Abstract
We investigate the impact of the DC current-induced Ampère–Oersted field on the dynamics of a vortex based spin-torque nano-oscillator. In this study we compare micromagnetic simulations performed using mumax and our analytical model based on the Thiele equation approach. The latter is improved by adding two important corrections to the Thiele equation approach. The first is related to the magneto-static contribution and depends on the aspect ratio of the magnetic dot. The second is a full analytical description of the Ampère–Oersted field contribution. The model describes quantitatively the simulation results in the resonant regime as well as the impact of the Ampère–Oersted field. Depending on the relative orientation between the vortex in-plane curling magnetisation (chirality) and the Ampère–Oersted field a strong splitting phenomenon appears in the fundamental properties (frequency and vortex core position) of the nano-oscillator. Thus, we show that the Ampère–Oersted field should not be neglected as it has a high impact on the spin-torque vortex oscillator dynamics.
Subject terms: Condensed-matter physics, Spintronics
Introduction
Most of the studies on spin-torque vortex oscillators (STVOs) neglect the Ampère–Oersted field (AOF) induced by the injected current (DC and/or AC)1–5. Moreover, it has also been shown that the AOF has an impact on the magnetisation dynamics of nanopillars6 as well as on the spin wave dynamics of spin-torque oscillators7. As far as the STVOs are concerned, the present study clearly shows that this contribution is not negligible and most importantly, is not avoidable by any means as it originates from the injected current responsible for the oscillatory excitation. Depending on the orientation of the polariser, the contributions arising from spin-transfer torque (STT)8 are different. To generate sustained oscillations thanks to the injected current, a DC and/or AC current is needed for a polariser with a perpendicular component. Whereas, for a polariser with a planar component, an AC current is required as oscillations are driven by the field-like torque (FLT)9 contribution in that case. For the sake of clarity, we choose to work with a perpendicular polariser and a DC current only.
Two improvements to the commonly used Thiele equation approach10 (TEA) are considered here. The first is related to the magneto-static contribution to the vortex energy as described by Gaididei et al.1. As the energy is highly dependent on the magnetic dot aspect ratio (with h the thickness of the free-layer and R the dot radius) a significant correction of this contribution when is different from zero has to be considered. The second contribution to the Thiele equation approach is an analytical description of the AOF to the potential energy that has been already considered by Khvalkovskiy et al.11 and Dussaux et al.12. The latter studies report this contribution for a limited displacement of the vortex core reduced position (). The version we propose in this manuscript is accurate for the whole range of validity of the vortex core position in a circular dot, i.e., . The analytical model for the AOF contribution has already been successfully used in a previous study13. For , the vortex core is expelled from the magnetic dot, or the vortex reaches a critical velocity that induces a polarity switch and the core damps back to the dot centre14,15. In some cases, when the vortex core is expelled, a dynamic C-like state may also be stabilised and gives rise to sustained oscillations as shown by Wittrock et al.16.
Methods
Micromagnetic simulations including the Ampère–Oersted field (, see Fig. 1) using mumax are performed17. The magnetic dot, i.e., the free layer of the magnetic tunnel junction (MTJ), under study has a radius R of 100 nm and a thickness h of 10 nm. The spacer is a tunnel barrier, typically MgO, and the polariser is a fixed polarised layer, with a unit vector polarisation , clamped by a synthetic antiferromagnet (SAF).
Figure 1.
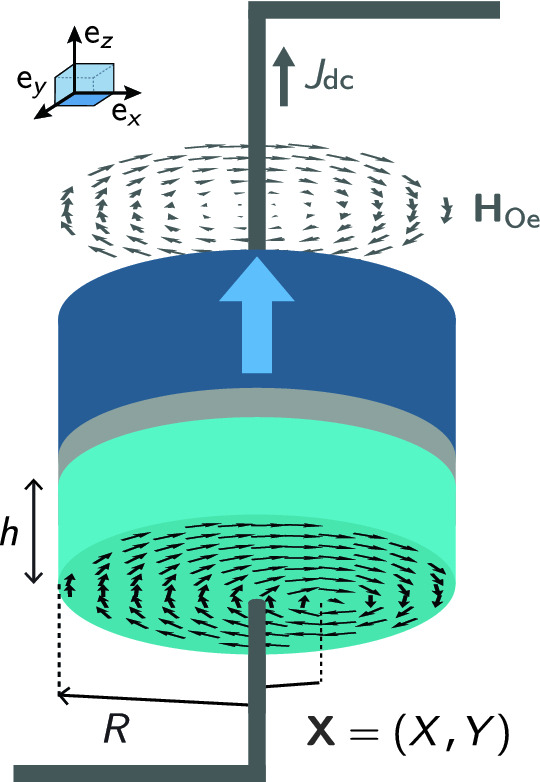
Illustration of the magnetic tunnel junction under study. The MTJ is a standard Py/MgO/SAF stack with a free permalloy (Py) layer dot, a nonmagnetic spacer (typically MgO), and a synthetic antiferromagnet (SAF) polariser that generates a perpendicular spin polarisation . In this illustration, the Ampère–Oersted field is parallel to the dot in-plane magnetisation (chirality ).
