Abstract
Background/Objectives:
Attitudes toward deprescribing could vary among subpopulations. We sought to understand patient attitudes toward deprescribing among patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
Design:
Retrospective cohort study
Setting:
Academic medical center in New York City
Participants:
Consecutive patients with HFpEF seen in July 2018-December 2019 at a program dedicated to providing care to older adults with HFpEF
Measurements:
We assessed the prevalence of vulnerabilities outlined in the domain management approach for caring for patients with heart failure and examined data on patient attitudes toward having their medicines deprescribed via the revised Patient Attitudes Toward Deprescribing (rPATD).
Results:
Among 134 patients with HFpEF, median age was 75 (interquartile range 69–82), 60.4% were women, and 35.8% were non-White. Almost all patients had polypharmacy (94.0%) and 56.0% had hyperpolypharmacy; multimorbidity (80.6%) and frailty (78.7%) were also common. Overall, 90.3% reported that they would be willing to have ≥1 of their medicines deprescribed if told it was possible by their doctors; and 26.9% reported that they would like to try stopping one of their medicines to see how they feel without it. Notably, 91.8% of patients reported that they would like to be involved in decisions about their medicines. In bivariate logistic regression, non-White participants were less likely to want to try stopping one of their medicines to see how they feel without it (OR 0.25, 95% CI [0.09–0.62], p=0.005).
Conclusions:
Patients with HFpEF contend with many vulnerabilities that could prompt consideration for deprescribing. Most patients with HFpEF were amenable to deprescribing. Race may be an important factor that impacts patient attitudes toward deprescribing.
Keywords: heart failure, polypharmacy, frailty, deprescribing
Introduction
Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) has been described as the quintessential geriatric syndrome,1 because it disproportionately impacts older adults2 and its pathophysiology is closely intertwined with aging processes.3 Moreover, polypharmacy and complex medication regimens are nearly universal in HFpEF;4,5 and conditions that impact the risk-benefit ratio of many medications, such as frailty and cognitive impairment, are highly prevalent.6 Given these vulnerabilities, adults with HFpEF have emerged as an important population for deprescribing efforts.7
Patient attitudes toward deprescribing are critical for implementing deprescribing, especially since deprescribing has been outlined as an essential part of a patient-centered approach of medication optimization.8 Patient attitudes toward deprescribing have previously been explored nationally9 demonstrating support, but attitudes could differ across specific subpopulations depending on sociodemographics, health status, and/or treatment setting. For example, in a recent qualitative study of adults with HFpEF, unique barriers to deprescribing cardiovascular medications emerged,7 suggesting that specific subpopulations might contend with unique issues that could impact patient attitudes toward deprescribing. The objective of this study was to understand attitudes toward deprescribing among patients with HFpEF referred to a specialist, and guide development of strategies for implementing deprescribing into clinical practice.
Methods
Setting:
We conducted a retrospective study of 134 consecutive patients with HFpEF seen in July 2018-December 2019 at the Weill Cornell HFpEF Program, a program dedicated to providing care to older adults with HFpEF. HFpEF was defined according to the presence of clinical characteristics of heart failure based on physician assessment with a documented left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) of at least 40% on the most recent echocardiogram within 6 months of the encounter.
This study was approved by the Weill Cornell Medicine Institutional Review Board, which waived informed consent.
Domain Management Approach:
The Weill Cornell HFpEF program routinely incorporates the domain management approach in the evaluation of all patients at their initial visit. Briefly, the domain management approach for providing care to patients with heart failure is a suggested framework put forth by the American College of Cardiology Geriatric Cardiology Section Leadership Council that outlines vulnerabilities across four domains of health: medical, mind and emotion, physical function, and social environment.6 We collected data on each of these domains.
