Abstract
Winter forage dearth is a major contributor to honey bee colony loss and can influence disease susceptibility. Honey bees possess a secretory head gland that interfaces with the social environment on many levels. During winter or forage dearth, colonies produce a long-lived (diutinus) worker phenotype that survives until environmental conditions improve. We used a known-age worker cohort to investigate microbiome integrity and social gene expression of workers in early and late winter. We provide additional context by contrasting host-microbial interactions from warm outdoor and cold indoor environments. Our results provide novel evidence that social immune gene expression is associated with worker longevity, and highlight the midgut as a target of opportunistic disease during winter. Host microbial interactions suggest opportunistic disease progression and resistance in long-lived workers, but susceptibility to opportunistic disease in younger workers that emerged during the winter, including increases in Enterobacteriaceae, fungal load and non-core bacterial abundance. The results are consistent with increased social immunity, including host associations with the social microbiota, and a social immune response by long-lived workers to combat microbial opportunism. The cost/benefit ratio associated with limited expression of the diutinus phenotype may be a strong determinant of colony survival during winter forage dearth.
Subject terms: Ecology, Evolution, Microbiology, Molecular biology
Introduction
Social insects are under strong selection to evolve antibiotic mechanisms that result in group hygiene, or social immunity1,2. There are fascinating social insect symbioses evolved to control the abundance of particular microbial species throughout the nest, hive or social environment3–6. The social context of disease susceptibility involves multiple factors that shape the evolution of life history, including resident microbial symbionts and resistance to opportunistic disease7–10. Many opportunistic disease states are associated with changes in core hindgut structure or the overgrowth of native colony microbiota, highlighting the importance of microbiome integrity or taxonomic membership in disease susceptibility. How, when and where opportunistic pathogens can invade the host depends in part on their ability to occupy sub-optimal or fringe niches with consistent host exposure, to form relationships with, or outcompete other resident microbes, and to evade host defenses8,11,12. A primary function of gut microbiota in eukaryotes is protection from pathogens, and many factors may weaken the core microbiota rendering the host organism susceptible to disease12–16. In humans, the skin and nasal pharyngeal microbiome are considered the first line of defense against pathogen colonization and infection17. Analogous to these protective human niches, the honey bee is host to a variety of microbiotas associated with a type of “social skin” that occurs throughout the colony and hive4,13,14,18,19. This social microbiota is associated with social nutrient processing and information sharing including the structurally complex worker mouthparts that perform these tasks and a secretory hypopharyngeal gland (HPG) in the worker head. The HPG produces a highly nutritious and bioactive jelly substance containing various cocktails of pro-oxidants, antioxidants and antimicrobial peptides that interface constantly with the microbiota and social network4,14,18.
A recently emerged model for gut microbiome studies, the honey bee worker hindgut microbiota is highly predictable by both taxonomy and structure, comprised primarily of five core phylotypes represented in every study7,12,20–24. In the rectum, Lactobacillus firm5, Lactobacillus Firm4, Bifidobacterium asteroides dominate, while Snodgrassella alvi, Gilliamella apicola and Lactobacillus Firm5 dominate the ileum. The structure and function of the hindgut microbiota is essential to the health of the individual worker and colony. The core phylotypes occur throughout the colony and hive environment, facilitating generational transmission25–27. Similar to the hindgut, a variety of niches throughout the colony and hive also contain a unique and predictable set of phylotypes4,19,22,28–30. The honey bee maintains a strict relationship with the microbes in its hindgut, and we predict similar functional pressure exists to control the microbiota throughout the interactive social environment.
Honey bee life-history and aging is extremely plastic; queens can live for years, and workers also exhibit considerable longevity differences associated with age, task, winter survival and forage dearth31–34. Similar to other model systems, the hindgut microbiota tracks the physiology of honey bee behavioral and reproductive phenotypes associated with age and nutritional state30,35. Worker bees acquire their highly structured hindgut microbiota in the first 1–4 days of adult life concurrent with the consumption of beebread; pollen, honey and worker secretions25,26. Host digested beebread is converted to an internal storage molecule, Vitellogenin (Vg), a large lipo-glyco-phosphoprotein. The role of Vg varies by tissue and caste and is associated with antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties36. Workers raised in stressed conditions do not establish a typical gut microbiota, and show deficient central metabolism including decreased insulin signaling and Vg production27, and as a social consequence, deficient HPG secretions.
The HPG can express a broad variety of nutritional and antimicrobial cocktails in response to social needs. Jelly contains antimicrobial peptides and social hygienic enzymes glucose oxidase (GOX), and superoxide dismutase (SOD). Mixed with glucose in honey, GOX produces gluconic acid and hydrogen peroxide. The honey bee social environment is coated with GOX and H2O2 providing a generalized social immune barrier1,37–39. Phenotypic plasticity within the worker caste is reflected in HPG gene expression; young nurses produce copious amounts of nutrient rich jelly, but the HPG shrinks in older foragers and secretes enzymes associated with honey processing40,41. The HPG of workers can resume past physiological states associated with youth, or shift forward to assume the task of an older bee42. The gland can also react more proximally to colony-level challenge associated with a variety of social pressures like emergency queen rearing43,44. In addition to providing shared nutrition, jelly produced in the HPG may transmit immune training molecular patterns across generations, extend life expectancy, modulate microbiota structure and prevent opportunistic disease44–46. Gene expression associated with individual and social immunity is costly, and only generated by well-nourished individuals38,47. Because internal Vitellogenin stores over winter rely on nutrition in the fall, the availability of pollen on the landscape is a major factor in brood production, colony growth and disease resistance48.
Honey bee colonies respond rapidly to environmental conditions. The proximal cue of artificial rainfall causes a shift to conservation physiology in a matter of hours49. Similarly, forage dearth and persistent low temperatures shift physiology towards colony thermoregulation and resource conservation including production of the diutinus worker phenotype, defined by worker longevity and conservation physiology. Diutinus workers consume and digest pollen in the fall, or at the beginning of a pollen dearth, then conserve the nutrition internally to provide for the growing colony when environmental conditions improve. With the coming of winter, pollen diversity and nutrition disappear completely across the northern landscape, and decrease drastically on the southern landscape. While the diutinus phenotype is well documented in northern climates, there is little to no data on its expression during mild winter conditions typical of the southern US including Texas, Florida and California where an economically significant number of commercial bee colonies overwinter annually. These mild winters involve a variety of indistinct or conflicting environmental cues, including warm daily temperatures, and the availability of pollen and nectar on the landscape. Subsequently, brood rearing over winter commonly discontinues in predictably cold (Northern) climates, but continues at significantly reduced levels in southern climates, stimulating foraging behavior throughout the winter50,51. The presence of brood in the hive environment accelerates both behavioral and cellular senescence among worker bees31. After approximately 10 days of foraging, workers experience a sharp increase in mortality31.
In continuously cold winter climates, the cohort of workers emerging in early winter express the diutinus phenotype, and can live 8X longer (240 days) than a worker during spring/summer colony growth52,53. Although a critical point in the life cycle, variation in gut and colony microbiota and physiology that accompanies this process is relatively unknown, as is the social immune status of diutinus workers during winter54,55. A recent investigation of the diutinus hindgut microbiota implied healthy physiology in cold, climate-controlled (7 °C) indoor conditions, in contrast, greatly reduced longevity and the proliferation of opportunistic bacteria were associated with the southern winter8. However, the putative opportunistic microbes were at extremely low abundance in the hindgut relative to the core microbiota. In this contribution, we investigate these same samples more deeply by examining the change in worker mouth and midgut microbiotas, and detailing the associated change in HPG gene expression. Like other examples from social insects5,6, we hypothesize that HPG social secretions nurture symbionts native to the alimentary tract, but are negatively associated with opportunists in the social and gut environment.
Methods
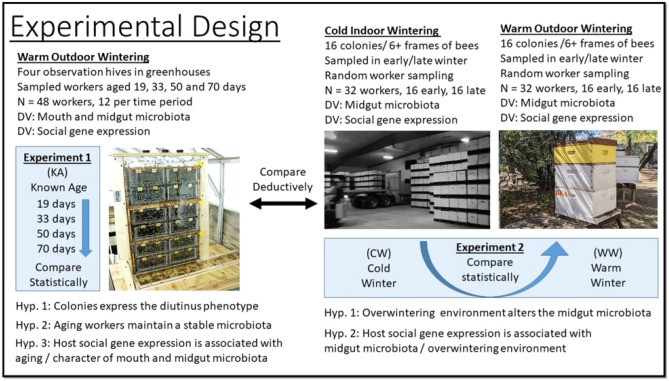
To gain an understanding of host-microbial interaction during winter, we performed two separate but related experiments (Fig. 1). We designed the first experiment to provide perspective on the relationships of mouth and midgut microbiota with HPG gene expression. We quantified HPG gene expression and the microbiotas associated with worker longevity from colonies kept in warm winter conditions. The second experiment compared HPG expression and various microbiota characteristics of the midgut associated with full-sized colonies placed in cold indoor climate-controlled wintering, and warm outdoor wintering. These results are associated with a published companion paper that sequenced the ileums and rectums from the same experimental samples8. Briefly, those results revealed statistically indistinguishable hindgut microbiotas in early winter, and little change in the hindgut microbiota of worker bees during winter regardless of climate or age. However, the authors suggested the potential for compromised host physiology in warm southern climates, revealed by low worker longevity from early to late winter, and significantly increased fungal load correlated with an increase in putatively opportunistic Enterobacteriaceae. The present manuscript more fully explores the microbiomes and host response associated with microbial opportunism and fungal growth in aging worker bees during winter dearth.
