Abstract
BACKGROUND:
Patients with sepsis often exhibit an acute inflammatory response, followed by an immunosuppressive phase with a poor immune response. However, the underlying mechanisms have not been fully elucidated.
METHODS:
We sought to comprehensively characterize the transcriptional changes in neutrophils of patients with sepsis by transcriptome sequencing. Additionally, we conducted a series of experiments, including real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and flow cytometry to investigate the role of arginase-1 signaling in sepsis.
RESULTS:
Through the analysis of gene expression profiles, we identified that the negative regulation of T cell activation signaling was enriched, and the expression of arginase-1 was high in neutrophils from patients with sepsis. Furthermore, we conducted flow cytometry and found that the function of CD8+ T cells in septic patients was impaired. Moreover, neutrophils from septic patients inhibited the percentage of polyfunctional effector CD8+ T cells through arginase-1. Additionally, the proportions of granzyme B+IFN-γ+CD8+ T and TNF-α+IFN-γ+CD8+ T cells increased after inhibition of arginase-1 signaling.
CONCLUSION:
The impaired effector function of CD8+ T cells could be restored by blocking arginase-1 signaling in patients with sepsis.
Keywords: Sepsis, Effector CD8+ T cells, Neutrophils, Arginase-1, Interferon-γ
INTRODUCTION
Sepsis is a life-threatening organ dysfunction mainly caused by an abnormal infection-induced immune response.[1-4] In the excessive inflammatory response stage of sepsis, the immune response to sepsis may further cause cell and tissue injury or multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS) with high morbidity and mortality.[5-7] In recent years, the incidence rate of sepsis has increased worldwide.[8,9] More attention has been given to the description of unique biological phenotypes in patients with sepsis;[10,11] however, the mechanisms underlying sepsis have not been fully elucidated.
Neutrophils play an important role in the innate immune system.[11] Although neutrophils survive for only several hours, they contribute to eradicating microorganisms and the survival of patients with sepsis. Neutrophils can effectively clear extracellular microorganisms mainly through direct phagocytosis.[12,13] Recent studies suggested that neutrophils can also clear pathogens through neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs).[14,15] In sepsis, the phenotype and function of circulatory neutrophils can be altered significantly.[16] In early sepsis, neutrophils can migrate from the bone marrow to peripheral blood, and the level of neutrophils can increase by ten-fold within several hours compared to healthy controls.[17]
Sepsis is always accompanied by an impaired immune response mediated by immunosuppressive mechanisms, including the expansion of regulatory T cells (Tregs) and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs), and the production of suppressive factors, including arginase-1 (ARG1).[1,18] Sepsis can expand a CD39+ plasmablast population and promote immunosuppression through adenosine-mediated inhibition of macrophage antimicrobial activity.[19] During sepsis, the level of plasma arginase is elevated. Human neutrophils also express a high level of ARG1, which can deplete arginine from the surrounding medium, suppressing the production of nitric oxide (NO) and impeding the clearance of pathogens.[20,21] In addition, the release of ARG1 from neutrophils has been associated with T cells dysfunction in various pathologies.[20,22]
This study provides insight into the dysfunction of CD8+ T cells in patients with sepsis. Herein, we evaluated the transcriptional profiles and the expression of ARG1 in neutrophils from septic patients and compared them with those of healthy controls. Moreover, we aimed to ascertain whether targeting ARG1 can be a promising approach for restoring the functions of CD8+ T cells in patients with sepsis.
METHODS
Isolation of samples, CD8+ T cells, and neutrophils
Peripheral-blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) were isolated by ficoll density gradients from patients with sepsis and healthy controls (Table 1 and Supplementary Figure 1), and resuspended in RPMI 1640 complete medium (10% fetal calf serum, and 1% streptomycin/penicillin). CD8+ T cells were purified from PBMCs of healthy controls by a magnetic-activated cell sorter (MACS) kit (Miltenyi Biotec, Germany). CD14-CD15+CD16+ neutrophils were sorted by FACS Aria (BD Bioscience, USA) from PBMCs of patients with sepsis.
Table 1.
