection. The GA allele of the rs11385942 variant is associated with enhanced expression of SLC6A20 (Solute Carrier Family 6 Member 20), and LZTFL1 (Leucine Zipper Transcription Factor Like 1) and reduced expression of CXCR6 (Chemokine Receptor Type 6) (The Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group, 2020). These three proteins are part of the genes that form the association signal at locus 3p21.31, collectively aggravating the likelihood of contracting COVID-19 infection (Kasela et al., 2021, Ma et al., 2021). This cluster is also linked with an increased risk of respiratory failure and necessity for mechanical ventilation (Anastassopoulou et al., 2020). Fine mapping of this structure identified over 20 variants; therefore, it is impossible to be infer which individual variant is responsible for this association (Yao et al., 2021). Using CRISPR/Cas genome editing various genes were found to be targets of locus 3p21.31 including CXCR6, SLC6A20, CCR9 (Kasela et al., 2021, Yao et al., 2021). It is important to note that the functional mechanisms between the proteins associated with locus 3p21.31 and COVID-19 severity remain ambiguous, requiring more further studies to understand the mechanism of this strong association (Kasela et al., 2021).
4.6. ABO locus
The correlation between the ABO system and COVID-19 evolution has been widely investigated. Studies have shown that Group O was allied with a lower risk of infection, while group A attributed to a higher risk owing to SNP rs657152 (The Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group, 2020, Wu et al., 2020, Zhao et al., 2021). Other SNPs located on the ABO locus were also found to protect the risk of critical illness from COVID-19 infection. These include rs199969472, rs34266669, rs76700116, rs7849280, rs34039247, rs10901251, rs9411475, and rs13291798 (Jelinek et al., 2022).
The lower susceptibility associated with blood group O was supported by a recent meta-analysis of 30 studies (Gutiérrez‐Valencia et al., 2022). Additionally, a recent cross-sectional study showed that blood group O offered a protective effect against developing critical COVID-19 (Jelinek et al., 2022). This could arise since human anti-A antibodies, found in patients with blood group O, are hypothesized to bind to the S protein of SARS-CoV-2, thereby hindering its attachment to the ACE2 receptor and preventing its invasion of lung tissue (R. Goel et al., 2021). However, another study showed that group A was associated with a statistically significantly lower incidence of intubation compared to O group, but, the susceptibility to infection remained lower in patients with group O (Zietz et al., 2020). It is poorly understood how specific blood groups affect COVID-19 infection course. It is hypothesized that specific ABO blood groups could alter the glycotransferase activity which results in an increased risk of venous thromboembolism which is a common complication of severe COVID-19 infection, thus, explaining the critical outcomes in some patients (Yildirim et al., 2021).
A meta-analysis, consisting of up to 49,562 patients from 19 countries, by Niemi et al revealed that ABO locus was a susceptibility rather a severity locus, as there was a significantly higher association with infections than with hospitalization (COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative et al., 2021). Another meta-analysis revealed there was no significant differences in hospitalization, ICU admission and mechanical ventilation among the different blood groups but mortality was higher in blood O compared to blood group B (Gutiérrez‐Valencia et al., 2022). Both meta-analyses, however, showed high heterogeneity and pooled various ethnicities together, therefore, their results should be interpreted with caution.
4.7. Androgen receptor gene
It is suggested that there is a substantial relationship between higher free androgen levels and SARS-CoV-2 susceptibility and evolution. It was thought to be mediated by ACE-2 and TMPRSS2 activity. However, the protein interaction map suggested a crosstalk between androgen receptor (AR) signaling pathways, inflammatory markers, and peptidases pertinent to the viral receptor and co-receptors (Samuel et al., 2020). Furthermore, new research shows no link between androgen deprivation and TMPRSS2 levels as previously thought (Rastrelli et al., 2021, Schroeder et al., 2021).
The polymorphic CAG nucleotide repeat segment near the N-terminal transactivation domain of AR is responsible for different variations in the course of COVID-19 infection, and the mortality rate among African Americans compared to other ethnic groups (Mohamed et al., 2021). The AR polyQ length is also associated with the function of the AR receptor. Shorter polymorphic glutamine repeats are linked with mild COVID-19 infection. Less than 22 glutamine repeats were associated with a protective effect, whereas longer polyQ was associated with a severe outcome of infection (Baldassarri et al., 2021).
4.8. Dipeptidyl Peptidases
The results of this review indicated that numerous dipeptidyl peptidases (DPP) were implicated with the risk of acquiring severe COVID-19 infection. DPP4 was previously associated with nasopharyngitis and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (MERS), serving as a receptor for MERS-CoV (Kleine-Weber et al., 2018). It is hypothesized that DPP4 could play a similar role for SARS-CoV-2. The rs13015258 variant was found to affect the key genes implicated in invasion of SARS-CoV-2 into cells. However, some studies suggested that DPP4 does not have a receptor role for SARS-CoV-2 (Hashemi et al., 2021, Wang et al., 2020).
Other DPPs were also associated with COVID-19, namely DPP7 and DPP9. A 1 base pair insertion in DPP7 was found in asymptomatic COVID-19 patients (Wang et al., 2020). It represents the rs11391519 variant, which is associated with decreased peptidase expression, therefore interfering with the immune response (Wang et al., 2020). The rs2109069 polymorphism of the DPP9 is associated with more severe manifestations and outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection due to increased risk of lung fibrosis (Hashemi et al., 2021).
5. Conclusion
Higher expression, polymorphisms, mutation, and deletion of several genes and their alleles could play a crucial role in determining the severity and clinical fate of COVID-19 patients. HLA polymorphisms appear to influence the course of COVID-19, however, further genome-wide association studies with larger patient populations are required to fully assess the role of several HLA loci in the course of COVID-19 infections. ACE-2, TMPRSS2, furin, and TLL-1 are associated with viral entry and binding to the host cells. Specific proteins such as TLR, IFNλ, and CCR5 govern the immune response to COVID-19. Further experimental studies are also needed to understand the functional significance of many of these associations with COVID-17 disease severity and susceptibility. This could prove important as genotyping can help identify the population at high risk and anticipate the severity of the disease. Additionally, vaccination can be prioritized in individuals with genetic susceptibility to severe COVID-19. Furthermore, early treatment aimed at some of the pathophysiological mechanisms altered by these genetic associations could minimize the severity and mortality risk.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Edited by: Andre van Wijnen
Appendix.
Search strategy for PubMed
((“COVID-19”[All Fields] OR “COVID-19”[MeSH Terms] OR “SARS-CoV-2”[All Fields] OR “sars-cov-2”[MeSH Terms] OR “Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2”[All Fields] OR “NCOV”[All Fields] OR “2019 NCOV”[All Fields]) AND (“Genetic Susceptibility” [Title/Abstract] OR “Genetic Predisposition” [Title/Abstract] OR “allelic variation” [Title/Abstract] OR “ACE” [All Fields] OR “TLR7” [All Fields] OR “HLA” [All Fields] OR “Polymorphism” [All Fields])) AND (“disease severity” [All Fields] OR “clinical outcome” [All Fields] OR “Disease Susceptibility” [All Fields] OR “clinical course”[All Fields])
Search strategy for Scopus
(ALL (covid-19 OR sars-cov-2) AND TITLE-ABS-KEY (genetic AND susceptibility OR genetic AND predisposition OR allelic AND variation OR ace OR tlr7 OR hla OR polymorphism) AND ALL (disease AND severity OR clinical AND outcome OR disease AND susceptibility OR clinical AND course))
References
- Agwa S.H.A., Kamel M.M., Elghazaly H., Abd Elsamee A.M., Hafez H., Girgis S.A., Ezz Elarab H., Ebeid F.S.E., Sayed S.M., Sherif L., Matboli M. Association between Interferon-Lambda-3 rs12979860, TLL1 rs17047200 and DDR1 rs4618569 variant polymorphisms with the course and outcome of SARS-CoV-2 patients. Genes. 2021;12:830. doi: 10.3390/genes12060830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amodio E., Pipitone R.M., Grimaudo S., Immordino P., Maida C.M., Prestileo T., Restivo V., Tramuto F., Vitale F., Craxì A., Casuccio A. SARS-CoV-2 viral load, IFNλ polymorphisms and the course of COVID-19: an observational study. JCM. 2020;9:3315. doi: 10.3390/jcm9103315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anastassopoulou C., Gkizarioti Z., Patrinos G.P., Tsakris A. Human genetic factors associated with susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease severity. Hum. Genomics. 2020;14:40. doi: 10.1186/s40246-020-00290-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andolfo I., Russo R., Lasorsa V.A., Cantalupo S., Rosato B.E., Bonfiglio F., Frisso G., Abete P., Cassese G.M., Servillo G., Esposito G., Gentile I., Piscopo C., Villani R., Fiorentino G., Cerino P., Buonerba C., Pierri B., Zollo M., Iolascon A., Capasso M. Common variants at 21q22.3 locus influence MX1 and TMPRSS2 gene expression and susceptibility to severe COVID-19. iScience. 2021;24 doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2021.102322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzurez A., Naka I., Miki S., Nakayama-Hosoya K., Isshiki M., Watanabe Y., Nakamura-Hoshi M., Seki S., Matsumura T., Takano T., Onodera T., Adachi Y., Moriyama S., Terahara K., Tachikawa N., Yoshimura Y., Sasaki H., Horiuchi H., Miyata N., Miyazaki K., Koga M., Ikeuchi K., Nagai H., Saito M., Adachi E., Yotsuyanagi H., Kutsuna S., Kawashima A., Miyazato Y., Kinoshita N., Kouno C., Tanaka K., Takahashi Y., Suzuki T., Matano T., Ohashi J., Kawana-Tachikawa A. Association of HLA- DRB1 *09:01 with severe COVID -19. HLA. 2021;98:37–42. doi: 10.1111/tan.14256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asselta R., Paraboschi E.M., Mantovani A., Duga S. ACE2 and TMPRSS2 variants and expression as candidates to sex and country differences in COVID-19 severity in Italy. Aging. 2020;12:10087–10098. doi: 10.18632/aging.103415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aung A.K., Aitken T., Teh B.M., Yu C., Ofori-Asenso R., Chin K.L., Liew D. Angiotensin converting enzyme genotypes and mortality from COVID-19: an ecological study. J. Infect. 2020;81:961–965. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2020.11.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldassarri M., Picchiotti N., Fava F., Fallerini C., Benetti E., Daga S., Valentino F., Doddato G., Furini S., Giliberti A., Tita R., Amitrano S., Bruttini M., Croci S., Meloni I., Pinto A.M., Iuso N., Gabbi C., Sciarra F., Venneri M.A., Gori M., Sanarico M., Crawley F.P., Pagotto U., Fanelli F., Mezzullo M., Dominguez-Garrido E., Planas-Serra L., Schlüter A., Colobran R., Soler-Palacin P., Lapunzina P., Tenorio J., Pujol A., Castagna M.G., Marcelli M., Isidori A.M., Renieri A., Frullanti E., Mari F., Montagnani F., Sarno L.D., Tommasi A., Palmieri M., Fabbiani M., Rossetti B., Zanelli G., Sestini F., Bergantini L., D’Alessandro M., Cameli P., Bennett D., Anedda F., Marcantonio S., Scolletta S., Franchi F., Mazzei M.A., Guerrini S., Conticini E., Cantarini L., Frediani B., Tacconi D., Feri M., Donati A., Guidelli L., Spargi G., Corridi M., Nencioni C., Croci L., Caldarelli G.P., Spagnesi M., Piacentini P., Desanctis E., Cappelli S., Canaccini A., Verzuri A., Anemoli V., Ognibene A., Vaghi M., Monforte A.D., Merlini E., Miraglia F.G., Mondelli M.U., Mantovani S., Girardis M., Venturelli S., Sita M., Cossarizza A., Antinori A., Vergori A., Emiliozzi A., Rusconi S., Siano M., Gabrieli A., Riva A., Francisci D., Schiaroli E., Paciosi F., Scotton P.G., Andretta F., Panese S., Baratti S., Scaggiante R., Gatti F., Parisi S.G., Castelli F., Quiros-Roldan E., Antoni M.D., Zanella I., Monica M.D., Piscopo C., Capasso M., Russo R., Andolfo I., Iolascon A., Fiorentino G., Carella M., Castori M., Merla G., Aucella F., Raggi P., Marciano C., Perna R., Bassetti M., Biagio A.D., Sanguinetti M., Masucci L., Valente S., Mencarelli M.A., Rizzo C.L., Bargagli E., Mandalà M., Giorli A., Salerni L., Zucchi P., Parravicini P., Menatti E., Trotta T., Giannattasio F., Coiro G., Lena F., Coviello D.A., Mussini C., Bosio G., Martinelli E., Mancarella S., Tavecchia L., Crotti L., Parati G. Shorter androgen receptor polyQ alleles protect against life-threatening COVID-19 disease in European males. EBioMed. 2021;65 doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barham H.P., Taha M.A., Broyles S.T., Stevenson M.M., Zito B.A., Hall C.A. Association between bitter taste receptor phenotype and clinical outcomes among patients with COVID-19. JAMA Netw Open. 2021;4 doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.11410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baştuğ S., Çavdarlı B., Baştuğ A., Şencan İ., Tunçez E., Yakışık Çakır E., Kemirtlek N., Sakar C., Erdem D., Güleç Ceylan G., Özkoçak Turan I., Kazancıoğlu S., Bodur H. Are angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE1/ACE2) gene variants associated with the clinical severity of COVID-19 pneumonia? a singlecenter cohort study. Anatol. J. Cardiol. 2022;26:133–140. doi: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2021.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben Shachar S., Barda N., Manor S., Israeli S., Dagan N., Carmi S., Balicer R., Zisser B., Louzoun Y. MHC haplotyping of SARS-CoV-2 patients: HLA subtypes are not associated with the presence and severity of COVID-19 in the Israeli population. J. Clin. Immunol. 2021;41:1154–1161. doi: 10.1007/s10875-021-01071-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernal E., Gimeno L., Alcaraz M.J., Quadeer A.A., Moreno M., Martínez-Sánchez M.V., Campillo J.A., Gomez J.M., Pelaez A., García E., Herranz M., Hernández-Olivo M., Martínez-Alfaro E., Alcaraz A., Muñoz Á., Cano A., McKay M.R., Muro M., Minguela A. Activating killer-cell immunoglobulin-like receptors are associated with the severity of coronavirus disease 2019. J. Infect. Diseases. 2021;224:229–240. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiab228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestle, D., Heindl, M.R., Limburg, H., Van Lam van, T., Pilgram, O., Moulton, H., Stein, D.A., Hardes, K., Eickmann, M., Dolnik, O., Rohde, C., Klenk, H.-D., Garten, W., Steinmetzer, T., Böttcher-Friebertshäuser, E., 2020. TMPRSS2 and furin are both essential for proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 in human airway cells. Life Sci. Alliance 3, e202000786. 10.26508/lsa.202000786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Booth A., Reed A.B., Ponzo S., Yassaee A., Aral M., Plans D., Labrique A., Mohan D. Population risk factors for severe disease and mortality in COVID-19: a global systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2021;16 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0247461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cafiero C., Rosapepe F., Palmirotta R., Re A., Ottaiano M.P., Benincasa G., Perone R., Varriale E., D’Amato G., Cacciamani A., Micera A., Pisconti S. Angiotensin system polymorphisms’ in SARS-CoV-2 positive patients: assessment between symptomatic and asymptomatic patients: a pilot study. PGPM. 2021;14:621–629. doi: 10.2147/PGPM.S303666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calabrese C., Annunziata A., Coppola A., Pafundi P.C., Guarino S., Di Spirito V., Maddaloni V., Pepe N., Fiorentino G. ACE gene I/D polymorphism and acute pulmonary embolism in COVID19 pneumonia: a potential predisposing role. Front. Med. 2021;7 doi: 10.3389/fmed.2020.631148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantalupo S., Lasorsa V.A., Russo R., Andolfo I., D’Alterio G., Rosato B.E., Frisso G., Abete P., Cassese G.M., Servillo G., Gentile I., Piscopo C., Della Monica M., Fiorentino G., Russo G., Cerino P., Buonerba C., Pierri B., Zollo M., Iolascon A., Capasso M. Regulatory noncoding and predicted pathogenic coding variants of CCR5 predispose to severe COVID-19. IJMS. 2021;22:5372. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J.-L., Su H.C., Abel L., Aiuti A., Almuhsen S., Arias A.A., Bastard P., Biggs C., Bogunovic D., Boisson B., Boisson-Dupuis S., Bolze A., Bondarenko A., Bousfiha A., Brodin P., Bustamante J., Butte M., Casari G., Ciancanelli M., Cobat A., Condino-Neto A., Cooper M., Dalgard C., Espinosa S., Feldman H., Fellay J., Franco J.L., Hagin D., Itan Y., Jouanguy E., Lucas C., Mansouri D., Meyts I., Milner J., Mogensen T., Morio T., Ng L., Notarangelo L.D., Okada S., Ozcelik T., Soler Palacín P., Planas A., Prando C., Puel A., Pujol A., Redin C., Renia L., Rodriguez Gallego J.C., Quintana-Murci L., Sancho-Shimizu V., Sankaran V., Seppänen M.R.J., Shahrooei M., Snow A., Spaan A., Tangye S., Tur J.P., Turvey S., Vinh D.C., von Bernuth H., Wang X., Zawadzki P., Zhang Q., Zhang S. A global effort to define the human genetics of protective immunity to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell. 2020;181:1194–1199. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascella, M., Rajnik, M., Aleem, A., Dulebohn, S.C., Di Napoli, R., 2022. Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19), in: StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL). [PubMed]