For the medical domain, we collected data on heart failure severity, multimorbidity, and polypharmacy. To determine heart failure severity, we used New York Heart Association (NYHA) class which was abstracted from clinician notes. To determine multimorbidity, we counted the number of chronic medical conditions and defined a count of ≥5 as multimorbidity. To determine polypharmacy, we counted the number of prescribed medications, and defined a count of ≥5 as polypharmacy10,11 and ≥10 medications as hyperpolypharmacy.12
For the mind and emotion domain, we collected data on cognitive impairment, depressive symptoms, and anxiety symptoms. We defined score <3 on the Mini-Cog as cognitive impairment;13,14 defined score ≥10 on the Patient Health Questionnaire-9 (PHQ-9) as moderate-severe depressive symptoms;15 and defined score ≥10 on the General Anxiety Disorder 7-item scale (GAD-7) as moderate-severe anxiety symptoms.16
For the physical function domain, we collected data on frailty and functional impairment. We defined score <10 on the Short Physical Performance Battery (SPPB) as frail.17,18 We defined a score <6 on the Katz Index of Independence in Activities of Daily Living as functional impairment.19
For the social environment domain, we collected data on living situation. To determine if a patient was living alone, we asked how many other individuals lived in their household.
Patient Attitudes Toward Deprescribing
The revised Patient Attitudes Toward Deprescribing tool (rPATD) is a 22-question survey that assesses a patient’s attitude toward their medications and toward the potential discontinuation of a medication.20 Questions address four key domains: Burden, Appropriateness, Concerns, and Involvement; and include two additional Global questions that assess patient willingness to accept having their medicines deprescribed and overall patient satisfaction with current medications. Questions are scored on a 5-point Likert scale with the following options: “strongly agree”, “agree”, “unsure”, “disagree”, and “strongly disagree”. Notably, the rPATD does not specify any specific class of medications. To better understand attitudes towards deprescribing among patients with HFpEF, we administered the rPATD at each patient’s first clinical encounter in the Weill Cornell HFpEF program.
Domain scores are calculated by converting each response within a domain to a score of 1 to 5, summing the responses, and subsequently dividing by the number of questions in the factor to generate a score between 1 and 5.20 Questions within the burden, concerns, and involvement domains were scored as such: strongly agree=5, agree=4, unsure=3, disagree=2, and strongly disagree=1. Questions within the appropriateness domain were reverse-scored to provide a unified directionality across domains.20
Statistical Analysis:
We calculated medians with interquartile ranges for continuous variables and proportions for categorical variables. To understand factors associated with a patient’s willingness to try discontinuing ≥1 of their medications, we conducted a logistic regression that examined the bivariate association between agreeing (Strongly Agree or Agree) with the statement “I would like to try stopping one of my medicines to see how I feel without it” and the following covariates: socio-demographics (age, sex, race, household income, and education), self-reported health (from the first question of the SF-12), and vulnerabilities from the domain management approach. Given low degree of missingness, we conducted a complete case analysis. All analyses were conducted using R-version 3.6.0. A p-value of <0.05 was required for statistical significance.
Results
Median age was 75 years (IQR 69–82); 53.7% were ≥75 years, 60.4% were women, and 35.8% were non-White (Table 1). For self-reported health, 38.1% of patients described their health as “excellent”, “very good”, or “good”; 35.8% described their health as “fair”; and 26.1% described their health as “poor”. Overall, 53.7% of the patients were classified as NYHA Class III-IV (Table 1).
Table 1.