Characteristics of sepsis patients and healthy controls
Ex vivo flow cytometry experiments
CD8+ T cells were cocultured with neutrophils and stimulated overnight with or without arginase inhibitor 1 (10 μmol/L; MedChemExpress, USA). Cells were stained with human monoclonal antibodies (as described in Supplementary Table 1). Before staining with antibodies, mouse serum was used to block the binding of nonspecific Fc-receptors. Next, intracellular staining of cytokines was performed with 4 h of stimulation with ionomycin (1 μg/mL; Calbiochem, Germany), phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) (50 ng/mL; Sigma, Germany) and monensin (10 μg/mL; Sigma, Germany). Anti-CD107a was added at the same time for 4 h. Cells were then collected and stained for surface or intracellular markers using antibodies (BD Biosciences, USA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Data were collected using the FCM LSR II flow cytometer (BD Biosciences, USA) and analyzed with FlowJo software (Tree Star, USA).
Transcriptome sequencing and analyses of gene expression
CD14-CD15+CD16+ neutrophils were isolated from PBMCs of patients with sepsis and healthy controls for transcriptome sequencing using the BGISEG platform (Beijing Genomics Institution). The heat map of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) was analyzed with MEV v4.8.1. DEGs were defined as those with a fold change ≥2.0 in the expression between two groups and signal values higher than background signals. An adjusted P-value was used to determine DEGs. Next, to obtain insights into the change in phenotype, enrichment analyses of DEGs were performed using the Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG, www.kegg.jp/) databases and Gene Ontology (GO, www.geneontology.org/).[23] Raw RNA-seq data have been deposited in the Gene Expression Omnibus Repository of the National Center for Biotechnology Information (accession number: GSE186054).
For gene expression analyses, total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, USA), and cDNA synthesis was performed using M-MLV Reverse Transcriptase (Invitrogen, USA) and random primers according to manufacturer’s instructions.[23] qRT-PCR was carried out using SYBR Premix Ex Taq (TaKaRa, Japan). Primers are listed in Supplementary Table 2.
Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 8 software were employed to perform statistical analysis. We used two-tailed unpaired or paired Student’s t-tests between two groups or one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) across multiple groups. Data were presented as mean ± standard deviation. A P-value<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Transcriptional profiles of neutrophils from septic patients
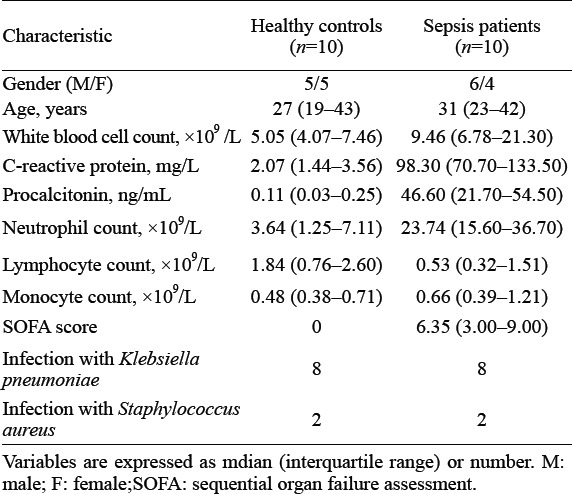
When diagnosed with sepsis, the number of neutrophils was significantly increased in blood (Table 1). Neutrophils can inhibit the effector function and activation of T cells.[14,24,25] Insufficient T cells activation was associated with an inability to recognize pathogens properly. To gain further mechanistic insights, we isolated neutrophils from patients with sepsis and healthy controls for whole-genome transcriptome analyses by microarrays (Figure 1A). The transcriptional profiles of neutrophils from patients with sepsis differed from those of healthy controls. A total of 2,365 genes exhibited upregulated expression, and 1,354 genes showed downregulated expression in septic patients compared with healthy controls (Figure 1B). Enrichment analyses using the GO database revealed varying immunological processes, including negative regulation of T cell activation (Figure 1C). By comparing septic patients with healthy controls, we found that acute inflammatory response signaling and negative regulation of T cell activation signaling were enriched in neutrophils from patients with sepsis (Figure 1C). In general, our data demonstrated differences in transcriptional profiles in neutrophils from patients with sepsis and healthy controls. Specifically, neutrophils from septic patients mainly showed the characteristics of negative regulation of T cell activation.
Figure 1.