To perform the micromagnetic simulations, the magnetic dot is subdivided into 2.5 by 2.5 nm squares in the xy-plane and two layers of 5 nm thickness each. This ensures that the micromagnetic cell dimensions are smaller than the characteristic exchange length for permalloy (about 5 nm). Without any external excitation, the magnetic ground state of such a dot is the so-called magnetic vortex. Typical material parameters for permalloy are used. For instance, the saturation magnetisation considered is emu/cm and the exchange stiffness constant is erg/cm. The Gilbert damping constant is fixed at . The magneto-crystalline anisotropy is neglected. The DC current density injected in the MTJ under study ranges from 0 to 10 MA/cm, in the positive z-direction. The spin-current polarisation of the junction is chosen to be .
The vortex core position is initially slightly off-centred and is internally computed by mumax while the frequency is extracted with a very accurate technique called “simple numerical instantaneous frequency approximation” (SNIFA)18 developed for that purpose. The current induced AOF is added to mumax as an external magnetic field as there is no built-in implementation. The micromagnetic simulations are performed for a sufficient duration ( to 3000 ns) to avoid to consider the transient regime. Furthermore, no bias external magnetic field is applied and the temperature is K.
There are three different configurations studied in order to quantify the impact of the Ampère–Oersted field on the vortex dynamics for a vortex polarity :
without the Ampère–Oersted field () contribution,
with the parallel to the dot in-plane magnetisation (chirality ),
with the anti-parallel to the dot in-plane magnetisation (chirality ).
The first case will be referred to later on in the text with the label “”, the second with the label “”, and the third with the label “”.
In order to understand the physics of the STVO dynamics, the Thiele equation approach is used10. In this approach, the vortex core is considered as a quasi-particle and is represented by its in-plane position inside the magnetic dot. Thus, the STVO dynamics can be described by:
| 1 |
where 19,20, with Oes the gyromagnetic ratio with g the electron spin g-factor, e the electron charge and the electron mass, with 11, and which are the three contributions of the energy. The restoring forces are expressed using their spring-like restoring force constants:
| 2 |
Three contributions are taken into account. The first one is related to the exchange energy and writes as follows1,19:
| 3 |
The second contribution is related to the Ampère–Oersted field and has been calculated under the two vortex ansatz (TVA). The following analytical expression is obtained (see the Supplementary material for details):
| 4 |
Finally, to enhance the precision of the model, a third contribution is considered. Indeed, a correction to the contribution of the magneto-static energy is made. The latter has been calculated by Gaididei et al.1 under the two vortex ansatz and gives which is the magneto-static energy for a given aspect ratio and reduced vortex position s. There exists an analytical solution1 for but only when and .
In this study, , thus, a different method is used instead (see Supplementary material). Let us note that this method is applicable to any , including . First, a Monte Carlo (MC) integration technique (non-deterministic) is used to obtain values of for a given and for s ranging between 0 and 1. Then is fitted with a power law and the resulting expression is derived. As a result, the contribution of the magneto-static energy for a given aspect ratio of the magnetic dot can be modelled as:
| 5 |
The coefficients and given for and are reported in the Supplementary material. For , which is in good agreement with the analytical results by Guslienko et al.20 with (diff. less than 0.2%). To simplify, is replaced by in the rest of the manuscript.
The spin-transfer torque component is composed of three terms: . The first two terms are respectively the perpendicular and parallel contribution of the Slonczewski spin-torque8 while the third one is the Zhang & Li field-like-torque (FLT)9.
In this study, a perpendicular polariser, i.e., , is used, as already investigated by Ivanov and Zaspel21 within TEA. So, (, proportional to in this case12) and () are equal to zero and only the contributes to the dynamics. , where with ,11, and = 800 emu/cm.
