Abstract
Ambient light stable 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirine photolabels are developed via stabilization of the strained three membered diazirine ring by replacing the phenyl ring with electron withdrawing heterocyclic rings. Photolabeling studies reveal that these ambient light stable photolabels are equally efficient in photolabeling target proteins as the traditional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyldiazirine and found to significantly increase the aqueous solubility of the photoaffinity labels.
Graphical Abstract
Ambient light stable 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirine photolabels were designed, synthesized and evaluated. In addition to the enhancement to ambient light stability, the modified photolabels were equally efficient in labeling biological targets. The new photolabels also increase the aqueous solubility of the photoaffinity labels by several folds.
Photoaffinity labeling (PAL) is an established approach to investigate interactions between a ligand and a biological receptor, utilizing a photoactivatable probe to form a covalent bond between the ligand and the biological receptor upon UV light irradiation of the ligand-receptor complex.1, 2 Many types of photoactivatable groups have been developed over the past 40 years, of which 3H-diazirines, arylazides, and benzophenones emerged as the widely used photoprobes.3, 4 3H-Diazirines, arylazides, and benzophenones photoreact into highly reactive intermediates such as carbenes, nitrenes, and biradicals respectively, which covalently crosslink to a biological receptor.5
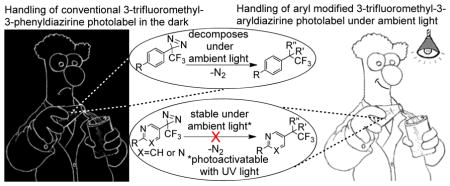
Ideally, a photoactivatable probe should be readily synthesized, chemically stable and susceptible to smooth photolysis at long wavelengths (λext ≥ 300 nm) to exclude photooxidative or other photochemical damage of the biological target. Comparative studies with ion channels,6 glucose transporter proteins,7 yeast RNA Polymerase III,8 and peptide thymopentin9 identified 3H-diazirines to be best suited for PAL, while arylazides and benzophenones failed at yielding respectable amounts of specific labeling products.1, 10 In particular, the 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyl-diazirine introduced by Brunner is the most widely used photolabel producing a singlet carbene as the reactive intermediate, which inserts into carbon-, nitrogen-, oxygen- or sulfur-containing bonds at almost diffusion-controlled reaction rates.4, 11 Despite the promise of photoactivatable 3H-diazirines as photolabeling agents, the cumbersome synthesis, the instability to ambient light conditions, and the limited aqueous solubility represent major drawbacks for PAL. Herein we report for the first time on the design, synthesis and evaluation of 3-pyridyl- and 3-pyrimidyl-substituted 3-trifluoromethyl-diazirines 1 and 2 (Fig. 1) as photoaffinity labels displaying favorable ambient light stability without compromising the photoactivated insertion reactivity.
Fig. 1.
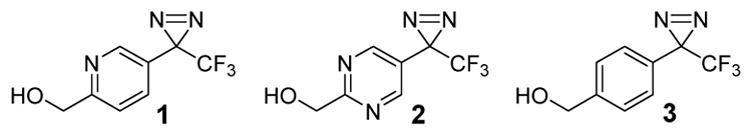
Design of ambient light stable pyridine and pyrimidine derived 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirines 1 and 2
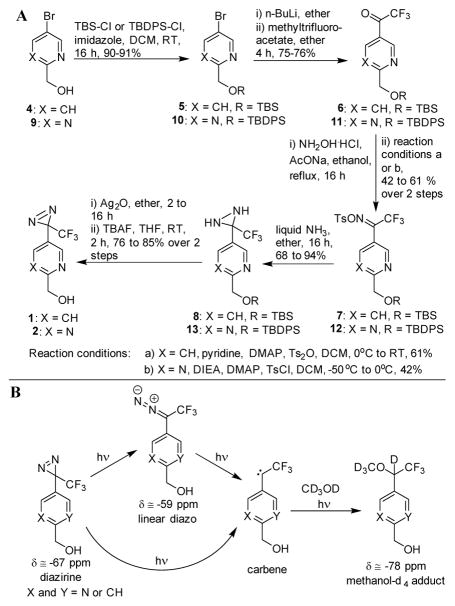
Ambient light conditions commonly promote the spontaneous decomposition of the 3H-diazirines due to ring strain energy of the three-membered diazirine ring. Based on previous reports, we speculated to minimize the ambient light mediated 3H-diazirine’s decay through electron withdrawing groups while retaining the ability to rapidly react with UV light (λext = 320 – 400 nm) to the corresponding carbene intermediate.12 As the trifluoromethyl substituent of 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyl-diazirine is a very strong electron withdrawing group,13 as well as previous studies have shown that aromatic diazirines photochemically produce higher ratios of carbene over the rearranged diazo byproduct compared to aliphatic diazirines,1, 14, 15 we decided to replace the phenyl group with an electron withdrawing pyridine or pyrimidine ring. Furthermore, we speculated that the use of a pyridyl- or pyrimidyl-substituent will slightly increase the insertion reactivity of the photoactivated intermediate as pyridyl carbenes have been shown to be more reactive than corresponding phenyl analogues.16 With this understanding, we prepared pyridine and pyrimidine photolabels 1 and 2 starting from the alcohols 4 and 917 (Scheme 1A). For comparative studies, we also prepared the conventional Brunner-type 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyl-diazirine 3 as previously reported.14, 18
Scheme 1.
