Abstract
The Incompatible Insect Technique (IIT) strategy involves the release of male mosquitoes infected with the bacterium Wolbachia. Regular releases of male Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes can lead to the suppression of mosquito populations, thereby reducing the risk of transmission of vector-borne diseases such as dengue. However, due to imperfect sex-sorting under IIT, fertile Wolbachia-infected female mosquitoes may potentially be unintentionally released into the environment, which may result in replacement and failure to suppress the mosquito populations. As such, mitigating Wolbachia establishment requires a combination of IIT with other strategies. We introduced a simple compartmental model to simulate ex-ante mosquito population dynamics subjected to a Wolbachia-IIT programme. In silico, we explored the risk of replacement, and strategies that could mitigate the establishment of the released Wolbachia strain in the mosquito population. Our results suggest that mitigation may be achieved through the application of a sterile insect technique. Our simulations indicate that these interventions do not override the intended wild type suppression of the IIT approach. These findings will inform policy makers of possible ways to mitigate the potential establishment of Wolbachia using the IIT population control strategy.
Keywords: Wolbachia, establishment, Aedes aegypti, compartmental modelling, simulation, Incompatible Insect Technique (IIT), Sterile Insect Technique (SIT), dengue, introgression
1. Introduction
The Aedes aegypti (Ae. aegypti) mosquito is an efficient vector of several arboviruses, such as dengue, Zika, chikungunya and yellow fever [1]. Vector-borne diseases are a significant cause of morbidity and mortality, accounting for over 17% of the global burden of infectious diseases [2]. Urbanisation, along with population growth, sterilization, and climate change, has led to an intensification of these viruses in already endemic areas, an expanded geographical coverage of the Ae. aegypti mosquito, and an increased case burden in the tropics [3,4,5]. Dengue is a major arboviral disease that imposes a substantial burden across the globe, with an annual estimated infections of 390 million [6] globally, with an associated economic cost of around USD 8.9 billion [7]. Other important arboviruses, such as Zika and Yellow fever, which are also transmitted by the Ae. aegypti mosquito, have been spreading rapidly through the tropical and subtropical regions [8,9]. At present, considerable resources are being invested in vector control measures, such as source reduction and larviciding to suppress immature and adult mosquito numbers, which remain key strategies in mitigating the impact of arboviral disease transmission [10]. Their efficacy in suppressing mosquito populations, however, is limited, and persistent dengue outbreaks continue to occur [11,12,13,14]. This demonstrates the need for novel efficacious and cost-effective alternatives for vector control [15,16].
One such technology is the Incompatible Insect Technique (IIT) strategy [17], which involves the release of male Ae. aegypti mosquitoes infected with the bacterium Wolbachia [18]. The eggs produced by wild type Ae. aegypti female mosquitoes that have mated with Wolbachia carrying males are inviable due to cytoplasmic incompatibility [18], leading to the suppression of the mosquito population with regular release of the Wolbachia-infected Ae. aegypti mosquitoes over time. Suppression-based programmes have been implemented in the US [19], China [20] and Singapore [21,22] to complement existing vector control efforts. Crucially, the efficacy of the suppression approach relies on the over-flooding ratio of the male Wolbachia-Aedes mosquitoes to wild type females and the success of mating [23]. However, due to imperfect sex-sorting with various insect sex-sorting technologies, fertile Wolbachia-infected female mosquitoes may be unintentionally released into the environment [24]. The release of female mosquitoes may have the unintended effect of population replacement rather than elimination [25]. In combination, these factors reduce the desired outcome of elimination and pose open questions on how planners can mitigate Wolbachia establishment using the suppression approach.
To prevent the establishment of the Wolbachia strain in the field population, IIT has been combined with Sterile Insect Techniques (SIT), such that Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes undergo low-dose irradiation to sterilize residual females prior to release [26]. In general, females are more sensitive to irradiation compared to male mosquitoes [27,28], such that the irradiation dose required to achieve complete female sterility has minimal impact on male fitness [29,30]. Another approach to counter the unintended establishment includes release of a second bi-directionally cytoplasmic incompatible Wolbachia strain, which also exhibits cytoplasmic incompatibility with the wild type mosquitoes as well as with the established Wolbachia strain [31]. While these measures are biologically sound and have been demonstrated to be valid in laboratory settings, specific implementation measures, such as the duration and intensity in a competitive ecological setting, is challenging to establish. To this end, our study seeks to simulate possible strategies to mitigate potential establishment of Wolbachia in the wild type Ae. aegypti population through simulation.
Mathematical models have been used to simulate insect population dynamics over time to guide the timing and release numbers of Wolbachia-infected insects into the field population for SIT and IIT control strategies [32,33]. Knipling’s models of discrete-time dynamics and a simple geometric population growth model provided the original mathematical frameworks that have been used to successfully guide insect control programmes [23,34]. More sophisticated models involve differential equations to model mosquito abundance and genotypes [35]. Other attempts comprise spatial-temporal models with multiple life stages [36] and complex agent-based simulations [37], which have been developed to study the insect elimination process. To simulate changes in the mosquito populations over time, as well as possible release/intervention strategies for Wolbachia, we generalize an ecological model that incorporates mosquito transition dynamics in the aquatic and adult stages, mortality in the various stages, and multiple Wolbachia strains within a competitive ecological environment.
This model seeks to address key questions related to potential intervention strategies to counter the establishment of the Wolbachia strain under the suppression approach, namely:
How does the Female Release Error Rate (FRER) under sex sorting impact the likelihood of Wolbachia establishment under the suppression approach?
Do the proposed intervention strategies undermine the original suppression approach (i.e., how do they affect the wild type population)?
Are the proposed intervention strategies effective in countering the establishment of Wolbachia?
Are there other potential issues surrounding the proposed intervention strategies?
These simulations address important questions and provide insights into the efficacy of release strategies to counter the establishment of the Wolbachia in the wild type Ae. aegypti population in the environment. These findings may be used to support the adoption of an appropriate release strategy. As these simulations are exploratory in nature, the model structure and parameters may be adjusted according to estimates from scientific literature and field studies, and generalised to different settings.
2. Materials and Methods
To examine the efficacy of strategies to counteract the establishment of Wolbachia using a suppression approach, we developed a data driven framework to simulate the possible ecological dynamics of mosquito populations under several strategies. As the ecological trajectories differed under each strategy, we assessed these strategies separately and determined their efficacy by tracking the female mosquito population over time. Below, in Table 1, we define key terminologies used to describe the methods and results of the study.
Table 1.
Glossary of terminology.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Incompatible Insect Technique (IIT) | A technique whereby Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes are released to mate with wild type females, preventing the formation of viable offspring due to cytoplasmic incompatibility. See [20]. |
| Sterile Insect Technique and Incompatible Insect Technique (SIT-IIT) | A technique whereby sterile Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes are released to mate with wild type females, preventing viable offspring from forming. The sterility is due to irradiation [20]. This may include the unintentional release of sterile irradiated females under non-zero FRERs. |
| Constant Release Strategy | A strategy whereby an equal number of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes is released at every release event throughout the IIT programme. The number of individuals released is not modified through monitoring of the wild type population. Number of Wolbachia-infected mosquitoes released per event = overflooding ratio × male population at start of programme. See [38]. |
| Female Release Error Rate (FRER) | The rate at which fertile Wolbachia-infected females are accidentally released with Wolbachia-infected males into the field, due to errors in the separation of sexes during the production phase. |
| Eliminated | A mosquito population is considered to have been eliminated when there are no mosquitoes alive in either the aquatic or adult stages in the model at the end of the simulation. See [38]. |
| Establishment | Having a stable female mosquito population infected with the released Wolbachia strain used for suppression at the simulation endpoint. |
2.1. Simulation of Wolbachia-IIT Programmes
Our study focused on a simulation of a Wolbachia-IIT programme, through the repeated release of male Ae. Aegypti, infected with wAlbB or wMel Wolbachia into an environment comprising wild type mosquito populations. Both Wolbachia strains, wAlbB and wMel have successfully been established in natural Ae. aegypti populations [39].