- Cheng, W., Hornung, R., Xu, K., Yang, C. hong, Li, J., 2021. Complement C3 identified as a unique risk factor for disease severity among young COVID-19 patients in Wuhan, China. Sci Rep 11, 7857. 10.1038/s41598-021-82810-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ciaglia E., Lopardo V., Montella F., Sellitto C., Manzo V., De Bellis E., Iannaccone T., Franci G., Zannella C., Pagliano P., Di Pietro P., Carrizzo A., Vecchione C., Conti V., Filippelli A., Puca A.A. BPIFB4 circulating levels and its prognostic relevance in COVID-19. J. Gerontol.: Series A. 2021;76:1775–1783. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glab208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COVID-19 Host Genetics Initiative, Niemi, M.E.K., Karjalainen, J., Liao, R.G., Neale, B.M., Daly, M., Ganna, A., Writing group, Writing group leaders, Pathak, G.A., Andrews, S.J., Kanai, M., Writing group members, Veerapen, K., Fernandez-Cadenas, I., Schulte, E.C., Striano, P., Marttila, M., Minica, C., Marouli, E., Karim, M.A., Wendt, F.R., Savage, J., Sloofman, L., Butler-Laporte, G., Kim, H.-N., Kanoni, S., Okada, Y., Byun, J., Han, Y., Uddin, M.J., Smith, G.D., Willer, C.J., Buxbaum, J.D., Analysis group, Manuscript analyses team leader, Manuscript analyses team member: meta-analysis, Mehtonen, J., Manuscript analyses team member: heritability, methods and supplements, Manuscript analyses team member: PHEWAS, Manuscript analyses team member: Mendelian randomization, Manuscript analyses team member: PC projection and gene prioritization, Manuscript analyses team member: gene prioritization, Finucane, H., Manuscript analyses team member: sensitivity analysis, Cordioli, M., Manuscript analyses team members: PC projection, Martin, A.R., Zhou, W., In silico analysis team members, Pasaniuc, B., Julienne, H., Aschard, H., Shi, H., Yengo, L., Polimanti, R., Ghoussaini, M., Schwartzentruber, J., Dunham, I., Project management group, Project management leader, Project management support, Chwialkowska, K., Francescatto, M., Trankiem, A., Balaconis, M.K., Phenotype steering group, Davis, L., Lee, Sulggi, Priest, J., Renieri, A., Sankaran, V.G., van Heel, D., Deelen, P., Richards, J.B., Nakanishi, T., Biesecker, L., Kerchberger, V.E., Baillie, J.K., Data dictionary, Mari, F., Bernasconi, A., Baillie, S.C., Canakoglu, A., Scientific communication group, Scientific communication leaders, Wolford, B., Scientific communication members, Faucon, A., Dutta, A.K., Schurmann, C., Harry, E., Birney, E., Nguyen, H., Nasir, J., Kaunisto, M., Solomonson, M., Dueker, N., Vadgama, N., Limou, S., Translators, Rahmouni, S., Mbarek, H., Darwish, D., Uddin, M.M., Albertos, R., Pérez-Tur, J., Li, Ruolin, Folkersen, L., Moltke, I., Koelling, N., Teumer, A., Kousathanas, A., Utrilla, A., Verdugo, R.A., Zárate, R., Medina-Gómez, C., Gómez-Cabrero, D., Carnero-Montoro, E., Cadilla, C.L., Moreno-Estrada, A., Garmendia, A., Moya, L., Sedaghati-Khayat, B., Boua, P.R., Favé, M.-J., Francioli, L., Lemaçon, A., Migeotte, I., Patel, S., Varnai, R., Szentpeteri, J.L., Sipeky, C., Colombo, F., von Hohenstaufen, K., Lio, P., Vallerga, C., Wang, Q., Tanigawa, Y., Im, H., Han, C., Song, H., Lim, J., Lee, Y., Kim, Sugyeong, Im, S., Atanasovska, B., Ahmad, H.F., Boer, C., Jansen, P., Franke, L., Kaja, E., Pasko, D., Kennis-Szilagyi, I., Kornilov, S.A., Prijatelj, V., Prokić, I., Sivanadhan, I., Perumal, S., Esmaeeli, S., Pearson, N.M., Website Development, Website development leaders, 23andMe, Analysis team leader, Auton, A., Data collection leaders, 23andMe COVID-19 Team*, Shelton, J.F., Shastri, A.J., Analysis team members, Filshtein-Sonmez, T., Coker, D., Symons, A., Esparza-Gordillo, J., Aslibekyan, S., O’Connell, J., Data collection members, Ye, C., Weldon, C.H., 23andMe COVID-19 Team, ACCOuNT, Analysis team leader, Perera, M., Data collection leaders, O’Leary, K., Tuck, M., O’Brien, T., Meltzer, D., O’Donnell, P., Nutescu, E., Analysis team members, Yang, G., Data collection members, Alarcon, C., Herrmann, S., Mazurek, S., Banagan, J., Hamidi, Z., Barbour, A., Raffat, N., Moreno, D., Admin team member, Friedman, P., Amsterdam UMC COVID Study Group, Analysis team leader, Ferwerda, B., Data collection leaders, van de Beek, D., Brouwer, M.C., Vlaar, A.P.J., Wiersinga, W.J., Analysis team members, Posthuma, D., Tissink, E., Koos Zwinderman, A.H., Uffelmann, E., Data collection members, van Agtmael, M., Algera, A.G., van Baarle, F., Bax, D., Beudel, M., Jan Bogaard, H., Bomers, M., Bonta, P.I., Bos, L., Botta, M., de Brabander, J., de Bree, G., de Bruin, S., Bugiani, M., Bulle, E., Chouchane, O., Cloherty, A., Dongelmans, D., Elbers, P., Fleuren, L., Geerlings, S., Geerts, B., Geijtenbeek, T., Girbes, A., Goorhuis, B., Grobusch, M.P., Hafkamp, F., Hagens, L., Hamann, J., Harris, V., Hemke, R., Hermans, S.M., Heunks, L., Hollmann, M., Horn, J., Hovius, J.W., de Jong, M.D., Koning, R., van Mourik, N., Nellen, J., Nossent, E.J., Paulus, F., Peters, E., van der Poll, T., Preckel, B., Prins, J.M., Raasveld, J., Reijnders, T., Schinkel, M., Schultz, M.J., Schuurman, A., Sigaloff, K., Smit, M., Stijnis, C.S., Stilma, W., Teunissen, C., Thoral, P., Tsonas, A., van der Valk, M., Veelo, D., de Vries, H., van Vugt, M., Wouters, D., Minnaar, R.P., Kromhout, A., van Uffelen, K.W.J., Wolterman, R.A., AncestryDNA COVID-19 Research Study, Analysis team leader, Roberts, G., Data collection leader, Park, D., Admin team leader, Ball, C.A., Analysis team members, Coignet, M., McCurdy, S., Knight, S., Partha, R., Rhead, B., Data collection members, Zhang, M., Berkowitz, N., Gaddis, M., Noto, K., Ruiz, L., Pavlovic, M., Admin team members, Hong, E.L., Rand, K., Girshick, A., Guturu, H., Baltzell, A.H., BelCovid, Analysis team leader, Data collection leaders, Rahmouni, S., Guntz, J., Admin team leader, Beguin, Y., Analysis team members, Pigazzini, S., Nkambule, L., Data collection members, Bouysran, Y., Busson, A., Peyrassol, X., Wilkin, F., Pichon, B., Smits, G., Vandernoot, I., Goffard, J.-C., Georges, M., Moutschen, M., Misset, B., Darcis, G., Guiot, J., Jadot, L., Azarzar, S., Dellot, P., Gofflot, S., Claassen, S., Bertrand, A., Parzibut, G., Clarinval, M., Moermans, C., Malaise, O., El Kandoussi, K., Thonon, R., Huynen, P., Mesdagh, A., Melo, S., Jacques, Nicolas, Di Valentin, E., Giroule, F., Collignon, A., Radermecker, C., Lebrun, M., Perée, H., Latour, S., Barada, O., Sanchez, J., Josse, C., Boujemla, B., Meunier, M., Mariavelle, E., Anania, S., Gazon, H., Juszczak, D., Fadeur, M., Camby, S., Meuris, C., Thys, M., Jacques, J., Henket, M., Léonard, P., Frippiat, F., Giot, J.-B., Sauvage, A.-S., Von Frenckell, C., Mni, M., Wéry, M., Staderoli, A., Belhaj, Y., Lambermont, B., Biobanque Quebec COVID-19, Analysis team leader, Data collection leader, Morrison, D.R., Admin team leaders, Mooser, V., Analysis team members, Forgetta, V., Li, Rui, Data collection members, Ghosh, B., Laurent, L., Belisle, A., Henry, D., Abdullah, T., Adeleye, O., Mamlouk, N., Kimchi, N., Afrasiabi, Z., Rezk, N., Vulesevic, B., Bouab, M., Guzman, C., Petitjean, L., Tselios, C., Xue, X., Afilalo, J., Afilalo, M., Oliveira, M., Brenner, B., Brassard, N., Durand, M., Admin team members, Schurr, E., Lepage, P., Ragoussis, J., Auld, D., Chassé, M., Kaufmann, D.E., Lathrop, G.M., Adra, D., BioVU, Analysis team leaders, Davis, L.K., Cox, N.J., Below, J.E., Analysis team members, Sealock, J.M., Faucon, A.B., Shuey, M.M., Polikowsky, H.G., Petty, L.E., Shaw, D.M., Chen, H.-H., Zhu, W., Bonn Study of COVID-19 Genetics, Data collection leader, Ludwig, K.U., Analysis team members, Schröder, J., Maj, C., Data collection members, Rolker, S., Nöthen, M.M., Fazaal, J., Keitel, V., Jensen, B.-E.O., Feldt, T., Kurth, I., Marx, N., Dreher, M., Pink, I., Cornberg, M., Illig, T., Lehmann, C., Schommers, P., Augustin, M., Rybniker, J., Knopp, L., Eggermann, T., Volland, S., Altmüller, J., Berger, M.M., Brenner, T., Hinney, A., Witzke, O., Bals, R., Herr, C., Ludwig, N., Walter, J., CHRIS, Analysis team leader, Fuchsberger, C., Data collection leaders, Pattaro, C., De Grandi, A., Admin team leader, Pramstaller, P., Analysis team members, Emmert, D., Melotti, R., Foco, L., Admin team members, Mascalzoni, D., Gögele, M., Domingues, F., Hicks, A., Colorado Center for Personalized Medicine (CCPM), Analysis team leader, Gignoux, C.R., Data collection leaders, Wicks, S.J., Crooks, K., Admin team leader, Barnes, K.C., Analysis team members, Daya, M., Shortt, J., Rafaels, N., Chavan, S., Columbia University COVID-19 Biobank, Analysis team leaders, Goldstein, D.B., Kiryluk, K., Data collection leaders, Sengupta, S., Chung, W., Reilly, M.P., Analysis team members, Khan, Atlas, Wang, C., Povysil, G., Bhardwaj, N., Gharavi, A.G., Ionita-Laza, I., Data collection members, Shang, N., O’Byrne, S.M., Nandakumar, R., Menon, A., So, Y.S., Hod, E., Admin team member, Pendrick, D., Corea (Genetics of COVID-19-related Manifestation), Analysis team leader, Kim, H.-N., Data collection leaders, Park, S.-K., Kim, H.-L., Kang, C.K., Lee, H.-J., Song, K.-H., Admin team leaders, Jae Yoon, K., Paik, N.-J., Analysis team members, Seok, W., Yoon, H., Data collection members, Joo, E.-J., Chang, Y., Ryu, S., Park, W.B., Su Park, J., Un Park, K., Ham, S.Y., Jung, J., Kim, E.S., Kim, H.B., COVID-19-Hostage, Analysis team leaders, Ellinghaus, D., Degenhardt, F., Cáceres, M., Juzenas, S., Lenz, T.L., Data collection leaders, Albillos, A., Julià, A., Heidecker, B., Garcia, F., Kurth, F., Tran, F., Hanses, F., Zoller, H., Holter, J.C., Fernández, J., Sander, L.E., Rosenstiel, P., Koehler, P., de Cid, R., Asselta, R., Schreiber, S., Hehr, U., Prati, D., Baselli, G., Valenti, L., Bujanda, L., Banales, J.M., Duga, S., D’Amato, M., Romero-Gómez, M., Buti, M., Invernizzi, P., Admin team leaders, Franke, A., Hov, J.R., Karlsen, T.H., Folseraas, T., Maya-Miles, D., Analysis team members, Teles, A., Azuure, C., Wacker, E.M., Uellendahl-Werth, F., ElAbd, H., Arora, J., Lerga-Jaso, J., Wienbrandt, L., Rühlemann, M.C., Wendorff, M., Vadla, M.S., Lenning, O.B., Özer, O., Myhre, R., Raychaudhuri, S., Tanck, A., Gassner, C., Hemmrich-Stanisak, G., Kässens, J., Figuera Basso, M.E., Schulzky, M., Wittig, M., Braun, N., Wesse, T., Albrecht, W., Yi, X., Data collection members, Ortiz, A.B., Chercoles, A.G., Ruiz, A., Mantovani, A., Holten, A.R., Mayer, Alena, Cherubini, A., Protti, A., Aghemo, A., Gerussi, A., Ramirez, A., Braun, A., Barreira, A., Lleo, A., Kildal, A.B., Glück, A., Nolla, A.C., Latiano, A., Dyrhol-Riise, A.M., Muscatello, A., Voza, A., Rando-Segura, A., Solier, A., Karina, B., Cortes, B., Mateos, B., Nafria-Jimenez, B., Schaefer, B., Bellinghausen,C., Ferrando, C., Quereda, C., Skurk, C., Thibeault, C., Spinner, C.D., Lange, C., Hu, C., Cappadona, C., Bianco, C., Sancho, C., Lihaug Hoff, D.A., Galimberti, D., Jiménez, D., Pestaña, D., Toapanta, D., Azzolini, E., Scarpini, E., Helbig, E.T., Urrechaga, E., Paraboschi, E.M., Pontali, E., Reverter, E., Navas, E., Arana, E., Sánchez, F.G., Ceriotti, F., Malvestiti, F., Mesonero, F., Pezzoli, G., Lamorte, G., Neb, H., My, I., Hernández, I., de Rojas, I., Galván-Femenia, I., Heyckendorf, J., Rybniker, J., Badia, J.R., Schneider, J., Goikoetxea, J., Kraft, J., Müller, K.E., Gaede, K.I., Garcia-Etxebarria, K., Tonby, K., Heggelund, L., Izquierdo-Sanchez, L., Sumoy, L., Lippert, L.J., Terranova, L., Garbarino, L., Téllez, L., Roade, L., Ostadreza, M., Intxausti, M., Kogevinas, M., Gutiérrez-Stampa, M.A., Vehreschild, M.J.G.T., Marquié, M., Castoldi, M., Cecconi, M., Boada, M., Seilmaier, M.J., Mazzocco, M., Rodríguez-Gandía, M., Ayo, N.I., Blay, N., Martínez, N., Norwegian SARS-CoV-2 Study Group*, Cornely, O.A., Palmieri, O., Tentorio, P., Rodrigues, P.M., España, P.P., Hoffmann, P., Bacher, P., Suwalski, P., de Pablo, R., Nieto, R., Badalamenti, S., Ciesek, S., Bombace, S., Wilfling, S., Brunak, S., Heilmann-Heimbach, S., The Humanitas COVID-19 Task Force*, The Humanitas Gavazzeni COVID-19 Task Force*, Ripke, S., Bahmer, T., Landmesser, U., Protzer, U., Rimoldi, V., Skogen, V., Andrade, V., Moreno, V., Poller, W., Farre, X., Wang, Xiaomin, Khodamoradi, Y., Karadeniz, Z., de Salazar, A., Palom, A., Garcia-Fernandez, A.-E., Blanco-Grau, A., Zanella, A., Bandera, A., Nebel, A., Biondi, A., Caballero-Garralda, A., Gori, A., Lind, A., Fracanzani, A.L., Peschuck, A., Pesenti, A., de la Horra, C., Milani, C., Paccapelo, C., Angelini, C., Cea, C., Muñiz-Diaz, E., Sandoval, Elena, Calderón, E.J., Solligård, E., Aziz, F., Martinelli-Boneschi, F., Peyvandi, F., Blasi, F., Medrano, F.J., Rodriguez-Frias, F., Müller, F., Grasselli, G., Costantino, G., Cardamone, G., Foti, G., Matullo, G., Kurihara, H., Afset, J.E., Damås, J.K., Ampuero, J., Martín, J., Erdmann, J., Bergan, J., Goerg, S., Ferrusquía-Acosta, J., Quero, J.H., Delgado, J., Guerrero, J.M., Risnes, K., Bettini, L.R., Moreira, L., Gustad, L.T., Santoro, L., Scudeller, L., Riveiro-Barciela, M., Schaefer, M., Carrabba, M., Valsecchi, M.G., Hernandez-Tejero, M., Acosta-Herrera, M., D’Angiò, M., Baldini, M., Cazzaniga, M., Ciccarelli, M., Bocciolone, M., Miozzo, M., Chueca, N., Montano, N., Faverio, P., Preatoni, P., Bonfanti, P., Omodei, P., Castro, P., Ferrer, R., Gualtierotti, R., Gallego-Durán, R., Morilla, R., Haider, S., Marsal, S., Aneli, S., Pelusi, S., Bosari, S., Aliberti, S., Dudman, S., Zheng, T., Pumarola, T., Cejudo, T.G., Monzani, V., Friaza, V., Peter, W., Dopazo, X., Norwegian SARS-CoV-2 Study Group, Humanitas COVID-19 Task Force, Duga, S., The Humanitas Gavazzeni COVID-19 Task Force, Admin team members, May, S., Grimsrud, M.M., deCODE, Analysis team leader, Gudbjartsson, D.F., Data collection leader, Stefansson, K., Analysis team members, Sulem, P., Sveinbjornsson, G., Melsted, P., Norddahl, G., Swerford Moore, K.H., Data collection members, Thorsteinsdottir, U., Holm, H., Determining the Molecular Pathways & Genetic Predisposition of the Acute Inflammatory Process Caused by SARS-CoV-2, Analysis team leader, Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E., Data collection leader, Bernardo, D., Analysis team member, Martínez-Bueno, M., Data collection member, Rello, S.R., Estonian Biobank, Analysis team leader, Magi, R., Data collection leader, Milani, L., Admin team leader, Metspalu, A., Analysis team members, Laisk, T., Läll, K., Lepamets, M., Data collection members, Esko, T., Reimann, E., Naaber, P., Laane, E., Pesukova, J., Peterson, P., Kisand, K., Tabri, J., Allos, R., Hensen, K., Starkopf, J., Ringmets, I., Tamm, A., Kallaste, A., Admin team members, Alavere, H., Metsalu, K., Puusepp, M., FinnGen, Data collection members, Kristiansson, K., Koskelainen, S., Perola, M., Donner, K., Kivinen, K., Palotie, A., Admin team member, FinnGen Admin team leader, Palotie, A., Functional Host Genomics in Infectious Diseases (FHoGID), Analysis team leader, Rivolta, Carlo, Data collection leaders, Bochud, P.