(A) Synthesis of pyridine and pyrimidine 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirines 1 and 2 (B) Photoactivation reaction of diazirine photoprobes
The photoactivation and the photostability of diazirines 1 – 3 were investigated first by 19F NMR utilizing deuterated methanol to scavenge the carbene intermediates.19, 20 Previous 19F NMR studies have demonstrated that photoactivation of diazirine 3 lead predominantly to the corresponding singlet carbene, which rapidly forms the methanol insertion product (Scheme 1B).14, 19 In parallel, a side reaction occurs by rearranging diazirine 3 into a linear diazo compound, which under continuous light exposure slowly decomposes to the reactive carbene leading ultimately to the methanol insertion product.
Similarly, a 19F NMR experimental set-up was chosen to monitor the photoactivation of diazirines 1–3. The exchange of the phenyl ring in the 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyl diazirine 3 by the electron withdrawing pyridine or pyrimidine ring did not affect the ratio between the carbene and the linear diazo intermediate (Supporting Information Fig. S1). Across control compound 3 and the modified photolabels 1 and 2, the linear diazo intermediate peaked at about 30% and decreased as irradiation continued. These results indicated that the photolabeling efficiency, with respect to the ratio of carbene to linear diazo ratio, would not be affected by switching the phenyl moiety with a pyridine or a pyrimidine.
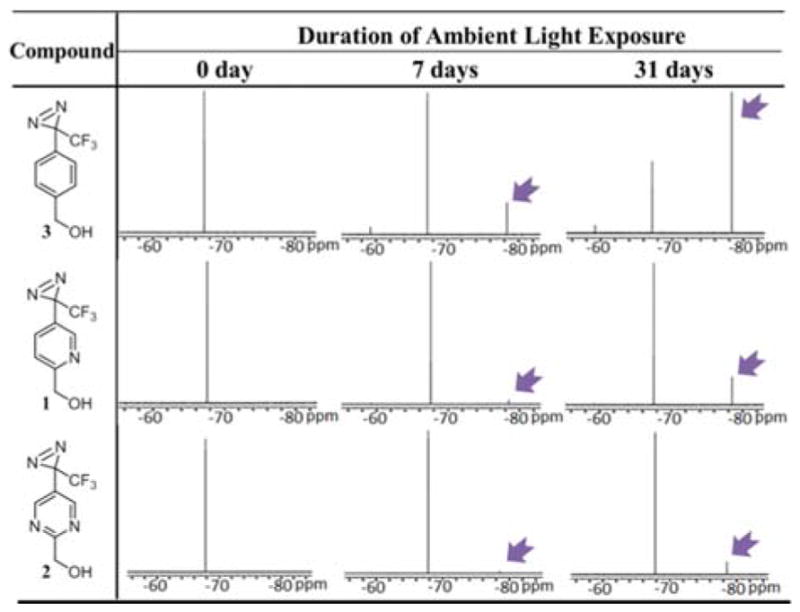
We subjected the modified 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirine photolabels 1 and 2 to an ambient light stability test along with the conventional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyl diazirine photolabel 3 to determine the effectiveness to increase the light stability of diazirine photolabels 1 and 2. Solutions of the conventional diazirine 3 and modified photolabels 1 and 2 in deuterated methanol were exposed to ambient light conditions using linear fluorescent lamps, and the rate of decomposition was observed over a period of one month. As shown by the 19F NMR, 3-phenyl diazirine 3 had already undergone significant photodecomposition after 7 days of light exposure (Table 1). In contrast, during the same period of ambient light exposure, pyridine photolabel 1 negligibly photodecomposed whereas pyrimidyl photolabel 2 was virtually unaffected. Exposing the probes 1–3 to light for a period of one month continued this stability trend. As determined by 19F NMR, only 27% of the conventional photolabel 3 remained intact after one month of ambient light exposure (Supporting Information Table S1), whereas 