We first simulated a baseline scenario (S1) with no interventions in place, followed by a Wolbachia-IIT programme that employed a constant release strategy to suppress the wild type mosquito population using wAlbB male mosquitoes (S2). For this release strategy, we considered overflooding ratios of 10,000 and 60,000 (See Table 2). These overflooding ratios scale the number of Wolbachia infected mosquitoes released with respect to the initial uninfected adult wild type population size. The overflooding ratios were combined with three levels of separation fidelity determined by Female Release Error Rates (FRER; Table 2) of 10−3, 10−9 and 0, which correspond to the demonstrated rates achievable using next-generation mechanical sex separation as of 2021 [38,40] and with IIT-SIT respectively.
Table 2.
Scenarios considered for modelling mosquito populations.
| Scenario | Release Intensity 1/Overflooding
Ratio 2 |
FRER 3 |
|---|---|---|
| Units | ’0,000 | |
| Baseline (S1) | – | – |
| Suppression Approach (S2) | 1 | 10−3, 10−9 |
| SIT-IIT Female (S3A) | 4, 6, 8 | |
| SIT-IIT Male + Female (S3B) | 4, 6, 8 | 10−3, 10−9, 0 |
| Second Strain Introduction (S4) | 4, 6, 8 | 10−3, 10−9, 0 |
1 Denotes the number of Wolbachia mosquitoes released per week. We focused on the simulations for S3A, S3B and. S4 under the release of 60,000 male mosquitoes per week unless specified otherwise. 2 Denotes the ratio of male Wolbachia mosquitoes released in relation to the initial wild type male population. 3 FRER denotes the female release error rates, i.e., the proportion of Wolbachia females released in comparison to the number of male Wolbachia mosquitoes released under the suppression strategy.
We considered two general strategies to counter the establishment of Wolbachia-infected female mosquitoes. First, we simulated the release of Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes, with the unintentional females released rendered infertile via irradiation under the SIT-IIT (S3A). This served as a correction of the FRERs under the original suppression approach (S2), thereby reducing the chance of establishment where fertile females are unintentionally released in the environment due to imperfect sex-sorting. Second, we simulated the release of Wolbachia-infected male rendered infertile via irradiation under SIT-IIT (S3B), with the unintentional females released rendered infertile via irradiation as well. The sterilization by irradiation of both male and female Wolbachia mosquitoes reduces the likelihood viable offspring and fertile Wolbachia mosquitoes mating [40]. At present, the use of IIT-SIT S3A has already been trialed in Singapore and China [26,41]. Third, we simulated the release of male mosquitoes infected with a second Wolbachia strain (wMel) to induce bi-directional cytoplasmic incompatibility with the first Wolbachia strain and wild type mosquito population (S4).
Additionally, we varied the release intensities, FRERs (Table 2) and intervention start and end dates (see Supplementary Material) to examine how quickly establishment may be mitigated and whether the former effect of wild-type elimination was moderated. In considering different intervention start and end dates, we explored two scenarios where (i) the interventions (S3A, S3B, S4) began after the end of the suppression approach (S2) and (ii) the interventions (S3A, S3B, S4) began before the end of the suppression approach (S2) (see Supplementary Material Table S2). In presenting our primary results in the following section, we refer to the scenario where the intervention strategies (S3A, S3B, S4) began after the end of the suppression approach unless stated otherwise.
We generated 1000 simulations for each scenario (S1–S4) to quantify the level of uncertainty in wild type suppression (S2) and intervention efficacy in countering establishment (S3A, S3B, S4). Each set of simulations was used to study the probabilities of: (i) unintended establishment of the first strain; (ii) wild type elimination, and (iii) eliminating establishment of the first strain. We incorporated parameter uncertainty for each simulation under every scenario by allowing each parameter to take a random draw from a uniform probability distribution over a plausible range. This allows for a plausible degree of variation that may be exhibited in a natural population. The resulting population trajectories produced under the simulations were therefore robust to a range of parameterisations and population outcomes.
2.2. Simulating Mosquito Populations over Time
We simulated changes in the mosquito populations over time using a discrete-time compartmental model, incorporating adult females (F), adult males (M) and an aggregated aquatic (A) stage that includes the egg, larvae and pupae stages in a competitive, well-mixed ecological environment. In this model, we incorporated three mosquito strains: the wild type and two different types of Wolbachia infected mosquitoes. The two Wolbachia considered were the wAlbB and wMel strains in this study.
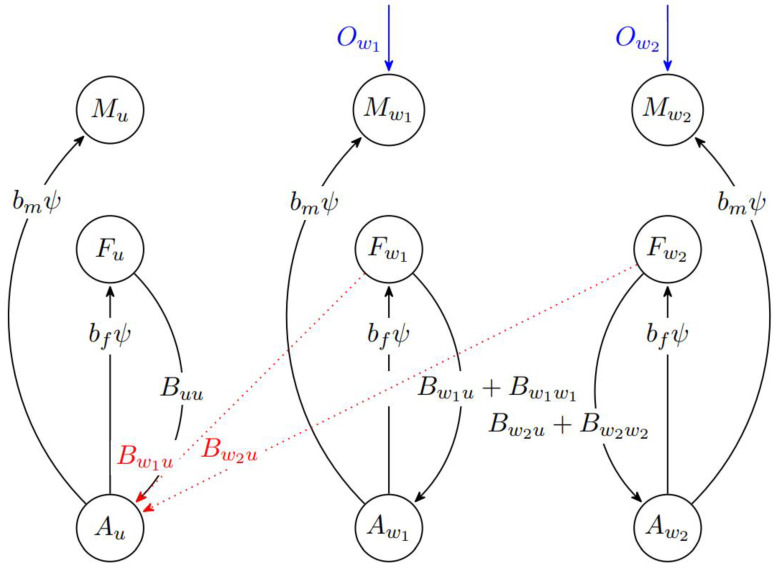
The mosquito populations were grouped into nine compartments, starting with a susceptible, uninfected aquatic stage and infected aquatic stages , , where the subscripts and refer to the wAlbB and wMel infected aquatic stage mosquitoes, respectively. Correspondingly, we denote , as the uninfected female and male adult mosquitoes and , , as the infected adult female and male adult mosquitoes (Figure 1). The eclosion rates of uninfected, wAlbB and wMel mosquitoes are , respectively. Death rates are given by for uninfected, wAlbB and wMel mosquitoes in the aquatic stage respectively.
Figure 1.