Figure 1.
Experimental design, sampling details and hypotheses. The blue boxes describe the manipulations performed in this study. DV is Dependent Variable. Cold winter warehouse photo provided by Agri-Stor Companies of Idaho.
Experiment 1: known age cohort
We used four observation hives to follow a known age (KA) cohort and validate chronological age. To control for age in the observation hive, newly emerged winged adults were sourced from brood frames of 20 healthy colonies. Late stage pupae emerged naturally from their natal frames over a period of ≤ 24 h while housed in a humidity (50%) and temperature-controlled (35 °C) room. All newly emerged bees were collected into a single container and randomized prior to colony assignment. We painted the thoraces of 2,000 newly emerged bees and divided them equally among four observation colonies. Observation hive colonies comprised of three or four frames containing brood, plentiful honey and beebread, were kept in greenhouses at the Carl Hayden Bee Research Center, Tucson AZ with exposure to diurnal cycles, access to the foraging environment and a small space heater for rare nights below freezing. Adult worker bees were introduced into observation hives on December 3rd, then sampled from Dec 22nd 2015–Feb 10th 2016. Samples of marked bees were collected at 19, 33, 50 and 70 days of age, and we analyzed 12 workers per age group (n = 48). Our 19 Day-old sample represents the age when workers have expelled the pollen from their guts and transitioned to foraging, while 33 days is the mean expected longevity of foragers in spring/summer. In the companion study, we estimated that only 10% of introduced bees survived until 50 days of age8. Thus, our 50 and 70-day-old samples were comprised of the longest-lived bees relative to average life expectancy in southern climates. From this sample set, we quantified the change in HPG gene expression in early and late winter of host genes related to reactive oxygen species, and antimicrobial peptide (AMP) expression. The ileum and rectum microbiota from these same worker samples (KA) was remarkably stable from 19 to 70 days of age while fungal load and bacterial diversity decreased significantly during winter in the hindgut8.
Experiment 2: overwintering climate comparison
In a second experiment, we hypothesized that the midgut microbiomes associated with warm vs. cold winter conditions would differ due to task differences experienced by the colony under different climatic conditions. We compared the midgut microbiota of colonies from southern outdoor climates to colonies kept indoors throughout the winter in cold climate controlled conditions. All colonies in this experiment had access to honey and beebread during winter, but the cold winter colonies became broodless, while the warm winter colonies continued to forage and rear small numbers of brood throughout the winter50,51. All full size colonies in both environments were 6 + frames of bees at the beginning of the experiment with no signs of disease.
The warm overwintering (WW) environment was the Santa Rita Experimental Range in southern Arizona 31°46′38″N, 110°51′47″W. We collected worker samples in mid-December 2015 and mid-February 2016. We placed cold winter (CW) colonies in a climate controlled storage facility at a constant 7 °C and 25% relative humidity with no access to environmental cues. Worker bees were sampled just prior to entering the cold storage facility in Firth, Idaho, USA, 43°18′45″N, 112°09′20″W in early winter, mid-October 2015, and directly after they were removed from cold storage and transported to the almond orchards in late winter, mid-February 2016, near Snelling, California, USA, 37°31′33″N, 120°31′52″W. From the edge of the brood nest, we sampled worker bees from 16 colonies per time point, per climate, performing molecular analysis on 64 total colony samples. The hindgut microbiotas of early winter bees did not differ by climate/locale but fungi increased significantly during winter in the hindguts of WW samples, concurrent with a slight but significant increase in an unknown Gilliamella spp. and Enterobacteriaceae8.
DNA analysis
We performed microbial DNA analysis on the mouthparts and midguts quantifying total bacteria and fungi. Immediately after being removed from − 80 °C individual bees were surface sterilized and dissected in 95% ethanol using sterile forceps and dissection scissors. We immediately placed all tissues into a 2 ml bead beating tube containing ~ 100 μl of 0.1 mm silica beads and 300 μl of 1X TE buffer (10 mM Tris–HCl, 1 mM EDTA) and immediately frozen on dry ice. All dissected tissues were stored at −80 °C. Prior to DNA extraction, each sample was bead beaten for a total of 2 min in 30 s intervals. To each sample, 100 μl lysis buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl, 2 mM EDTA, 5% Triton X-100, 80 mg/ml lysozyme, pH 8.0) was added and the samples were incubated at 37 °C for 30 min. Total genomic DNA was extracted using a Fermentas GeneJet Genomic DNA Purification Kit (#K0722) following the protocol for gram-positive bacteria. Miseq amplification and analysis was performed as in8. We estimated the size of the bacterial/fungal communities in the ileum and rectum using degenerate primers56,57. We amplified the 16 s gene template using forward primer 27F (5’-AGAGTTTGATCCCTCAG-3’) and reverse primer 1522R (5’-AAGGAGGTGATCCAGCCGCA-3’). The 18 s gene template was amplified using forward primer PanFungal_18S_F (5’-GGRAAACTCACCAGGTCCAG-3’) and reverse primer PanFungal_18S_R (5’-GSWCTATCCCCAKCACGA-3’). We created plasmid vectors using Invitrogen’s pCRTM2.1 TOPO™ cloning vectors per the manufacture’s specifications.
Microbiota sequencing
For all samples (Experiment 1; n = 48, Experiment 2; n = 64), the V6–V8 region of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified using universal (degenerate) PCR primers 799F (acCMGGATTAGATACCCKG) and bac1193R (CRTCCMCACCTTCCTC). We amplified DNA using the HotStarTaq Plus Master Mix Kit (Qiagen, Germantown, MD, USA) under the following conditions: 94C for 3 min, followed by 28 cycles of 94 °C for 30 s, 53 °C for 40 s and 72 °C for 1 min, with a final elongation step at 72 °C for 5 min. We used the PCR products to prepare DNA libraries following Illumina MiSeq DNA library preparation protocol. Sequencing was performed at the University of Arizona Genetics Core (UAGC) on a MiSeq following the manufacturer’s guidelines. Resulting sequences were processed using MOTHUR v1.4358, and command lines are listed in Supplementary Table S1.
Expression analysis
RNA was extracted from the hypopharyngeal glands of all 112 workers from both experiments. Heads were surface sterilized and dissected in RNAlater™ using sterile forceps and dissection scissors. All samples were immediately placed into a 1.5 ml centrifuge tube containing 200 µL of Fermentas Lysis Buffer supplemented with β-mercaptoethanol and immediately frozen on dry ice. All samples were stored at −80 °C. Total RNA was extracted using a Fermentas GeneJet RNA Purification Kit (#K0732) following the protocol for Total Insect RNA Purification. Complementary DNA (cDNA) was generated using the Thermo Scientific RevertAid First Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (#K1622) following the First Strand cDNA Synthesis protocol. We quantified the expression of eight genes relative to the housekeeping gene β-actin: three antimicrobial peptides; Hymenoptaecin, Defensin-1 and Abaecin; three antioxidant genes; Catalase, Zn/Cu Superoxide Dismutase (Zn/CuSOD) and Mn Superoxide Dismutase (MnSOD); the redox “social immunity” enzyme Glucose Oxidase (GOX) and finally, Vitellogenin (Vg) as a marker of nutritional state. Briefly, all reactions were performed in a 12 μl volume (6ul of Bio Rad iTaq Universal SYBR Green Supermix, 0.5 μl of 10 μM forward and reverse primer [see59 for primer details], 3 μl of molecular grade water and 2 μl of template). Cycle conditions were 95 °C for 30 s and then 40 × of 95 °C for 20 s and 60 °C for 30 s59. Amplification was normalized to β-actin expression.
Nosema quantification
The midgut is the site of Nosema infection, a highly specialized fungal microsporidian that is a ubiquitous opportunist of honey bee midguts. To determine Nosema infection status in the midgut we ran a modified version of the qPCR protocol reported in60. For each 10 µl reaction we used 5 µl of Luna qPCR master mix (New England Biolabs), 0.25 µM of each primer, 1 µl of template and 3.5 µl molecular grade water. We used N. ceranae specific primers NcF (AAGAGTGAGACCTATCAGCTAGTTG) and NcR (CCGTCTCTCAGGCTCCTTCTC) and N. apis specific primers NaF (GCCCTCCATAATAAGAGTGTCCAC) and NaR (ATCTCTCATCCCAAGA). To confirm efficiencies reported in60 we ran a temperature and concentration gradient qPCR with a known Nosema rich DNA sample. Amplification efficiency was calculated by the CFX manager software and were close to 100% (97.1% and 98.3% respectively). Using a CFX96 real time system (BioRad, Hercules, CA) we ran the following thermocycler program: 95 °C for 3 min followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 10 s and 63 °C for 30 s. Each sample and negative controls were run in triplicate. Using the same reagent mixture (with a 57 °C annealing/extension step), we used β-actin specific primers ActinF (TGCCAACACTGTCCTTTCTG) and ActinR (AGAATTGACCCACCAATCCA). We used the average of the three reactions to determine N. ceranae load relative to β-actin expression. We compared the relative qPCR measures to a previous microscopic assessment of Nosema abundance based spore counts from midgut samples of (CW) workers maintained indoors at 7 °C and 25% RH.