From Eq.(1) one can rewrite the STVO dynamics as:
| 6 |
where . This equation can be reduced to a homogeneous system of linear first-order differential equations:
| 7 |
where the parameters and are given as follows:
| 8 |
| 9 |
This shows that the dynamics of our STVO is described by the simple harmonic oscillator equation: . Considering and as being constant one can prove that the solution of this system writes:
| 10 |
In general and are not constant, but in the steady-state oscillating regime they effectively are. Important properties of the STVO can be derived from this regime of oscillation.
From the first parameter, i.e., , it is straightforward to identify the vortex gyrotropic frequency of oscillation as . The second parameter, i.e., , is responsible for the transient regime. When , the transient dynamics is in the damping regime leading to giving rise to the resonant regime. When , the transient dynamics is in the driving regime () and leads to the steady-state oscillating regime where and s becomes constant. The first critical current can thus be analytically defined by the limit when and . Mathematically this condition translates to:
| 11 |
The critical current is thus given by the following expression:
| 12 |
The corrections allow having a model valid for s up to 0.8 which is the limit of the vortex existence. As mentioned already, for the vortex becomes unstable and switches polarity in this case, i.e., for . The vortex core position s depends on the current density . Thus, one can define a second critical current which represents the current density above which the vortex core polarity switches. Once the vortex switches polarity, the model well describes the dynamics of the STVO providing the opposite polarity (damping regime). Thus, the critical current establishes the limit between the steady-state oscillating regime and the second resonant regime due to the reversal of the core polarity.
To summarise, there are two resonant regimes () and one steady-state regime (in-plane gyrotropic oscillation of the vortex core with ). To be in the steady-state oscillating regime, two conditions need to be fulfilled: and . For both resonant regimes, at least one of these conditions is not satisfied and the existence of the second critical current originates from the fact that when then and the vortex core switches polarity so that the first condition is not fulfilled anymore. Corrections to the other terms (s-dependence of G and D for instance) are being considered under a data-driven approach and will be discussed in a future communication.
Discussion
The critical current and the vortex gyrotropic frequency given by the analytical model and micromagnetic simulations are compared. The critical current is extracted from the micromagnetic simulations by the following method. First, the reduced vortex core position s is plotted as a function of the current density (see Fig. 2b). Then, the points for (i.e., when the steady-state is reached and before reaching the limits of vortex stability) are fitted after an interpolation which increases the fit precision. The function used for the fit is (see Fig. 2b). The critical current is the value of the fit when and is strongly impacted by the AOF. Indeed, depends on the chirality as previously shown by Dussaux et al.12 and one can see that . The critical current , for both chiralities, is very close to the values determined by the TEA as shown in Table 1. The ratio between the critical currents and is about 1.5 as also reported by Guslienko et al.22 and detailed in Table 1.
Figure 2.
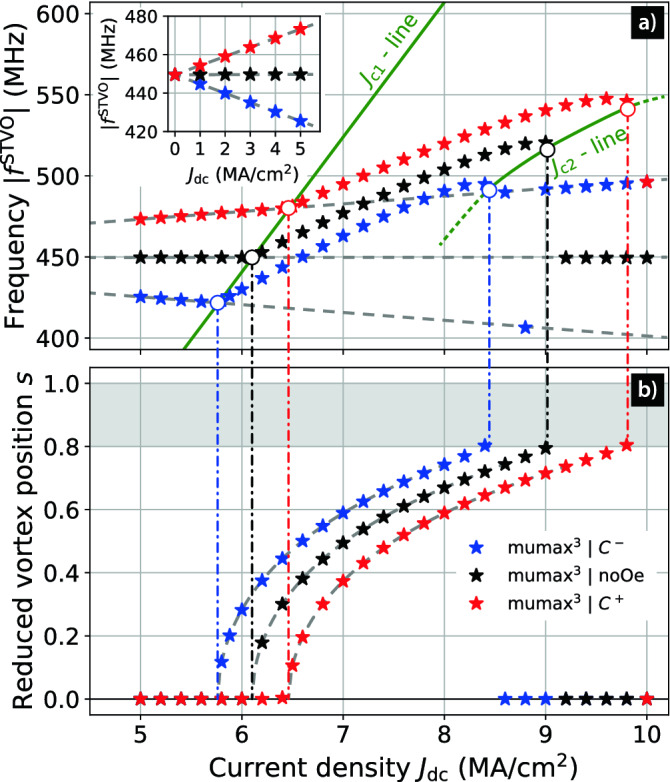
Vortex dynamical properties vs. DC current excitation. (a) The absolute values of the vortex gyrotropic frequency and (b) the vortex reduced position s as a function of the DC current density . The colours black, red and blue correspond to simulations without AOF (), with AOF and () and with AOF and (), respectively. The frequency is fitted with a linear function of in the first resonant regime () for each configuration. The resulting fits are plotted with grey dashed lines. The critical current is extracted from and gives rise to the first green -line. The -line represents the transition between the first resonant regime and the steady-state oscillating regime. The -line links the points originating from the micromagnetic data and is also well approximated by the analytical counterpart . The and values are plotted across both sub-figures by corresponding dash-dotted lines. The -line represents the transition from the steady-state oscillating regime to the second resonant regime as for , the vortex core polarity switches from to and becomes positive.