Schematic of the mosquito ecological model incorporating suppression and interventions to mitigate establishment. The circles represent specific mosquito populations, and the lines represent the transitions from one mosquito population to another, with the values within the lines representing transition rates between populations. The blue lines represent the release of male Wolbachia inoculated mosquitoes at rates or . The birthing rates capture the uninfected offspring that are produced when the uninfected males mate with the uninfected females. When the wAlbB or wMel-infected males mate with the uninfected females, inviable offspring are produced due to CI. Uninfected males mating with the infected wAlbB or wMel-infected female produces a fraction of infected offspring by vertical transmission. Mating between wAlbB or wMel-infected males with wAlbB or wMel-infected females respectively produces a fraction of infected offspring. Mating between wAlbB-infected males (or wMel-infected males) with wMel females (or wAlbB females) resulted in inviable offspring due to CI.
The parameters and govern the proportion of female and male adult mosquitoes being enclosed after the aquatic stage, respectively. After the transition to the adult stage (i.e., , , , , , ), there is a probability of mating between adults of different sexes, subject to their respective populations at that point of time. Births are subject to constraints in the carrying capacity of the population. We consider the following equation ascertaining the effective number of aquatic stage births between wAlbB infected female and uninfected wild-type male mosquitoes:
| (1) |
where denotes the degree of cytoplasmic incompatibility, and the proportion of uninfected wild type mosquitoes at that time point. Mating between irradiated male and female Wolbachia mosquitoes resulted in inviable offspring due to sterility. We assume 100% sterility following irradiation, consistent with previous studies that achieved full sterility under lab and semi-field conditions [41,42]. and denote the total number of aquatic mosquitoes in the population and the total aquatic carrying capacity of the population, respectively. Therefore, ξ governs the breeding constraints in the environment. This results in future aquatic stage mosquitoes being produced at a higher rate when the current population of aquatic mosquitoes is low and at a lower rate when the current population of aquatic mosquitoes is high. These constraints also provide a simple representation of higher aquatic stage mortality at higher aquatic populations. The multiple between the two adult stage mosquito populations help ascertain the number of births in the next time step. Each adult population has a respective birth equation subject to these constraints; their specifications are described in full detail in the Supplementary Material, together with all parameters used for the model obtained from literature-derived sources.
3. Results
To address the questions proposed by this study, we focused on a subset of the mosquito populations that are of key entomological and epidemiological interest, that is, the wild type, wAlbB and wMel female mosquito populations. In Table 3 we show the following key findings regarding elimination of key mosquito populations:
Table 3.
Successful elimination of specific mosquito populations at simulation endpoint. “Yes” indicates the successful elimination of the respective mosquito population. “No” indicates that there was no elimination of the respective mosquito population.“N/A” indicates that the population was not released under that scenario.
| Population | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strategy | S3A | S3B | S4 | ||||||
| Error Rates | 10−3 | 10−9 | 0 | 10−3 | 10−9 | 0 | 10−3 | 10−9 | 0 |
| wAlbB Female | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Wild Female | No | No | No | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| wMel Female | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | No | No | Yes |
3.1. How Does the Error Rate under Sex Sorting Impact the Likelihood of Wolbachia Establishment under the Suppression Approach?
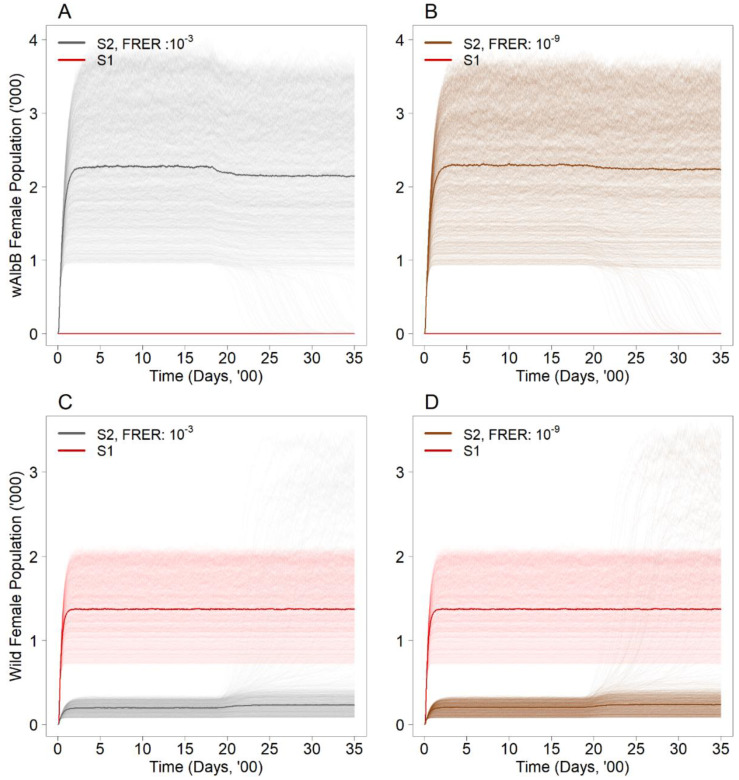
In general, the suppression approach (S2) with constant releases for 100 weeks resulted in the establishment of wAlbB even under very low female release error rates (FRERs). Under FRERs of 10−3 and 10−9, which correspond to the sex sorting error rates of current and next-generation sex sorting technologies [40,41], we found that establishment would occur under the simulated release of 10,000 male Wolbachia mosquitoes per week in an environment where the aquatic carrying capacity is 10,000 (Figure 2A,B). However, the established wAlbB population remained relatively constant between levels of 2210 (95% UI: 2152–2268) and 2141 (95% UI: 2083–2199) under both FRERs, demonstrating that establishment eventually stabilized at a certain level even under the continued constant release of Wolbachia male mosquitoes under different FRERs.
Figure 2.
Number of Wolbachia-infected female mosquitoes (wAlbB) in the population with (A) FRER: 10−3 and (B) FRER: 10−9 under the suppression approach (S2) with the same male release intensity. Number of wild type female mosquitos in the population with (C) FRER: 10−3 and (D) FRER: 10−9 under the suppression approach (S2) with the same male release intensity. The lighter shade solid lines represent the 1000 simulations, and the dark solid lines represent the median of the 1000 simulations. The red solid line represents the baseline scenario (S1).
3.2. Do the Proposed Intervention Strategies Undermine the Original Suppression Approach (i.e., How Do They Affect the Wild Type Population)?
The suppression approach (S2) using the first strain at FRERs of 10−3 and 10−9 resulted in an 82.4% (95% UI: 80.0–85.0%) and 82.5% (95% UI: 79.7–85.4%) decline in the wild-type female population, respectively (Figure 2C,D), relative to the baseline (S1) equilibrium wild-type population. These results confirm the levels of suppression achieved on the wild type female mosquito population from ecological experiments [43,44].