Statistical analysis
We analyzed microbial community structure and abundance with two different approaches: MANOVA performed on centered log ratios and non-parametric Wilcoxon tests. The MANOVA accounts for microbiota structure while the Wilcoxon test examines OTU abundance normalized by bactquant results without regard to microbiota structure. We compared differences in the microbial community structure by known chronological age (KA samples) as well as within, and between WW and CW environments. To allow the use of parametric multivariate analyses61, we converted bacterial abundances to ratio abundances among all OTUs62 using the software CoDaPack’s centered log-ratio (CLR) transformation63. We compared microbiota structure by chronological age (known age cohort) and season (pre/post winter) within and between climates using one-way MANOVA. Pillai’s Trace test statistic was used for all MANOVA’s to account for deviations in normality and homogeneity of covariance. Subsequent univariate tests followed by FDR correction for multiple comparisons were used to explore differences between dependent variables (OTU’s).
We compared total microbial load for bacteria, fungi and Nosema using one-way ANOVA (FDR corrected for multiple comparisons). All analyses were conducted in either JMP_v13 (JMP_1989–2007) and/or SAS_v9.4 (2013). Pillai’s Trace test statistic was used for all MANOVAs to account for deviations in normality and homogeneity of covariance. Statistically significant MANOVA results were further analyzed with pairwise ANOVA tests followed by FDR correction for multiple comparisons. We analyzed total cell number using pairwise Wilcoxon tests (Steel–Dwass correction for multiple comparisons). To normalize to absolute abundance, the proportional abundance of OTUs returned by amplicon sequencing was multiplied by the total bacterial 16S rRNA gene copies determined with qPCR for each individual tissue type. To account for variability in 16S copy numbers across taxa the 16S total was divided by the number of 16S rRNA gene copy numbers present within each bacterial genome. The remaining OTUs (14–6294) were summed, and assigned a gene copy number of 4.2, the average for all bacteria64. This value represents a general measure of non-core bacterial abundance as it contains > 99% of the OTUs. To examine hypotheses of host microbial interaction, we generated Spearman's rank correlation coefficient among the dependent variables independently for each treatment condition, and across the entire data set.
Results
Experiment 1: known age cohort microbiota
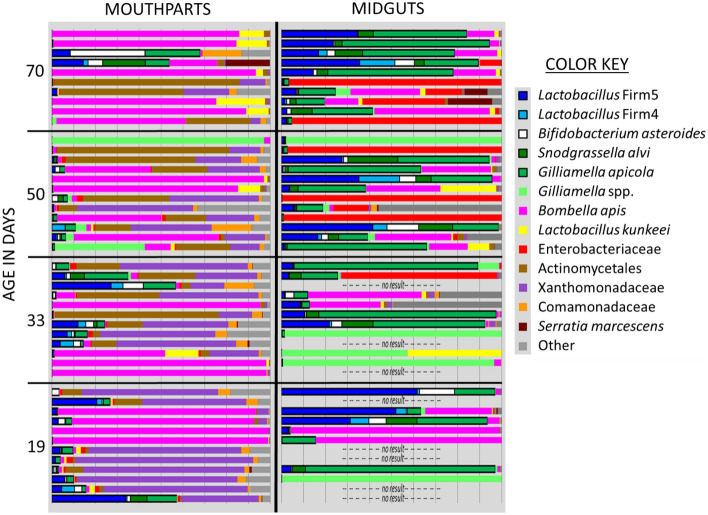
To compliment previous results from the hindgut8, we deep-sequenced the mouthpart and midgut microbiota of aging worker bees over wintered in southern Arizona. As the winter progressed, we sequenced known age (KA) workers at 19, 33, 50 and 70 days of age resulting in a total of 46 mouthpart and 38 midgut microbiota libraries (Fig. 1, Experiment 1). Bacterial diversity on the mouthparts was greatest in 33-day-old bees and decreased in older bees (Fig. 2). The mean number of unique OTUs detected on the mouth did not differ from that detected in the midgut and did not change with age (mouth = 57, midgut = 62). The mouth and midgut environments contained many of the same bacteria, including all five of the core hindgut phylotypes, but showed very distinct microbiotas (Fig. 3). Based on a Wilcoxon rank sum test comparing 19/33 day old bees to 50/70 day old bees, bacterial load remained steady on the mouth with age, but increased in the midgut (W46 = 166, p = 0.03). In contrast, total fungal load decreased slowly and significantly on the mouthparts of aging bees (W46 = 114, p = 0.0004) but remained steady in the midgut.
Figure 2.
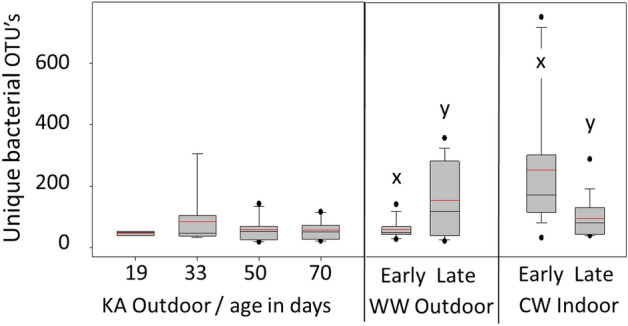
Bacterial diversity in midguts of worker bees depicted as the number of amplicon sequence variants or unique OTUs. Known age (KA) bees did not differ in diversity by age class from early to late winter. Diversity increased significantly in the warm winter (WW) outdoor environment (t30 = 2.89, p = 0.007) and decreased significantly in the cold winter (CW) indoor environment (t32 = 2.89, p = 0.008). Grey boxes contain 50% of the variation, whiskers contain 90%, and the dots represent the range. The horizontal red bar is the mean and black is the median. Boxplots created with SigmaPlot (Systat Software, San Jose, CA).
Figure 3.
Relative OTU abundance for mouthpart (n = 46) and midgut (n = 38) microbiotas of KA worker bees maintained in Tucson AZ, USA. The five core hindgut bacteria at the top of the key are outlined with a black border. Ages on the y-axis coincide with sampling dates; Newly emerged bees were marked and introduced to colonies in Early December, then sampled in late December at 19 days old, mid-January at 33 days old, late January at 50 Days old and mid-February at 70 days old. Significantly larger microbiotas are associated with B. apis (Pink) on the mouthparts, and Enterobacteriacae (Red) and Gilliamella spp. (GFP green) in the midgut.
The mouthpart microbiota was comprised of Bombella apis (previously referred to as Parasacharribacter apium or Alpha 2.2), Actinomycetales, Xanthomonadaceae, Delftia (Comamonadaceae), an unknown Gilliamella spp., and Lactobacillus kunkeei. Enterobacteriaceae occurred at low abundance on 95% of the mouthparts, and Actinomycetales, Xanthomonadaceae and Delftia had 100% prevalence and relatively even abundance. B. apis and L. kunkeei were both prevalent on the mouth but varied considerably in relative and normalized abundance (Fig. 3). The mouth microbiota of the aging bee (KA) differed from early to late winter. On the mouthparts of aging bees, Actinomycetales and the unknown Gilliamella spp. increased while Xanthomonadaceae decreased from twenty-six to nine percent of the total mouthpart community. Relative abundance of Enterobacteriaceae on the mouth also decreased significantly with age (Supplementary Table S1). We examined the aging bees by predicted task, assuming 19–33 days old bees were potential foragers or young workers and 50–70 day old bees were long-lived workers. According to this grouping, non-core bacterial abundance on the mouth decreased with age, while the relative abundance of L. firm5, L. firm4 and B. asteroides on the mouth also decreased with age (Fig. 3).
The aging worker midgut supported Enterobacteriaceae, Bombella apis, an unknown Gilliamella spp., L. kunkeei and the five core hindgut bacteria. The triad signature of Actinomycetales, Xanthomonadaceae, and Delftia was present in nearly every midgut at low relative abundance (Fig. 3). All five of the core hindgut bacteria increased with age (Fig. 3); Snodgrassella alvi and G. apicola increased significantly, while L. firm5 and B. asteroides also increased, trending towards significance (Supplementary Table S1). A putative midgut opportunist; Enterobacteriaceae also increased markedly with age. Although at low absolute abundance in KA midguts, the relative abundance of both Delftia (Comamonadaceae) and Xanthomonadaceae decreased with age during winter. Both Lachnospiraceae and Serratia were at low abundance in the KA mouthparts and midguts, present in < 50% of samples (Supplementary Table S1).