79% of the pyridine photolabel 1 and 90 % of the pyrimidine photolabel 2 remained unaffected. Similar stability trends were observed when photolabels 1–3 were exposed to light from an incandescent bulb (Supporting Information Table S2). No appreciable decomposition of diazirines 1–3 was detected in a control experiment when compounds 1–3 were kept in the dark at room temperature for a period of one month (Supporting Information Table S3), suggesting probes 1 and 2 to be equally stable compared to the conventional phenyldiazirine 3. Furthermore, the near-UV/Vis absorption spectra show that the maximum absorption λmax was 350 nm for 1–3, whereas the absorption coefficient ε was decreased by approximately 15% for pyiridine 1 and 30% for pyrimidine 2 (Supporting Information Table S4). Importantly, these results proved our hypothesis of increasing the ambient light stability by stabilizing the diazirine ring with electron withdrawing substitutions to be correct.
Table 1.
Comparison of ambient light stability of modified trifluoromethylaryl diazirines 1 and 2 versus the conventional trifluoromethylphenyl diazirine 3. A solution of trifluoromethylaryl diazirines 1, 2 or 3 in d4-methanol was exposed to light from two linear fluorescent lamps (28 W each) at room temperature and the photodecomposition of the diazirines were followed by 19F NMR. The picture shots of the 19F NMR shows that upon exposure to ambient light the conventional trifluoromethylphenyl diazirine decomposes faster as indicated by the decomposition product peak (pointed out by arrow), while the pyridinyl derivative is much more resistant to the photodecomposition and the pyrimidinyl diazirine is virtually intact.
|
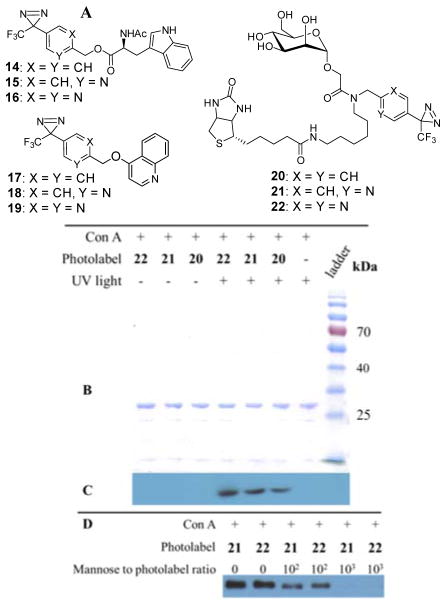
Photolabeling experiments are commonly conducted in aqueous buffer solutions, and it was predicted that pyridine and pyrimidine probes 1 and 2 will possess a better aqueous solubility than the conventional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyl diazirine 3. To demonstrate the aqueous solubility enhancements of pyridine and pyrimidine photoprobes, compounds 1–3 were derivatized with N-acetyl tryptophan or 4-quinolinol to yield corresponding esters 14–16 or ethers 17–19 (Fig. 2A). The aqueous solubility of compounds 14–19 were experimentally determined at pH = 7.4 and 5.0 using a previously reported HPLC-based assay (Supporting Information Table S4).21 As expected, in comparison to conventional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyl-diazirines 14 and 17, the pyridyl probes 15 and 18 were approximately 30–250-fold more soluble, whereas pyrimidinyl probes 16 and 19 were 100–7,500 times more soluble.
Fig. 2.