-Y., Bibert, Stéphanie, Boillat, N., Nussle, Semira Gonseth, Albrich, W., Analysis team members, Quinodoz, Mathieu, Kamdar, Dhryata, Data collection members, Suh, Noémie, Neofytos, Dionysios, Erard, Véronique, Voide, Cathy, FHoGID*, RegCOVID*, P-PredictUs*, SeroCOVID*, CRiPSI*, FHoGID, Bochud, P.Y., Rivolta, C., Bibert, S., Quinodoz, M., Kamdar, D., Neofytos, D., Erard, V., Voide, C., Friolet, R., Vollenweider, P., Pagani, J.L., Oddo, M., zu Bentrup, F.M., Conen, A., Clerc, O., Marchetti, O., Guillet, A., Guyat-Jacques, C., Foucras, S., Rime, M., Chassot, J., Jaquet, M., Viollet, R.M., Lannepoudenx, Y., Portopena, L., RegCOVID, Desgranges, F., Filippidis, P., Guéry, B., Haefliger, D., Kampouri, E.E., Manuel, O., Munting, A., Papadimitriou-Olivgeris, M., Regina, J., Rochat-Stettler, L., Suttels, V., Tadini, E., Tschopp, J., Van Singer, M., Viala, B., P-PredictUs, Boillat-Blanco, N., Brahier, T., Hügli, O., Meuwly, J.Y., Pantet, O., SérocoViD, Nussle, S. Gonseth, Bochud, M., D’Acremont, V., Younes, S.E., CRiPSI, Albrich, W.C., Suh, N., Cerny, A., O’Mahony, L., von Mering, C., Bochud, P.Y., Frischknecht, M., Kleger, G.-R., Filipovic, M., Kahlert, C.R., Wozniak, H., Negro, T.R., Pugin, J., Bouras, K., Knapp, C., Egger, T., Perret, A., Montillier, P., di Bartolomeo, C., Barda, B., GCAT Genomes For Life, Analysis team leader, de Cid, R., Data collection leaders, Carreras, A., Moreno, V., Analysis team members, Galván-Femenía, I., Blay, N., Farré, X., Sumoy, L., Data collection members, Cortés, B., Mercader, J.M., Guindo-Martinez, M., Torrents, D., Garcia-Aymerich, J., Castaño-Vinyals, G., Dobaño, C., GEN-COVID Multicenter Study, Analysis team leaders, Gori, M., Data collection leaders, Renieri, A., Mondelli, M.U., Castelli, F., Vaghi, M., Rusconi, S., Montagnani, F., Bargagli, E., Franchi, F., Mazzei, M.A., Cantarini, L., Tacconi, D., Feri, M., Scala, R., Spargi, G., Nencioni, C., Bandini, M., Caldarelli, G.P., Spagnesi, M., Canaccini, A., Ognibene, A., D’Arminio Monforte, A., Girardis, M., Antinori, A., Francisci, D., Schiaroli, E., Scotton, P.G., Panese, S., Scaggiante, R., Monica, M.D., Capasso, M., Fiorentino, G., Castori, M., Aucella, F., Di Biagio, A., Masucci, L., Valente, S., Mandalà, M., Zucchi, P., Giannattasio, F., Coviello, D.A., Mussini, C., Bosio, G., Tavecchia, L., Crotti, L., Rizzi, M., La Rovere, M.T., Sarzi-Braga, S., Bussotti, M., Ravaglia, S., Artuso, R., Perrella, A., Romani, D., Bergomi, P., Catena, E., Vincenti, A., Ferri, C., Grassi, D., Pessina, G., Tumbarello, M., Di Pietro, M., Sabrina, R., Luchi, S., Barbieri, C., Acquilini, D., Andreucci, E., Paciosi, F., Segala, F.V., Tiseo, G., Falcone, M., Lista, M., Poscente, M., De Vivo, O., Petrocelli, P., Guarnaccia, A., Baroni, S., Perticaroli, V., Admin team leaders, Furini, S., Dei, S., Analysis team members, Benetti, E., Picchiotti, N., Sanarico, M., Ceri, S., Pinoli, P., Raimondi, F., Biscarini, F., Stella, A., Bergomi, M., Zguro, K., Capitani, K., Tanfoni, M., Data collection members, Fallerini, C., Daga, S., Baldassarri, M., Fava, F., Frullanti, E., Valentino, F., Doddato, G., Giliberti, A., Tita, R., Amitrano, S., Bruttini, M., Croci, S., Meloni, I., Mencarelli, M.A., Lo Rizzo, C., Pinto, A.M., Beligni, G., Tommasi, A., Di Sarno, L., Palmieri, M., Carriero, M.L., Alaverdian, D., Iuso, N., Inchingolo, G., Busani, S., Bruno, R., Vecchia, M., Belli, M.A., Mantovani, S., Ludovisi, S., Quiros-Roldan, E., Antoni, M.D., Zanella, I., Siano, M., Emiliozzi, A., Fabbiani, M., Rossetti, B., Zanelli, G., Bergantini, L., D’Alessandro, M., Cameli, P., Bennet, D., Anedda, F., Marcantonio, S., Scolletta, S., Guerrini, S., Conticini, E., Frediani, B., Spertilli, C., Donati, A., Guidelli, L., Corridi, M., Croci, L., Piacentini, P., Desanctis, E., Cappelli, S., Verzuri, A., Anemoli, V., Pancrazi, A., Lorubbio, M., Merlini, E., Miraglia, F.G., Venturelli, S., Cossarizza, A., Vergori, A., Gabrieli, A., Riva, Agostino, Paciosi, F., Andretta, F., Gatti, F., Parisi, S.G., Baratti, S., Piscopo, C., Russo, R., Andolfo, I., Iolascon, A., Carella, M., Merla, G., Squeo, G.M., Raggi, P., Marciano, C., Perna, R., Bassetti, M., Sanguinetti, M., Giorli, A., Salerni, L., Parravicini, P., Menatti, E., Trotta, T., Coiro, G., Lena, F., Martinelli, E., Mancarella, S., Gabbi, C., Maggiolo, F., Ripamonti, D., Bachetti, T., Suardi, C., Parati, G., Bottà, G., Di Domenico, P., Rancan, I., Bianchi, F., Colombo, R., Genes & Health, Analysis team leader, van Heel, D.A., Data collection leader, Hunt, K.A., Admin team leader, Trembath, R.C., Analysis team members, Huang, Q.Q., Martin, H.C., Data collection members, Mason, D., Trivedi, B., Wright, J., Admin team members, Finer, S., Genes & Health Research Team*, Griffiths, C.J., Genes & Health Research Team, Akhtar, S., Anwar, M., Arciero, E., Ashraf, Samina, Breen, G., Chung, R., Curtis, C.J., Chowdhury, M., Colligan, G., Deloukas, P., Durham, C., Finer, S., Griffiths, C., Huang, Q.Q., Hurles, M., Hunt, K.A., Hussain, Shapna, Islam, K., Khan, Ahsan, Khan, Amara, Lavery, C., Lee, S.H., Lerner, R., MacArthur, D., MacLaughlin, B., Martin, H., Mason, D., Miah, S., Newman, B., Safa, N., Tahmasebi, F., Trembath, R.C., Trivedi, B., van Heel, D.A., Wright, J., Genes for Good, Analysis team leader, Smith, A.V., Data collection members, Boughton, A.P., Li, K.W., LeFaive, J., Annis, A., Genetic determinants of COVID-19 complications in the Brazilian population, Analysis team leader, Data collection leader, Jannes, C.E., Admin team leaders, Krieger, J.E., Pereira, A.C., Analysis team members, Velho, M., Marques, E., Data collection members, Lima, I.R., Tada, M.T., Valino, K., Genetic influences on severity of COVID-19 illness in Korea, Analysis team leaders, McCarthy, M., Rosenberger, C., Data collectionleader, Lee, Jong Eun, Analysis team members, Chang, D., Hammer, C., Hunkapiller, J., Mahajan, A., Pendergrass, S., Sucheston-Campbell, L., Yaspan, B., Data collection members, Lee, H.S., Shin, E., Jang, H.Y., Kim, Sunmie, Kym, S., Kim, Y.-S., Jeong, H., Kwon, K.T., Kim, S.-W., Kim, J.Y., Jang, Y.R., Kim, H. ah, Lee, J.Y., Lee, Jeong Eun, Lee, Shinwon, Choe, K.-W., Kang, Y.M., Jee, S.H., Jung, K.J., Genomic epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2host genetics in coronavirus disease 2019, Data collection leaders, Parikh, V., Ashley, E., Wheeler, M., Rivas, M., Bustamante, C., Pinksy, B., Febbo, P., Farh, K., Schroth, G.P., deSouza, F., Admin team leaders, Dalton, K., Christle, J., Analysis team members, Deboever, C., Szalma, S., Tanigawa, Y., Rubinacci, S., Delaneau, O., Data collection members, Gorzynski, J., de Jong, H., Sutton, S., Youlton, N., Joshi, R., Jimenez-Morales, D., Hughes, C., Amar, D., Ioannidis, A., Hershman, S., Kirillova, A., Seo, K., Huang, Y., Shoura, M., Hammond, N., Watson, N., Raja, A., Huang, C., Sahoo, M., Wang, H., Admin team member, Zhen, J., Genotek COVID-19 study, Analysis team leader, Rakitko, A., Admin team leader, Ilinsky, V., Analysis team members, Yermakovich, D., Popov, I., Chernitsov, A., Kovalenko, E., Krasnenko, A., Plotnikov, N., Stetsenko, I., Kim, A., Helix & Healthy Nevada Project Exome+ COVID-19 Phenotypes, Analysis team leader, Cirulli, E.T., Analysis team members, Schiabor Barrett, K.M., Bolze, A., White, S., Washington, N.L., Lu, J.T., Data collection members, Riffle, S., Tanudjaja, F., Wang, Xueqing, Ramirez, J.M., Leonetti, N., Sandoval, Efren, Neveux, I., Dabe, S., Grzymski, J.J., 24Genetics & IdiPaz Genomic Variants associated to COVID-19 infection outcome, Analysis team leader, Esteban Miñano, J.I., Data collection leader, Aguirre, L.A., Admin team leader, López-Collazo, E., Analysis team members, de la Mata Pazos, M., Cerrato, L., Folkersen, L., Data collection members, Lozano-Rodríguez, R., Avendaño-Ortiz, J., Arcos, V.T., Montalbán-Hernández, K.M., Quiroga, J.V., Pascual-Iglesias, A., Admin team members, Maroun-Eid, C., Martín-Quirós, A., Japan Coronavirus Taskforce, Analysis team leaders, Namkoong, H., Okada, Y., Imoto, S., Data collection leaders, Katayama, K., Fukunaga, K., Kitagawa, Yuko, Sato, T., Hasegawa, N., Kumanogoh, A., Kimura, A., Ai, M., Tokunaga, K., Admin team leaders, Kanai, T., Miyano, S., Ogawa, Seishi, Analysis team members, Edahiro, R., Sonehara, K., Shirai, Y., Kanai, M., Data collection members, Ishii, M., Kabata, H., Masaki, K., Kamata, H., Ikemura, S., Chubachi, S., Okamori, S., Terai, H., Tanaka, H., Morita, A., Lee, H., Asakura, T., Sasaki, J., Morisaki, H., Uwamino, Y., Nanki, K., Mikami, Y., Tomono, K., Kato, K., Matsuda, F., Takahashi, Meiko, Hizawa, N., Takeda, Y., Hirata, H., Shiroyama, T., Miyawaki, S., Suzuki, K., Maeda, Y., Nii, T., Noda, Y., Niitsu, T., Adachi, Y., Enomoto, T., Amiya, S., Hara, R., Takahashi, Kunihiko, Anzai, T., Hasegawa, T., Ito, S., Koike, R., Endo, A., Uchimura, Y., Miyazaki, Y., Honda, T., Tateishi, T., Tohda, S., Ichimura, N., Sonobe, K., Sassa, C., Nakajima, J., Nannya, Y., Omae, Y., Takahashi, Kazuhisa, Harada, N., Hiki, M., Takagi, H., Nakamura, A., Tagaya, E., Kawana, M., Arimura, K., Ishiguro, T., Takayanagi, N., Isono, T., Takaku, Y., Takano, K., Anan, R., Nakajima, Y., Nakano, Y., Nishio, K., Ueda, S., Hayashi, R., Tateno, H., Hase, I., Yoshida, Shuichi, Suzuki, S., Mitamura, K., Saito, Fumitake, Ueda, T., Azuma, M., Nagasaki, T., Yasui, Y., Hasegawa, Y., Mutoh, Y., Yoshiyama, T., Shoko, T., Kojima, M., Adachi, T., Ishikawa, M., Takahashi, Kenichiro, Watanabe, K., Manabe, T., Ito, F., Fukui, T., Funatsu, Y., Koh, H., Hirai, Y., Kawashima, H., Narita, A., Niwa, K., Sekikawa, Y., Saito, Fukuki, Yoshiya, K., Yoshihara, T., Suzuki, Y., Nakayama, S., Masuzawa, K., Nishi, K., Nishitsuji, M., Tani, M., Inoue, T., Hirano, T., Kobayashi, K., Miyazawa, N., Kimura, Y., Sado, R., Ogura, T., Kitamura, H., Murohashi, K., Nakachi, I., Baba, R., Arai, D., Fuke, S., Saito, H., Kuwahara, N., Fujiwara, A., Okada, T., Baba, T., Noda, J., Mashimo, S., Yagi, K., Shiomi, T., Hashiguchi, M., Odani, T., Mochimaru, T., Oyamada, Y., Mori, N., Izumi, N., Nagata, K., Taki, R., Murakami, K., Yamada, M., Sugiura, H., Hayashi, K., Shimizu, T., Gon, Y., Fujitani, S., Tsuchida, T., Yoshida, T., Kagaya, T., Kita, T., Sakagami, S., Kimizuka, Y., Kawana, A., Nakamura, Y., Ishikura, H., Takata, T., Kikuchi, T., Taniyama, D., Nakamura, M., Kodama, N., Kaneyama, Y., Maeda, S., Nagasaki, Y., Okamoto, M., Ishihara, Sayoko, Ito, A., Chihara, Y., Takeuchi, M., Onoi, K., Hashimoto, N., Wakahara, K., Ando, A., Masuda, M., Wakabayashi, A., Watanabe, H., Sageshima, H., Nakada, T.-A., Abe, R., Shimada, T., Kawamura, K., Ichikado, K., Nishiyama, Kenta, Yamasaki, M., Hashimoto, S., Kusaka, Y., Ohba, T., Isogai, S., Takada, M., Kanda, H., Komase, Y., Sano, F., Asano, K., Oguma, T., Harada, M., Takahashi, T., Shibusawa, T., Abe, S., Kono, Y., Togashi, Y., Izumo, T., Inomata, M., Awano, N., Ogawa, Shinichi, Ogata, T., Ishihara, Shoichiro, Kanehiro, A., Ozaki, S., Fuchimoto, Y., Kitagawa, Yuichiro, Yoshida, Shozo, Ogura, S., Nishiyama, Kei, Yoshida, K., Beppu, S., Fukuyama, S., Eriguchi, Y., Yonekawa, A., Inoue, Y., Yamagata, K., Chiba, S., Narumoto, O., Nagai, H., Ooshima, N., Motegi, M., Sagara, H., Tanaka, A., Ohta, S., Shibata, Y., Tanino, Y., Sato, Y., Yamada, Y., Hashino, T., Shinoki, M., Iwagoe, H., Imamura, T., Umeda, A., Shimada, H., Endo, M., Hayashi, S., Takahashi, Mai, Nakano, S., Yatomi, M., Maeno, T., Ishii, T., Utsugi, M., Ono, A., Kanaoka, K., Ihara, S., Komuta, K., Lifelines, Analysis team leader, Franke, L., Data collection leader, Boezen, M., Analysis team members, Claringbould, A., Lopera, E., Warmerdam, R., Vonk, Judith.M., van Blokland, I., Data collection members, Lanting, P., Ori, A.P.S., Lung eQTL Consortium, Data collection members, Obeidat, M., Hernández Cordero, A.I., Sin, D.D., Bossé, Y., Joubert, P., Hao, K., Nickle, D., Timens, W., van den Berge, M., Mass General Brigham-Host Vulnerability to COVID-19, Analysis team leaders, Feng, Y.-C.A., Mercader, J., Data collection leaders, Weiss, S.T., Karlson, E.W., Smoller, J.W., Murphy, S.N., Meigs, J.B., Woolley, A.E., Admin team leader, Green, R.C., Data collection member, Perez, E.F., Michigan Genomics Initiative (MGI), Analysis team leader, Wolford, B., Admin team leader, Zöllner, S., Analysis team members, Wang, J., Beck, A., Mount Sinai Health System COVID-19 Genomics Initiative, Analysis team leader, Sloofman, L.G., Data collection leaders, Ascolillo, S., Sebra, R.P., Collins, B.L., Levy, T., Admin team leaders, Sealfon, S.C., Analysis team members, Jordan, D.M., Thompson, R.C., Gettler, K., Chaudhary, K., Belbin, G.M., Preuss, M., Hoggart, C., Choi, S., Underwood, S.J., Data collection members, Salib, I., Britvan, B., Keller, K., Tang, L., Peruggia, M., Hiester, L.L., Niblo, K., Aksentijevich, A., Labkowsky, A., Karp, A., Zlatopolsky, M., Zyndorf, M., Admin team members, Charney, A.W., Beckmann, N.D., Schadt, E.E., Abul-Husn, N.S., Cho, J.H., Itan, Y., Kenny, E.E., Loos, R.J.F., Nadkarni, G.N., Do, R., O’Reilly, P., Huckins, L.M., MyCode Health Initiative, Analysis team leaders, Ferreira, M.A.R., Abecasis, G.R., Data collection leaders, Leader, J.B., Cantor, M.N., Admin team leaders, Justice, A.E., Carey, D.J., Analysis team members, Chittoor, G., Josyula, N.S., Kosmicki, J.A., Horowitz, J.E., Baras, A., Data collection members, Gass, M.C., Yadav, A., Admin team member, Mirshahi, T., Netherlands Twin Register, Analysis team leader, Jan Hottenga, J., Data collection leader, Bartels, M., Admin team leader, de Geus, E.J.C., Analysis team member, Nivard, M.G., Penn Medicine Biobank, Analysis team leaders, Verma, A., Ritchie, M.D., Admin team leader, Rader, D., Analysis team members, Li, B., Verma, S.S., Lucas, A., Bradford, Y., Population controls, Analysis team leader, Zara, F., Analysis team members, Salpietro, V., Scala, M., Iacomino, M., Scudieri, P., Bocciardi, R., Data collection members, Minetti, C., Riva, Antonella, Vari, M.S., Rahier, J.-F., Giorgio, E., Carli, D., Data collection leaders, Louis, E., Bulik, C.M., Landén, M., Brusco, A., Ferrero, G.B., Admin team leaders, Madia, F., Fundín, B., Qatar Genome Program, Analysis team leader, Data collection leader, Ismail, S.I., Analysis team members, Saad, C., Al-Sarraj, Y., Data collection members, Badji, R.M., Al-Muftah, W., Al Thani, A., Afifi, N., Study of the COVID-19 host genetics in the population of Latvia, Analysis team leader, Klovins, J., Data collection leader, Rovite, V., Analysis team members, Rescenko, R., Peculis, R., Data collection member, Ustinova, M., The genetic predisposition to severe COVID-19, Analysis team leader, Data collection leader, Zeberg, H., Analysis team members, Data collection members, Frithiof, R., Hultström, M., Lipcsey, M., UCLA Precision Health COVID-19 Host Genomics Biobank, Analysis team leader, Johnson, Ruth, Data collection leader, UCLA Health ATLAS & Data Mart Working Group*, UCLA Health ATLAS & Data Mart Working Group, Geschwind, D.H., Admin team leaders, Freimer, N., Butte, M.J., Geschwind, D.H., Pasaniuc, B., Analysis team members, Ding, Y., Chiu, A., Chang, T.S., Boutros, P., UK 100,000 Genomes Project (Genomics England), Analysis team leader, Moutsianas, L., Data collection leaders, Caulfield, M.J., Scott, R.H., Analysis team members, Walker, Susan, Stuckey, A., Odhams, C.A., Rhodes, D., Data collection members, Fowler, T., Rendon, A., Chan, G., Arumugam, P., UK Biobank, Analysis team leaders, Karczewski, K.J., Wilson, D.J., Spencer, C.A., Data collection leaders, Crook, D.W., Wyllie, D.H., O’Connell, A.M., Admin team leader, Analysis team members, Atkinson, E.G., Kanai, M., Tsuo, K., Baya, N., Turley, P., Gupta, R., Walters, R.K., Palmer, D.S., Sarma, G., Solomonson, M., Cheng, N., Lu, W., Churchhouse, C., Goldstein, J.I., King, D., Seed, C., Daly, M.J., Neale,B.M., Bryant, S., Satterstrom, F.K., Band, G., Earle, S.G., Lin, S.