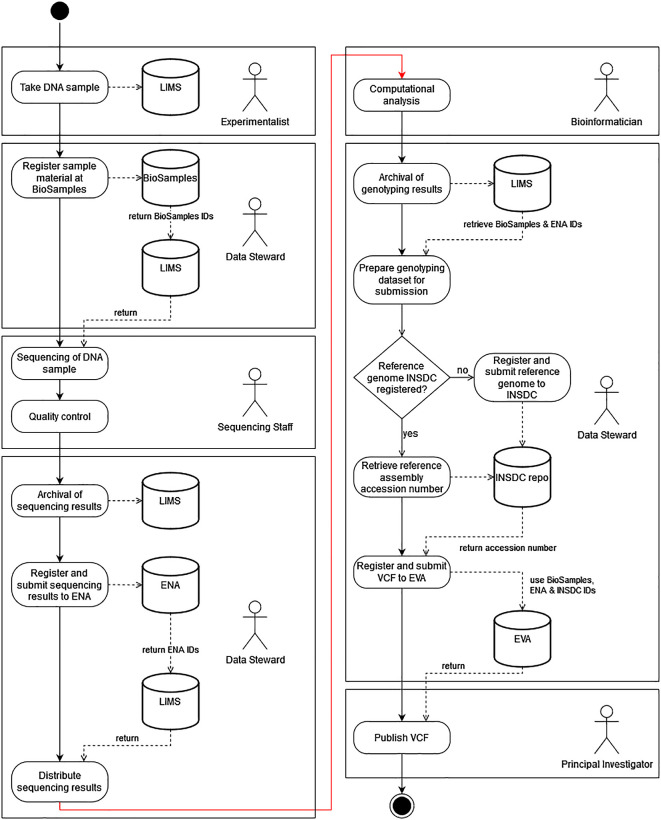
Figure 2. The recommended workflow for the submission of genotypic data to public EMBL-EBI databases.
DNA samples are collected by an Experimentalist and their metadata are stored in a Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS). The Data Steward then registers these samples with BioSamples and in return receives unique BioSamples IDs back, which the Data Steward adds to the created samples in the LIMS. The sequencing and quality control of these samples is then carried out by the Sequencing Staff and the primary sequence data is fed into the LIMS and linked to the sample data by the Data Steward. The sequencing results are then registered and submitted to the European Nucleotide Archive (ENA) using the BioSamples IDs to link the initially submitted samples to the generated sequencing reads. The study identifiers (ENA IDs) are assigned by ENA and added to the samples by the Data Steward in LIMS. The Bioinformatician then analyses the data and produces the genotyping results. Afterwards, the Data Steward prepares these data for transmission by linking them to the already created sample data from the LIMS and extracting the required metadata and adding it to the header of the Variant Call Format (VCF) file. If the reference genome used for genotyping is not yet available in public repositories, it will now be transferred by the Data Steward to one of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration (INSDC) databases. Otherwise, the metadata-enriched VCF file can be registered and submitted to the European Variation Archive (EVA). The identifiers assigned by EVA are then transmitted back and the Principal Investigator can approve the publication of the data.