Nosema ceranae, a ubiquitous midgut pathogen, was at generally low absolute abundance in the midgut of aging bees. Many samples from all KA age groups did not rise above the limit of detection. Nonetheless, N. ceranae levels differed significantly among age classes, peaking at 33 days of age and declining thereafter. Young (19-day-old) and the oldest (70-day-old) bees contained significantly less N. ceranae than 33-day-old bees (Supplementary Table S2).
Experiment 1: known age cohort gene expression
To test the hypothesis that social gene expression of long-lived worker honey bees affects the colony and/or gut microbiome, we examined associations of HPG gene expression with the aging microbiota (KA samples) of the mouth and midgut in early and late winter (Table 1, see Supplementary Table S3 for details). The relative HPG expression of five genes regulating oxidative state and AMP production increased significantly with age (Table 1). ROS associated gene expression had a strong and significant negative association with both non-core bacterial abundance and fungal load on the mouth. Actinomycetales increased significantly with age on the mouth and was positively associated with ROS gene expression. Xanthomonadaceae decreased significantly with age on the mouthparts, and was negatively correlated with ROS associated gene expression (see Supplementary Table S4 for details).
Table 1.
Change (Δ) in hypopharygeal gland gene expression over winter.
| Change (Δ) during winter | Warm winter known age* | Warm winter random sample | Cold winter random sample | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gene | Z | p | Δ | Z | p | Δ | Z | p | Δ |
| Nutritional state | |||||||||
| Vitellogenin | 0.69 | 0.49 | NC | − 2.00 | 0.05 | ↓ | 0.42 | 0.68 | NC |
| Antimicrobial peptides | |||||||||
| Hymenoptaecin | 2.69 | 0.007 | ↑ | − 1.52 | 0.13 | ↓ | 1.34 | 0.18 | ↓ |
| Defensin-1 | − 0.67 | 0.53 | NC | 1.62 | 0.11 | ↓ | 2.18 | 0.03 | ↓ |
| Abaecin | 2.87 | 0.004 | ↑ | − 2.21 | 0.03 | ↑ | 1.42 | 0.16 | ↓ |
| Oxidative state | |||||||||
| Glucose Oxidase | 2.80 | 0.005 | ↑ | 0.02 | 0.98 | NC | 2.05 | 0.04 | ↓ |
| Cu/ZnSOD | 5.14 | 0.0001 | ↑ | − 0.58 | 0.56 | NC | − 0.18 | 0.86 | NC |
| MnSOD | 5.57 | 0.0001 | ↑ | 1.10 | 0.27 | NC | − 0.66 | 0.51 | NC |
*The change (Δ) in expression during winter compares 19/33 days to 50/70 days of age. In the warm winter and cold winter environments, we compared randomly sampled in-hive workers in early vs. late winter. See Table S3 for details.
The midgut showed very different host-microbial relationships than the mouthparts. Both GOX and SOD expression (CuZnSOD and MnSOD) were strongly and positively associated with abundance of the core five hindgut phylotypes in the midgut. The strongest positive relationship within this core group was Snodgrassella alvi, a microaerophilic bacterium important for gut function. In contrast to the mouth, Enterobacteriaceae and ROS gene expression were positively correlated in the midgut. Because both the core hindgut bacteria and Enterobacteriaceae increased in the midguts of aging bees during winter, total bacterial load in the midgut was also positively associated with ROS gene expression. The expression of both SOD genes were strongly and positively correlated with the group of five core hindgut bacteria, as was GOX, a pro-oxidant widely considered the primary social immune gene (Supplementary Table S4).
Relative to β-actin, the expression of two of three measured AMPs increased significantly with age, Hymenoptaecin and Abaecin (Supplementary Table S4). Most notably, not one of the five core hindgut bacteria was significantly associated with AMP expression on the mouth or in the midgut consistent with their long-term co-evolution with honey bee defensive peptides. However, defensin-1 was negatively correlated with L. kunkeei abundance on the mouth and in the midgut. Abaecin expression was negatively correlated with B. apis abundance in the midgut. Both Hymenoptaecin and Abaecin were positively associated with the abundance of Actinomycetales on the mouthparts (Supplementary Table S4).
Experiment 2: overwintering climate microbiota
We sequenced the midgut microbiota of worker bees kept outdoors in southern Arizona or indoors in Idaho at 7 °C and 25% RH. These samples are referred to throughout the manuscript as the WW and CW samples (Fig. 1, Experiment 2), and are the same individuals sequenced for ileum and rectum microbiota in a companion manuscript8. Based on the total number of unique 16S rRNA gene sequences, or amplicon sequence variants (ASVs) found in each midgut, bacterial diversity increased significantly from early to late winter in the WW environment (Fig. 2, t30 = 2.89, p = 0.008, μ = 59 early, 154 late), and decreased significantly in the CW environment; (Fig. 2, t32 = 2.89, p = 0.007, μ = 253 early, 94 late). Both bacterial and fungal load from early to late winter remained unchanged in CW midguts, but increased significantly in WW midguts (Fig. 4, Bacteria: W30 = 43, p = 0.003, Fungi: W30 = 42, p = 0.0008). Fungal load was positively associated with diversity abundance, and both factors increased significantly during winter in WW bees and decreased in CW bees.
Figure 4.
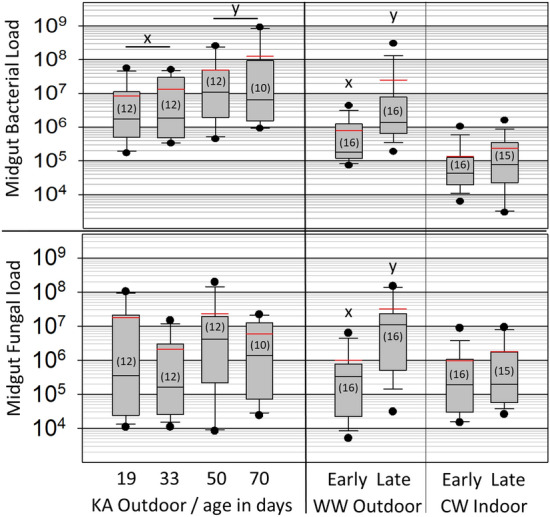
Bacterial and fungal load in the worker midgut of over wintering honey bees. The y-axis is log10 transformed and represents 16S rRNA copy number (bacterial load) and 18S rRNA copy number (fungal load). The WW samples differed significantly from early to late winter for both fungal load (W32 = 42, p = 0.0008) and bacterial load (W30 = 43, p = 0.003). See “Methods” for more sampling details. Grey boxes contain 50% of the variation, whiskers contain 90%, and the dots represent the range. The horizontal red bar is the mean and black is the median. Bacterial load corresponds to microbiotas in Fig. 3 (KA) and Fig. 5 (WW/CW). Sample sizes in parentheses. Boxplots created with SigmaPlot (Systat Software, San Jose, CA).
Although separated by 1000 miles, WW and CW midgut environments were comprised of the same OTUs, including all five core hindgut phylotypes, Bombella apis, L. kunkeei, Actinomycetales, Xanthomonadaceae, and Delftia (Comamonadaceae), The latter three OTUs had 100% prevalence and relatively even abundance across both groups (Fig. 5). Core hindgut bacteria increased significantly in the midguts of CW bees over winter, but decreased in WW bees (Fig. 5, Supplementary Table S1).
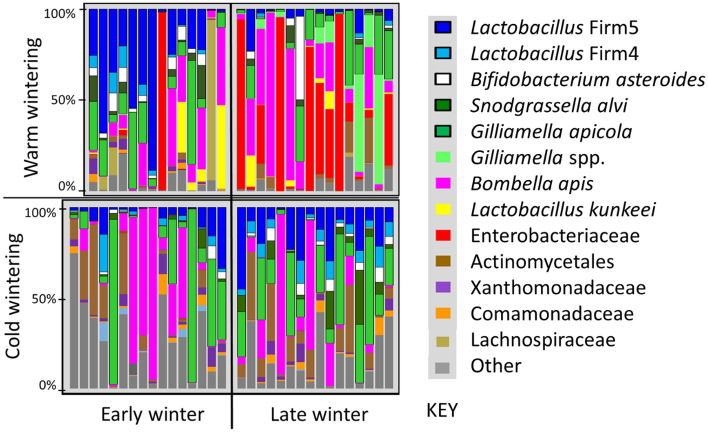
Figure 5.
Relative abundance of midgut microbiotas (KEY = OTUs) in early and late winter of worker bees from colonies placed in an indoor climate-controlled facility: “Cold wintering”, or outdoors in Southern Arizona, USA: “Warm wintering”, on the y-axis. Each vertical bar is the midgut microbiota of a single bee from a different colony (n = 14 or 16). Outlined in bold within the key, the core five hindgut bacteria declined significantly in the warm outdoor environment, but increased significantly in the cold indoor environment. Significantly larger midgut microbiotas are associated with Enterobacteriaceae (RED) and Gilliamella spp. (GFP green). See Supplementary Table S1 and results for more details.