Table 1.
Comparison of and given by Eq. (12) under TEA and micromagnetic simulations (MMS) after fitting the J-dependence of s (see Fig. 2b) for the different relative orientations of the AOF and the in-plane magnetisation.
| noOe | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| (MA/cm) | 6.88 | 6.45 | 6.08 |
| (MA/cm) | 6.47 | 6.11 | 5.77 |
| (MA/cm) | 9.83 | 9.10 | 8.43 |
| 1.52 | 1.50 | 1.46 |
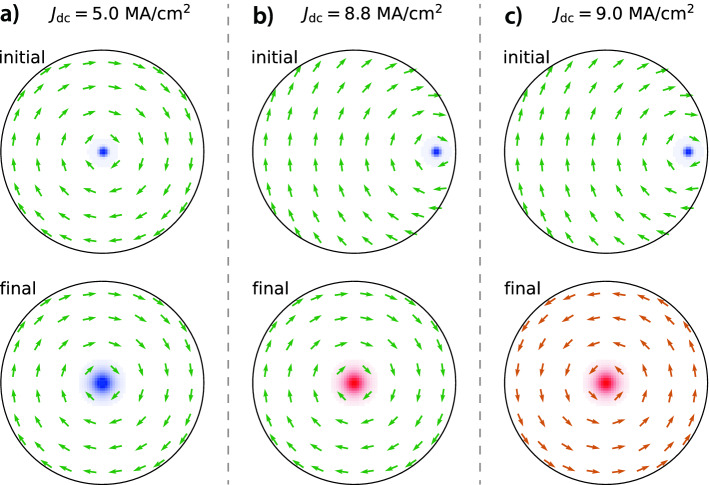
The splitting due to the AOF can be clearly seen in Fig. 2 as it has a strong impact on s, , , and depending on the vortex chirality. In addition, one can see that to the right of the -line, i.e., for , the vortex polarity switches and the chirality of the vortex initially at also switches for all points except for 8.8 MA/cm (see Fig. 2a and Fig. 3). Indeed, the AOF favours the chirality leading to an in-plane magnetisation parallel to , i.e., the chirality in our case.
Figure 3.
Magnetisation of the magnetic dot at the beginning (initial state) and at the end (final state) of the micromagnetic simulations. The x-y component of the magnetisation is represented by green (clockwise chirality) or orange (counterclockwise chirality) arrows while the z component is represented by a colour code, i.e., dark blue for , white for , and dark red for . The vortex core is initially placed at nm and nm for and at nm and nm for . The initial state of the vortex is and . To simplify the visualisation, the arrows represent the averaged magnetisation over multiple cells. (a) For and 5.0 MA/cm, the vortex final state is damped back to the dot centre as at least one of the conditions for steady-state oscillations is not fulfilled, namely . Here, the chirality and the polarity do not change. (b) For and with 8.8 MA/cm, only the vortex core polarity switches from (blue) to (red). Here, the same chirality as in the beginning nucleates. (c) For and 9.0 MA/cm, both the vortex core polarity switches from (blue) to (red) and the vortex chirality switches as it is initially clockwise () and becomes counterclockwise () at the end of the simulation.
To simplify the expression of given by Eq. (9) , one can consider and the resonant regime () leading to . Thus, can be reduced to . In this regime , , and G can be considered as constant and G can be rewritten as as all components of G are positive excepted P which can be either or . The angular frequency can then be approximated by the following linear equation: with and . As is positive because and , for the sign of is given by the sign of and thus by P. In other words, the polarity P determines the vortex rotational direction.
From Fig. 2a, and are extracted with a linear fit and the results are given in Table 2. The frequency is almost the same for the three curves as anticipated because it does not depend on . In addition, the sign of the slope depends of the chirality () and is close to zero without AOF23 as expected from the analytical model.
Table 2.