(A) Compounds 14–19 synthesized for solubility studies and photoaffinity probes 20, 21 and 22 designed to evaluate photolabeling activities (B) Coomassie stained gel of photolabeled Con A and control samples (C) Western blot analysis to detect biotinylation of Con A through photolabeling. The western blot indicates that Con A is photolabeled with the pyridinyl and pyrimidinyl photolabels 21 and 22 as effectively as the conventional phenyl derived photolabel 20. (D) Photolabeling of Con A with 21 and 22 in the presence of the native ligand mannose at different concentrations. The western blot analysis suggests that the extent of photolabeling of Con A with photoprobes 21 or 22 correlates indirectly to the concentration of competing mannose ligand.
To investigate whether pyridyl- and pyrimidyl-substituted diazirines 1 and 2 are suitable for photoaffinity labeling of protein targets, mannose photoaffinity probes 20–22 were designed to label concanavalin A (Con A) (Fig. 2A). Previously, a specifically designed diazirine-derived mannose photoaffinity probe was reported to covalently crosslink to Con A at the saccharide binding sites.22 Diazirine probes 20–22 were designed with a biotin moiety to facilitate western blot visualization and post-labeling enrichment (synthesis of 20, 21 and 22 detailed in Supporting Information Scheme S3).
In the first labeling experiment, probes 20–22 were incubated with Con A and subjected to photoaffinity labeling by exposure to UV light (> 320 nm). In another set of experiment, probes 20–22 were incubated with Con A without being exposed to UV light to investigate if there is any labelling in the absence of photoactivation. As a control, Con A in incubation buffer in absence of any photoaffinity probe was also subjected to photoactivation under UV light. The control, which contained Con A without any photoaffinity probe, was visualized with coomassie stain but did not make any visible spot in the anti-biotin peroxidase antibody western blot (Fig. 2B and 2C). In contrast, the samples containing Con A and label 20, 21 or 22 that were photoactivated with UV light were visible with both coomassie stain and anti-biotin peroxidase antibody western blot. This data indicates that the biotin containing photoaffinity labels derived from the modified photoaffinity labels 21 and 22 and the conventional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyldiazirine photoaffinity label 20 successfully labeled the protein target upon photoactivation. However, samples containing Con A along with photoaffinity labels 20, 21 or 22 that were not photoactivated with UV light were detected only with coomassie stain and not in the western blot analysis, proving that Con A is tagged only upon photoactivation of the photoaffinity probes. These data suggest that the modified labels 1 and 2 are capable of tagging proteins upon photoactivation as efficiently as the conventional diazirine photolabel 3.
Since mannose is the natural ligand of Con A, addition of mannose prior to the photolabeling should inhibit the binding of the photoaffinity labels 20–22 to Con A and impede thephotoaffinity labeling. In presence of mannose ligand, we observed that the crosslinking of 20–22 was significantly suppressed (Fig. 2D) depending on the concentration of mannose ligand. These results suggested that the photolabeling of 20–22 occurred at the mannose-specific binding sites of the target protein Con A and not in an unspecific way on the protein surface.
Finally, in order to determine the photolabeled site of Con A, samples photolabeled with 20–22 were subjected to trypsin digestion and subsequent analysis by liquid chromatography coupled to a linear ion trap-Orbitrap spectrometry. The labeled peptides with a neutral mass of 1826.9023, 1827.8971 and 1828.8940 Da, for the samples photolabeled with 20, 21 and 22 respectively, were found (Fig. 3A). Upon subtracting the mass of denitrogenated photolabels from the mass of labeled peptides, all the resultant masses corresponded to the mass of the peptide sequence Val91 - Lys101 (VGLSASTGLYK) with high mass accuracy (< 3 ppm) (Supporting Information Table S5). Further fragmentation of the labeled peptide in the Orbitrap mass spectrometer confirmed the identity and sequence of the labeled peptide (Supporting Information Table S6 and Fig. S3). It is noteworthy that Hamachi and co-workers previously reported the same peptide sequence (Val91 - Lys101) to be labeled, in their efforts to photolabel Con A with their 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyldiazirine derived photoaffinity label.22 Computational modeling studies (Fig. 3B) revealed that the peptide sequence Val91 - Lys101 forms the lip of the mannose binding pocket in Con A, accounting for the consistent labeling at this position. The mass spectroscopic analysis has confirmed that the ambient light stable pyridinyl and pyrimidinyl photolabels also undergoes the binding site specific labeling much like the conventional phenyl derived photolabels.
Fig. 3.