Participant Characteristics and Domain Vulnerabilities
| Participant Characteristic | Value |
|---|---|
| Age, median (IQR) | 75 (69–82) |
| Age ≥ 75, n (%) | 72/134 (53.7) |
| Sex Male, n (%) | 53/134 (39.6) |
| Race Non-White, n (%) | 48/134 (35.8) |
| Household Income | |
| <$35,000, n (%) | 62/134 (46.3) |
| ≥$35,000, n (%) | 48/134 (35.8) |
| Missing, n (%) | 24/134 (17.9) |
| Education < High School, n (%) | 21/133 (15.8) |
| Self-Reported Health per SF-12 | |
| Excellent/Very Good/Good, n (%) | 51/134 (38.1) |
| Fair, n (%) | 48/134 (35.8) |
| Poor, n (%) | 35/134 (26.1) |
| Medical Domain | |
| NYHA Class III or IV, n (%) | 72/134 (53.7) |
| Number of comorbidities, median (IQR) | 7 (5–9) |
| ≥ 5 comorbidities, n (%) | 108/134 (80.6) |
| Number of regular medications, median (IQR) | 10 (4, 16) |
| Polypharmacy, n (%) | 126/134 (94.0) |
| Hyperpolypharmacy, n (%) | 75/134 (56.0) |
| Mind and Emotion Domain | |
| Cognitive Impairment, n (%) | 28/126 (22.2) |
| Depression Symptoms, n (%) | 33/134 (24.6) |
| Anxiety Symptoms, n (%) | 21/134 (15.7) |
| Physical Function Domain | |
| Frail, n (%) | 96/122 (78.7) |
| Functional Impairment, n (%) | 17/134 (12.7) |
| Social Environment Domain | |
| Lives Alone, n (%) | 30/134 (22.4) |
Abbreviations: SF-12 – 12-Item Short Form Survey; NYHA - New York Heart Association.
All patients had ≥1 domain vulnerability. Within the medical domain, 94.0% had ≥1 vulnerability (80.6% had multimorbidity, 94.0% had polypharmacy and 56.0% had hyperpolypharmacy). Among the mind and emotion domain, 41.8% had ≥1 vulnerability (22.2% had cognitive impairment, 24.6% had moderate-severe depressive symptoms, and 15.7% had moderate-severe anxiety symptoms). Within the physical function domain, 82.1% had ≥1 vulnerability (78.7% had frailty and 12.6% had functional impairment). Among the social environment domain, 22.4% lived alone.
Overall, 68.7% were satisfied with their current medications. However, 90.3% were willing to discontinue ≥1 medicines if told it was possible by their doctors (Figure 1). The factor score was 2.8/5 for the burden domain, 3.4/5 for the appropriateness domain, 2/5 for the concerns domain, and 4/5 for the involvement domain—higher values indicate higher perceived reported burden related to medications, belief in appropriateness of medications, concerns about stopping medications, and desire for