-K., Arning, N., Data collection members, Armstrong, J., Rudkin, J.K., Admin team members, Callier, S., Bryant, S., Cusick, C., UK Blood Donors Cohort, Analysis team leaders, Soranzo, N., Zhao, J.H., Data collection leaders, Danesh, J., Di Angelantonio, E., Analysis team member, Butterworth, A.S., VA Million Veteran Program (MVP), Analysis team leaders, Sun, Y.V., Huffman, J.E., Data collection leader, Cho, K., Admin team leaders, O’Donnell, C.J., Tsao, P., Gaziano, J.M., Analysis team member, Peloso, G., Data collection member, Ho, Y.-L., Val Gardena, Analysis team leader, Data collection leader, Mian, M., Data collection member, Scaggiante, F., Admin team members, CHOP_CAG, Chang, X., Glessner, J.R., Hakonarson, H., GenOMICC/ISARIC4C, Data collection leaders, McGuigan, P.J., Prockter Moore, L.S., Vizcaychipi, M.P., Hall, K., Campbell, A., Nichol, Ailstair, Ward, G., Page, V.J., Semple, M.G., Adeniji, K., Agranoff, D., Agwuh, K., Ail, D., Aldera, E.L., Alegria, A., Angus, B., Ashish, A., Atkinson, D., Bari, S., Barlow, G., Barnass, S., Barrett, N., Bassford, C., Basude, S., Baxter, D., Beadsworth, M., Bernatoniene, J., Berridge, J., Best, N., Bothma, P., Chadwick, D., Brittain-Long, R., Bulteel, N., Burden, T., Burtenshaw, A., Caruth, V., Chambler, D., Chee, N., Child, J., Chukkambotla, S., Clark, T., Collini, P., Cosgrove, C., Cupitt, J., Cutino-Moguel, M.-T., Dark, P., Dawson, C., Dervisevic, S., Donnison, P., Douthwaite, S., Drummond, A., DuRand, I., Dushianthan, A., Dyer, T., Evans, C., Eziefula, C., Fegan, C., Finn, A., Fullerton, D., Garg, S., Garg, A., Gkrania-Klotsas, E., Godden, J., Goldsmith, A., Graham, C., Hardy, E., Hartshorn, S., Harvey, D., Havalda, P., Hawcutt, D.B., Hobrok, M., Hodgson, L., Hormis, A., Jacobs, M., Jain, S., Jennings, P., Kaliappan, A., Kasipandian, V., Kegg, S., Kelsey, M., Kendall, J., Kerrison, C., Kerslake, I., Koch, O., Koduri, G., Koshy, G., Laha, S., Laird, S., Larkin, S., Leiner, T., Lillie, P., Limb, J., Linnett, V., Little, J., Lyttle, M., MacMahon, M., MacNaughton, E., Mankregod, R., Masson, H., Matovu, E., McCullough, K., McEwen, R., Meda, M., Mills, G.H., Minton, J., Ward, K., Mirfenderesky, M., Mohandas, K., Mok, Q., Moon, J., Moore, E., Morgan, P., Morris, C., Mortimore, K., Moses, S., Mpenge, M., Mulla, R., Murphy, M., Nagel, M., Nagarajan, T., Nelson, M., O’Shea, M.K., Otahal, I., Ostermann, M., Pais, M., Panchatsharam, S., Papakonstantinou, D., Paraiso, H., Patel, Brij, Pattison, N., Pepperell, J., Peters, M., Phull, M., Pintus, S., Pooni, J.S., Post, F., Price, D., Prout, R., Rae, N., Reschreiter, H., Reynolds, T., Richardson, N., Roberts, M., Roberts, D., Rose, Alistair, Rousseau, G., Ryan, B., Saluja, T., Shah, A., Shanmuga, P., Sharma, A., Shawcross, A., Sizer, J., Shankar-Hari, M., Smith, R., Snelson, C., Spittle, N., Staines, N., Stambach, T., Stewart, R., Subudhi, P., Szakmany, T., Tatham, K., Thomas, Jo, Thompson, Chris, Thompson, Robert, Tridente, A., Tupper-Carey, D., Twagira, M., Ustianowski, A., Vallotton, N., Vincent-Smith, L., Visuvanathan, S., Vuylsteke, Alan, Waddy, S., Wake, R., Walden, A., Welters, I., Whitehouse, T., Whittaker, P., Whittington, A., Papineni, P., Wijesinghe, M., Williams, Martin, Wilson, L., Cole, Sarah, Winchester, S., Wiselka, M., Wolverson, A., Wooton, D.G., Workman, A., Yates, B., Young, P., Analysis team members, Beale, R., Bretherick, A.D., Clohisey, S., Fourman, M.H., Furniss, J., Gountouna, E., Grimes, G., Haley, C., Harrison, D., Hayward, C., Keating, Sean, Klaric, L., Klenerman, P., Law, Andy, Meynert, A.M., Millar, J., Pairo-Castineira, E., Parkinson, N., Ponting, C.P., Porteous, D.J., Rawlik, K., Richmond, A., Rowan, K., Russell, C.D., Scott, R.H., Shen, X., Shih, B., Tenesa, A., Vitart, V., Wang, B., Wilson, J.F., Wu, Y., Yang, J., Yang, Z., Zechner, M., Zhai, R., Zheng, C., Norman, L., Pius, R., Drake, T.M., Fairfield, C.J., Knight, S.R., Mclean, K.A., Murphy, D., Shaw, C.A., Dalton, J., Girvan, M., Saviciute, E., Roberts, S., Harrison, J., Marsh, L., Connor, M., Halpin, S., Jackson, C., Gamble, C., Leeming, G., Law, Andrew, Wham, M., Hendry, R., Scott-Brown, J., Data collection members, Begg, C., Hinds, C., Wai Ho, A.Y., Horby, P.W., Knight, J., Ling, L., Maslove, D., McAuley, D., Montgomery, H., Nichol, Alistair, Openshaw, P.J.M., Semple, M.G., Shankar-Hari, M., Summers, C., Walsh, T., Armstrong, L., Bates, H., Dooks, E., Farquhar, F., Hairsine, B., McParland, C., Packham, S., Alldis, Z., Astin-Chamberlain, R., Bibi, F., Biddle, J., Blow, S., Bolton, M., Borra, C., Bowles, R., Burton, M., Choudhury, Y., Collier, David, Cox, A., Easthope, A., Ebano, P., Fotiadis, S., Gurasashvili, J., Halls, R., Hartridge, P., Kallon, D., Kassam, J., Lancoma-Malcolm, I., Matharu, M., May, P., Mitchelmore, O., Newman, T., Patel, M., Pheby, J., Pinzuti, I., Prime, Z., Prysyazhna, O., Shiel, J., Taylor, Melanie, Tierney, C., Wood, S., Zak, A., Zongo, O., Forsey, M., Kaliappan, A., Nicholson, Anne, Riches, J., Vertue, M., Wasson, C., Finn, S., Green, J., Collins, Erin, King, B., Grauslyte, L., Hussain, M., Phull, M., Pogreban, T., Rosaroso, L., Salciute, E., Franke, G., Wong, J., George, A., Akeroyd, L., Bano, S., Bromley, M., Gurr, L., Lawton, T., Morgan, J., Sellick, K., Warren, D., Wilkinson, B., McGowan, J., Ledgard, C., Stacey, A., Pye, K., Bellwood, R., Bentley, M., Hobrok, M., Loosley, R., McGuinness, H., Tench, H., Wolf-Roberts, R., Gibson, S., Lyle, A., McNeela, F., Radhakrishnan, J., Hughes, A., Ali, A., Brady, M., Dale, S., Dance, A., Gledhill, L., Greig, J., Hanson, K., Holdroyd, K., Home, M., Kelly, D., Kitson, R., Matapure, L., Melia, D., Mellor, S., Nortcliffe, T., Pinnell, J., Robinson, M., Shaw, L., Shaw, R., Thomis, L., Wilson, A., Wood, T., Bayo, L.-A., Merwaha, E., Ishaq, T., Hanley, S., Antcliffe, D., Banach, D., Brett, S., Coghlan, P., Fernandez, Z., Gordon, A., Rojo, R., Arias, S.S., Templeton, M., Jha, R., Krishnamurthy, V., Lim, Lai, Bi, R., Scholefield, B., Ashton, L., Williams, Alison, Cheyne, C., Saunderson, A., Allan, A., Anderson, F., Kaye, C., Liew, J., Medhora, J., Scott, T., Trumper, E., Botello, A., Polgarova, P., Stroud, K., Meaney, E., Jones, M., Ng, A., Agrawal, S., Pathan, N., White, D., Daubney, E., Elston, K., Parker, R., Reddy, A., Turner-Bone, I., Wilding, L., Harding, P., Jacob, R., Jones, C., Denmade, C., Croft, M., White, I., Lim, Li, Griffin, D., Muchenje, N., Mupudzi, M., Partridge, R., Conyngham, J.-A., Thomas, R., Wright, M., Corral, M.A., Bastion, V., Clarke, D., David, B., Kent, H., Lorusso, R., Lubimbi, G., Murdoch, S., Penacerrada, M., Thomas, Alastair, Valentine, J., Vochin, A., Wulandari, R., Djeugam, B., Dawson, J., Garrioch, S., Tolson, M., Aldridge, J., de Almeida Martins, L.G., Carungcong, J., Beavis, S., Dale, K., Gascoyne, R., Hawes, J., Pritchard, K., Stevenson, L., Whileman, A., Cowley, A., Highgate, J., Crawley, R., Crew, A., Cunningham, M., Daniels, A., Harrison, L., Hope, S., Inweregbu, K., Jones, S., Lancaster, N., Matthews, J., Nicholson, Alice, Wray, G., Benham, L., Bradshaw, Z., Brown, J., Caswell, M., Cupitt, J., Melling, S., Preston, S., Slawson, N., Stoddard, E., Warden, S., Combes, E., Joefield, T., Monnery, S., Beech, V., Trotman, S., Hopkins, B., Scriven, J., Thrasyvoulou, L., Willis, H., Anderson, Susan, Birch, Janine, Collins, Emma, Hammerton, K., O’Leary, R., Abernathy, C., Foster, L., Gratrix, A., Martinson, V., Parkinson, P., Stones, E., Carbral-Ortega, L., Kapoor, R., Loader, D., Castle, K., Brandwood, C., Smith, L., Clark, R., Birchall, Katie, Kolakaluri, L., Baines, D., Sukumaran, A., Mapfunde, I., Meredith, M., Morris, L., Ryan, L., Clark, A., Sampson, J., Peters, C., Dent, M., Langley, M., Ashraf, Saima, Wei, S., Andrew, A., Chablani, M., Kirkby, A., Netherton, K., Bates, M., Dasgin, J., Gill, J., Nilsson, A., Scriven, J., Apetri, E., Basikolo, C., Blackledge, B., Catlow, L., Charles, B., Dark, P., Doonan, R., Harris, J., Harvey, A., Horner, D., Knowles, K., Lee, Stephanie, Lomas, D., Lyons, C., Marsden, T., McLaughlan, D., McMorrow, L., Pendlebury, J., Perez, J., Poulaka, M., Proudfoot, N., Slaughter, M., Slevin, K., Taylor, Melanie, Thomas, V., Walker, D., Michael, A., Collis, M., Clark, Martyn, Coulding, M., Jude, E., McCormick, J., Mercer, O., Potla, D., Rehman, H., Savill, H., Turner, V., Davey, M., Golden, D., Seaman, R., Hunt, Jodie, Dearden, J., Dobson, E., Mulcahy, M., Munt, S., O’Connor, G., Philbin, J., Rishton, C., Tully, R., Winnard, S., Cagova, L., Fofano, A., Garner, L., Holcombe, H., Mepham, S., Mitchell, A.M., Mwaura, L., Praman, K., Vuylsteke, Alain, Zamikula, J., Bercades, G., Brealey, D., Hass, I., MacCallum, N., Martir, G., Raith, E., Reyes, A., Smyth, D., Taylor, A., Hughes, R.A., Thomas, H., Rees, A., Duskova, M., Phipps, J., Brooks, S., Edwards, M., Alexander, P., Allen, S., Bradley-Potts, J., Brantwood, C., Egan, J., Felton, T., Padden, G., Ward, L., Moss, S., Glasgow, S., Beesley, K., Board, S., Kubisz-Pudelko, A., Lewis, A., Perry, J., Pippard, L., Wood, D., Buckley, C., Brown, Alison, Gregory, J., O’Connell, S., Smith, T., Belagodu, Z., Fuller, B., Gherman, A., Olufuwa, O., Paramsothy, R., Stuart, C., Oakley, N., Kamundi, C., Tyl, D., Collins, K., Silva, P., Taylor, J., King, L., Coates, C., Crowley, M., Wakefield, P., Beadle, J., Johnson, L., Sargeant, J., Anderson, M., Jardine, C., Williams, D., Parris, V., Quaid, S., Watson, E., Melville, J., Naisbitt, J., Joseph, R., Lazo, M., Walton, O., Neal, A., Hill, M., Kannan, T., Wild, L., Allan, E., Darlington, K., Davies, F., Easton, J., Kumar, S., Lean, R., Menzies, D., Pugh, R., Qiu, X., Davies, L., Williams, H., Scanlon, J., Davies, G., Mackay, C., Lewis, J., Rees, S., Coetzee, S., Gales, A., Otahal, I., Raj, M., Sell, C., Langton, H., Prout, R., Watters, M., Novis, C., Arbane, G., Bociek, A., Campos, S., Grau, N., Jones, T.O., Lim, R., Marotti, M., Ostermann, M., Shankar-Hari, M., Whitton, C., Barron,A., Collins, C., Kaul, S., Passmore, H., Prendergast, C., Reed, A., Rogers, P., Shokkar, R., Woodruff, M., Middleton, H., Polgar, O., Nolan, C., Thwaites, V., Mahay, K., Sri-Chandana, C., Scherewode, J., Stephenson, L., Marsh, S., Bancroft, H., Bellamy, M., Carmody, M., Daglish, J., Moore, F., Rhodes, J., Sangombe, M., Kadiri, S., Scriven, J., Ayers, A., Harrison, W., North, J., Cavazza, A., Cockrell, M., Corcoran, E., Depante, M., Finney, C., Jerome, E., McPhail, M., Nayak, M., Noble, H., O’Reilly, K., Pappa, E., Saha, Rohit, Saha, S., Smith, John, Knighton, A., Gill, M., Paul, P., Ratnam, V., Shelton, S., Wynter, I., Baptista, D., Crowe, R., Fernandes, R., Herdman-Grant, R., Joseph, A., Loveridge, A., McKenley, I., Morino, E., Naranjo, A., Simms, R., Sollesta, K., Swain, A., Venkatesh, H., Khera, J., Fox, J., Barber, R., Hewitt, C., Hilldrith, A., Jackson-Lawrence, K., Shepardson, S., Wills, M., Butler, S., Tavares, S., Cunningham, A., Hindale, J., Arif, S., George, L., Twiss, S., Wright, D., Holland, M., Keenan, N., Lyons, M., Wassall, H., Marsh, C., Mahenthran, M., Carter, E., Kong, T., Adanini, O., Bhatia, N., Msiska, M., Mew, L., Mwaura, E., Stewart, R., Williams, F., Wren, L., Sutherland, S.-B., Battle, C., Brinkworth, E., Harford, R., Murphy, C., Newey, L., Rees, T., Williams, Marie, Arnold, S., Brealey, D., Hardy, J., Houlden, H., Moncur, E., Raith, E., Tariq, A., Tucci, A., Convery, K., Fottrell-Gould, D., Hudig, L., Keshet-Price, J., Randell, G., Stammers, K., Abdelrazik, M., Bakthavatsalam, D., Elhassan, M., Ganesan, A., Haldeos, A., Moreno-Cuesta, J., Purohit, D., Vincent, R., Xavier, K., Rohit, K., Alasdair, F., Saleem, M., David, C., Jenkins, Samuel, Lamond, Z., Wall, A., Yates, B., Reynolds, J., Campbell, H., Thompsom, M., Dodds, S., Duffy, S., Butcher, D., O’Sullivan, S., Butterworth-Cowin, N., Deacon, B., Hibbert, M., Pothecary, C., Tetla, D., Woodford, C., Durga, L., Kennard-Holden, G., de Gordoa, L.O.-R., Peasgood, E., Phillips, C., Skinner, D., Gaylard, J., Mullan, D., Newman, J., Davies, E., Roche, L., Sathe, S., Brimfield, L., Daly, Z., Pogson, D., Rose, S., Collins, A., Khaliq, W., Gude, E.T., Allen, L., Beranova, E., Crisp, N., Deery, J., Hazelton, T., Knight, A., Price, C., Tilbey, S., Turki, S., Turney, S., Giles, J., Booth, S., Bell, G., English, K., Katary, A., Wilcox, L., Campbell, R., Clarke, N., Whiteside, J., Mascarenhas, M., Donaldson, A., Matheson, J., Barrett, F., O’Hara, M., O’Keefe, L., Bradley, C., Collier, Dawn, Hormis, A., Walker, R., Maynard, V., Patel, T., Smith, M., Chukkambotla, S., Kazi, A., Hartley, J., Dykes, J., Hijazi, M., Keith, S., Khan, M., Ryan-Smith, J., Springle, P., Thomas, Jacqueline, Truman, N., Saad, S., Coleman, D., Fine, C., Matt, R., Gay, B., Dalziel, J., Ali, S., Goodchild, D., Harling, R., Bhatterjee, R., Goddard, W., Davison, C., Duberly, S., Hargreaves, J., Bolton, R., Laha, S., Verlander, M., Williams, Alexandra, Blackman, H., Creagh-Brown, B., Donlon, S., Michalak-Glinska, N., Mtuwa, S., Pristopan, V., Salberg, A., Smith, E., Stone, S., Piercy, C., Verula, J., Burda, D., Montaser, R., Harden, L., Mayangao, I., Marriott, C., Bradley, P., Harris, C., Cooper, J., Finch, C., Liderth, S., Quinn, A., Waddington, N., Fidler, K., Tagliavini, E., Donnelly, K., Abel, L., Brett, M., Digby, B., Gemmell, L., Hornsby, J., MacGoey, P., O’Neil, P., Price, R., Rodden, N., Rooney, K., Sundaram, R., Thomson, N., Flanagan, R., Hughes, G., Latham, S., McKenna, E., Anderson, J., Hull, R., Rhead, K., Branney, D., Frankham, J., Pitts, S., White, N., Cristiano, D., Dormand, N., Farzad, Z., Gummadi, M., Liyanage, K., Patel, B.V., Salmi, S., Sloane, G., Thwaites, V., Varghese, M., Zborowski, A.C., Bean, S., Burt, K., Spivey, M., Eastgate-Jackson, C., Filipe, H., Martin, D., Maharajh, A., Garcia, S.M., De Neef, M., Deacon, B., Lynch, C., Pothecary, C., Roche, L., Howe, G.S., Singh, J., Turner, K., Ellis, H., Stroud, N., Cherian, S., Cutler, S., Heron, A.E., Roynon-Reed, A., Szakmany, T., Williams, G., Richards, O., Cheema, Y., Ahmad, N., Barker, J., Bauchmuller, K., Bird, S., Cawthron, K., Harrington, K., Jackson, Y., Kibutu, F., Lenagh, B., Masuko, S., Mills, G.H., Raithatha, A., Wiles, M., Willson, J., Newell, H., Lye, A., Nwafor, L., Jarman, C., Rowland-Jones, S., Foote, D., Cole, Joby, Thompson, Roger, Watson, J., Hesseldon, L., Macharia, I., Chetam, L., Smith, Jacqui, Ford, A., Anderson, Samantha, Birchall, Kathryn, Housley, K., Walker, Sara, Milner, L., Hanratty, H., Trower, H., Phillips, P., Oxspring, S., Donne, B., Bevan, E., Martin, J., Trodd, D., Watson, G., Brown, C.W., Bunni, L., Jennings, C., Latif, M., Marshall, R., Subramanian, G., Bandla, N., Gellamucho, M., Davies, M., Thompson, Christopher, Trim, F., Eapen, B., Ahmed, C., Baines, B., Clamp, S., Colley, J., Haq, R., Hayes, A., Hulme, J., Hussain, Samia, Joseph, S., Kumar, R., Maqsood, Z., Purewal, M., Chandler, B., Elliott, K., Mallinson, J., Turnbull, A., Dent, K., Horsley, E., Akhtar, M.N., Pearson, S., Potoczna, D., Spencer, S., Blakemore, H., Borislavova, B., Faulkner, B., Gendall, E., Goff, E., Hayes, K., Thomas, M., Worner, R., Smith, K., Stephens, D., Delgado, C.C., Dawson, D., Ding, L., Durrant, G., Ezeobu, O., Farnell-Ward, S., Harrison, Abiola, Kanu, R., Leaver, S., Maccacari, E., Manna, S., Saluzzio, R.P., Queiroz, J., Samakomva, T., Sicat, C., Texeira, J., Da Gloria, E.F., Lisboa, A., Rawlins, J., Mathew, J., Kinch, A., Hurt, W.J., Shah, N., Clark, V., Thanasi, M., Yun, N., Patel, K., Crickmore, V., Debreceni, G., Wilkins, J., Nicol, L., Burn, I., Hambrook, G., Manso, K., Penn, R., Shanmugasundaram, P., Tebbutt, J., Thornton, D., Rostron, A., Roy, A., Woods, L., Cornell, S., Wakinshaw, F., Rogerson, K., Jarmain, J., Anderson, P., Archer, K., Austin, K., Davis, Caroline, Durie, A., Kelsall, O., Thrush, J., Vigurs, C., Wild, L., Wood, H.