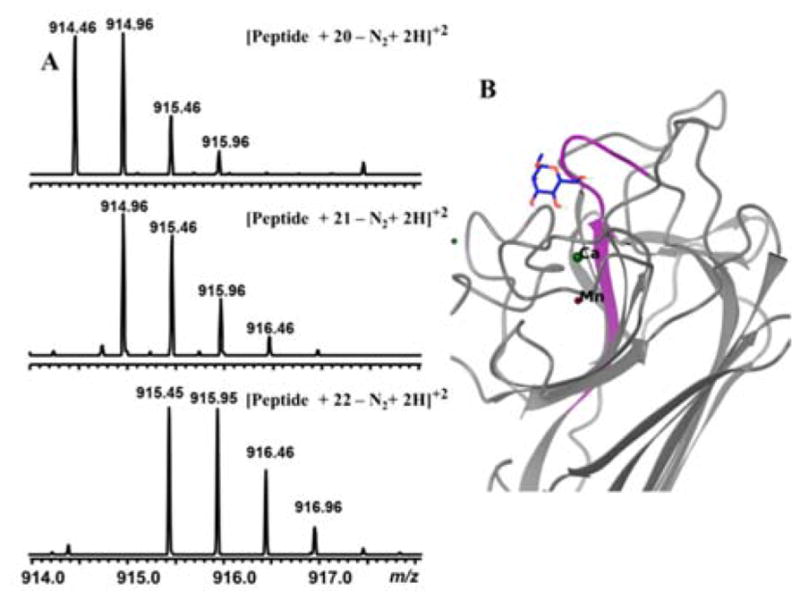
(A) Mass spectra of peptides labeled with photolabels 20–22. The MS/MS analysis and high accuracy mass (< 3 ppm) analysis revealed that the crosslinked peptide is Val91 - Lys101 (VGLSASTGLYK) residue. (B) Virtual docking of the native ligand mannose bound to Con A (PDB ID: 3CNA). Note that peptide Val91-Lys101 (VGLSASTGLYK) (highlighted in purple) has been labeled by the photoaffinity probes 20–22, which indicates that photoprobes 20–22 are binding and labeling the protein at the saccharide binding sites of Con A.
In Conclusion, ambient light stable photolabels have been developed by substituting the phenyl ring in 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyldiazirine by a pyridine or pyrimidine ring in 3-position. Subsequent photoactivation and photoaffinity labeling studies of these pyridine or pyrimidine photolabels with Con A revealed that they are as efficient as the conventional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-phenyldiazirine probes. Furthermore, the pyridine and pyrimidine photolabels also showed significant aqueous solubility improvements over the conventional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirine photolabel. The favorable physicochemical properties including the improved ambient light stability of the pyridine and pyrimidine photolabels render significant advantages over the traditional 3-trifluoromethyl-3-aryldiazirine not only for the actual photolabeling experiment but also during the synthesis of the photoaffinity probes. We are currently investigating the possibility to use pyridine- and pyrimidine-substituted 3-trifluoromethyl-diazirines for the identification of biological targets associated to anti-malarial, anti-leishmanial and anti-bacterial agents.23
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the National Institutes of Health (R01 GM097118). We thank Dr. S. Mahajan and Dr. D. Ramamoorthy for their guidance with the western blot and virtual docking studies respectively.