involvement in medication management. Within the burden domain, 69.4% felt they were taking a large amount of medicines, but only 22.3% felt that their current medicines were a burden. Within the appropriateness domain, 26.9% reported that they would like to try stopping one of their medicines to see how they feel without it. Regarding the involvement domain, 91.8% reported that they would like to be involved in decisions about their medicines.
Figure 1: Participant Responses to the rPATD.
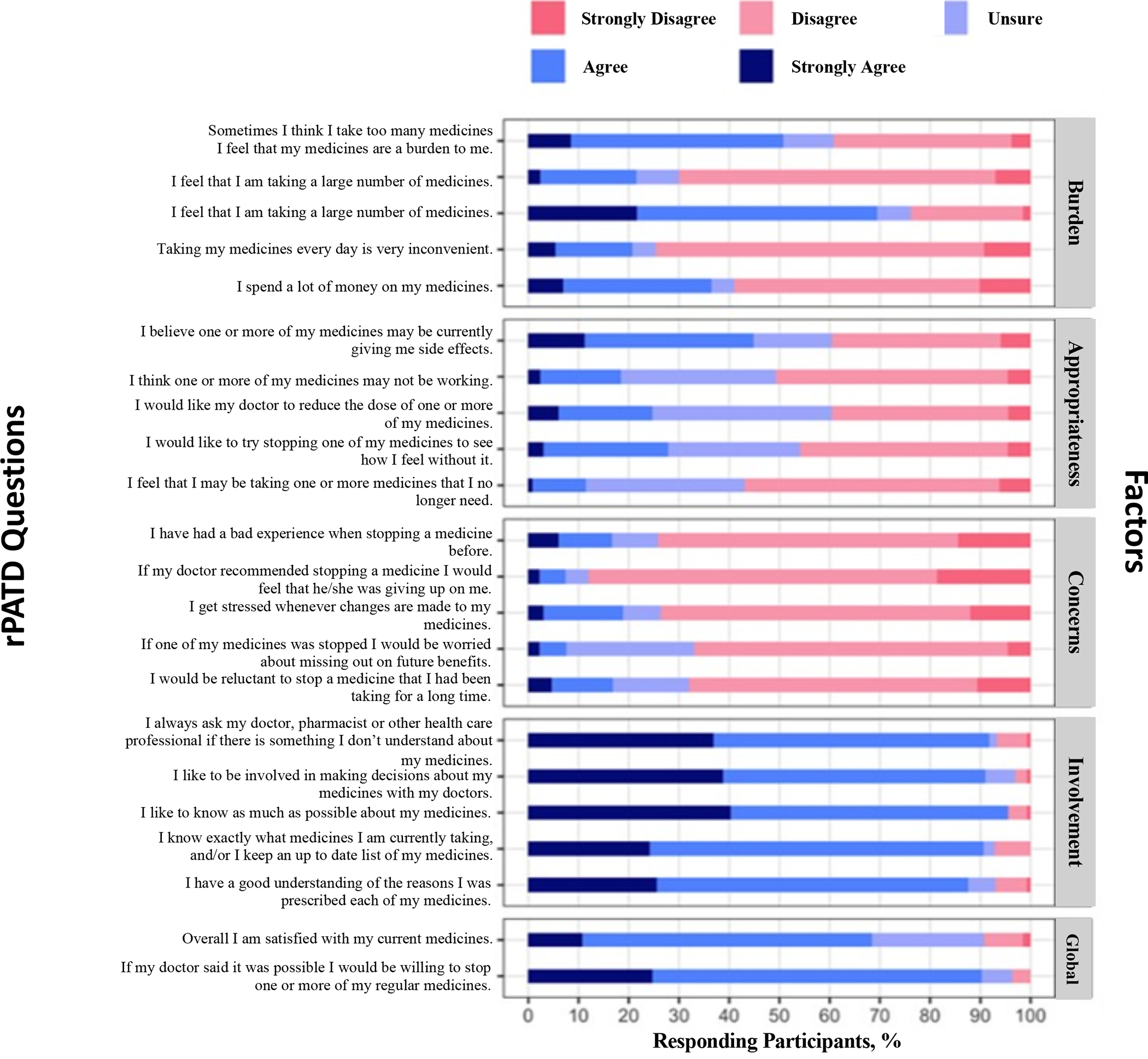
The distribution of responses to the revised Patients’ Attitudes Towards Deprescribing (rPATD) Questionnaire are shown. Questions are grouped into Burden, Appropriateness, Concerns, and Involvement; and there are two Global questions. Abbreviations: rPATD - Revised Patients’ Attitudes Towards Deprescribing.
In bivariate logistic regression, we found that patients who identified as non-White were less likely to want to try stopping one of their medicines to see how they feel without it (OR 0.25, 95% CI 0.09–0.62, p-value 0.005) (Table 2). None of the vulnerabilities from the domain management approach were statistically significant for an association.
Table 2.
Factors Associated with Patient Willingness to Try Deprescribing
| Characteristic | OR (95% CI) | P value |
|---|---|---|
| Age ≥ 75 | 0.77 (0.36–1.65) | 0.50 |
| Sex - Male | 0.89 (0.40–1.92) | 0.77 |
| Race Non-White | 0.25 (0.09–0.62) | 0.005 |
| Household Income < $35,000 | 0.68 (0.29–1.59) | 0.37 |
| Education < High School | 0.77 (0.24–2.16) | 0.64 |
| Self-Reported Health per SF-12 | ||
| Excellent/Very Good/Good | Reference | |
| Fair | 1.18 (0.47–2.95) | 0.73 |
| Poor | 1.65 (0.63–4.33) | 0.30 |
| Medical Domain | ||
| NYHA Class III or IV | 1.08 (0.50–2.35) | 0.85 |
| ≥ 5 comorbidities | 0.79 (0.31–2.11) | 0.62 |
| Hyperpolypharmacy | 0.68 (0.31–1.45) | 0.32 |
| Mind and Emotion Domain | ||
| Cognitive Impairment | 0.64 (0.22–1.66) | 0.38 |
| Depression Symptoms | 1.18 (0.48–2.74) | 0.71 |
| Anxiety Symptoms | 1.05 (0.35–2.83) | 0.93 |
| Physical Function Domain | ||
| Frail | 0.85 (0.34–2.28) | 0.73 |
| Functional Impairment | 0.52 (0.11–1.71) | 0.32 |
| Social Environment Domain | ||
| Lives Alone | 2.23 (0.93–5.29) | 0.07 |
Abbreviations: OR - odds ratio; CI - confidence interval; SF-12 – 12-Item Short Form Survey; NYHA - New York Heart Association.