The midgut microbiota from early to late winter differed by overwintering climate (Fig. 5). The CW midguts did not differ from early to late winter when comparing OTU abundance normalized by bactquant and corrected for multiple comparisons (Supplementary Table S1). In CW samples, L. firm5 and L. firm4 increased significantly in ratio abundance from early to late winter, and the other core bacteria trended in the same direction (Fig. 5). From early to late winter, the CW colonies experienced a loss of diversity and a loss of non-core bacterial abundance (Figs. 2 and 5). While the CW microbiota changed very little in terms of abundance and composition, colonies experiencing a warm outdoor environment changed drastically for both measures (Figs. 5 and 6).
Figure 6.
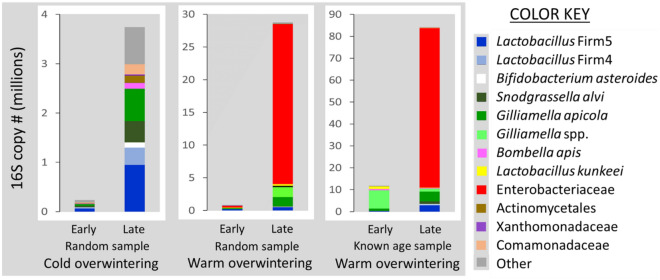
Mean normalized abundance of the midgut microbiota by overwintering environment and sample set. Worker bees were sampled in early or late winter. Random samples are in-hive worker bees of unknown age selected from around the brood nest (n = 16 per time point). Known age samples are aged 19/33 days (early, n = 16) and 50/70 days (late, n = 22). Normalized abundance values for each y-axis are in millions and differ significantly by sample set. See “Methods” for detailed information.
Rare or absent in the CW samples, Enterobacteriaceae and an unknown Gilliamella spp. were abundant in the midguts of late WW samples (Figs. 5 and 6). Increasing in absolute abundance from early to late winter (WW) were Enterobacteriaceae, an unnamed Gilliamella spp. (3% different from either G. apis or G. apicola), Gilliamella apicola, Bombella apis, Actinomycetales and non-core diversity abundance (Supplementary Table S1). Enterobacteriaceae and the Gilliamella spp. accounted for the vast majority of the bacterial increase in midgut microbiota size from early to late winter (Fig. 6). Although at low abundance in WW midguts, Xanthomonadaceae decreased significantly during winter. MANOVA comparisons indicate phylotypes L. Firm5 and L. Firm4 decreased relative to the total microbiota. However, the WW microbiota increased 10X in size during winter (Fig. 6), such that the absolute cell numbers of L. Firm5 did not differ between treatments, but the ratio abundance of L. Firm5 relative to the whole community decreased significantly (Fig. 5). L. Firm5 and L. Firm4 decreased significantly in WW midguts during winter when considered as a proportion of the community whole, as did the less abundant OTUs; Xanthomonadaceae and Delftia (Comamonadaceae). Enterobacteriaceae, Gilliamella spp. and Actinomycetales increased in normalized abundance, and relative to the total community (Supplementary Table S1).
Associated with small mouthpart microbiomes, Actinomycetales was present in every midgut of the CW samples. Moreover, the CW samples had a signature of three inter-correlated OTUs associated with small, presumably healthy midgut microbiotas; Xanthomonadaceae, Actinomycetales, and Delftia, a Commomonadaceae. These bacteria appear in most next generation sequencing datasets, and can also be abundant in the HPG and royal jelly.
Levels of Nosema ceranae differed by overwintering climate. Similar to many other microbial metrics, levels of N. ceranae remained unchanged from early to late winter in the CW samples. In the WW samples, N. ceranae increased significantly from early to late winter. Biologically, N. ceranae was at low abundance during winter in both environments based on perceived colony health, a low Ct positive control and high Ct values or non-amplification of many experimental samples (Supplementary Table S2).
Experiment 2: overwintering climate gene expression
In the CW indoor environment, HPG expression differed from early to late winter for two of seven genes (Table 1). Glucose oxidase, and Defensin-1 expression decreased significantly from early to late winter. The remaining genes either decreased slightly in expression or remained unchanged. Gene expression was associated with host microbial metrics. HPG expression of Defensin-1 decreased concurrently from early to late winter with bacterial diversity in CW midguts (Supplementary Table S4). GOX expression decreased as S. alvi midgut abundance increased. For consideration independent of corrected p-value in the CW samples, S. alvi was positively associated with total bacterial cell abundance, and GOX expression was negatively associated with the abundance of fungi, Bifidobacterium asteroides, and G. apicola in the midgut. Catalase expression was negatively associated with bacterial diversity in the midgut (Supplementary Table S4).
In the WW outdoor environment, HPG expression differed from early to late winter for two of seven genes (Table 1, Supplementary Table S3). As a marker of nutritional state, vitellogenin expression decreased significantly from early to late winter, while Abaecin expression increased. Vitellogenin expression was negatively correlated with late winter increases of bacterial diversity, non-core bacterial abundance, and fungal abundance. Abaecin expression was negatively associated with Xanthomonadaceae abundance in the midgut from early to late winter, but positively associated with Enterobacteriaceae (Supplementary Table S4). Hymenoptacin and Defensin-1 expression decreased markedly, but not significantly from early to late winter (Supplementary Table S3). Both genes were negatively correlated with the midgut increase in Nosema ceranae abundance. Hymenoptacin expression was negatively correlated with bacterial diversity, fungal abundance and Actinomycetales. Oxidative state interactions associated with the WW microbiota were limited to Nosema ceranae and bacterial diversity, which became more abundant in late winter midguts concurrent with a significant decrease in GOX expression from the social gland (Table 1, Supplementary Table S4).
Discussion
We describe a novel relationship in honey bees involving the mouth, midgut and hindgut microbiota, and social gene expression of aging workers during winter forage dearth. We propose that the hypopharyngeal gland (HPG) performs a vital defensive role during forage dearth in winter, rivaling its established role in providing shared nutrition for colony members during periods of growth. Our results reveal associations of microbiota and social immunity by overwintering environment and highlight the potential role of HPG secretions in mitigating the mouthpart microbiota and shaping the hindgut microbiota during winter. Our results are similar to host-microbial dynamics seen in other social insect species including host secretions that nurture defensive symbionts and reduce colony pathogens2,6,47,65. We suggest one mechanistic hypothesis for the lack of immune genes in the honey bee genome66; the introduced and resident social microbiota may be mitigated in part by the redox potential of the individual and the group1,27.
Our results correspond with those presented in a companion paper that deep sequenced the ileum and rectum microbiotas from the same three (KA, CW, WW) sample sets presented here8. It is clear from these and other results that physiologically distinct gut niches are altered somewhat synchronously by microbial opportunism or perturbation8,14. Fungal abundance and bacterial diversity decreased significantly and collectively on the mouthparts, ileums and rectums of aging (KA) bees8 (Figs. 2 and 4), and showed a strong negative association with the expression of GOX and both SOD genes from the HPG. Resulting gene expression relative to the general microbial character and taxonomy of all four alimentary tract niches suggests a systemic host-microbial dynamic throughout the entire alimentary tract.
All cold winter (CW) colonies survived the winter, produced the diutinus phenotype, and showed a broad collection of factors that distinguish them from the two warm winter apiaries. The entire CW gut microbiota (midgut, pylorus/ileum, rectum) was either improved from early to late winter or not diminished (Fig. 5)8, fungi remained low and constant throughout the entire alimentary tract (Fig. 4)8, and bacterial diversity throughout the gut decreased significantly (Fig. 2). The expression of genes associated with oxidative stress and microbial control remained constant in the HPG; both defensin-1 and GOX production decreased significantly over winter consistent with a stable social environment and little microbial challenge (Table 1); similar to other findings from healthy hives kept in cold winter conditions67. The abundance of Nosema ceranae, a destructive midgut parasite, also remained low and constant in the midgut from early to late winter. The same two bacterial opportunists detected in warm winter apiaries also occurred in CW samples, but at negligible prevalence and abundance, decreasing from early to late winter in the worker hindgut8.
In contrast, colonies kept in warm winter conditions (KA and WW) did not produce an overt diutinus phenotype, with only 10% of workers surviving beyond 50 days of age8. In practice, both longevity and Vitellogenin rich metabolism are indicative of diutinus workers. During winter forage dearth in the southern climate, we documented unique gene expression associated with worker longevity (Table 1, KA samples). The Vg levels of randomly sampled workers (WW samples) from late winter were significantly depleted, while Vg levels of much older workers from the same climate conditions remained unchanged in late winter, perhaps an indicator of conservation physiology and incomplete expression of the diutinus phenotype. While the average longevity is too low for diutinus bees, we cannot conclude whether the social immune gene expression associated with longevity and higher Vg expression is somewhat diutinus in nature (Table 1).