The transcriptional profiles of neutrophils from patients with sepsis differed from those of healthy controls. A: the protocol of isolation of neutrophils from healthy controls (n=3) and patients with sepsis (n=3); B: the top-200 genes with differential expression (fold change greater than two-fold) in neutrophils from patients with sepsis compared with those in healthy controls were selected for heat map analyses; each column depicts one sample; C: enrichment analyses of differentially expressed genes were performed (using the Gene Ontology database) to evaluate enriched biological processes between neutrophils from patients with sepsis and healthy controls; enrichment of regulation of negative regulation of T cell activation-related biological processes was included.
Increased expression of ARG1 in neutrophils
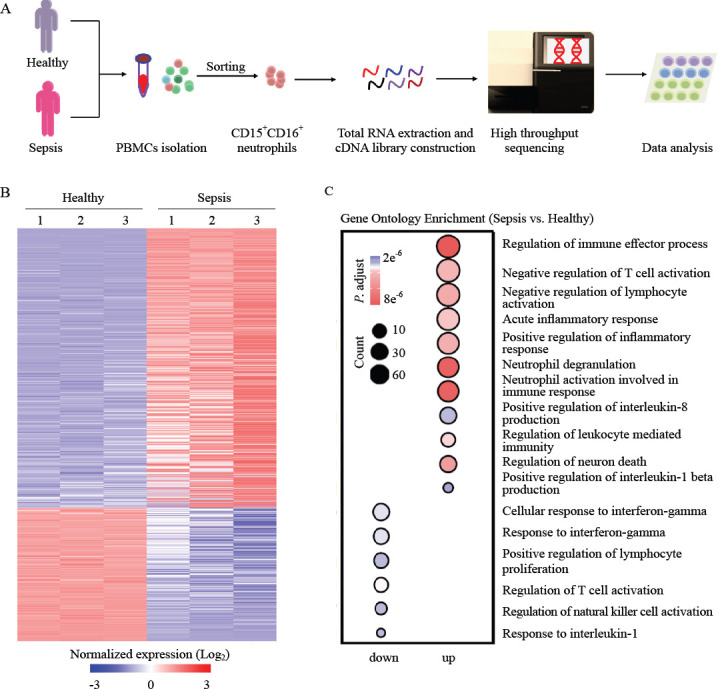
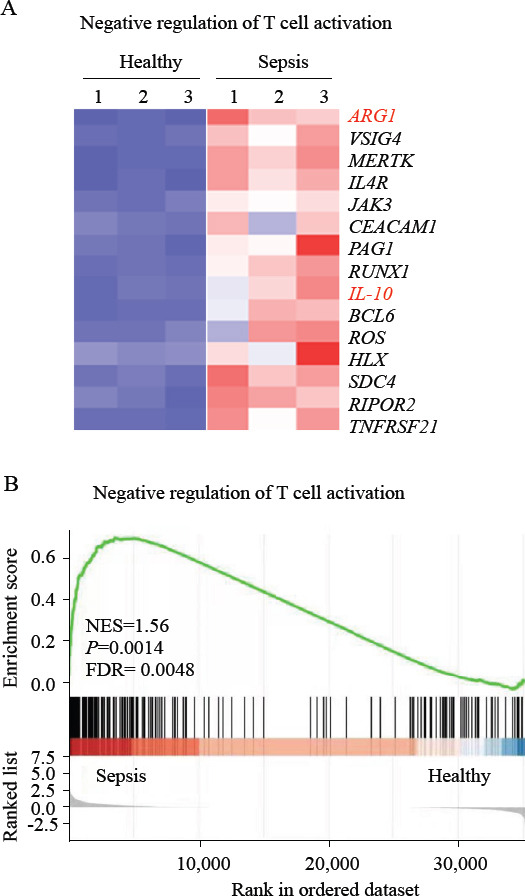
Human neutrophils express high amounts of ARG1, which could significantly downregulate T-cell activation.[18] To determine whether there was an increase in the expression of ARG1 in the neutrophils of patients with sepsis, we first performed DEGs analysis and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA). Meanwhile, we found an increase in the expression of DEGs related to the negative regulation of T cells activation in neutrophils of patients with sepsis compared with that in neutrophils of healthy controls (Figure 2). Of these, there was an 82-fold increase in ARG1 expression (Figure 2A), implying its significant role in regulating the activation of T cells. These results demonstrated the impaired activation of T cells in the sepsis microenvironment. To determine the expression of ARG1 and some other immunosuppressive-related genes such as IL-10, which has long been described as one of the mediators of sepsis-induced immunosuppression,[26-29] we purified neutrophils from patients with sepsis and healthy controls to carry out PCR. Notably, the expression of ARG1 was increased in the neutrophils of septic patients (Figures 2A and 3A-D). The expression of ARG1 in neutrophils from healthy controls was low (Figures 2A and 3A-D). This difference in expression was also confirmed using flow cytometry (Figure 3E). These data suggested that in neutrophils from patients with sepsis, ARG1 expression was significantly upregulated.