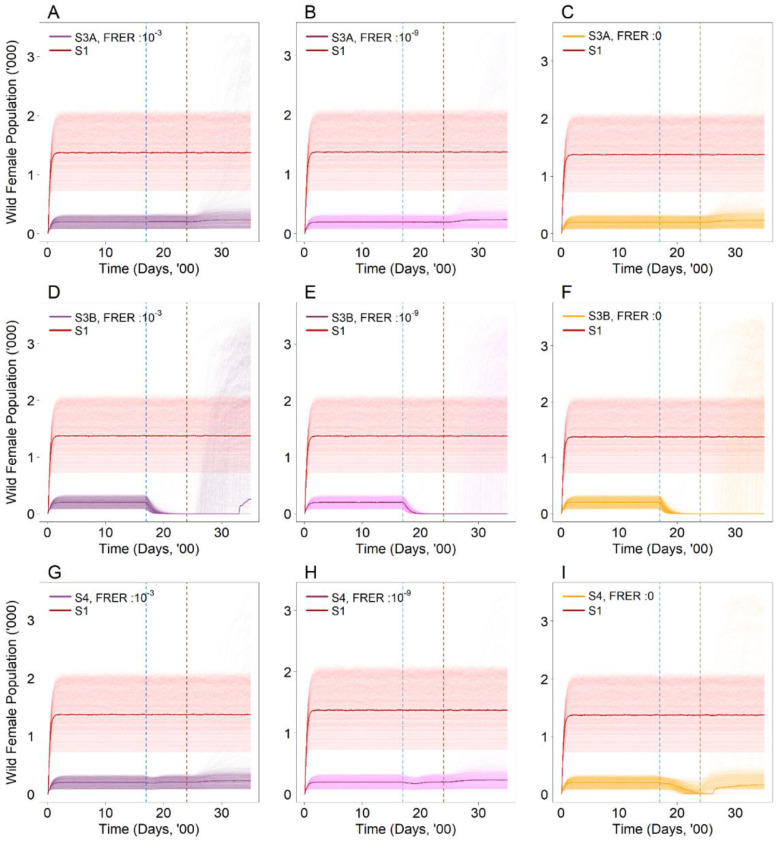
Under SIT-IIT of female mosquitoes (S3A) with an FRER of 10−9 (Figure 3B), the equilibrium wild type female population remained suppressed, with a decline of 82.7% (95% UI: 81.0–84.3%) in the wild type female mosquito populations compared to the baseline of having no releases in place (S1) (Figure 3B). The equilibrium levels observed were similar to that of the pure suppression approach (S2) (Figure 2C,D). In addition, the decline and the eventual equilibrium levels in the wild type female population did not vary considerably under different FRERs for this particular strategy (S3A) (Figure 3A,C).
Figure 3.
Number of wild type female mosquitoes in the population with (A) FRER: 10−3, (B) FRER: 10−9 and (C) FRER: 0 under the first strain female irradiation (S3A) with the same male release intensity. Number of wild type female mosquitoes in the population with (D) FRER: 10−3, (E) FRER: 10−9 and (F) FRER: 0 under the first strain male and female irradiation (S3B) with the same male release intensity. Number of wild type female mosquitoes in the population with (G) FRER: 10−3, (H) FRER: 10−9 and (I) FRER: 0 under the second strain introduction (S4) with the same male release intensity. The lighter shade solid lines represent the 1000 simulations, and the dark solid lines represent the median of the 1000 simulations. The blue and brown dotted vertical line represents the start and end of the intervention (S3A, S3B and S4) respectively. The red solid line represents the baseline scenario (S1).
Under SIT-IIT of male and female mosquitoes (S3B) with varying FRERs, the wild type female population was eliminated at the simulation endpoint (Figure 3D–F). However, under an alternative intervention start and end point where the interventions began before the end of the suppression approach (see Supplementary Material), the wild type female population was only eliminated at smaller FRERs of 10−9 and 0, but not under an FRER of 10−3 (see Supplementary Material). This was due to a rebound in the population sometime after the intervention had ceased. In contrast, elimination was not observed under the pure suppression approach (S2) (Figure 2C,D).
Lastly, by introducing a second Wolbachia strain (S4) with non-zero FRERs, the equilibrium wild type female population remained suppressed, with a decline of between 82.9–83.2% in the wild type female mosquito populations compared to the baseline of having no releases in place (S1) (Figure 3G,H). These results were consistent under the alternative intervention start and end dates (see Supplementary Material). In contrast, under FRER = 0, the wild type female population was eliminated at the simulation endpoint (Figure 3I). However, under the alternative intervention start and end dates (see Supplementary Material), the wild type female population declined to low levels before stabilizing at non-zero levels at the simulation endpoint (see Supplementary Material). The equilibrium levels observed under non-zero FRERs (Figure 3G,H) were similar to that of the suppression approach (S2) (Figure 2C,D), while a zero-equilibrium endpoint was reached under FRER = 0 (Figure 3I).
Collectively, these results demonstrate that the intervention strategies do not undermine the suppression achieved under the original suppression strategy (S2), with the equilibrium endpoint levels for the wild type population stabilising at comparable or lower levels than observed before.