Independent of the diutinus distinction, results from the warm winter sample sets suggest microbial opportunism and disease susceptibility that varied by age cohort. The midguts of both KA and WW treatment groups were overgrown with Enterobacteriaceae and Gilliamella spp. in late winter (Fig. 6). The mouthparts of the oldest (KA) bees showed a significant reduction in fungal load with age (Fig. 4), and this pattern was repeated in the hindgut (ileums and rectums) of these same bees8. In contrast, fungal load, Nosema disease and bacterial diversity increased significantly during winter in the midguts of randomly sampled WW bees (Figs. 2 and 4), concurrent with significant fungal increases recorded for the ileum and rectum8. According to our estimates of worker age, this randomly sampled cohort was less than 30-days-old. Based on these results we suggest that longevity-associated physiology and associated HPG gene expression suppresses fungal growth and bacterial diversity at the individual and social level, and may influence the hindgut microbiota over extended time scales.
Host immune response and various microbial metrics differed significantly between KA and WW samples (Table 1). The significant upregulation of Vitellogenin (Vg), GOX, SODs and AMPs in the HPG of the oldest KA bees is consistent with a social host response to a microbially challenging overwintering environment (Table 1). Vitellogenin is an indicator of nutritional state and a potent antioxidant68, while superoxide dismutase (MnSOD, and CuZnSOD) are able to scavenge excess oxidants associated with metabolic demand or microbial challenge and convert them into less harmful molecules69. Of these two, only CuZnSOD is secreted by the HPG70, while increased expression of MnSOD is an indication of increased mitochondrial function (Table 1). Produced in response to social role, glucose oxidase (GOX) is omnipresent throughout social resource space, and is considered an immediate form of social immune response38. GOX functions as a pro-oxidant (generates reactive oxygen species; ROS) that thwarts microbial growth by converting omnipresent glucose into hydrogen peroxide and gluconic acid throughout social resource space. In general, the core hindgut bacteria appear resilient to GOX expression. The abundance of all five core-hindgut bacteria in the midgut were positively associated with the expression of GOX in the HPG (Supplementary Table S4) highlighting a fundamental host-microbial relationship27 that likely facilitates hindgut microbiome establishment/maintenance and limits microbial opportunism.
Social immunity from early to late winter differed by age and winter environment; GOX expression increased significantly with age in the (KA) samples, remained unchanged in the WW samples, and decreased significantly in the diutinus CW samples (Table 1). The resulting host-microbial dynamics by sample set suggest a fundamental ecological interpretation associated with the control of ROS at the level of the individual and social group. To review, S. alvi, is partnered with the metabolism of G. apicola in the ileum of a healthy worker host, contributing to the production of an anoxic hindgut environment27. We hypothesize that oxidative control of the gut is associated with the increased abundance and structure of the core hindgut phylotypes in the midgut, as modeled for the ileum microbiota27. In the cold indoor environment, GOX expression decreased significantly, while the abundance of core hindgut bacteria S. alvi, G. apicola and B. asteroides increased. In fact, all five of the core hindgut bacteria increased significantly as a correlated group in the CW midgut, while less abundant OTUs, and bacterial diversity decreased (Fig. 5). The core five hindgut bacteria are well equipped to exploit low oxygen gut environments and many strains are capable of producing their own catalase and SOD71,72. Several commensal bacteria, like Lactobacillus species, secrete ROS into their surroundings, and this activity discourages the growth of other commensal organisms including fungi. The collective results indicate that CW colonies possessed a healthy microbiota, including low fungal abundance and low microbial diversity, and did not require a social immune response.
In the warm southern environment, GOX and SOD expression increased significantly from early to late winter in the HPG of the oldest workers (KA samples), associated with a significant reduction in fungal abundance and bacterial diversity on the mouthparts. Older KA worker bees had a strong immune response and low levels of fungal infection and bacterial diversity, while younger bees (WW) sampled at the same time from the same environment appeared more susceptible to dysbiosis. In the WW samples, comprised mostly of middle-aged bees born during the winter, GOX production was unchanged from early to late winter, concurrent with significant increases in Nosema ceranae, bacterial diversity and fungal abundance. Although both WW and KA midguts were dysbiotic in late winter, the significant decrease in Vg expression of WW bees in late winter suggests they could not afford to mount an immune response. Although much older at 50–70 days of age, the long-lived (KA) workers possessed the molecular resources to mount a social immune response to bacterial and fungal opportunism in late winter (Table 1). We hypothesize that many of the microbial differences between older and younger cohorts in late winter involve social and individual immune expression, particularly the control of reactive oxygen species.
Changes in HPG metabolism also suggest that older bees are mitigating microbial growth on the mouthparts. Concurrent with increased upregulation of GOX, SOD, Abaecin and Hymenoptacin in (KA) bees from early to late winter, the abundance of Xanthomonadaceae (an aerobe), fungal load, and bacterial diversity all decreased significantly on the mouthparts (Fig. 3, Table 1). Although Hymenoptacin and Abecin are active against a variety of gram negative and enteric pathogens including Enterobacteriaceae73, their expression in the HPG was unassociated with the majority of bacteria in the midgut or mouth of (KA) bees. Most notably, none of the core-five hindgut bacteria were significantly associated with AMP expression, consistent with their long-term co-evolution with secreted honey bee defensive peptides. Abaecin is highly effective against Xanthomonas campestris, a well-known plant pathogen74. Known age bees showed a significant reduction of Xanthomonadaceae throughout the gut8 from early to late winter. The same Xanthomonadaceae OTU is prevalent and abundant in the microbiota of the HPG and jelly according to two studies14,18. This indicates a host response targeted towards a resident colony opportunist but requires further study. Under the same conditions, Actinomycetales became significantly more abundant on the mouthparts. Actinomycetes are typically anaerobic and well known for antibiotic richness, and the suppression of fungal growth75. There is a wide variety of native and relatively unknown Actinobacteria in the social environment of honey bee colonies22. The associations of this particular Actinobacterial OTU with host-microbial metrics differed by sample set and niche, suggesting it is an influential member of the mouthpart (colony) microbiota with a close association to colony fungi.
The honey bee midgut is a likely target for opportunistic fungi and bacteria in southern climates during winter. Regardless of age, we discovered that the midgut microbiota can be volatile in late winter harboring 105–106 bacterial cells when healthy, but 107–109 cells when dysbiotic (Fig. 6). These midgut microbiotas showed two general enterotypes; smaller microbiotas with somewhat even distributions of 5–9 OTUs and significantly larger microbiotas dominated by one or two OTUs (Fig. 6). Based on absolute abundance, Enterobacteriaceae was the dominant bacterium in the midgut of both outdoor southern experiments sampled in late winter regardless of age or host gene expression. Enterobacteriaceae are part of the native social microbiota, but are not core gut bacteria and many are associated with disease and winter dearth76. In both the KA and WW samples, blooms of Enterobacteriaceae and an undescribed Gilliamella spp. dominated the midgut microbiota of many individuals and colonies (Fig. 6). The abundance of these two putative opportunists was strongly inter-correlated (Rs = 0.78, p = 0.0001), and both were strongly associated with significant increases of total gut fungi and bacterial diversity abundance throughout the entire gut from early to late winter8. The hindgut (both ileum and rectum) of these same KA and WW samples also experienced a significant increase of the same two OTUs, but they were < 1% of the hindgut microbiome cell count8, suggesting the hindgut was largely uncompromised. The relationship of host gene expression with these two putative opportunists was similar to that for the pervasive midgut pathogen Nosema, supporting the hypothesis of opportunism.
The general relationship of oxidative stress with the honey bee gut and social microbiome merits further study. Oxidative stress can either deter or encourage opportunistic infection77, and may become difficult to manage in the midgut of aging workers during winter dearth. Our results show that the Enterobacteriaceae OTU detected by this study can evade honey bee defenses on the mouth and crop, then proliferate in the aging worker midgut (Fig. 6). Labeled the honey bee assassin78, Serratia marcescens was abundant in the midguts of two 70-day-old worker bees. While our midgut dominant Enterobacteriaceae OTU is undescribed, a variety of Enterobacteriaceae are found consistently throughout the social environment. Among these, Serratia marsescens and Enterobacter spp. are demonstrated chitinolytic78, which may provide a growth advantage once they attain the midgut environment. Similar to glucose oxidase GOX in honey bees, the NOX /DUOX enzyme system plays a key role in midgut mucosal immunity of Drosophila and Anopheles by generating ROS79,80. This site-specific response prevents the overproliferation of midgut opportunists, and similar factors may influence microbial balance of the honey bee at both the individual and social level.
Conclusion
Our results suggests that the midgut of late winter bees is vulnerable to microbial opportunism following an age associated transition in physiology, and if not countered by host gene expression, such opportunism may contribute to dysbiosis and premature senescence of workers and colonies. There are many potential explanations for the host-microbial interactions presented here. We have highlighted one parsimonious perspective evoking social dynamics in response to environmental conditions. Our hypotheses are supported by demonstrated host behavior and physiology32,81,82 and a growing understanding of beneficial, opportunistic and pathogenic honey bee microbes in the gut and social environment7,13,83. We note that host niches and associated microbiotas are far more complex than discussed, and that detailed experimentation is required to test hypotheses generated by this study.