Comparison of and between the TEA and the fit from micromagnetic simulations (MMS) ().
| TEA | MMS | TEA | MMS | TEA | MMS | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MHz) | 492.53 | 449.51 | 492.53 | 449.57 | 492.53 | 449.56 |
| (MHz cm/A) | 0 | 0.03 | 4.69 | 4.74 | − 4.69 | − 4.82 |
These results show the importance of the AOF which must be taken into account to precisely describe the dynamics of STVO in the resonant regime as well as in the steady-state oscillating regime (here by applying a DC current). In addition, the impact of the AOF on the STVO dynamics depends on the magnetic dot properties including both material and geometry.
The injected DC current responsible for the steady-state oscillations and thus should be seen as a way to modify the vortex position s. The intrinsic property of the dynamics of the STVO is rather given by the gyrotropic frequency vs. the reduced vortex core position s as shown in Fig. 4, considering only the data from the steady-state oscillating regime. Indeed, the gyrotropic frequency depends only on s for each configuration as it modifies the energy W of the dot. Here s depends on but there are others means for modifying the vortex position s (in-plane field, AC current, stray field antenna, etc.). The splitting is due to the fact that the energy W changes when the chirality changes as shown in Eq. (2) while keeping the DC current orientation constant with the adequate sign for obtaining the steady-state regime. As illustrated in Fig. 1, the curling AOF is counterclockwise when .
Figure 4.
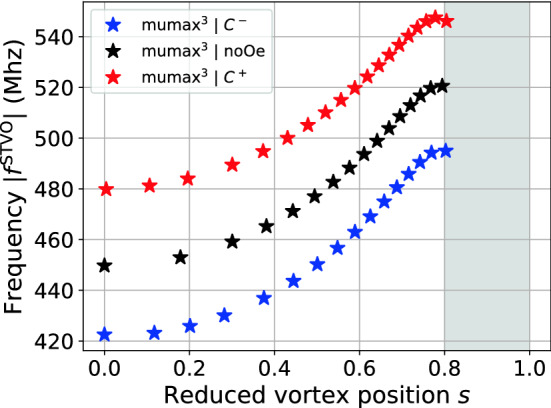
STVO intrinsic property. The gyrotropic frequency as a function of the reduced vortex core position s. Only data in the steady-state oscillating regime is shown here.
Figure 4, shows the relation between the reduced vortex core position s and the frequency in the steady-state oscillating regime. The latter increases with s, as seen in the study by Dussaux et al12. Depending on the applied current, one can tune the frequency on a range of roughly 75 MHz, for each case. A maximum appears just before the vortex polarity reversal which happens at . A clear splitting due to the AOF field is exhibited. Its magnitude, evaluated with , decreases slightly for increasing s. Our model predicts this behaviour as , the spring-like constant associated to the AOF, decreases constantly with s (see Fig. 2b).
As mentioned previously, the resonant regime is quantitatively described by the improved analytical model. However, the steady-state oscillating regime, as shown in Fig. 4, is at this stage only described qualitatively (not shown here) and further work on the s-dependence of the G and D terms is needed. The important message of Fig. 4 is that for a given energy configuration of such a STVO where the chirality is a key parameter, micromagnetic simulations show that the frequency is intrinsically depending on the vortex core position. The same holds for the resonant regime.
Conclusion
In conclusion, a splitting is observed due to the AOF which depends on the chirality of the vortex. The improved analytical model which is valid for , thanks to corrections of the magneto-static and AOF contributions, is coherent with the micromagnetic simulation results for and in the resonant regime. This shows the importance of the AOF for understanding the complex nonlinear dynamics of vortex based nano-oscillators. The splitting shown and modelled here represents a supplementary degree of freedom of such oscillators with potentially a high impact on future applications. For instance, we believe that our analytical model is a first step towards making a fast model for the simulation of STVOs in the framework of reservoir computing24 and build complex hardware-based neuromorphic computing devices.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
Computational resources have been provided by the Consortium des Équipements de Calcul Intensif (CÉCI), funded by the Fonds de la Recherche Scientifique de Belgique (F.R.S.-FNRS) under Grant No. 2.5020.11 and by the Walloon Region. F.A.A. is a Research Fellow of the F.R.S.-FNRS. The authors thank Alexandre Abreu de Araujo and Philippe Talatchian for helpful discussions and feedback.
Author contributions
The study was designed by F.A.A. who created the analytical model. F.A.A. designed the micromagnetic simulations performed by S.d.W.. C.C., F.A.A, and S.d.W. contributed to the text as well as to the analysis of the results.