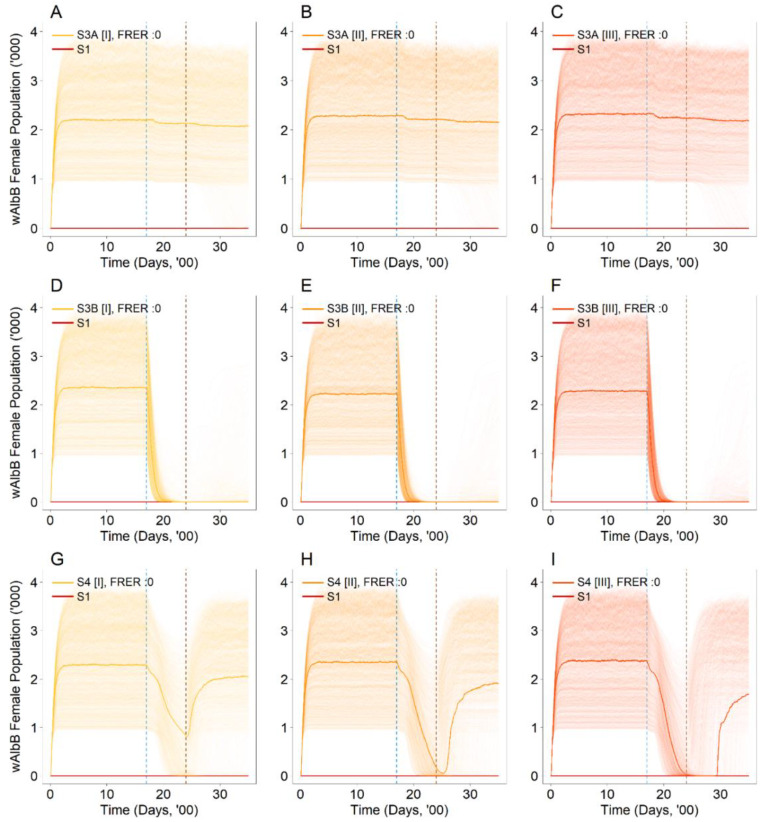
3.3. Are the Proposed Intervention Strategies Effective in Countering the Establishment of Wolbachia?
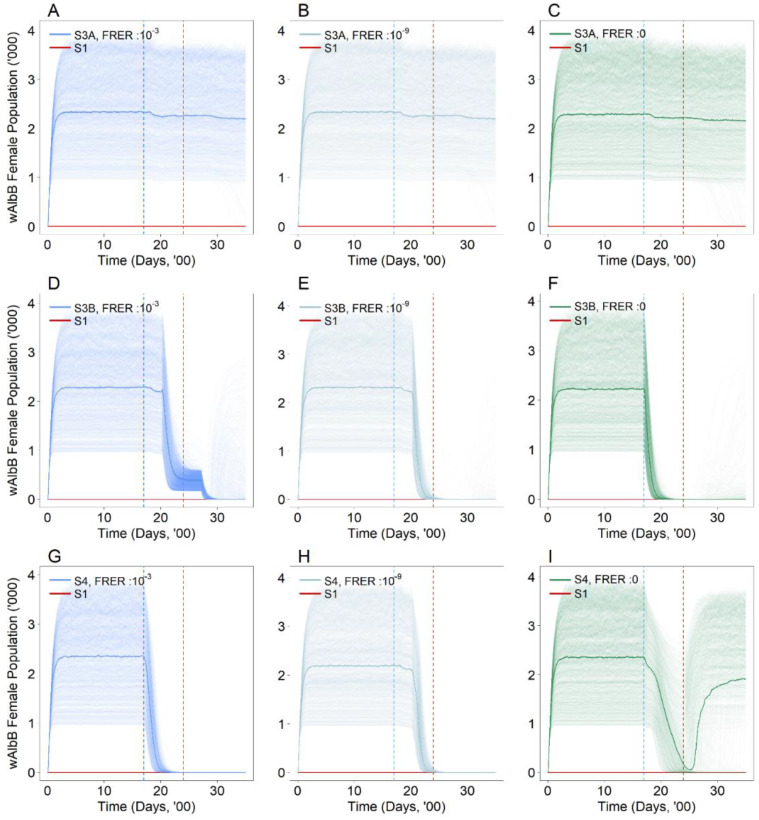
Rendering the first strain Wolbachia female mosquitoes infertile by irradiation (S3A) did not mitigate the establishment of the original female Wolbachia strain under all FRERs (Figure 4A–C). These results were consistent under alternative intervention start and end dates (see Supplementary Material). Under S3A, only the females were rendered infertile. Mating between the fertile first strain Wolbachia males and the established Wolbachia females within the environment may have still occurred, preventing the elimination of these established Wolbachia females. However, under S3B where both males and females were sterilised by irradiation, offspring were not produced between the Wolbachia-infected males and females, resulting in the eventual elimination of the established female Wolbachia mosquitoes (Figure 4D–F). These results were consistent under alternative intervention start and end dates (see Supplementary Material). Likewise, the introduction of the second Wolbachia strain S4 resulted in the elimination of the established female Wolbachia mosquitoes (Figure 4G–I). Under alternative intervention start and end dates where the interventions began before the end of the suppression approach and at an FRER level of 0, the Wolbachia female population level dipped to near zero before re-establishing again at the simulation endpoint (see Supplementary Material). Again, this was due to a rebound in the population sometime after the intervention had ceased.
Figure 4.
Number of Wolbachia (wAlbB) female mosquitoes in the population with (A) FRER: 10−3, (B) FRER: 10−9 and (C) FRER: 0 under the first strain female irradiation (S3A) with the same male release intensity. Number of wild type female mosquitoes in the population with (D) FRER: 10−3, (E) FRER: 10−9 and (F) FRER: 0 under the first strain male and female irradiation (S3B) with the same male release intensity. Number of wild type female mosquitoes in the population with (G) FRER: 10−3, (H) FRER: 10−9 and (I) FRER: 0 under the second strain introduction (S4) with the same male release intensity. The lighter shade solid lines represent the 1000 simulations, and the dark solid lines represent the median of the 1000 simulations. The blue and brown dotted vertical line represents the start and end of the intervention (S3A, S3B and S4) respectively. The red solid line represents the baseline scenario (S1).
Under the use of irradiated first strain males and females S3B, the rate of elimination of the female Wolbachia population increased with a lower FRER (Figure 4D–F). This increased rate of elimination resulted in a reduction in the time (no. of days) required to bring down the female population and to eventually become eliminated. However, under the second strain introduction S4, the rate of elimination declined with a lower FRER (Figure 4G–I). This decline in the elimination rate resulted in a longer period of time (no. of days) required to bring down the female population and to eventually become eliminated. These findings were largely consistent under the alternative intervention start and end date scenario, apart from the second strain introduction S4 with an FRER of 0 where re-establishment occurred.
Under S3B, the released Wolbachia males were rendered sterile, which conferred sterility when mating with the wild type and the established Wolbachia females. Under S4, the introduction of males infected with the second Wolbachia strain resulted in bi-directional cytoplasmic-incompatibility with both the wild type and established Wolbachia females. These separate effects under the individual strategies worked to eliminate the established first strain Wolbachia female mosquitoes.
3.4. Are There Other Potential Issues Surrounding the Proposed Intervention Strategies?
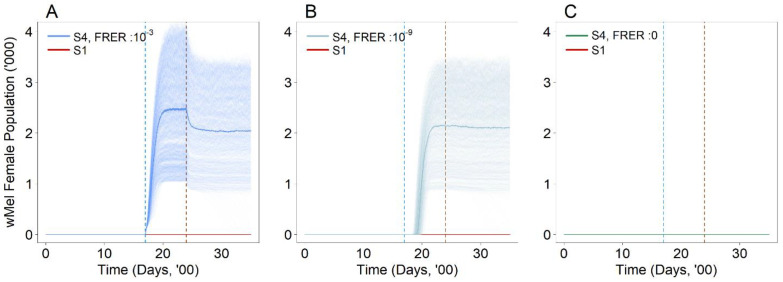
While introducing the second Wolbachia strain (S4) was effective as an intervention to eliminate the established first strain Wolbachia female mosquitoes, the second Wolbachia strain might establish in the population if the FRER is non-zero (Figure 5A,B). This arises due to the unintended release of female second strain Wolbachia mosquitoes into the environment under imperfect sex separation and resulted in establishment even under a very low FRER of 10−9 (Figure 5B). Under non-zero FRERs, the eventual second strain Wolbachia female population mirrored that of the original establishment levels of the first Wolbachia strain (Figure 2A,B). Establishment of the second strain did not occur under zero FRER (Figure 5C).
Figure 5.
Number of second strain Wolbachia (wMel) female mosquitoes in the population with (A) FRER: 10−3, (B) FRER: 10−9 and (C) FRER: 0 under the second strain introduction (S4) with the same male release intensity. The lighter shade solid lines represent the 1000 simulations, and the dark solid lines represent the median of the 1000 simulations. The blue and brown dotted vertical line represents the start and end of the intervention (S4) respectively. The red solid line represents the baseline scenario (S1).
In introducing the second Wolbachia strain (S4), adequate release numbers were required for the elimination of the original Wolbachia female population. Given fewer release numbers (S4 [I]) (Figure 6G), the wAlbB female mosquito population (i.e., original Wolbachia strain used for suppression) declined steadily during the intervention but did not reach elimination at the end of the intervention. Subsequently, the wAlbB female mosquito population rose again and stabilized at a non-zero levels at the simulation endpoint. At higher release numbers (S4 [II] and S4 [III]), (Figure 6H,I), the wAlbB female mosquito population was eliminated at a faster rate before the end of the intervention and stabilized at zero thereafter. These results demonstrate the importance of determining the necessary threshold for the male release numbers to ensure the complete and sustained elimination of the original Wolbachia strain.
Figure 6.
Number of Wolbachia (wAlbB) female mosquitoes in the population with FRER: 0 with (A) Reduced intensity of 40,000 releases per week (S3A [I]), (B) Baseline intensity of 60,000 releases per week (S3A [II]) and (C) Increased intensity of 80,000 releases per week (S3A [II]) of male releases under the first strain female irradiation (S3A). Number of Wolbachia (wAlbB) female mosquitoes in the population with FRER: 0 with (D) Reduced intensity of 40,000 releases per week (S3B [I]), (E) Baseline intensity of 60,000 releases per week (S3B [II]) and (F) Increased intensity of 80,000 releases per week (S3B [II]) of male releases under the first strain male and female irradiation (S3B). Number of Wolbachia (wAlbB) female mosquitoes in the population with FRER: 0 with (G) Reduced intensity of 40,000 releases per week (S3B [I]), (H) Baseline intensity of 60,000 releases per week (S3B [II]) and (I) Increased intensity of 80,000 releases per week (S3B [II]) of male releases under the second strain introduction (S4). The lighter shade solid lines represent the 1000 simulations, and the dark solid lines represent the median of the 1000 simulations. The blue and brown dotted vertical line represents the start and end of the intervention (S3A, S3B and S4) respectively. The red solid line represents the baseline scenario (S1).