Our findings provide a novel perspective on health and disease in the social group context. Climate controlled indoor wintering was remarkably stable according to our metrics, suggesting that all sampled worker bees had effectively transitioned to the diutinus phenotype. In contrast, colonies kept outdoors in mild winter environments did not express the diutinus phenotype, and suffered dysbiosis that proliferates primarily in the midgut. Workers born during the winter in southern environments were susceptible to opportunism, while older workers funded by fall nutrition were expressing genes associated with individual and social immunity82,84,85. At the colony level, the cost/benefit ratio associated with immune gene expression may be a major factor in surviving mild winters outdoors. Ultimately, our findings suggest that plasticity of lifespan in honey bees was a major factor shaping host-microbial evolution at both the individual and colony level.
Supplementary Information
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Brendon Mott, Duan Copeland, Vincent Ricigliano, Jay Evans and Randy Oliver for their input. Special thanks to Caroline Ratliff and Mike Lamoreaux of Agri-Stor Companies of Idaho for discussion and providing a photo of a climate-controlled storage facility for overwintering honey bees. The manuscript benefited from the comments of two anonymous reviewers.
Author contributions
K.E.A. designed the experiment and wrote the manuscript. P.M. and K.E.A. performed the experiment, analyzed the data, and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
Kirk E. Anderson was funded by the USDA-ARS, research plan 305 Anderson 2022-21000-021-00D. The ARS is an equal opportunity employer and provider.
Data availability
Next gene sequencing libraries of the mouth and midgut were deposited in GenBank under Sequence Read Archive (SRA) accession PRJNA742765. Associated with the same KA WW and CW sample sets, next gene sequencing libraries for the ileum and rectum were deposited in GenBank under Sequence Read Archive (SRA) accessions PRJNA705676 (WW and CW samples) and PRJNA705672 (KA samples).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
These authors contributed equally: Kirk E. Anderson and Patrick Maes.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1038/s41598-022-14442-0.
References
- 1.Evans JD, Spivak M. Socialized medicine: individual and communal disease barriers in honey bees. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010;103:S62–S72. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2009.06.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Hughes DP, Pierce NE, Boomsma JJ. Social insect symbionts: evolution in homeostatic fortresses. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2008;23:672–677. doi: 10.1016/j.tree.2008.07.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Simone M, Evans JD, Spivak M. Resin collection and social immunity in honey bees. Evolution. 2009;63:3016–3022. doi: 10.1111/j.1558-5646.2009.00772.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Dalenberg H, Maes P, Mott B, Anderson KE, Spivak M. Propolis envelope promotes beneficial bacteria in the honey bee (Apis mellifera) mouthpart microbiome. Insects. 2020;11:1–12. doi: 10.3390/insects11070453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Poulsen M, Bot ANM, Nielsen MG, Boomsma JJ. Experimental evidence for the costs and hygienic significance of the antibiotic metapleural gland secretion in leaf-cutting ants. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 2002;52:151–157. doi: 10.1007/s00265-002-0489-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rosengaus RB, Traniello JFA, Lefebvre ML, Maxmen AB. Fungistatic activity of the sternal gland secretion of the dampwood termite Zootermopsis angusticollis. Insect. Soc. 2004;51:259–264. doi: 10.1007/s00040-004-0749-x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kwong WK, Moran NA. Gut microbial communities of social bees. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016;14:374–384. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Maes PW, Floyd AS, Mott BM, Anderson KE. Overwintering honey bee colonies: effect of worker age and climate on the hindgut microbiota. Insects. 2021;12:1–16. doi: 10.3390/insects12030224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Brown BP, Wernegreen JJ. Deep divergence and rapid evolutionary rates in gut-associated Acetobacteraceae of ants. BMC Microbiol. 2016;16:140. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0721-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Douglas AE. The microbial dimension in insect nutritional ecology. Funct. Ecol. 2009;23:38–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2435.2008.01442.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kešnerová L, et al. Gut microbiota structure differs between honeybees in winter and summer. ISME J. 2020;14:801–814. doi: 10.1038/s41396-019-0568-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Raymann K, Shaffer Z, Moran NA. Antibiotic exposure perturbs the gut microbiota and elevates mortality in honeybees. PLoS Biol. 2017;15:1–22. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.2001861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Anderson KE, Ricigliano VA. Honey bee gut dysbiosis: a novel context of disease ecology. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2017;22:125–132. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2017.05.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Maes PW, Rodrigues PAP, Oliver R, Mott BM, Anderson KE. Diet-related gut bacterial dysbiosis correlates with impaired development, increased mortality and Nosema disease in the honeybee (Apis mellifera) Mol. Ecol. 2016;25:5439–5450. doi: 10.1111/mec.13862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Miller DL, Smith EA, Newton ILG. A bacterial symbiont protects honey bees from fungal disease. bioRxiv. 2020 doi: 10.1101/2020.01.21.914325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Motta EVS, Raymann K, Moran NA. Glyphosate perturbs the gut microbiota of honey bees. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2018;115:10305–10310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1803880115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Grice EA, Segre JA. The skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011;9:244–253. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Corby-Harris V, et al. Origin and effect of Alpha 2.2 Acetobacteraceae in honey bee larvae and description of Parasaccharibacter apium gen. nov., sp. nov. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014;80:7460–7472. doi: 10.1128/AEM.02043-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Floyd AS, et al. Microbial ecology of european foul brood disease in the honey bee (Apis mellifera): towards a microbiome understanding of disease susceptibility. Insects. 2020;11:1–16. doi: 10.3390/insects11090555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Babendreier D, Joller D, Romeis J, Bigler F, Widmer F. Bacterial community structures in honeybee intestines and their response to two insecticidal proteins. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2007;59:600–610. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6941.2006.00249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sabree ZL, Hansen AK, Moran NA. Independent studies using deep sequencing resolve the same set of core bacterial species dominating gut communities of honey bees. PLoS ONE. 2012;7:e41250. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Anderson KE, et al. Microbial ecology of the hive and pollination landscape: bacterial associates from floral nectar, the alimentary tract and stored food of honey bees (Apis mellifera) PLoS ONE. 2013;8:e83125. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Rokop ZP, Horton MA, Newton ILG. Interactions between cooccurring lactic acid bacteria in honey bee hives. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2015;81:7261–7270. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01259-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Cox-foster DL, et al. A metagenomic survey of microbes in honey bee colony collapse disorder. Science. 2007;318:283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1146498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Anderson KE, Rodrigues PAP, Mott BM, Maes P, Corby-Harris V. Ecological succession in the honey bee gut: shift in lactobacillus strain dominance during early adult development. Microb. Ecol. 2016;71:1008–1019. doi: 10.1007/s00248-015-0716-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Powell JE, Martinson VG, Urban-Mead K, Moran NA. Routes of acquisition of the gut microbiota of the honey bee Apis mellifera. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014;80:7378–7387. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01861-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Zheng H, Powell JE, Steele MI, Dietrich C, Moran NA. Honeybee gut microbiota promotes host weight gain via bacterial metabolism and hormonal signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2017;114:4775–4780. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1701819114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Anderson KE, et al. Hive-stored pollen of honey bees: many lines of evidence are consistent with pollen preservation, not nutrient conversion. Mol. Ecol. 2014 doi: 10.1111/mec.12966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ludvigsen J, et al. Shifts in the midgut/pyloric microbiota composition within a honey bee apiary throughout a season. Microb. Environ. 2015;30:235–244. doi: 10.1264/jsme2.ME15019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Corby-Harris V, Maes P, Anderson KE. The bacterial communities associated with honey bee (Apis mellifera) foragers. PLoS ONE. 2014;9:e95056. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0095056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Münch D, Kreibich CD, Amdam GV. Aging and its modulation in a long-lived worker caste of the honey bee. J. Exp. Biol. 2013;216:1638–1649. doi: 10.1242/jeb.078915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Amdam GV. Social context, stress, and plasticity of aging. Aging Cell. 2011;10:18–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2010.00647.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Haddad LS, Kelbert L, Hulbert AJ. Extended longevity of queen honey bees compared to workers is associated with peroxidation-resistant membranes. Exp. Gerontol. 2007;42:601–609. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2007.02.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Robinson, G. E. Hormonal and genetic control of honeybee division of labour. Behav. Physiol. Bees 14–27 (1991).