-L., Tranter, H., Harrison, Alison, Cowley, N., McAlindon, M., Burtenshaw, A., Digby, S., Low, E., Morgan, A., Cother, N., Rankin, T., Clayton, S., McCurdy, A., Allibone, S., Mary-Genetu, R., Kasipandian, V., Patel, A., Mac, A., Murphy, A., Mahjoob, P., Nazari, R., Worsley, L., Fagan, A., Mohamed Ali, I.A., Beaumont, K., Blunt, M., Coton, Z., Curgenven, H., Elsaadany, M., Fernandes, K., Ally, S.M., Rangarajan, H., Sarathy, V., Selvanayagam, S., Vedage, D., White, M., Fernandez-Roman, J., Hamilton, D.O., Johnson, E., Johnston, B., Martinez, M.L., Mulla, S., Shaw, D., Waite, A.A.C., Waugh, V., Welters, I.D., Williams, K., Bemand, T., Black, E., Rosa, A.D., Howle, R., Jhanji, S., Baikady, R.R., Tatham, K.C., Thomas, B., Halkes, M., Mercer, P., Thornton, L., West, J., Baird, T., Ruddy, J., Reece-Anthony, R., Birt, M., Cowton, A., Kay, A., Kent, M., Potts, K., Wilkinson, A., Naylor, S., Brown, E., Clark, Michele, Purvis, S., Cole, Jade, Davies, M., Davies, R., Duffin, D., Hill, H., Player, B., Thomas, E., Williams, Angharad, Beith, C.M., Black, K., Clements, S., Morrison, A., Strachan, D., Taylor, Margaret, Clarkson, M., D’Sylva, S., Norman, K., Coventry, T., Fowler, S., MacMahon, M., McGregor, Amanda, Brady, A., Chan, R., Little, J., McIvor, S., Prady, H., Whittle, H., Mathew, B., Clapham, M., Harper, R., Poultney, U., Rice, P., Smith, T., Mutch, R., Baird, Y., Butler, A., Chadbourn, I., Folkes, L., Fox, H., Gardner, A., Gomez, R., Hobden, G., Hodgson, L., King, Kirsten, Margarson, M., Martindale, T., Meadows, E., Raynard, D., Thirlwall, Y., Helm, D., Margalef, J., Greer, S., Shuker, K., Tridente, A., Smuts, S., Duffield, J., Smith, O., Mallon, L., Claire, W., Birkinshaw, I., Carter, J., Howard, K., Ingham, J., Joy, R., Pearson, H., Roche, S., Scott, Z., Knights, E., Price, A., Thomas, Alice, Thorpe, C., Abraheem, A., Bamford, P., Cawley, K., Dunmore, C., Faulkner, M., Girach, R., Jeffrey, H., Jones, R., London, E., Nagra, I., Nasir, F., Sainsbury, H., Smedley, C., Khade, R., Sundar, A., Tsinaslanidis, G., Behan, T., Burnett, C., Hatton, J., Heeney, E., Mitra, A., Newton, M., Pollard, R., Stead, R., Birch, Jenny, Bough, L., Goodsell, J., Tutton, R., Williams, P., Williams, S., Winter-Goodwin, B., Auld, F., Donnachie, J., Edmond, I., Prentice, L., Runciman, N., Salutous, D., Symon, L., Todd, A., Turner, P., Short, A., Sweeney, L., Murdoch, E., Senaratne, D., Burns, K., Higham, A., Anderson, T., Hawcutt, D., O’Malley, L., Rad, L., Rogers, N., Saunderson, P., Allison, K.S., Afolabi, D., Whitbread, J., Jones, D., Dore, R., Lankester, L., Nikitas, N., Wells, C., Stowe, B., Spencer, K., Cathcart, S., Duffy, K., Puxty, A., Puxty, K., Turner, L., Ireland, J., Semple, G., Barry, P., Hilltout, P., Evitts, J., Tyler, A., Waldron, J., Irvine, V., Shelley, B., Akinkugbe, O., Bamford, A., Beech, E., Belfield, H., Bell, M., Davies, C., Jones, G.A.L., McHugh, T., Meghari, H., O’Neill, L., Peters, M.J., Ray, S., Tomas, A.L., Easthope, A., Gorman, C., Gupta, A., Timlick, E., Brady, R., Bonner, S., Hugill, K., Jones, Jessica, Liggett, S., Bashyal, A., Davidson, N., Hutton, P., McKechnie, S., Wilson, J., Flint, N., Rekha, P., Hales, D., Cruz, C., Pattison, N., Gopal, S., Harris, N., Lake, V., Metherell, S., Radford, E., Clement, I., Patel, Bijal, Gulati, A., Hays, C., Webster, K., Hudson, A., Webster, A., Stephenson, E., McCormack, L., Slater, V., Nixon, R., Hanson, H., Fearby, M., Kelly, S., Bridgett, V., Robinson, P., Almaden-Boyle, C., Austin, P., Cabrelli, L., Cole, Stephen, Casey, M., Chapman, S., Whyte, C., Brayne, A., Fisher, E., Hunt, Jane, Jackson, P., Kaye, D., Love, N., Parkin, J., Tuckey, V., van Koutrik, L., Carter, S., Andrew, B., Findlay, L., Adams, K., Bruce, M., Connolly, K., Duncan, T., T.-Michael, H., Lindergard, G., Hey, S., Fox, C., Alfonso, J., Durrans, L.J., Guerin, J., Blackledge, B., Harris, J., Hruska, M., Eltayeb, A., Lamb, T., Hodgkiss, T., Cooper, Lisa, Rothwell, J., Dennis, C., McGregor, Alastair, Parris, V., Srikaran, S., Sukha, A., Davies, K., O’Brien, L., Omar, Z., Otahal, I., Perkins, E., Lewis, T., Sutherland, I., Brooke, H., Buckley, S., Suarez,J.C., Charlesworth, R., Hansson, K., Norris, J., Poole, A., Rose, Alastair, Sandhu, R., Sloan, B., Smithson, E., Thirumaran, M., Wagstaff, V., Metcalfe, A., Camsooksai, J., Humphrey, C., Jenkins, Sarah, Reschreiter, H., Wadams, B., DeAth, Y., Adams, C., Agasou, A., Arden, T., Bowes, A., Boyle, P., Beekes, M., Button, H., Capps, N., Carnahan, M., Carter, A., Childs, D., Donaldson, D., Hard, K., Hurford, F., Hussain, Y., Javaid, A., Jones, James, Jose, S., Leigh, M., Martin, T., Millward, H., Motherwell, N., Rikunenko, R., Stickley, J., Summers, J., Ting, L., Tivenan, H., Tonks, L., Wilcox, R., Bokhari, M., Linnett, V., Lucas, R., McCormick, W., Ritzema, J., Sanderson, A., Wild, H., Baxter, N., Henderson, S., Kennedy-Hay, S., McParland, Christopher, Rooney, L., Sim, M., McCreath, G., Brunton, M., Caterson, J., Coles, H., Frise, M., Rai, S.G., Jacques, Nicola, Keating, L., Tilney, E., Bartley, S., Bhuie, P., Downes, C., Holding, K., Riches, K., Hilton, M., Hayman, M., Subramanian, D., Daniel, P., Zitter, L., Benyon, S., Marriott, S., Park, L., Keenan, S., Gordon, E., Quinn, H., Baines, K., Andrew, G., Baillie, J.K., Barclay, L., Callaghan, M., Campbell, R., Clark, S., Hope, D., Marshall, L., McCulloch, C., Briton, K., Singleton, J., Birch, S., Higham, A., Simpson, Kerry, Craig, J., Demetriou, C., Eckbad, C., Hierons, S., Howie, L., Mitchard, S., Ramos, L., Serrano-Ruiz, A., White, K., Kelly, F., Amin, V., Anastasescu, E., Anumakonda, V., Karthik, K., Kausar, R., Reid, K., Smith, Jacqueline, Imeson-Wood, J., Bellini, A., Bryant, J., Mayer, Anton, Pickard, A., Roe, N., Sowter, J., Howlett, A., Criste, K., Cusack, R., Golder, K., Golding, H., Jones, O., Leggett, S., Male, M., Marani, M., Prager, K., Williams, T., Roberts, B., Salmon, K., Gondo, P., Hadebe, B., Kayani, A., Masunda, B., Ahmed, A., Morris, A., Jakkula, S., Long, K., Whiteley, S., Wilby, E., Ogg, B., Moultrie, S., Odam, M., Bewley, J., Garland, Z., Grimmer, L., Gumbrill, B., Johnson, Rebekah, Sweet, K., Webster, D., Efford, G., Bennett, S., Goodwin, E., Jackson, M., Kent, A., Tibke, C., Woodyatt, W., Zaki, A., Daniel, A., Finn, J., Saha, Rajnish, Staines, N., Easthope, A., Bremmer, P., Allan, J., Geary, T., Houston, G., Meikle, A., O’Brien, P., Bell, D., Boyle, R., Douglas, K., Glass, L., Lee, E., Lennon, L., Rattray, A., Charnock, R., McFarland, D., Cosgrove, D., Attwood, B., Parsons, P., Carmody, S., Oblak, M., Popescu, M., Thankachen, M., Baruah, R., Morris, S., Ferguson, S., Shepherd, A., Altabaibeh, A., Alvaro, A., Gilbert, K., Ma, L., Mostoles, L., Parmar, C., Simpson, Kathryn, Jetha, C., Booker, L., Pratley, A., Cosier, T., Millen, G., Richardson, N., Schumacher, N., Weston, H., Rand, J., Alex, B., Bach, B., Barclay, W.S., Bogaert, D., Chand, M., Cooke, G.S., Docherty, A.B., Dunning, J., da Silva Filipe, A., Fletcher, T., Green, C.A., Harrison, E.M., Hiscox, J.A., Ijaz, S., Khoo, S., Klenerman, P., Lim, W.S., Mentzer, A.J., Merson, L., Noursadeghi, M., Moore, S.C., Palmarini, M., Paxton, W.A., Pollakis, G., Price, N., Rambaut, A., Robertson, D.L., Russell, C.D., Sancho-Shimizu, V., Scott, J.T., de Silva, T., Sigfrid, L., Solomon, T., Sriskandan, S., Stuart, D., Tedder, R.S., Thomson, E.C., Roger Thompson, A.A., Thwaites, R.S., Turtle, L.C.W., Gupta, R.K., Palmieri, C., Swann, O.V., Zambon, M., Dumas, M.-E., Griffin, J.L., Takats, Z., Chechi, K., Andrikopoulos, P., Osagie, A., Olanipekun, M., Liggi, S., Lewis, M.R., Correia, G. dos S., Sands, C.J., Takis, P., Maslen, L., Greenhalf, W., Shaw, V., McDonald, S.E., Keating, Seán, Ahmed, K.A., Armstrong, J.A., Ashworth, M., Asiimwe, I.G., Bakshi, S., Barlow, S.L., Booth, L., Brennan, B., Bullock, K., Catterall, B.W.A., Clark, J.J., Clarke, E.A., Cooper, Louise, Cox, H., Davis, Christopher, Dincarslan, O., Dunn, C., Dyer, P., Elliott, A., Evans, A., Finch, L., Fisher, L.W.S., Foster, T., Garcia-Dorival, I., Greenhalf, W., Gunning, P., Hartley, C., Jensen, R.L., Jones, C.B., Jones, T.R., Khandaker, S., King, Katharine, Kiy, R.T., Koukorava, C., Lake, A., Lant, S., Latawiec, D., Lavelle-Langham, L., Lefteri, D., Lett, L., Livoti, L.A., Mancini, M., McDonald, S., McEvoy, L., McLauchlan, J., Metelmann, S., Miah, N.S., Middleton, J., Mitchell, J., Moore, S.C., Murphy, E.G., Penrice-Randal, R., Pilgrim, J., Prince, T., Reynolds, W., Ridley, P.M., Sales, D., Shaw, V.E., Shears, R.K., Small, B., Subramaniam, K.S., Szemiel, A., Taggart, A., Tanianis-Hughes, J., Thomas, Jordan, Trochu, E., van Tonder, L., Wilcock, E., Zhang, J.E., Flaherty, L., Maziere, N., Cass, E., Carracedo, A.D., Carlucci, N., Holmes, A., Massey, H., Murphy, Lee, Wrobel, N., McCafferty, S., Morrice, K., MacLean, A., Admin team members, Armstrong, R., Boz, C., Brown, Adam, Clark, R., Coutts, A., Cullum, L., Day, N., Donnelly, L., Duncan, E., Fawkes, A., Finernan, P., Gilchrist, T., Golightly, A., Hafezi, K., Law, D., Law, R., Law, S., Macgillivray, L., Maclean, A., Mal, H., McCafferty, S., Mcmaster, E., Meikle, J., Moore, S.C., Morrice, K., Murphy, Lee, Oosthuyzen, W., Paterson, T., Stenhouse, A., Swets, M., Szoor-McElhinney, H., Taneski, F., Wackett, T., Ward, M., Weaver, J., Wrobel, N., Coyle, J., Gallagher, B., Lidstone-Scott, R., Hamilton, D., Schon, K., Furlong, A., Biggs, H., Griffiths, F., Andrews, E., Brickell, K., Smyth, M., Murphy, Lorna, Carson, G., Hardwick, H., Donohue, C., COVID-19 HGI corresponding authors, 2021. Mapping the human genetic architecture of COVID-19. Nature 600, 472–477. 10.1038/s41586-021-03767-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- D’Amico S., Tempora P., Lucarini V., Melaiu O., Gaspari S., Algeri M., Fruci D. ERAP1 and ERAP2 enzymes: a protective shield for RAS against COVID-19? IJMS. 2021;22:1705. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darbeheshti F., Mahdiannasser M., Uhal B.D., Ogino S., Gupta S., Rezaei N. Interindividual immunogenic variants: susceptibility to coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus and influenza virus. Rev. Med. Virol. 2021;31 doi: 10.1002/rmv.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Sousa E., Ligeiro D., Lérias J.R., Zhang C., Agrati C., Osman M., El-Kafrawy S.A., Azhar E.I., Ippolito G., Wang F.-S., Zumla A., Maeurer M. Mortality in COVID-19 disease patients: Correlating the association of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) with severe acute respiratory syndrome 2 (SARS-CoV-2) variants. Int. J. Infect. Diseases. 2020;98:454–459. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delanghe, J.R., De Buyzere, M.L., Speeckaert, M.M., 2021. Genetic Polymorphisms in the Host and COVID-19 Infection, in: Rezaei, N. (Ed.), Coronavirus Disease - COVID-19, Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp. 109–118. 10.1007/978-3-030-63761-3_7. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dobrindt K., Hoagland D.A., Seah C., Kassim B., O’Shea C.P., Iskhakova M., Fernando M.B., Deans P.J.M., Powell S.K., Javidfar B., Murphy A., Peter C., Møeller R., Garcia M.F., Kimura M., Iwasawa K., Crary J., Kotton D.N., Takebe T., Huckins L.M., tenOever B.R., Akbarian S., Brennand K.J. Common genetic variation in humans impacts in vitro susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection (preprint) Cell Biol. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.09.20.300574. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebrahimi S., Ghasemi-Basir H.R., Majzoobi M.M., Rasouli-Saravani A., Hajilooi M., Solgi G. HLA-DRB1*04 may predict the severity of disease in a group of Iranian COVID-19 patients. Hum. Immunol. 2021;82:719–725. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2021.07.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fadista J., Kraven L.M., Karjalainen J., Andrews S.J., Geller F., Baillie J.K., Wain L.V., Jenkins R.G., Feenstra B. Shared genetic etiology between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and COVID-19 severity. EBioMed. 2021;65 doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falahi S., Zamanian M.H., Feizollahi P., Rezaiemanesh A., Salari F., Mahmoudi Z., Gorgin Karaji A. Evaluation of the relationship between IL-6 gene single nucleotide polymorphisms and the severity of COVID-19 in an Iranian population. Cytokine. 2022;154 doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2022.155889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallerini, C., Daga, S., Mantovani, S., Benetti, E., Picchiotti, N., Francisci, D., Paciosi, F., Schiaroli, E., Baldassarri, M., Fava, F., Palmieri, M., Ludovisi, S., Castelli, F., Quiros-Roldan, E., Vaghi, M., Rusconi, S., Siano, M., Bandini, M., Spiga, O., Capitani, K., Furini, S., Mari, F., GEN-COVID Multicenter Study, Valentino, F., Doddato, G., Giliberti, A., Tita, R., Amitrano, S., Bruttini, M., Croci, S., Meloni, I., Mencarelli, M.A., Lo Rizzo, C., Pinto, A.M., Di Sarno, L., Beligni, G., Tommasi, A., Iuso, N., Montagnani, F., Fabbiani, M., Rossetti, B., Zanelli, G., Bargagli, E., Bergantini, L., D’Alessandro, M., Cameli, P., Bennett, D., Anedda, F., Marcantonio, S., Scolletta, S., Franchi, F., Mazzei, M.A., Guerrini, S., Conticini, E., Cantarini, L., Frediani, B., Tacconi, D., Spertilli, C., Feri, M., Donati, A., Scala, R., Guidelli, L., Spargi, G., Corridi, M., Nencioni, C., Croci, L., Caldarelli, G.P., Spagnesi, M., Romani, D., Piacentini, P., Desanctis, E., Cappelli, S., Canaccini, A., Verzuri, A., Anemoli, V., Ognibene, A., Monforte, A.D., Miraglia, F.G., Girardis, M., Venturelli, S., Busani, S., Cossarizza, A., Antinori, A., Vergori, A., Emiliozzi, A., Gabrieli, A., Riva, A., Scotton, P.G., Andretta, F., Panese, S., Scaggiante, R., Gatti, F., Parisi, S.G., Baratti, S., Antoni, M.D., Monica, M.D., Piscopo, C., Capasso, M., Russo, R., Andolfo, I., Iolascon, A., Fiorentino, G., Carella, M., Castori, M., Merla, G., Squeo, G.M., Aucella, F., Raggi, P., Marciano, C., Perna, R., Bassetti, M., Di Biagio, A., Sanguinetti, M., Masucci, L., Valente, S., Mandalà, M., Giorli, A., Salerni, L., Zucchi, P., Parravicini, P., Menatti, E., Trotta, T., Giannattasio, F., Coiro, G., Lena, F., Coviello, D.A., Mussini, C., Bosio, G., Martinelli, E., Mancarella, S., Tavecchia, L., Gori, M., Crotti, L., Parati, G., Gabbi, C., Zanella, I., Rizzi, M., Maggiolo, F., Ripamonti, D., Bachetti, T., La Rovere, M.T., Sarzi-Braga, S., Bussotti, M., Chiariello, M., Belli, M.A., Dei, S., Renieri, A., Mondelli, M.U., Frullanti, E., 2021. Association of Toll-like receptor 7 variants with life-threatening COVID-19 disease in males: findings from a nested case-control study. eLife 10, e67569. 10.7554/eLife.67569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Fernandez C., Rysä J., Almgren P., Nilsson J., Engström G., Orho-Melander M., Ruskoaho H., Melander O. Plasma levels of the proprotein convertase furin and incidence of diabetes and mortality. J. Intern. Med. 2018;284:377–387. doi: 10.1111/joim.12783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira Caceres, M.M., Sosa, J.P., Lawrence, J.A., Sestacovschi, C., Tidd-Johnson, A., Rasool, M.H.U., Gadamidi, V.K., Ozair, S., Pandav, K., Cuevas-Lou, C., Parrish, M., Rodriguez, I., Fernandez, J.P., Division of Research & Academic Affairs, Larkin Community Hospital, South Miami, Florida, USA, Department of Medicine, American University of Antigua, Coolidge, Antigua, Family Medicine, Larkin Community Hospital Palm Springs Campus, Hialeah, Florida, USA, Family Medicine, Larkin Community Hospital South Campus, Miami, Florida, USA, Pulmonary Disease and Critical Care Medicine, Larkin Community Hospital Palm Springs Campus, Hilaeah, Florida, USA, 2022. The impact of misinformation on the COVID-19 pandemic. AIMSPH 9, 262–277. 10.3934/publichealth.2022018.