4. Discussion
The Wolbachia-IIT strategy has been shown to be a promising method for suppressing mosquito populations [41,45] and our results validate these findings. This study, together with IIT field trials invites comparison with the SIT approach, which has also demonstrated success in suppressing mosquito populations [46]. However, under SIT, there are several drawbacks when the technique is employed independently [46]. Firstly, SIT comprises the release of female mosquitoes, which contributes to pest biting and potential pathogen transmission. Secondly, a constant balance between sterility and mating competitiveness is required, which may not allow for ideal mosquito suppression. Finally, irradiation alone only suppressed mosquito populations, but does not achieve wild-type elimination. A combination of SIT and IIT can circumvent these issues, which may allow for the desired effect of population elimination.
At baseline, we demonstrated a significant reduction in the wild type mosquito population (Figure 2C,D) of up to 83%, which is similar to field studies available in the current literature [26,40,41]. High levels of suppression achieved in the field can be attributed to the complementary effects of Wolbachia-IIT with conventional vector control measures [47], with high community acceptance in places where it is trialed [45,46,48,49,50] contributing in part to its success. Successfully suppressing the wild type population may increase the likelihood of establishment of the Wolbachia strain due to lowered competition from wild type mosquitoes in the environment. This could result in Wolbachia mosquitoes replacing the wild type population, jeopardizing the suppression effort and rendering the strategy unsuccessful. Intervention measures are therefore required to prevent the establishment of Wolbachia in wild type mosquito populations. As such, we sought to implement possible strategies for mitigating the establishment of the formerly released Wolbachia strain (wAlbB) within an appropriate modelling framework.
We presented several key strategies which may be used to mitigate the potential establishment of the released Wolbachia strain. Namely, (i) the persistent use of irradiated male and female Wolbachia mosquitoes via SIT-IIT (S3B) and (ii) the release of a second Wolbachia strain (wMel, S4) after establishment of the former Wolbachia wAlbB has occurred. Under S3B, even if imperfect sex sorting (FRER > 0) persists together with SIT-IIT, the established wAlbB female mosquito population can be successfully eliminated. Similarly, under S4, the established female wAlbB female mosquito population can be successfully eliminated, but under non-zero FRERs for the wMel releases, the establishment of wMel female mosquito populations will occur. In both cases, the wild type mosquito population remains suppressed compared to the baseline levels, demonstrating that these interventions do not undermine the accrued suppression benefits from the originally released Wolbachia strain. These findings support the use of a hybrid approach [38], where areas with high dengue burden may benefit from the release of non-irradiated Wolbachia male mosquitoes to significantly reduce high mosquito populations, followed by the use of irradiated male and female mosquitoes (S3B) to counter the potential issue of establishment.
Among the various release ratios and female release error rates explored under S3B and S4, we found that higher release ratios were more effective in driving down the female population of the released Wolbachia strain (See Supplementary Material). These interventions, however, required a specific threshold value for the elimination of the Wolbachia strain (See Supplementary Material). To take over the established Wolbachia mosquito population’s niche—considering, for example, the intrinsic rate of population growth—the release of a minimum number of sterile or bi-directionally cytoplasmic incompatible mosquitoes may be required. The release numbers and intensity govern the probability of mating between the released sterile/bi-directionally cytoplasmic incompatible male mosquitoes with the established Wolbachia female mosquitoes. Consequently, whether the niche is taken over depends on the release numbers and intensity. Under fewer number of mosquitoes being released this threshold might not be achieved and the probability of mating between the released Wolbachia males and established Wolbachia females may be insufficient to take over this niche, preventing the successful elimination of the established Wolbachia-infected Ae. aegypti strain. While actual mosquito populations are difficult to ascertain in the real world, our results demonstrate the need to couple proposed interventions with entomological surveillance to assess the efficacy of interventions targeted at mitigating establishment and for the appropriate timing of intervention scale ups and/or rollbacks.
In our study, we explored the possibility of establishment under a constant release strategy and several interventions to mitigate this. Pagendam et al. highlighted the possibility for adaptive and crude adaptive releases under IIT to mitigate establishment [39]. However, implementing these strategies appears difficult in practice as they require release numbers to be tailored to time-specific population size estimates. Conversely, the same number of Wolbachia-infected males were released at every release event under the constant release approach in S3B,4, negating the need for real-time and accurate population surveillance. Scaling up such a strategy in terms of release numbers and frequency would be far simpler, without additional resources required for operational purposes.
We followed Pagendam et al. [39], Jansen et al. [51] and Magori et al. [39] by incorporating stochasticity into our model simulations by nesting the biologically plausible range of parameters in each simulation run. This has several benefits over purely deterministic models, such as the incorporation of uncertainty intervals in the evolution of each mosquito population and, therefore, the likelihood under which establishment may be mitigated given a specific intervention. Crucially, stochastic models such as ours can help capture important facets in mosquito population dynamics, such as the uncertainty in each mosquito’s mortality and birth rates, thereby mimicking the large range of possible outcomes observed in the field; these can drastically change the eventual behaviour of the mosquito populations in the simulation, especially when particular subgroups of interest become minute in size.
In tackling the question about strategies to mitigate Wolbachia establishment, we required a simulation framework that could easily parameterize various facets about the mosquito populations. Existing stochastic models were difficult to adapt, with Jansen et al. [51] assuming constant population size over time—which does not hold under the IIT approach—and with Magori et al. [37] requiring that multiple spatially explicit parameters be identified, such as the breeding container locations and numbers. The three-strain compartmental model introduced in this study relied on a literature-derived range of parameters and could be used to draw realistic conclusions about the dynamics of general mosquito populations in an environment where IIT, SIT-IIT and/or a second Wolbachia strain strategies are employed.
Empirical evidence suggests that mosquito larval breeding sites are often fragmented [52], with the degree of population mixing determined by mosquito dispersal and oviposition behaviour [52]. In our study, we adopted a simple representation of density-dependent competition in a large well-mixed population from a single breeding site. We also assumed a linear increase in larval mortality and birth rates. These assumptions likely oversimplify the complex dynamics of the density-dependent competition across a fragmented landscape, which may have implications on the ecological trajectories of the mosquito population. Absolute population numbers were also taken to be arbitrary as any non-zero starting population in the compartmental model eventually converges to an equilibrium population based on model parameters. Therefore, the efficacy of the strategies in our study were evaluated based only after mosquito populations converged to equilibrium and was taken relative to each respective mosquito population, before and after the intervention occurred.
In our study, an independent IIT programme had been initiated to suppress mosquito populations, resulting in the issue of establishment of the Wolbachia strain in the field [38,41]. We therefore explored strategies such as SIT and the introduction of a second bi-directionally cytoplasmic incompatible Wolbachia strain to complement the existing IIT strategy and mitigate establishment. Future programmes should, however, take pre-emptive measures to prevent the issue of establishment, such as a highly efficient sex-sorting system [40] or by employing SIT-ITT from the beginning to ensure population elimination and prevent establishment.