Figure 2.
Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) analysis and gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) of neutrophils. A: heat map of negative regulation of T cell activation-related genes with differential expression in neutrophils from patients with sepsis compared with those from healthy controls; B: GSEA revealed an increase in negative regulation of T cell activation processes in neutrophils from patients with sepsis compared with that in healthy controls. NES: normalized enrichment score; FDR: false discovery rate.
Figure 3.
Neutrophils expression of arginase-1 in patients with sepsis. A-D: ARG1, IL-10, PAG1, and RUNX1 expression in neutrophils from patients with sepsis and healthy controls, as assessed by qRT-PCR. Data were representative of six experiments; E: representative histograms (left) and percentage statistics (right) calculated for the expression of arginase-1 in neutrophils of patients with sepsis (red; n = 6) and healthy controls (blue; n = 6). Data were analyzed by two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-test; data were presented as mean ± standard deviation.
Neutrophils inhibited CD8+ T cells immune response by ARG1 signaling ex vivo
To further demonstrate that inhibition of ARG1 signaling could restore the effector function of CD8+ T cells of septic patients, we first processed the neutrophils from septic patients with arginase inhibitor 1. The expression of ARG1 was decreased (Figure 4A). Next, we purified CD8+ T cells from PBMCs of healthy controls and neutrophils from patients with sepsis (Figure 4B). After CD8+ T cells were cocultured with neutrophils from septic patients, the percentage of IFN-γ and TNF-α were coexpression. In addition, granzyme B and CD107a were coexpression, as well as IFN-γ and granzyme B coexpression by CD8+ T cells were significantly decreased. However, after being treated with arginase inhibitor 1, the percentage of IFN-γ and TNF-α coexpression and IFN-γ and granzyme B coexpression by CD8+ T cells were significantly restored (Supplementary Figure 2; Figure 4C and D). Importantly, we found that the polyfunctional effector CD8+ T cells were significantly decreased in septic patients compared with that of healthy controls (Figures 4C and D). In general, these findings suggested that the immune response of CD8+ T cells from septic patients was impaired, and the inhibition of ARG1 signaling may be related to the recovery of effector function of CD8+ T cells.
Figure 4.
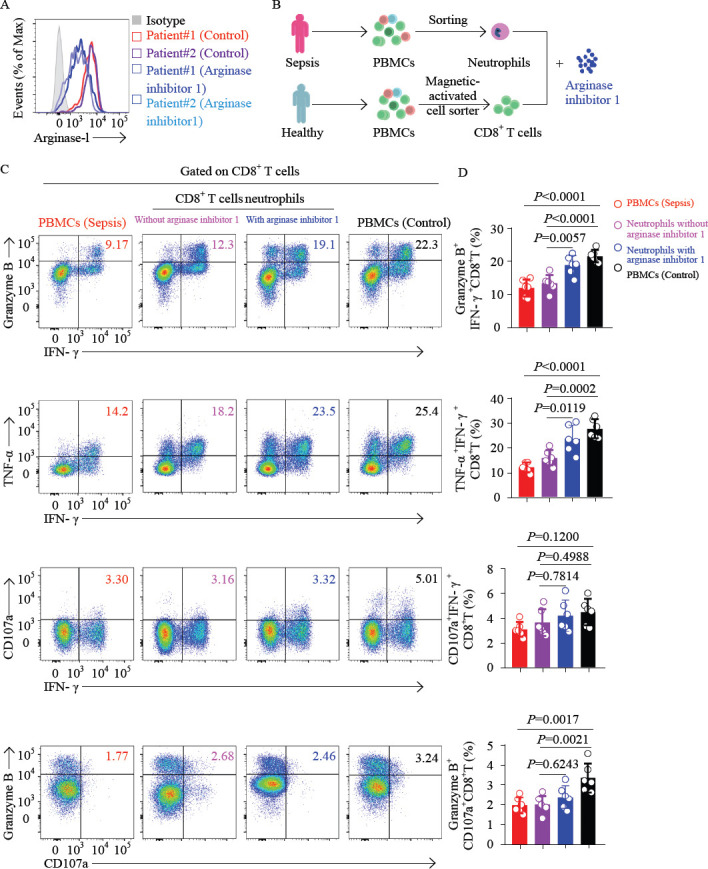
Inhibition of arginase-1 signaling elevates the percentage of polyfunctional effector CD8+ T cells. A: representative histograms showing the analysis of arginase-1 expression in neutrophils of two patients with sepsis after being treated with arginase inhibitor 1; B: the protocol of the isolation of CD8+ T cells from patients with sepsis and healthy controls; and CD14-CD15+CD16+ neutrophils from patients with sepsis. Purified CD8+ T cells from healthy controls were cocultured with neutrophils (ratio = 3:1), treated with or without arginase inhibitor 1 (10 μmol/L); C and D: PBMCs of septic patients (red), or CD8+ T cells purified from healthy controls