Footnotes
Electronic Supplementary Information (ESI) available: Synthetic schemes, tables, figures, photoactivation studies, NMR spectra, experimental procedures of synthesis and photolabeling. See DOI: 10.1039/x0xx00000x
Notes and references
- 1.Das J. Chem Rev. 2011;111:4405. doi: 10.1021/cr1002722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li Z, Wang D, Li L, Pan S, Na Z, Tan CY, Yao SQ. J Am Chem Soc. 2014;136:9990. doi: 10.1021/ja502780z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Smith E, Collins I. Future Med Chem. 2015;7:159. doi: 10.4155/fmc.14.152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Hatanaka Y, Sadakane Y. Curr Top Med Chem. 2002;2:271. doi: 10.2174/1568026023394182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kotzybahibert F, Kapfer I, Goeldner M. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 1995;34:1296. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Dorman G. Bioorg Chem of Biol Signal Transduction. 2001;211:169. [Google Scholar]; Gartner CA. Curr Med Chem. 2003;10:671. doi: 10.2174/0929867033457890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Nakayama H, Hatanaka Y, Taki M, Yoshida E, Kanaoka Y. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1993;707:349. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1993.tb38067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Yang J, Clark AE, Kozka IJ, Cushman SW, Holman GD. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Tate JJ, Persinger J, Bartholomew B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998;26:1421. doi: 10.1093/nar/26.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Weber PJA, BeckSickinger AG. J Pept Res. 1997;49:375. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1997.tb00889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hashimoto M, Hatanaka Y. Eur J Org Chem. 2008;2008:2513. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Dubinsky L, Krom BP, Meijler MM. Bioorg Med Chem. 2012;20:554. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2011.06.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Liu BL, Kang DS. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 1994;34:418. [Google Scholar]; He YG, Junk CP, Cawley JJ, Lemal DM. J Am Chem Soc. 2003;125:5590. doi: 10.1021/ja030077y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.True JE, Thomas TD, Winter RW, Gard GL. Inorg Chem. 2003;42:4437. doi: 10.1021/ic0343298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brunner J, Senn H, Richards FM. J Biol Chem. 1980;255:3313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Erni B, Khorana HG. J Am Chem Soc. 1980;102:3888. [Google Scholar]; Bonneau R, Liu MTH. J Am Chem Soc. 1996;118:7229. [Google Scholar]; Akasaka T, Liu MTH, Niino Y, Maeda Y, Wakahara T, Okamura M, Kobayashi K, Nagase S. J Am Chem Soc. 2000;122:7134. doi: 10.1021/ja0116876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Wakahara T, Niino Y, Kato T, Maeda Y, Akasaka T, Liu MTH, Kobayashi K, Nagase S. J Am Chem Soc. 2002;124:9465. doi: 10.1021/ja0116876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Moss RA, Jang EG, Kim HR, Ho GJ, Baird MS. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992;33:1427. [Google Scholar]; Moss RA, Perez LA, Turro NJ, Gould IR, Hacker NP. Tetrahedron Lett. 1983;24:685. [Google Scholar]; Soundararajan N, Platz MS, Jackson JE, Doyle MP, Oon SM, Liu MTH, Anand SM. J Am Chem Soc. 1988;110:7143. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Hasnik Z, Silhar P, Hocek M. Synlett. 2008;2008:543. [Google Scholar]
- 18.Husain SS, Nirthanan S, Ruesch D, Solt K, Cheng Q, Li GD, Arevalo E, Olsen RW, Raines DE, Forman SA, Cohen JB, Miller KW. J Med Chem. 2006;49:4818. doi: 10.1021/jm051207b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kumar AB, Anderson JM, Manetsch R. Org Biomol Chem. 2011;9:6284. doi: 10.1039/c1ob05748k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Daghish M, Hennig L, Findeisen M, Giesa S, Schumer F, Hennig H, Beck-Sickinger AG, Welzel P. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2002;41:2293. doi: 10.1002/1521-3773(20020703)41:13<2293::AID-ANIE2293>3.0.CO;2-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zhang YL, Burdzinski G, Kubicki J, Vyas S, Hadad CM, Sliwa M, Poizat O, Buntinx G, Platz MS. J Am Chem Soc. 2009;131:13784. doi: 10.1021/ja9046119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cross RM, Monastyrskyi A, Mukta TS, Burrows JN, Kyle DE, Manetsch R. J Med Chem. 2010;53:7076. doi: 10.1021/jm1007903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nagase T, Nakata E, Shinkai S, Hamachi I. Chem Eur J. 2003;9:3660. doi: 10.1002/chem.200304925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Van Horn KS, Burda WN, Fleeman R, Shaw LN, Manetsch R. J Med Chem. 2014;57:3075. doi: 10.1021/jm500039e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Cross RM, Flanigan DL, Monastyrskyi A, LaCrue AN, Sáenz FE, Maignan JR, Mutka TS, White KL, Shackleford DM, Bathurst I, Fronczek FR, Wojtas L, Guida WC, Charman SA, Burrows JN, Kyle DE, Manetsch R. J Med Chem. 2014;57:8860. doi: 10.1021/jm500942v. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]; Van Horn KS, Zhu X, Pandharkar T, Yang S, Vesely B, Vanaerschot M, Dujardin JC, Rijal S, Kyle DE, Wang MZ, Werbovetz KA, Manetsch R. J Med Chem. 2014;57:5141. doi: 10.1021/jm5000408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.