Chougule P, Herlenius G, Hernandez NM, Patil PB, Xu B, Sumitran-Holgersson S. Isolation and characterization of human primary enterocytes from small intestine using a novel method. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 2012;47:1334–1343. http://dx.doi.org/10.3109/10.3109/00365521.2012.708940
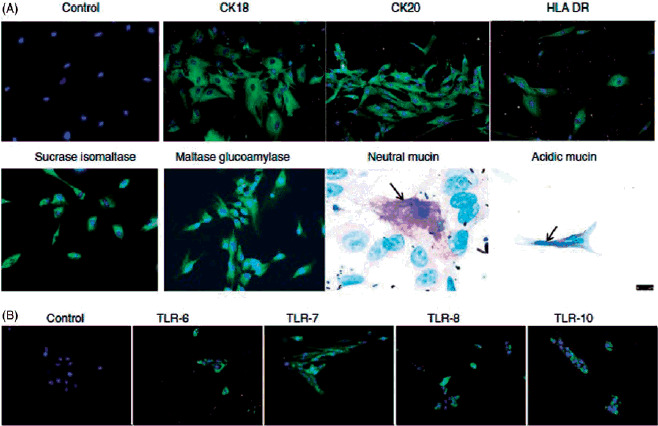
When the above article was first published, incorrect image files were provided for Figure 3. Please see the original and revised images below:
Figure 3:
Original:
Revised:
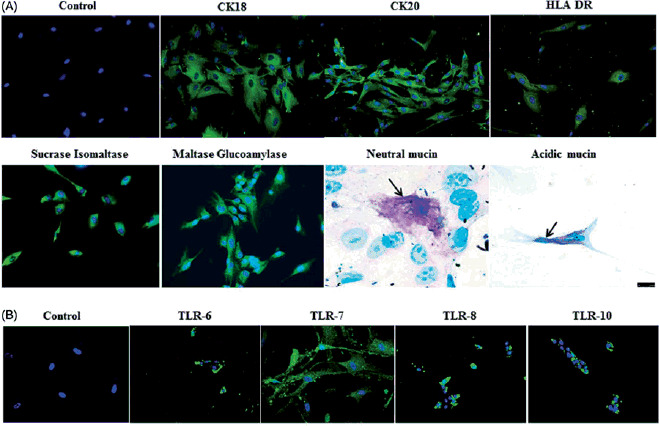
Figure caption:
Immunocytochemical staining of isolated human enterocytes for epithelial markers. (A) Top panel: isolated and cultured human EpCAM cells stained positive for cytokeratins 18, 20 and on activation with IFN-g also expressed HLA-DR. Bottom panel: enterocyte-specific markers such as maltase glucoamylase and sucrose isomaltase were also found to be expressed by the cells. Staining for mucins showed the presence of few secretory epithelial cells – goblet cells which stained pink/magenta, or blue indicating the presence of neutral and acidic mucins. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of human enterocytes with antibodies to Toll-like receptors (TLRs) showed that these cells expressed TLR-6, -7, -8 and -10, thus confirming our FACS results. Magnification 20×, neutral mucin and acidic mucin 60×.