and cocultured with neutrophils, and treated with (blue) or without (purple) arginase inhibitor 1 (10 μmol/L) overnight, or PBMCs of healthy controls (black), were stimulated with PMA for 4 h. CD8+ T cells were gated for analysis. Representative flow cytometry plots (C) and pool data (D) of the proportion of IFN-γ and granzyme B coexpression, IFN-γ and TNF-α coexpression, IFN-γ and CD107a coexpression, as well as CD107a and granzyme B coexpression by CD8+ T cells. n 6. For (D), data were analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test; Data are presented as mean ± standard deviation.
DISCUSSION
Our current study provided direct evidence that the expression of ARG1 in the neutrophils of septic patients was high. Moreover, we demonstrated that ARG1 inhibition significantly restored the effector function of CD8+ T cells. In summary, our results provided three main insights into the underlying mechanisms and potential for sepsis therapy.
First, to elucidate the immunological characteristics of septic patients, we performed routine laboratory tests. Consistent with the results of other studies, we found that the number of neutrophils was significantly increased,[16,30-32] while the lymphocytes were decreased in septic patients. To investigate the difference in neutrophils between septic patients and healthy controls, we performed RNA-seq analysis and found that the transcriptional profiles of the neutrophils differed between the two groups. Additionally, we verified that negative regulation of T cell activation signaling was enriched in neutrophils from patients with sepsis. Furthermore, we observed high expression of several immunosuppressive indicators, such as IL-10 and ARG1 in neutrophils from septic patients.
Next, to confirm that ARG1 expression was high in neutrophils from septic patients, we performed qRT-PCR and flow cytometry. The expression of ARG1 was significantly increased in neutrophils from patients with sepsis. CD8+ T cells play important roles in the host defense against infections.[33-36] However, in patients with sepsis, the immune response of CD8+ T cells was impaired. As ARG1 was reported to be associated with T-cell dysfunction in several pathologies,[18,20,22] we considered whether inhibition of ARG1 would contribute to restoring the function of CD8+ T cells.
Third, consistent with expectations, we demonstrated that the effector function of CD8+ T cells was impaired in septic patients. Furthermore, after coculturing with neutrophils from septic patients, the immune response of CD8+ T cells from healthy controls decreased significantly. Additionally, arginase inhibitor 1 led to the marked restoration of immune function of CD8+ T cells ex vivo. However, several important questions remain to be answered, including the challenges of developing and using new model systems. Furthermore, we did not clarify other mechanisms that could lead to sepsis and the dysfunction of CD8+ T cells. We also did not explain how ARG1 obstructs the function of CD8+ T cells in sepsis.
CONCLUSION
Our results reveal the transcriptional profile features of patients with sepsis and indicate that inhibition of ARG1 might help relieve sepsis.