Discussion
Our study demonstrated that patients with HFpEF universally contend with vulnerabilities that may be relevant for deprescribing. In a prior survey of geriatric cardiologists, vulnerabilities across medical, mind and emotion, physical, and social domains were cited as important factors when considering optimal prescribing practices.21 This supports the need to better delineate the role of deprescribing in HFpEF.
Patient reluctance has been reported as an important barrier to deprescribing cardiovascular medications.22 Our study now shows that the vast majority (90%) of patients with HFpEF are willing to have their medicines deprescribed if told it was possible by their doctor. This is consistent with a recent survey of Medicare beneficiaries in the United States with lower comorbidity and medication burden than patients in this study;9 and supports the concept that even patients with a severe debilitating cardiovascular condition referred to a cardiovascular subspecialist are amenable to having their medicines deprescribed. Beta-blockers have been suggested as a potential target for deprescribing 7,23,24 given limited data supporting its benefits25,26 and potential for harm.27 However, there are many barriers to deprescribing cardiovascular medications that remain on both the patient- and physician-level.7,22 As outlined in a recent publication from the American College of Cardiology Geriatric Cardiology Section Leadership Council, future work will be necessary to better incorporate deprescribing into the cardiovascular clinicians’ armamentarium of strategies for improving outcomes.28
The majority of patients in this study reported general satisfaction with their medications. Compared to two prior studies exploring attitudes towards having their medicines deprescribed from Switzerland29 and Australia30, our study population had similar factor scores across all 4 domains. Despite most reporting that they believed that they were taking a large amount of medications, less than a quarter reported that their current medications were a burden. This observation adds to a growing body of literature showing that patients often have mixed feelings about deprescribing. For example, in a study of patients with HFpEF, participants reported that they did not like taking so many medications, but they were uncomfortable with stopping them.7 Contributors to these inconsistencies are not yet fully understood. Prior work has shown that patients may not understand that risks and potential benefits of a given medication can change over time.31,32 Consequently, patients may not appreciate the value of the deprescribing process and may not understand that deprescribing is meant as a strategy to improve outcomes. Coupled with our finding that the vast majority of patients wish to be involved in decisions about their medications, our study supports the need to develop strategies that can facilitate patient-physician communication regarding medication regimen.22
Given the complexity of patient attitudes toward deprescribing, we sought to examine whether factors related to demographics, self-reported health, or domain vulnerabilities were associated with patients’ desires to have their medications deprescribed. In a simple bivariate analysis, we found that non-White patients were less likely to want to try stopping one of their medicines to see how they feel without it. This observation was in contradistinction to the lack of association with any of the domain vulnerabilities, and suggests that non-clinical factors may be playing an important role in patient attitudes toward deprescribing. Our findings corroborate a prior study of Medicare beneficiaries, which similarly showed that non-White participants were less likely to agree with the statement “I would like to reduce the number of medicines I am taking.”9 Trust between the patient and physician has been identified as an important facilitator to deprescribing.33 Prior work has shown variation in the degree of trust that patients of different races have in the healthcare system.34 Future work should examine whether interventions that build trust between the patient and physician can modify attitudes toward deprescribing.