- Giammaria D., Pajewski A. Can early treatment of patients with risk factors contribute to managing the COVID-19 pandemic? J. Global Health. 2020;10 doi: 10.7189/jogh.10.010377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glotov O.S., Chernov A.N., Scherbak S.G., Baranov V.S. Genetic risk factors for the development of COVID-19 coronavirus infection. Russ. J. Genet. 2021;57:878–892. doi: 10.1134/S1022795421080056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Go C.C., Pandav K., Sanchez-Gonzalez M.A., Ferrer G. Potential role of xylitol plus grapefruit seed extract nasal spray solution in COVID-19: case series. Cureus. 2020 doi: 10.7759/cureus.11315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goel, R., Bloch, E.M., Pirenne, F., Al‐Riyami, A.Z., Crowe, E., Dau, L., Land, K., Townsend, M., Jecko, T., Rahimi‐Levene, N., Patidar, G., Josephson, C.D., Arora, S., Vermeulen, M., Vrielink, H., Montemayor, C., Oreh, A., Hindawi, S., Berg, K., Serrano, K., So‐Osman, C., Wood, E., Devine, D.V., Spitalnik, S.L., the ISBT COVID‐19 Working Group, 2021. ABO blood group and COVID‐19: a review on behalf of the ISBT COVID‐19 Working Group. Vox Sang 116, 849–861. 10.1111/vox.13076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Goel R.R., Kotenko S.V., Kaplan M.J. Interferon lambda in inflammation and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021;17:349–362. doi: 10.1038/s41584-021-00606-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez J., Albaiceta G.M., Cuesta-Llavona E., García-Clemente M., López-Larrea C., Amado-Rodríguez L., López-Alonso I., Melón S., Alvarez-Argüelles M.E., Gil-Peña H., Vidal-Castiñeira J.R., Corte-Iglesias V., Saiz M.L., Alvarez V., Coto E. The Interferon-induced transmembrane protein 3 gene (IFITM3) rs12252 C variant is associated with COVID-19. Cytokine. 2021;137 doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaudo S., Amodio E., Pipitone R.M., Maida C.M., Pizzo S., Prestileo T., Tramuto F., Sardina D., Vitale F., Casuccio A., Craxì A. PNPLA3 and TLL-1 polymorphisms as potential predictors of disease severity in patients with COVID-19. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021;9 doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.627914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunal O., Sezer O., Ustun G.U., Ozturk C.E., Sen A., Yigit S., Demirag M.D. Angiotensin-converting enzyme-1 gene insertion/deletion polymorphism may be associated with COVID-19 clinical severity: a prospective cohort study. Ann. Saudi Med. 2021;41:141–146. doi: 10.5144/0256-4947.2021.141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez-Valencia M., Leache L., Librero J., Jericó C., Enguita Germán M., García-Erce J.A. ABO blood group and risk of COVID -19 infection and complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Transfusion. 2022;62:493–505. doi: 10.1111/trf.16748. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashemi S.M.A., Thijssen M., Hosseini S.Y., Tabarraei A., Pourkarim M.R., Sarvari J. Human gene polymorphisms and their possible impact on the clinical outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Arch. Virol. 2021;166:2089–2108. doi: 10.1007/s00705-021-05070-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathaway D., Pandav K., Patel M., Riva-Moscoso A., Singh B.M., Patel A., Min Z.C., Singh-Makkar S., Sana M.K., Sanchez-Dopazo R., Desir R., Fahem M.M.M., Manella S., Rodriguez I., Alvarez A., Abreu R. Omega 3 fatty acids and COVID-19: a comprehensive review. Infect. Chemother. 2020;52:478. doi: 10.3947/ic.2020.52.4.478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hippisley-Cox J., Young D., Coupland C., Channon K.M., Tan P.S., Harrison D.A., Rowan K., Aveyard P., Pavord I.D., Watkinson P.J. Risk of severe COVID-19 disease with ACE inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: cohort study including 8.3 million people. Heart. 2020;106:1503–1511. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2020-317393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Krüger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.-H., Nitsche A., Müller M.A., Drosten C., Pöhlmann S. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou Y., Zhao J., Martin W., Kallianpur A., Chung M.K., Jehi L., Sharifi N., Erzurum S., Eng C., Cheng F. New insights into genetic susceptibility of COVID-19: an ACE2 and TMPRSS2 polymorphism analysis. BMC Med. 2020;18:216. doi: 10.1186/s12916-020-01673-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovhannisyan A., Madelian V., Avagyan S., Nazaretyan M., Hyussyan A., Sirunyan A., Arakelyan R., Manukyan Z., Yepiskoposyan L., Mayilyan K.R., Jordan F. HLA-C*04:01 affects HLA class I heterozygosity and predicted affinity to SARS-CoV-2 peptides, and in combination with age and sex of armenian patients contributes to COVID-19 severity. Front. Immunol. 2022;13 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.769900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang C., Wang Y., Li X., Ren L., Zhao J., Hu Y., Zhang L., Fan G., Xu J., Gu X., Cheng Z., Yu T., Xia J., Wei Y., Wu W., Xie X., Yin W., Li H., Liu M., Xiao Y., Gao H., Guo L., Xie J., Wang G., Jiang R., Gao Z., Jin Q., Wang J., Cao B. Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China. The Lancet. 2020;395:497–506. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubacek, J., Dusek, L., Majek, O., Adamek, V., Cervinkova, T., Dlouha, D., Pavel, J., Adamkova, V., 2021. CCR5Δ32 Deletion as a Protective Factor in Czech First-Wave COVID-19 Subjects. Physiol Res 111–115. 10.33549/physiolres.934647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Íñiguez M., Pérez-Matute P., Villoslada-Blanco P., Recio-Fernandez E., Ezquerro-Pérez D., Alba J., Ferreira-Laso M.L., Oteo J.A. ACE gene variants rise the risk of severe COVID-19 in patients with hypertension, dyslipidemia or diabetes: a Spanish pilot study. Front. Endocrinol. 2021;12 doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.688071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irham L.M., Chou W.-H., Calkins M.J., Adikusuma W., Hsieh S.-L., Chang W.-C. Genetic variants that influence SARS-CoV-2 receptor TMPRSS2 expression among population cohorts from multiple continents. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020;529:263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.05.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyer, G.R., Samajder, S., Zubeda, S., S, D.S.N., Mali, V., Pv, S.K., Sharma, A., Abbas, N.Z., Bora, N.S., Narravula, A., Hasan, Q., 2020. Infectivity and Progression of COVID-19 Based on Selected Host Candidate Gene Variants. Front. Genet. 11, 861. 10.3389/fgene.2020.00861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Jelinek H.F., Mousa M., Alkaabi N., Alefishat E., Daw Elbait G., Kannout H., AlHumaidan H., Selvaraj F.A., Imambaccus H., Weber S., Uddin M., Abdulkarim F., Mahboub B., Tay G., Alsafar H. Allelic variants within the ABO blood group phenotype confer protection against critical COVID-19 hospital presentation. Front. Med. 2022;8 doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.759648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karakaş Çelik S., Çakmak Genç G., Pişkin N., Açikgöz B., Altinsoy B., Kurucu İşsiz B., Dursun A. Polymorphisms of ACE (I/D) and ACE2 receptor gene (Rs2106809, Rs2285666) are not related to the clinical course of COVID-19: a case study. J. Med. Virol. 2021;93:5947–5952. doi: 10.1002/jmv.27160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasela S., Daniloski Z., Bollepalli S., Jordan T.X., tenOever B.R., Sanjana N.E., Lappalainen T. Integrative approach identifies SLC6A20 and CXCR6 as putative causal genes for the COVID-19 GWAS signal in the 3p21.31 locus. Genome Biol. 2021;22:242. doi: 10.1186/s13059-021-02454-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khayat A.S., de Assumpção P.P., Meireles Khayat B.C., Thomaz Araújo T.M., Batista-Gomes J.A., Imbiriba L.C., Ishak G., de Assumpção P.B., Moreira F.C., Burbano R.R., Ribeiro-dos-Santos A., Ribeiro-dos-Santos Â.K., dos Santos N.P.C., dos Santos S.E.B. ACE2 polymorphisms as potential players in COVID-19 outcome. PLoS ONE. 2020;15 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleine-Weber H., Elzayat M.T., Hoffmann M., Pöhlmann S. Functional analysis of potential cleavage sites in the MERS-coronavirus spike protein. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:16597. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-34859-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotsev S.V., Miteva D., Krayselska S., Shopova M., Pishmisheva-Peleva M., Stanilova S.A., Velikova T. Hypotheses and facts for genetic factors related to severe COVID-19. WJV. 2021;10:137–155. doi: 10.5501/wjv.v10.i4.137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotur N., Skakic A., Klaassen K., Gasic V., Zukic B., Skodric-Trifunovic V., Stjepanovic M., Zivkovic Z., Ostojic O., Stevanovic G., Lavadinovic L., Pavlovic S., Stankovic B. Association of vitamin D, zinc and selenium related genetic variants with COVID-19 disease severity. Front. Nutr. 2021;8 doi: 10.3389/fnut.2021.689419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kousathanas, A., Pairo-Castineira, E., Rawlik, K., Stuckey, A., Odhams, C.A., Walker, S., Russell, C.D., Malinauskas, T., Wu, Y., Millar, J., Shen, X., Elliott, K.S., Griffiths, F., Oosthuyzen, W., Morrice, K., Keating, S., Wang, B., Rhodes, D., Klaric, L., Zechner, M., Parkinson, N., Siddiq, A., Goddard, P., Donovan, S., Maslove, D., Nichol, A., Semple, M.G., Zainy, T., Maleady-Crowe, F., Todd, L., Salehi, S., Knight, J., Elgar, G., Chan, G., Arumugam, P., Patch, C., Rendon, A., Bentley, D., Kingsley, C., Kosmicki, J.A., Horowitz, J.E., Baras, A., Abecasis, G.R., Ferreira, M.A.R., Justice, A., Mirshahi, T., Oetjens, M., Rader, D.J., Ritchie, M.D., Verma, A., Fowler, T.A., Shankar-Hari, M., Summers, C., Hinds, C., Horby, P., Ling, L., McAuley, D., Montgomery, H., Openshaw, P.J.M., Elliott, P., Walsh, T., Tenesa, A., GenOMICC Investigators, 23andMe, Covid-19 Human Genetics Initiative, Fawkes, A., Murphy, L., Rowan, K., Ponting, C.P., Vitart, V., Wilson, J.F., Yang, J., Bretherick, A.D., Scott, R.H., Hendry, S.C., Moutsianas, L., Law, A., Caulfield, M.J., Baillie, J.K., 2022. Whole genome sequencing reveals host factors underlying critical Covid-19. Nature. 10.1038/s41586-022-04576-6.
