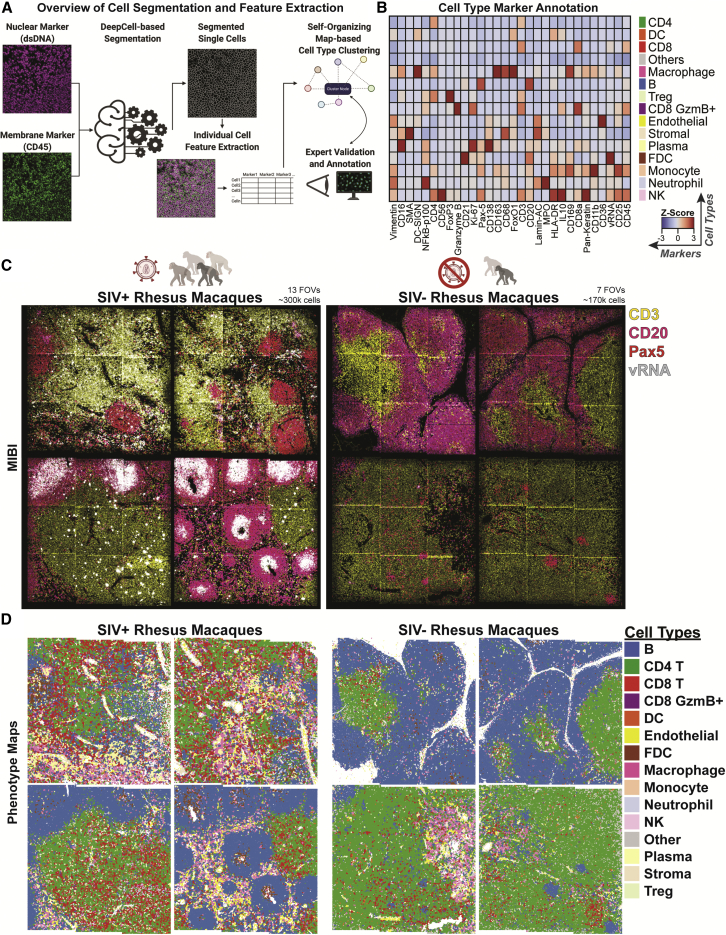
Figure 2.
Unsupervised computation methods for rapid feature extraction and phenotypic identification from multiplexed imaging data
(A) An overview of the deep learning-enabled segmentation, feature extraction, and self-organizing map-based cell type clustering and annotation used in this study.
(B) A heatmap depicting the Z scores of marker expression and cell types identified in all FOVs.
(C) Representative FOVs of tissues from SIV-infected and control animals pseudocolored to show regions enriched in B and T cells and in SIV vRNA. Each FOV is 1.2 × 1.2 mm, with 20 FOVs acquired across four SIV-infected and two SIV-uninfected rhesus macaques to generate ∼470,000 spatially resolved cells.
(D) Individual cells from the representative FOVs in (C) colored by their cellular phenotypes.
See also Figure S2.