Strengths of this study include use of the domain management approach to comprehensively characterize a study population with a high burden of comorbidities and polypharmacy; and the routine administration of the rPATD. There are also some important limitations to this study that should be considered. The data was derived from a single institution, which may impact generalizability. Additionally, patients were seen at a specialized HFpEF Program, which may represent a selected subpopulation. There are other elements beyond living alone that may represent important limitations in the social domain, such as access to transportation and health insurance status, which future studies should examine. The rPATD does not itself specify attitudes towards different medication classes. From these data, it is not possible to know whether patients responded to rPATD items with all medicines in mind or whether they may have focused on cardiac medicines given the cardiac clinic setting. Finally, the small sample size precluded a multivariable analysis. Future analyses incorporating larger sample sizes and/or qualitative study design are needed to better understand the role of non-clinical factors on patient attitudes toward deprescribing
Conclusion
Patients with HFpEF contend with myriad vulnerabilities that are important to consider when making decisions about medications. While a majority of patients in this study did not report that they wanted to stop their medications, most would be amenable to having their medicines deprescribed if prompted by their physician. This supports the need for strategies to facilitate discussion about deprescribing among patients with HFpEF and their physicians. Finally, our findings suggest that race could be an important factor impacting patient attitudes toward deprescribing, and thus warrants further investigation.
Key Points:
Patients with HFpEF contend with many vulnerabilities that could prompt consideration for deprescribing.
Most patients with HFpEF are amenable to deprescribing if prompted by their physician.
Race may be an important factor that impacts patient attitudes toward deprescribing.
This work demonstrates that patients with HFpEF contend with a high degree of medical comorbidities and polypharmacy, and are amenable to deprescribing even when referred to a specialist.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge Yunyue Zhang, Yinuo Liu, and Yiwen Wang (Masters Students from the Weill Cornell Medicine Department of Population Health Sciences) for their assistance with data management and statistical analysis.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: Dr. Goyal reports personal fees for medico-legal consulting in heart failure.
References
- 1.Upadhya B, Taffet GE, Cheng CP, Kitzman DW. Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction in the elderly: scope of the problem. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2015;83:73–87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Goyal P, Almarzooq ZI, Horn EM, et al. Characteristics of Hospitalizations for Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Am J Med. 2016;129(6):635 e615–626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Paulus WJ, Tschope C. A novel paradigm for heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: comorbidities drive myocardial dysfunction and remodeling through coronary microvascular endothelial inflammation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013;62(4):263–271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Brinker LM, Konerman MC, Navid P, et al. Complex and Potentially Harmful Medication Patterns in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. Am J Med. 2020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Unlu O, Levitan EB, Reshetnyak E, et al. Polypharmacy in Older Adults Hospitalized for Heart Failure. Circulation Heart failure. 2020:Circheartfailure120006977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Gorodeski EZ, Goyal P, Hummel SL, et al. Domain Management Approach to Heart Failure in the Geriatric Patient: Present and Future. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2018;71(17):1921–1936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Goyal P, Requijo T, Siceloff B, et al. Patient-Reported Barriers and Facilitators to Deprescribing Cardiovascular Medications. Drugs & aging. 2020;37(2):125–135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Scott IA, Hilmer SN, Reeve E, et al. Reducing inappropriate polypharmacy: the process of deprescribing. JAMA Intern Med. 2015;175(5):827–834. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Reeve E, Wolff JL, Skehan M, Bayliss EA, Hilmer SN, Boyd CM. Assessment of Attitudes Toward Deprescribing in Older Medicare Beneficiaries in the United States. JAMA Internal Medicine. 2018;178(12):1673–1680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Masnoon N, Shakib S, Kalisch-Ellett L, Caughey GE. What is polypharmacy? A systematic review of definitions. BMC Geriatr. 2017;17(1):230–230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Blyth FM, et al. Polypharmacy cutoff and outcomes: five or more medicines were used to identify community-dwelling older men at risk of different adverse outcomes. J Clin Epidemiol. 