- Langton D.J., Bourke S.C., Lie B.A., Reiff G., Natu S., Darlay R., Burn J., Echevarria C. The influence of HLA genotype on the severity of COVID-19 infection. HLA. 2021;98:14–22. doi: 10.1111/tan.14284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanjanian H., Moazzam-Jazi M., Hedayati M., Akbarzadeh M., Guity K., Sedaghati-khayat B., Azizi F., Daneshpour M.S. SARS-CoV-2 infection susceptibility influenced by ACE2 genetic polymorphisms: insights from Tehran Cardio-Metabolic Genetic Study. Sci. Rep. 2021;11:1529. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80325-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latini A., Agolini E., Novelli A., Borgiani P., Giannini R., Gravina P., Smarrazzo A., Dauri M., Andreoni M., Rogliani P., Bernardini S., Helmer-Citterich M., Biancolella M., Novelli G. COVID-19 and genetic variants of protein involved in the SARS-CoV-2 entry into the host cells. Genes. 2020;11:1010. doi: 10.3390/genes11091010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim, K.-H., Staudt, L.M., 2013. Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology 5, a011247–a011247. 10.1101/cshperspect.a011247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Littera R., Campagna M., Deidda S., Angioni G., Cipri S., Melis M., Firinu D., Santus S., Lai A., Porcella R., Lai S., Rassu S., Scioscia R., Meloni F., Schirru D., Cordeddu W., Kowalik M.A., Serra M., Ragatzu P., Carta M.G., Del Giacco S., Restivo A., Deidda S., Orrù S., Palimodde A., Perra R., Orrù G., Conti M., Balestrieri C., Serra G., Onali S., Marongiu F., Perra A., Chessa L. Human leukocyte antigen complex and other immunogenetic and clinical factors influence susceptibility or protection to SARS-CoV-2 infection and severity of the disease course. Sardinian Exp. Front. Immunol. 2020;11 doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.605688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorente, L., Martín, M.M., Franco, A., Barrios, Y., Cáceres, J.J., Solé-Violán, J., Perez, A., Marcos y Ramos, J.A., Ramos-Gómez, L., Ojeda, N., Jiménez, A., Lorente, Leonardo, Franco, Andrés, Barrios, Yvelise, Perez, Alina, Jiménez, Alejandro, Pérez-Cejas, A., Pérez-Llombet, A., Uribe, L., González, L., Alvarez, R., Martín, María M., Alcoba-Flórez, J., Estupiñan, A., Cáceres, Juan J., Vega, P., Gonzalez, L., Solé-Violán, Jordi, Ojeda, Nazario, López, S., Rodríguez-Pérez, A., Domínguez, C., Marcos y Ramos, José Alberto, Zapata, M.F., Ramos-Gómez, Luis, Ortiz-López, R., 2021. HLA genetic polymorphisms and prognosis of patients with COVID-19. Medicina Intensiva 45, 96–103. 10.1016/j.medin.2020.08.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Ma Y., Huang Y., Zhao S., Yao Y., Zhang Y., Qu J., Wu N., Su J. Integrative genomics analysis reveals a 21q22.11 locus contributing risk to COVID-19. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021;30:1247–1258. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddab125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, Z.S., Fadhil, H.Y., Abdul Hussein, T.A., Ad’hiah, A.H., 2022. Severity of coronavirus disease 19: Profile of inflammatory markers and ACE (rs4646994) and ACE2 (rs2285666) gene polymorphisms in Iraqi patients. Meta Gene 31, 101014. 10.1016/j.mgene.2022.101014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Gómez, L.E., Herrera-López, B., Martinez-Armenta, C., Ortega-Peña, S., Camacho-Rea, M. del C., Suarez-Ahedo, C., Vázquez-Cárdenas, P., Vargas-Alarcón, G., Rojas-Velasco, G., Fragoso, J.M., Vidal-Vázquez, P., Ramírez-Hinojosa, J.P., Rodríguez-Sánchez, Y., Barrón-Díaz, D., Moreno, M.L., Martínez-Ruiz, F. de J., Zayago-Angeles, D.M., Mata-Miranda, M.M., Vázquez-Zapién, G.J., Martínez-Cuazitl, A., Barajas-Galicia, E., Bustamante-Silva, L., Zazueta-Arroyo, D., Rodríguez-Pérez, J.M., Hernández-González, O., Coronado-Zarco, R., Lucas-Tenorio, V., Franco-Cendejas, R., López-Jácome, L.E., Vázquez-Juárez, R.C., Magaña, J.J., Cruz-Ramos, M., Granados, J., Hernández-Doño, S., Delgado-Saldivar, D., Ramos-Tavera, L., Coronado-Zarco, I., Guajardo-Salinas, G., Muñoz-Valle, J.F., Pineda, C., Martínez-Nava, G.A., López-Reyes, A., 2022. ACE and ACE2 Gene Variants Are Associated With Severe Outcomes of COVID-19 in Men. Front. Immunol. 13, 812940. 10.3389/fimmu.2022.812940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Maslove, D.M., Sibley, S., Boyd, J.G., Goligher, E.C., Munshi, L., Bogoch, I.I., Rochwerg, B., 2021. Complications of Critical COVID-19. Chest S0012369221040940. 10.1016/j.chest.2021.10.011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Mathur R., Rentsch C.T., Morton C.E., Hulme W.J., Schultze A., MacKenna B., Eggo R.M., Bhaskaran K., Wong A.Y.S., Williamson E.J., Forbes H., Wing K., McDonald H.I., Bates C., Bacon S., Walker A.J., Evans D., Inglesby P., Mehrkar A., Curtis H.J., DeVito N.J., Croker R., Drysdale H., Cockburn J., Parry J., Hester F., Harper S., Douglas I.J., Tomlinson L., Evans S.J.W., Grieve R., Harrison D., Rowan K., Khunti K., Chaturvedi N., Smeeth L., Goldacre B. Ethnic differences in SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19-related hospitalisation, intensive care unit admission, and death in 17 million adults in England: an observational cohort study using the OpenSAFELY platform. The Lancet. 2021;397:1711–1724. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00634-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medetalibeyoglu A., Bahat G., Senkal N., Kose M., Avci K., Sayin G.Y., Isoglu-Alkac U., Tukek T., Pehlivan S. Mannose binding lectin gene 2 (rs1800450) missense variant may contribute to development and severity of COVID-19 infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021;89 doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millett G.A., Jones A.T., Benkeser D., Baral S., Mercer L., Beyrer C., Honermann B., Lankiewicz E., Mena L., Crowley J.S., Sherwood J., Sullivan P.S. Assessing differential impacts of COVID-19 on black communities. Ann. Epidemiol. 2020;47:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.annepidem.2020.05.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed M.S., Moulin T.C., Schiöth H.B. Sex differences in COVID-19: the role of androgens in disease severity and progression. Endocrine. 2021;71:3–8. doi: 10.1007/s12020-020-02536-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monticelli M., Mele B.H., Andreotti G., Cubellis M.V., Riccio G. Why does SARS-CoV-2 hit in different ways? host genetic factors can influence the acquisition or the course of COVID-19. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2021;64 doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2021.104227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muniyappa R., Gubbi S. COVID-19 pandemic, coronaviruses, and diabetes mellitus. Am. J. Physiol.-Endocrinol. Metabol. 2020;318:E736–E741. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00124.2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz-Fernández L., Sawalha A.H. Genetic variability in the expression of the SARS-CoV-2 host cell entry factors across populations. Genes Immun. 2020;21:269–272. doi: 10.1038/s41435-020-0107-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Page, M.J., McKenzie, J.E., Bossuyt, P.M., Boutron, I., Hoffmann, T.C., Mulrow, C.D., Shamseer, L., Tetzlaff, J.M., Akl, E.A., Brennan, S.E., Chou, R., Glanville, J., Grimshaw, J.M., Hróbjartsson, A., Lalu, M.M., Li, T., Loder, E.W., Mayo-Wilson, E., McDonald, S., McGuinness, L.A., Stewart, L.A., Thomas, J., Tricco, A.C., Welch, V.A., Whiting, P., Moher, D., 2021. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ n71. 10.1136/bmj.n71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Palacios Y., Ruiz A., Ramón-Luing L.A., Ocaña-Guzman R., Barreto-Rodriguez O., Sánchez-Monciváis A., Tecuatzi-Cadena B., Regalado-García A.G., Pineda-Gudiño R.D., García-Martínez A., Juárez-Hernández F., Farias-Contreras J.P., Fricke-Galindo I., Pérez-Rubio G., Falfán-Valencia R., Buendia-Roldan I., Medina-Quero K., Chavez-Galan L. Severe COVID-19 patients show an increase in soluble TNFR1 and ADAM17, with a relationship to mortality. IJMS. 2021;22:8423. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey R.K., Srivastava A., Singh P.P., Chaubey G. Genetic association of TMPRSS2 rs2070788 polymorphism with COVID-19 case fatality rate among Indian populations. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2022;98 doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2022.105206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paniri A., Hosseini M.M., Akhavan-Niaki H. First comprehensive computational analysis of functional consequences of TMPRSS2 SNPs in susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 among different populations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dynamics. 2021;39:3576–3593. doi: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1767690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parasher A. COVID-19: current understanding of its pathophysiology, clinical presentation and treatment. Postgrad. Med. J. 2021;97:312–320. doi: 10.1136/postgradmedj-2020-138577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisanti S., Deelen J., Gallina A.M., Caputo M., Citro M., Abate M., Sacchi N., Vecchione C., Martinelli R. Correlation of the two most frequent HLA haplotypes in the Italian population to the differential regional incidence of Covid-19. J. Transl. Med. 2020;18:352. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02515-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahimi P., Tarharoudi R., Rahimpour A., Mosayebi Amroabadi J., Ahmadi I., Anvari E., Siadat S.D., Aghasadeghi M., Fateh A. The association between interferon lambda 3 and 4 gene single-nucleotide polymorphisms and the recovery of COVID-19 patients. Virol. J. 2021;18:221. doi: 10.1186/s12985-021-01692-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rastrelli G., Di Stasi V., Inglese F., Beccaria M., Garuti M., Di Costanzo D., Spreafico F., Greco G.F., Cervi G., Pecoriello A., Magini A., Todisco T., Cipriani S., Maseroli E., Corona G., Salonia A., Lenzi A., Maggi M., De Donno G., Vignozzi L. Low testosterone levels predict clinical adverse outcomes in SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia patients. Andrology. 2021;9:88–98. doi: 10.1111/andr.12821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray P.R., Wangzhou A., Ghneim N., Yousuf M.S., Paige C., Tavares-Ferreira D., Mwirigi J.M., Shiers S., Sankaranarayanan I., McFarland A.J., Neerukonda S.V., Davidson S., Dussor G., Burton M.D., Price T.J. A pharmacological interactome between COVID-19 patient samples and human sensory neurons reveals potential drivers of neurogenic pulmonary dysfunction. Brain, Behav., Immun. 2020;89:559–568. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2020.05.078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rokni M., Heidari Nia M., Sarhadi M., Mirinejad S., Sargazi S., Moudi M., Saravani R., Rahdar S., Kargar M. Association of TMPRSS2 gene polymorphisms with COVID-19 severity and mortality: a case-control study with computational analyses. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2022 doi: 10.1007/s12010-022-03885-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo R., Andolfo I., Lasorsa V.A., Cantalupo S., Marra R., Frisso G., Abete P., Cassese G.M., Servillo G., Esposito G., Gentile I., Piscopo C., Della Monica M., Fiorentino G., Russo G., Cerino P., Buonerba C., Pierri B., Zollo M., Iolascon A., Capasso M. The TNFRSF13C H159Y variant is associated with severe COVID-19: a retrospective study of 500 patients from southern Italy. Genes. 2021;12:881. doi: 10.3390/genes12060881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saad H., Jabotian K., Sakr C., Mahfouz R., Akl I.B., Zgheib N.K. The Role of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 1 Insertion/Deletion Genetic Polymorphism in the Risk and Severity of COVID-19 Infection. Front. Med. 2021;8:798571. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.798571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabater Molina M., Nicolás Rocamora E., Bendicho A.I., Vázquez E.G., Zorio E., Rodriguez F.D., Gil Ortuño C., Rodríguez A.I., Sánchez-López A.J., Jara Rubio R., Moreno-Docón A., Marcos P.J., García Pavía P., Villa R.B., Gimeno Blanes J.R. Polymorphisms in ACE, ACE2, AGTR1 genes and severity of COVID-19 disease. PLoS ONE. 2022;17 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0263140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel R.M., Majd H., Richter M.N., Ghazizadeh Z., Zekavat S.M., Navickas A., Ramirez J.T., Asgharian H., Simoneau C.R., Bonser L.R., Koh K.D., Garcia-Knight M., Tassetto M., Sunshine S., Farahvashi S., Kalantari A., Liu W., Andino R., Zhao H., Natarajan P., Erle D.J., Ott M., Goodarzi H., Fattahi F. Androgen signaling regulates SARS-CoV-2 receptor levels and is associated with severe COVID-19 symptoms in men. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27:876–889.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2020.11.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarfraz, Z., Sarfraz, A., Barrios, A., Garimella, R., Dominari, A., Kc, M., Pandav, K., Pantoja, J.C., Retnakumar, V., Cherrez-Ojeda, I., 2021. Cardio-Pulmonary Sequelae in Recovered COVID-19 Patients: Considerations for Primary Care. J Prim Care Community Health 12, 215013272110237. 10.1177/21501327211023726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Schönfelder K., Breuckmann K., Elsner C., Dittmer U., Fistera D., Herbstreit F., Risse J., Schmidt K., Sutharsan S., Taube C., Jöckel K.-H., Siffert W., Kribben A., Möhlendick B. The influence of IFITM3 polymorphisms on susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and severity of COVID-19. Cytokine. 2021;142 doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2021.155492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder M., Schaumburg B., Mueller Z., Parplys A., Jarczak D., Roedl K., Nierhaus A., de Heer G., Grensemann J., Schneider B., Stoll F., Bai T., Jacobsen H., Zickler M., Stanelle-Bertram S., Klaetschke K., Renné T., Meinhardt A., Aberle J., Hiller J., Peine S., Kreienbrock L., Klingel K., Kluge S., Gabriel G. High estradiol and low testosterone levels are associated with critical illness in male but not in female COVID-19 patients: a retrospective cohort study. Emerg. Microb. Infect. 2021;10:1807–1818. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2021.1969869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sieron, L., Lesiak, M., Schisler, I., Drzazga, Z., Fertala, A., Sieron, A.L., 2019. Functional and structural studies of tolloid-like 1 mutants associated with atrial-septal defect 6. Bioscience Reports 39, BSR20180270. 10.1042/BSR20180270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Smulski C.R., Eibel H. BAFF and BAFF-receptor in B cell selection and survival. Front. Immunol. 2018;9:2285. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosa, J.P., Ferreira Caceres, M.M., Ross-Comptis, J., Hathaway III, D., Mehta, J., Pandav, K., Pakala, R., Butt, M., Dogar, Z.G., Belizaire, M.-P., El Mazboudi, N., Pormento, M.K.L., Zaidi, M., Devender, H.M., Loh, H., Garimella, R., Brahmbhatt, N., 2021. Web-Based Apps in the fight against COVID-19. J Med Artif Intell 4, 1–1. 10.21037/jmai-20-61.
- Srivastava A., Bandopadhyay A., Das D., Pandey R.K., Singh V., Khanam N., Srivastava N., Singh P.P., Dubey P.K., Pathak A., Gupta P., Rai N., Sultana G.N.N., Chaubey G. Genetic association of ACE2 rs2285666 polymorphism with COVID-19 spatial distribution in India. Front. Genet. 2020;11 doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.564741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stopsack K.H., Mucci L.A., Antonarakis E.S., Nelson P.S., Kantoff P.W. TMPRSS2 and COVID-19: serendipity or opportunity for intervention? Cancer Discov. 2020;10:779–782. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suryamohan K., Diwanji D., Stawiski E.W., Gupta R., Miersch S., Liu J., Chen C., Jiang Y.-P., Fellouse F.A., Sathirapongsasuti J.F., Albers P.K., Deepak T., Saberianfar R., Ratan A., Washburn G., Mis M., Santhosh D., Somasekar S., Hiranjith G.H., Vargas D., Mohan S., Phalke S., Kuriakose B., Antony A., Ustav M., Jr, Schuster S.C., Sidhu S., Junutula J.R., Jura N., Seshagiri S. Human ACE2 receptor polymorphisms and altered susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2. Commun. Biol. 2021;4:475. doi: 10.1038/s42003-021-02030-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda M. Proteolytic activation of SARS-CoV-2 spike protein. Microbiol. Immunol. 2022;66:15–23. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talalaev M., Pandav K., Mehendale M., Gonzalez L., Yatzkan M.C., Yatzkan G.D., Perez-Fernandez J. Treatment with therapeutic plasma exchange in severe COVID-19 pneumonia: a case report and review of the literature. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2022;36 doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2022.101587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teimouri, H., Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Golestan University of Medical Sciences, Gorgan, Iran, Maali, A., Pasteur Institute of Iran, 2020. Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Host Pattern-Recognition Receptors Show Association with Antiviral Responses against SARS-CoV-2, in-silico Trial. JoMMID 8, 65–70. 10.29252/JoMMID.8.2.65.