Footnotes
Funding: This work was supported by the Research Fund for the Key Laboratory of Anhui Province (KLICD-2022-Z2), the Scientific Research Fund of Anhui Medical University (2011×kj083) and the Scientific Research Fund of the First People’s Hospital of Hefei (201642).
Ethical approval: The studies were approved by the local Ethics Board of the First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University (No. PJ2019-06-09). Experiments were conducted in accordance with the ethical guidelines of the 1975 Declaration of Helsinki, the Principles of Good Clinical Practice, and the guidelines of China’s regulatory requirements. Each participant provided written informed consent.
Conflicts of interest: The authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Contributors: All authors have read and approved the article. XKD designed and performed the experiments, analyzed and interpreted the data. ZXD, YYT and HRB helped to perform the experiments, collected samples and information from patients. HZ and DYW supervised the project, provided strategic planning, and interpreted some data. XKD wrote the manuscript with HZ.
All the supplementary files in this paper are available at http://wjem.com.cn.
REFERENCES
- 1.Chen J, Wei HM. Immune intervention in sepsis. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:718089. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.718089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Prescott HC, Angus DC. Enhancing recovery from sepsis:a review. JAMA. 2018;319(1):62–75. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.17687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.van der Poll T, van de Veerdonk FL, Scicluna BP, Netea MG. The immunopathology of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Immunol. 2017;17(7):407–20. doi: 10.1038/nri.2017.36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Gotts JE, Matthay MA. Sepsis:pathophysiology and clinical management. BMJ. 2016;353:i1585. doi: 10.1136/bmj.i1585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spinella PC, Tucci M, Fergusson DA, Lacroix J, Hébert PC, Leteurtre S, et al. Effect of fresh vs standard-issue red blood cell transfusions on multiple organ dysfunction syndrome in critically ill pediatric patients:a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2019;322(22):2179–90. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.17478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Rhee SG. Overview on peroxiredoxin. Mol Cells. 2016;39(1):1–5. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2016.2368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Huang M, Cai SL, Su JQ. The pathogenesis of sepsis and potential therapeutic targets. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(21):5376. doi: 10.3390/ijms20215376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fleischmann C, Scherag A, Adhikari NKJ, Hartog CS, Tsaganos T, Schlattmann P, et al. Assessment of global incidence and mortality of hospital-treated sepsis. Current estimates and limitations. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2016;193(3):259–72. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201504-0781OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhang H, Zeng L, Xie M, Liu J, Zhou BR, Wu RL, et al. TMEM173 drives lethal coagulation in sepsis. Cell Host Microbe. 2020;27(4):556–70.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2020.02.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Karakike E, Giamarellos-Bourboulis EJ. Macrophage activation-like syndrome:a distinct entity leading to early death in sepsis. Front Immunol. 2019;10:55. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.00055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liu L, Sun BW. Neutrophil pyroptosis:new perspectives on Sepsis. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2019;76(11):2031–42. doi: 10.1007/s00018-019-03060-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Group RC, Horby P, Mafham M, Linsell L, Bell JL, Staplin N, et al. Effect of hydroxychloroquine in hospitalized patients with covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2020;383(21):2030–40. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2022926. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Castanheira FVS, Kubes P. Neutrophils and NETs in modulating acute and chronic inflammation. Blood. 2019;133(20):2178–85. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-11-844530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Dąbrowska D, Jabłońska E, Garley M, Ratajczak-Wrona W, Iwaniuk A. New aspects of the biology of neutrophil extracellular traps. Scand J Immunol. 2016;84(6):317–22. doi: 10.1111/sji.12494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Yamamoto K, Yamada H, Wakana N, Kikai M, Terada K, Wada N, et al. Augmented neutrophil extracellular traps formation promotes atherosclerosis development in socially defeated apoE?/? mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(2):490–6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.04.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ocana A, Nieto-Jiménez C, Pandiella A, Templeton AJ. Neutrophils in cancer:prognostic role and therapeutic strategies. Mol Cancer. 2017;16(1):137. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0707-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Manz MG, Boettcher S. Emergency granulopoiesis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2014;14(5):302–14. doi: 10.1038/nri3660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sippel TR, Shimizu T, Strnad F, Traystman RJ, Herson PS, Waziri A. Arginase I release from activated neutrophils induces peripheral immunosuppression in a murine model of stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2015;35(10):1657–63. doi: 10.1038/jcbfm.2015.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nascimento DC, Viacava PR, Ferreira RG, Damaceno MA, Piñeros AR, Melo PH, et al. Sepsis expands a CD39+plasmablast population that promotes immunosuppression via adenosine-mediated inhibition of macrophage antimicrobial activity. Immunity. 2021;54(9):2024–41.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Darcy CJ, Woodberry T, Davis JS, Piera KA, McNeil YR, Chen YW, et al. Increased plasma arginase activity in human sepsis:association with increased circulating neutrophils. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2014;52(4):573–81. doi: 10.1515/cclm-2013-0698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Reizine F, Lesouhaitier M, Gregoire M, Pinceaux K, Gacouin A, Maamar A, et al. SARS-CoV-2-induced ARDS associates with MDSC expansion, lymphocyte dysfunction, and arginine shortage. J Clin Immunol. 2021;41(3):515–25. doi: 10.1007/s10875-020-00920-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Pang R, Zhou H, Huang YF, Su YB, Chen XH. Inhibition of host arginase activity against staphylococcal bloodstream infection by different metabolites. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1639. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Cong JJ, Wang XW, Zheng XH, Wang D, Fu BQ, Sun R, et al. Dysfunction of natural killer cells by FBP1-induced inhibition of glycolysis during lung cancer progression. Cell Metab. 2018;28(2):243–55.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2018.06.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Batlle E, Massagué J. Transforming growth factor-βsignaling in immunity and cancer. Immunity. 2019;50(4):924–40. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.03.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Lee KH, Kronbichler A, Park DDY, Park Y, Moon H, Kim H, et al. Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) in autoimmune diseases:a comprehensive review. Autoimmun Rev. 2017;16(11):1160–73. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2017.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bergmann CB, Salyer CE, Beckmann N, Caldwell CC. Intraperitoneal neutrophil IL-10 production is promoted by interferon γin a murine model of sepsis model in the acute phase of sepsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;530(1):278–84. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.07.089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Steinhauser ML, Hogaboam CM, Kunkel SL, Lukacs NW, Strieter RM, Standiford TJ. IL-10 is a major mediator of sepsis-induced impairment in lung antibacterial host defense. J Immunol. 1999;162(1):392–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fu BQ, Wang DY, Shen XK, Guo C, Liu YY, Ye Y, et al. Immunomodulation induced during interferon-αtherapy impairs the anti-HBV immune response through CD24+ CD38hi B cells. Front Immunol. 2020;11:591269. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.591269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wang DY, Zheng XH, Fu BQ, Nian ZG, Qian YB, Sun R, et al. Hepatectomy promotes recurrence of liver cancer by enhancing IL-11-STAT3 signaling. EBioMedicine. 2019;46:119–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.07.058. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Park I, Kim M, Choe K, Song E, Seo H, Hwang Y, et al. Neutrophils disturb pulmonary microcirculation in Sepsis-induced acute lung injury. Eur Respir J. 2019;53(3):1800786. doi: 10.1183/13993003.00786-2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mortaz E, Alipoor SD, Adcock IM, Mumby S, Koenderman L. Update on neutrophil function in severe inflammation. Front Immunol. 2018;9:2171. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Seree-Aphinan C, Vichitkunakorn P, Navakanitworakul R, Khwannimit B. Distinguishing sepsis from infection by neutrophil dysfunction:a promising role of CXCR2 surface level. Front Immunol. 2020;11:608696. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.608696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shen XK, Fu BQ, Liu YY, Guo C, Ye Y, Sun R, et al. NKp30+NK cells are associated with HBV control during pegylated-interferon-alpha-2b therapy of chronic hepatitis B. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38778. doi: 10.1038/srep38778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Kurachi M. CD8+ T cell exhaustion. Semin Immunopathol. 2019;41(3):327–37. doi: 10.1007/s00281-019-00744-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kumar BV, Connors TJ, Farber DL. Human T cell development, localization, and function throughout life. Immunity. 2018;48(2):202–13. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2018.01.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Shen XF, Cao K, Jiang JP, Guan WX, Du JF. Neutrophil dysregulation during sepsis:an overview and update. J Cell Mol Med. 2017;21(9):1687–97. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