2012;65(9):989–995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Gnjidic D, Hilmer SN, Blyth FM, et al. High-Risk Prescribing and Incidence of Frailty Among Older Community-Dwelling Men. 2012;91(3):521–528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Borson S, Scanlan J, Brush M, Vitaliano P, Dokmak A. The mini-cog: a cognitive ‘vital signs’ measure for dementia screening in multi-lingual elderly. International journal of geriatric psychiatry. 2000;15(11):1021–1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Borson S, Scanlan JM, Chen P, Ganguli M. The Mini-Cog as a screen for dementia: validation in a population-based sample. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2003;51(10):1451–1454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB. The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med. 2001;16(9):606–613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Spitzer RL, Kroenke K, Williams JBW, Löwe B. A Brief Measure for Assessing Generalized Anxiety Disorder: The GAD-7. Archives of Internal Medicine. 2006;166(10):1092–1097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Guralnik JM, Simonsick EM, Ferrucci L, et al. A short physical performance battery assessing lower extremity function: association with self-reported disability and prediction of mortality and nursing home admission. Journal of gerontology. 1994;49(2):M85–94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Pavasini R, Guralnik J, Brown JC, et al. Short Physical Performance Battery and all-cause mortality: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Medicine. 2016;14(1):215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wallace M, Shelkey M. Reliability and Validity of Katz ADL Index. 2008;108(4). [Google Scholar]
- 20.Reeve E, Low LF, Shakib S, Hilmer SN. Development and Validation of the Revised Patients’ Attitudes Towards Deprescribing (rPATD) Questionnaire: Versions for Older Adults and Caregivers. Drugs Aging. 2016;33(12):913–928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Goyal P, Gorodeski EZ, Flint KM, et al. Perspectives on Implementing a Multidomain Approach to Caring for Older Adults With Heart Failure. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(12):2593–2599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Goyal P, Anderson TS, Bernacki GM, et al. Physician Perspectives on Deprescribing Cardiovascular Medications for Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2020;68(1):78–86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Yum B, Archambault A, Levitan EB, et al. Indications for beta-Blocker Prescriptions in Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2019;67(7):1461–1466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Meyer M, LeWinter MM. Heart Rate and Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction: Time to Slow beta-Blocker Use? Circ Heart Fail. 2019;12(8):e006213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Yamamoto K, Origasa H, Hori M, Investigators JD. Effects of carvedilol on heart failure with preserved ejection fraction: the Japanese Diastolic Heart Failure Study (J-DHF). Eur J Heart Fail. 2013;15(1):110–118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Cleland JGF, Bunting KV, Flather MD, et al. Beta-blockers for heart failure with reduced, mid-range, and preserved ejection fraction: an individual patient-level analysis of double-blind randomized trials. Eur Heart J. 2018;39(1):26–35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Silverman DN, Plante TB, Infeld M, et al. Association of beta-Blocker Use With Heart Failure Hospitalizations and Cardiovascular Disease Mortality Among Patients With Heart Failure With a Preserved Ejection Fraction: A Secondary Analysis of the TOPCAT Trial. JAMA Netw Open. 2019;2(12):e1916598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Krishnaswami A, Steinman MA, Goyal P, et al. Deprescribing in Older Adults With Cardiovascular Disease. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2019;73(20):2584–2595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Achterhof AB, Rozsnyai Z, Reeve E, et al. Potentially inappropriate medication and attitudes of older adults towards deprescribing. PLoS One. 2020;15(10):e0240463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Reeve E, Low LF, Hilmer SN. Attitudes of Older Adults and Caregivers in Australia toward Deprescribing. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2019;67(6):1204–1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Reeve E, To J, Hendrix I, Shakib S, Roberts MS, Wiese MD. Patient Barriers to and Enablers of Deprescribing: a Systematic Review. Drugs Aging. 2013;30(10):793–807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Anderson K, Stowasser D, Freeman C, Scott I. Prescriber barriers and enablers to minimising potentially inappropriate medications in adults: a systematic review and thematic synthesis. BMJ Open. 2014;4(12):e006544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Reeve E, Wiese MD, Hendrix I, Roberts MS, Shakib S. People’s attitudes, beliefs, and experiences regarding polypharmacy and willingness to Deprescribe. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society. 2013;61(9):1508–1514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Boulware LE, Cooper LA, Ratner LE, LaVeist TA, Powe NR. Race and trust in the health care system. Public Health Rep. 2003;118(4):358–365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