5. Conclusions
To mitigate establishment of the released Wolbachia strain, our study suggests the irradiation of male and female Wolbachia mosquitoes under SIT-IIT with all FRERs can be effective. Our simulations indicate that this intervention does not override the intended effect of wild type suppression under the IIT approach.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at: https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/v14061132/s1, Table S1: Parameters used for core ecological model; Table S2: Different intervention start/endpoints used for simulation; Figure S1: Alternative scenario wildtype female mosquito population; Figure S2: Alternative scenario wAlb female population; Figure S3: Alternative scenario wMel female mosquito population. Reference [53] was cited in the Supplementary Material.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, J.T.L., S.S. (Shuzhen Sim), C.H.T. and L.C.N.; Methodology, J.T.L. and S.S. (Stacy Soh); Software, S.S. (Stacy Soh) and J.T.L.; Writing—original draft preparation, S.S. (Stacy Soh) and J.T.L.; Writing—review and editing, S.S. (Stacy Soh), J.T.L., S.S. (Shuzhen Sim), C.H.T., S.H.H., L.C.N., J.O., A.R.C., A.S., B.S.D., K.W.T. and J.R.K.; Supervision, J.T.L., S.S. (Shuzhen Sim), C.H.T. and L.C.N.; Project administration, J.T.L. and S.S. (Shuzhen Sim). All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
All data and parameters used in this study are available from the Supplementary Material and https://github.com/stacysoh/wolbEstab (accessed on 7 April 2022).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Funding Statement
This research received no external funding.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Souza-Neto J.A., Powell J.R., Bonizzoni M. Aedes aegypti vector competence studies: A review. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2019;67:191–209. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2018.11.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.World Health Organization Vector-Borne Diseases Fact Sheet. 2017. [(accessed on 30 December 2021)]. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/vector-borne-
- 3.Evelyn M., Murray A., Quam M.B., Wilder-Smith A. Epidemiology of dengue: Past, present and future prospects. Clin. Epidemiol. 2013;5:299. doi: 10.2147/CLEP.S34440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gubler D.J. Dengue, Urbanization and Globalization: The Unholy Trinity of the 21st Century. Trop. Med. Health. 2011;39((Suppl. S4)):S3–S11. doi: 10.2149/tmh.2011-S05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cattarino L., Rodriguez-Barraquer I., Imai N., Cummings D.A.T., Ferguson N.M. Mapping global variation in dengue transmission intensity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2020;12:105788. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aax4144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bhatt S., Gething P.W., Brady O.J., Messina J.P., Farlow A.W., Moyes C.L., Drake J.M., Brownstein J.S., Hoen A.G., Sankoh O., et al. The global distribution and burden of dengue. Nature. 2013;496:504–507. doi: 10.1038/nature12060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Shepard D.S., Undurraga E.A., Halasa Y.A., Stanaway J.D. The global economic burden of dengue: A systematic analysis. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016;16:935–941. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(16)00146-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Silva J.V.J., Jr., Lopes T.R.R., de Oliveira-Filho E.F., Oliveira R.A.S., Durães-Carvalho R., Gil L.H.V.G. Current status, challenges and perspectives in the development of vaccines against yellow fever, dengue, Zika and chikungunya viruses. Acta Trop. 2018;182:257–263. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2018.03.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kantor I.N. Dengue, zika, chikungunya y el desarrollo de vacunas Dengue, zika, chikungunya and the development of vaccines. Medicina. 2018;78:23–28. (In Spanish) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Achee N.L., Gould F., Perkins T.A., Reiner R.C., Morrison A.C., Ritchie S.A., Gubler D.J., Teyssou R., Scott T.W. A Critical Assessment of Vector Control for Dengue Prevention. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015;9:e0003655. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0003655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Lim J.T., Dickens B.S., Haoyang S., Ching N.L., Cook A.R. Inference on dengue epidemics with Bayesian regime switching models. PLOS Comput. Biol. 2020;16:e1007839. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Lim J.T., Dickens B.L., Ong J., Aik J., Lee V.J., Cook A.R., Ng L.C. Decreased dengue transmission in migrant worker populations in Singapore at-tributable to SARS-CoV-2 quarantine measures. J. Travel Med. 2021;28:taaa228. doi: 10.1093/jtm/taaa228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Lim J.T., Chew L.Z.X., Choo E.L.W., Dickens B.S.L., Ong J., Aik J., Ng L.C., Cook A.R. Increased Dengue Transmissions in Singapore Attributable to SARS-CoV-2 Social Distancing Measures. J. Infect. Dis. 2020;223:399–402. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Lim J.T., Dickens B.S.L., Chew L.Z.X., Choo E.L.W., Koo J.R., Aik J., Ng L.C., Cook A.R. Impact of sars-cov-2 interventions on dengue transmission. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2020;14:e0008719. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Leigh R., Bowman S.D., McCall P.J. Is dengue vector control deficient in effec-tiveness or evidence?: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2016;10:e0004551. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0004551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Scott A.R., Kyran M.S. Reflections from an old Queenslander: Can rear and release strategies be the next great era of vector control. Proc. R. Soc. B. 2019;286:20190973. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2019.0973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Laven H. Eradication of Culex pipiens fatigans through Cytoplasmic Incompatibility. Nature. 1967;216:383–384. doi: 10.1038/216383a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sinkins S.P. Wolbachia and cytoplasmic incompatibility in mosquitoes. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2004;34:723–729. doi: 10.1016/j.ibmb.2004.03.025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Mains J.W., Kelly P.H., Dobson K.L., Petrie W.D., Dobson S.L. Localized control of Aedes aegypti (Diptera: Culicidae) in Miami, FL, via inun-dative releases of Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes. J. Med. Entomol. 2019;56:1296–1303. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjz051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zheng X., Zhang D., Li Y., Yang C., Wu Y., Liang X., Liang Y., Pan X., Hu L., Sun Q., et al. Incompatible and sterile insect techniques combined eliminate mosquitoes. Nature. 2019;572:56–61. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1407-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wolbachia-Aedes Mosquito Suppression Strategy. [(accessed on 30 December 2021)]; Available online: https://www.nea.gov.sg/corporatefunctions/resources/research/wolbachia-aedes-mosquito-suppression-strategy.