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-022-14574-3.
References
- 1.Gaididei Y, Kravchuk VP, Sheka DD. Magnetic vortex dynamics induced by an electrical current. Int. J. Quantum Chem. 2010;110:83–97. doi: 10.1002/qua.22253. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Belanovsky AD, et al. Phase locking dynamics of dipolarly coupled vortex-based spin transfer oscillators. Phys. Rev. B. 2012;85:100409. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.85.100409. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Abreu Araujo F, et al. Optimizing magnetodipolar interactions for synchronizing vortex based spin-torque nano-oscillators. Phys. Rev. B. 2015;92:045419. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.92.045419. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Locatelli N, et al. Efficient synchronization of dipolarly coupled vortex-based spin transfer nano-oscillators. Sci. Rep. 2015;5:1–10. doi: 10.1038/srep17039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Skirdkov P, Popkov A, Zvezdin K. Vortex spin-torque diode: The impact of dc bias. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2018;113:242403. doi: 10.1063/1.5064440. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Carpentieri M, et al. Effect of the classical ampere field in micromagnetic computations of spin polarized current-driven magnetization processes. J. Appl. Phys. 2005;97:10C713. doi: 10.1063/1.1853291. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Lee K-J, Deac A, Redon O, Nozieres J-P, Dieny B. Excitations of incoherent spin-waves due to spin-transfer torque. Nat. Mater. 2004;3:877–881. doi: 10.1038/nmat1237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Slonczewski JC. Current-driven excitation of magnetic multilayers. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 1996;159:L1–L7. doi: 10.1016/0304-8853(96)00062-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Li Z, Zhang S. Magnetization dynamics with a spin-transfer torque. Phys. Rev. B. 2003;68:024404. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.68.024404. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Thiele A. Steady-state motion of magnetic domains. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1973;30:230. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.30.230. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Khvalkovskiy A, Grollier J, Dussaux A, Zvezdin KA, Cros V. Vortex oscillations induced by spin-polarized current in a magnetic nanopillar: Analytical versus micromagnetic calculations. Phys. Rev. B. 2009;80:140401. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.80.140401. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Dussaux A, et al. Field dependence of spin-transfer-induced vortex dynamics in the nonlinear regime. Phys. Rev. B. 2012;86:014402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevB.86.014402. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Abreu Araujo F, Grollier J. Controlling the synchronization properties of two dipolarly coupled vortex based spin-torque nano-oscillators by the intermediate of a third one. J. Appl. Phys. 2016;120:103903. doi: 10.1063/1.4962014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Guslienko KY, Lee K-S, Kim S-K. Dynamic origin of vortex core switching in soft magnetic nanodots. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008;100:027203. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.027203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guslienko, K. Y., Aranda, G. R. & Gonzalez, J. Spin torque and critical currents for magnetic vortex nano-oscillator in nanopillars. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series292, 012006 (2011). IOP Publishing
- 16.Wittrock S, et al. Beyond the gyrotropic motion: Dynamic c-state in vortex spin torque oscillators. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2021;118:012404. doi: 10.1063/5.0029083. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Vansteenkiste A, et al. The design and verification of mumax3. AIP Adv. 2014;4:107133. doi: 10.1063/1.4899186. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Abreu Araujo, F. Python package SNIFA. https://pypi.org/project/snifa/.
- 19.Guslienko KY, et al. Eigenfrequencies of vortex state excitations in magnetic submicron-size disks. J. Appl. Phys. 2002;91:8037–8039. doi: 10.1063/1.1450816. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Guslienko KY. Low-frequency vortex dynamic susceptibility and relaxation in mesoscopic ferromagnetic dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006;89:022510. doi: 10.1063/1.2221904. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Ivanov B, Zaspel C. Excitation of spin dynamics by spin-polarized current in vortex state magnetic disks. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007;99:247208. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.99.247208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Guslienko KY, Sukhostavets OV, Berkov DV. Nonlinear magnetic vortex dynamics in a circular nanodot excited by spin-polarized current. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014;9:1–7. doi: 10.1186/1556-276X-9-386. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Choi Y-S, Kim S-K, Lee K-S, Yu Y-S. Understanding eigenfrequency shifts observed in vortex gyrotropic motions in a magnetic nanodot driven by spin-polarized out-of-plane dc current. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008;93:182508. doi: 10.1063/1.3012380. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Abreu Araujo F, et al. Role of non-linear data processing on speech recognition task in the framework of reservoir computing. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-56991-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.