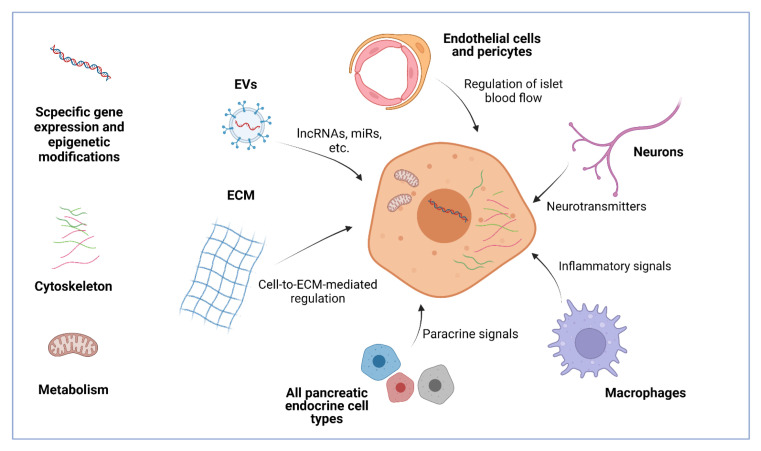
Figure 2.
The microenvironment of beta cells includes many components such as pancreatic islet endocrine cells, endothelial cells, pericytes, neurons, macrophages, the extracellular matrix (ECM), and EVs (extracellular vesicles). All of them send different signals to beta cells, affecting their viability, proliferation, gene expression, and functions such as GSIS. These effects can be both negative and positive. Intracellular regulatory signals include genetic and epigenetic cues, cytoskeleton, and metabolic states. By intensifying some regulators and blocking others, it is possible to promote maturation, GSIS, and graft survival, which are all crucial for stem cell therapy of diabetes. LncRNAs-long non-coding RNAs; miRs-microRNAs. Created with BioRender.com.