- 22.Soh S., Ho S.H., Seah A., Ong J., Dickens B.S., Tan K.W., Koo J.R., Cook A.R., Tan K.B., Sim S., et al. Economic impact of dengue in Singapore from 2010 to 2020 and the cost-effectiveness of Wolbachia interventions. PLOS Glob. Public Health. 2021;1:e0000024. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgph.0000024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Knipling E.F. Possibilities of Insect Control or Eradication Through the Use of Sexually Sterile Males1. J. Econ. Èntomol. 1955;48:459–462. doi: 10.1093/jee/48.4.459. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mains J.W., Brelsfoard C.L., Rose R.I., Dobson S.L. Female adult Aedes albopictus suppression by Wolbachia-infected male mosquitoes. Sci. Rep. 2016;6:33846. doi: 10.1038/srep33846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xi Z., Khoo C.C., Dobson S.L. Wolbachia establishment and invasion in an Aedes aegypti laboratory population. Science. 2005;310:326–328. doi: 10.1126/science.1117607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Zhang D., Lees R.S., Xi Z., Gilles J.R.L., Bourtzis K. Combining the sterile insect technique with Wolbachia-based approaches: II-a safer approach to Aedes albopictus population suppression programmes, designed to minimize the consequences of inadvertent female release. PloS ONE. 2015;10:e0135194. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Bond J.G., Osorio A.R., Avila N., Gómez-Simuta Y., Marina C.F., Fernández-Salas I., Liedo P., Dor A., Carvalho D.O., Bourtzis K., et al. Optimization of irradiation dose to Aedes aegypti and Ae. albopictus in a sterile insect technique program. PLoS ONE. 2019;14:e0212520. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0212520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Darrow D.I. The effect of gamma irradiation on reproduction and life span of the mosquito Culex tarsalis Coquillett. Mosq. News. 1968;28:21–24. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Zhang N., Lees R.S., Xi Z., Bourtzis K., Gilles J.R.L. Combining the Sterile Insect Technique with the Incompatible Insect Technique: III-Robust Mating Competitiveness of Irradiated Triple Wolbachia-Infected Aedes albopictus Males under Semi-Field Conditions. PLoS ONE. 2016;11:e0151864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Madakacherry O., Lees R.S., Gilles J.R.L. Aedes albopictus (Skuse) males in laboratory and semi-field cages: Release ratios and mating competitiveness. Acta Trop. 2014;132:S124–S129. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2013.11.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li Y., Baton L.A., Zhang D., Bouyer J., Parker A.G., Hoffmann A.A., Ng L.C., Tan C.H., Xi Z. Reply to: Issues with combining incompatible and sterile insect techniques. Nature. 2021;590:E3–E5. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-03165-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Engelstädter J., Telschow T., Hammerstein P. Infection dynamics of different Wolbachia-types within one host population. J. Theor. Biol. 2004;231:345–355. doi: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2004.06.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Farkas J.Z., Hinow P. Structured and Unstructured Continuous Models for Wolbachia Infections. Bull. Math. Biol. 2010;72:2067–2088. doi: 10.1007/s11538-010-9528-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Knipling E.F. Sterile-Male Method of Population Control: Successful with some insects, the method may also be effective when applied to other noxious animals. Science. 1959;130:902–904. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3380.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Hancock P.A., Sinkins S.P., Charles H., Godfray J. Population dynamic models of the spread of Wolbachia. Am. Nat. 2011;177:323–333. doi: 10.1086/658121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Dufourd C., Dumont Y. Impact of environmental factors on mosquito dispersal in the prospect of sterile insect technique control. Comput. Math. Appl. 2013;66:1695–1715. doi: 10.1016/j.camwa.2013.03.024. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Magori K., Legros M., Puente M.E., Ficks D.A., Scott T.W., Lloyd A.L., Gould F. Skeeter Buster: A stochastic, spatially explicit modeling tool for studying Ae-des aegypti population replacement and population suppression strategies. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2009;3:e508. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0000508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Pagendam D.E., Trewin B.J., Snoad N., Ritchie S.A., Hoffmann A.A., Staunton K.M., Paton C., Beebe N. Modelling the Wolbachia incompatible insect technique: Strategies for effective mosquito population elimination. BMC Biol. 2020;18:161. doi: 10.1186/s12915-020-00887-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ross P.A., Gu X., Robinson K.L., Yang Q., Cottingham E., Zhang Y., Yeap H.L., Xu X., Endersby-Harshman N.M., Hoffmann A.A. A wAlbB Wolbachia Transinfection Displays Stable Phenotypic Effects across Divergent Aedes aegypti Mosquito Backgrounds. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2021;87:e0126421. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01264-21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Crawford J.E., Clarke D.W., Criswell V., Desnoyer M., Cornel D., Deegan B., Gong K., Hopkins K.C., Howell P., Hyde J.S. Efficient production of male Wolbachia-infected Aedes aegypti mosquitoes enables large-scale suppression of wild populations. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020;38:482–492. doi: 10.1038/s41587-020-0471-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee C.N., Project Wolbachia-Singapore Consortium Wolbachia-mediated sterility sup-presses Aedes aegypti populations in the urban tropics. medRxiv. 2021 doi: 10.1101/2021.06.16.21257922. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ranathunge T., Harishchandra J., Maiga H., Bouyer J., Gunawardena Y.I.N.S., Hapugoda M. Development of the Sterile Insect Technique to control the dengue vector Aedes aegypti (Linnaeus) in Sri Lanka. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0265244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Martín-Park A., Che-Mendoza A., Contreras-Perera Y., Pérez-Carrillo S., Puerta-Guardo H., Villegas-Chim J., Guillermo-May G., Medina-Barreiro A., Delfín-González H., Méndez-Vales R., et al. Pilot trial using mass field-releases of sterile males produced with the incompatible and sterile insect techniques as part of integrated Aedes aegypti control in Mexico. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2022;16:e0010324. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Hoffmann A.A., Montgomery B.L., Popovici J., Iturbeormaetxe I., Johnson P.H., Muzzi F., Greenfield M., Durkan M., Leong Y.S., Dong Y., et al. Successful establishment of Wolbachia in Aedes populations to suppress dengue transmission. Nature. 2011;476:454–457. doi: 10.1038/nature10356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rašić G., Endersby N.M., Williams C., Hoffmann A.A. UsingWolbachia-based release for suppression of Aedesmosquitoes: Insights from genetic data and population simulations. Ecol. Appl. 2014;24:1226–1234. doi: 10.1890/13-1305.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Benedict M.Q. Sterile Insect Technique: Lessons from the Past. J. Med Èntomol. 2021;58:1974–1979. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjab024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Dame D.A., Curtis C.F., Benedict M.Q., Robinson A.S., Knols B.G. Historical applications of induced sterilisation in field populations of mosquitoes. Malar. J. 2009;8:S2. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-8-S2-S2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Bartumeus F., Costa G.B., Eritja R., Kelly A.H., Finda M., Lezaun J., Okumu F., Quinlan M.M., Thizy D.C., Toé L.P., et al. Sustainable innovation in vector control requires strong partnerships with communities. PLOS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2019;13:e0007204. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Liew C., Soh L.T., Chen I., Ng L.C. Public sentiments towards the use of Wolbachia-Aedes technology in Singapore. BMC Public Health. 2021;21:1417. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-11380-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Liew C., Soh L.T., Chen I., Li X., Sim S., Ng L.C. Area-Wide Integrated Pest Management. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2021. Community Engagement for Wolbachia-Based Aedes aegypti Population Suppression for Dengue Control: The Singapore Experience; pp. 747–761. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Vincent A.A., Jansen M.T., Godfray H.C.J. Stochastic spread of Wolbachia. Proc. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2008;275:2769–2776. doi: 10.1098/rspb.2008.0914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.McCormack C.P., Ghani A.C., Ferguson N.M. Fine-scale modelling finds that breeding site fragmentation can reduce mosquito population persistence. Commun. Biol. 2019;2:273. doi: 10.1038/s42003-019-0525-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Joubert D.A., Walker T., Carrington L.B., De Bruyne J.T., Kien D.H.T., Hoang N.L.T., Chau N.V.V., Iturbe-Ormaetxe I., Simmons C.P., O’Neill S.L. Establishment of a Wolbachia superinfection in Aedes aegypti mosquitoes as a potential approach for future resistance management. PLoS Pathogens. 2016;12:e1005434. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
All data and parameters used in this study are available from the Supplementary Material and https://github.com/stacysoh/wolbEstab (accessed on 7 April 2022).