Fig. 2|. CCR5 regulates the temporal window of memory linking.
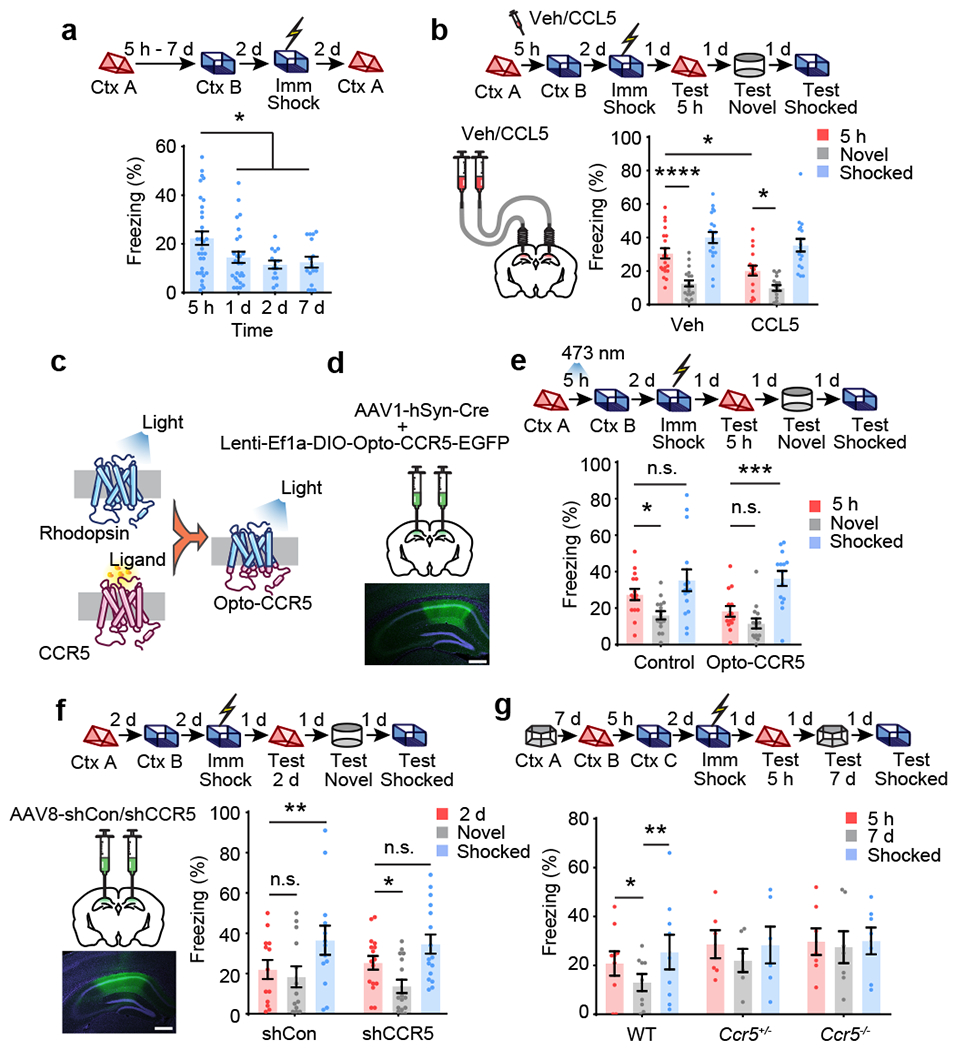
a, Characterization of the temporal window for contextual memory linking (Ctx A, Context A; Ctx B, Context B; 5h n=32, 1d n=26, 2d n=14, 7d n=16 mice; *P < 0.05, one-way ANOVA).
b, CCL5 infusion in dCA1 attenuated 5h contextual memory linking (Veh n=20, CCL5 n=17 mice; *P < 0.05, ****P <0.0001, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
c, Schematics of the Opto-CCR5 construct.
d, Schematics of viral constructs injection. Scale bar, 500 μm.
e, Optogenetic activation of neuronal CCR5 impaired 5h contextual memory linking (Control n=15, Opto-CCR5 n=14 mice; *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
f, Left: Schematics of AAV8-shCon or AAV8-shCCR5 intrahippocampal injection. Scale bar, 500 μm. Right: Ccr5 knockdown in dCA1 neurons extended the temporal window of contextual memory linking (shRNA-Con n=13, shRNA-CCR5 n=16 mice; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
g, Ccr5 knockout extended the temporal window of contextual memory linking (WT n=9, Ccr5+/− n=6, Ccr5−/− n=7 mice; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, two-way repeated measures ANOVA).
All results shown as mean ± s.e.m.