- The GenOMICC Investigators, The ISARIC4C Investigators, The COVID-19 Human Genetics Initiative, 23andMe Investigators, BRACOVID Investigators, Gen-COVID Investigators, Pairo-Castineira, E., Clohisey, S., Klaric, L., Bretherick, A.D., Rawlik, K., Pasko, D., Walker, S., Parkinson, N., Fourman, M.H., Russell, C.D., Furniss, J., Richmond, A., Gountouna, E., Wrobel, N., Harrison, D., Wang, B., Wu, Y., Meynert, A., Griffiths, F., Oosthuyzen, W., Kousathanas, A., Moutsianas, L., Yang, Z., Zhai, R., Zheng, C., Grimes, G., Beale, R., Millar, J., Shih, B., Keating, S., Zechner, M., Haley, C., Porteous, D.J., Hayward, C., Yang, J., Knight, J., Summers, C., Shankar-Hari, M., Klenerman, P., Turtle, L., Ho, A., Moore, S.C., Hinds, C., Horby, P., Nichol, A., Maslove, D., Ling, L., McAuley, D., Montgomery, H., Walsh, T., Pereira, A.C., Renieri, A., Shen, X., Ponting, C.P., Fawkes, A., Tenesa, A., Caulfield, M., Scott, R., Rowan, K., Murphy, L., Openshaw, P.J.M., Semple, M.G., Law, A., Vitart, V., Wilson, J.F., Baillie, J.K., 2021. Genetic mechanisms of critical illness in COVID-19. Nature 591, 92–98. 10.1038/s41586-020-03065-y. [DOI] [PubMed]
- The Severe Covid-19 GWAS Group, 2020. Genomewide Association Study of Severe Covid-19 with Respiratory Failure. N Engl J Med 383, 1522–1534. 10.1056/NEJMoa2020283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Tomita Y., Ikeda T., Sato R., Sakagami T. Association between HLA gene polymorphisms and mortality of COVID-19: An in silico analysis. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2020;8:684–694. doi: 10.1002/iid3.358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traets M.J.M., Nijhuis R.H.T., Morré S.A., Ouburg S., Remijn J.A., Blok B.A., de Laat B., Jong E., Herder G.J.M., Fiolet A.T.L., Verweij S.P. Association of genetic variations in ACE2, TIRAP and factor X with outcomes in COVID-19. PLoS ONE. 2022;17 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0260897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Made, C.I., Simons, A., Schuurs-Hoeijmakers, J., van den Heuvel, G., Mantere, T., Kersten, S., van Deuren, R.C., Steehouwer, M., van Reijmersdal, S.V., Jaeger, M., Hofste, T., Astuti, G., Corominas Galbany, J., van der Schoot, V., van der Hoeven, H., Hagmolen of ten Have, W., Klijn, E., van den Meer, C., Fiddelaers, J., de Mast, Q., Bleeker-Rovers, C.P., Joosten, L.A.B., Yntema, H.G., Gilissen, C., Nelen, M., van der Meer, J.W.M., Brunner, H.G., Netea, M.G., van de Veerdonk, F.L., Hoischen, A., 2020. Presence of Genetic Variants Among Young Men With Severe COVID-19. JAMA 324, 663. 10.1001/jama.2020.13719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Verma S., Abbas M., Verma S., Khan F.H., Raza S.T., Siddiqi Z., Ahmad I., Mahdi F. Impact of I/D polymorphism of angiotensin-converting enzyme 1 (ACE1) gene on the severity of COVID-19 patients. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2021;91 doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Huang S., Gao R., Zhou Y., Lai C., Li Z., Xian W., Qian X., Li Z., Huang Y., Tang Q., Liu P., Chen R., Liu R., Li X., Tong X., Zhou X., Bai Y., Duan G., Zhang T., Xu X., Wang J., Yang H., Liu S., He Q., Jin X., Liu L. Initial whole-genome sequencing and analysis of the host genetic contribution to COVID-19 severity and susceptibility. Cell Discov. 2020;6:83. doi: 10.1038/s41421-020-00231-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren R.L., Birol I. HLA alleles measured from COVID-19 patient transcriptomes reveal associations with disease prognosis in a New York cohort. PeerJ. 2021;9 doi: 10.7717/peerj.12368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner J., Suwalski P., Holtgrewe M., Rakitko A., Thibeault C., Müller M., Patriki D., Quedenau C., Krüger U., Ilinsky V., Popov I., Balnis J., Jaitovich A., Helbig E.T., Lippert L.J., Stubbemann P., Real L.M., Macías J., Pineda J.A., Fernandez-Fuertes M., Wang X., Karadeniz Z., Saccomanno J., Doehn J.-M., Hübner R.-H., Hinzmann B., Salvo M., Blueher A., Siemann S., Jurisic S., Beer J.H., Rutishauser J., Wiggli B., Schmid H., Danninger K., Binder R., Corman V.M., Mühlemann B., Arjun Arkal R., Fragiadakis G.K., Mick E., Comet C., Calfee C.S., Erle D.J., Hendrickson C.M., Kangelaris K.N., Krummel M.F., Woodruff P.G., Langelier C.R., Venkataramani U., García F., Zyla J., Drosten C., Alice B., Jones T.C., Suttorp N., Witzenrath M., Hippenstiel S., Zemojtel T., Skurk C., Poller W., Borodina T., Pa-COVID S.G., Ripke S., Sander L.E., Beule D., Landmesser U., Guettouche T., Kurth F., Heidecker B. Increased risk of severe clinical course of COVID-19 in carriers of HLA-C*04:01. EClinMed. 2021;40 doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.101099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu Y., Feng Z., Li P., Yu Q. Relationship between ABO blood group distribution and clinical characteristics in patients with COVID-19. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2020;509:220–223. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto N., Ariumi Y., Nishida N., Yamamoto R., Bauer G., Gojobori T., Shimotohno K., Mizokami M. SARS-CoV-2 infections and COVID-19 mortalities strongly correlate with ACE1 I/D genotype. Gene. 2020;758 doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.144944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yao Y., Ye F., Li K., Xu P., Tan W., Feng Q., Rao S. Genome and epigenome editing identify CCR9 and SLC6A20 as target genes at the 3p21.31 locus associated with severe COVID-19. Sig. Transduct. Target Ther. 2021;6:85. doi: 10.1038/s41392-021-00519-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yildirim Z., Sahin O.S., Yazar S., Bozok Cetintas V. Genetic and epigenetic factors associated with increased severity of Covid-19. Cell Biol. Int. 2021;45:1158–1174. doi: 10.1002/cbin.11572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung Y., Cheng C., Chan H., Xia J.T., Lau K., Wong R.S.M., Wu A.K.L., Chu R.W., Wong A.C.C., Chow E.Y.D., Yip S., Leung J.N.S., Lee C., Ng M.H.L. Association of HLA-B22 serotype with SARS-CoV -2 susceptibility in Hong Kong Chinese patients. HLA. 2021;97:127–132. doi: 10.1111/tan.14135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q., Bastard, P., Liu, Z., Le Pen, J., Moncada-Velez, M., Chen, J., Ogishi, M., Sabli, I.K.D., Hodeib, S., Korol, C., Rosain, J., Bilguvar, K., Ye, J., Bolze, A., Bigio, B., Yang, R., Arias, A.A., Zhou, Q., Zhang, Y., Onodi, F., Korniotis, S., Karpf, L., Philippot, Q., Chbihi, M., Bonnet-Madin, L., Dorgham, K., Smith, N., Schneider, W.M., Razooky, B.S., Hoffmann, H.-H., Michailidis, E., Moens, L., Han, J.E., Lorenzo, L., Bizien, L., Meade, P., Neehus, A.-L., Ugurbil, A.C., Corneau, A., Kerner, G., Zhang, P., Rapaport, F., Seeleuthner, Y., Manry, J., Masson, Cecile, Schmitt, Yohann, Schlüter, A., Le Voyer, T., Khan, T., Li, J., Fellay, J., Roussel, L., Shahrooei, Mohammad, Alosaimi, M.F., Mansouri, Davood, Al-Saud, H., Al-Mulla, F., Almourfi, F., Al-Muhsen, S.Z., Alsohime, F., Al Turki, S., Hasanato, R., van de Beek, D., Biondi, A., Bettini, L.R., D’Angio’, M., Bonfanti, P., Imberti, L., Sottini, A., Paghera, S., Quiros-Roldan, E., Rossi, C., Oler, A.J., Tompkins, M.F., Alba, C., Vandernoot, I., Goffard, J.-C., Smits, G., Migeotte, I., Haerynck, F., Soler-Palacin, P., Martin-Nalda, A., Colobran, R., Morange, P.-E., Keles, S., Çölkesen, F., Ozcelik, T., Yasar, K.K., Senoglu, S., Karabela, Ş.N., Rodríguez-Gallego, C., Novelli, G., Hraiech, S., Tandjaoui-Lambiotte, Y., Duval, X., Laouénan, C., COVID-STORM Clinicians, COVID Clinicians, Imagine COVID Group, French COVID Cohort Study Group, CoV-Contact Cohort, Amsterdam UMC Covid-19 Biobank, COVID Human Genetic Effort, NIAID-USUHS/TAGC COVID Immunity Group, Snow, A.L., Dalgard, C.L., Milner, J.D., Vinh, D.C., Mogensen, T.H., Marr, N., Spaan, A.N., Boisson, B., Boisson-Dupuis, S., Bustamante, J., Puel, A., Ciancanelli, M.J., Meyts, I., Maniatis, T., Soumelis, V., Amara, A., Nussenzweig, M., García-Sastre, A., Krammer, F., Pujol, A., Duffy, D., Lifton, R.P., Zhang, S.-Y., Gorochov, G., Béziat, V., Jouanguy, E., Sancho-Shimizu, V., Rice, C.M., Abel, L., Notarangelo, L.D., Cobat, A., Su, H.C., Casanova, J.-L., Foti, G., Bellani, G., Citerio, G., Contro, E., Pesci, A., Valsecchi, M.G., Cazzaniga, M., Abad, J., Aguilera-Albesa, S., Akcan, O.M., Darazam, I.A., Aldave, J.C., Ramos, M.A., Nadji, S.A., Alkan, G., Allardet-Servent, J., Allende, L.M., Alsina, L., Alyanakian, M.-A., Amador-Borrero, B., Amoura, Z., Antolí, A., Arslan, S., Assant, S., Auguet, T., Azot, A., Bajolle, F., Baldolli, A., Ballester, M., Feldman, H.B., Barrou, B., Beurton, A., Bilbao, A., Blanchard-Rohner, G., Blanco, I., Blandinières, A., Blazquez-Gamero, D., Bloomfield, M., Bolivar-Prados, M., Borie, R., Bosteels, C., Bousfiha, A.A., Bouvattier, C., Boyarchuk, O., Bueno, M.R.P., Bustamante, J., Cáceres Agra, J.J., Calimli, S., Capra, R., Carrabba, M., Casasnovas, C., Caseris, M., Castelle, M., Castelli, F., de Vera, M.C., Castro, M.V., Catherinot, E., Chalumeau, M., Charbit, B., Cheng, M.P., Clavé, P., Clotet, B., Codina, A., Colkesen, F., Çölkesen, F., Colobran, R., Comarmond, C., Dalmau, D., Darley, D.R., Dauby, N., Dauger, S., de Pontual, L., Dehban, A., Delplancq, G., Demoule, A., Diehl, J.-L., Dobbelaere, S., Durand, S., Eldars, W., Elgamal, M., Elnagdy, M.H., Emiroglu, M., Erdeniz, E.H., Aytekin, S.E., Euvrard, R., Evcen, R., Fabio, G., Faivre, L., Falck, A., Fartoukh, M., Faure, M., Arquero, M.F., Flores, C., Francois, B., Fumadó, V., Fusco, F., Solis, B.G., Gaussem, P., Gil-Herrera, J., Gilardin, L., Alarcon, M.G., Girona-Alarcón, M., Goffard, J.-C., Gok, F., González-Montelongo, R., Guerder, A., Gul, Y., Guner, S.N., Gut, M., Hadjadj, J., Haerynck, F., Halwani, R., Hammarström, L., Hatipoglu, N., Hernandez-Brito, E., Heijmans, C., Holanda-Peña, M.S., Horcajada, J.P., Hoste, L., Hoste, E., Hraiech, S., Humbert, L., Iglesias, A.D., Íñigo-Campos, A., Jamme, M., Arranz, M.J., Jordan, I., Jorens, P., Kanat, F., Kapakli, H., Kara, I., Karbuz, A., Yasar, K.K., Keles, S., Demirkol, Y.K., Klocperk, A., Król, Z.J., Kuentz, P., Kwan, Y.W.M., Lagier, J.-C., Lambrecht, B.N., Lau, Y.-L., Le Bourgeois, F., Leo, Y.-S., Lopez, R.L., Leung, D., Levin, M., Levy, M., Lévy, R., Li, Z., Linglart, A., Loeys, B., Lorenzo-Salazar, J.M., Louapre, C., Lubetzki, C., Luyt, C.-E., Lye, D.C., Mansouri, Davood, Marjani, M., Pereira, J.M., Martin, A., Pueyo, D.M., Martinez-Picado, J., Marzana, I., Mathian, A., Matos, L.R.B., Matthews, G.V., Mayaux, J., Mège, J.-L., Melki, I., Meritet, J.-F., Metin, O., Meyts, I., Mezidi, M., Migeotte, I., Millereux, M., Mirault, T., Mircher, C., Mirsaeidi, M., Melián, A.M., Martinez, A.M., Morange, P., Mordacq, C., Morelle, G., Mouly, S., Muñoz-Barrera, A., Naesens, L., Nafati, C., Neves, J.F., Ng, L.F.P., Medina, Y.N., Cuadros, E.N., Ocejo-Vinyals, J.G., Orbak, Z., Oualha, M., Özçelik, T., Pan-Hammarström, Q., Parizot, C., Pascreau, T., Paz-Artal, E., Pellegrini, S., de Diego, Rebeca Pérez, Philippe, A., Philippot, Q., Planas-Serra, L., Ploin, D., Poissy, J., Poncelet, G., Pouletty, M., Quentric, P., Raoult, D., Rebillat, A.-S., Reisli, I., Ricart, P., Richard, J.-C., Rivet, N., Rivière, J.G., Blanch, G.R., Rodrigo, C., Rodriguez-Gallego, C., Rodríguez-Palmero, A., Romero, C.S., Rothenbuhler, A., Rozenberg, F., Ruiz del Prado, M.Y., Riera, J.S., Sanchez, O., Sánchez-Ramón, S., Schluter, A., Schmidt, M., Schweitzer, C.E., Scolari, F., Sediva, A., Seijo, L.M., Sene, D., Senoglu, S., Seppänen, M.R.J., Ilovich, A.S., Shahrooei, Mohammad, Slabbynck, H., Smadja, D.M., Sobh, A., Moreno, X.S., Solé-Violán, J., Soler, C., Soler-Palacín, P., Stepanovskiy, Y., Stoclin, A., Taccone, F., Tandjaoui-Lambiotte, Y., Taupin, J.-L., Tavernier, S.J., Terrier, B., Thumerelle, C., Tomasoni, G., Toubiana, J., Alvarez, J.T., Trouillet-Assant, S., Troya, J., Tucci, A., Ursini, M.V., Uzunhan, Y., Vabres, P., Valencia-Ramos, J., Van Braeckel, E., Van de Velde, S., Van Den Rym, A.M., Van Praet, J., Vandernoot, I., Vatansev, H., Vélez-Santamaria, V., Viel, S., Vilain, C., Vilaire, M.E., Vincent, A., Voiriot, G., Vuotto, F., Yosunkaya, A., Young, B.E., Yucel, F., Zannad, F., Zatz, M., Belot, A., Bole-Feysot, C., Lyonnet, S., Masson, Cécile, Nitschke, P., Pouliet, A., Schmitt, Yoann, Tores, F., Zarhrate, M., Abel, L., Andrejak, C., Angoulvant, F., Bachelet, D., Basmaci, R., Behillil, S., Beluze, M., Benkerrou, D., Bhavsar, K., Bompart, F., Bouadma, L., Bouscambert, M., Caralp, M., Cervantes-Gonzalez, M., Chair, A., Coelho, A., Couffignal, C., Couffin-Cadiergues, S., D’Ortenzio, E., Da Silveira, C., Debray, M.-P., Deplanque, D., Descamps, D., Desvallées, M., Diallo, A., Diouf, A., Dorival, C., Dubos, F., Duval, X., Eloy, P., Enouf, V.V., Esperou, H., Esposito-Farese, M., Etienne, M., Ettalhaoui, N., Gault, N., Gaymard, A., Ghosn, J., Gigante, T., Gorenne, I., Guedj, J., Hoctin, A., Hoffmann, I., Jaafoura, S., Kafif, O., Kaguelidou, F., Kali, S., Khalil, A., Khan, C., Laouénan, C., Laribi, S., Le, M., Le Hingrat, Q., Le Mestre, S., Le Nagard, H., Lescure, F.-X., Lévy, Y., Levy-Marchal, C., Lina, B., Lingas, G., Lucet, J.C., Malvy, D., Mambert, M., Mentré, F., Mercier, N., Meziane, A., Mouquet, H., Mullaert, J., Neant, N., Noret, M., Pages, J., Papadopoulos, A., Paul, C., Peiffer-Smadja, N., Petrov-Sanchez, V., Peytavin, G., Picone, O., Puéchal, O., Rosa-Calatrava, M., Rossignol, B., Rossignol, P., Roy, C., Schneider, M., Semaille, C., Mohammed, N.S., Tagherset, L., Tardivon, C., Tellier, M.-C., Téoulé, F., Terrier, O., Timsit, J.-F., Trioux, T., Tual, C., Tubiana, S., van der Werf, S., Vanel, N., Veislinger, A., Visseaux, B., Wiedemann, A., Yazdanpanah, Y., Alavoine, L., Amat, K.K.A., Behillil, S., Bielicki, J., Bruijning, P., Burdet, C., Caumes, E., Charpentier, C., Coignard, B., Costa, Y., Couffin-Cadiergues, S., Damond, F., Dechanet, A., Delmas, C., Descamps, D., Duval, X., Ecobichon, J.-L., Enouf, V., Espérou, H., Frezouls, W., Houhou, N., Ilic-Habensus, E., Kafif, O., Kikoine, J., Le Hingrat, Q., Lebeaux, D., Leclercq, A., Lehacaut, J., Letrou, S., Lina, B., Lucet, J.-C., Malvy, D., Manchon, P., Mandic, M., Meghadecha, M., Motiejunaite, J., Nouroudine, M., Piquard, V., Postolache, A., Quintin, C., Rexach, J., Roufai, L., Terzian, Z., Thy, M., Tubiana, S., van der Werf, S., Vignali, V., Visseaux, B., Yazdanpanah, Y., van Agtmael, M., Algera, A.G., van Baarle, F., Bax, D., Beudel, M., Bogaard, H.J., Bomers, M., Bos, L., Botta, M., de Brabander, J., de Bree, G., Brouwer, M.C., de Bruin, S., Bugiani, M., Bulle, E., Chouchane, O., Cloherty, A., Elbers, P., Fleuren, L., Geerlings, S., Geerts, B., Geijtenbeek, T., Girbes, A., Goorhuis, B., Grobusch, M.P., Hafkamp, F., Hagens, L., Hamann, J., Harris, V., Hemke, R., Hermans, S.M., Heunks, L., Hollmann, M.W., Horn, J., Hovius, J.W., de Jong, M.D., Koning, R., van Mourik, N., Nellen, J., Paulus, F., Peters, E., van der Poll, T., Preckel, B., Prins, J.M., Raasveld, J., Reijnders, T., Schinkel, M., Schultz, M.J., Schuurman, A., Sigaloff, K., Smit, M., Stijnis, C.S., Stilma, W., Teunissen, C., Thoral, P., Tsonas, A., van der Valk, M., Veelo, D., Vlaar, A.P.J., de Vries, H., van Vugt, M., Wiersinga, W.J., Wouters, D., Zwinderman, A.H. (Koos), van de Beek, D., Abel, L., Aiuti, A., Al Muhsen, S., Al-Mulla, F., Anderson, M.S., Arias, A.A., Feldman, H.B., Bogunovic, D., Bolze, A., Bondarenko, A., Bousfiha, A.A., Brodin, P., Bryceson, Y., Bustamante, C.D., Butte, M., Casari, G., Chakravorty, S., Christodoulou, J., Cirulli, E., Condino-Neto, A., Cooper, M.A., Dalgard, C.L., David, A., DeRisi, J.L., Desai, M., Drolet, B.A., Espinosa, S., Fellay, J., Flores, C., Franco, J.L., Gregersen, P.K., Haerynck, F., Hagin, D., Halwani, R., Heath, J., Henrickson, S.E., Hsieh, E., Imai, K., Itan, Y., Karamitros, T., Kisand, K., Ku, C.-L., Lau, Y.-L., Ling, Y., Lucas, C.L., Maniatis, T., Mansouri, Davoud, Marodi, L., Meyts, I., Milner, J., Mironska, K., Mogensen, T., Morio, T., Ng, L.F.P., Notarangelo, L.D., Novelli, A., Novelli, G., O’Farrelly, C., Okada, S., Ozcelik, T., de Diego, Rebeca Perez, Planas, A.M., Prando, C., Pujol, A., Quintana-Murci, L., Renia, L., Renieri, A.,Rodríguez-Gallego, C., Sancho-Shimizu, V., Sankaran, V., Barrett, K.S., Shahrooei, Mohammed, Snow, A., Soler-Palacín, P., Spaan, A.N., Tangye, S., Turvey, S., Uddin, F., Uddin, M.J., van de Beek, D., Vazquez, S.E., Vinh, D.C., von Bernuth, H., Washington, N., Zawadzki, P., Su, H.C., Casanova, J.-L., Jing, H., Tung, W., Luthers, C.R., Bauman, B.M., Shafer, S., Zheng, L., Zhang, Z., Kubo, S., Chauvin, S.D., Meguro, K., Shaw, E., Lenardo, M., Lack, J., Karlins, E., Hupalo, D.M., Rosenberger, J., Sukumar, G., Wilkerson, M.D., Zhang, X., 2020. Inborn errors of type I IFN immunity in patients with life-threatening COVID-19. Science 370, eabd4570. 10.1126/science.abd4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhang Z., Ohto U., Shibata T., Krayukhina E., Taoka M., Yamauchi Y., Tanji H., Isobe T., Uchiyama S., Miyake K., Shimizu T. Structural Analysis reveals that toll-like receptor 7 is a dual receptor for guanosine and single-stranded RNA. Immunity. 2016;45:737–748. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J., Yang Y., Huang H., Li D., Gu D., Lu X., Zhang Z., Liu L., Liu T., Liu Y., He Y., Sun B., Wei M., Yang G., Wang X., Zhang L., Zhou X., Xing M., Wang P.G. Relationship between the ABO blood group and the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) susceptibility. Clin. Infect. Diseases. 2021;73:328–331. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng M., Karki R., Williams E.P., Yang D., Fitzpatrick E., Vogel P., Jonsson C.B., Kanneganti T.-D. TLR2 senses the SARS-CoV-2 envelope protein to produce inflammatory cytokines. Nat. Immunol. 2021;22:829–838. doi: 10.1038/s41590-021-00937-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zietz M., Zucker J., Tatonetti N.P. Associations between blood type and COVID-19 infection, intubation, and death. Nat. Commun. 2020;11:5761. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19623-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]