- 35.Anderson KE, et al. The queen gut refines with age: longevity phenotypes in a social insect model. bioRxiv. 2018 doi: 10.1101/297507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Amdam GV, Norberg K, Hagen A, Omholt SW. Social exploitation of vitellogenin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003;100:1799–1802. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0333979100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jones B, Shipley E, Arnold KE. Social immunity in honeybees—density dependence, diet, and body mass trade-offs. Ecol. Evol. 2018;8:4852–4859. doi: 10.1002/ece3.4011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Alaux C, Ducloz F, Crauser D, Le Conte Y. Diet effects on honeybee immunocompetence. Biol. Lett. 2010;6:562–565. doi: 10.1098/rsbl.2009.0986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ohashi K, Natori S, Kubo T. Expression of amylase and glucose oxidase in the hypopharyngeal gland with an age-dependent role change of the worker honeybee (Apis mellifera L.) Eur. J. Biochem. 1999;265:127–133. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.1999.00696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vannette, R. L., Mohamed, A. & Johnson, B. R. Forager bees (Apis mellifera) highly express immune and detoxification genes in tissues associated with nectar processing. Sci. Rep.5, (2015). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 41.Ohashi K, Natori S, Kubo T. Change in the mode of gene expression of the hypopharyngeal gland cells with an age-dependent role change of the worker honeybee Apis mellifera L. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997;249:797–802. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1997.t01-1-00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Huang ZY, Robinson GE. Regulation of honey bee division of labor by colony age demography. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 1996;39:147–158. doi: 10.1007/s002650050276. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Vojvodic S, et al. The transcriptomic and evolutionary signature of social interactions regulating honey bee caste development. Ecol. Evol. 2015;5:4795–4807. doi: 10.1002/ece3.1720. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ohashi K, et al. Functional flexibility of the honey bee hypopharyngeal gland in a dequeened colony. Zool. Sci. 2000;17:1089–1094. doi: 10.2108/zsj.17.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Harwood, G., Salmela, H., Freitak, D. & Amdam, G. Social immunity in honey bees: royal jelly as a vehicle in transferring bacterial pathogen fragments between nestmates. J. Exp. Biol.224 (2021). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 46.Santos KS, et al. Profiling the proteome complement of the secretion from hypopharyngeal gland of Africanized nurse-honeybees (Apis mellifera L.) Insect. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2005;35:85–91. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2004.10.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Cremer S, Armitage SAO, Schmid-Hempel P. Social immunity. Curr. Biol. 2007;17:693–702. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2007.06.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Mattila HR, Otis GW. Dwindling pollen resources trigger the transition to broodless populations of long-lived honeybees each autumn. Ecol. Entomol. 2007;32:496–505. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2311.2007.00904.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Crailsheim K, Riessberger U, Blaschon B, Nowogrodzki R, Hrassnigg N. Short-term effects of simulated bad weather conditions upon the behaviour of food-storer honeybees during day and night (Apis mellifera carnica Pollmann) Apidologie. 1999;30:299–310. doi: 10.1051/apido:19990406. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Ricigliano VA, et al. Honey bees overwintering in a southern climate: Longitudinal effects of nutrition and queen age on colony-level molecular physiology and performance. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28732-z. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Ricigliano VA, et al. Honey bee colony performance and health are enhanced by apiary proximity to US Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) lands. Sci. Rep. 2019;9:1–11. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-41281-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Fukuda HSK. Seasonal change of the honey bee worker longevity in Sapporo, North Japan with notes on some factors affecting life span. Ecol. Soc. Jpn. 1966;16:206–212. [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mattila HR, Harris JL, Otis GW. Timing of production of winter bees in honey bee (Apis mellifera) colonies. Insect. Soc. 2001;48:88–93. doi: 10.1007/PL00001764. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Feliciano-Cardona S, et al. Honey bees in the tropics show winter bee-like longevity in response to seasonal dearth and brood reduction. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2020;8:1–8. doi: 10.3389/fevo.2020.571094. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Döke MA, Frazier M, Grozinger CM. Overwintering honey bees: biology and management. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2015;10:185–193. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2015.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Liu CM, et al. BactQuant: an enhanced broad-coverage bacterial quantitative real-time PCR assay. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:56. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-56. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Liu CM, et al. FungiQuant: a broad-coverage fungal quantitative real-time PCR assay. BMC Microbiol. 2012;12:1. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-12-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Schloss PD, et al. Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2009;75:7537–7541. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01541-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Evans JD. Beepath: an ordered quantitative-PCR array for exploring honey bee immunity and disease. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2006;93:135–139. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2006.04.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Bourgeois AL, Rinderer TE, Beaman LD, Danka RG. Genetic detection and quantification of Nosema apis and N. ceranae in the honey bee. J. Invertebr. Pathol. 2010;103:53–58. doi: 10.1016/j.jip.2009.10.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Pearson, K. Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution. On a form of spurious correlation which may arise when indices are used in the measurement of organs. Proc. R. Soc. Lond.60, 489–498 (1986).
- 62.Gloor GB, Reid G. Compositional analysis: a valid approach to analyze microbiome high throughput sequencing data. Can. J. Microbiol. 2016;703:0821. doi: 10.1139/cjm-2015-0821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Comas, M. CoDaPack 2.0: a stand-alone, multi-platform compositional software. Options 1–10 (2011).
- 64.Větrovský T, Baldrian P. The variability of the 16S rRNA gene in bacterial genomes and its consequences for bacterial community analyses. PLoS ONE. 2013;8:1–10. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0057923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Yek SH, Nash DR, Jensen AB, Boomsma JJ. Regulation and specificity of antifungal metapleural gland secretion in leaf-cutting ants. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2012;279:4215–4222. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2012.1458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Evans JD, et al. Immune pathways and defence mechanisms in honey bees Apis mellifera. Insect. Mol. Biol. 2006;15:645–656. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2583.2006.00682.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Steinmann N, Corona M, Neumann P, Dainat B. Overwintering is associated with reduced expression of immune genes and higher susceptibility to virus infection in honey bees. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:1–18. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Seehuus S-CC, Norberg K, Gimsa U, Krekling T, Amdam GV. Reproductive protein protects functionally sterile honey bee workers from oxidative stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2006;103:962–967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0502681103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Liu JR, Yang YC, Shi LS, Peng CC. Antioxidant properties of royal jelly associated with larval age and time of harvest. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008;56:11447–11452. doi: 10.1021/jf802494e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Li-E M, Jia L, Yan J, Xiao-Wen L, Xin L. Isolation, purification and characterization of superoxide dismutase from royal jelly of the Italian worker bee, Apis mellifera. Acta Entomol. Sin. 2004;47:171–177. [Google Scholar]
- 71.Bottacini, F. et al. Bifidobacterium asteroides PRL2011 genome analysis reveals clues for colonization of the insect gut. 7, 1–14 (2012). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 72.Killer, J., Dubná, S., Sedláček, I. & Švec, P. Lactobacillus apis sp. nov., from the stomach of honeybees (Apis mellifera), having an in vitro inhibitory effect on the causative agents of American and European foulbrood. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol.64, 152–157 (2014). [DOI] [PubMed]
- 73.Casteels P, et al. Isolation and characterization of abaecin, a major antibacterial response peptide in the honeybee (Apis mellifera) Eur. J. Biochem. 1990;187:381–386. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15315.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Casteels P, Ampe C, Jacobs F, Tempst P. Functional and chemical characterization of hymenoptaecin, an antibacterial polypeptide that is infection-inducible in the honeybee (Apis mellifera) J. Biol. Chem. 1993;268:7044–7054. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)53143-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Barke J, et al. A mixed community of actinomycetes produce multiple antibiotics for the fungus farming ant Acromyrmex octospinosus. BMC Biol. 2010;8:109. doi: 10.1186/1741-7007-8-109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Lyapunov, Y. E., Kuzyaev, R. Z., Khismatullin, R. G. & Bezgodova, O. A. Intestinal enterobacteria of the hibernating Apis mellifera mellifera L. bees. Microbiology77, 373–379 (2008). [PubMed]
- 77.Paiva CN, Bozza MT. Are reactive oxygen species always detrimental to pathogens? Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014;20:1000–1034. doi: 10.1089/ars.2013.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Burritt NL, et al. Sepsis and hemocyte loss in honey bees (Apis mellifera) Infected with Serratia marcescens strain sicaria. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:1–26. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0167752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Bae YS, Choi MK, Lee WJ. Dual oxidase in mucosal immunity and host-microbe homeostasis. Trends Immunol. 2010;31:278–287. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2010.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Ha EM, Oh CT, Bae YS, Lee WJ. A direct role for dual oxidase in Drosophila gut immunity. Science. 2005;80(310):847–850. doi: 10.1126/science.1117311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Crailsheim K, Hrassnigg N, Gmeinbauer R, Szolderits MJ, Schneider LHW. Pollen utilization in non-breeding honeybees in Winter. J. Insect. Phys. 1993;39:369–373. doi: 10.1016/0022-1910(93)90024-L. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Corona, M. & Robinson, G. E. Genes of the antioxidant system of the honey bee: annotation and phylogeny. 15, 687–701 (2006). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 83.Schwarz RS, Huang Q, Evans JD. Hologenome theory and the honey bee pathosphere. Curr. Opin. Insect. Sci. 2015;10:1–7. doi: 10.1016/j.cois.2015.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Corona M, Hughes KA, Weaver DB, Robinson GE. Gene expression patterns associated with queen honey bee longevity. Mech. Age. Dev. 2005;126:1230–1238. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2005.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Santos, D. E., Souza, A. D. O., Tibério, G. J., Alberici, L. C. & Hartfelder, K. Differential expression of antioxidant system genes in honey bee (Apis mellifera L.) caste development mitigates ROS-mediated oxidative damage in queen larvae. 20200173, (2020). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Next gene sequencing libraries of the mouth and midgut were deposited in GenBank under Sequence Read Archive (SRA) accession PRJNA742765. Associated with the same KA WW and CW sample sets, next gene sequencing libraries for the ileum and rectum were deposited in GenBank under Sequence Read Archive (SRA) accessions PRJNA705676 (WW and CW samples) and PRJNA705672 (KA samples).